Module 1 Learning Catalytics
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
what has a dimorphic lifestyle?
a. Blastomyces dermatitidis
b. Coccidiodes imitis
c. Candida albicans
d. Aspergillus flavus
a
what has a causes valley fever?
a. Blastomyces dermatitidis
b. Coccidiodes imitis
c. Candida albicans
d. Aspergillus flavus
b
what is the most common cause of yeast infections?
a. Blastomyces dermatitidis
b. Coccidiodes imitis
c. Candida albicans
d. Aspergillus flavus
c
what produces aflatoxin?
a. Blastomyces dermatitidis
b. Coccidiodes imitis
c. Candida albicans
d. Aspergillus flavus
d
which of the following pathogens is part of the Animal kingdom?
a. Schistosoma mansoni
b. Trypanosoma cruzi
c. Plasmodium falciparum
d. Toxoplasma gondii
e. Giardia lamblia
a
why are malaria vaccines more effective at preventing infections than traditional "malaria pills"? (select all that apply)
a. Malaria vaccines inhibit earlier stages of the Plasmodium falciparum transmission cycle than pills.
b. Malaria vaccines are effective for people already infected with Plasmodium falciparum, like malaria pills.
c. Malaria vaccines target the sporozoite stage of Plasmodium falciparum instead of the schizont stage.
d. Malaria vaccines target the oocyte/cyst stage of the Plasmodium falciparum life cycle.
a; c
which has a low G+C gram-positive?
a. Staphylococcus aureus
b. Treponema pallidum
c. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
d. Fusobacterium spp.
a
which is a spirochete?
a. Staphylococcus aureus
b. Treponema pallidum
c. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
d. Fusobacterium spp.
b
which has high G+C gram-positive?
a. Staphylococcus aureus
b. Treponema pallidum
c. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
d. Fusobacterium spp.
c
which if CFB group?
a. Staphylococcus aureus
b. Treponema pallidum
c. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
d. Fusobacterium spp.
d
intracellular pathogens that persist inside of their host cells after engulfment must prevent which of the following host cell processes?
a. endocytosis
b. protein synthesis
c. autophagy
d. phagocytosis
e. receptor-ligand binding
d
Lactobacillus spp. bacteria in the vaginal tract create a low-pH environment that inhibits the growth of potentially pathogenic microbes. Which term best describes the relationship between Lactobacillus bacteria and their human hosts? (*hint: 2 answers could work)
a. amensalism
b. commensalism
c. parasitism
d. mutualism
e. neutralism
b; d
what is the proteobacteria class of Rickettsia?
a. alphaproteobacteria
b. betaproteobacteria
c. gammaproteobacteria
d. epsilonproteobacteria
a
what is the proteobacteria class of Neisseria?
a. alphaproteobacteria
b. betaproteobacteria
c. gammaproteobacteria
d. epsilonproteobacteria
b
what is the proteobacteria class of Salmonella?
a. alphaproteobacteria
b. betaproteobacteria
c. gammaproteobacteria
d. epsilonproteobacteria
c
what is the proteobacteria class of Campylobacter?
a. alphaproteobacteria
b. betaproteobacteria
c. gammaproteobacteria
d. epsilonproteobacteria
d
what refers to unassisted movement of molecules across a membrane?
simple diffusion
what refers to channels or gates allowing molecules to pass through a membrane going DOWN their concentration gradient?
facilitated diffusion
what refers to an energy source is required to move molecules across a membrane AGAINST their concentration gradient?
active transport
what term refers to a curved rod cell-shape?
vibrio
what term refers to a straight rod cell-shape?
bacillus
what term refers to a sphere cell-shape?
coccus
what term refers to a corkscrew cell-shape?
spirillum
which of the following bacterial structures can contribute to their ability to initiate infections or resist immune system clearance?
a. pilus
b. capsule
c. biofilm
d. endospore
e. plasmid
a, b, c, d, e
which property of light is the most important for the structure and function of microscopes?
a. refraction
b. diffraction
c. reflection
d. absorption
e. interference
a
put these components of indirect immunofluorescence in order based on what they bind or are attached to. The right-most (smallest) position is the target of detection and the left-most (largest) position is the component that is seen by the microscopist.
Secondary antibody
Fluorochrome
Primary antibody
Antigen
antigen, primary antibody, secondary antibody, fluorochrome
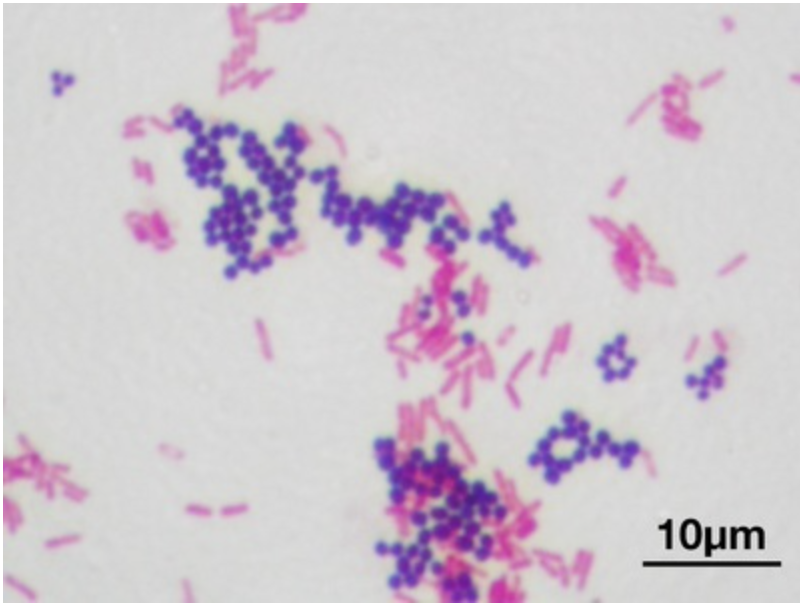
considering that the cell wall of bacteria is negatively-charged, both Crystal Violet and Safranin dyes can be classified as: (select all that apply)
a. basic dyes
b. acidic dyes
c. positive stains
d. negative stains
a; c
BOTH prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells lack of membrane-bound organelles. true or false?
false
BOTH prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have linear chromosomes. true or false?
false
BOTH prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have ribosomes. true or false?
true
BOTH prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane. true or false?
true
BOTH prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have a cell wall. true or false?
true
BOTH prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have a nucleus. true or false?
false
BOTH prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have a cytoplasm. true or false?
true
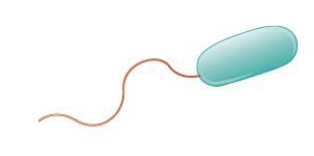
what is this?
monotrichous
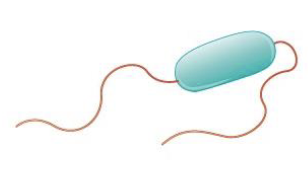
what is this?
amphitrichous
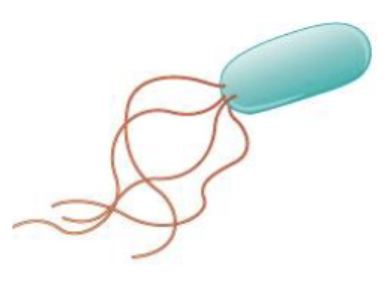
what is this?
lophotrichous
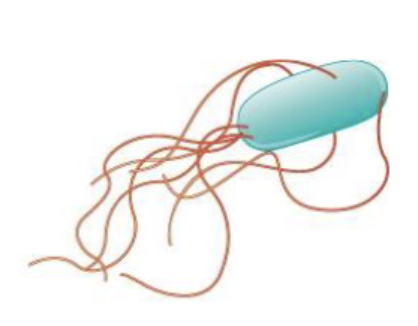
what is this?
peritrichous