Ch 21: Viruses
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
true or false. viruses are parasitic entities.
true
true or false. viruses are part of the bacteria family.
false. viruses cannot fit into any domain of life
true or false. viruses cannot infect organisms as diverse as bacteria, plants, and animals.
false. viruses can infect organisms as diverse as bacteria, plants, and animals
true or false. viruses are cellular, have metabolism, grow, and do cellular division.
false. viruses are non-cellular, have no metabolism, no growth, and no cell division
true or false. viruses are copy and replicate themselves.
true.
true or false. viruses are completely dependent on the host for resources to produce progeny viruses
true
what are the 3 main component of a virus?
capsid
nucleic acid genome
envelope
capsid
outer protein coat
nucleic acid genome
single or double-stranded DNA or RNA
envelope (not all viruses have)
membrane covering capsid
where is the envelope derived?
from the plasma membrane of the host
protein and phospholipids
viruses cannot ________ on their own. they require cellular machinery of ____ cells to survive and replicate.
replicate, host
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
detects extremely small DNA/RNA of viruses
immunoassays
detect antigens or antibody reaction
Chamberland-Pasteur porcelain filter
removes all bacteria from a water sample
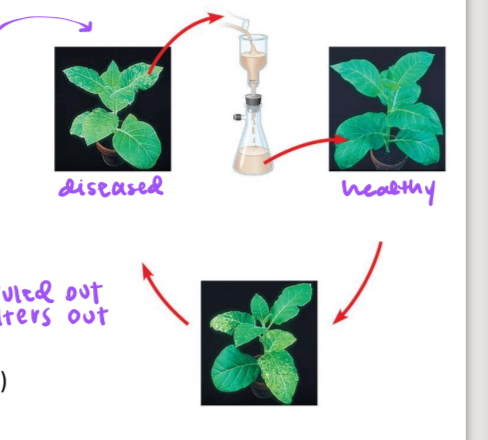
Adolph Meyer 1886
demonstrated that a disease of tobacco plants - tobacco mosaic disease - could be transferred from a diseased plant to a healthy one via liquid plant extracts
Dmitri Ivanowski 1892
demonstrated the disease could be transmitted via liquid plant extracts even after the Chamberland-Pasteur filter had removed all viable bacteria from the extract
bacteria ruled out as culprit b/c filter took it out → virus
what type of microscopy developed in the 1930s allowed for the first view of viruses?
electron microscopy
what was the first virus to be seen and described?
tobacco mosaic virus (TMV)
scanning electron microscope
scans surface of viruses
transmission electron microscope
scans internal structures of viruses
true or false. there is no known fossil record of the evolution of viruses
true
what are the 3 main hypothesis of virus evolution?
H1: regressive
H2: progressive or escapist
H3: self-replicating
H1: regressive
viruses evolved from free-living cells or from intracellular prokaryotic parasites
H2: progressive or escapist
viruses originated from pieces of RNA and DNA that escaped from a host cell and gained the ability to move between cells
H3: self-replicating
viruses may have originated from self-replicating entities similar to transposons or other mobile genetic elements
viral morphology: size
extremely small, single virion is between 20-250nm in diameter
viral morphology: noncellular
viruses lack almost all cell components except for the nucleic core
viral morphology: make up
made of nucleic core, capsid, and sometimes outer envelope
bacteria size
.1-5 nm
eukaryote size
100nm

helical
long and cylindrical
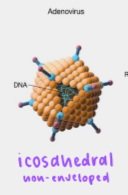
icosahedral
roughly spherical-shape
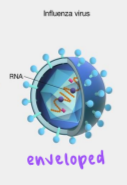
enveloped
have membranes surrounding the capsids
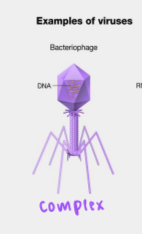
complex/head and tail
infect bacteria and have a head that is similar to icosahedral viruses and a tail shaped like helical viruses
the virus core contains nucleic acid
either DNA or RNA (but not both)
either single-stranded or double-stranded
circular or linear
either in one piece or in multiple segments
viral genome
total genetic content of the virus
viral genomes are very smalle
only contain those genes that encode proteins that the virus cannot get from the host cell
viral DNA directs the ____ cell to make new virus ______
host, copies
true or false. RNA viruses cannot encode their own enzymes
false.
important RNA viral enzyme
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp)
RNA viruses use enzymes that make more errors
RdRp makes more errors, lacks error checking ability
true or false. RNA viruses mutate more frequently than DNA viruses
true
true or false. if a virus cannot get a specific protein from the host, they are able to encode the protein
true
true or false. RNA viruses do not have their own enzymes and use the enzymes of the host, specifically DNA polymerase
false. DNA viruses do not have their own enzymes and use the enzymes of the host, specifically DNA polymerase
where do DNA viruses replicate?
in the nucleus
where do RNA viruses duplicate?
in the cytoplasm
true or false. DNA viruses mutate more than RNA viruses
false. DNA viruses (chicken pox) do not mutate as often as RNA viruses (flu virus)
DNA viruses
often double-stranded, but can be single-stranded
replication takes place in the nucleus (in most)
a few have DNA polymerases and can complete replication in the host cell’s cytoplasm
ex: smallpox virus
where does the smallpox DNA replicate?
in the cytoplasm
RNA viruses
usually single-stranded, but can be double-stranded
replication takes place in the cytoplasm (in most)
mutation happens at a very high rate b/c RNA polymerase does not have proofreading capabilities
ex. influenza, coronavirus
why do RNA viruses replicate in the cytoplasm?
b/c they encode their own enzymes, do not need DNA polymerase (in nucleus) and its easier for them to do it in the cytoplasm
how were viruses classified in the past?
nucleic acid type
capsid structure
enveloped/non-enveloped (influenza, HIV/ common cold)
genome structure
what is the current way to classify viruses?
how viruses send out their messenger RNA
central dogma
replication: DNA polymerase (DNA → DNA)
transcription: RNA polymerase (DNA → RNA)
translation: ribosome (RNA → protein)
reverse transcription
uses reverse transcriptase to convert RNA → DNA
used by retroviruses (HIV)
what is the most commonly and currently used system of virus classification?
baltimore classficaiton
who is the baltimore classification developed by?
nobel-prize winning biologist David Baltimore in the early 1970s
how does the baltimore classification group viruses?
according to how their mRNA is produced during the replicative cycle of the virus
Group I: characteristics
ds-DNA
Group I: mode of mRNA production
mRNA is transcribed directly from the DNA template
uses host enzymes to make mRNA, uses DNA polymerase
Group I: example
Herpes simplex (herpesvirus)
Group II: characteristics
ss-DNA
Group II: mode of mRNA production
DNA is converted to a double-stranded form before RNA is transcribed
ssDNA → dsDNA → mRNA
Group II: example
canine parvovirus (parvovirus)
Group III: characteristics
ds-RNA
Group III: mode of mRNA production
mRNA is transcribed from the RNA genome by using its own enzyme
dsRNA → separates into ssRNA → mRNA
Group III: example
childhood gastroenteritis (rotavirus)
Group IV: characteristics
ssRNA (+) polar
Group IV: mode of mRNA production
genome functions as mRNA (+)
Group IV: example
common cold (picornavirus) and COVID-19
Group V: characteristics
ssRNA (-) polar
Group V: mode of mRNA production
mRNA is transcribe from the RNA genome
genome is complementary to mRNA
ssRNA→ mRNA RdRp
Group V: example
rabies (rhabdovirus)
Group VI: characteristics
ss RNA viruses w/ reverse transcriptase
Group VI: mode of mRNA production
reverse transcriptase makes DNA from the RNA genome: DNA is then incorporated in the host genome: mRNA is transcribed from the incorporated DNA
converts RNA → DNA, DNA is then converted in the host genome
unless someone has HIV, they won’t have reverse transcriptase
Group VI: example
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
Group VII: characteristics
dsDNA w/ reverse transcriptase
Group VII: mode of mRNA production
the viral genome is dsDNA, but viral DNA is replicated through an RNA intermediate: the RNA may serve directly as mRNA or as a template to make mRNA
dsDNA → ssRNA intermediate, functions as mRNA necessary for genome replication Rbds DNA
Group VII: example
hepatitis B virus (hepadnavirus)
steps of viral infection
attachment
entry
replication and assembly
egress (release)
Attachment
receptors on the surface of the host cell bind to virus capsid proteins or virus envelope glycoproteins
have caro groups attached to them
viruses can attach only to cells that have the right receptor molecules
therefore, viruses can be very specific about what species or cell type they can infect
what must be compatible for attachment of the virus to occur?
protein of the virus and receptor of the host
what is the protein on HIV?
GP120: attachment must happen before HIV enter the immune cell
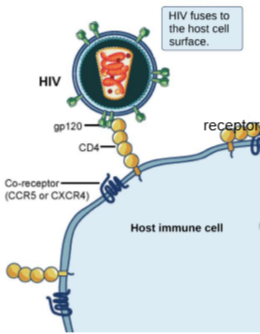
HIV, an __________, ____________ virus, attaches to the CD4 receptor of an immune cell and fuses w/ the cell _________.
enveloped, icosahedral, membrane
entry
viruses may enter eukaryotic cells by (a) endocytosis, or if enveloped, by (b) fusion w/ the cell’s membrane
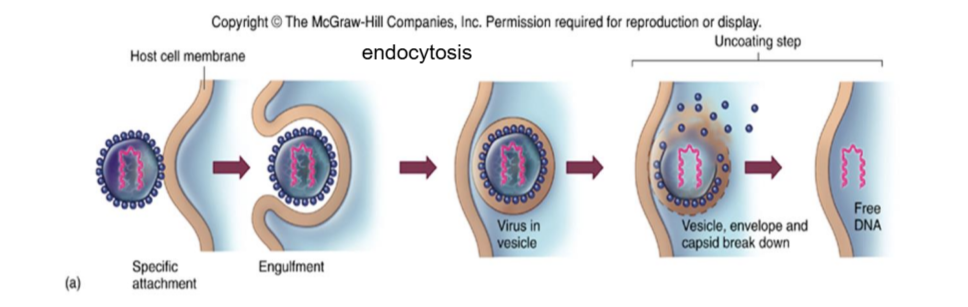
endocytosis
virus engulfment → becomes a vesicle, envelope and capsid break down → free DNA
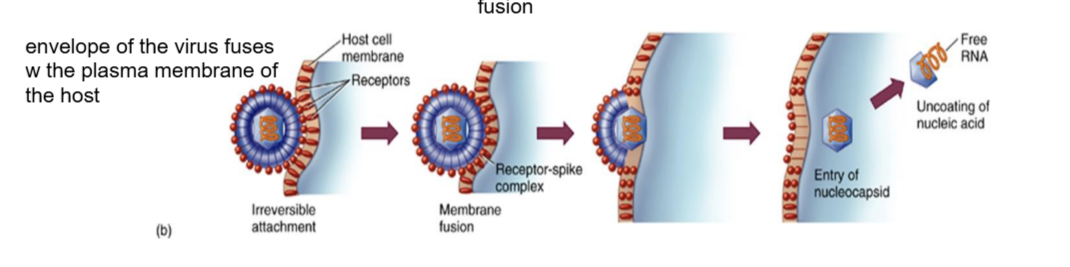
fusion w/ the cell’s membrane
envelope of the virus fuses w/ the plasma membrane of the host
what does replication and assembly depend on?
the viral genome
replication and assembly: DNA viruses
usually use host-cell proteins and enzymes to replicate the viral DNA and to transcribe viral mRNA → then used to direct viral protein synthesis
replication and assembly: RNA viruses
RNA viruses usually use the RNA core as a template for synthesis of viral genomic RNA and mRNA
the viral mRNA directs the host cell to synthesize viral enzymes and capsid proteins and assemble new virions
uses RdRp, RNA genome contains the code for RdRp, host actually makes RdRp
replication and assembly: RNA retroviruses
have an RNA genome that must have reverse transcribed into DNA, which then is incorporated into the host cell genome
DNA directs synthesis and assembly of new viruses
RNA→ DNA→host
what type of cells does reverse transcriptase not occur in?
uninfected host cells
what is reverse transcriptase derived from?
the expression of viral genes within the infected host cells
true or false. only infected host cell have reverse transcriptase.
true
what do DNA viruses use to replicate the viral DNA?
host-cell proteins and enzymes
what do RNA viruses use as a template for synthesis of viral genomic RNA and mRNA?
RNA core
what does the viral mRNA direct the host cell to synthesize and assemble?
to synthesize viral enzymes and capsid proteins and to assemble new virions
what is the DNA viruses viral mRNA used for?
to direct viral protein synthesis