Bone Anatomy
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
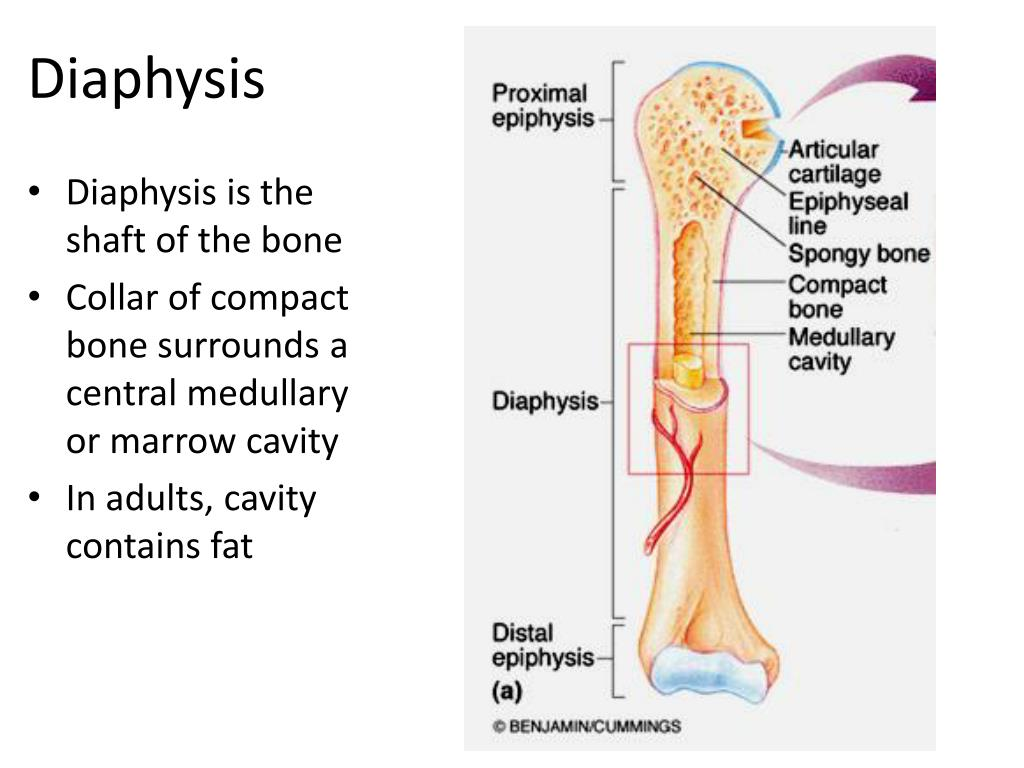
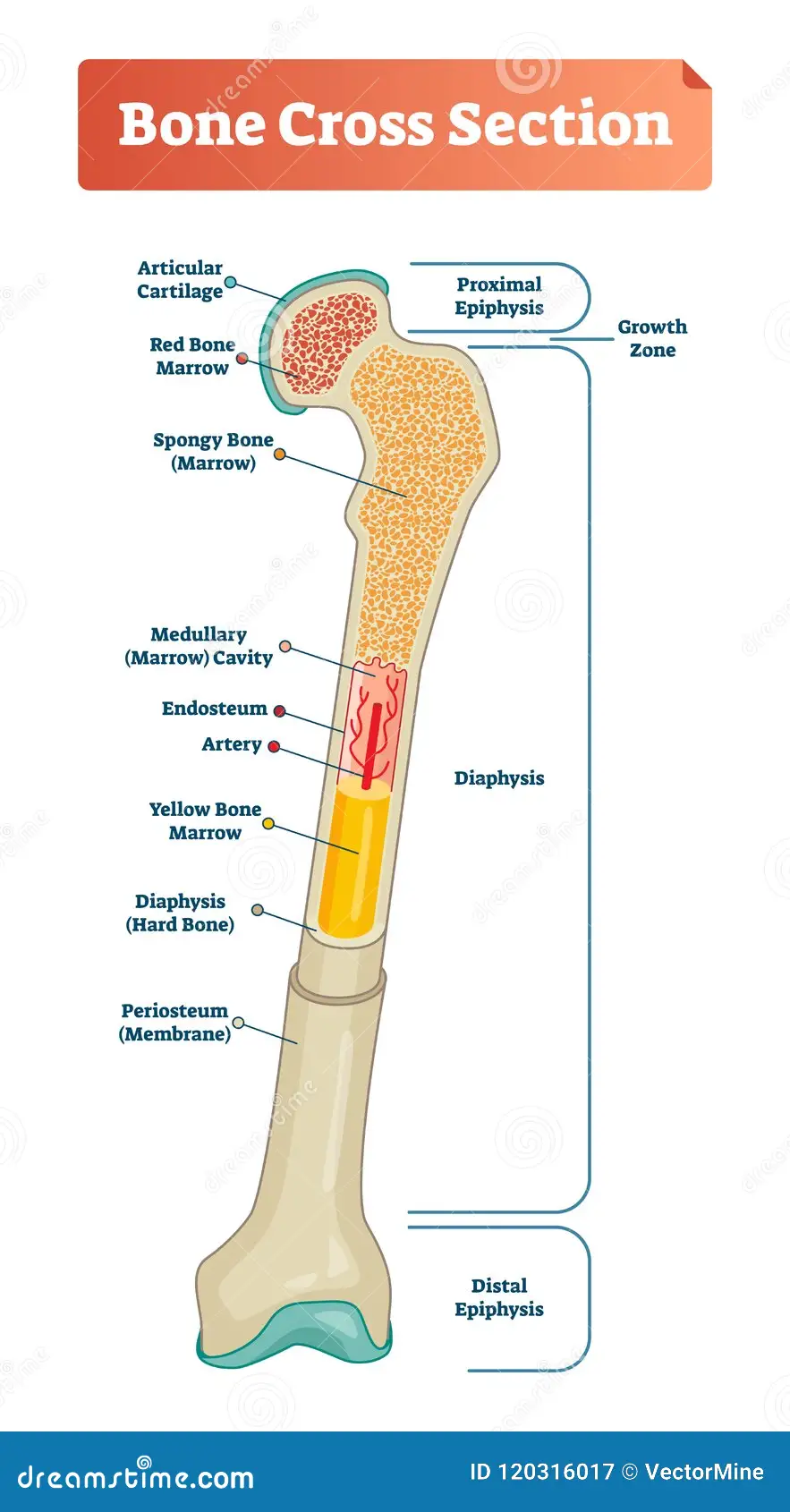
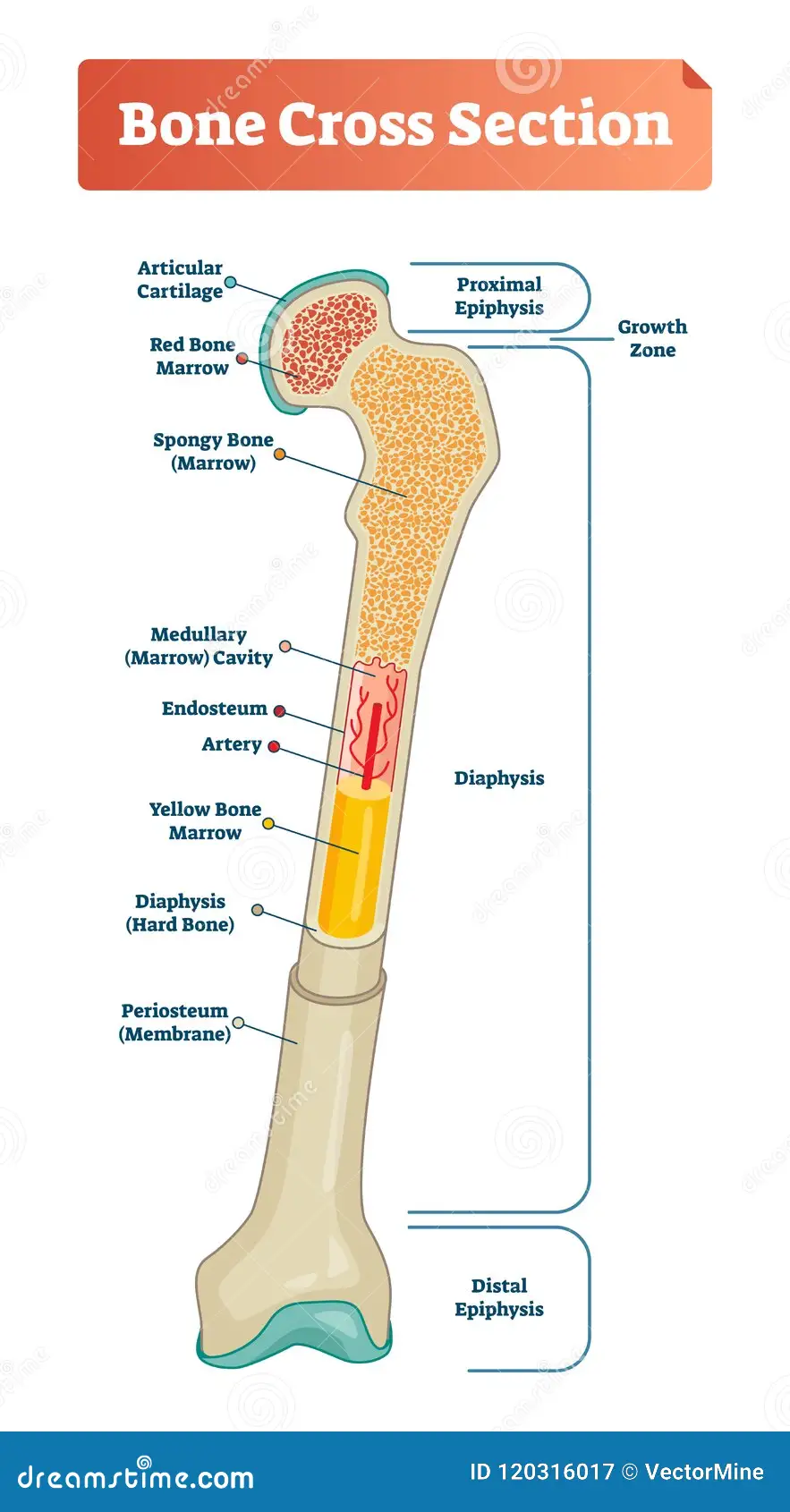
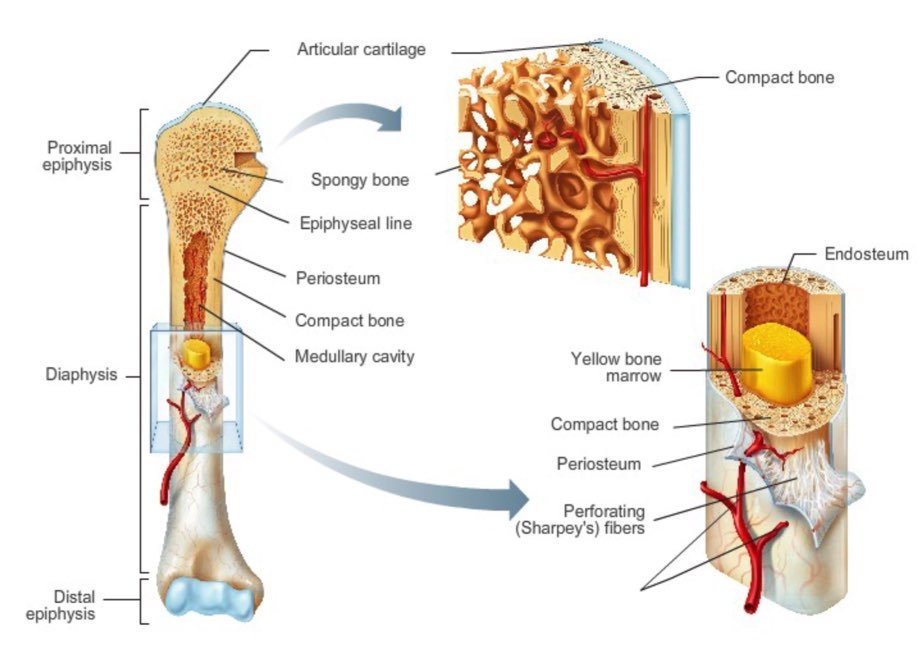
diaphysis -
- shaft
- composed of compact bone
periosteum covering for what
outside covering of the diaphysis (shaft)
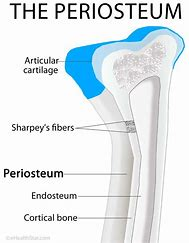
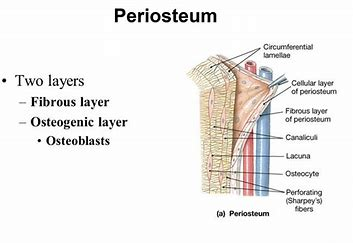
periosteum: tissue
fibrous connective tissue membrane that protects
Sharpey's fibers
secure periosteum to underlying bone
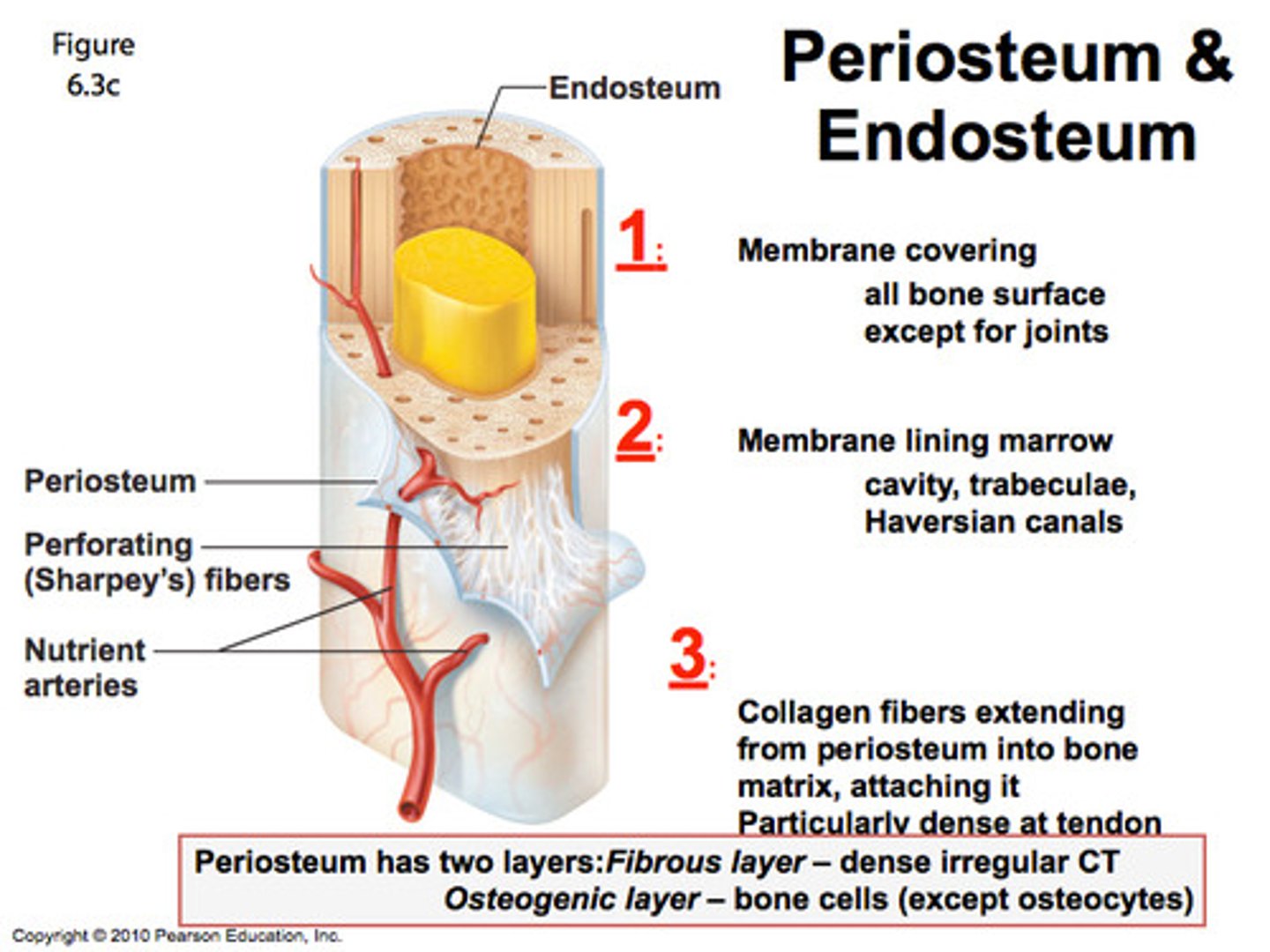
arteries
supply bone cells with nutrients
epiphysis
- ends of the bone
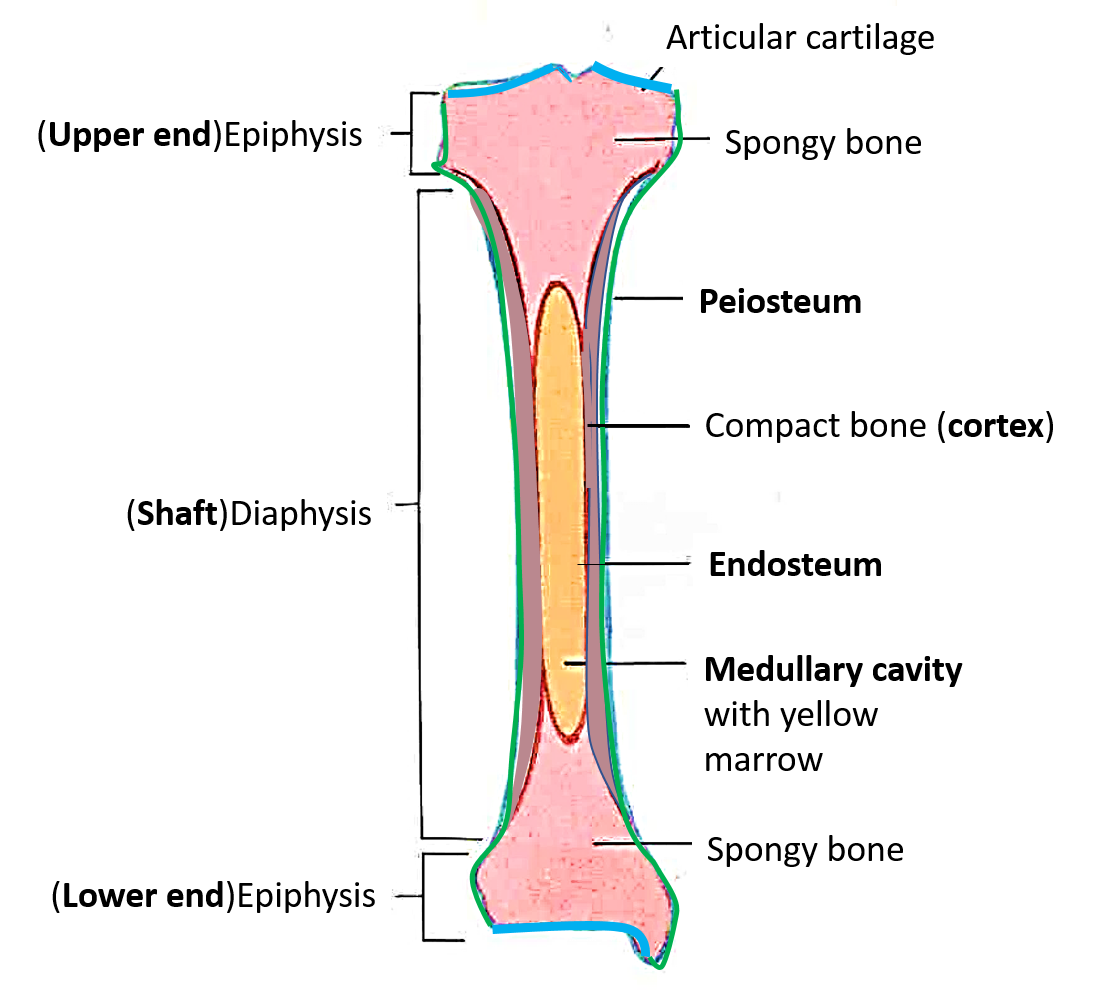
epiphysis: consists of
consists of thin layer of compact bone enclosing spongy bone
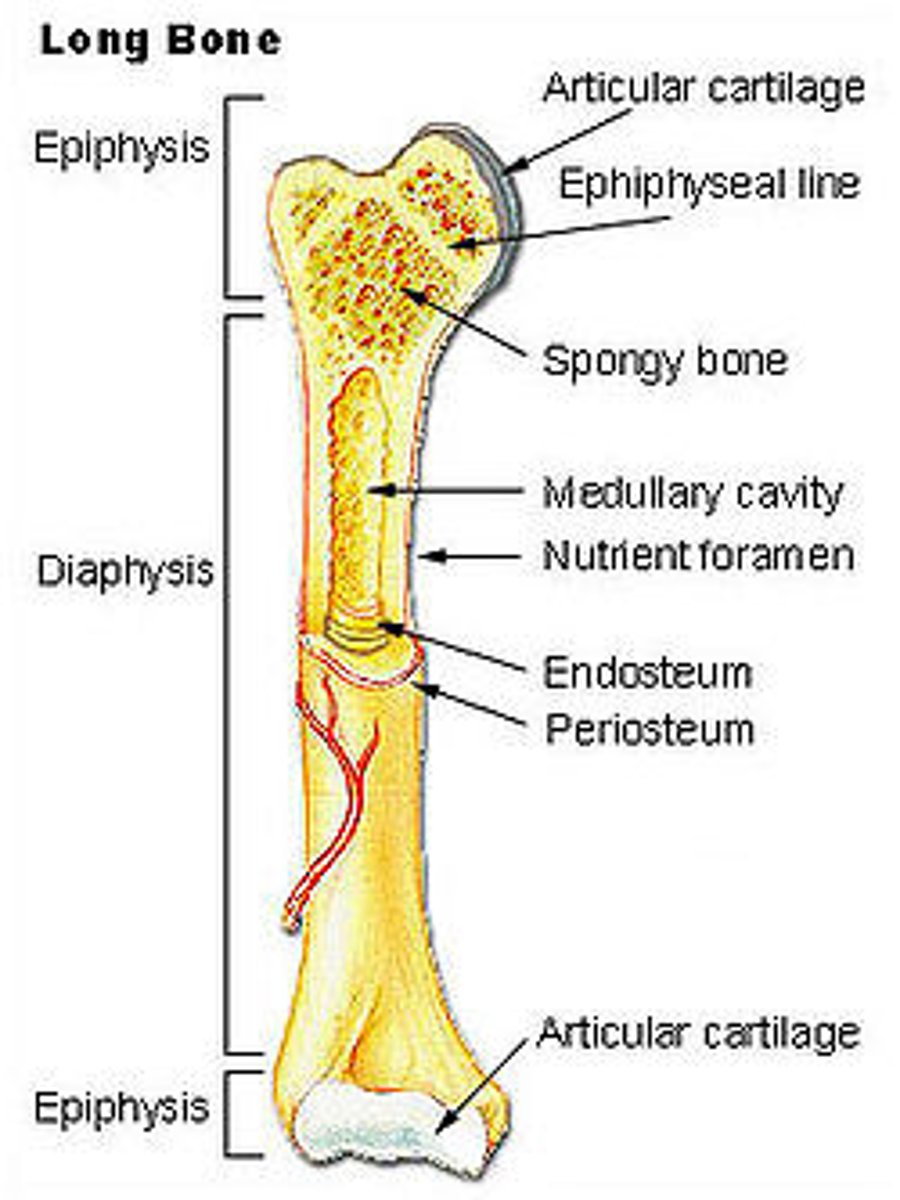
articular cartilage convers
covers the external surface of epiphyses
articular cartilage made of what
hyaline cartilage which decreases friction at joint surfaces
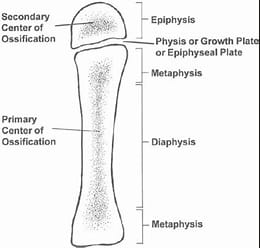
epiphyseal line
thin line of bony tissue spanning epiphyseal
remnant of epiphyseal plate
epiphyseal plate
flat plate of hyaline cartilage
cause lengthwise growth of long bone (ends at puberty)
yellow marrow
inside medullary cavity and storage area for adipose (fat)
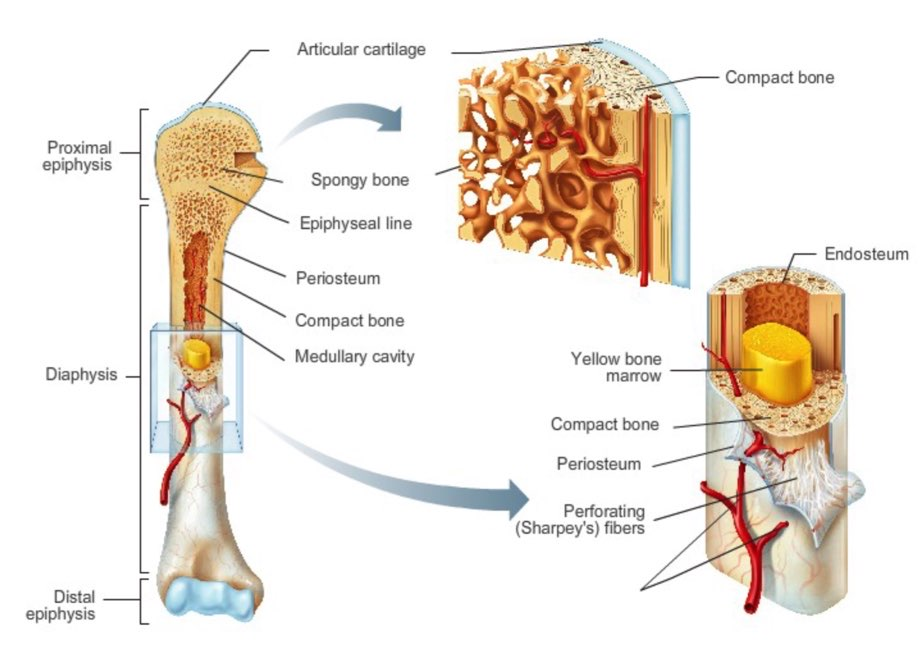
red marrow
fills cavity of shaft in infants only
in adult found in flat bones and epiphysis of long bones
projections and processes
grow out from the bone surface
depressions or cavities
indentations
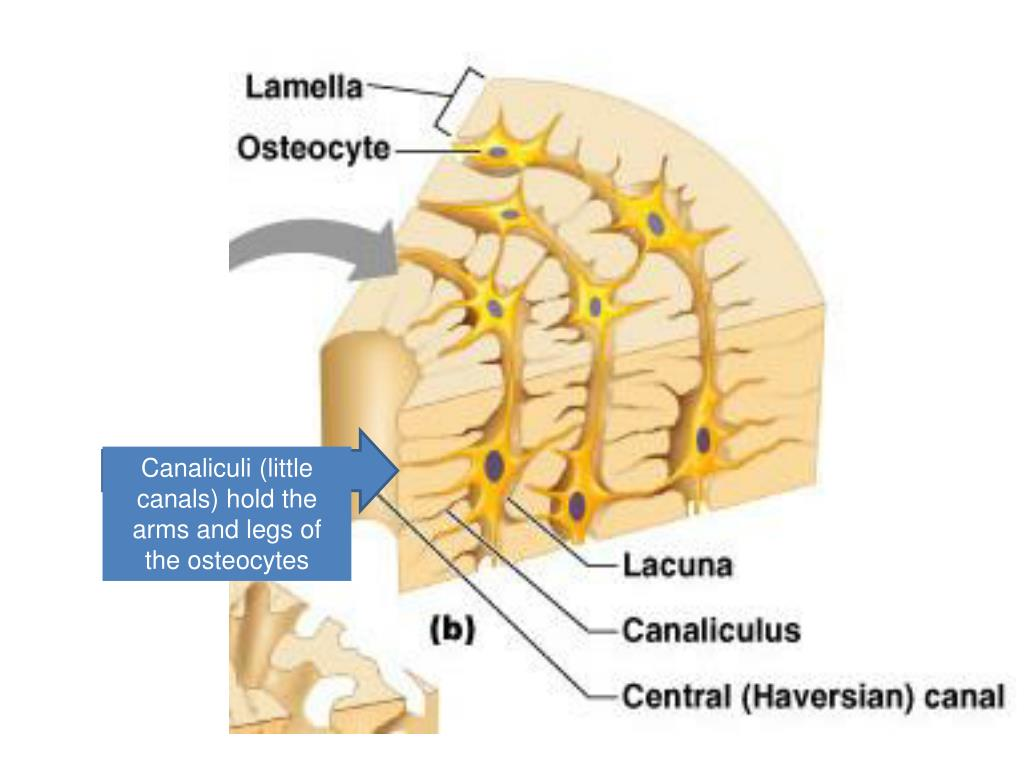
osteocyte
mature bone cell
lacunae
cavities containing bone cells (osteocytes)
carries blood vessels and nerves
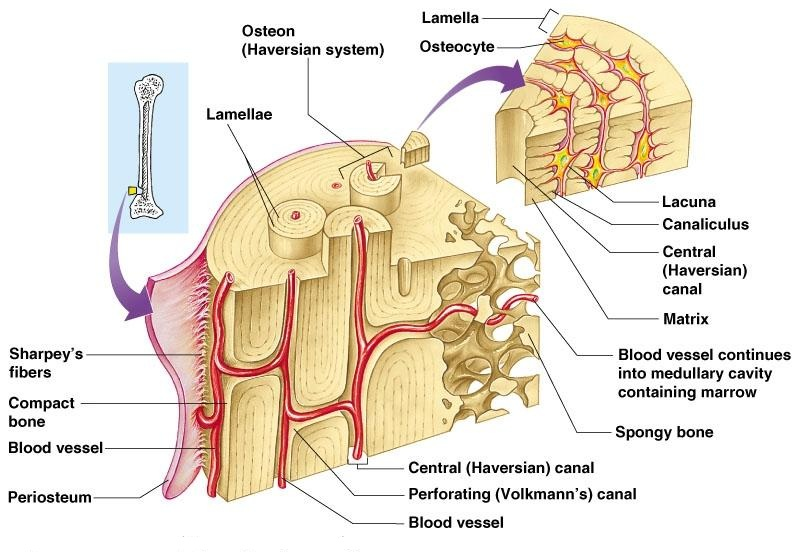
lamellae
rings around the central canal
sites of lacunae
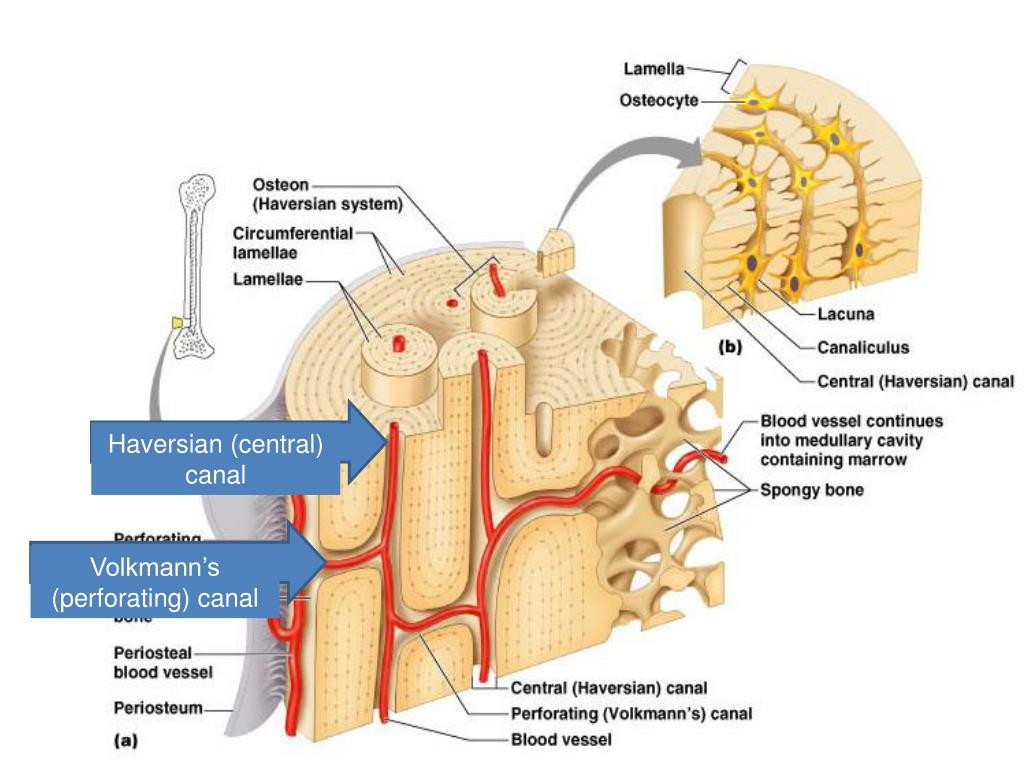
central (Haversian) canal
opening in the center of an osteon
carries blood vessels and nerves
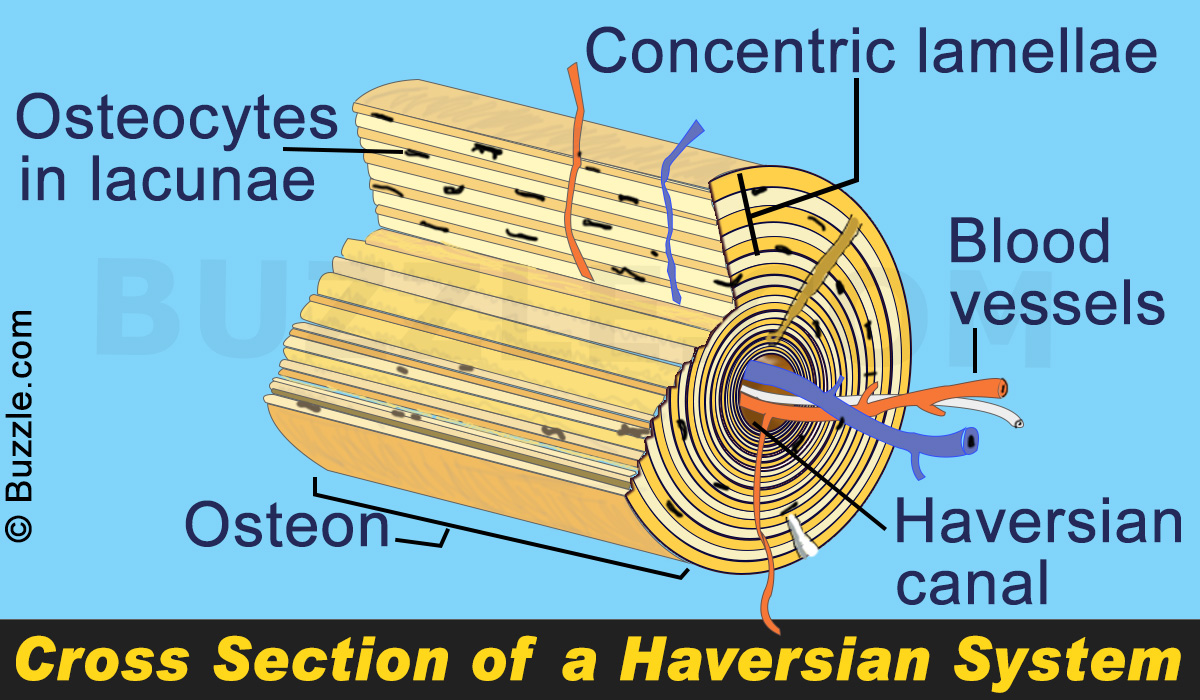
osteon (Haversian) system
system of interconnected canals in bones
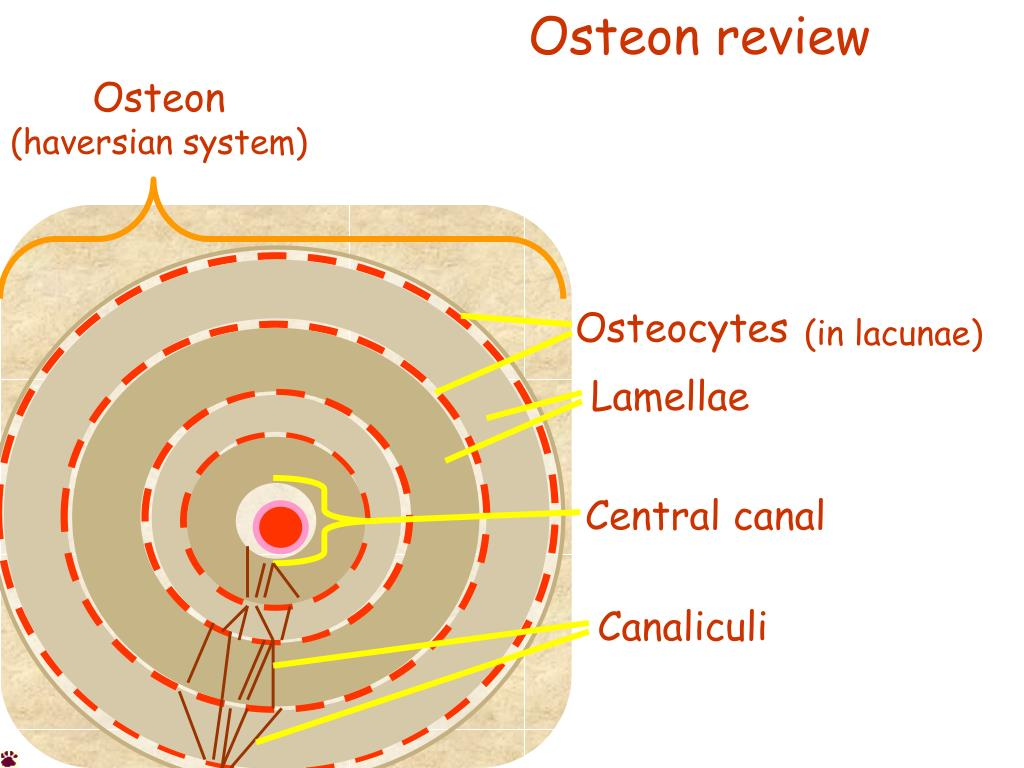
canaliculi
tiny canals that radiate from the central canal to lacunae
form a transport system that connects all bones to nutrient supply through hard matrix
perforating (Volkman’s) canal
canal perpendicular to the central canal
carries blood vessels and nerves