Unit 5: Mental and Physical Health
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
health psychology
The study of how biological, psychological, and social factors affect our health and well-being
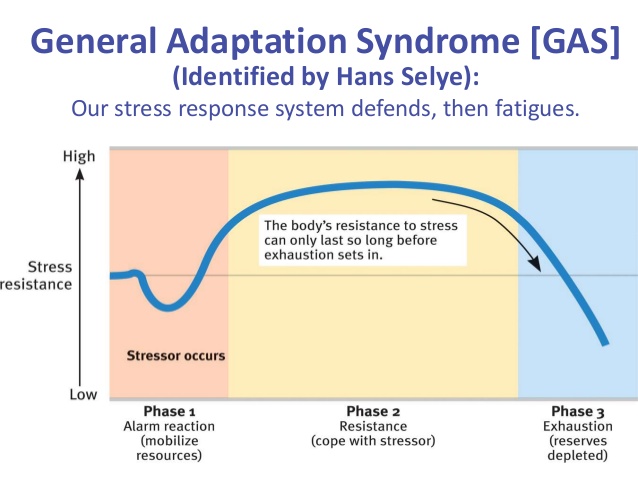
general adaptation syndrome (GAS)
Selye’s concept of the body’s adaptive response to stress in three phases — alarm, resistance, exhaustion.
1.Alarm Stage
The body detects external stress and initiates the "fight or flight" response.
2. Resistance Stage
The body tries to adapt to the ongoing stress.
3. Exhaustion Stage
What happens: The body's resources are depleted after prolonged exposure to stress.
tend-and-befriend response
under stress, people (especially women) may nurture themselves and others (tend) and bond with and seek support from others (befriend).

problem-focused coping
attempting to alleviate stress directly — by changing the stressor or the way we interact with that stressor.
emotion-focused coping
attempting to alleviate stress by avoiding or ignoring a stressor and attending to emotional needs related to our stress reaction.

learned helplessness
the hopelessness and passive resignation humans and other animals learn when unable to avoid repeated aversive events.
positive psychology
The branch of psychology that focus on the study of positive emotions, strengths, and factors that contribute to human fluourishing aiming to enhance well-being, happiness, and life satisfaction rather than just treating mental illness.
subjective well-being
is a person's self-perceived happiness and life satisfaction. It's about how you personally feel about your life
feel-good, do-good phenomenon
people’s tendency to be helpful when in a good mood.
adaptation-level phenomenon
our tendency to form judgments (of sounds, of lights, of income) relative to a neutral level defined by our prior experience.
relative deprivation
the perception that we are worse off relative to those with whom we compare ourselves.
broaden-and-build theory
proposes that positive emotions broaden our awareness, which over time helps us build novel and meaningful skills and resilience that improve well-being.
character strengths and virtues
a classification system to identify positive traits; organized into categories of wisdom, courage, humanity, justice, temperance, and transcendence.
psychological disorder
a disturbance in people’s thoughts, emotions, or behaviors that causes distress or suffering and impairs their daily lives.
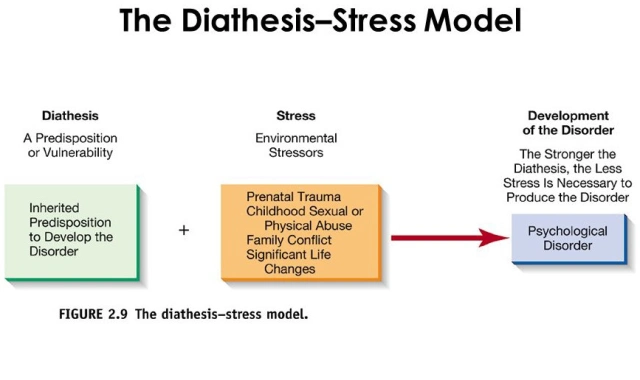
diathesis-stress model
the concept that genetic predispositions (diathesis) combine with environmental stressors (stress) to influence psychological disorder.
DSM-5-TR
the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Text Revision; a widely used system for classifying psychological disorders.
anxiety disorders
a group of disorders characterized by excessive fear and anxiety and related maladaptive behaviors.
social anxiety disorder
An intense fear of social situation where an individual worries about being judged or embarrassed, often leading to avoidance.
generalized anxiety disorder
Excessive worry about various aspects of life, lasting for at least six months, often accompanied by physical and cognitive symptoms.
panic disorder
an anxiety disorder marked by unpredictable, minutes-long episodes of intense dread in which a person may experience terror and accompanying chest pain, choking, or other frightening sensations; often followed by worry over a possible next attack.
agoraphobia
fear or avoidance of situations, such as crowds or wide open places, where one may experience a loss of control and panic.
specific phobia
an anxiety disorder marked by a persistent, irrational fear and avoidance of a specific object, activity, or situation.
obsessive-compulsive disorder, (OCD)
a disorder characterized by unwanted repetitive thoughts (obsessions), actions (compulsions), or both.
hoarding disorder
a persistent difficulty parting with possessions, regardless of their value.
posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
a disorder characterized by haunting memories, nightmares, hypervigilance, avoidance of trauma-related stimuli, social withdrawal, jumpy anxiety, numbness of feeling, and/or insomnia that lingers for four weeks or more after a traumatic experience.
trauma & stressor related disorders
Mental health conditions triggered by exposure to a traumatic or stressful event, causing significant emotional, psychological, and behavioral distress. Symptoms include: hypervigilance, server anxiety, flashbacks, insomnia, emotional detachment, and hostility.
bipolar disorders
a group of disorders in which a person alternates between the hopelessness and lethargy of depression and the overexcited state of mania.
major depressive disorder
Persistent sadness, loss of interests or pleasure, and other cognitive and physical symptoms that significantly impair daily functioning. Symptoms include: depressed mood most of the day, significant weight loss or gain, fatigue or loss of energy, diminished interest in activates, insomnia or hypersomnia, feeling of worthlessness.
persistent depressive disorder
Characterized by mild to moderate depressive symptoms that persist for at least two years and interfere with daily functioning.
It's like "walking through life with a constant weight on your shoulders."
bipolar I disorder
the most severe form, in which people experience a euphoric, talkative, highly energetic, and overly ambitious state that lasts a week or longer.
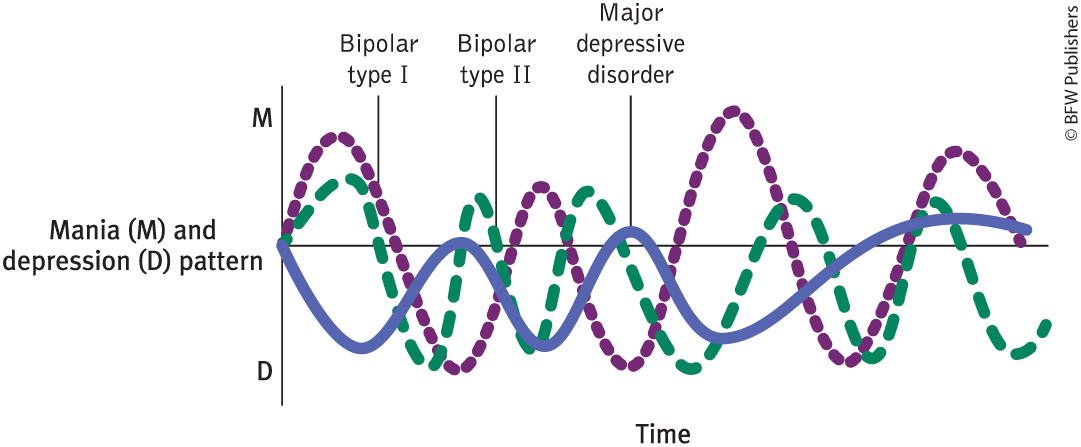
mania
a hyperactive, wildly optimistic state in which dangerously poor judgment is common.
bipolar II disorder
Involves at least one hypomanic episode and one major depressive episode, but never a full manic episode, making the mood swings less serve than bipolar I.
rumination
compulsive fretting; overthinking our problems and their causes.
schizophrenia
Characterized by delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thinking or speech, disorganized motor behavior, and negative symptoms (such as diminished emotional expression (flat affect). Some causes can be prenatal viruses or overactivity of dopamine in certain brain regions.
psychotic disorders
a group of disorders marked by irrational ideas, distorted perceptions, and a loss of contact with reality.
delusion
a false belief, often of persecution or grandeur, that may accompany psychotic disorders.
chronic schizophrenia
A long-term, persistent form, where symptoms fluctuate over time but tend to result in ongoing difficulties with social, occupational, and daily functioning. Treatment can help, but full recovery is less common.
acute schizophrenia
a form of schizophrenia that can begin at any age; a sudden onset of serve psychotic symptoms, such as delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized thinking, often triggered by stress or trauma.
dissociative disorders
disorders involve a disconnection from consciousness, memory, or identity, often as a response to trauma or extreme stress. People may:
Feel detached from themselves.
Experience memory loss.
Develop different identities.
dissociative identity disorder (DID)
A fragmentation of identity with two or more distinct identity states, each with its own way of thinking, behaving, and remembering life events. (formerly known as multiple personality disorder).
dissociative amnesia
a disorder in which people with intact brains reportedly experience memory gaps; people with ____________ may report not remembering trauma-related specific events, people, places, or aspects of their identity and life history.
personality disorders
a group of disorders characterized by enduring inner experiences or behavior patterns that differ from someone’s cultural norms and expectations, are pervasive and inflexible, begin in adolescence or early adulthood, are stable over time, and cause distress or impairment.
antisocial personality disorder
a personality disorder in which a person exhibits a lack of conscience for wrongdoing, even toward friends and family members; may be aggressive and ruthless or a clever con artist.
feeding and eating disorders
a group of disorders characterized by altered consumption or absorption of food that impairs health or psychological functioning. (_______ disorders typically occur in infants and young children, whereas ______ disorders affect people who self-feed.)
anorexia nervosa
an eating disorder in which a person (usually an adolescent female) maintains a starvation diet despite being significantly underweight, and has an inaccurate self-perception; sometimes accompanied by excessive exercise.
bulimia nervosa
an eating disorder in which a person’s binge eating (usually of high-calorie foods) is followed by inappropriate weight-loss-promoting behavior, such as vomiting, laxative use, fasting, or excessive exercise.
neurodevelopmental disorders
These disorders appear early in life/childhood and impact brain development, behavior, and social functioning. Ex: Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) & ADHD
autism spectrum disorder (ASD)
a disorder that appears in childhood and is marked by limitations in communication and social interaction, and by rigidly fixated interests and repetitive behaviors. Some symptoms are decreased sharing of interests with others, difficulty appreciating their own & others' emotions, aversion to maintaining eye contact, lack of proficiency with use of non-verbal gestures, stilted or scripted speech, interpreting abstract ideas literally.
attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
Persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that interfere with daily functioning or development.
deinstitutionalization
the process, begun in the late twentieth century, of moving people with psychological disorders out of institutional facilities.
psychotherapy
Focuses on changing thoughts, emotions, and behaviors through structured talk therapy.
insight therapies
therapies that aim to improve psychological functioning by increasing a person’s awareness of underlying motives and defenses.
Humanistic Therapy or Person-Centered Therapy
Focuses on a person's inherent goodness and potential. The therapist creates a nurturing environment where the client feels safe to explore their thoughts and emotions. Therapist uses techniques such as active listening and unconditional positive regard.
active listening
The therapist fully concentrates on what the client shares, often paraphrasing to validate feelings and clarify confusion. The goal is to make the client feel heard and respected, encouraging them to open up.
unconditional positive regard
Complete acceptance and support regardless of what the client thinks, feels, or does. Carl Rogers believed would help clients develop self-awareness and self-acceptance.
behavioral therapy
therapy that uses learning principles to reduce unwanted behaviors. Some techniques involved in this therapy is exposure therapy, systematic desensitization, aversion therapy, token economy, and biofeedback.
counterconditioning
behavior therapy procedures that use classical conditioning to evoke new responses to stimuli that are triggering unwanted behaviors; include exposure therapies and aversive conditioning.
exposure therapy
Used to treat anxiety and phobias by gradually exposing a person to what they fear in a safe and controlled way.
systematic desensitization
A type of exposure therapy used for phobias, where clients are exposed to increasingly intense versions of feared stimuli while practicing relaxation technique
virtual reality exposure therapy
a counterconditioning technique that treats anxiety through creative electronic simulations in which people can safely face specific fears, such as flying, spiders, or public speaking.
token economy
Clients earn tokens for displaying desired behaviors. This approach uses operant conditioning with positive reinforcements for targeted behaviors. Tokens can be exchanged later for various rewards.
cognitive therapy
A type of psychotherapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative or distorted though patterns to improve emotions and behaviors.
Sometimes the way we think about a situation is more of a problem than the actual situation itself.
rational-emotive behavior therapy (REBT)
Focuses on disrupting irrational beliefs that lead to negative emotions or self-defeating behaviors. Example: If someone believes "I must be perfect or I'm worthless," ______ helps them reframe it to "I can make mistakes and still be valuable."
Uses the ABCDE model:
A (Activating Event): The external event that causes a reaction.
B (Belief): The irrational thought or belief about the event.
C (Consequence): The emotional and behavioral result.
D (Disputation): Challenging the irrational belief.
E (Effective New Belief): Adopting a more rational and positive perspective.
cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
A structured, evidence-based psychotherapy that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors to improve.
Cognitive Influences: Focuses on identifying and changing distorted or negative thought patterns
Behavioral Influences: Uses behavioral strategies, like reinforcement and exposure, to change unhelpful actions.
Change the way you think, and you can change how you feel and act.
group therapy
therapy conducted with groups rather than individuals, providing benefits from group interaction.
family therapy
therapy that treats people in the context of their family system. Views an individual’s unwanted behaviors as influenced by, or directed at, other family members.
therapeutic alliance
a bond of trust and mutual understanding between a therapist and client, who work together constructively to overcome the client’s problem.
antipsychotic drugs
Block dopamine receptors to reduce excessive dopamine activity, addressing symptoms like delusions or hallucinations in schizophrenia
antianxiety drugs
Enhance the action of GABA, producing a calming effect to reduce anxiety symptoms. Primarily used for generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety, etc.
antidepressant drugs
Boost levels of serotonin to regulate mood. Used to treat depressive disorders, anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive and related disorders, and posttraumatic stress disorder.
electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
is a medical treatment where small electrical currents are passed through the brain to trigger a brief seizure.
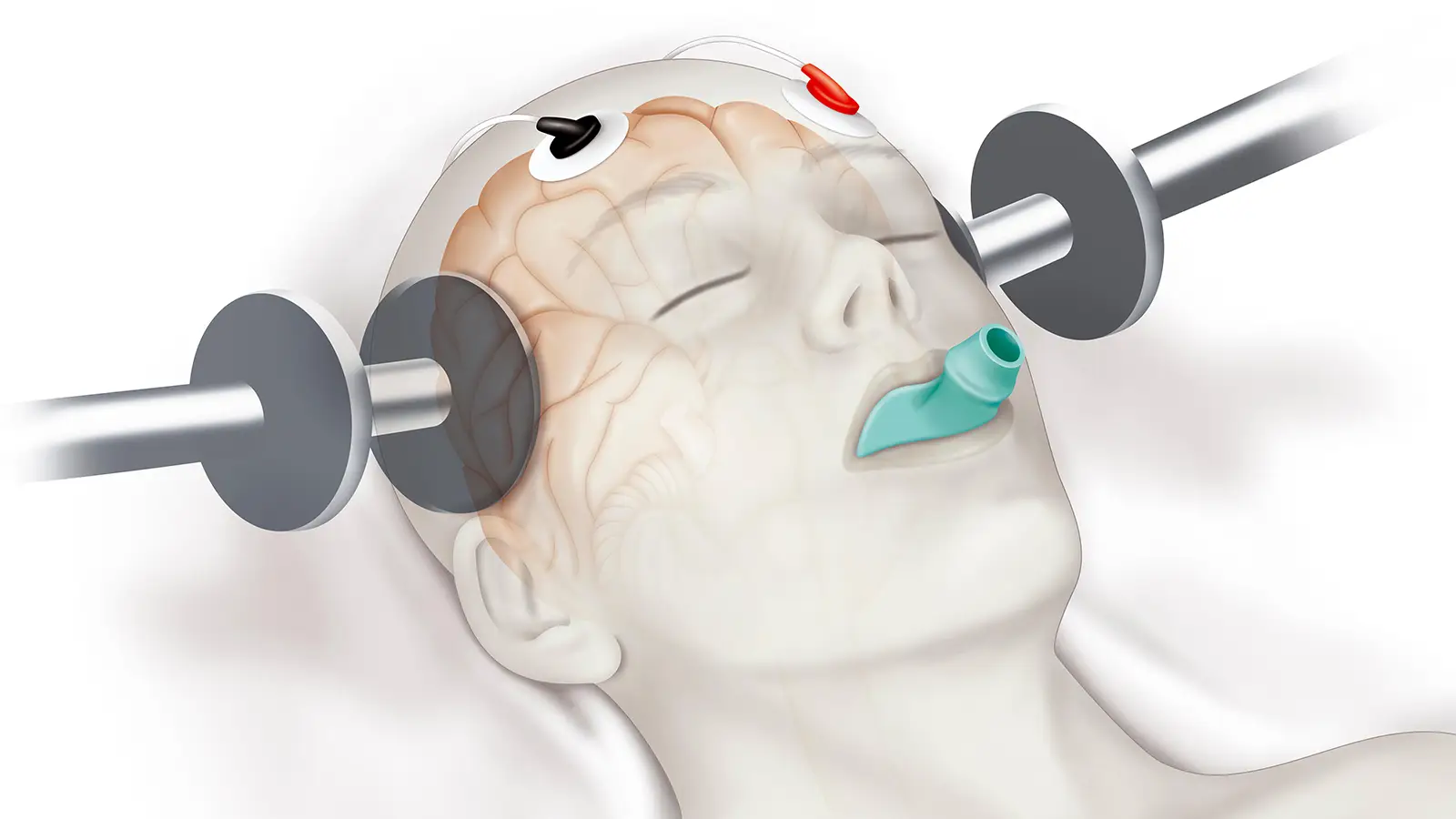
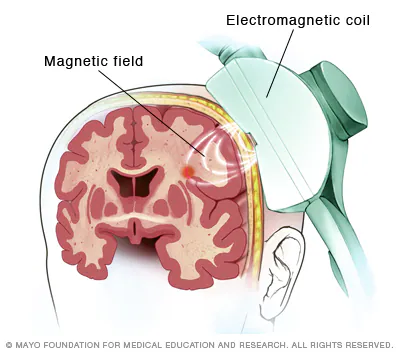
transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
is a non-invasive treatment that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in specific regions of the brain, typically associated with mood regulation.
lobotomy
The procedure cut the nerves connecting the frontal lobes to the emotion-controlling centers of the inner brain.
hypnosis
a state of focused attention, heighted suggestibility, and deep relaxtion.
posttraumatic growth
positive psychological changes following a struggle with extremely challenging circumstances and life crises. Leading to increased personal strength, deeper relationships, greater appreciation for life, new perspectives, or spiritual development.
Cluster A (Odd or Eccentric)
personality disorders characterized by social awkwardness, suspiciousness, and difficulty relating to others.
Cluster B (Dramatic or Erratic)
personality disorders characterized by intense emotions, impulsive behaviors, and/or a strong need for attention or admiration. Ex: narcissistic personality disorder
Cluster C (Anxious or Fearful)
personality disorder characterized by anxiety, fearfulness, and/or behaviors aimed at avoiding perceived harm or rejection. Ex: AvPD, DPD, and OCPD
resistance
the personal strength that helps people cope with stress and recover from adversity and even trauma.
aerobic exercise
sustained exercise that increases heart and lung fitness; also helps alleviate anxiety.
mindfulness meditation
a reflective practice in which people attend to current experiences in a nonjudgmental and accepting manner.
Taijin Kyofusho
a form of social anxiety that is mainly found in Japanese culture, here the fear focuses on offending or displeasing others rather than personal embrassment.
Catatonic state
a condition where someone is awake but appears unresponsive to their environment, exhibiting symptoms like stillness, unusual postures, and resistance to movement. (It's often associated schizophrenia)
False Memories
occurs if the individual is asked leading questions while in the hypnotic state, which may unintentionally suggest or implant details that did no actually happen.
psychodynamic therapy
Focuses on uncovering unconscious thoughts, feelings, and conflicts that shape behavior. Unresolved experiences from the past, especially childhood, can influence present emotions and relationships. Terms include, free association and dream interpretation.
free association
which is a technique that encourages patients to speak freely about any thoughts, words, or images that come to mind. (used in psychodynamic therapy)
Manifest Content
the actual storyline of the dream
Latent Content
the deeper, symbolic meaning that reflects hidden desires, fears, or conflicts.
Cognitive Restructuring
A technique where therapists help a client recognize, challenge, and replace maladaptive thoughts with more realistic and positive thoughts.
Fear Hierarchies
A list of anxiety-provoking situations that is arranged from least frightening most frightening to gradually face and overcome their fear.
Cognitive Triad
A concept in cognitive therapy that describes three negative thought patterns - about oneself, the world, and the future - that contributes to mental health issues.
Biofeedback
A technique that teaches individuals to control physiological processes (like heart rate or muscle tension) by providing real-time feedback from monitoring devices.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
Is a cognitive-behavioral therapy that teaches skills to mange intense emotions, tolerate distress, improve relationships, and practice mindfulness, epically for people with emotional regulation difficultly.
Emotional Regulation
Distress Tolerance
Interpersonal Effectiveness
Mindfulness
Tardive Dyskinesia
A side from prolonged use of antipsychotic medications. Involuntary, repetitive movements of the face, mouth, and extremities.
Alarm Reaction
The sympathetic nervous system kicks in, triggering the fight-or-flight response.
Heart rate increases
Pupils dilate
Adrenaline pumps
Dream Interpretation
Analyzing dreams for symbols and deeper meanings to understand internal struggles. (used in psychodynamic therapy)
Maladaptive Thinking
Negative though patterns that contribute to emotional distress and unhealthy behaviors.
Obsessive-Compulsive Personality Disorder (OCPD)
Preoccupation with order, perfectionism, and control. Distinct from Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), which involves unwanted and intrusive thoughts.
Industrial-Organizational Psychologists
psychologists who applies psychological theories and principles to organizations. It focuses on increasing workplace productivity and related issues such as physical and mental well-being (burnout) of employees.
Positive Subjective Experience
Personal internal feelings of happiness, joy, contentment, or other pleasant emotions that contribute to an individual’s sense of well being.