impact prediction and charcetization
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
impact prediction
core compoent of EA that requires foerthout and foresight about potential implications of a prposed project
the source-pathway-recptor relathonship
prediction is about understanidng the causal chain
source- the impact/actvity thats maybe harmful
pathway - mechanasim by whchthe activty interacts with evnrometn
recptor - envorma or human compent affected
environomental change
measurable differnce in an enviormental or socioeconomic prapeter over a specificed time
change can be natural or caused by differnt actions not just the project
enviornmental effect ( impact)
specific portion of enviornmental change that can be attributed soley to the project
the differnce btwn predicted future conditon with the project vs. future condition WITHOUT THE PROJECT
prediction indicators
condition-based
direct measures of enviormental state
stress based
- meaures of disturbances that lead to imapcts
cummaltive impacts
the total effect on a given VC resulting from incrmental impact of the proepsed project when added to impacts of all other past, present and foreseae future actions
death by a thousand cuts problem
projects indivudal imapct seems minor but can be the tipping pont that pushes a resource or ecosystem beyone critical threshold
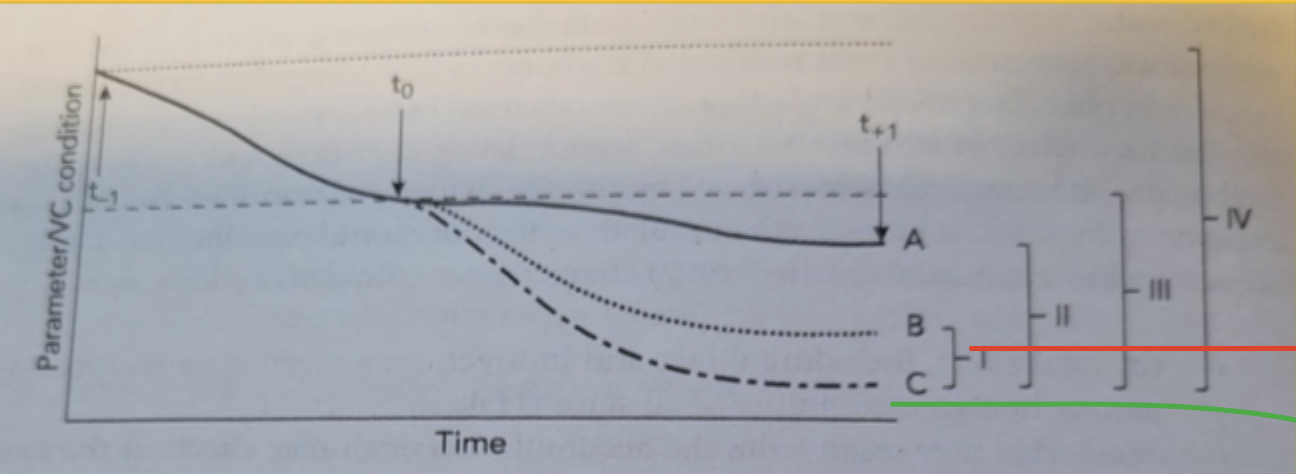
explain this graph
cummaltive impacts graph
common approaches used to predict for EIA
analogue
expert judgment
modeling and extrapolation
threshold-based ( MAELs)
scenarios
analouge appraoches
learn from past by examining observed impacts of similar existing projects in comparable environoments
most common
using literature and studies
expert judgment approach
relying on opinons of dscilary experts, local communites and traditonal knoweldge holders
Judgment has to be critical - they have to show their work and findings based on something concrete - show data from past sites,
modeling and extrapolation approach
create simplfied mathematical or conceptual represenations of real world systems to forecast outcomes
threshold-based MAELs
instead of predicting a specified outcome , focus shifts to managing project to ensure imapct doesnt exceed a predefind limit
Side steps the need for PERCISE prediciton - once you reach that threshold is when mtiigation starts - just a threshold and once your reach that threshold you do something about it
scenarios approach
developing plausible, coherent stories or alternative images of the future to explore outcomes under differnt assumtions
comes in handy when navigating tradeoffs
what could happen, tool for exploring uncertainity
what is the purpose of scenarios
chalenge assumptions and test a proejcts resilence agains a range of potential futures
what are scenarios useful for
long term predictions where trends are highly uncertian
exploring induced imapcts that arent under the propoents direct control
assessing cummlative imapcts invovling hypotehtical future devlopments
explain cone of uncertainty
possible, plausabile and probalby based on past trends, wildcards
plausible is where
Where most of the serious secneario planning happens - blievveable, coheranet scenarios
what is characterizing predicted impacts for
comparing and priotizing differnt impacts
focusing managament and mtiigation efforts
making a final determinaton of impact signifigance
classification critera of charectizing impacts
order
nature
magnitude
spatial extent
frquency and duration
reversibity
likelihood
order of impact
the causal relationship of th eimpact to the projects action
direct- 1st order - ex. flood for dam
an immdiate result of a project activity
indirect- 2nd order - more mecury level in fish b/c of dcay of flooded OM
an effect that stems from direct impact
induced (usually socioeconomic) - new buisness ipening to service mining workforce
effect resulting from spin off activities triggered by proect
nature of interaction
how the impact interacts with other impacts
additive
the total impact is the sum of idnivudal imapcts
synergistic
total impact is greater than the sum of idnivudal imapcts
One we want to look out for
Not a simple addicitivve effect, can combien and form a worse impact
antagonistic
one adverse impact partically canels out another - LESS COMMON
accuracy vs precsions
accuracte prediction
about the closness to the true value/outcome
precise prediction
the level of exatness, youre being more detailed and seeing if it matches
magnitude
size, degree or concentraion of impact
magnitude doesnt equal signfigance
small mag. impact on rare or senstive recpetor. could be highly signficant
direction - refers to wheter change is postive, pad or neutral realtive to baseline
spatial extent
geographic area affected by the impact
onsite imapcts - contained w/in projects physical footprint
enviormental changes that ocur within defined boundaries of the proejct
offsite impacts
enviormental changes that are triggered by project but ocur outside its phsycial boundaries
in fly in fly out operations
onsite impat. is at the remote mine
but sig. offiste soical imapcts occurs in workers home communties (stress, family disruption etc.)
frequency duration and reversible
frquency
how often imapct or disturbance occurs
duration
length of time impact happens - short or long term
reversibliliy
if affected componet can be returned to conditon near its predisturbance state after project ends or impact is permenant and orginal state cnat happen
likeihood
proabilty that predicted impact wil occur
risk
fuction that combines probabilty (likehood) of adverse event happpen and the severity of the consequences if event happens
risk assemtn - process of idintify, anlayzing and evlauting risks
helps decionmakers understand full spectrum of potential outcomes
critical risks
low proablty but high conswquece event
imprtant to detail in report
problem of false certainty
findings with a high degree of confidence can lead to over confidence in mitigation and poor decision -making
uncertainty matrix
location
wheres the uncertaintiy? - in input data, underlying assumtions or predicitive models
level
how greats the uncetatiny - is it statistical ( known probabilities), scenario ( known posiblites, unknown proabilites, or system ( we dont know what we dont know)
Nature
can it be reduced? is it knoweldge related ( more research will help) or due to inherent varialbity ( more rearch wont help)