FIN exam 2: Elimination GI
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
GI elimination
The excretion of waste product
Bowel elimination
The process of expelling stool
Functions of GI (2)
Breakdown and absorption of nutrients from foods ingested
Elimination of waste
Upper GI tract function
Involved in digestion and absorption of nutrients
Upper GI tract parts (4)
Mouth
Esophagus
Stomach
Small intestine
Upper GI tract accessory digestive organs (3)
Liver
Gallbladder
Pancreas
Lower GI tract function
Involves the process of waste formation
Lower GI tract part
Colon
Peristalsis
movement of fecal matter
What stimulates peristalsis?
Smooth muscles
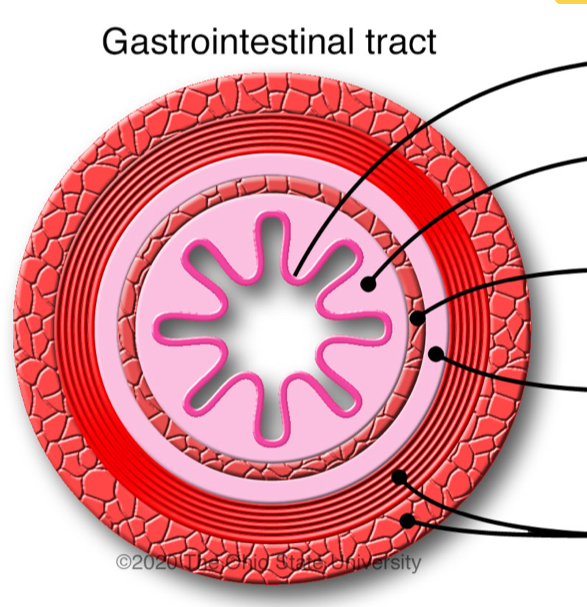
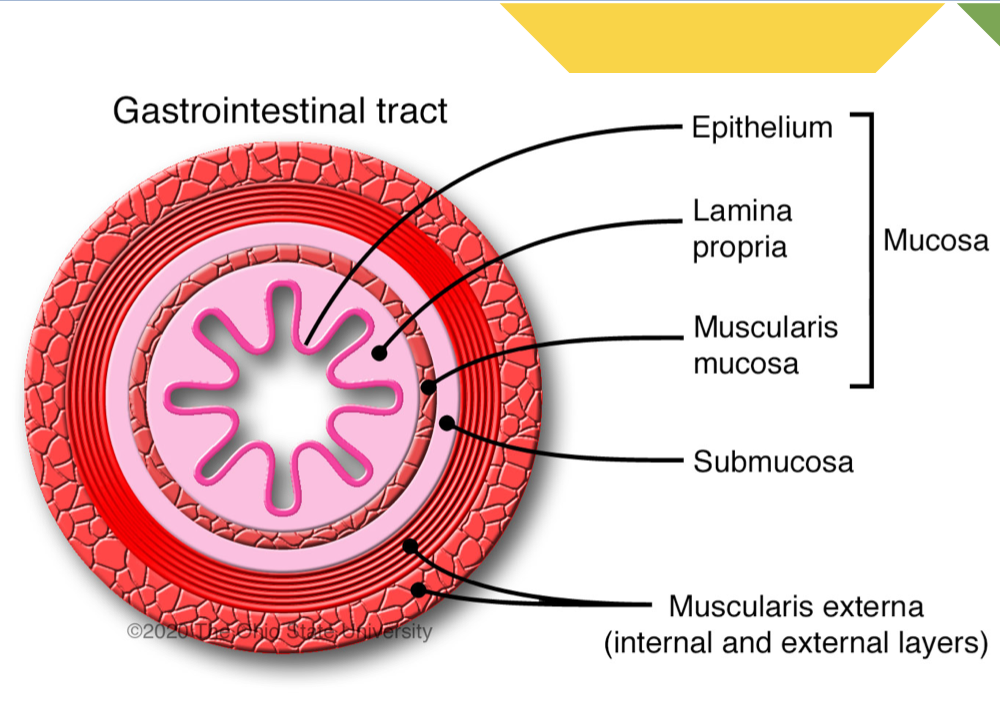
Label layers of GI tract
Elimination is involuntary or involuntary?
Both
What does pressure stimulate during elimination that allows for the passage of stool?
Stimulates parasympathetic nerve fibers (sacral + spinal cord)
Steps of elimination (6)
pressure
parasympathetic nerve fibers stimulated
rectum contracts
internal anal sphincter relaxes
voluntary relaxation of external anal sphincter
Stool passage
Pressure stimulates ________ nerve fibers, allowing for…
Parasympathetic
Passage of stool
Voluntary relaxation of external anal sphincter allows for…
Passage of stool
Nursing skills for elimination (6)
Assessment
Enema (last resort)
Nastrogastric tube for gastric decompression
Ostomy care
Medication administration (must give correct med, e.g. do not use stool softeners for those with diarrhea)
Nutrition education
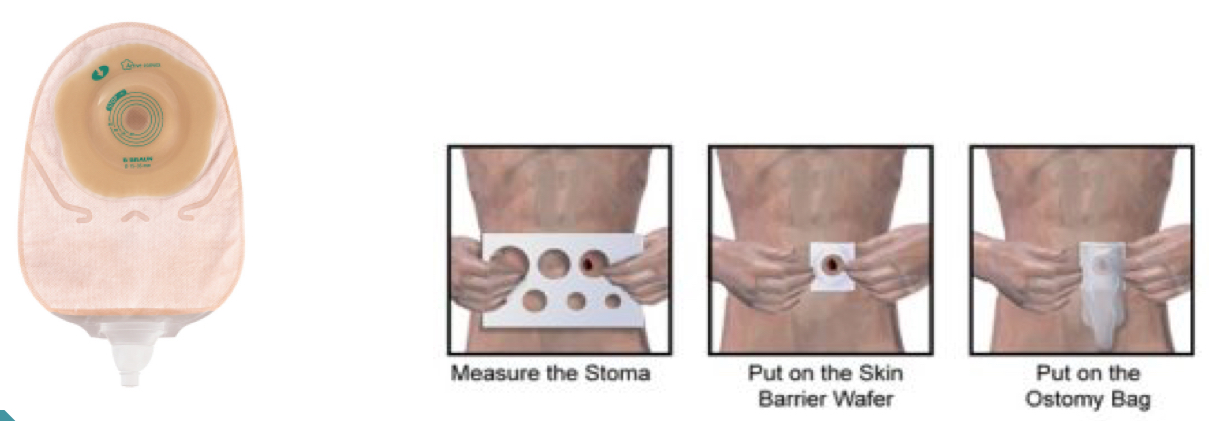
Ostomy care and when is it used?
surgically created opening on the abdomen for the elimination of body waste
Used for someone who has chronic inflammatory disease
Must ensure it’s clean and secured
GI assessments (6)
X-ray
Endoscopy
Colonoscopy
NG tube sucks out stomach contents — can assess contents of stomach
CAT scan
Readi-cad (drink 1hr before CAT scan to help with imaging; oral contrast)
Invasive procedures/surgical interventions
Colectomy
Colon resection
Removing portion of bowel, for treatment cancerous tumor, or traumatic injury
Ends can remain ‘reanastmosed’
surgical procedure to reconnect two previously separated sections of a bodily structure
Colonoscopy/ileostomy
Diversion of the intestine (colon or sm intestine) through a stoma on the skin
Temporary or permanent
Rectal prolapse repair
Rectal prolapse is when the rectum falls though anal opening
requires surgery to put it back in
Hemorrhiodectomy
Excision of internal or external hemorrhoids
only for patients who have severe pain/discomfort
Fecal collection system
flexible tube inserted into rectum, which collects liquid stool
in cases of c. Diff or extreme diarrhea
Helps to prevent skin breakdown
Why do people with c. Diff get a fecal collection system?
because the infection causes frequent, watery diarrhea
Ostomy
Surgically created opening on the abdomen that allows bodily waste to exit the body when the usual path is blocked or cannot function properly
Example: ileostomy
Bowel regimen medications (9)
Senna
Polyethylene Glycol (MiraLAX)
Bisacodyl
Docusate (colase)
Lactulose
Magnesium citrate
Fleet enema
Psyllium (metamucil)
Glycerin suppository
Senna class and form
Stimulant laxative
Tablet/liquid
When is senna used?
when someone hasn’t had bowel movements in a few days
Senna side effects (3)
Abdominal cramping
Diarrhea
Nausea
Polyethylene glycol (miralax) class and form
Osmotic laxative
Powder/packet
Polyethylene side effects (5)
Bloating
Cramping
Gas
Nausea
Diarrhea
Milk of Magnesia (MOM) class and form
Osmotic laxative
Liquid form
MOM side effects (3)
Abd cramping
Diarrhea
Nausea
Bisacodyl class and form
Stimulant laxative
Po/suppository form (solid med into rectum)
Bisacodyl side effects (5)
Abd cramping
Diarrhea
Nausea
Dehydration
Laxative dependence
Dosustate (colace) class and form
Stool softener (emollient laxative)
Capsule/liquid
Docusate side effects (2)
Mild cramping
Diarrhea
Lactulose class and form
Osmotic laxative
Liquid form
Lactulose side effects (4)
Bloating
Gas
Cramping
Diarrhea
Magnesium citrate class and form
Osmotic laxative
Liquid
Mg citrate side effects (4)
Diarrhea
Cramping
Electrolyte imbalance (w/ excessive use)
Fleet enema class and form
Saline laxative
Rectal enema
Fleet enema side effects (4)
Cramping
Diarrhea
Rectal irritation
Electrolyte imbalance
How is fleet enema administered?
patient lies on left side for liquid to be inserted into their rectum
they try to hold the liquid in for at least 15 minutes
Psyllium (Metamucil) class and form
bulk forming laxative — increases peristalsis
Powder/packet — mix with liquid
Psyllium side effects (1)
Loose stool
Glycerine suppository class and form
Hyperosmotic properties (provides rectal stimulation and lubrication)
Suppository (bowel movement in 15-60 mins)
Constipation
Difficulty passing stool
Constipation consistency (3)
Hard
Dry
Formed
Clinical constipation presentation (5)
Abdominal bloating
Gas
Cramping
Pain
Nausea/vomiting
Possible causes of chronic constipation (3)
lack of dietary fiber
medications (e.g., opiods or iron supplements)
decreased fluid drinking
Diet to alleviate constipation (3)
High fiber meals
Increase fluid intake
Encourage movement
Diarrhea
frequent passing of watery stool, loose stools
>3 /day or volume of 200g/day
Acute vs Persistent vs Chronic Diarrhea
Acute: associated with bacterial/viral illness and usually resolves within a few days
Persistent: days to weeks
Chronic: can persist for weeks
What is the primary concern with diarrhea?
Dehydration and electrolyte imbalance can occur quickly
must be monitored
Hypokalemia (low K+ in blood)
Diarrhea causes (9)
Medication effect
Intestinal obstruction
Tube feeding
Dumping syndrome (food moves too quickly from the stomach into the small intestine)
GI disease — IBS
IBD
Infection (viral/bacterial)
AIDS
Parasitic
What labs/imaging should be ordered for diarrhea?
Labs
Stool tests
Blood tests
Imaging
CT
MRI
Colonoscopy
Endoscopy
Why should you wait to give patients medications when they have diarrhea?
since it can possibly be caused by infectious processes, you do not want to give medications until after you determine if the patient doesn’t have an infection
Constipation and diarrhea are usually not a huge problem, but they can become _____ because…
Deadly
Blood flow to bowels can be cut off
Constipation can lead to blockage and infection
Diarrhea can lead to extreme dehydration and electrolyte loss
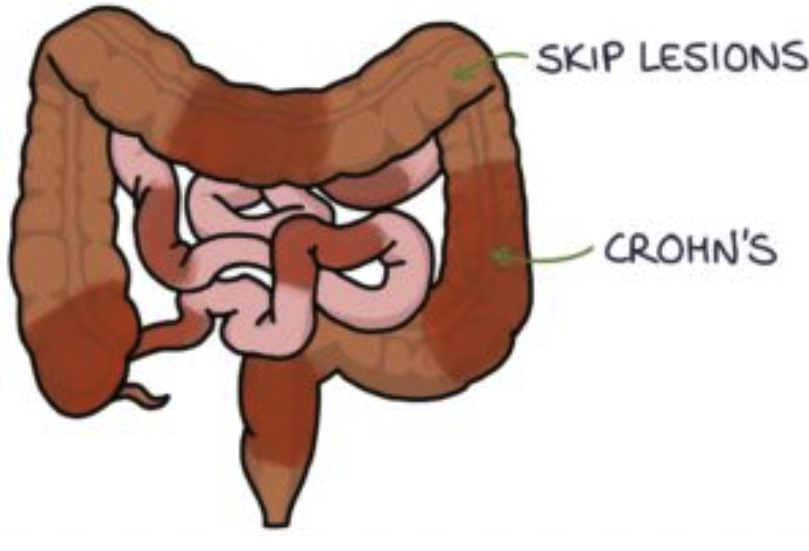
Crohn’s Disease
chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that can affect any part of the digestive tract
What parts of the GI tract does Crohn’s affect?
ANY part of the GI tract
Mouth to anus
What part of the bowel walls does Crohn’s affect?
All parts
transmural inflammation
Transmural inflammation
Inflammation of the entire bowel wall
Skip lesions
areas of inflammation or tissue damage in the gastrointestinal tract that are separated by healthy tissue
What labs/imaging should be ordered for Crohn’s disease?
Labs
Blood
Stool
Scans
MRI
CT
Ultrasound
What does imaging show with Crohn’s disease?
Inflammation that gives the mucosal tissue a cobblestone-like appearance
Symptoms of Crohn’s (4)
Abdominal pain
Diarrhea (not bloody)
Weight loss
Fatigue
Crohn’s has risks of developing… (2)
Malnutrition
Dehydration
Crohn’s medications (2)
Antiinflammatories
Immunosuppresants
Ulcerative Colitis
IBD that primarily affects colon, causing inflammation and ulcers in the lining of these organs
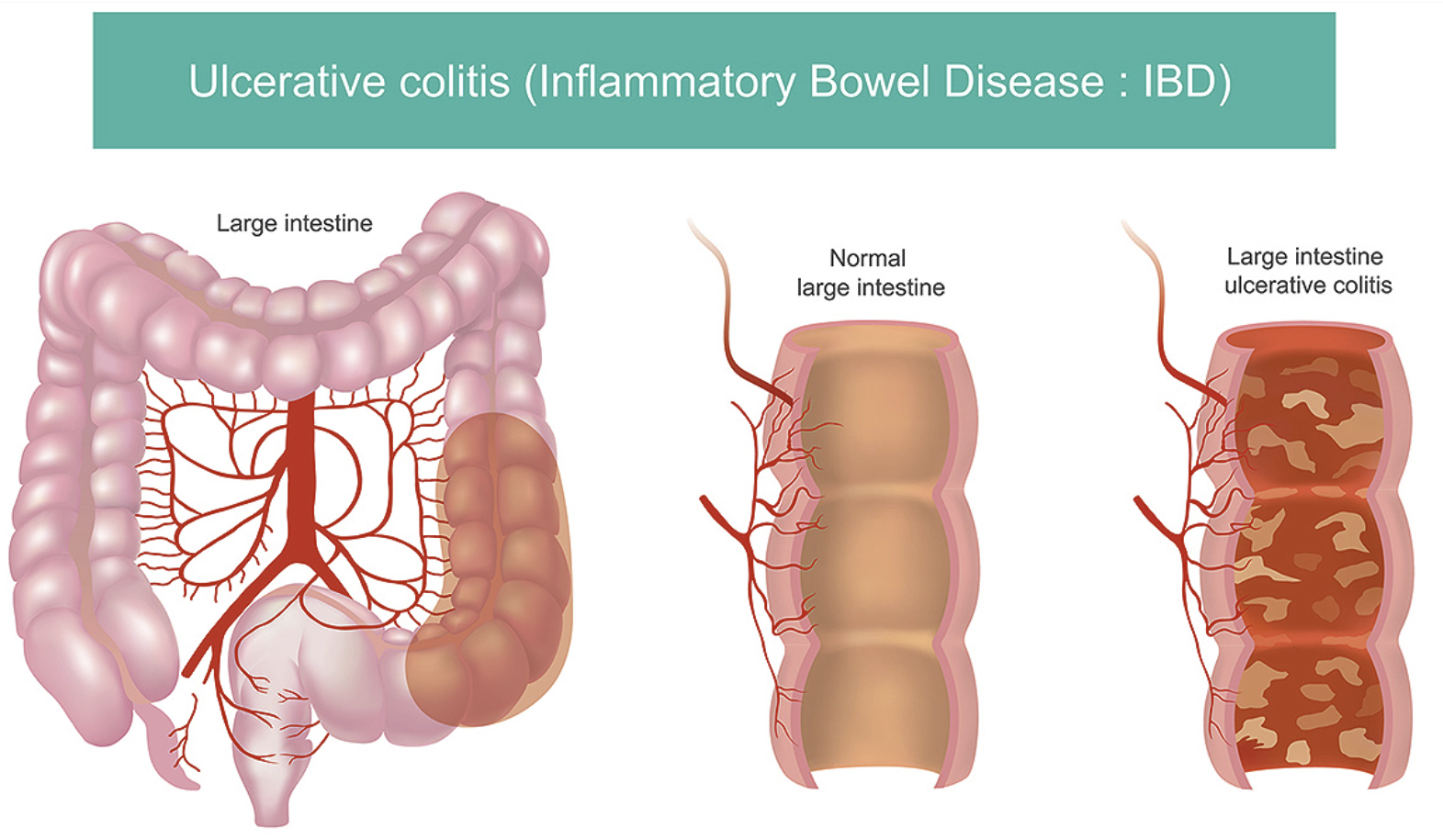
Place that Ulcerative colitis affects
Colon
Location of inflammation for Ulcerative colitis
Mucosa and submucosa of the colon wall
Ulcerative colitis continuous lesions
continuous inflammation throughout area
Symotoms of Ulcerative colitis
Bloody diarrhea
Urgency
Abdominal cramping
Must monitor _____ and _____ with Ulcerative colitis
fluid and electrolytes
Provide _____ and _____ support for patients with Crohn’s and Ulcerative colitis
Emotional and psychological support
***Ulcerative colitis vs Crohn’s location
UC is only in the colon
Crohn’s can be present anywhere in the digestive tract
***UC vs Crohn’s inflammation pattern
UC: limited to the mucosa and submucosa
Crohn’s: has skip lesions and is transmural
**UC vs Crohn’s symptoms
UC: bloody diarrhea, urgency, abd cramping
Crohn’s: non-bloody diarrhea, abd pain, weight loss, fatigue
IBD medications for Crohn’s vs Ulcerative colitis
Crohn’s: Animosalicylates, corticosteroids, immunosupressants, anti-TNF, anti-integrin, nutrition therapy, antibiotics
UC: Animosalicylates, corticosteroids, immunosupressants, anti-TNF, anti-integrin
abx and nutrition therapy not typically used
IBD medications in order of administration (4)
Anti-inflammatories — MOST COMMON
Cortical steroids
Immunosuppressants
Biological agents (for severe cases)
Indicators of bowel obstructions (3)
Severe pain
Vomiting (stool could be in there)
Absent bowel sounds
What is the technical term for the movement of fecal matter through the GI tract?
A. Digestion
B. Peristalsis
C. Defecation
D. Constipation
B. Peristalsis
Name a commonly used bowel regimen medication that can be mixed with water for administration?
A. Senna
B. Colace
C. Miralax
D. Ducolax
C. Miralax
Which bowel disorder is characterized by ulcerations from mouth to anus?
A. Diarrhea
B. Chronic Constipation
C. Crohn's Disease
D. Ulcerative Colitis
C. Crohn's Dx
Electrolyte abnormalities are commonly associated with which elimination disorder?
A. Constipation
B. Crohn's Disease
C. Diarrhea
D. Colorectal Cancer
C. Diarrhea
Which dietary advice is most appropriate during an acute flare of ulcerative colitis?
A. High-fiber to promote bowel motility
B. High-protein, low-residue diet to reduce stool frequency
C. Encourage carbonated beverages for hydration
D. Strict fasting for 72 hours
B. High-protein, low-residue diet to reduce stool frequency
Which chronic complication is a patient with ulcerative colitis at increased risk for?
A. Pancreatic Cancer
B. Colon Cancer
C. Renal Cell Carcinoma
D. Esophageal Cancer
B. Colon Cancer
Which clinical sign would indicate a complication of ulcerative colitis requiring immediate intervention?
A. Mild abd cramping with 2-3 stool/day
B. Abdominal distention with decreased bowel sounds
C. Fatigue and mild anemia on lab work
D. Weight loss of 5lbs over one month
B. Abdominal distention with decreased bowel sounds
Toxic megacolon — inflammation becomes so bad that it paralyzes the colon muscles
Which area of the GI tract is commonly affected by Crohn's Dx?
A. Sigmoid Colon
B. Rectum
C. Terminal Ileum and colon
D. Esophagus
C. Terminal Ileum and colon
Which of the following statements would be an appropriate nursing education point for a patient with
Crohn's Disease?
A. Smoking reduces the frequency of flares
B. A high-fiber diet is recommended during a flare
C. Continue medications even if you feel well
D. Limit fluid intake during diarrhea
C. Continue medications even if you feel well
A: smoking worsens it
B: high fiber can irritate inflamed bowel
D: fluid should be increased since so much fluid is being lost to diarrhea
Key takeaways:
differentiate btwn diarrhea and constipation
understand Crohn’s vs UC
Review key nursing interventions and common treatments for GI elimination concepts