Foundations in Biology - Biological molecules
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Water is a metabolite. What does this mean?
It's used in metabolic reactions such as condensation and hydrolisis
Name the types of metabolism
Catabolism- breaking down large into small
Anabolism- molecular build up from small to large
What is the advantage of waters high specific heat capacity?
Lots of energy os required to heat it therefore it doesn't go through massive temperature fluctuations
What is a macromolecule
Made from smaller subunits whereas polymer is made from always repeating subunits
how does sweating cool down the body?
Sweet is released on the skin and due to waters high latent heat of vaporisation it provides a cooling effect upon evaporation.
How does ice being less dense than water affect organisms?
In winter ice is formed on water and as ice is less dense than water due to semi crystalline structure it floats to the surface this provides an insulation affect meaning aquatic life is safer as it near impossible to freeze a body of water all the way through.
Why is water a good solvent
It has negatively charged o2 and positively H+ so it’s polar and interacts with charged regions to dissolve the substance (other polar molecules)
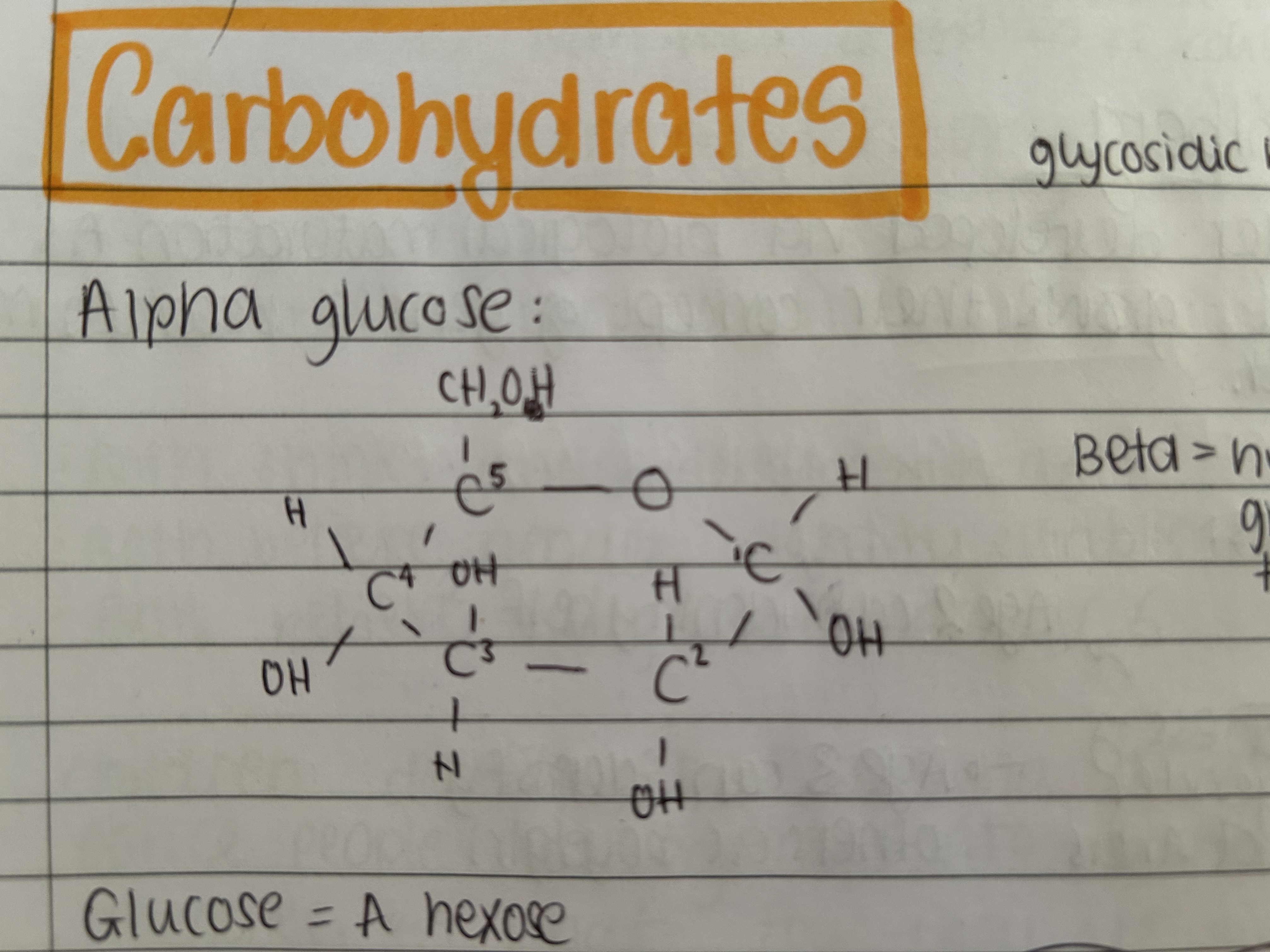
What is the difference between alpha and beta glucose?
The hydroxyl group on carbon 1 of alpha glucose is below the ring whereas the hydroxyl group on beta glucose is above the ring.
What elements make up carbohydrates?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
What elements make up protein base structure?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
What elements make up lipids?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
What are examples of monosaccharides?
glucose, fructose, galactose
What are examples of disaccharides?
sucrose, lactose, maltose
What are the Monomers of Maltose?
glucose and glucose
What are the Monomers of sucrose?
glucose and fructose
What are the Monomers of Lactose?
glucose and galactose
What is the structure of Amylose?
It's an unbranched chain of glucose joined by 1,4 glycosidic bonds as a result it's coiled
What is the structure of Amylopectin
It's branched and joined together by 1,4 glycosidic bonds however its branches join with 1,6 glycosidic bonds. Due tot he presence of branches it is digested rapidly
What is the structure of cellulose?
It's a long, unbranched chain of beta glucose joined by glycosidic bonds. Hydrogen bonds hold multiple chains together forming microfibrils.
What is the structure of glycogen?
It's a highly branched straight chain of alpha glucose joined with 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds. It's extremely large but very compact.
What is a saturated lipid and where is it found?
Saturated lipids are found in animal fat and contain no CC double bond.
What is an unsaturated lipid and where is it found?
Unsaturated lipids are found in plant oils and DO contain a CC double bond
What is a lipids function
Buoyancy
Protection for vital organs
Insulation
Storage of energy via adipose tissue
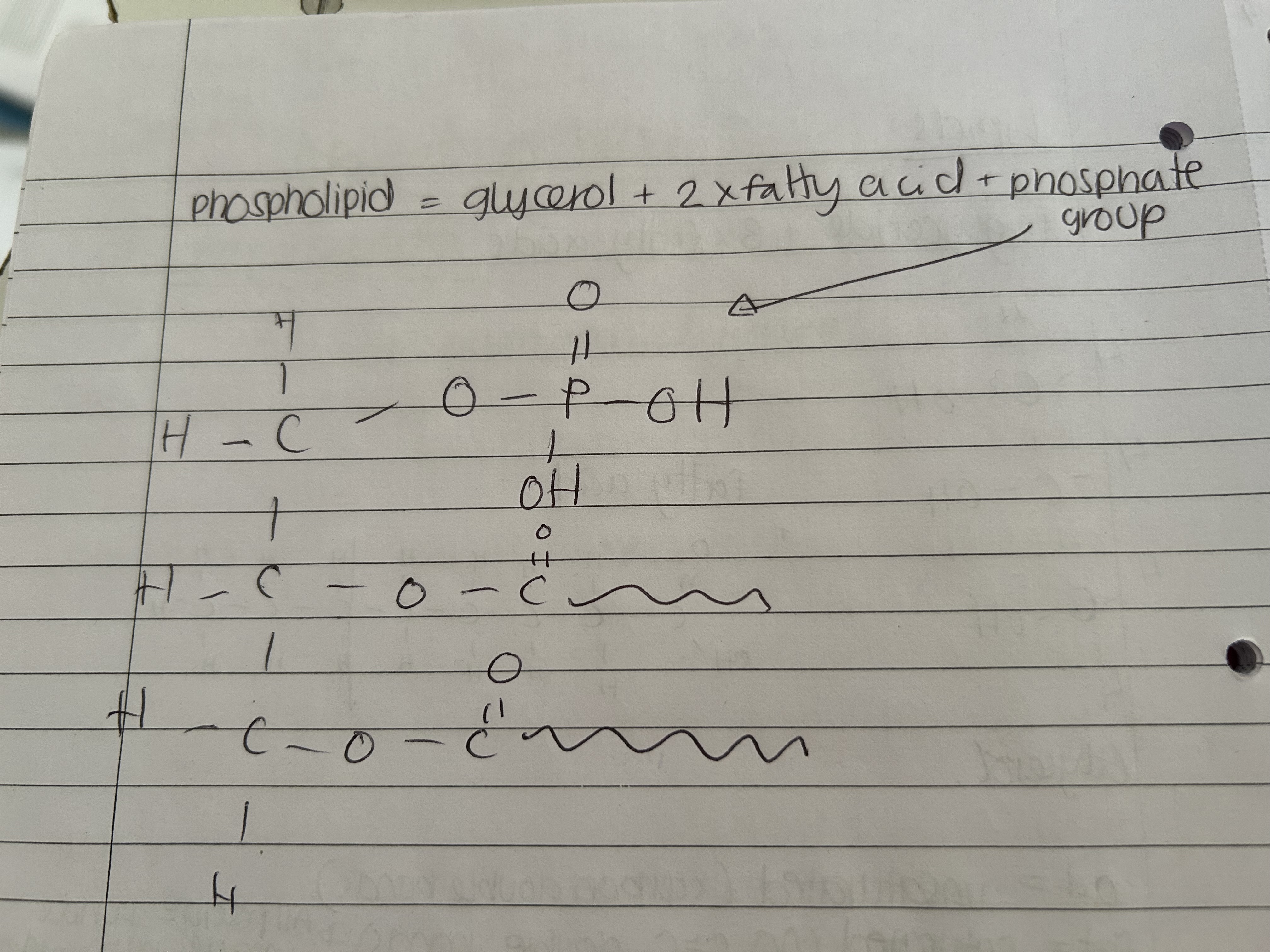
What is the structure of a phospholipid?
One phosphate head attached to a glycerine which has two fatty acids attached.The phosphate group is hydrophilic
What is the function of H+ in the body?
It determines the pH of certain areas
What is the function of Fe2+ in the body?
It's a component of haemoglobin which carry's oxygen in red blood cells
What is the function of Na+ in the body?
It is involved in the co-transport of glucose and amino acids
What is the function of Phosphate ions in the body?
They are components in DNA and ATP.
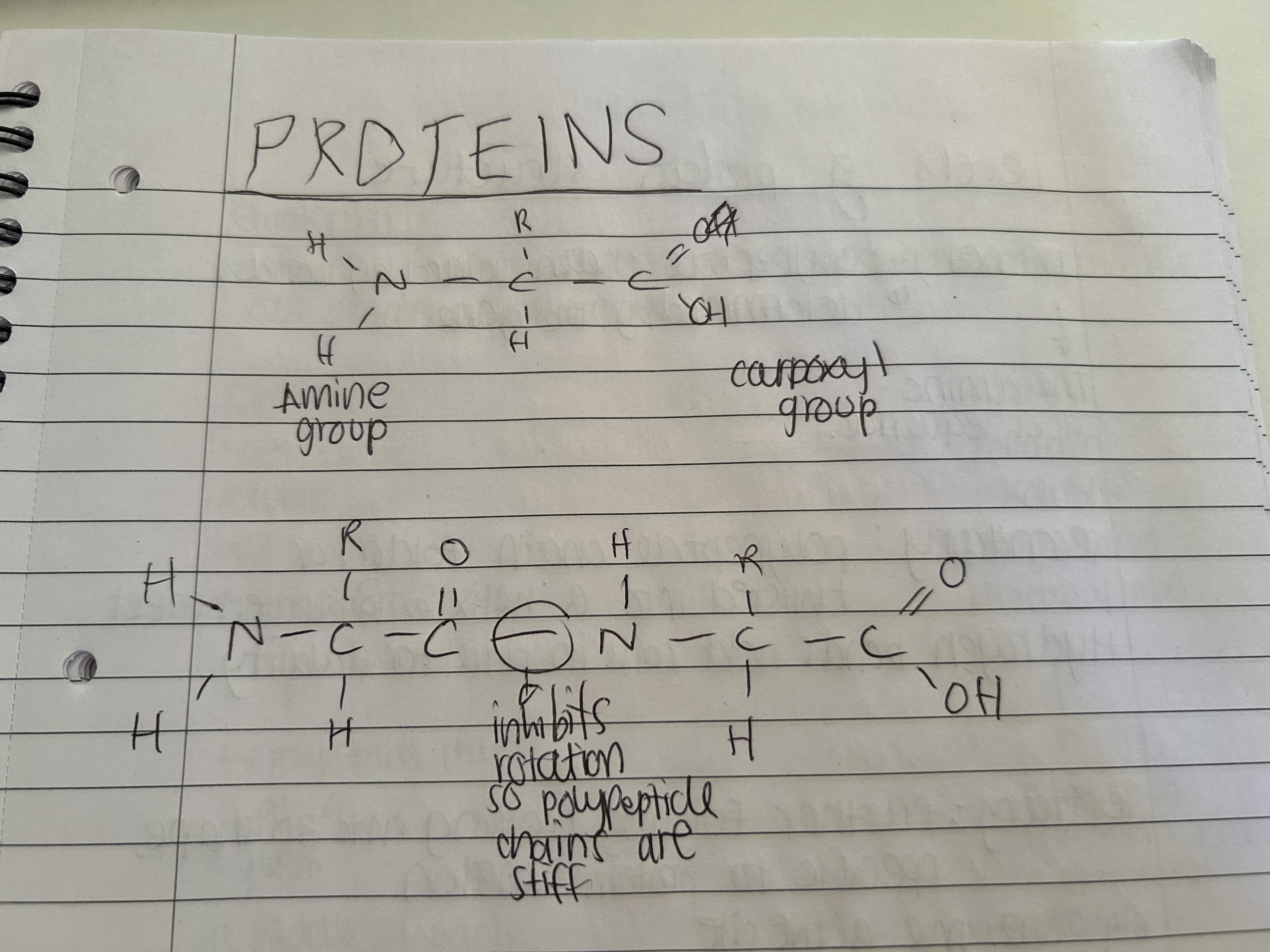
Outline the primary structure of proteins
A straight chain of amino acids bonded with polypeptide bonds.
Outline the secondary structure of proteins
It's the shape an amino acid chain takes either alpha helix or beta pleated sheet. They are held together by hydrogen bonds.
Outline the tertiary structure of proteins
It's is the 3D structure a protein takes it can either be globular or fibrous they are held together by Disulfide bridges, hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds and hydrophobic interactions.
Outline the quaternary structure of proteins
A quaternary structure is formed when two or more polypeptide chains associate to form a single protein.
How do amino acids act as buffers ?
The carboxyl and amine groups ionise. The carboxyl acts like an acid and loses a H+ whereas the amine gains a H+, acting like a base
It is amphoteric as it has both acidic and base properties
Desc H bonds in a protein.
Between polar groups, electronegative of CO- and electro positive of OH or NH
Desc disulphide bonds in a protein
Strong covalent bonds
Between Sulfur containing R groups (cysteine)
Form strong links to strengthen the tertiary structure
Desc ionic bond in a protein
Between ionised R groups that have become negative or positive and so are attracted to eachother
Desc globular protein
Metabolic role
Ball shape
Soluble
Eg haemoglobin ( has 4 pp: 2 alpha 2 beta with haem group at centre of each with iron inside that)
Desc a fibrous protein
Structural role
Long strands
Insoluble
Eg collagen in skin teeth bones so very essential for structure
Draw alpha glucose structure
Draw lipid structure

Draw phospholipid structure
Draw protein structure
What is the test for proteins
Biuret- add a couple drops, turns from blue to purple
Test for lipids
Emulsion test - add ethanol, then distilled water as lipids insoluble in water but soluble in ethanol
Starch test
Iodine drops
Reducing sugar test
Benedict’s- add drops
Boil in water bath for 3-5 mins
Non reducing sugar test (dis)
take last result
Boil in dilute Hcl to hydrolyse the sugar
Nuetralise by adding sodium bicarbonate
Repeat Benedict’s
Difference between deoxybribose and ribose
Deoxy had hydrogen atom at c2 ribose has OH
What is a purine
Larger, double carbon nitrogen ring (A and G)
What is a pyrimidine
Single carbon nitrogen ring
C and T
Desc semi conserve replication
DNA gyrase unwinds
DNA helices unzips breaking H bonds and leaving two single strands with exposed bases
Free DNA nucleotides line up via complementary base pairing
DNA polymerase catalyses their addition in 5-3’ directions
Leading strand made continuously lagging has to be joined by dna ligase (Okazaki fragments)
What is degenerate code
More than one codon for an AA
What is universal code
Same codons same AA in all organisms
What is non overlapping code
Bases are only read once
What is DNA transcription + method
Copying DNA into mRNA as dna too large to leave nucleus
Dna helices unzips, making a sense and an antisesnse strand (template) and sense strand
RNA nucleotides attach to exposed bases Free DNA
RNA polymerase joins forming phosphodiester bonds
Dna returns to double helix
Desc DNA translation
Small subunit of ribosome binds at start codon
tRNA with complementary anticodon attaches held via hydrogen bonds
tRNA attaches again joining peptide bond and catalysed by peptidyl transferase, part of rNA
Another tRNA comes and the first gets released