Cattle Surgery, Anesthesia, and Lameness Flashcards
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering common surgical procedures, anesthesia techniques, and lameness issues in cattle.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Standing Surgery
Preferred over general anesthesia for many cattle procedures like castration, C-section, GI issues, enucleation, dehorning, and distal limb injuries.
General anesthesia
only used when procedure is difficult or analgesia is not sufficient with local anesthesia
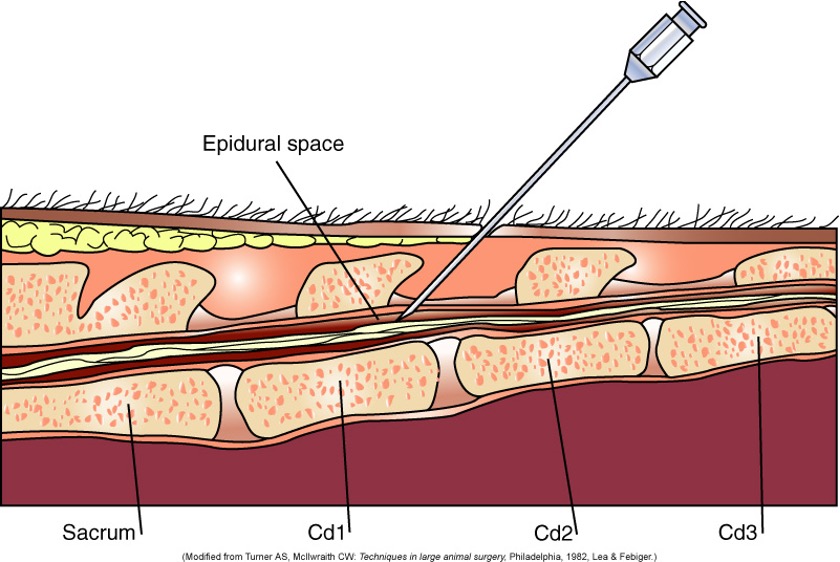
Caudal Epidural Analgesia
1st intercoccygeal space
Local anesthetic technique that desensitizes the anus, perineum, vulva, caudal vagina, and caudal thighs.
Ruminant Anesthesia Risks
Ruminants are prone to regurgitation/aspiration pneumonia, rumen distension (bloat), hypoventilation/hypoxia and compartment syndrome.
Xylazine in Ruminants
Alpha 2 Agonist, commonly used preanesthetic; ruminants are highly sensitive and require 1/10th of the horse dose. Can cause bloat, bradycardia, hypoventilation and uterine contractions.
Can be passed in milk to nursing calves, kids, or lambs
Triple Drip
Anesthetic protocol of xylazine, ketamine and guaifenesin, potential for severe CV and respiratory depression.
Double Drip
Anesthetic protocol using ketamine and guaifenesin.
Castration Methods
Surgical (knife), banding (elastrator bands). Older animals need sedation/local anesthesia.
Dehorning
Removal of horns to prevent interference management practices and decrease danger. Best done at less than 1 month of age.
Barnes dehorner
most common lever-type dehorner that cuts and scoops the horn in one motion
Polled
Term for genetically lacking horns.
Disbudding
Removal of horn buds before horn eruption, using heat cautery or chemical pastes.
Lameness in Cattle
Affects herd productivity, fertility and economics
90% occurs in the foot, mostly rear feet.
Lameness Clinical Signs
Swelling of the foot, spreading of dewclaws.
Preventing Lameness
“Cow comfort”-the less time on concrete, the better, deep bedding in free stalls
Proper equipment-remove any sharp objects, particularly where cattle are crowded (sorting pens, water tanks feedbunks, etc.)
Dairy- routine foot trimming (twice yearly)
Most frequent causes of lameness
Laminitis
Diseases of claw
Digital dermatitis
Foot rot
Deep infections
Laminitis
affected by nutrition (high energy-carbohydrate diet)
Digital dermatitis
affected by environment (dairy cattle housed on concrete)
Claw disease (poor genetics)
overgrown claws, abnormal claw growth, solar abscesses/bruising)
Laminitis
Inflammation of laminae, disturbance of blood flow in corium, separation of coffin bone from laminae.
Can result from metritis/mastitis
acidosis is a major predisposing factor
Acidosis results from high concentrate diet
Occurs more commonly in lateral claw of rear feet, medial claw of front feet
Most common clinical sign is “walking on egg shells”-stiff, stilted gait with back hunched
Difficult to treat-mainly nursing care-deep bedding, stall confinement, claw block if only one foot affected
May become chronic problem
Claw diseases
Most common- subsolar abscesses
Environment-induced (concrete)
Teatment-opening of abscess, if possible, claw block application, stall confinement, deep bedding
Antibiotics ineffective for most causes of lameness, except footrot
Digital Dermatitis
Also known as footwarts, papillomatous digital dermatitis, hairy heel warts, strawberry foot. More common in dairy cattle, large wart-like lesions in interdigital space towards heel region.
Extremely painful to touch!
Antibiotics ineffective
Topical sprays (strong iodine, formalin) applied directly to wart may decrease size, but no cure and transmission still likely with current treatments
Foot Rot
Caused by bacteria, Fusobacterium necrophorum, that lives in the soil (moist environment)-enters through skin in the interdigital space)
Clinical signs: Lameness, inflammation, swelling, and odor
Can be distinguished from deep infection by the fact that it usually causes symmetrical swelling
Responds to antibiotic therapy and environment change
Teatment: Debridement, topical antibacterial agents, foot baths, and management
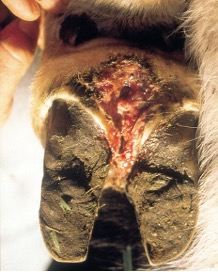
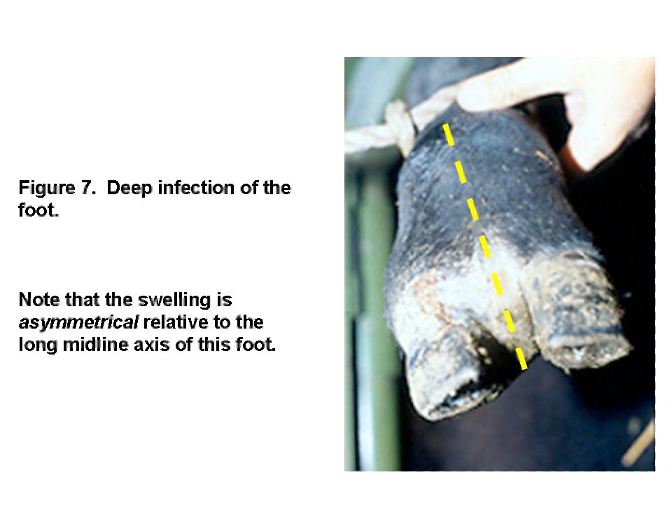
Deep Infection
Caused by subsolar abcesses/ulcers, penetrating foreign bodies, lacerations that go undiagnosed and can lead to invasion of bone, joints-septic arthritis
Usually cause asymmetrical swelling of distal limb and foot due to inflammation focus on affected digiT