Long Quiz 1
1/168
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
169 Terms
K2EDTA
K3EDTA
Anticoagulant for Lavander
Immunohematology
Blood Donor Screening
CBC
Lavander Tube is used for?
Spray-coated K2EDTA
Anticoagulant in Pink Tube
Pink Tube
Tube used for Blood Bank
WHITE - Plasma Prepration Tube (PPT)
LIGHT GREEN - Plasma Separator Tube (PST)
ORANGE - Rapid Serum Tube (OST)
GOLD - Serum Separator Tube (SST)
Also known as PLASMA PREPARATION TUBE (PPT)
WHITE - Plasma Prepration Tube (PPT)
LIGHT GREEN - Plasma Separator Tube (PST)
ORANGE - Rapid Serum Tube (OST)
GOLD - Serum Separator Tube (SST)
Also known as PLASMA SEPARATOR TUBE (PST)
WHITE - Plasma Prepration Tube (PPT)
LIGHT GREEN - Plasma Separator Tube (PST)
ORANGE - Rapid Serum Tube (OST)
GOLD - Serum Separator Tube (SST)
Also known as RAPID SERUM TUBES (OST)
WHITE - Plasma Prepration Tube (PPT)
LIGHT GREEN - Plasma Separator Tube (PST)
ORANGE - Rapid Serum Tube (OST)
GOLD - Serum Separator Tube (SST)
Also known as SERUM SEPARATOR TUBE (SST)
LIGHT BLUE
3.2% Sodium Citrate
9:1 (Blood:Anticoagulant)
BLACK
3.8% Sodium Citrate
4:1 (Blood:Anticoagulant)
Anticoagulant and Blood Anticoag ratio for:
Light Blue
Black
Light Blue (3.2% Sodium Citrate)
Tube used for Coagulation Studies
Black (3.8% Sodium Citrate)
Tube used for Westergren Sedimentation Rate
Green (Hepatrin + Lithium/Sodium/Ammonium)
Tube used for STAT CHEMISTRY TEST
Lithium Heparin
Sodium Heparin
Ammonium Heparin
3 different anticoagulant in GREEN TUBE
Light Green (Lithium Hepatin + Sepator gel)
Tube used for Potassium Determination
Lithium Heparin + Separtor gel
Additive is LIGHT GREEN TUBE
Gray (Sodium Flouride)
Tube used for Blood Alcohol Level
Sodium Flouride
may contain:
Potassium Oxalate
Na2EDTA
Anticoagulant for GRAY TUBE
Royal Blue
Tube used for Toxicology, Trace Metal, Nutritional Analyses
Tan (K2EDTA)
Tube used for Lead Determination
Yellow (ASD) —basta related to genetics or DNA
Used for Cellular Studies, HLA phenotyping, DNA and Paternity Test
Yellow (SPS)
yellow (asd) —genetics or DNA
Used for Blood Culture (inihibits phagocytosis and complement action)
Orange
Green = STAT PLASMA CHEMISTRY
Tube used for STAT SERUM CHEMISTRY
Gold
Tube used for MOST CHEMISTRY TEST
Thrombin + Seperation Gel
Anticoagulant in Orange tube
Weekly
How often should phlebotomy trays be emptied and disinfected
Hypodermic Needle
Type of needle used in syringe method
Gauge 18 —blood transfusion
Gauge 21 —routine venipuncture
Gauge 25-27 —subcutaneous puncture
What are the uses of each of these needle gauge:
Gauge 18
Gauge 21
Gauge 25-27
Blood Pressure Cuff
What can be use instead of tourniquet
EDTA
Cirtrate
Oxalate
Anticoagulant that prevents clotting by Binding in Calcium
Heparin
Anticoagulant that prevents clotting by inhibiting THROMBIN (factor IIa) in coagulation cascade
70% isoprophyl alcohol
1-10% povidone iodine pads/ tincture of iodine/ chlorhexidine
(30-60 secods)
Two-Step Cleansing for Blood Culture Specimen collection
Ask physicians permission
What should be done if collecting though the veins of the feet?
Skin Puncture
Technique of choice to obstain blood from newborns and pediatric patients
Severe Burns
Veins are being reserved
Extremely obses
Elderly patients
Skin puncture procedure may be used for adult patients with:
.
.
.
.
Lateral or Medial plantar surface of the heel
Skin puncture collection site for INFANTS (under 1 year)
Palmar surface of distal portion of 3rd and 4th finger (NON DOMINANT HAND)
Skin puncture collection site for Children (>1yr) and Adults
perpendicular
When skin puncture, the puncture should be _____ to the fingerprint
Microcollection Tube
In Skin Puncture, what must be filled first? Capillary tubes or Microcollection Tube
warmed in incubator at 37*C for 30minutes
Sample for patients with COLD AGGLUTININS must be?
Bilirubin
Beta-carotene
Vitamin A
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B12
Folate
Porphyrins
Photosensitive Analytes
Chain of Custody
Refers to the Documentation of sample handling
Soap and Water
Benzalonium Chloride (Zephiran Chloride) —non alcohol
When collecting blood of Blood Alcohol test, what must be used to cleanse the site?
30-60 seconds
70% alcohol should be scrubbed to the site for ______
Threatens the intergrity of fistula and vascular graft, leading to serious complicaitons
Why should arm with fistula never be collected for blood?
Alteration of result (both blodd vessels have diff blood composition)
Why should artery never be punctured in venipucnture?
High risk of nerve, tendon, and arterial injury
Why should veins on wrist (lateral and palma surface) never be collected for blood sample
26
COLOR CODE FOR LANCETS:
Green
28
COLOR CODE FOR LANCETS:
Purple
30
COLOR CODE FOR LANCETS:
Blue
32
COLOR CODE FOR LANCETS:
Blue-green
plastic tubes and Mylar-coated glass
OSHA suggest the use of capillary tube made of ______ or ______ to avoid injury by broken glass and exposure to bloodborne pathogens
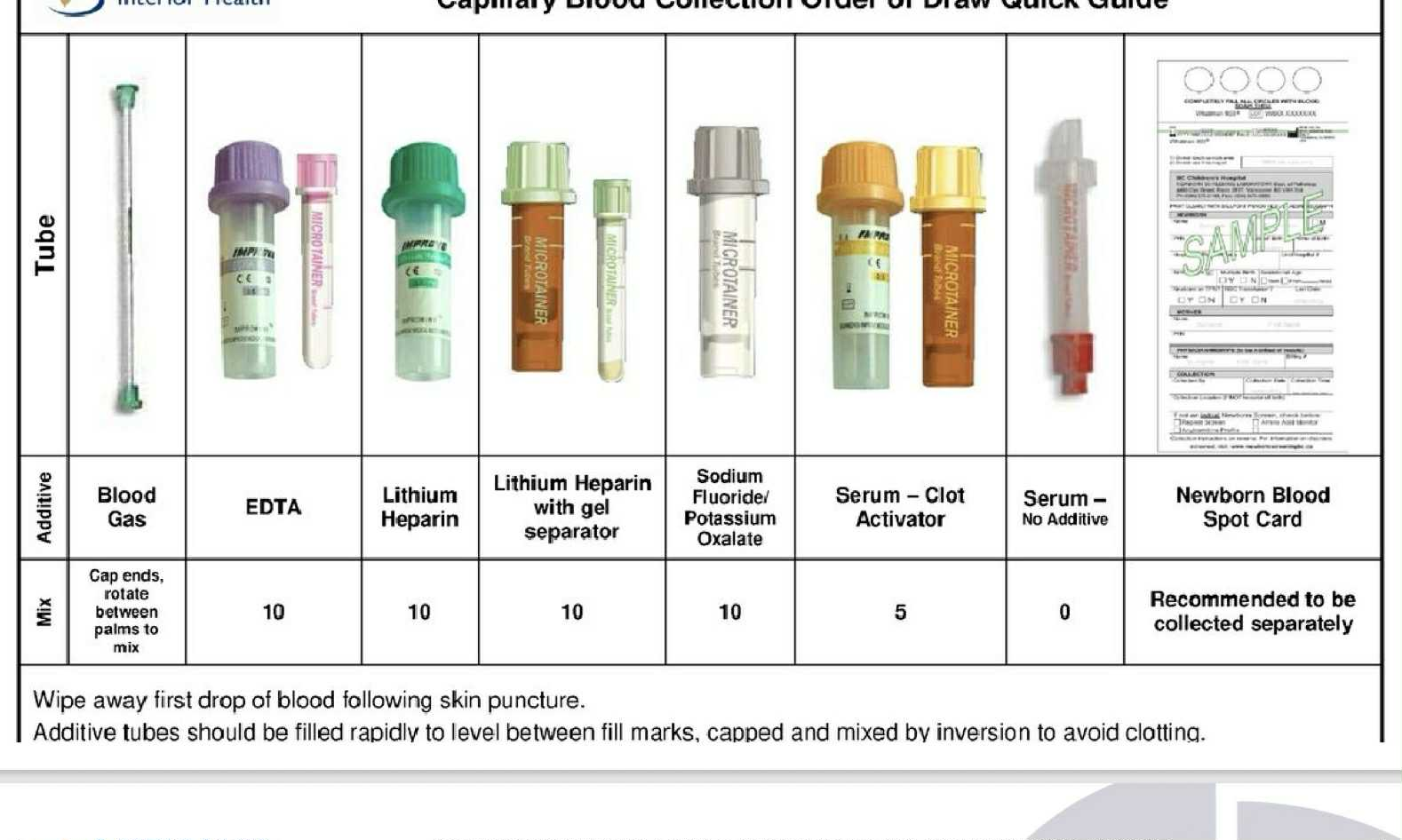
Blood Gas —-rotate between palm
EDTA ——10
Lithium Heparin ——10
Lithium Heparin (w/ gel separator) ——10
Sodium Flouride/ Potassium Oxalate ——10
Serum (w/ clot activator) —— 5
Serum (no additive) —— 0
Newborn Blood Spot Card ——collected separately
CAPILLARY TUBE ORDER OF DRAW (w/ inversion)

Ammonia
Lactic Acid
Acetone
Free Fatty Acids
Pyruvate
Glucagon
Gastrin
……
Analytes that require chilling
binds to calcium
How do EDTA prevents blood from clotting
Within 6 hours of collection
4*C = 24hrs
When shoud CBC test at ROOM TEMPERATURE
Within 24hrs of collection
Room Temp = 6hrs
When should CBC be tested at 4*C CELSIUS
Within 3hrs of collection
When should peripheral blood films (PBF) be prepared?
Counts exceed the linearity of instrument
Instrument is nonfunctional
Remote Laboraties
Disaster Situation
When should Manual Cell Count be done?
Hayem’s
Gower’s
Toisson’s
Bethel’s
Dacie’s Fluid —BEST RBC DILUTING FLUID
NSS
3.8 Sodium Citrate
RBC Diluting Fluids (what is preferred)
1:200
(TWO HUNDRED HA!!)
Ratio of RBC:Diluting Fluid
THOMA PIPETTE:
Markings: 0.5, 1, 101
Volume = 100uL
Markings and Volume of THOMA PIPETTE
16 Squares
How many squares are there in EACH WBC SQUARE?
25 squares
How many squares are there in EACH RBC SQUARE?
WBC = 1mm2
RBC = 0.4mm2
Area of each WBC and RBC Squares
5 squares x 0.2mm = 0.2 mm2
Total counting Area for RBC Squares
10
Depth Factor

RBC Count Calculations
1mm3 = 1 microliter (uL)
1 liter = 1 uL x 106
1mm3 = ???
1 liter = ???
Packed Cell Volume (PCV)
Other term for Hematocrit
Percentage
Liters / Liter
Hematocrit is reported as _____ or _____
0.05 mL
Volume of Blood in Microhematocrit Tube (Capillary Tube)
Insufficient Centrifugation
Including the Buffy Coat
RBC Disorders
Blood Loss
Dehydration
HEMATOCRIT SOURCE OF ERROR:
Flase Increase
Improper Sealing
Short Draw
Improper Collection
Increase Centrifugation
HEMATOCRIT SOURCE OF ERROR:
Flase Decrease
Cyanmethemoglobin Method
Preferred method for HEMOGLOBIN DETERMINATION
Drabkin Solution
Potassium Ferricyanide
Potassium cyanide
Sodium Bicarbonate
Surfactant
What diluent is used for Cyanmethemoglobin Method
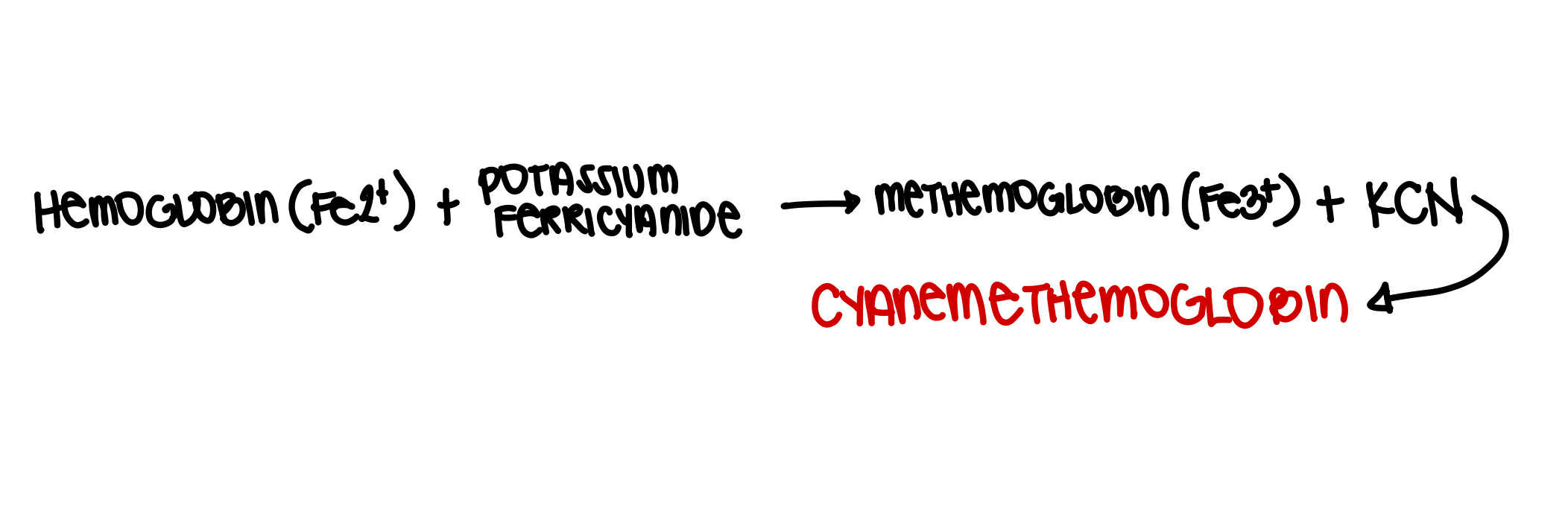
It lyses the RBC to release hemoglobin
Potassium Ferricyanide = oxidizes hemoglobin to methemoglobin (Fe3+)
Potassium Cyanide = converts methemoglobin to cyanmethemoglobin
Drabkin solution is used for Hemoglobin Determination (Cyanmethemoglobin). What is its principle?
Hemoglobin x 3 = Hematocrit ± 3
Rules of Three?
Blood Film should be examined for abnormal RBC
Rules of Three (Hemoglobin x 3 = Hematocrit ± 3)
What must be done if values do not agree?
Microcytic = 80 fL (femtoliters)
Macrocytic = 100 fL (femtoliters)
Mean Cell Volume:
Microcytic
Macrocytic
26 to 32 pg (pictograms)
Mean Cell Hemoglobin:
Normal Range
Hypochromic = <32 g/dL
Normochromic = 32-36 g/dL
Hyperchromic = >36 g/dL
Mean Cell Hemoglobin Concentration:
Hypochromic
Normochromic
Hyperchromic
Spherocytes
MCHC between 36-38 g/dL must be checked for _______
NOTE: normal range is 32-36 g/dL
error in hemoglobin value
MCHC between 38 g/dL must be checked for _______
NOTE: normal range is 32-36 g/dL
Mean Cell Hemoglobin Concentration
Presence of COLD AGGLUTININS can cause an increase of what RBC INDICES?
1 day - peripheral blood ha!
How long does a RETICULOCYTE normally spends time in peripheral blood before developing to mature RBC
Reticulocyte (last immature RBC stage)
RBC stage that is used to asses the erythropoietic activity of the bone marrow
New Methylene Blue (NMB)
Brilliant Crysel Blue (BCB)
Supravital stains for RBC
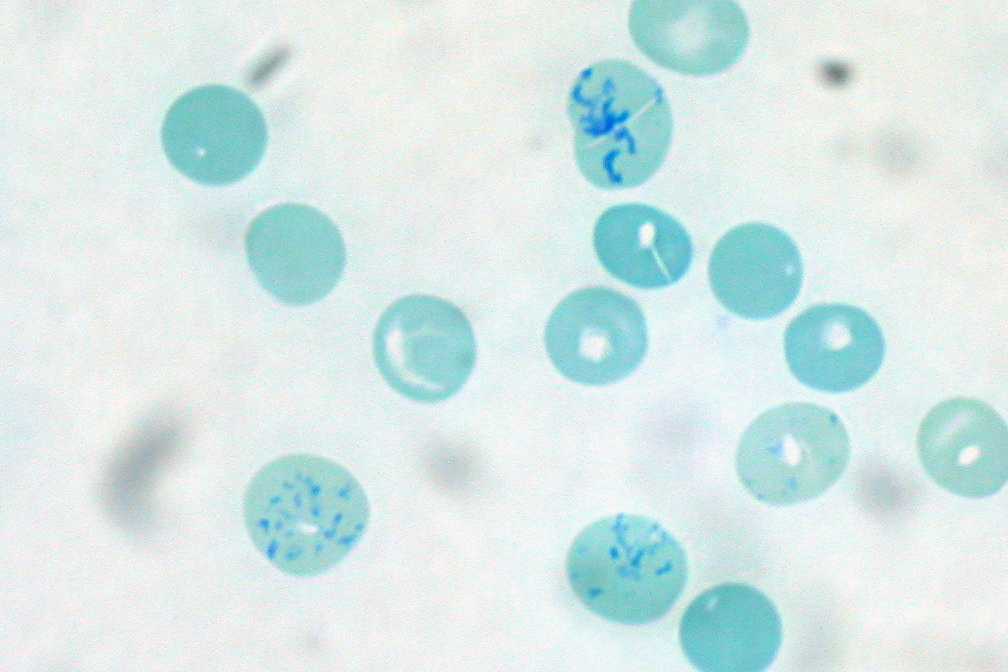
Non-Nucleated RBC with particles of blue-stained granular filamentous material
How can you describe a RETICULOCYTE under a microscope, stained with supravital stain (e.g. NMB)

(# Reticulocyte ÷ 1000) x 100 = Reticulocyte (%)
Formula for Reticulocyte percentage
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
This test is ordered with other tests to detect and monitor the course of INFLAMMATION (non specific test)
Distance of mililiters that the RBC fall in one hour
(unit = mm/hr)
Principle of ESR