GCSE Design Technology Edexcel: Core Content and Papers and Boards (copy)
1/297
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
298 Terms
4 benefits of new technology to industry?
- Better efficiency -> cut costs
-> quicker release of products to market
- Less human error
- Easier manipulation of information/logistics
How is unemployment caused by new technologies?
Unemployment can be caused by new technology performing better than a lower skilled workforce. With robotics, factories can be opened for longer, quality's improved and its safer.
3 advantages of countries gaining people?
- Labour shortages can be overcome
- Migrants are often prepared to take lower paid jobs
- Adds cultural diversity
What is demographic movement?
Demographic movement is the way in which a population's structure alters an changes, eg due to an aging population.
Who are decisions made by in private businesses?
The owner
Advantage of private businesses? (regarding technology)
Often flexible to adopt, adapt and exploit new technologies.
Disadvantage of private businesses? (regarding technology)
May not have funds to invest in cutting edge manufacturing equipment.
What is an enterprise?
a business, particularly one started by someone who shows initiative by taking risk setting up, investing in and running it.
What is crowd funding and how does it help technology?
Crowd funding allows new products to be launched. Many people donate online to bring a product to life. Has to managed appropriately though to succeed.
What is government funding?
Government Funding is available to new businesses that will contribute to the economy.
What are not-for-profit organisations?
Not-for-profit organisations reinvest money in new technologies to help their cause. For eg Charity: Water Aid worked with Google to identify water flow at its projects.
How can companies reduce transportation costs?
Use electric vehicles
Fewer journeys
Lighter/compact products
How does the government encourage reduction of pollution?
Carbon tax
Subsidies
What are the 4 R's?
Reduce, reuse, recycle, recover
What is crowd funding?
a method of raising funds from many people for an enterprise via online platforms
What is sustainability?
The ability to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
Advantage of emerging technologies on children?
improve academic and practical skills, e.g. Minecraft offers more creative learning opportunities than traditional toys
Disadvantage of emerging technologies on children?
Could spend more time on electronics rather than socialising and keeping fit
What is pollution?
the release of contaminating substances that are likely to harm the natural environment.
What is recycling?
the process converting waste material into other usable products, such as glass bottles made from recycled glass.
Consumer:
a person who uses goods and services
What is culture?
The way a group of people behave, dress, eat and live. Can be influenced by anything from religion, tradition and history to local food sources, climate and artistic expression
How does social integration have an impact on technology?
Minority populations that live in clusters causes social segregation. Could create social barriers, and limit education, jobs and technologies
3 examples of how technology is changing society
- Change in working hours and shift patterns
- Internet of Things
- Remote working
How is technology causing a change in working hours?
Due to accessibility of work through the internet, maximising the work potential of a person.
Why are materials seperated?
It means fewer useful materials are sent to landfill sites or scrap
Ways to reduce transport costs?
- Produce products locally
- Reduce package sizes
- Reduce overall volumes of products
What is the standardised design and components technique?
- The same components or modular systems are used across many designs
- Usually an individual part, manufactured in large numbers, to an internationally accepted standard.
What is Just-In-Time production?
Computerised stock control ensures that parts are only received when they are needed in the production process and go straight to the production site rather than being stored
What is lean manufacturing?
Reducing or eliminating waste in design, manufacturing distribution and customer services
What is batch production?
A set number of products are manufactured that are made in limited quantities or for a limited time
What is continuous production?
Manufacturing of identical high demand products, 24 hours a day
What is one-off production?
A single unique product made for a specific client need
What is mass production?
Very high volumes of a product produced over an extended period of time in order to meet with the demands of mass marketing
What should fairtraders do? (4 things)
- Use raw materials from sustainable sources
- Try to buy materials locally
- Reduce energy consumption (eg renewables)
- Minimise waste to the environment
Four considerations about "Who will benefit?"
- Use raw materials from sustainable sources
- Try to buy materials locally
- Reduce energy consumption (eg renewables)
- Minimise waste to the environment
Three considerations about "Who made it?"
- Hiring low-paid workers in some countries leads to child labour and other exploitation
- Workers' rights should be a big priority
- Health and safety should be checked in factory locations
Two considerations about "Where was it made?"
- Cheap labour in other countries: saves costs, exploits workers
- New technologies may produce less pollution and waste
Whch materials should designers opt to use if they want to be environmentally friendly?
- Designers should select materials that are recyclable, lighter and less toxic.
Two considerations regarding the use of materials and the environment
- Consider mined metals, eg energy is needed to convert ore into metal.
- Consider oil is a finite resource that pollutes when refined and doesn't decompose but it is used for plastics.
Problems with renewables?
- Renewables harm habitats and cause visual and noise pollution
- Cleaner energy tends to cost more
Problems with fossil fuels?
- The extraction, transportation and emissions of fossil fuels harm the environment.
How to reduce emissions of CO2 during transport?
Transporting goods uses petroleum, so use energy-efficient or electric vehicles
What is the carbon footprint?
The amount of CO2 emission that can be linked back a company/individual's activities
Five ways to reduce the carbon footprint of something?
- Maximise energy efficiency
- Analyse supply chain
- Recycle
- Use renewable energy
- Identify carbon offsetting methods to reduce amount of emissions
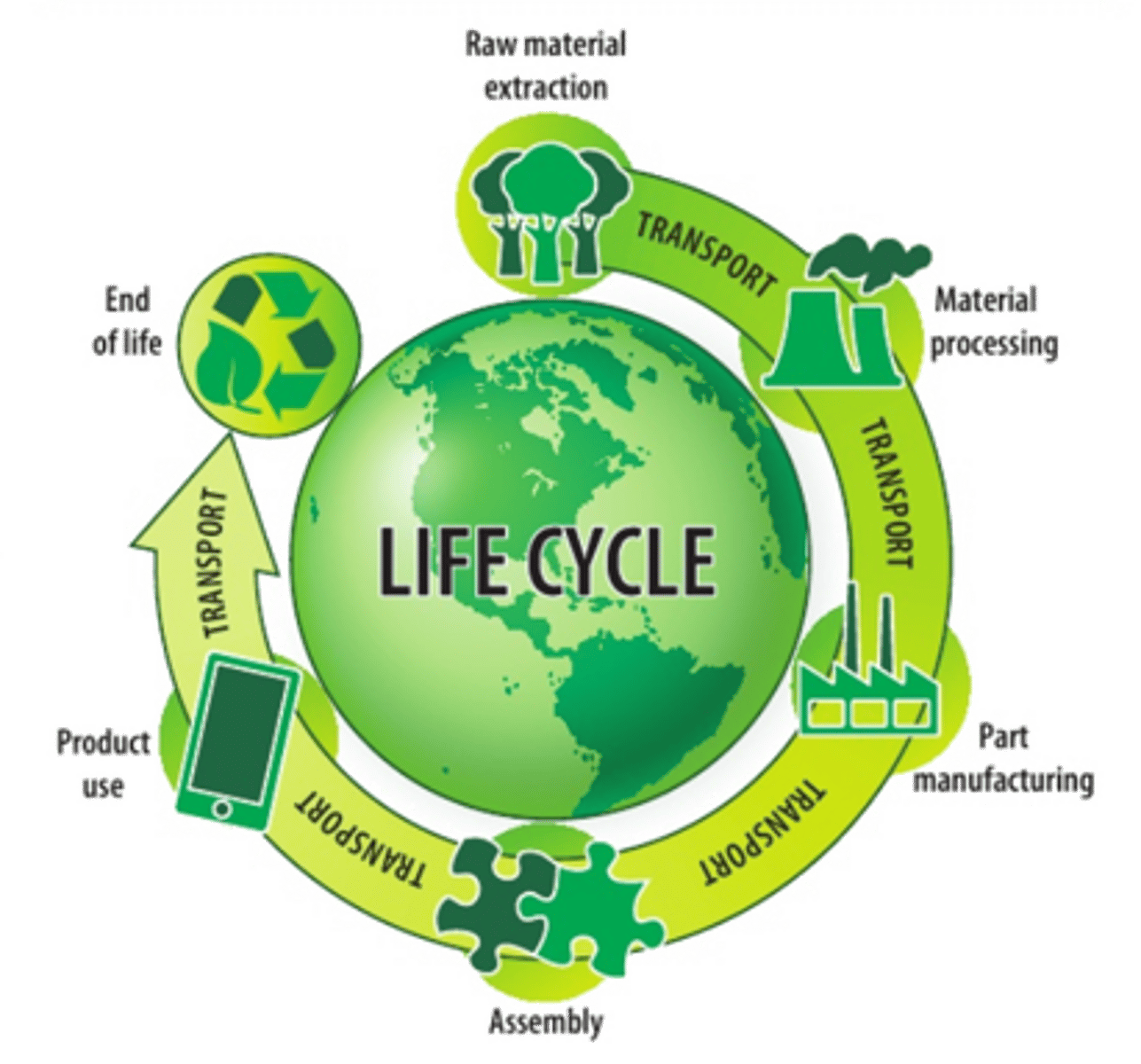
What is a LCA?
Life Cycle Analysis:
A systematic inventory of environmental impacts at every stage of a products life
5 steps of an LCA?
1. Raw material extraction and processing
2. Product/part manufacture and assembly
3. Product/part transportation and distribution
4. Product/consumer use
5. Product disposal or recovery at the end of its useful life.
What it is and how it is converted into Biodiesel
Made from natural elements such as plants, vegetables and fermented waste cooking oil Can be used in diesel-powered vehicles without modifying the engine
What biomass is and how it is converted into energy?
- Organic matter derived from organisms, such as wood, crops, rubbish, landfill gas and alcohol fuels
- Can be used directly via combustion (of wood or biodegradable wastes) to produce heat, or converted to electricity
Name 4 power systems
- Batteries/cells
- Solar cells
- Mains electricty
- Wind power
What are modern materials?
Materials that do not occur naturally, but are existing materials that have been altered to improve their properties
What are smart materials?
Exisiting or modern materials with physical properties that can be varied by an external input such as light or temperature
What are Shape-memory alloys (SMA's)?
Shape-memory alloys can be plastically deformed (changed/stretched/crumpled) and will turn back to their original shape when heated or a current applied
What is photochromic glass? How does it work?
Photochromic glass darkens when exposed to light and reverses in the dark. Particles of silver halide are added to the glass which react with UV light causing a chemical reaction that changes the glass's colour.
Two applications of photochromic glass?
- Sunglasses
- Plane cockpit windows
What is reactive glass?
Uses electrochromic technology to change from transparent to opaque by applying voltage while allowing light to pass through.
Two applications of reactive glass?
Welding masks and windows
What do piezoelectric materials do?
Generate a small electric charge when compressed (sensors) and can work in reverse, generating movement when an electric charge is applied (actuators)
Applications for piezoelectric materials?
Genertaing electricity, SENSORS: burglar alarms, seat belt sensors keypads, microphones,
ACTUATORS: precise precision control eg digital cameras, nozzles.
What are nanomaterials?
Nanomaterials are made of components less than 100 nm in at least on direction. Can be particles nanowires nanotubes etc.
Three applications of nanomaterials?
- Sunscreen
- Tennis rackets
- Fire-retardant.
What are temperature-responsive polymers?
Can change physical properties with a change in temperature
Two applications of temperature-responsive polymers? (explain aswell)
- Deliver drugs, cell/proteins to patients when mixed with a liquid polymer. A gel deposit forms and the drug is released in a controlled way using temperature.
- Sensors and gel activators
What is conductive ink and what does it contain?
Contain pigments that allow a current to flow, usually made with silver, carbon or graphite
Two applications of conductive ink?
- RFID tagging
- Temporary circuit boards
What is a composite?
A composite consists of reinforcing materials and a bonding agent called the matrix
What is plywood?
- Manufactured board of wood veneers bonded with glue to produce a flat sheet
- Always has an odd number of layers (at least three) as they balance the stresses around the central core, making it stable in all directions
- The veneers' grain direction runs at 90° to the sheets above and below it, which also increases the stability
- Graded for exterior or interior use depending upon the glue's water resistance
Examples of plywood (4)
- Sheds, cladding, flooring, furniture
Description of fibre/carbon/glass
- Plastic can be reinforced with fine glass or carbon fibers to make a higher strength-to-weight ratio than its component parts
- Loose or woven fibers form a flexible fabric and are built up in layers with polyester resin
- Reinforced plastic can be sanded for a smooth finish and painted or colour added at the start of the process
Two examples of fibre/carbon/glass composites
- Glass reinforced plastic (GRP) is easily formed into shapes-it is best suited to large structural items, such as boat hulls, pond liners, car bodies, baths or showers
- Carbon fibre reinforced plastic (CFRP) is more expensive than glass fibre but is much stronger- it is used in structural parts such as propeller blades, body armour and golf clubs
Description of robotic materials
Materials that couple sensing, activation (movement), computation and communication and can react to their surroundings autonomously
Three examples of robotic materials
- Vehicles or uniforms that change colour to match their surroundings
- Prosthetics with a sense of touch
- Plane wings that change shape depending on wind conditions
What are agrotextiles?
- Improve or increase agricultural production
- May be made from nylon, polyester, polyethene polypropene or natural materials like jute and wool
- Often biodegradable and offer solar and ultraviolet protection
Examples of agrotextiles (5)
- Shading
- Thermal insulation
- Netting
- Wind-breaks
- Weed suppression
What are construction textiles?
Developed to improve construction appearance and longevity
Examples of construction textiles (structures (2) + during construction (4) )
Structures: waterproof membrane, concrete reinforcement
During construction: hoardings nets, awnings, tarpaulins, canopies
What are geotextiles?
Used in civil engineering where soil, rock or other geotechnical material needs to be stabilised, filtered drained or reinforced Retain their structure in the ground
Example of geotextiles?
Non-woven or woven mats for reinforcing banks or draining flat land
What are domestic textiles?
Used domestically, even if developed for other purposes
Examples of domestic textiles?
- Cleaning wipes
- Furnishings
- Wadding
- Linings
- Carpets
- Flooring
What are environmentally friendly textiles?
Use organically grown fibres such as hemp, wool, cotton or bamboo or recycled materials
Examples of environmentally friendly textiles? (3)
- Geotextiles
- Agrotextiles
- Fashion
What are protective textiles?
Provide protection against heat, harmful chemicals, gases pesticides and even bullets
Examples of protective textiles (4)
- Clothing: heat and radiation protection for firefighters, molten metal protection for welders
- Tents for severe weather
- Parachutes and mountain safety ropes
- Disposable chemical protection overalls
What are sports textiles? What do/can they do?
Combine function with comfort for high performance
Can be lightweight
Streamlined and breathable
Remove moisture
Sense heart rate
Control bacteria
Block UVA/UVB rays
Resist impact
Examples of sports textiles (4)
- Running shoes
- Cycling shorts
- Rugby tops
- Swimsuits
Advantage of sports textiles
- Can improve athletic performance
What is compressive strength?
the ability of material to resist squashing.
What is tensile strength?
the ability of a material to resist stretching.
What are veneers?
slices of wood that are 3 mm or less, used to build up manufactured boards or to protectively coat other woods.
What are the four basic types of movement?
Rotary
Linear
Reciprocation
Oscillation
What is oscillating motion? Give an example.
Swinging from side to side, like a pendulum in a clock.
What is rotary motion? Give an example.
Turning in a circle, such as a wheel turning
What is linear motion? Give an example.
Moving in a straight line, such as on a paper trimmer
What is reciprocating motion? Give an example.
Moving backwards and forwards in a straight line, as in cutting with a saw
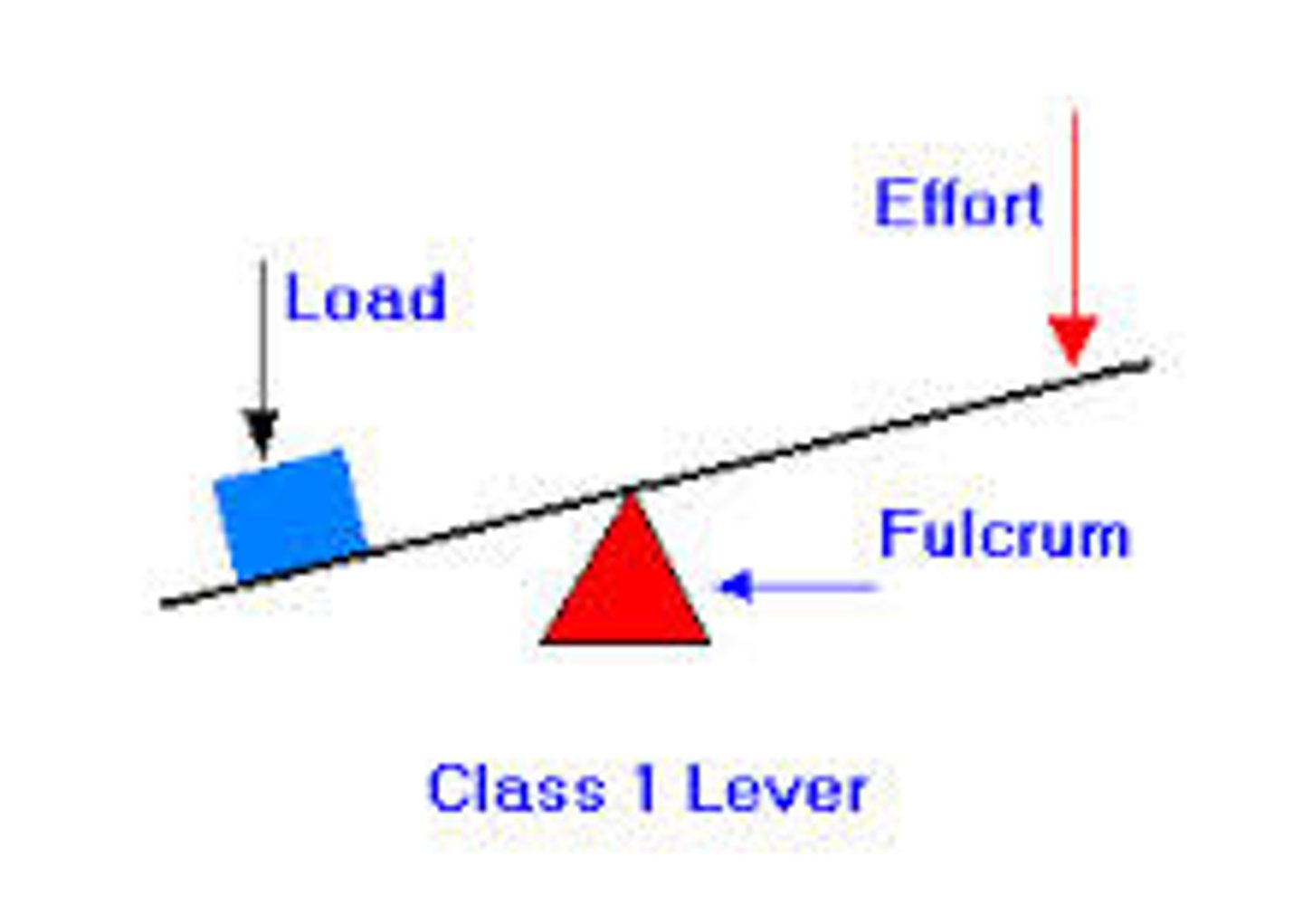
What is a lever?
A fixed rigid beam requiring a fulcrum, load and effort to provide mechanical advantage
What is the effort?
Force applied to a lever
What is the fulcrum?
The pivot point of a lever
What is the load?
Amount of weight lifted
What is a class 1 lever?