Sensation & Perception : Depth Perception
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Monocular Cues
Depth perception with one eye
Accommodation
Oculomotor Cue
Lens shape changes
Flattened Accommodation
Far object (3m max)
Curved Accommodation
Close object (20cm maximum)
Pictorial Cues
See depth in painting, photograph, and other 2D images
Overlap
Near object blocks the view of further object
Occluded portion is visually filled
Farther
______ distance → smaller retinal image size
Closer
_____ to the horizon → looks farther away
Linear Perspectives
Physical parallel lines in the real world appears to converge into “vanishing point”
Farther
______ → more blurring
Shorter, bluer, less
______ wavelength are scattered more, so very distant object looks slightly ____ and _____ distinct.
Atmospheric Perspectives
Mountains in Wyoming look closer than actual distance
Brighter
Relative Brightness : _____ → closer
Brighter
Shadow : Surfacing facing light → _____
True
T/F : In regards to shadows, light comes from above.
Texture Gradients
Linear Perspective + Relative Size = ______ ______
Distant
More _____ parts → smaller elements and more densely packed
texture
Change in _____ → Change in the direction or distance
Motion Parallax
When the observer is in motion, direction and speed of the motion of object depends on the object distance
Closer
_____ → opposite direction
Farther
_____ → slower
Deletion
Object moves backwards in relation to the background
Accretion
Object moves forward in relation to background
Binocular Depth Perception
Depth perception with 2 eyes
30% faster
Convergence
Converging angle of 2 eyes will be larger with closer object (closed)
Physiological cue
Binocular Disparity
Differences of the images from 2 eyes
Corresponding Points
Retinal images on each eye connect to the same part of visual cortex to create a unified perception of depth.
Uncorresponding Points
Retinal images to the different part of the cortex creating a perception of depth that does not match between the two eyes.
Horopter
Imaginary curve that pass the fixation point and corresponding points
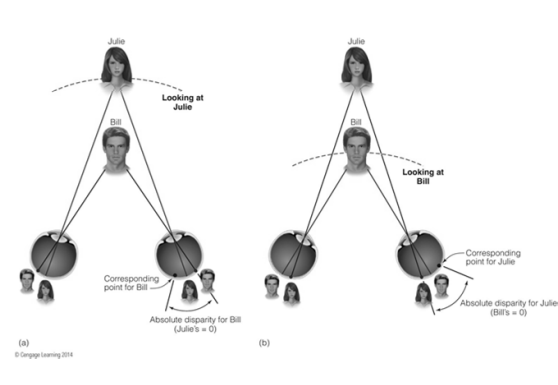
Crossed Disparity
Images move out to the sides of the retinas
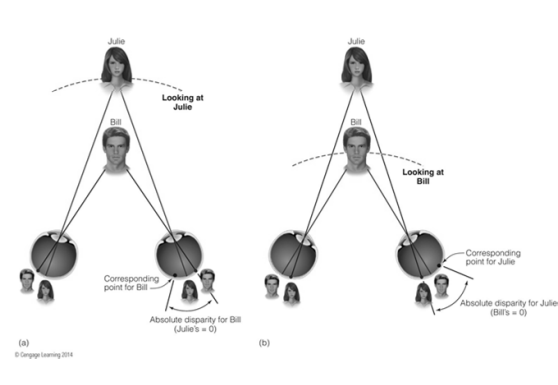
Uncrossed Disparity
Images move inward on the retinas
Stereopsis
Sense of depth through binocular disparity
Stereoscope
Projection of two slightly different images to 2 eyes produces 3D perception of an object
Autostereoscope
Repeated images in the picture produce 3D
Passive, Active, Lenticular
3 Types of 3D TV
Polarized glasses
Passive
Active
Electronic shutter glasses
Lenticular
Mini senses on screen, no glasses needed
Binocular depth cells, disparity selective cells
Neurons that respond best to binocular disparity are _______ ______ _____ or ______ ______ ______.
Binocular, Binocular disparity
Blake & Hirsch Experiment : Cats were reared, results show that they had few _______ neurons and were unable to use _____ _____ to perceive depth.
Visual Angle
Retinal image angle that is formed based on object size
Smaller, smaller
As distance grows larger, retinal image size grows _____ and the angle gets ______.
Size Constancy
Perception of constant object size regardless of the distance from which it is viewed.
Size contancy
Holway & Boring (1941) : With depth cues → good ____ ____
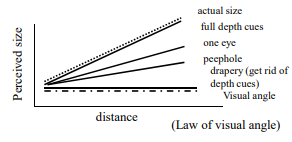
Emmert’s Law
The perceived size of an object is directly related to the distance from which it is viewed. As the distance increases, the eyes receive a smaller retinal image, yet the brain compensates for this to maintain a perception of size.
Emmert’s Law Equation
S = K (R x D)
K = Constant
R = Retinal Image Size
D = Distance
Muller-Lyer Illusion
A visual illusion where lines of equal length appear to be different lengths due to the addition of arrow-like endings, highlighting the role of perceptual cues in depth perception.
Conflicting Cues Theory
Our perception of the line length depends on…
Actual length of vertical lines
Overall length of figure
Ponzo Illusion
A visual illusion that occurs when two horizontal lines are placed over converging lines, leading individuals to perceive the top line as longer than the bottom line, demonstrating depth perception effects.
Explanation for Ponzo Illusion
Misapplied size-constancy scaling
Based on linear perspective cues, causing the brain to interpret objects at a distance as larger than nearby objects.
Ames Room
A distorted room that creates an optical illusion, making people appear to grow or shrink depending on their position in the room. This effect demonstrates how perception can be influenced by depth cues.
Size-Distance Scaling, Relative Size
Explanations for Ames Room
Ames Room Explanation : Size-Distance Scaling
Woman on the left has smaller visual angle (R)
Due to the perceived distance (D) being the same, her perceived size (S) is smaller
Ames Room Explanation : Relative Size
Perception of size depends on size relative to other objects
One woman fills distance between top & bottom of room
Other woman fills part of distance
Thus, woman on right appears taller
Moon Illusion
Moon appears larger on the horizon than when it is higher in the sky
Apparent-Distance Theory
Horizon moon is surrounded by depth cues while moon higher in the sky has none.
Angular Size-Contrast Theory
Moon appears smaller when surrounded by larger objects
Frontal Eyes
____ ____ = Result in overlapping fields of view, are necessary for binocular disparity
Lateral Eyes
____ ____ = Do not result in overlapping fields of view, provide a wider view
Motion Parallax
Locusts use ____ ____ well to judge distance of objects in the dark.