APES Unit 5 Vocab Land and Water Use
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
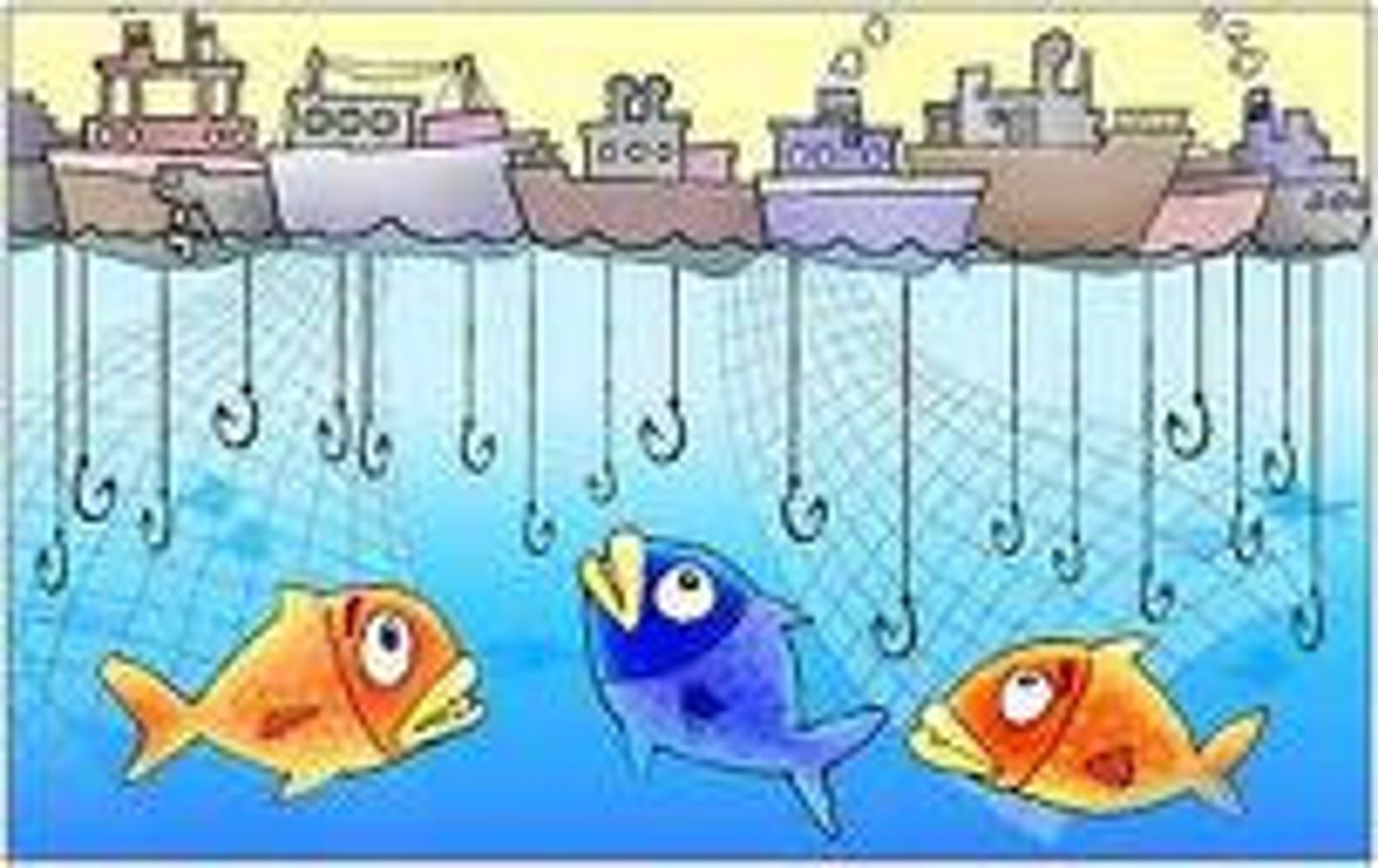
Tragedy of the Commons
Overuse of shared resources because individuals act in self-interest rather than long-term sustainability.

Sustainability
Using resources in ways that meet current needs without harming future generations.
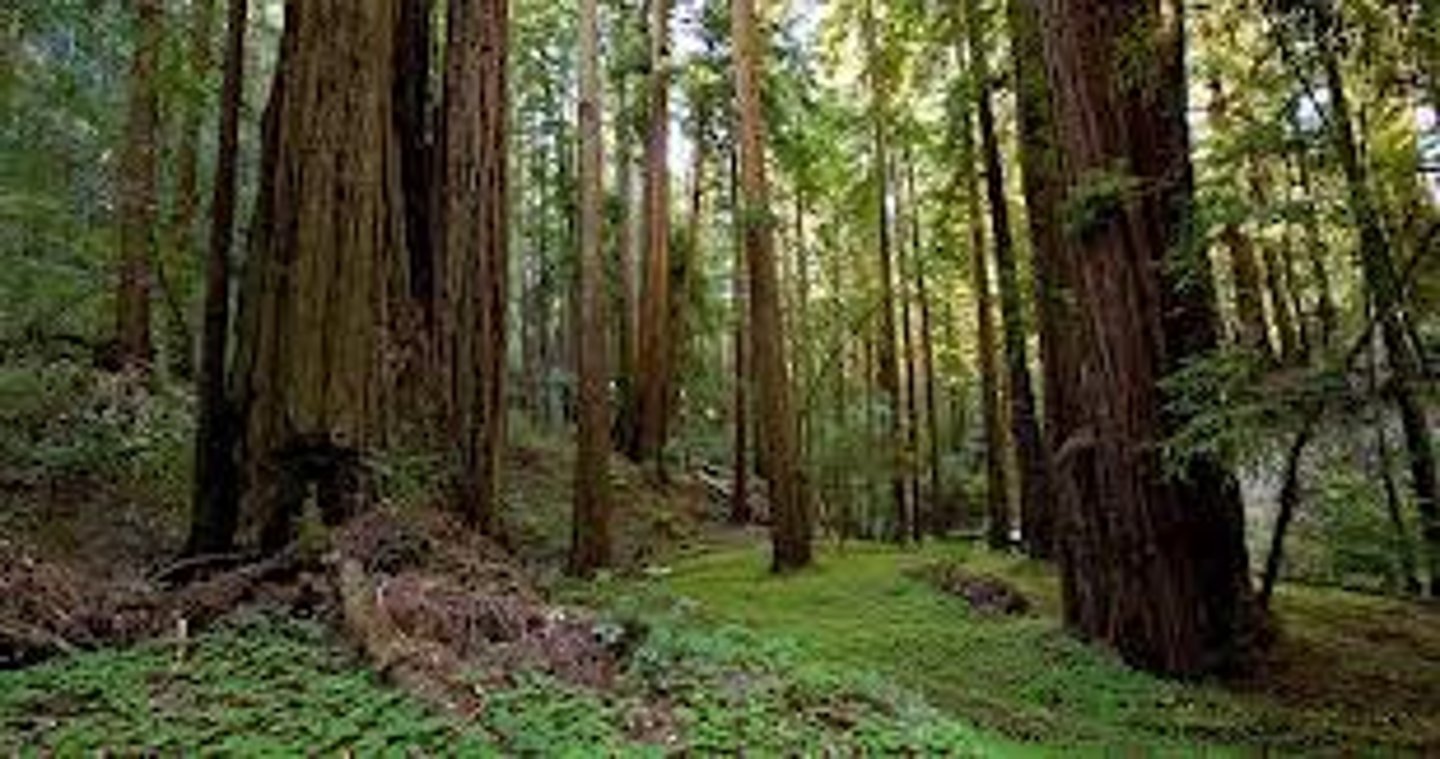
Old Growth Forest
Forests that have never been logged and contain mature, biodiverse ecosystems.

Floodplains
Flat areas next to rivers that naturally flood and deposit nutrient-rich sediment.
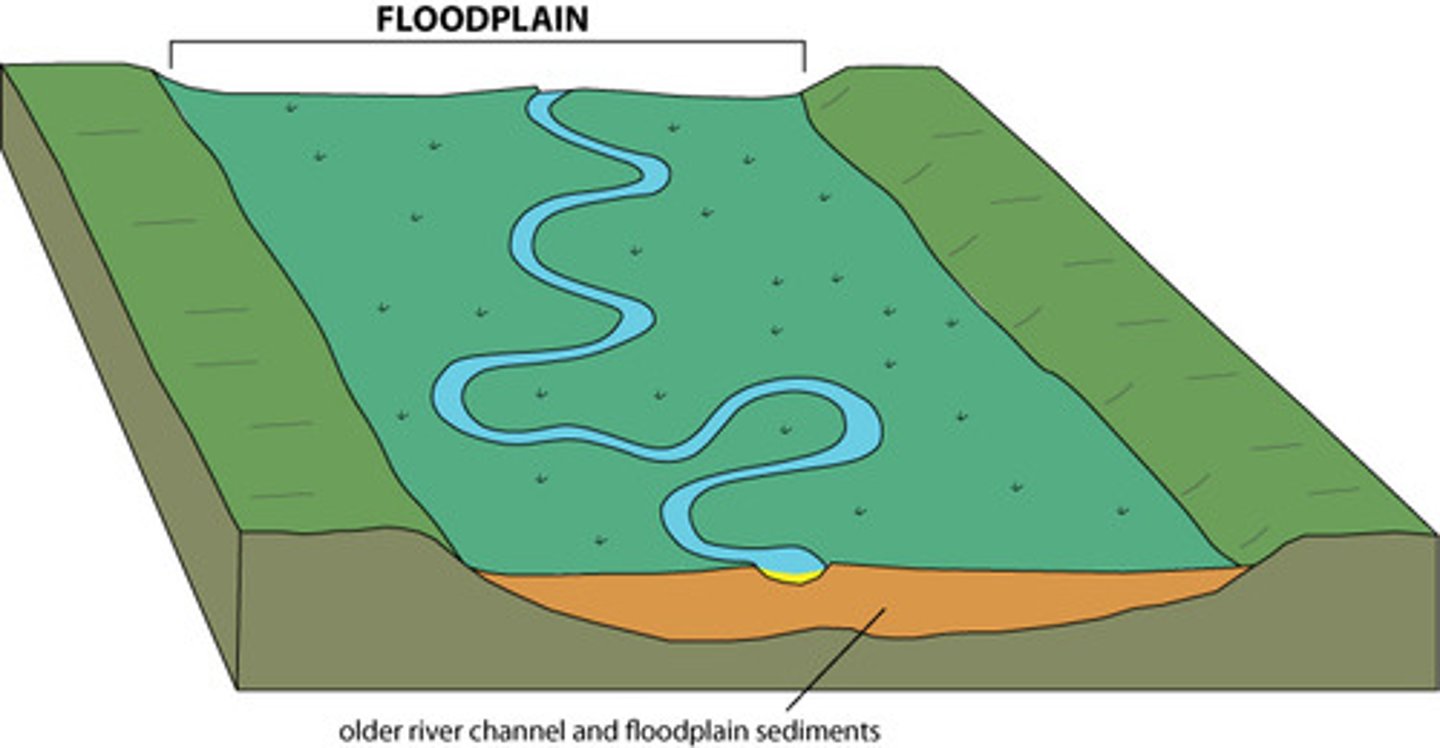
Levees/Dikes/Embankments
Raised structures built to prevent rivers from flooding surrounding land.
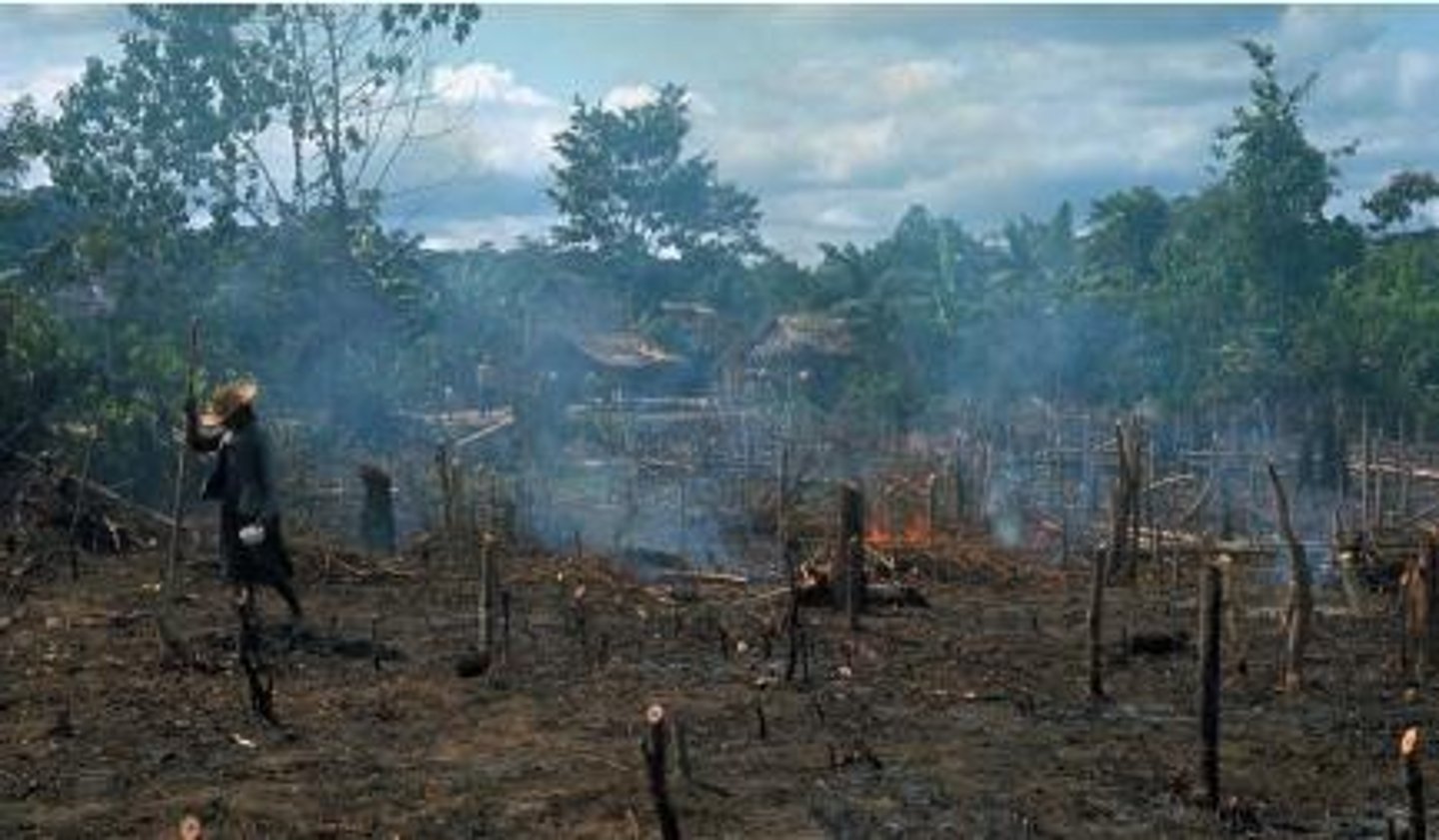
Slash and burn agriculture
Cutting and burning vegetation to clear land and release nutrients for farming.

Industrialized agriculture/Agribusiness
Large-scale farming using machines, synthetic chemicals, and monocultures.
The Green Revolution
Global increase in food production through high-yield crops, fertilizers, pesticides, and irrigation.
Mechanization
Use of machines in agriculture to increase efficiency and reduce labor.
GMOs
Organisms whose genes have been altered to improve traits like yield or pest resistance.
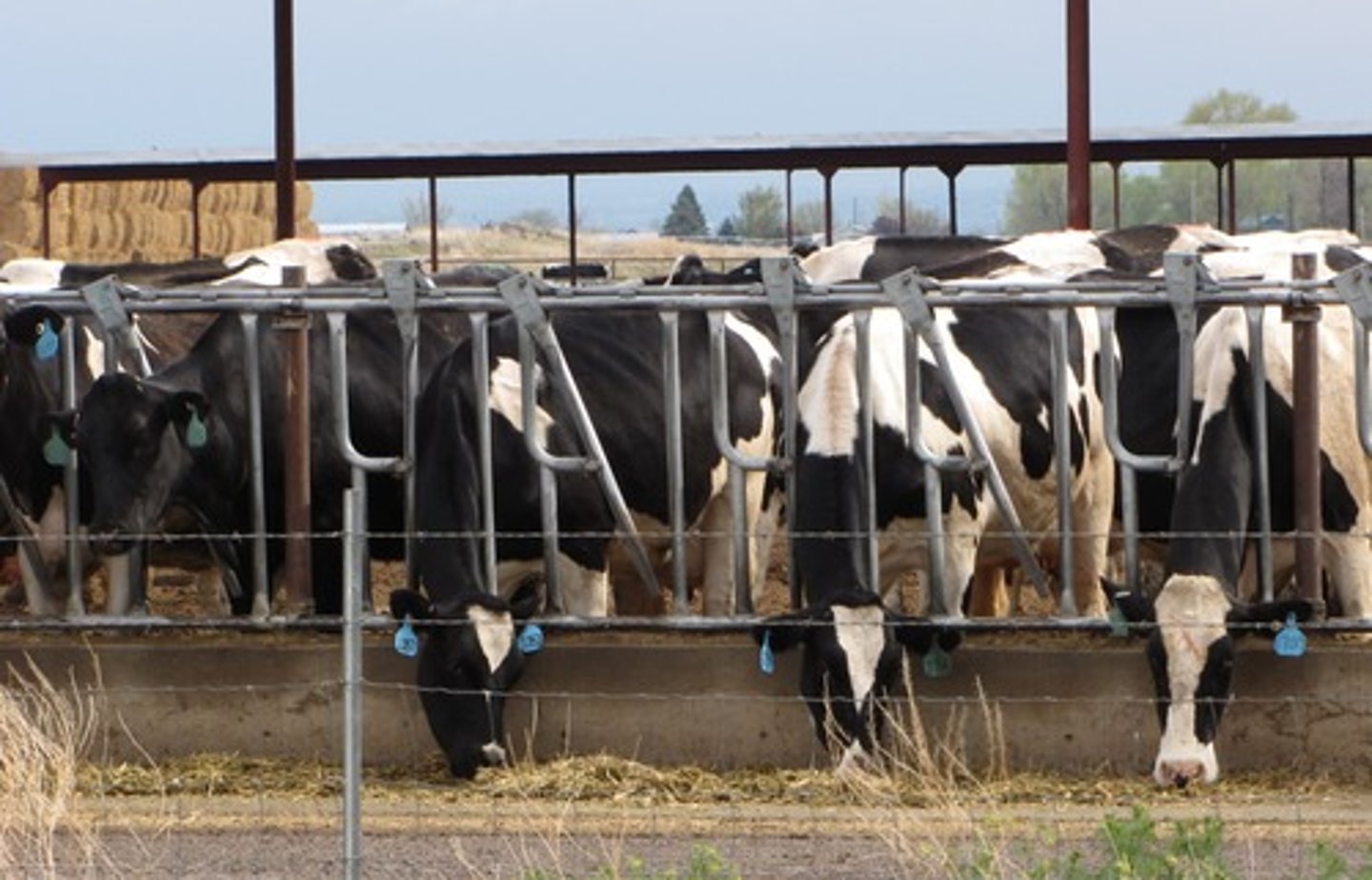
CAFO (Concentrated Animal Feeding Operation)/Feedlots
High-density animal farming systems used to maximize meat production.

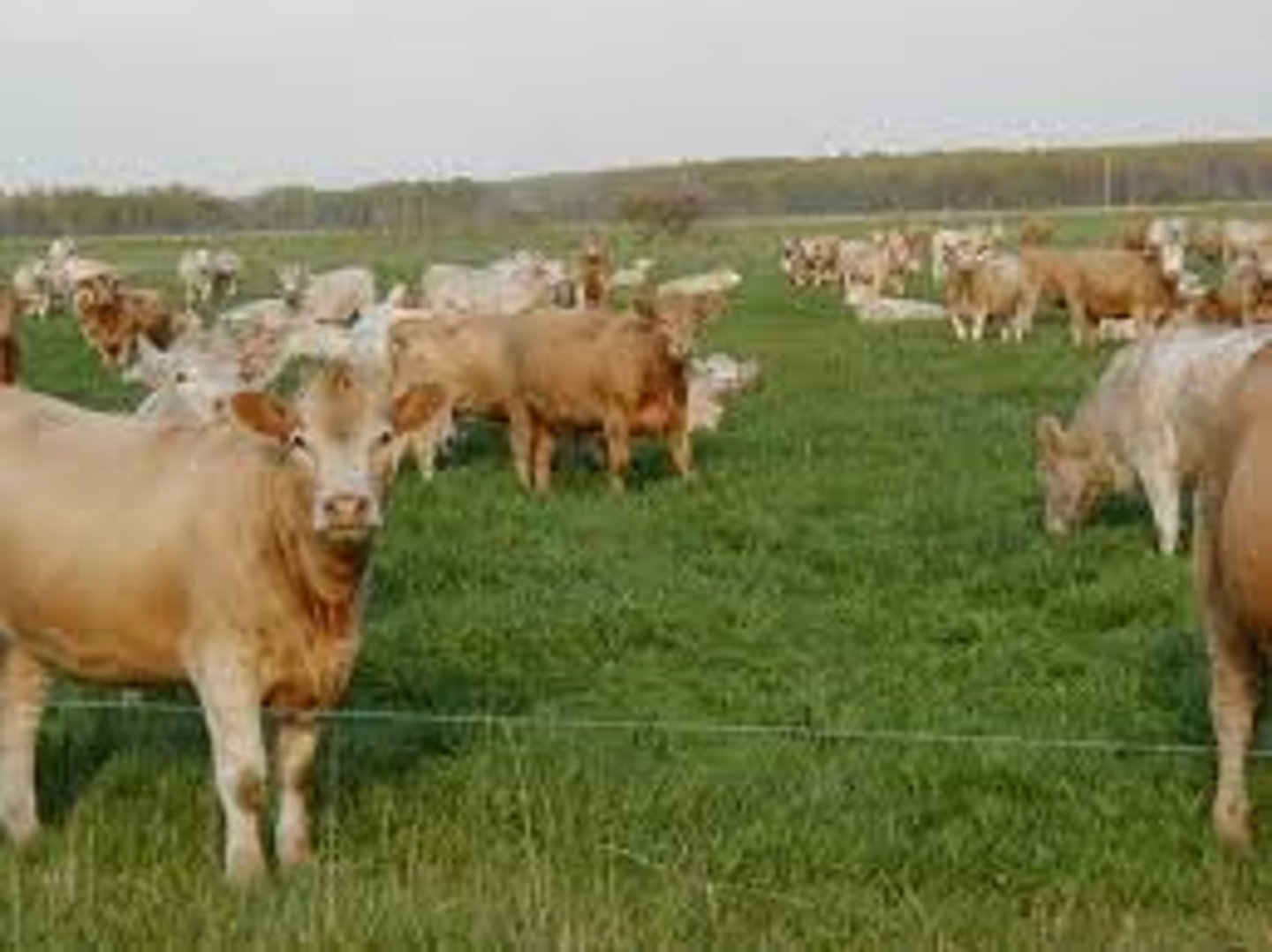
Free-range animal operations
Farming where animals roam outdoors and are not confined to feedlots.

Rotational grazing
Moving livestock between pastures to reduce overgrazing and improve soil health.
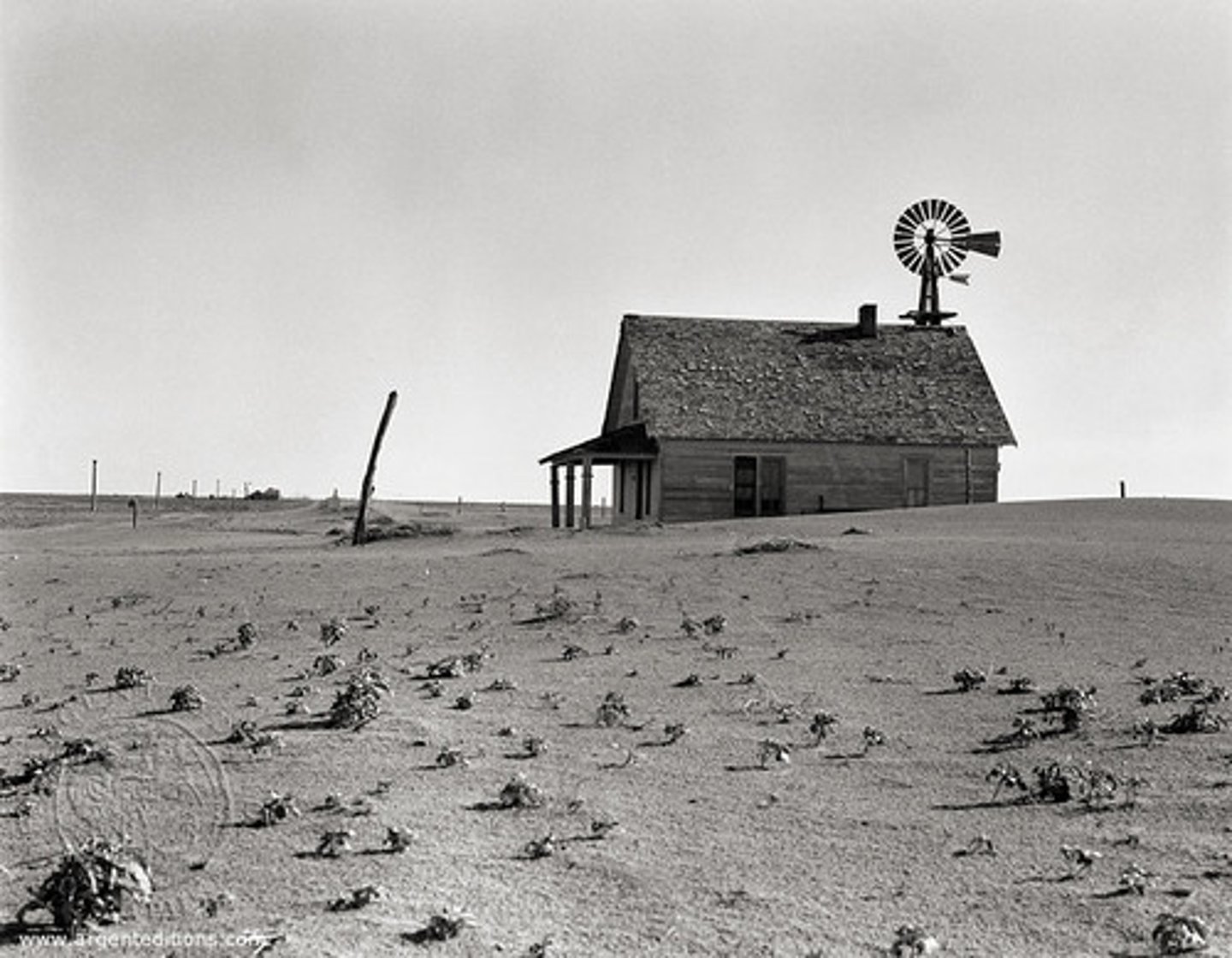
Dust Bowl
1930s event where poor farming practices and drought caused massive soil erosion.

Contour plowing
Plowing along natural land contours to reduce erosion.
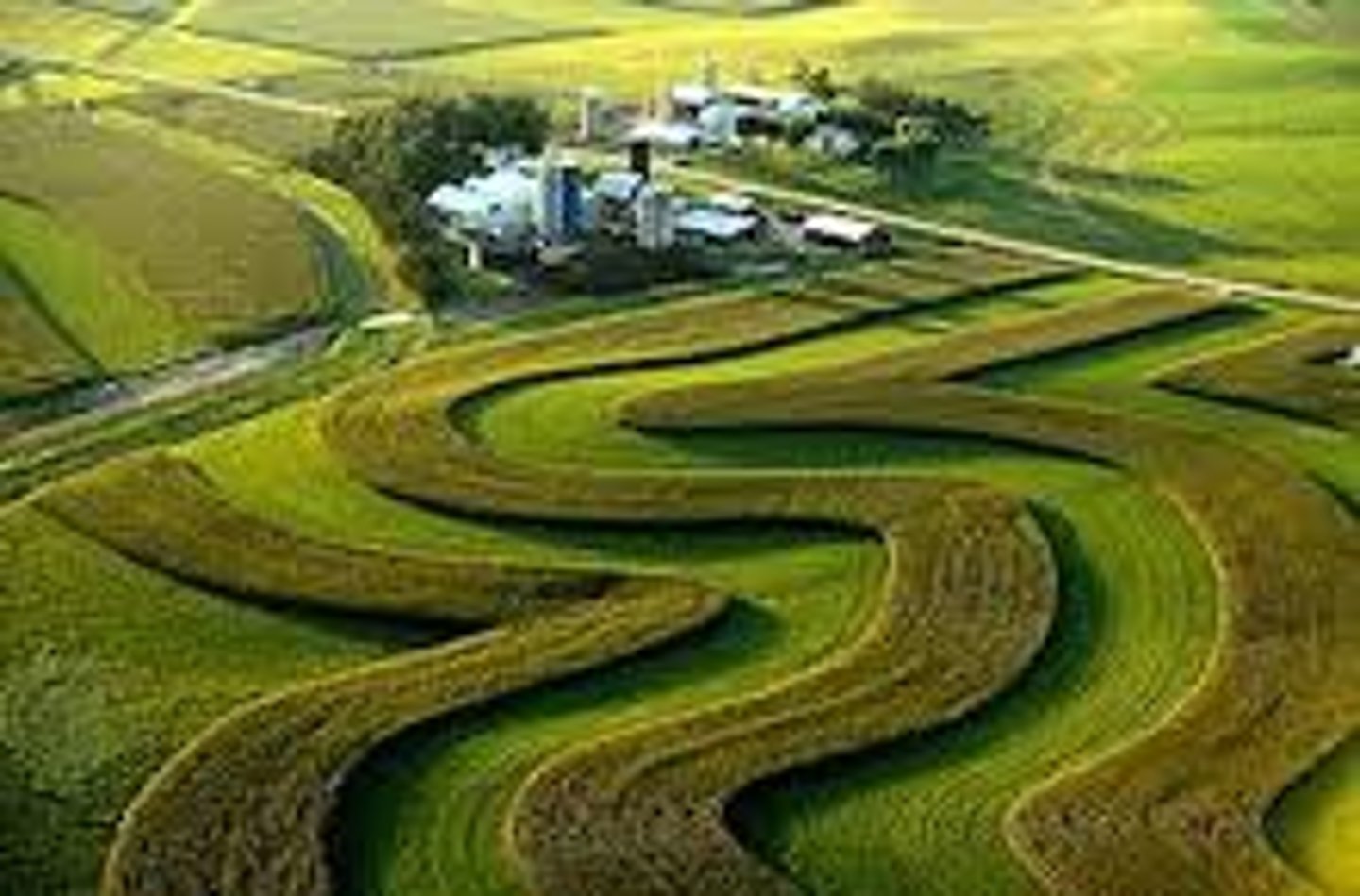

Windbreaks
Rows of trees or shrubs planted to block wind and reduce soil erosion.
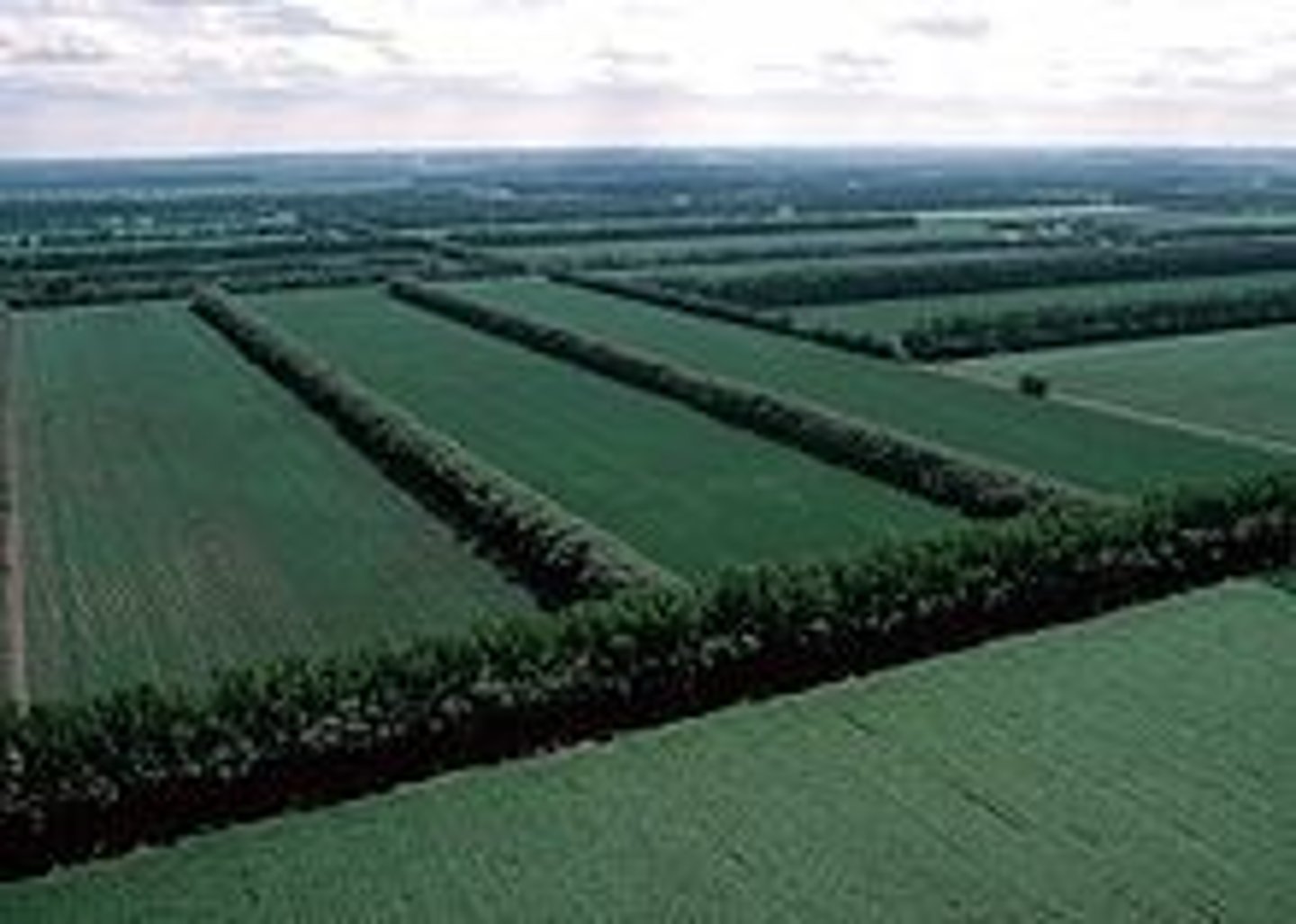

Perennial crops
Crops that live for multiple years and reduce the need for replanting.
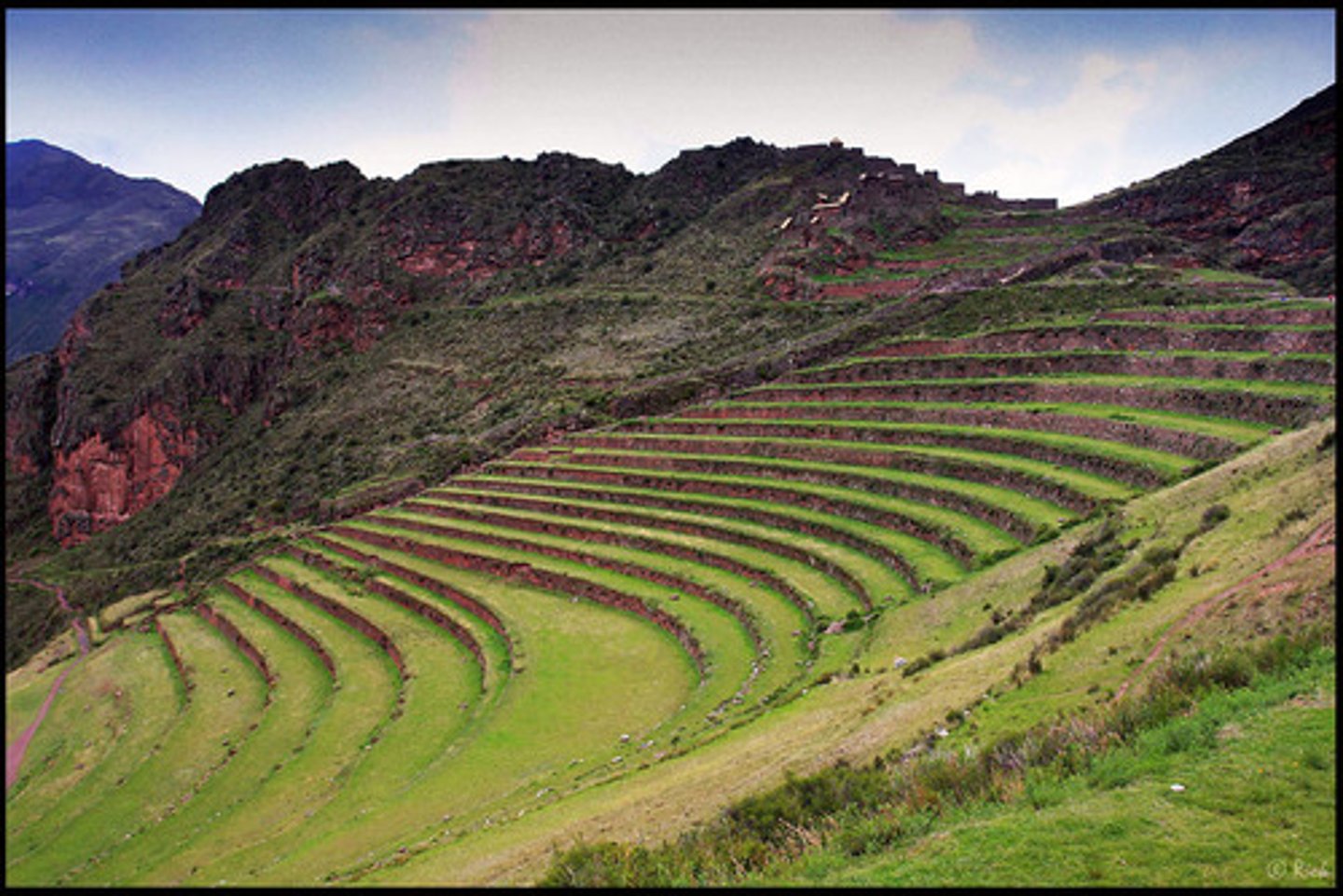
Terracing
Creating step-like fields on slopes to reduce runoff and soil erosion.

Crop rotation
Growing different crops in succession on the same field to maintain soil nutrients.
Monoculture
Growing only one crop over a large area, increasing pest and disease risks.
Polyculture
Growing multiple crops together to increase biodiversity and resilience.
Cover crops
Plants grown between main crops to prevent erosion and improve soil health.
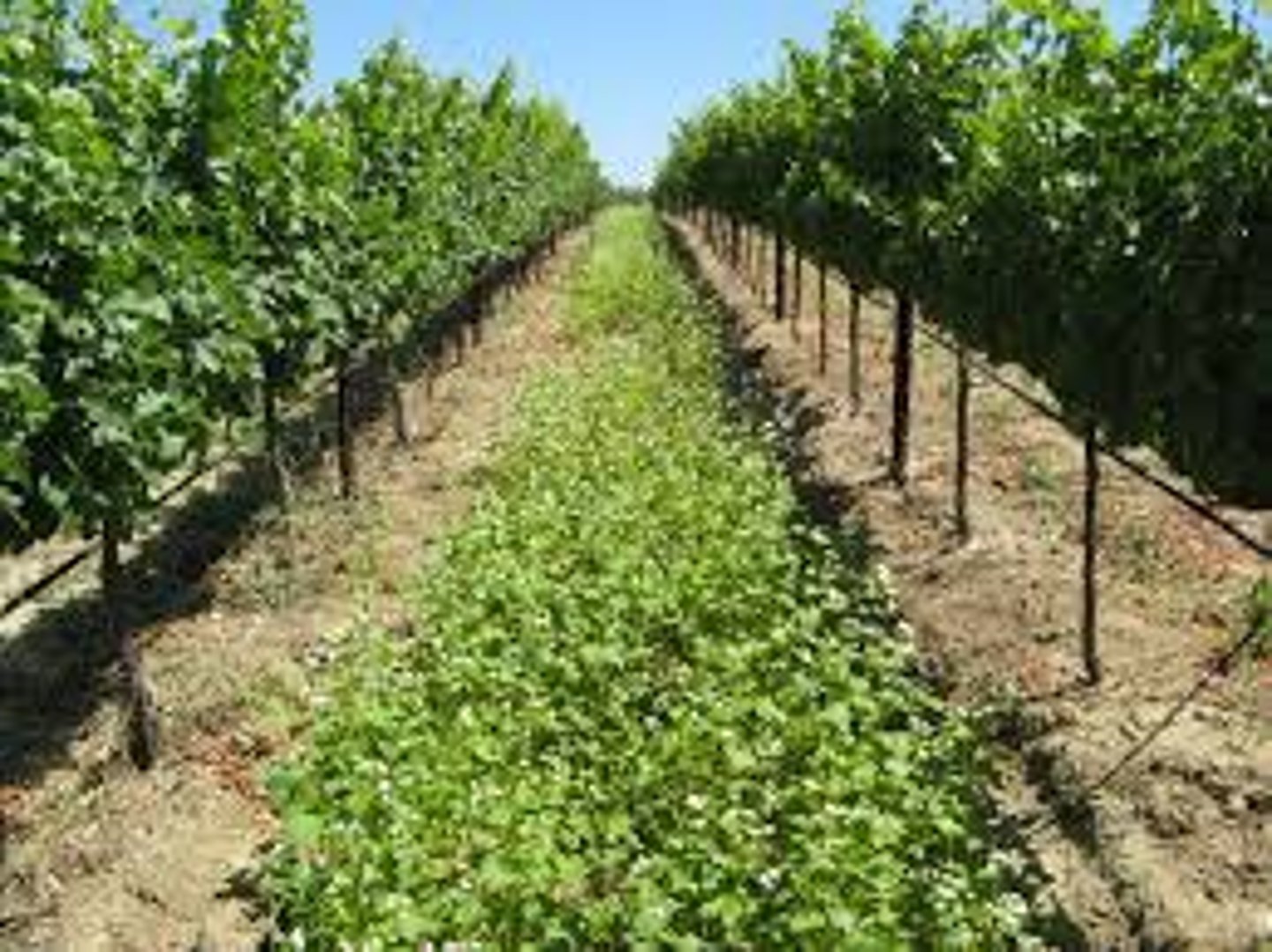

Intercropping/Strip cropping
Planting different crops in alternating rows to reduce pests and erosion.
Arable land
Land suitable for crop production.
Tilling
Turning over soil to prepare for planting, often increasing erosion and carbon release.

Waterlogging
Soil oversaturated with water, suffocating plant roots.
Aquifer
Underground layer of rock or sediment that stores groundwater.
Water Table
The upper level of groundwater saturation in soil or rock.
Fertilizer (organic & inorganic)
Substances that supply nutrients to plants; organic from natural sources, inorganic from synthetic chemicals.
Pesticide
Chemicals used to kill pests such as insects, weeds, or fungi.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Pest control that combines biological, physical, and chemical methods to minimize pesticide use.
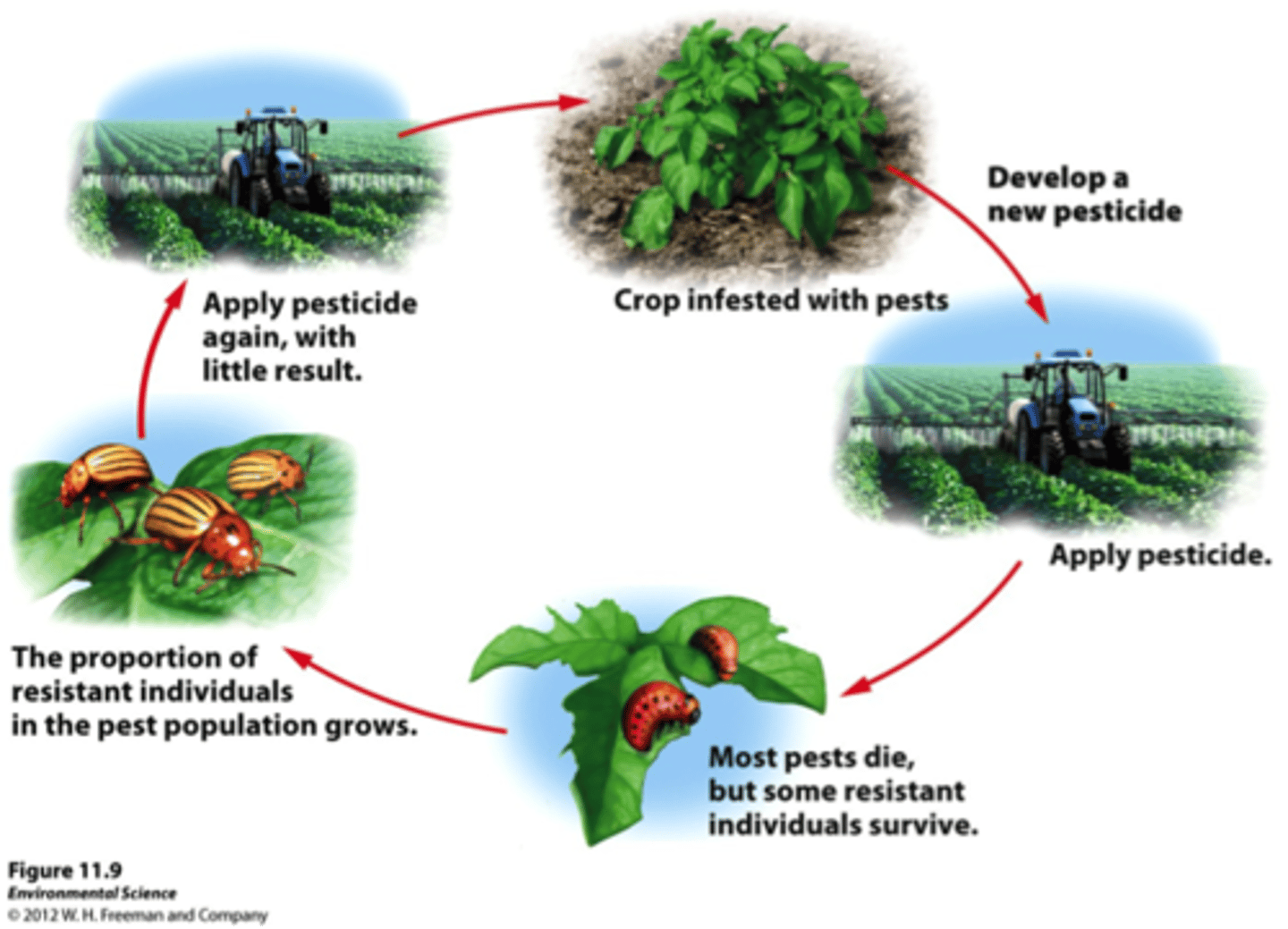
Pesticide resistance
When pests evolve to survive exposure to a pesticide.
Pesticide treadmill
Cycle where increasing pesticide use leads to resistance and even more pesticide use.
Biological Control
Using natural predators or organisms to reduce pest populations.

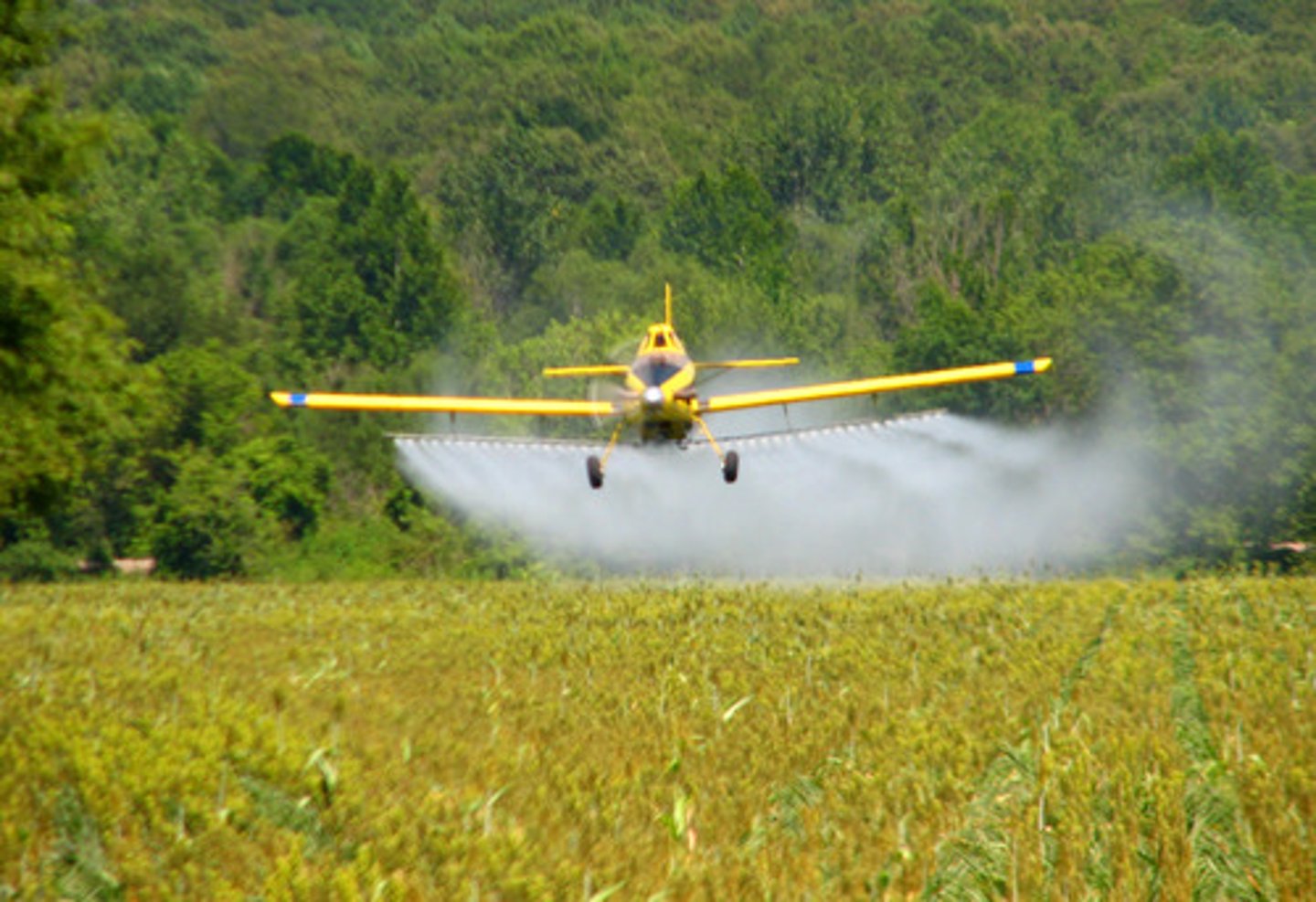
Crop dusting
Spraying pesticides or fertilizers from aircraft.

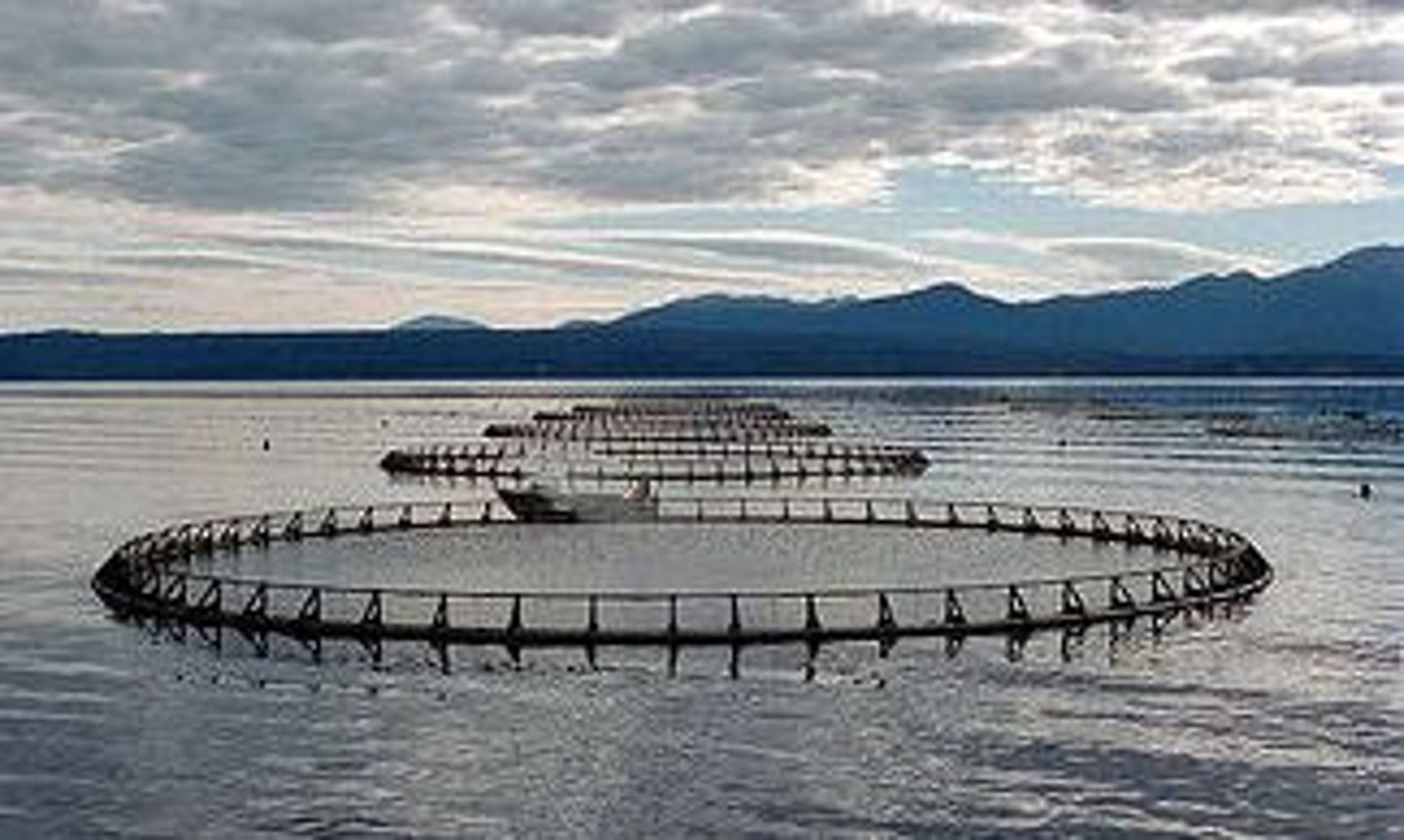
Aquaculture
Farming of fish, shellfish, or aquatic plants.

Overburden
Soil and rock removed to access mineral deposits in mining.
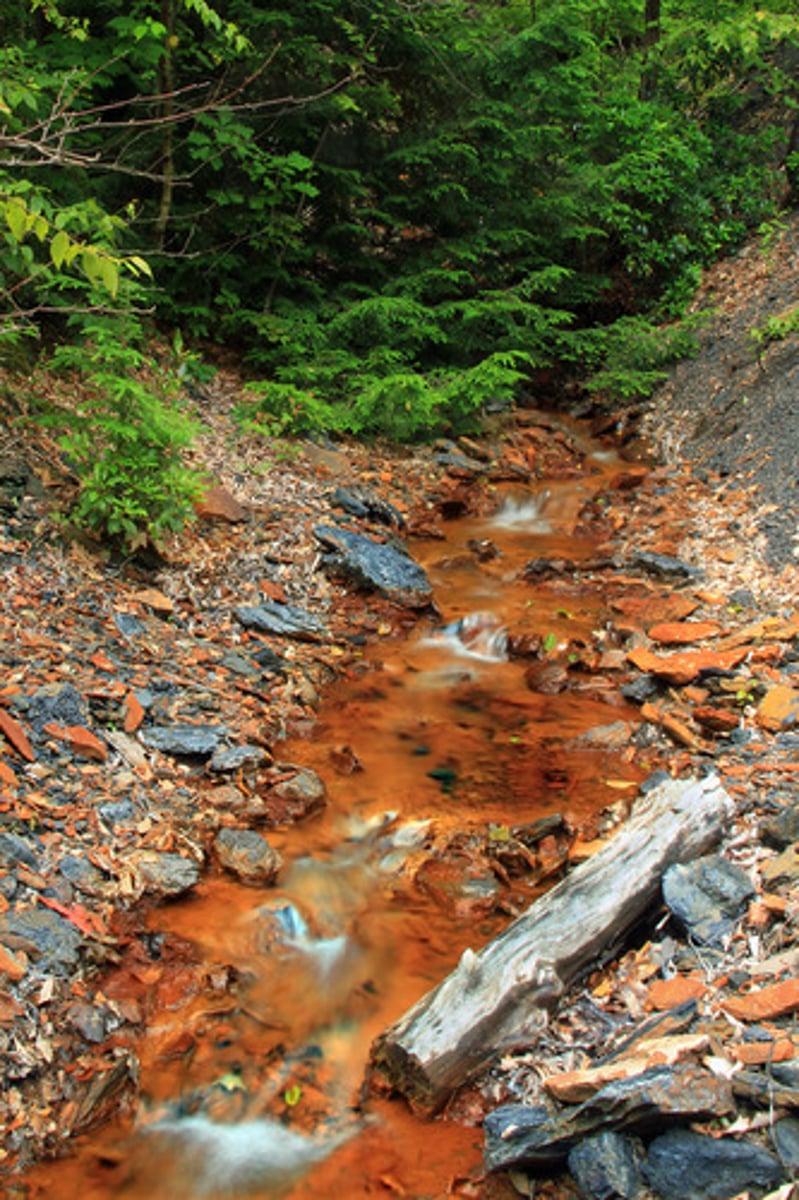
Acid mine drainage
Acidic water formed when mine waste reacts with air and water, polluting streams.

Tailings & slag
Waste materials left after mineral extraction and smelting.
Leachate
Contaminated water that drains through waste, often from landfills or mines.
Reclamation
Restoring mined or disturbed land to a usable state.
Urban heat island effect
Cities becoming warmer than surrounding areas due to concrete, asphalt, and reduced vegetation.
Urbanization
Growth of cities as people move from rural to urban areas.

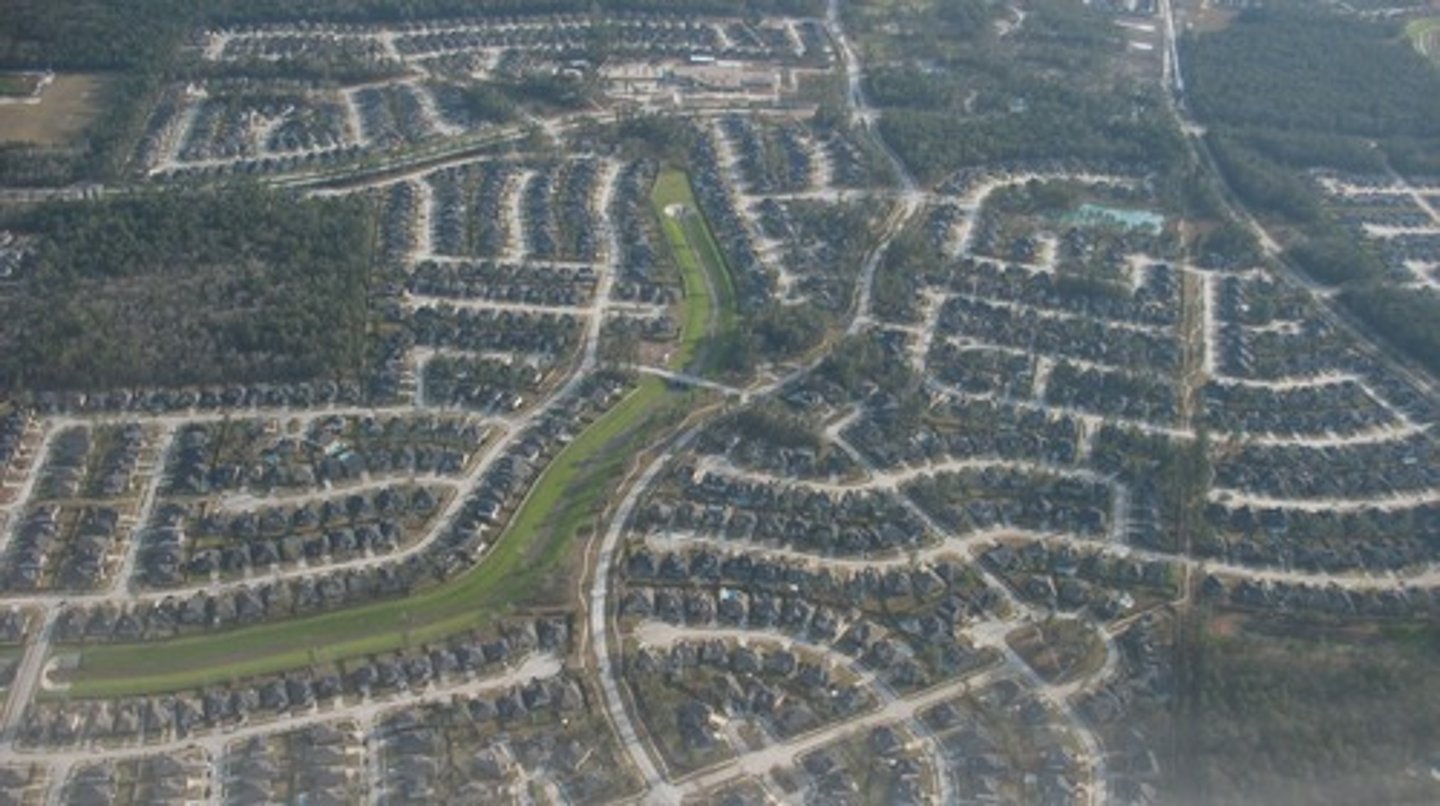
Urban sprawl
Spread of low-density development outward from a city.

Impervious surfaces
Surfaces like concrete that do not absorb water, increasing runoff.

Urban blight
Deterioration of urban areas due to neglect, population loss, or economic decline.
Brownfields
Contaminated former industrial or commercial sites requiring cleanup.
Saltwater intrusion
Movement of saltwater into freshwater aquifers, often from over-pumping groundwater.
Ecological footprint
Measure of how much land and resources a person or population consumes.
Anthropogenic
Caused or influenced by human activity.