TYPES OF TISSUES
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
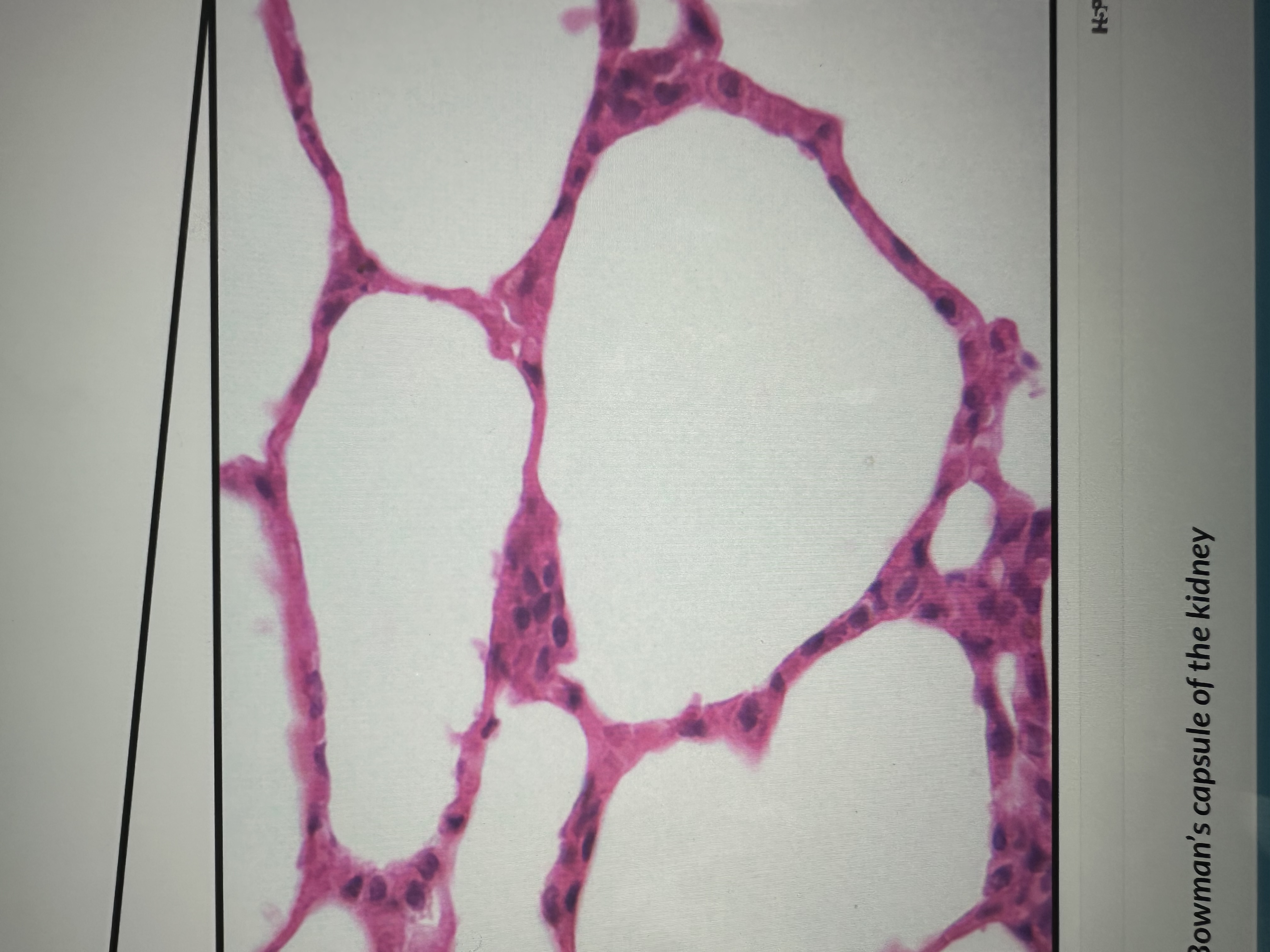
single layered flattened cells
Simple squamous epithelium
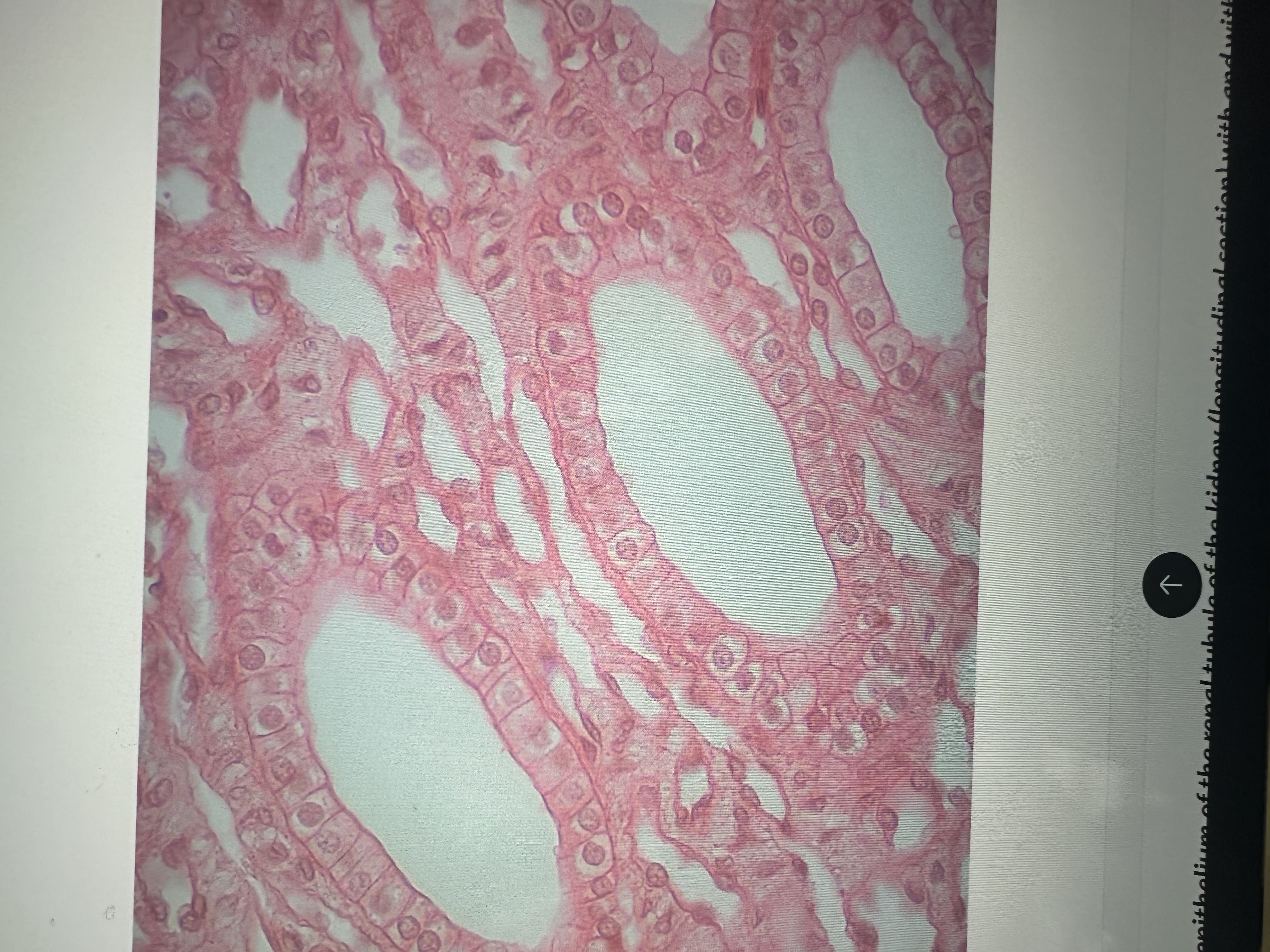
single layer of cubed cells
Simple cuboidal epithelium
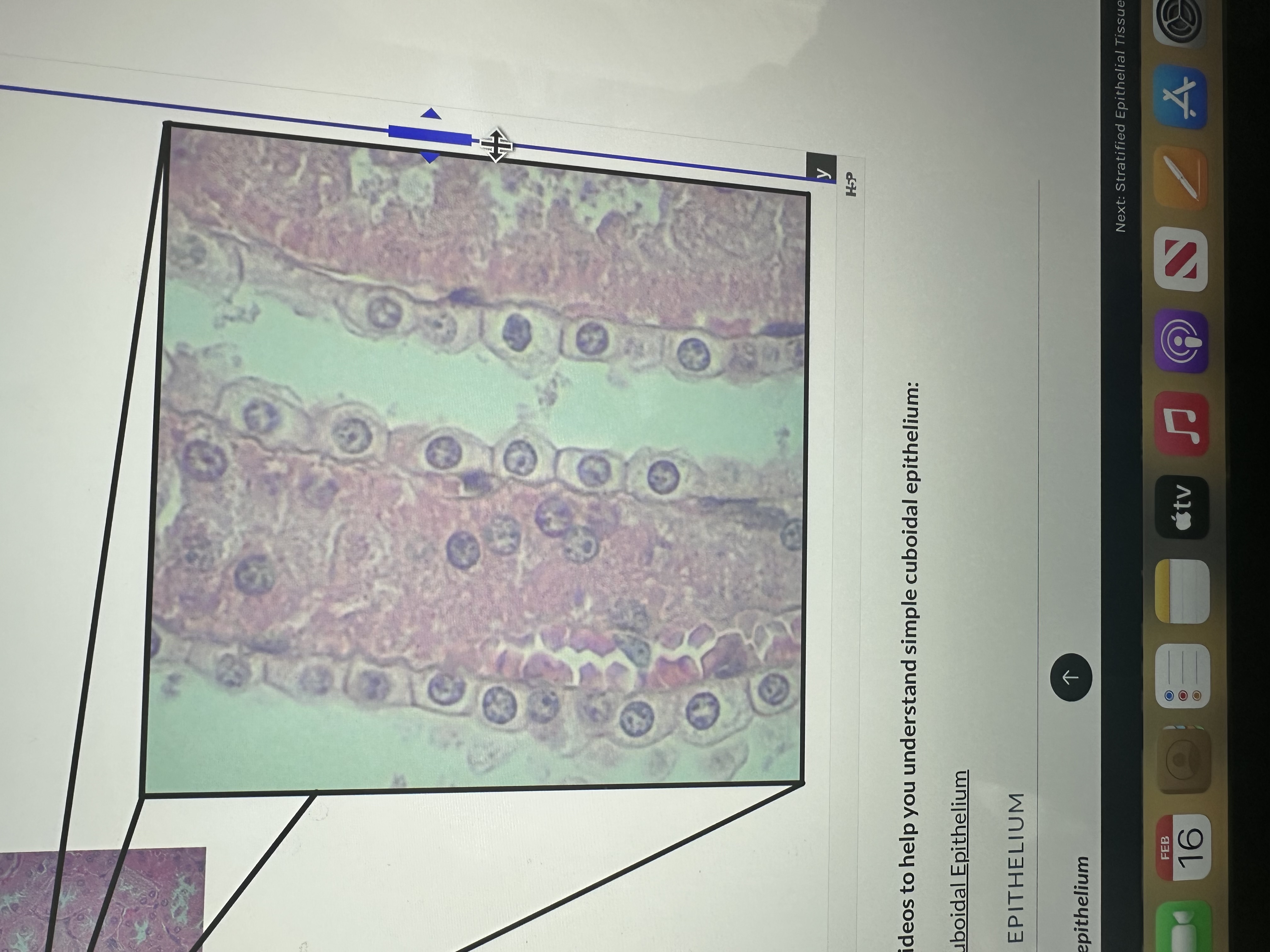
single layer of cubed cells
Simple cuboidal epithelium
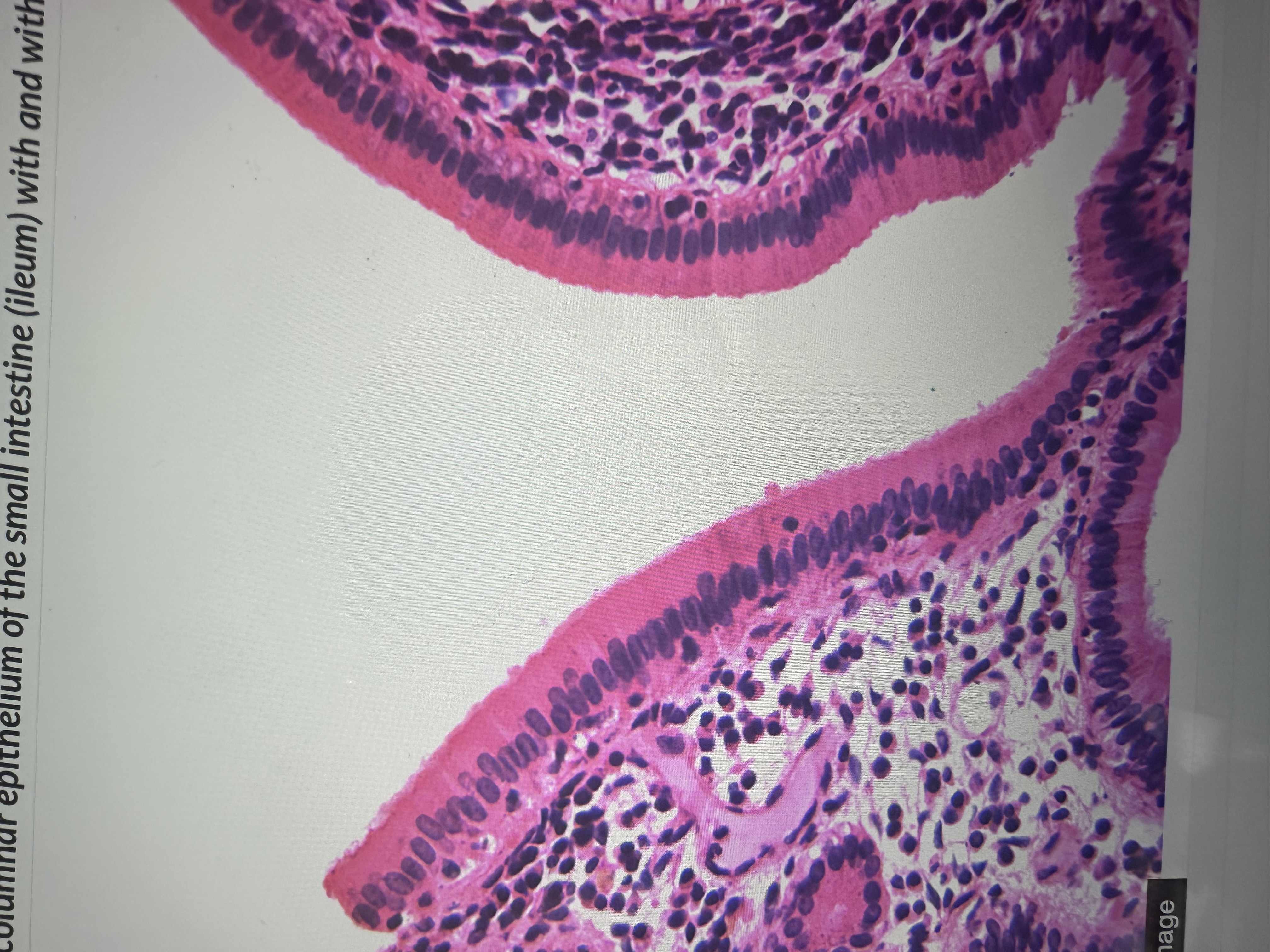
single layer of elongated rectangular
Simple columnar epithelium
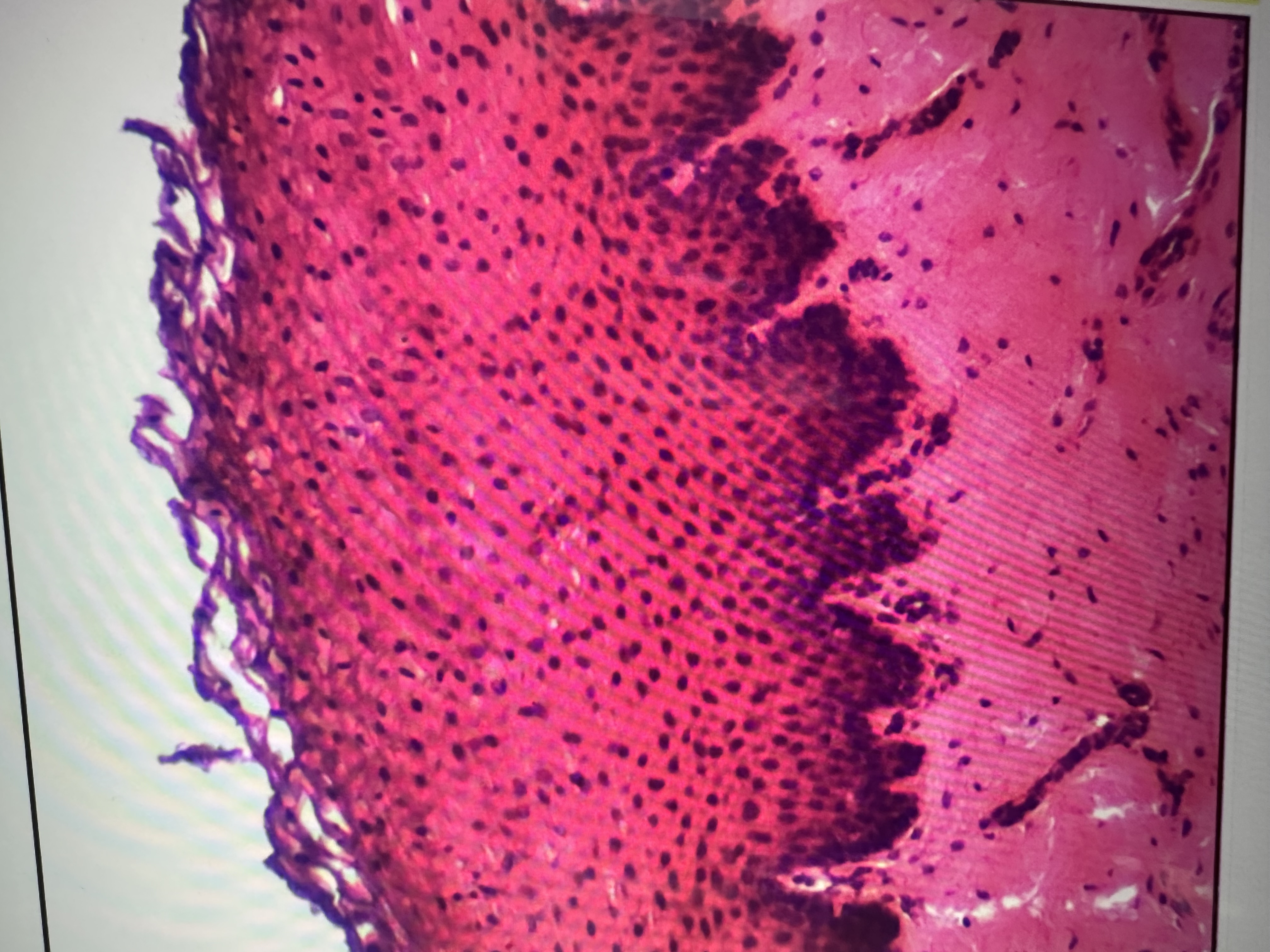
Multiple layers. Apical are flattened and basal might be cuboidal
Stratified squamous epithelium
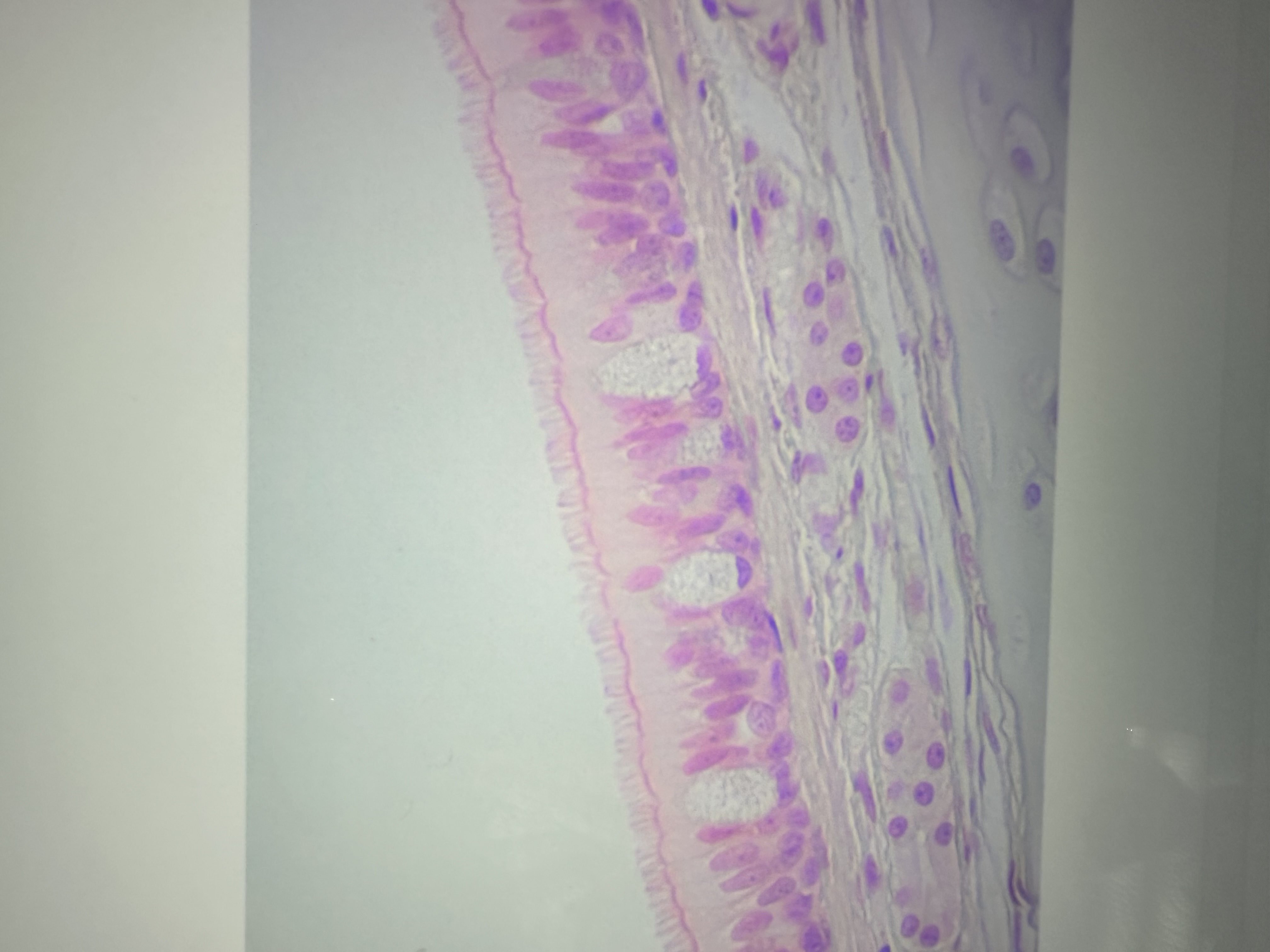
Single layer of colum shaped cells that look like they have multiple layers, because some cells do not reach the surface
Ciliates pseudostratified columnar epithelium
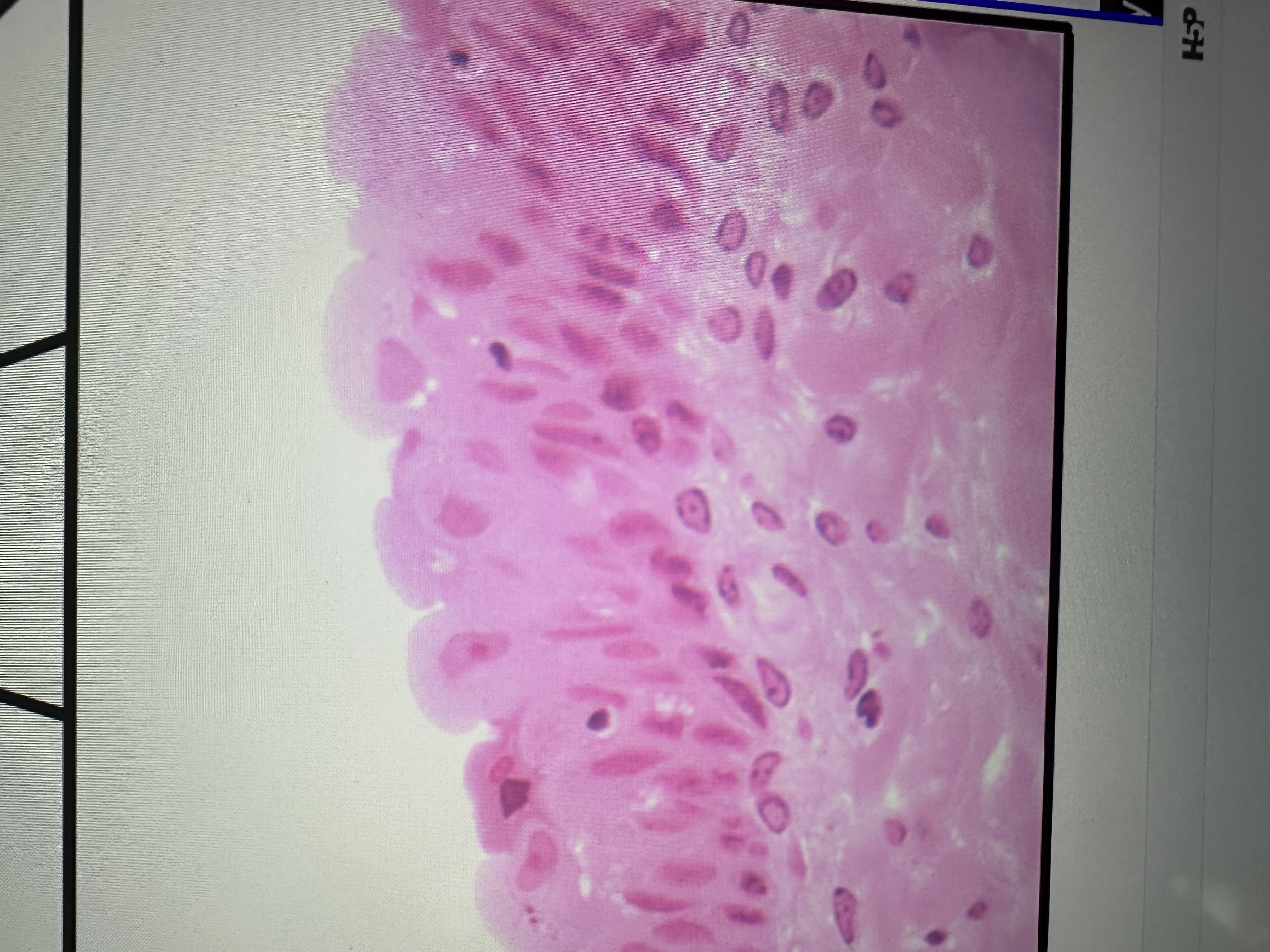
Multiple layers. Alicia cells may appear cuboidal or squamous
Transitional epithelium
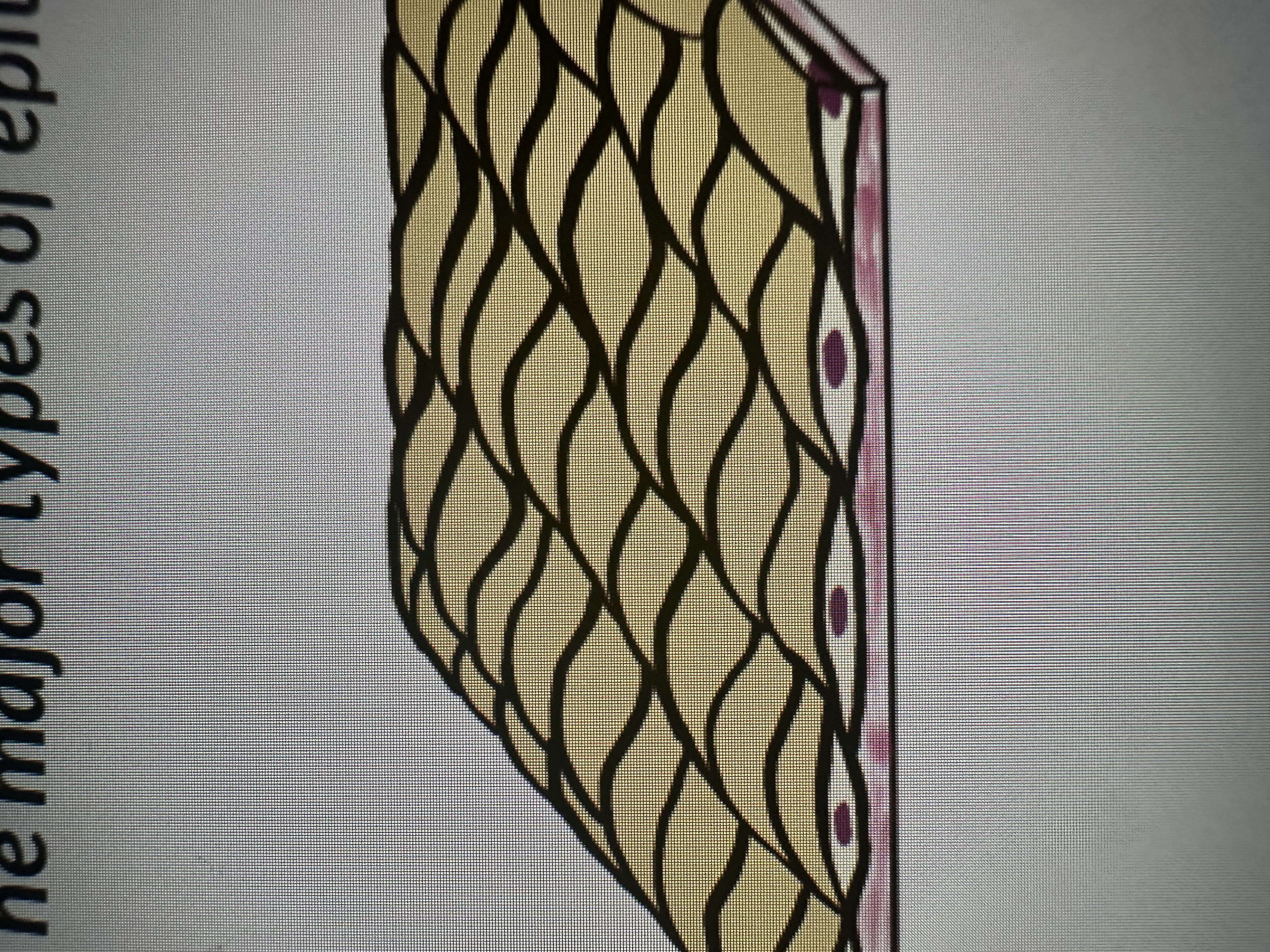
Simple squamous
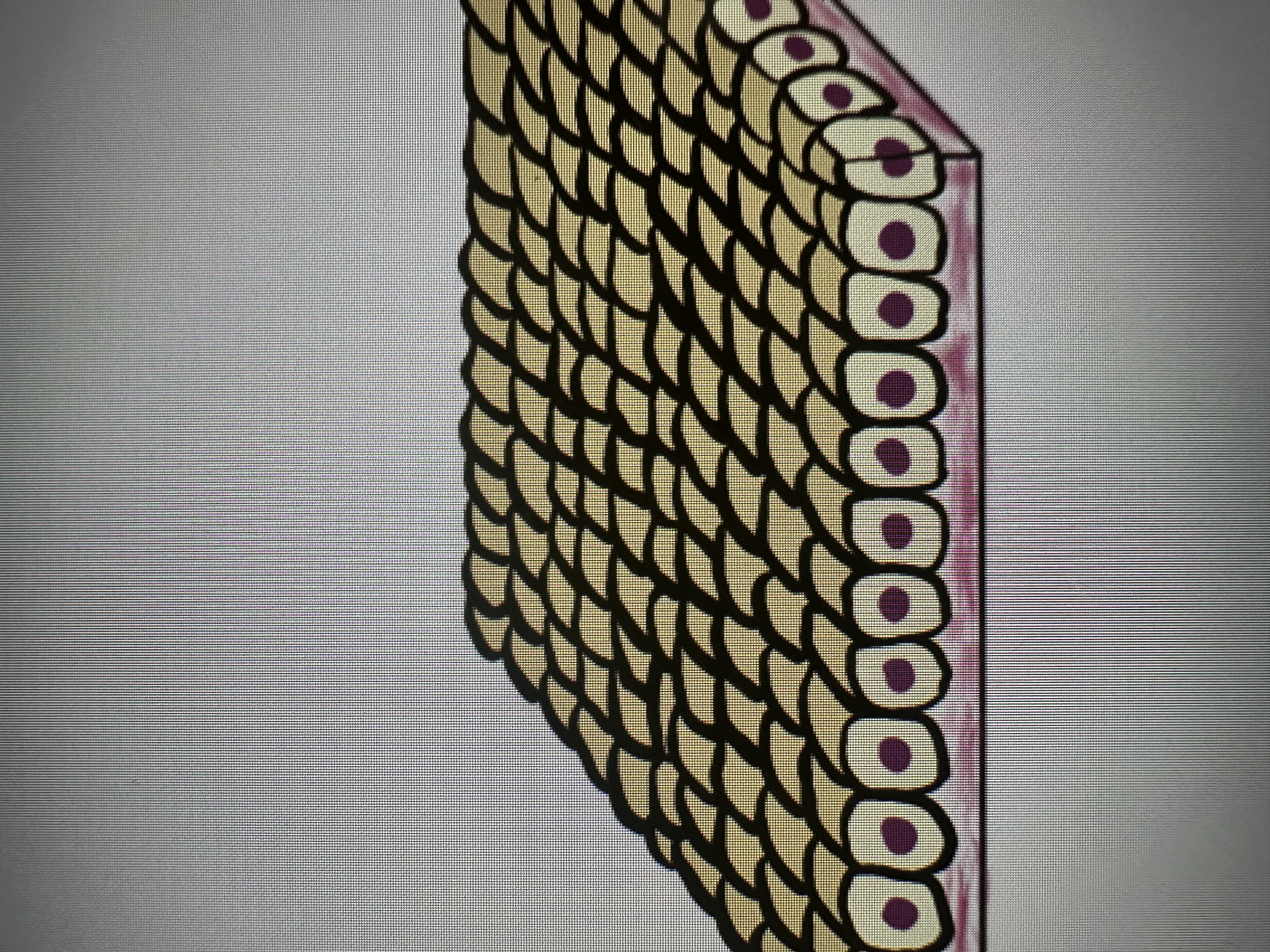
Simple cuboidal epithelium
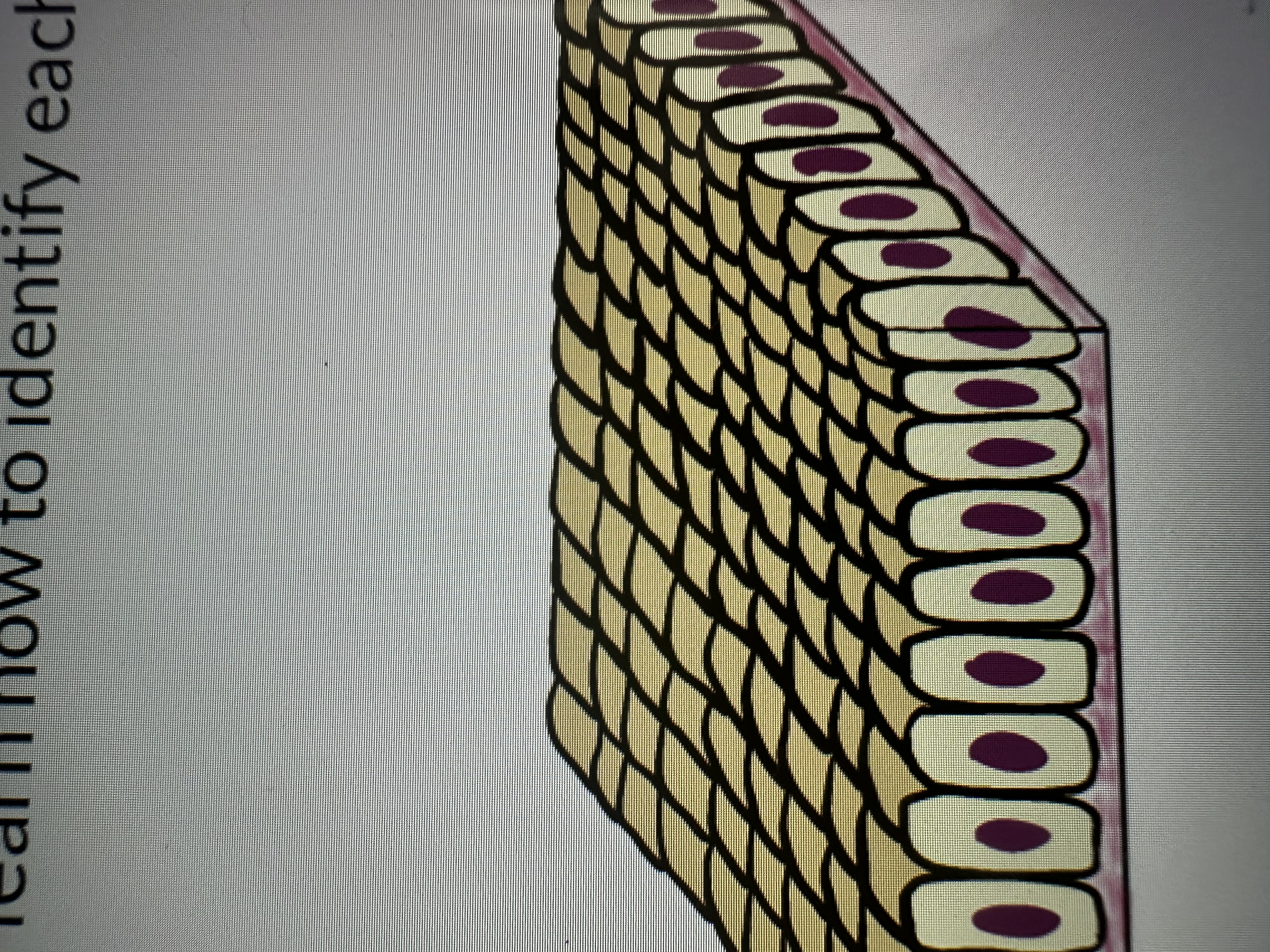
Simple columnar epithelium
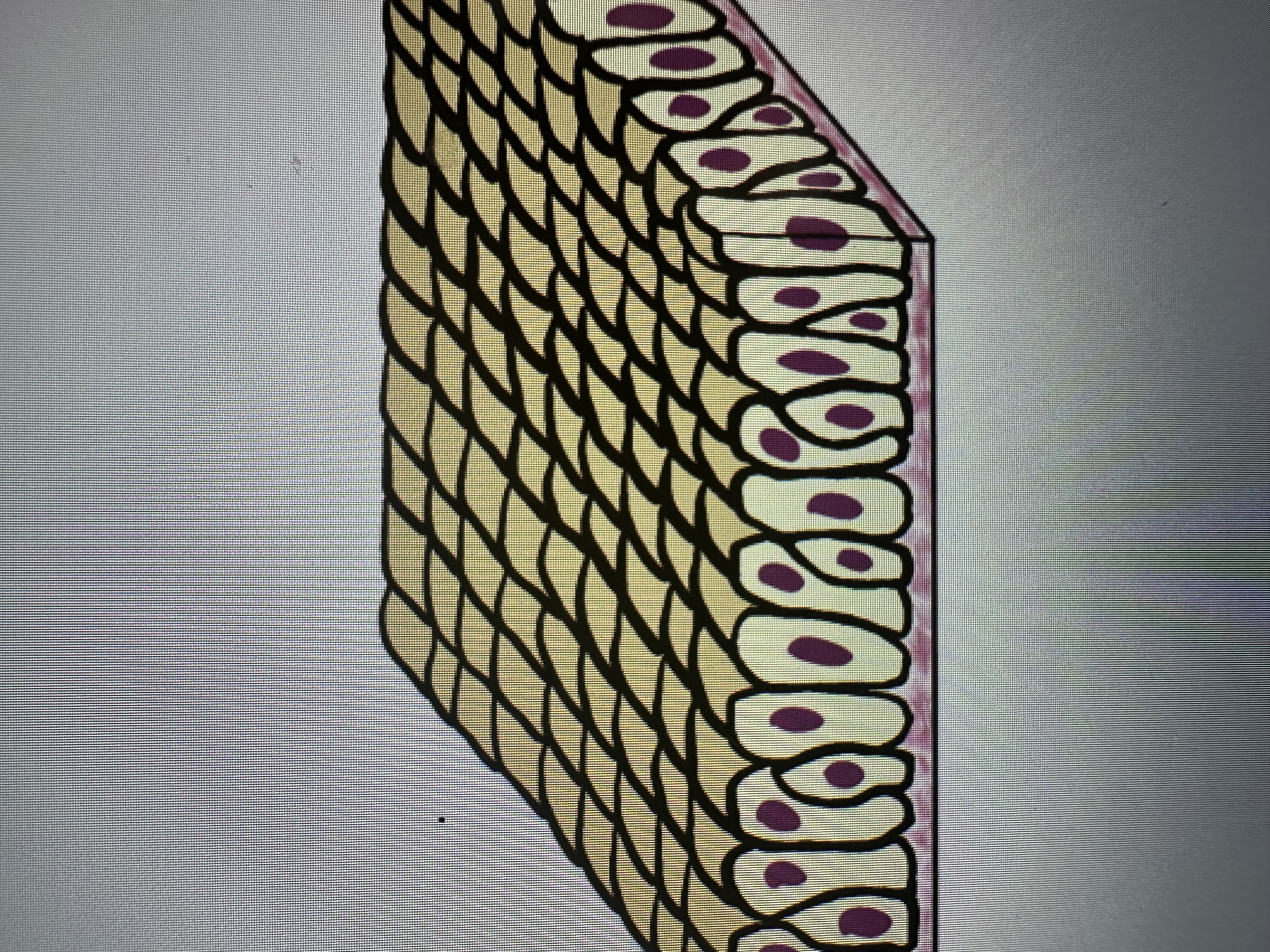
Pseudo stratified columnar epithelium

Stratified squamous epithelium
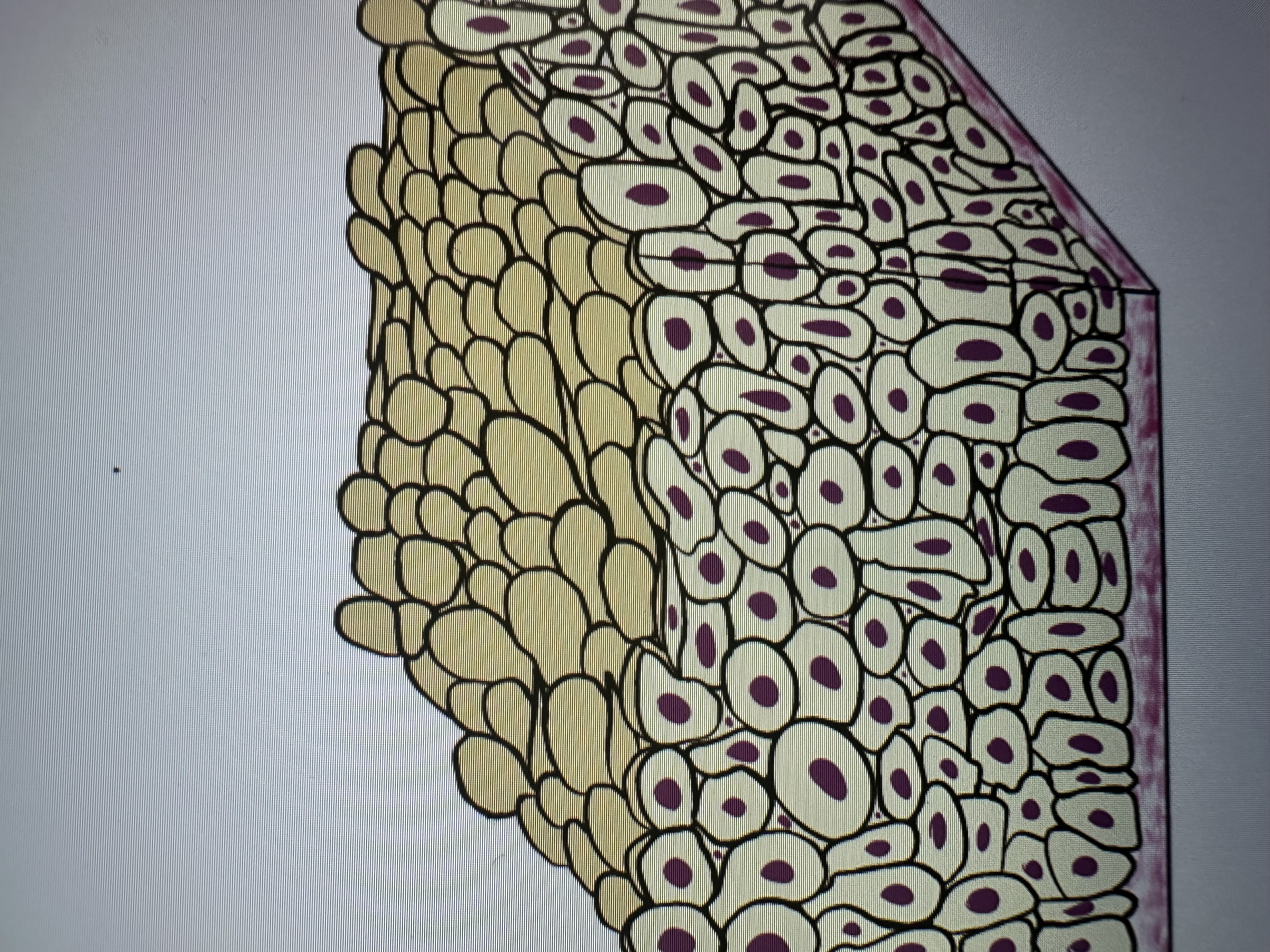
Transitional epithelium
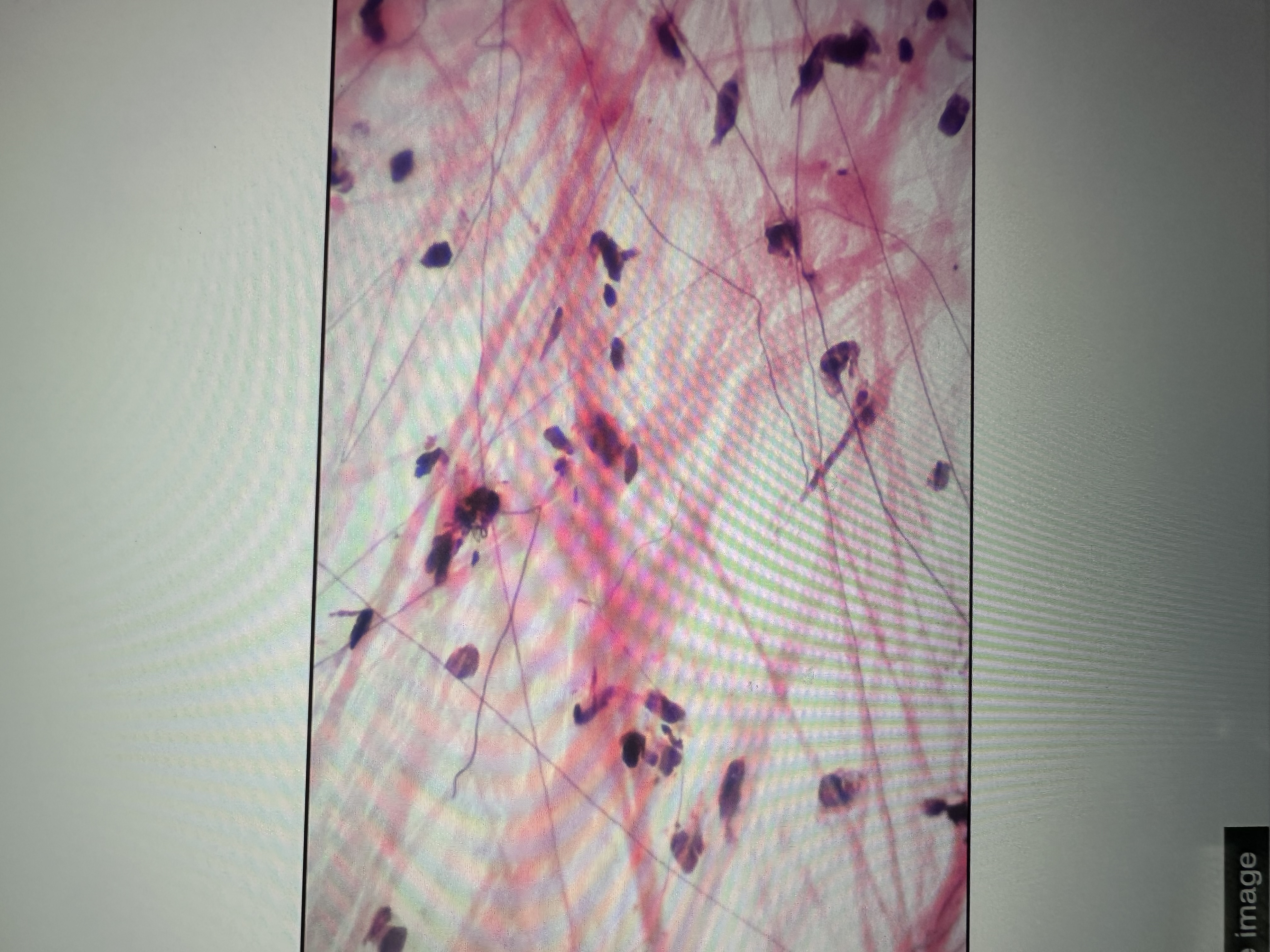
Has fibroblasts, collagen fibers, elastic fibers
connective tissue proper loose areolar
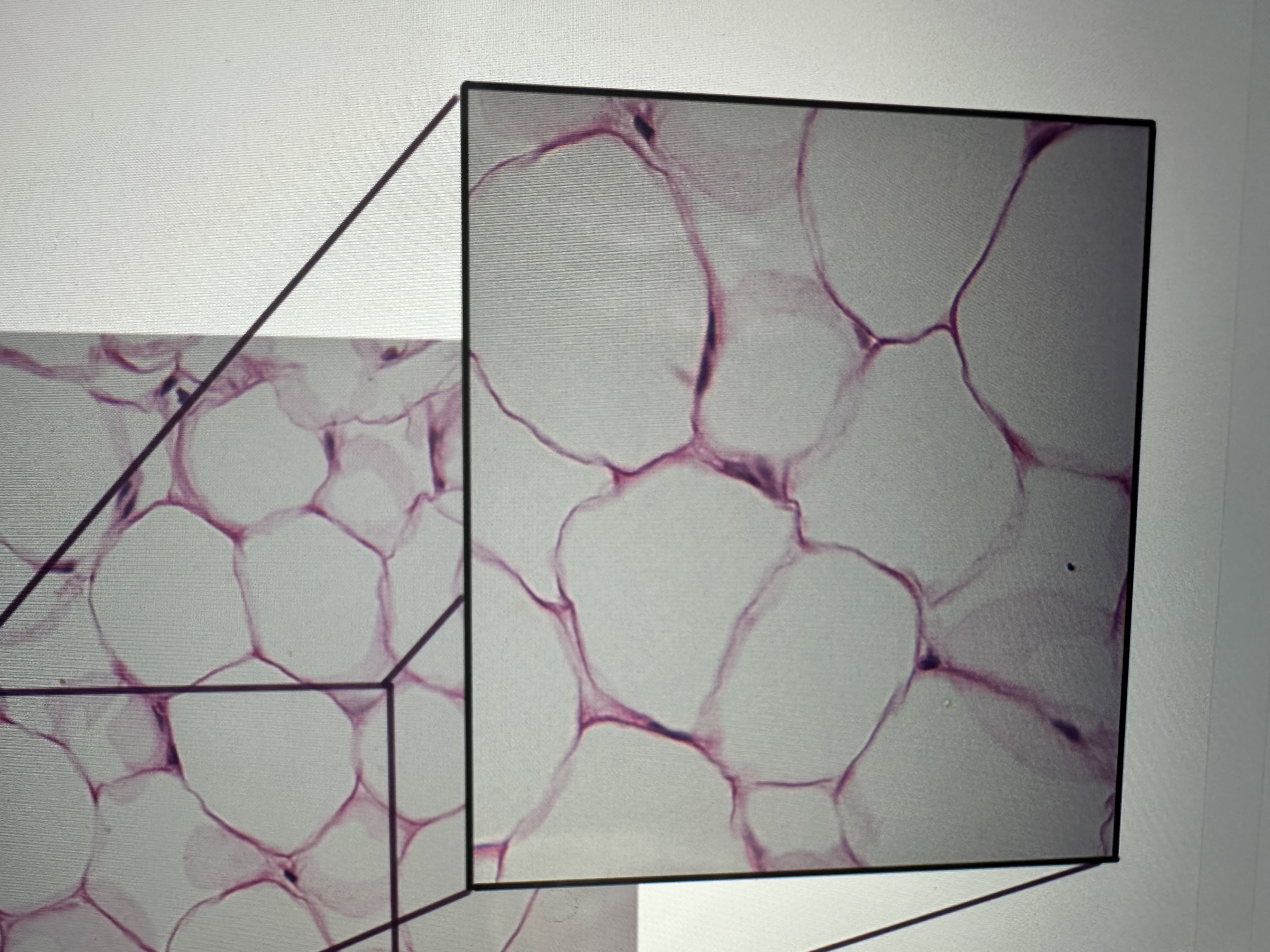
Has adipocytes
connective tissue proper adipose
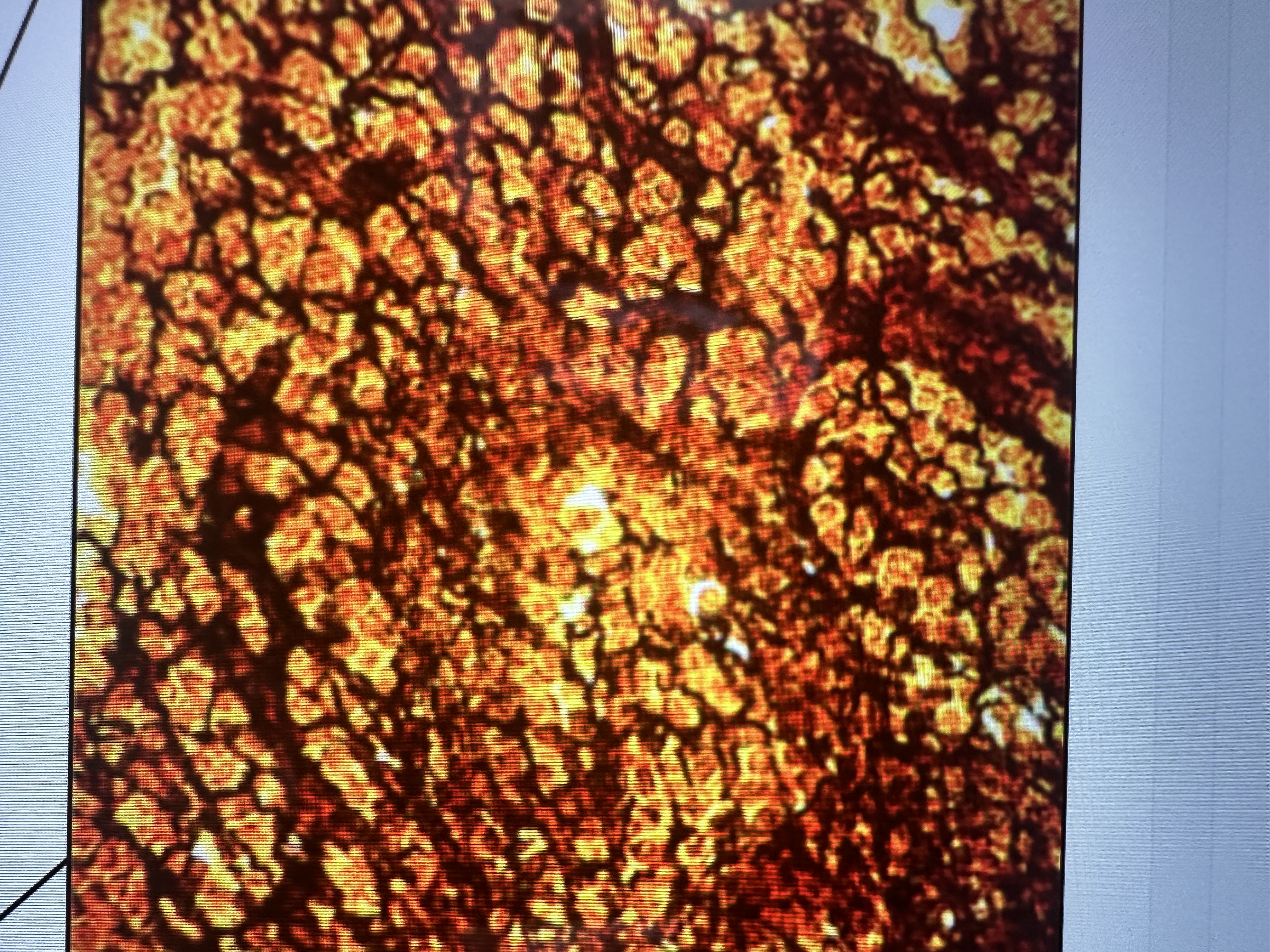
Has fibroblasts , lymphocytes
connective tissue proper loose reticular
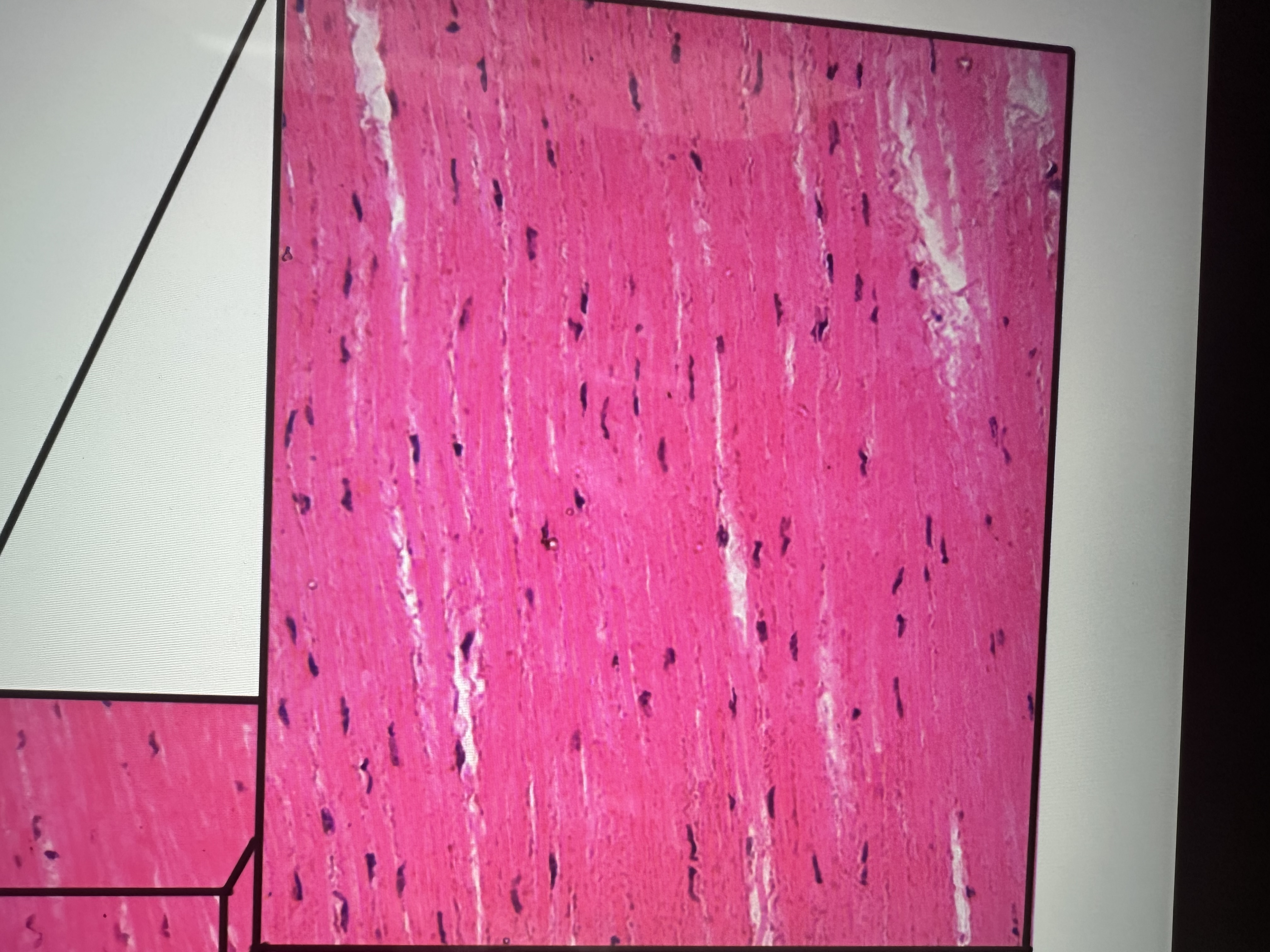
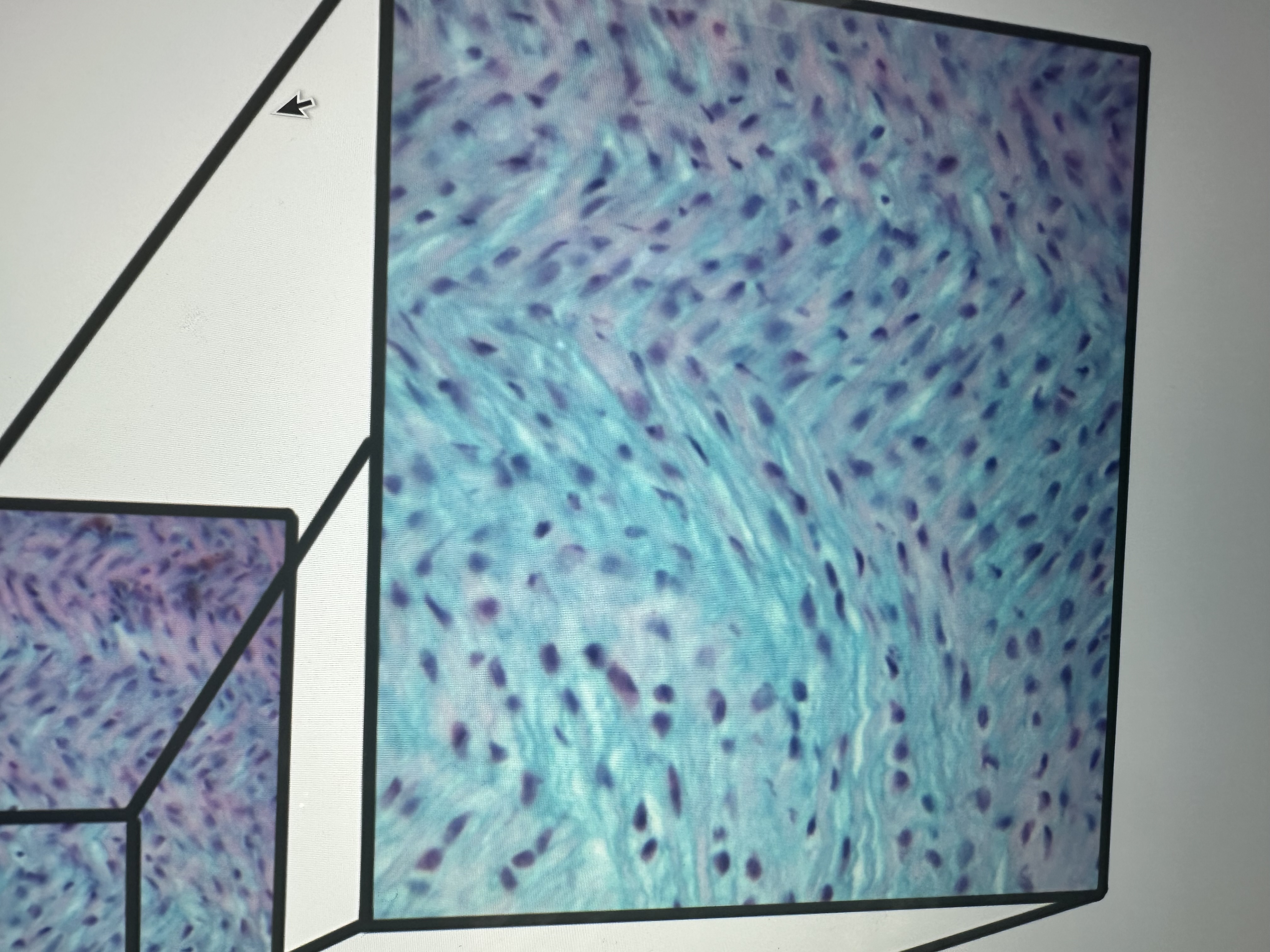
Has fibroblasts , wavy collagen fibers
connective tissue proper dense regular
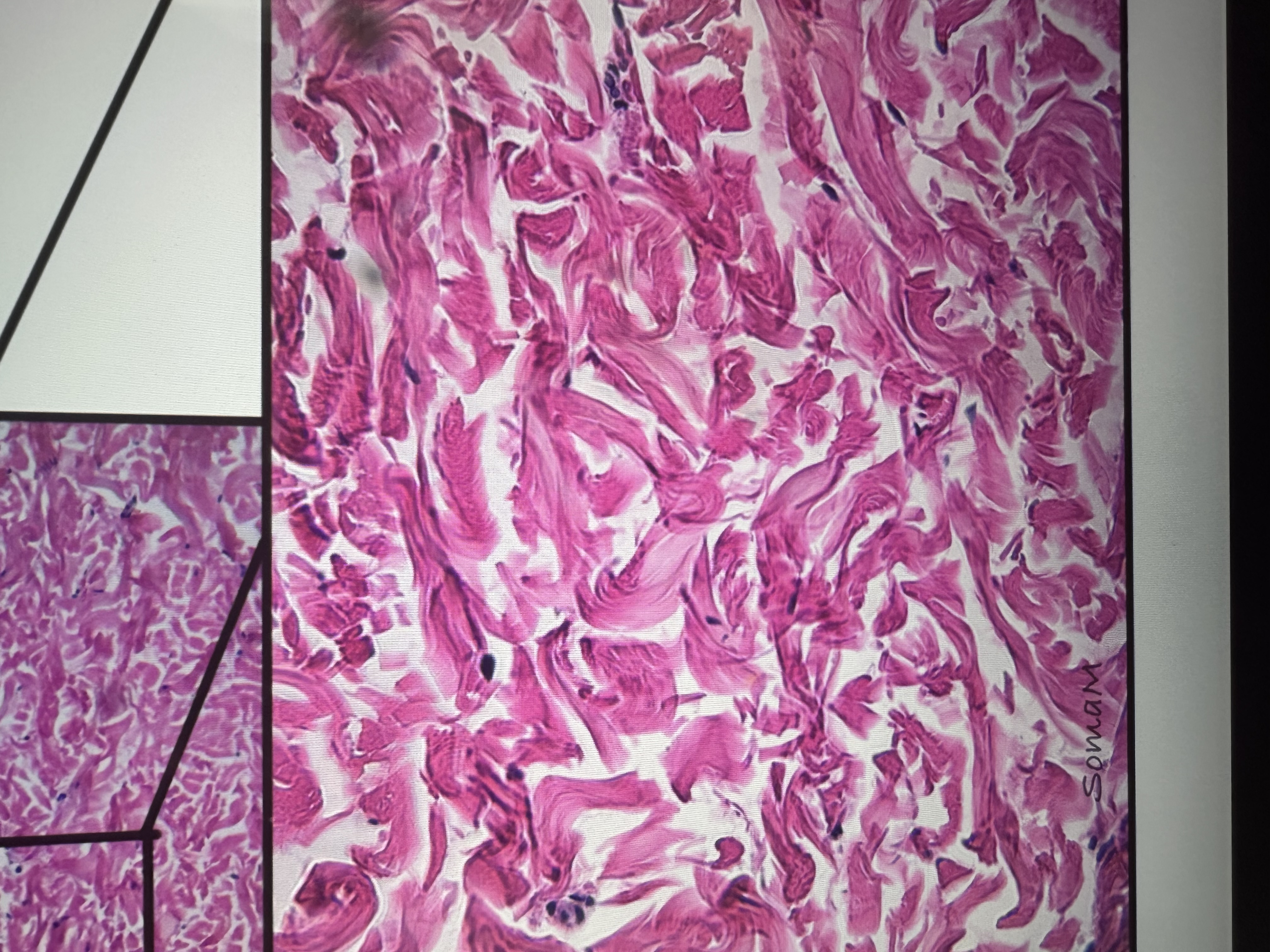
Has fibroblasts, collagen fibers
connective tissue proper dense irregular
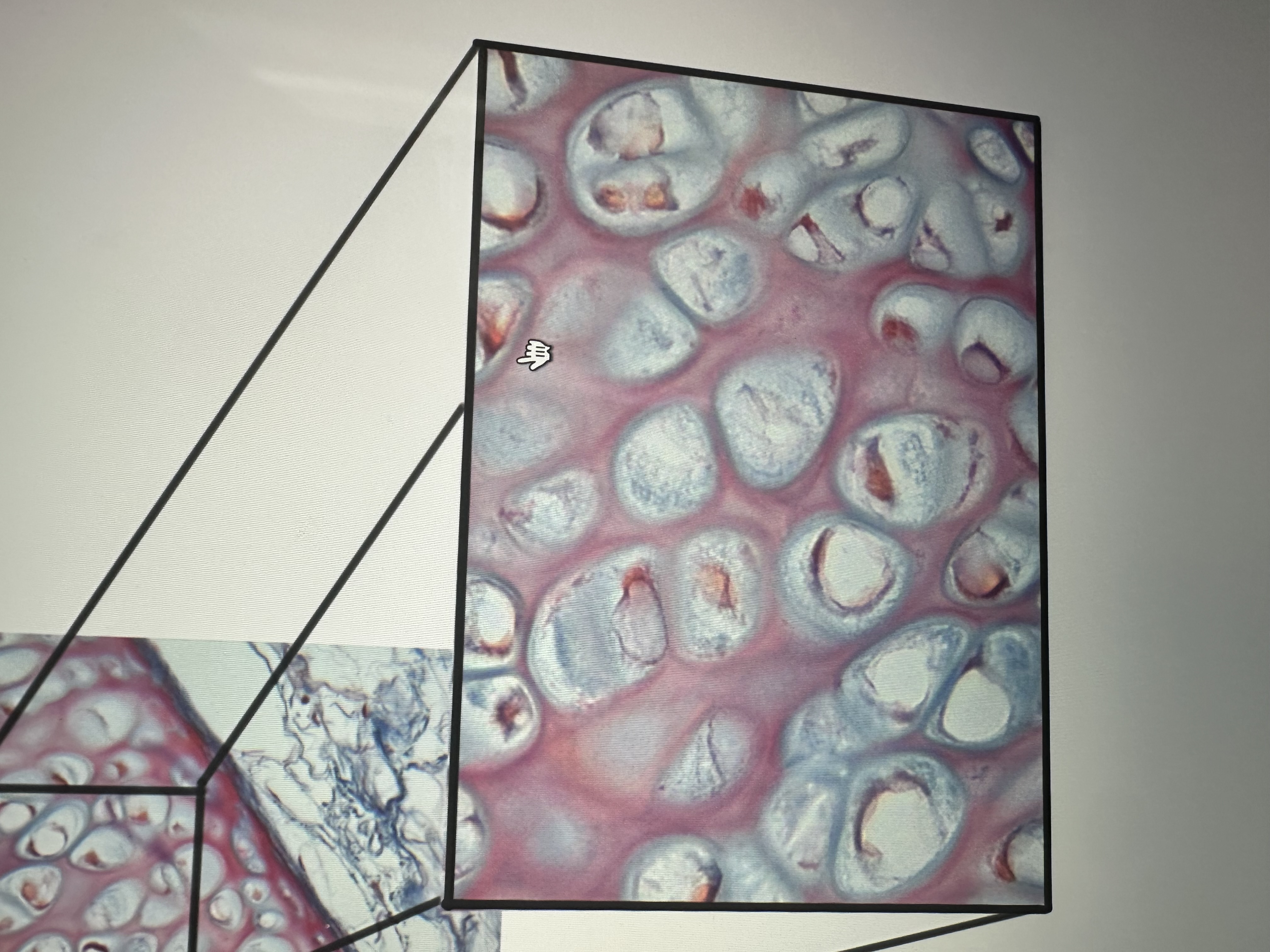
Has chondrocytes inside the lacunae
hyaline cartilage
Has elastic fibers and lacunae
elastic cartilage
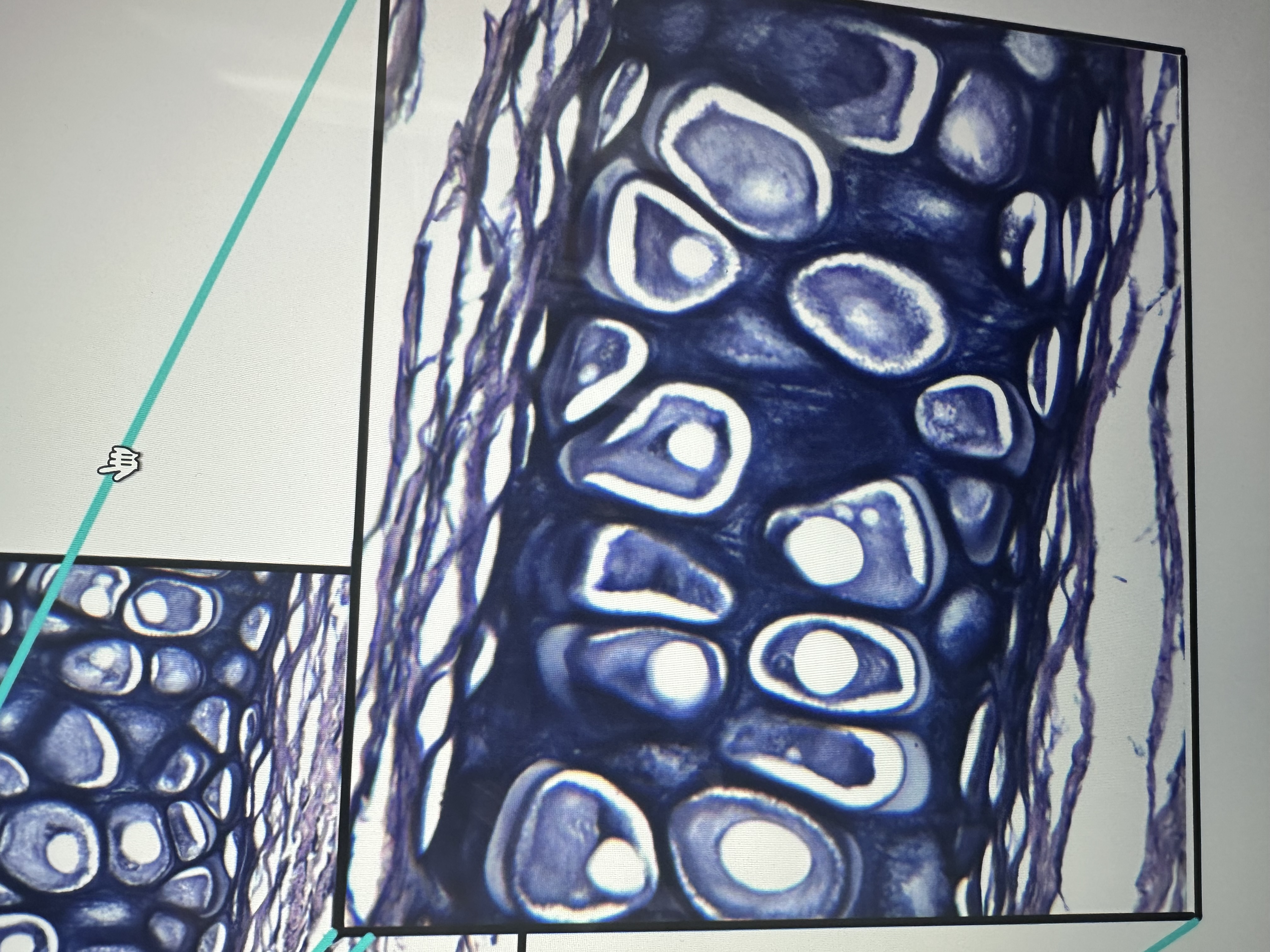
Has blue collagen fibers , lacunae, chondrocytes
fibrocartilage
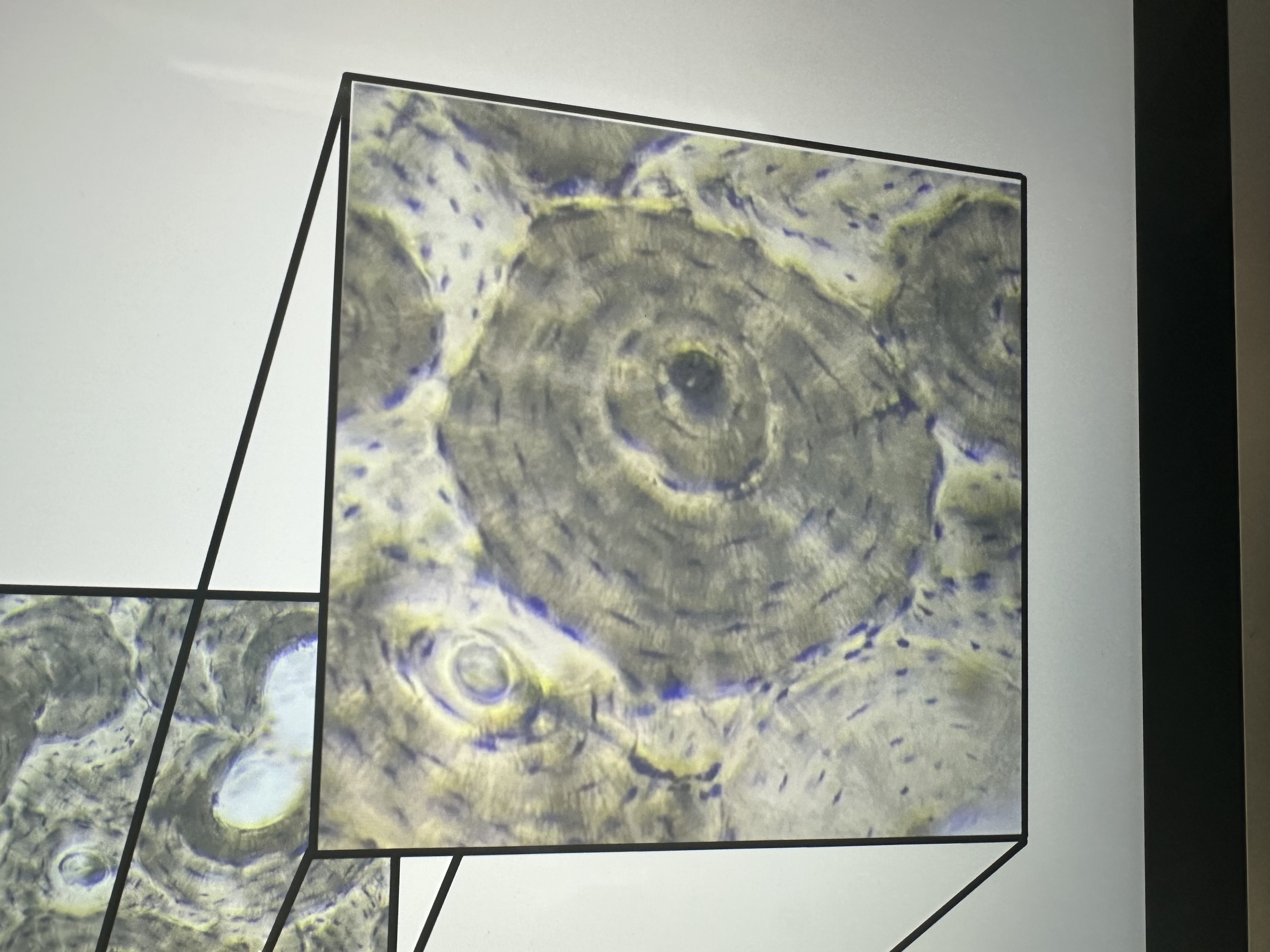
Osteons, lacunae
osseous tissue
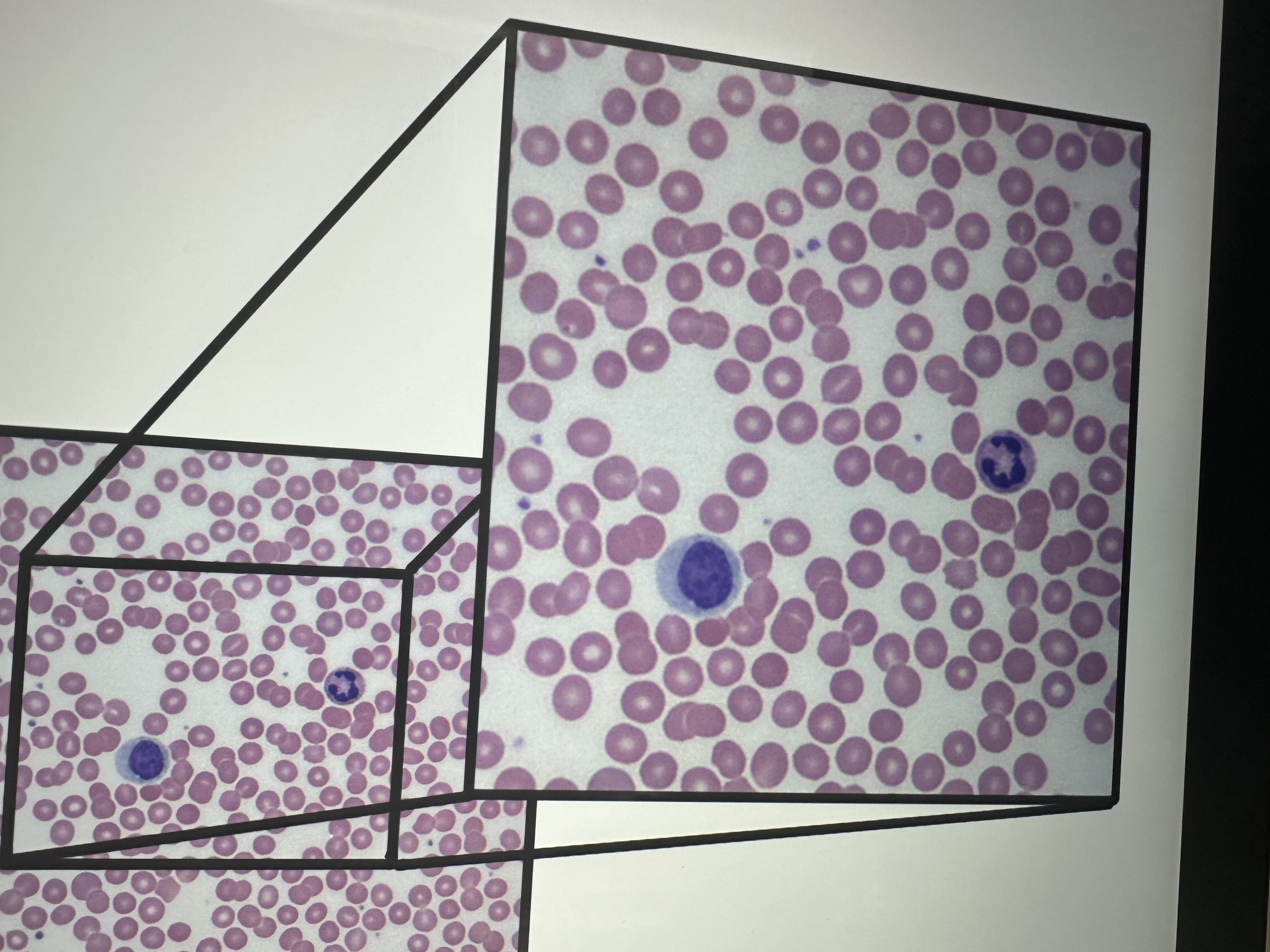
Red blood cells, platelets, lymphocytes, nitrifulls
blood
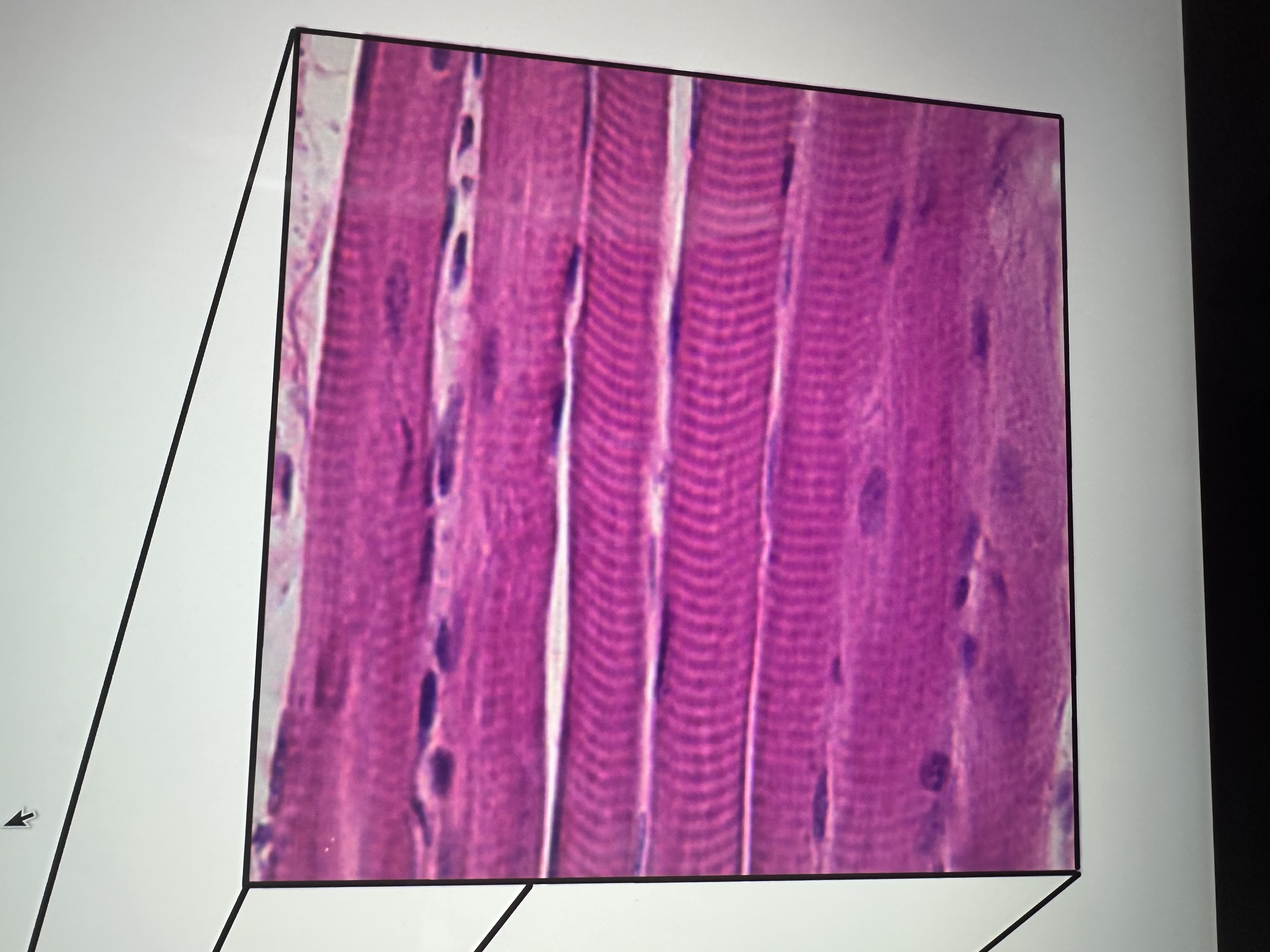
Has striations
skeletal muscle
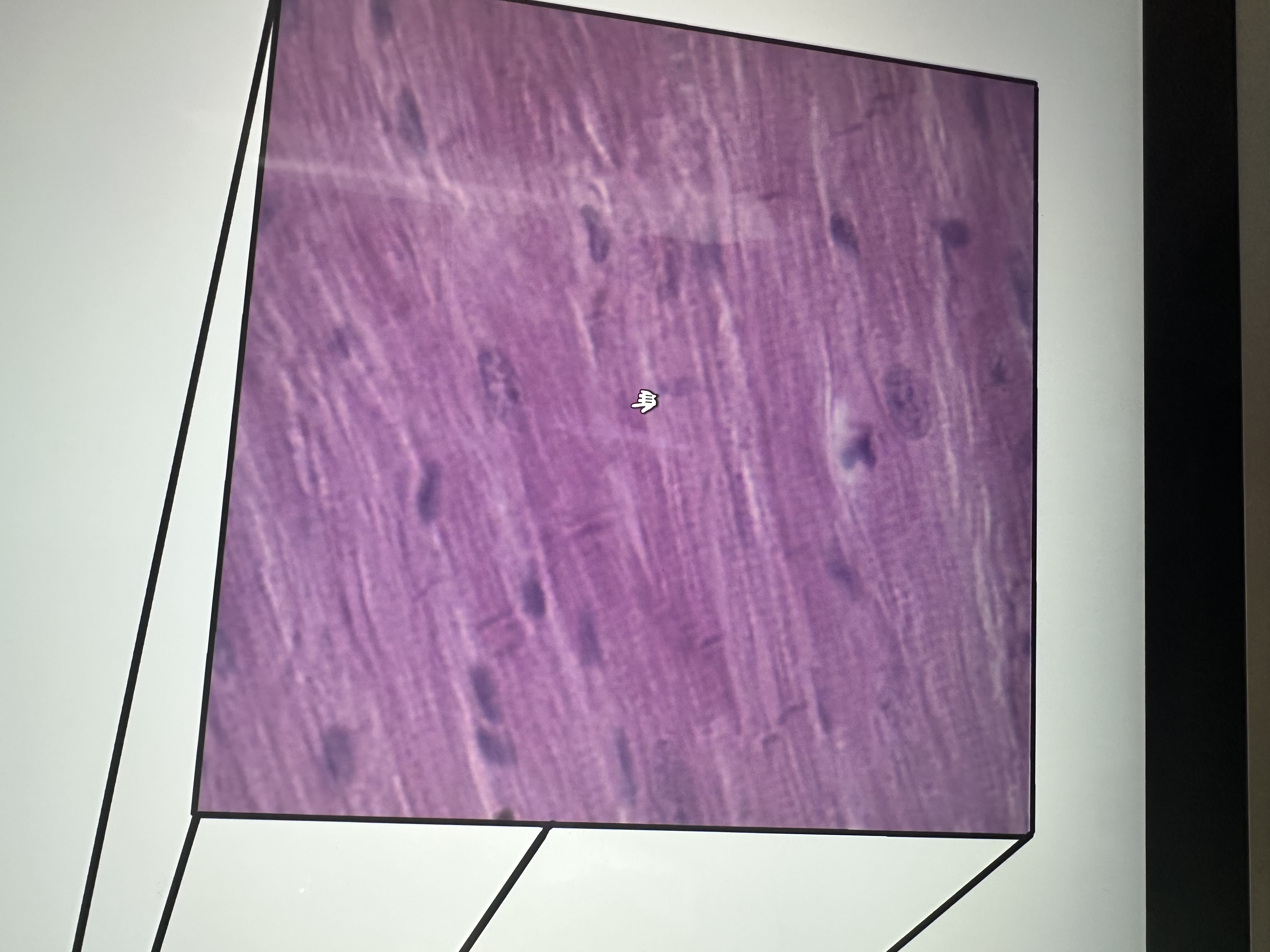
Has intercalated discs, striations
cardiac muscle
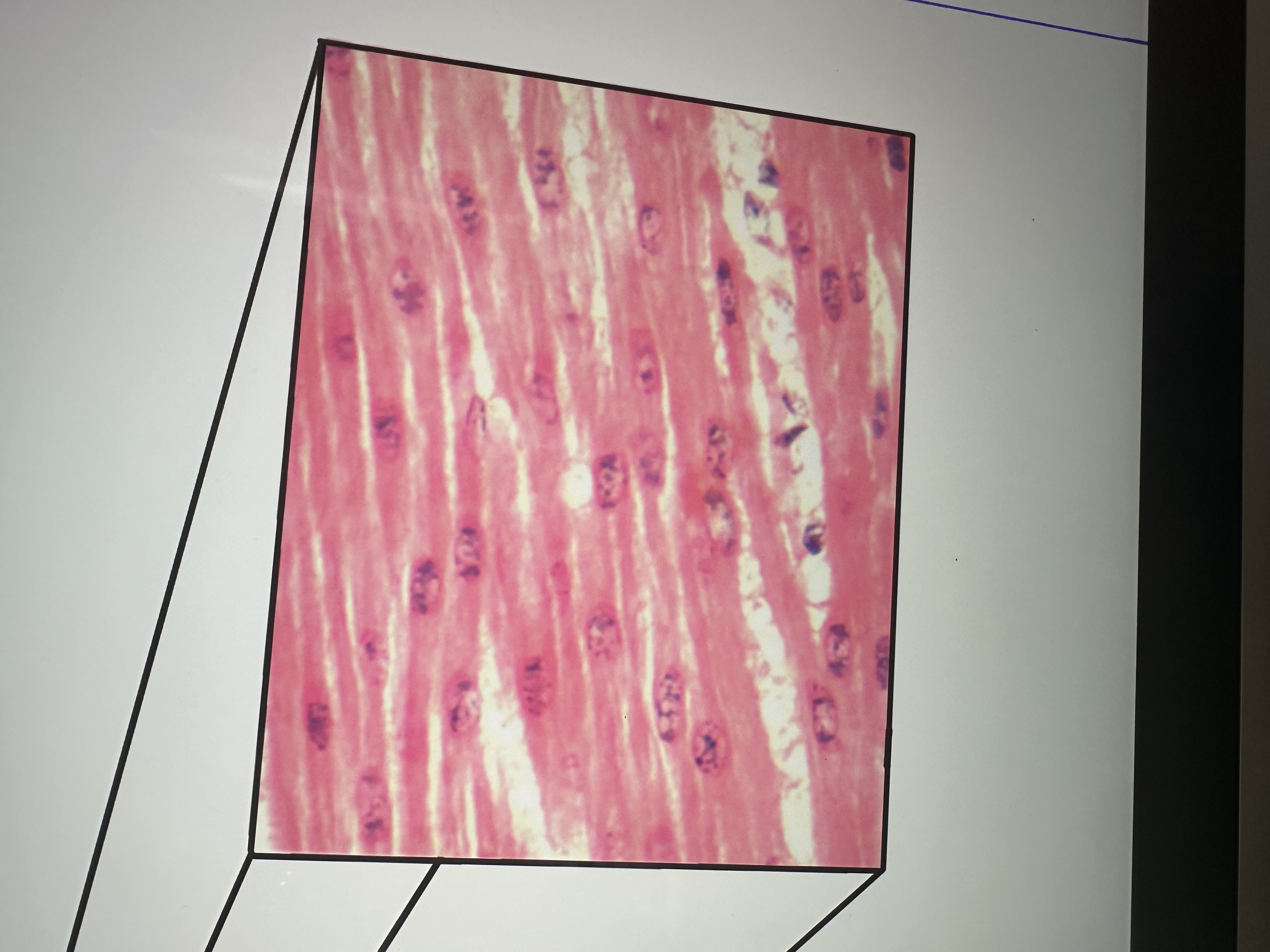
Nucleus in center of cells, no striations
smooth muscle
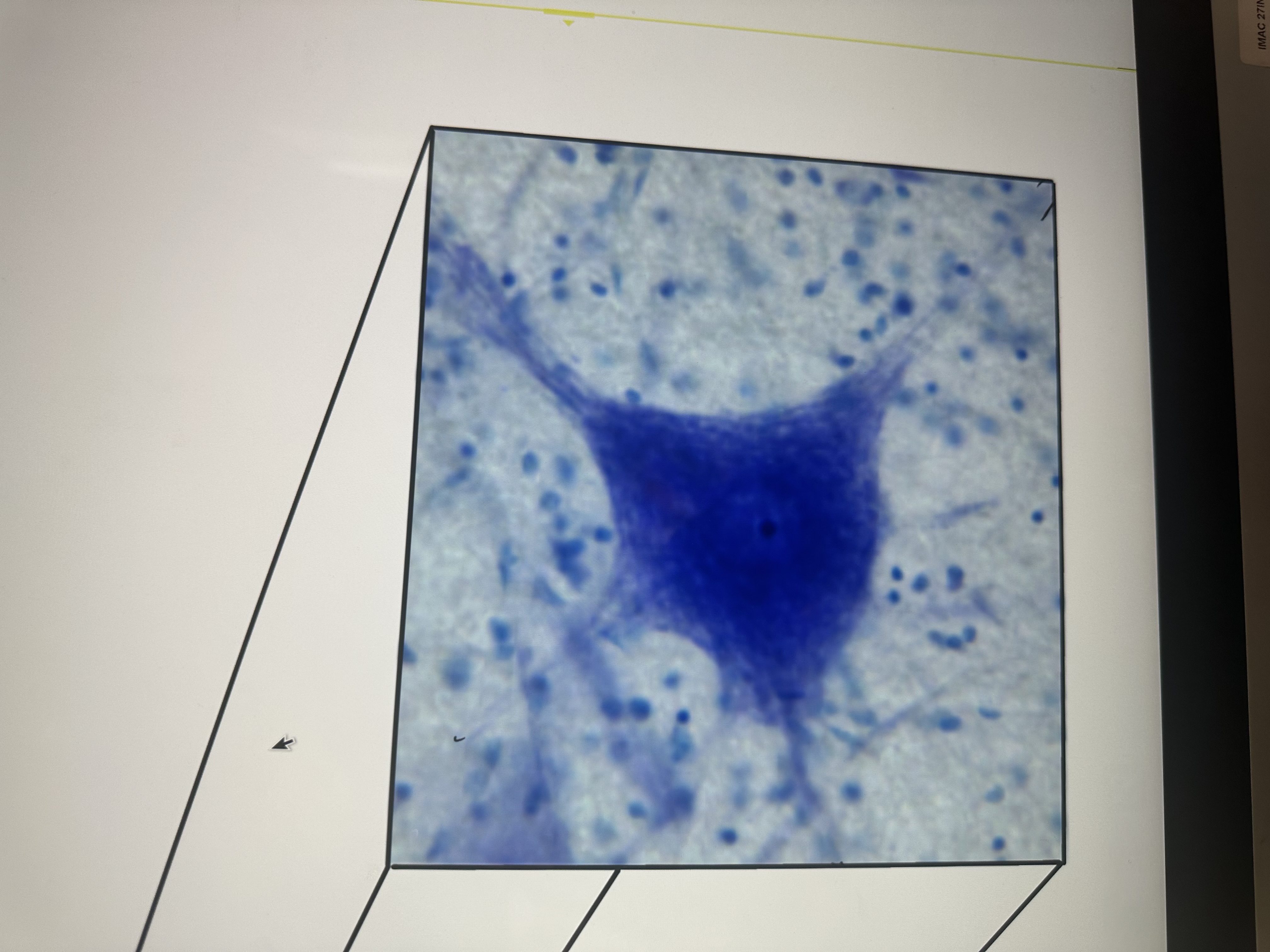
Has neurons and cell bodies
nervous tissue
function of areolar connective tissue + location
anchors skin tissues to deeper tissues (skin)
function of adipose connective tissue + location
stores fat ( behind and around eyes)
function of reticular connective tissue + location
supports immune cells ( lymph nodes)
function of dense regular connective tissue + location
allows a degree of stretching ( tendons)
function of dense irregular connective tissue + location
provides strength and resistance to pulling forces ( skin)
function of hyaline cartilage + location
provide support to joints and other body structures ( embryonic skeleton)
function of elastic cartilage + location
provide flexibility to parts of the body that need to move. ( ears epiglottis)
function of fibrocartilage + location
Strongest of the cartilages, resists compression forces of certain joints ( intervertebral discs)
function of osseous tissue + location
Provides strength and protection to bones ( bone)
function of blood = location
transport nutrients ( blood vessels)
function of skeletal muscle + location
Move skeleton and support joints ( head and neck)
function of cardiac muscle
Pump blood through the body ( heart)
functions of smooth muscle + location
Allows for movement of substances such as food and blood through the organs/body ( walls of our organs)
function of nervous tissues + location
allows our body to send and receive information incredibly quickly. (brain)
simple squamous epithelium function + location
Allows for gas exchange between lungs and blood vessels ( alveoli of the lung)
simple cuboidal epithelium function + location
Absorption and/or secretion ( kidneys)
simple columnar function + location
absorption, recreation of mucus ( intestines)
stratified epithelial function + location
protects tissues from abrasion ( esophagus)
pseudo stratified columnar epithelium function + location
secrete mucus ( upper respiratory tract)
transitional epithelium function + location
stretches readily when bladder is full ( ureters, bladder)