Lecture 6 - Neural Lipids in their Specialised Membranes
1/268
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
269 Terms
Why do nerve cells modify the lipid composition of their membranes?
To ease vesicle fusion, regulate ion fluxes, and create specialised microenvironments that contribute to cellular communication
How does the chemical diversity of membrane lipids affect cell function?
Controls protein traffic, facilitates recognition between cells, and produces hundreds of lipid mediators that carry information within and across cells
What proportion of the human brain (dry weight) is made up of lipids?
About half
What is the objective of neural lipidomics?
To understand how neural lipids work together and contribute to brain function
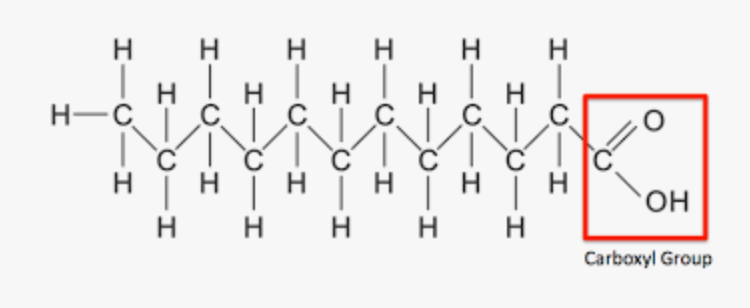
What is the structure of fatty acids?
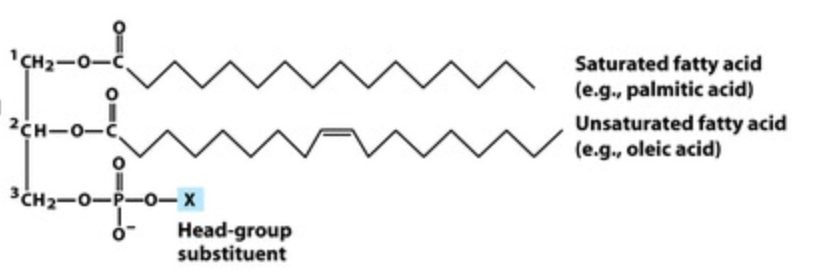
What is the structure of glycerophospholipids?
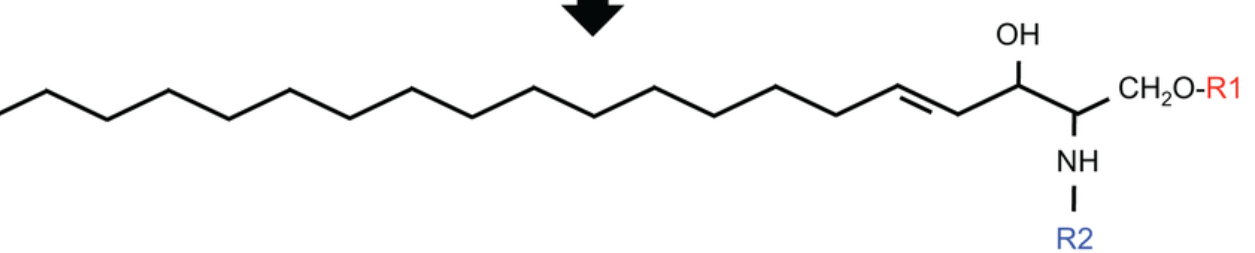
What is the structure of sphingolipids?
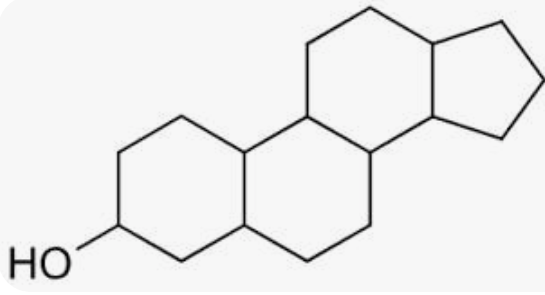
What is the structure of sterol lipids?
What functional group is present at one end of a fatty acid?
A carboxyl group (–COOH)
What is found at the other end of a fatty acid?
A hydrophobic tail
Can fatty acids be saturated or unsaturated?
Yes, they can be either saturated or unsaturated
Are fatty acids ever free in membranes?
No, they are always attached to phospholipids or sphingolipids
What is one main role of fatty acids in the body?
Used in energy storage
What role do unsaturated fatty acids play in neurons?
Help maintain flexible membranes for synaptic function
What forms the backbone of glycerophospholipids?
Glycerol
How many fatty acid tails do glycerophospholipids have, and what is their property?
Two fatty acid tails, which are hydrophobic
What does the head group of glycerophospholipids contain, and what is its property?
A phosphate-containing head group, which is hydrophilic
Are glycerophospholipids amphiphilic or not?
Yes, they are amphiphilic
What structural role do glycerophospholipids play in cells?
They form the lipid bilayer of membranes
How do glycerophospholipids support membrane proteins?
They provide a platform for membrane proteins
Why are glycerophospholipids critical in neurons?
Essential for neuronal membranes and synaptic vesicles
What is the backbone of sphingolipids?
Sphingosine (not glycerol)
What molecule do sphingolipids often contain?
A fatty acid, forming a ceramide
What are the two main types of sphingolipids?
Sphingomyelin (a phospholipid) and glycosphingolipids (e.g., cerebrosides, gangliosides)
What structural role do sphingolipids play in cells?
They are components of cell membranes
What functional roles do sphingolipids have?
Involved in cell recognition and signal transduction
Why are sphingolipids important in the nervous system?
Defects can cause neurodegenerative and storage diseases
What is the core structure of sterol lipids?
A rigid four-ring structure
What is the most important sterol in the body?
Cholesterol
How do sterol lipids affect membranes?
They regulate membrane fluidity and stabilise lipid bilayers
Why are sterol lipids essential in the nervous system?
Required for myelin formation, synapse formation, and steroid hormone synthesis
What types of molecules are lipids?
Hydrophobic or amphipathic small molecules
How are lipids derived?
By condensation of hydrocarbon units in chains or rings
Are most lipids soluble in water?
No, most are not water-soluble
How abundant are poorly unsaturated fatty acids in normal cells versus the brain?
Rare in normal cells, but they make up most of the composition in the brain
What is the simplest phospholipid?
Phosphatidic acid
Which head group does phosphatidylethanolamine contain?
Ethanolamine
Which head group does phosphatidylcholine contain?
Choline
Which head group does phosphatidylserine contain?
Serine
Which head group does phosphatidylglycerol contain?
Glycerol
Which head group does phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate contain?
myo-Inositol 4,5-bisphosphate
What is cardiolipin derived from?
Phosphatidyl-glycerol
Which phospholipid is zwitterionic rather than anionic?
Phosphatidylcholine
What types of fatty acid chains can phospholipids have?
Saturated, straight chains or cis-double bond kinked chains
What is the backbone of sphingolipids made of?
Sphingosine (no glycerol)
What is unique about the sphingosine backbone?
It always contains one trans double bond, making it very rigid
What is the simplest sphingolipid and what is its polar head?
Ceramide, with hydrogen as the polar head
Is ceramide toxic or non-toxic?
Toxic
Which sphingolipid has choline as the polar head and is the most common?
Sphingomyelin
What sugar do cerebrosides contain in the nervous system versus elsewhere?
Galactose in the nervous system, glucose elsewhere
How can cerebrosides be modified?
They can be sulfated to form sulfatides
What do globosides contain?
Two or more sugars
What do gangliosides contain?
Complex oligosaccharides (many sugars)
What is the functional role of attaching sugars to sphingolipids?
Allows for cell recognition
What is another name for Krabbe’s disease?
Globoid cell leukodystrophy
When do symptoms of Krabbe’s disease normally develop and what is the typical prognosis?
Symptoms develop before six months of age, with death usually by two years
What type of genetic inheritance does Krabbe’s disease have?
Autosomal-recessive
Which enzyme is deficient in Krabbe’s disease?
Galactosylceramidase (galactocerebroside β-galactosidase)
What type of disorder is Krabbe’s disease classified as?
A metabolic disorder
What happens to myelin and myelin-forming cells in Krabbe’s disease?
Rapid and nearly complete disappearance in CNS & PNS
What cellular changes are seen in Krabbe’s disease?
Reactive astrocytic gliosis and infiltration of multi-nucleated macrophages (globoid cells)
What is the normal function of galactosylceramidase?
Catabolises galactosylsphingosine (psychosine) into sphingosine and galactose
Why is Krabbe’s disease toxic to oligodendrocytes?
Accumulation of galactosylsphingosine (psychosine) is highly toxic to oligodendrocytes and other cells
What is the most abundant sterol in animals?
Cholesterol
What is the structure of cholesterol?
Small polar head, rigid sterol rings, and a flexible (floppy) tail
What is cholesterol a precursor for?
Bile acids, steroid hormones, and oxysterols
What structural role does cholesterol play in membranes?
Major component; controls membrane fluidity and packing, provides mechanical strength, and supports membrane organisation and stability
How water-soluble is cholesterol?
It is water-insoluble
What proportion of the body’s cholesterol is in the brain?
About 25%
What is the most abundant molecule in the myelin membrane and what role does it play?
Cholesterol; it drives myelination
What disease does the Npc1-/- mouse model represent?
Niemann-Pick Disease type C (lysosomal storage disorder)
What is defective in Niemann-Pick Disease type C?
A cholesterol transporter in lysosomes loses function
What happens to cholesterol in the Npc1-/- mouse?
Cholesterol is trapped in lysosomes and cannot be transferred to growing myelin sheaths
How do lipids function in energy storage in neural tissue?
As triglycerides and fatty acids
What structural role do lipids play in neural tissue?
Insulating myelin to reduce ion leakage and speed up electrical signals
What role do lipid microdomains (lipid rafts) play in neurons?
Control protein trafficking, neuronal polarisation, exocytosis, and rearranging dendritic spines for synaptic plasticity
How do lipids participate in signal transduction?
By directly binding to proteins (lipid anchors) and producing signalling molecules like endocannabinoids, eicosanoids, and docosanoids
What is the lipid and protein composition of the myelin sheath?
Lipid 80%, Protein 20%
How many lipids per protein are in the myelin sheath?
200 lipids per protein
What is the lipid and protein composition of the plasma membrane
Lipid 50%, Protein 50%
How many lipids per protein are in the plasma membrane?
50 lipids per protein
What is the lipid and protein composition of the inner mitochondrial membrane?
Lipid 25%, Protein 75%
How many lipids per protein are in the inner mitochondrial membrane?
40 lipids per protein
What are the most abundant lipids in myelin?
Cholesterol
Galactocerebroside
Sulfatide
Plasmalogens
Who first studied the structure of myelin around 1950?
Betty Geren and James Robertson
How is myelin structured around an axon?
As a spiral wrap of the oligodendrocyte (CNS) or Schwann cell (PNS) membrane
What does the glial cell do during myelin formation?
Extends a sheet of membrane around the axon
What happens to cytoplasm and extracellular matrix during myelin wrapping?
Most cytoplasm inside the cell and extracellular matrix outside are squeezed out
What holds the layers of myelin together?
Protein-lipid and protein-protein interactions
What is the role of Myelin Basic Protein (MBP)?
Major cytoplasmic adhesive protein; binds inner surfaces of myelin
What is the role of Proteolipid Protein (PLP)?
Stabilises extracellular membrane contacts
How do sulfatides and Gal-Cerebrosides contribute to myelin?
Interact with PLP to stabilise compact myelin
What is MAG (Myelin-Associated Glycoprotein) and where is it expressed?
Minor myelin protein expressed on the inner surface of myelin near axons, especially at paranodal junctions
How do gangliosides support the axon-myelin interface?
Interact with MAG on the axonal membrane to support the axon-myelin connection
How do plasmalogen levels change with age?
Increase up to 30–40 years, then decline with age
What neurological condition has been linked to loss of plasmalogens?
Onset of dementia in Alzheimer’s disease
How do plasmalogens affect myelin membranes?
They are more compact than regular phospholipids, increasing lipid packing density and stabilising the membrane
What happens in the absence of plasmalogens?
Causes demyelination, loss of myelin compaction, and axonal loss (shown in transgenic mice lacking plasmalogens)
What happens to amphipathic lipids in water?
They aggregate into bilayers due to the hydrophobic effect
How can lipid bilayers vary physically?
They can be more or less thick and fluid