Unit 5: Rotational Motion
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
the motion of an object around a fixed line called the “axis of rotation” or around a fixed point called the “fulcrum” or “pivot”
rotational motion
rotational motion is also called
angular
when something simply spins or rotates, does it have linear or angular velocity?
angular
how far something turns in a certain amount of time
angular velocity
angular displacement is measured in
theta (an angle)
change in angular velocity over time
angular acceleration
Let’s consider the Earth:
(a) What is the magnitude of the angular velocity (or angular speed) of the Earth as it spins on it axis?
Answer in radians/sec.
(b) What is the direction of the Earth’s angular velocity?
a) (pi)/43200 radians/s
(b) West to East, or counterclockwise if viewed from North Pole
θ
angle (radians)
⍵
angular velocity (radians/s)
α
angular acceleration (radians / s2)
angular displacement formula
θ = θi + ⍵i(t) + ½ αt²
angular velocity formula
⍵ = ⍵i + αt
angular acceleration formula
⍵² = ⍵i² + 2α(θ-θi)
what type of force causes a wheel to spin?
force that is not directed at the axis (perpendicular to the lever arm in a way)
torque is produced from
a force that does NOT go through the axle or pivot
lever arm for torque is
r
torque formula
τ = r⊥F = r F sinθ
how is torque different from force
it makes things rotate, not accelerate
torque units
Nm
lever arm units
m
Force units
N
Suppose we apply a force of 10 Newtons to the edge of the wheel, which has a radius of 0.5 meters. What is the size of the torque?
5 Nm
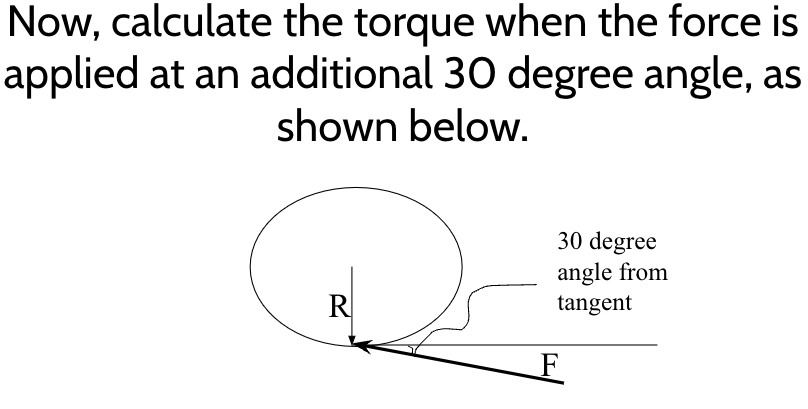
R = 0.5 and F = 10
4.33 Nm
To describe how an object will rotate….and the amount of torque required to start it or stop it….we need to know the mass of the object and how far from the pivot the mass is concentrated. This is called
moment of inertia
moment of inertia is
(coefficient)mr²
t/f: an object has its moment of inertia whether it is spinning or stationary
t; moment of inertia is a physical property that depends on the mass distribution relative to the axis of rotation.
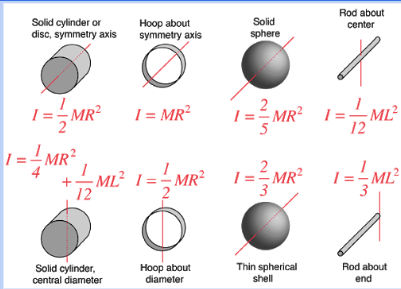
Suppose all of these objects (with the same mass and radius) were allowed to race down a ramp, and were let go from the same height at the same time. Which would reach the bottom of the ramp last? Why?
The hollow one.
The object with the most rotational inertia will reach the bottom of the ramp last. Look for the one with the largest coefficient!
moment of inertia (I) units
kg m²
t/f: coefficient of inertia is between 0 and 1
t
law of rotational inertia
An object rotating about an axis tends to keep rotating about that axis.
what is needed to change to rotational state of motion of an object?
torque
resistance of an object to changes in its rotational motion is called
rotational inertia
rotational version of Newton’s second law:
∑𝝉 = I𝜶
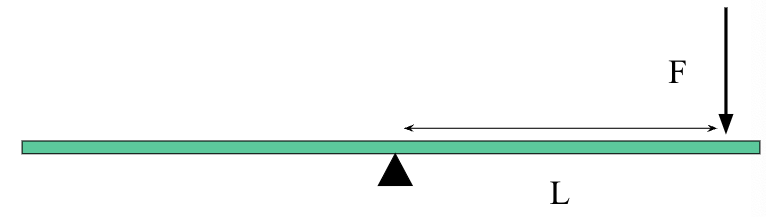
If the green board is balanced at its center on the fulcrum and a force, F, is applied as shown, then the distance L is the “lever arm”, since it is the perpendicular distance from the line of the force to the pivot or fulcrum. The torque produced by the force would cause the board to rotate - use the right hand rule to predict the direction of rotation and torque vector.
The force produces a torque that is equal to F times L and produces a clockwise rotation of the board. The torque is pointed into the screen.
when net torque is 0, the object (does/does not) rotate and is in _____________ given that the board is uniform and the pivot is at the center of the board so Fg is not causing torque on the board.
does not; rotational equilibrium
t/f: if a pivot is NOT to the center of a fulcrum, Fg can cause torque on it
t
Objects are in static equilibrium if:
1. The net force in the x-direction is zero.
2. The net force in the y-direction is zero.
3. The net torque is zero.
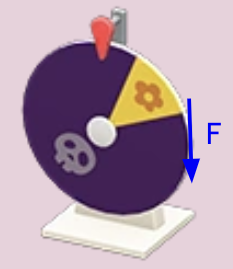
What direction is the torque from my pushing force on the wheel?
into the screen
t/f: Each particle or point on the rotating body has an instantaneous linear velocity AND instantaneous tangential linear acceleration.
true, as each point moves in a circular path.
linear velocity formula (from rotational velocity)
v = r ⍵
tangential linear acceleration formula
aT = r 𝛼
what does rolling withOUT slipping require
a lot of friction
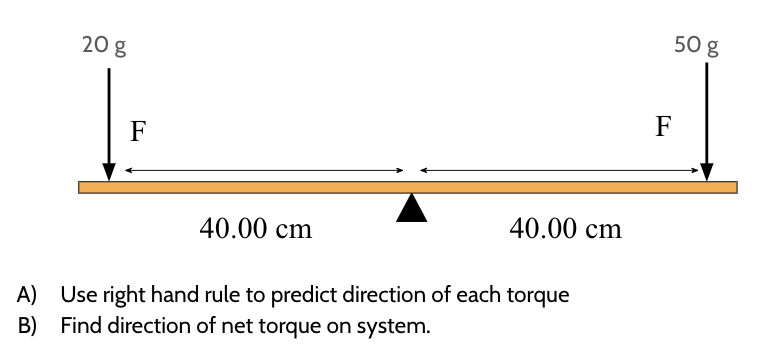
A) 20g torque is towards you, 50g torque is into the screen
B) 120 Nm
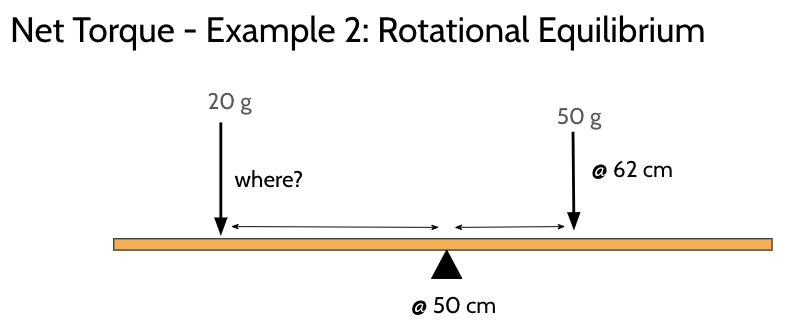
147 cm