Anatomy - Lecture 13: Mediastinum subdivisions, anterior & middle mediastinum (heart)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is the mediastinum?
central portion between 2 pleural sacs limited on either sides by the mediastinal pleura
What are the boundaries of the mediastinum?
front → sternum
behind → T1-T12 vertebrae
above → thoracic inlet
below → diaphragm
on each side → mediastinal pleura
At which level does the imaginary horizontal plane extend and divide the mediastinum into superior and inferior?
sternal angle to the lower border of T4
How is the mediastinum divided?
mediastinum
superior
inferior
anterior
middle
posterior
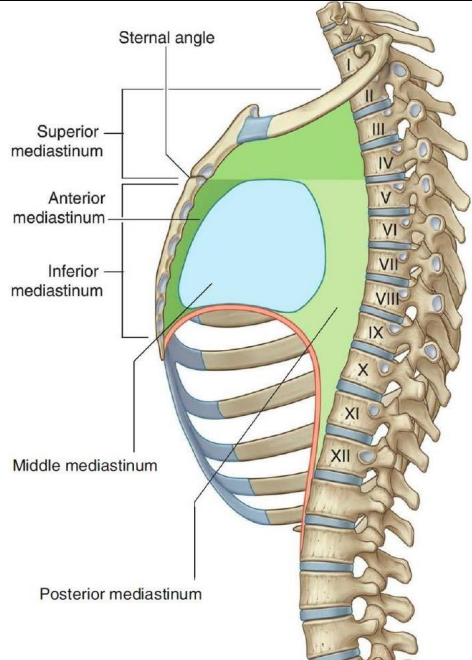
What are the boundaries of the anterior mediastinum?
front → body of the sternum
behind → pericardium
above → imaginary horizontal plane extending from sternal angle to the lower border of T4
below → diaphragm
on each side → mediastinal pleura
What are the contents of the anterior mediastinum?
superior and inferior sterno-pericardial ligaments
thymus gland
loose areolar tissue
retrosternal lymph nodes
Where is the thymus gland located?
behind manubrium and partly behind body of the sternum (both superior and inferior mediastinum)
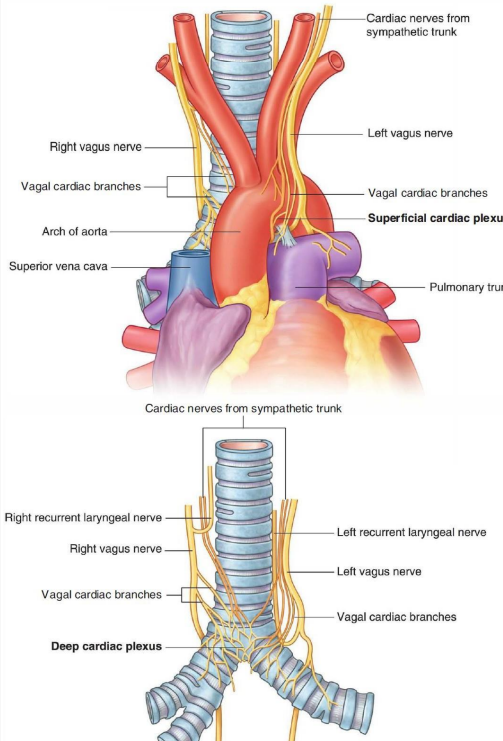
What are the contents of the middle mediastinum?
heart enclosed in the pericardium
nerves
phrenic
deep cardiac plexus
lymph nodes (tracheobronchial nodes)
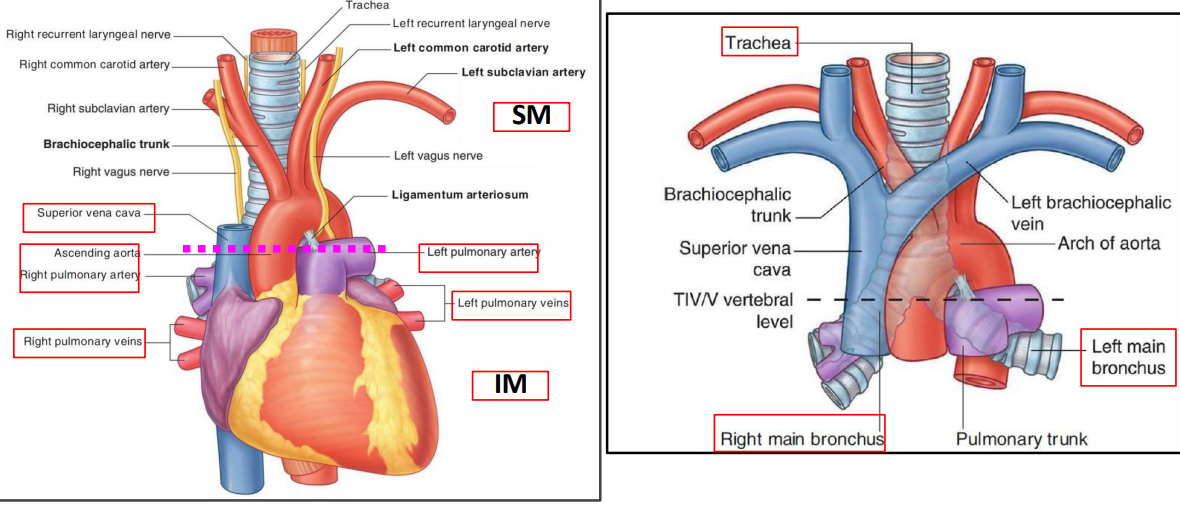
arteries
ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk dividing into right and left pulmonary arteries
veins
lower part of the superior vena cava
arch of azygos
4 pulmonary veins
tubes
bifurcation of trachea
What are the properties of the pericardium?
conical fibroserous sac
encloses the heart and roots of great vessels
consists of two layers
fibrous pericardium
serous pericardium
What are the relations of the fibrous pericardium?
apex → continuous with tunica adventitia of great vessels
base → blends with central tendon of diaphragm
anteriorly → attached to sternum by sterno-pericardial ligaments
behind → related to the posterior mediastinum
on each side → related to the mediastinal pleura
through these attachments, pericardium maintains the thoracic position of heart
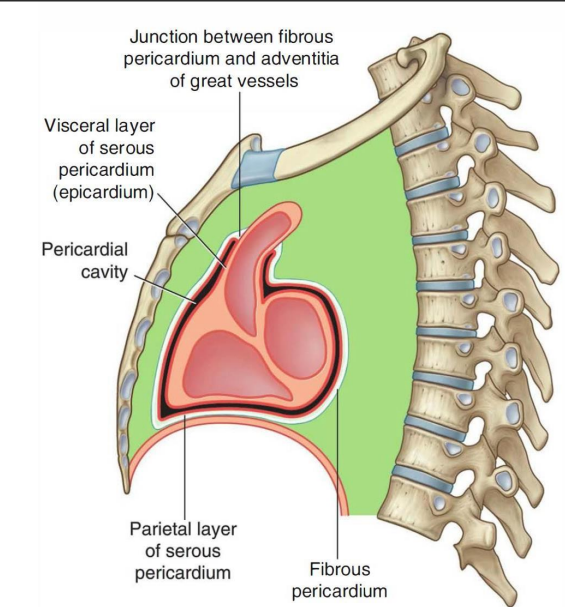
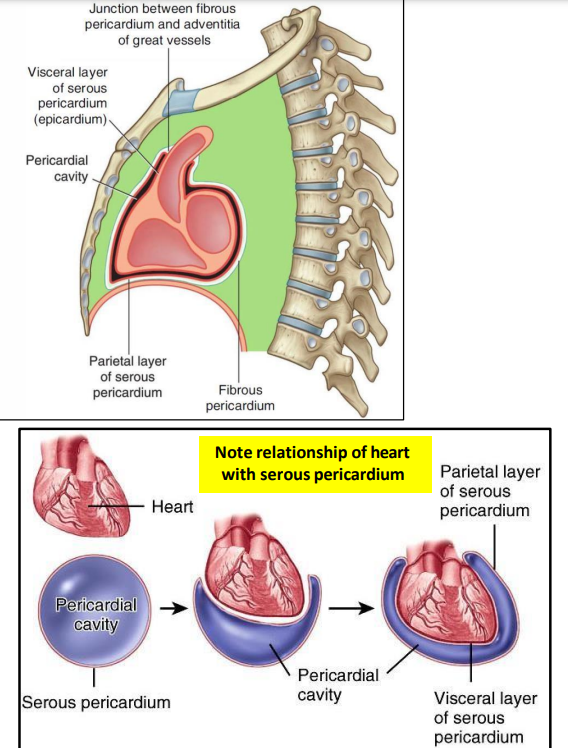
What are the properties of the serous pericardium?
closed sac lies within fibrous pericardium
lined by mesothelium
consists of visceral and parietal layers
parietal layer lines the fibrous pericardium
visceral layer (epicardium) covers the heart and roots of great vessels
pericardial cavity → between 2 layers
filled with pericardial fluid
allows free movement of the heart
fluid provides lubrication
What is inflammation of the serous pericardium called?
pericarditis, causes chest pain
What is the nerve supply of the pericardium?
parietal is pain sensitive and visceral is insensitive
pain of pericarditis originates in parietal pericardium alone and transmitted by the phrenic nerve
cardiac pain (angina) originates in cardiac muscle or vessels and transmitted by sympathetic nerves
What is the arterial supply of the pericardium?
branches from the the thoracic, musculophrenic artery and descending thoracic arteries
What is the drainage of fluid from the pericardial cavity called?
pericardiocentesis
relieve cardiac tamponade
wide bore needle inserted through the left 5th or 6th intercostal space near sternum
What are the properties of the heart?
muscular organ
placed obliquely behind body of sternum and costal cartilages
has 4 chambers
2 atria
2 ventricles
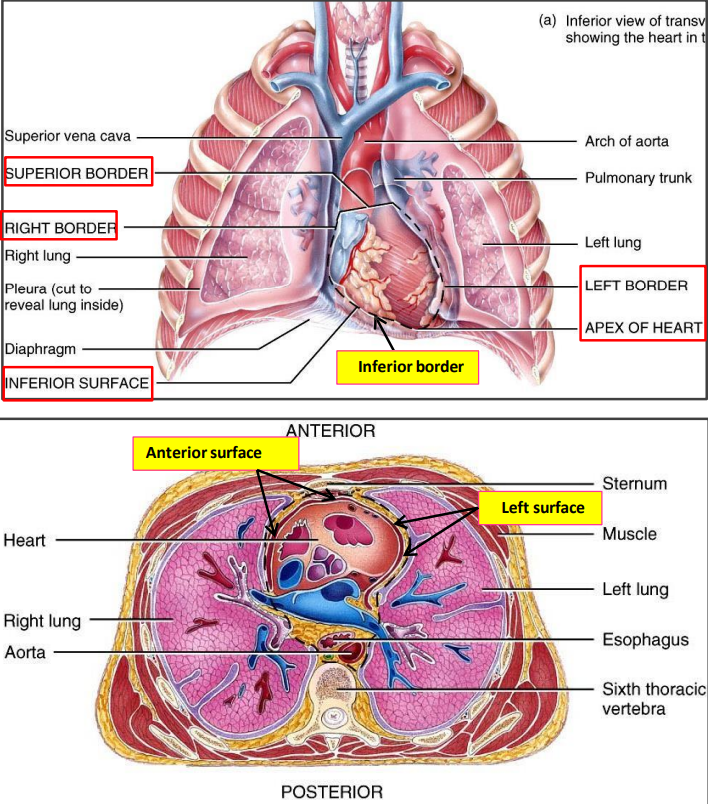
heart presents
apex
base
three surfaces
sternocostal (anterior)
diaphragmatic (inferior)
left
four borders
superior → two atria
inferior → two ventricles
right → right atrium
left → left ventricle and left auricle
grooves/sulci (sulci are occupied by vessels)
atrioventricular groove (coronary sulcus) → between atria and ventricles
interventricular sulcus → between two ventricles
interatrial sulcus → between two atria
auricles → extensions of atrium
What are the properties of the apex?
formed by the left ventricle
located in the left 5th intercostal space
lies just medial to the midclavicular line
What are the properties of the base/posterior surface of the heart?
formed by two atria
openings of four pulmonary veins and superior & inferior vena cava
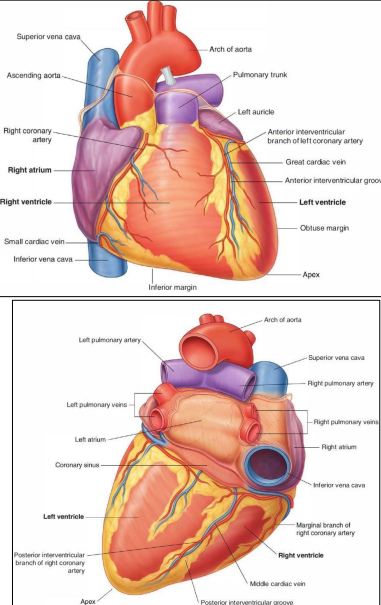
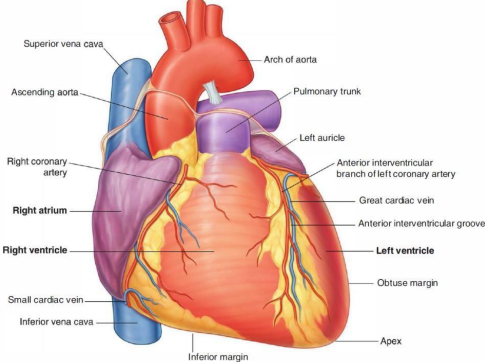
What are the properties of the sternocostal surface of the heart?
formed by the right atrium and ventricle, left ventricle and auricle
has anterior interventricular sulcus & right part of the coronary sulcus
What are the properties of the diaphragmatic surface of the heart?
formed by the right & left ventricles
rests on the central tendon of the diaphragm
has posterior interventricular sulcus
How does the blood flow through the heart?
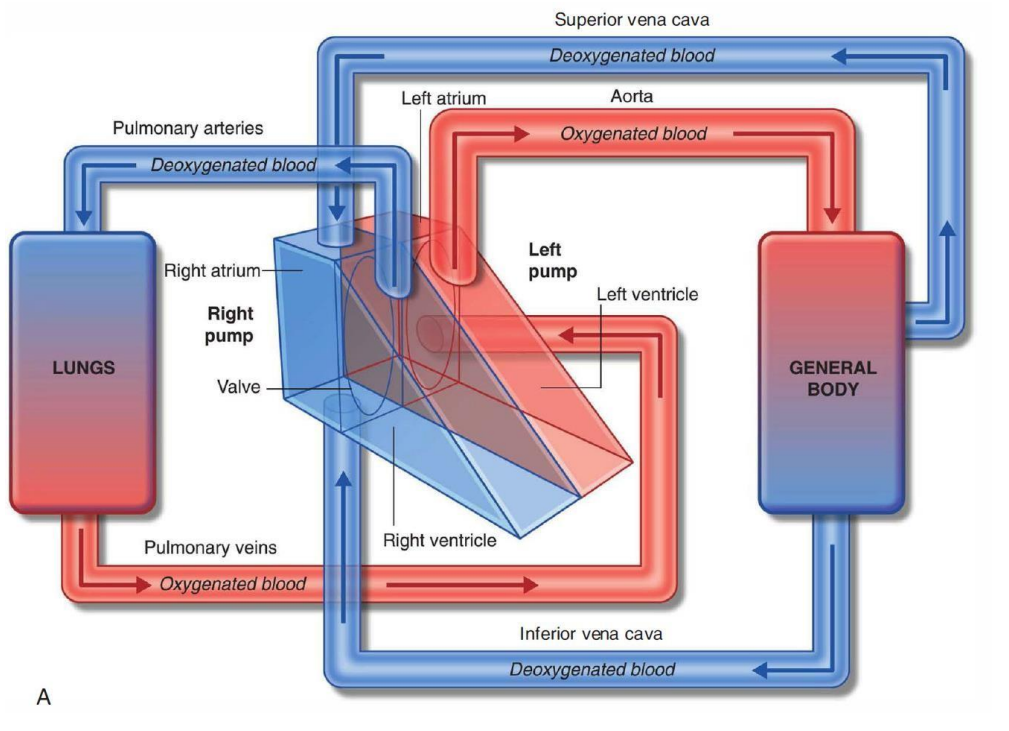
What separates the right and left atriums?
inter-atrial septum
What separates right and left ventricles?
inter ventricular septum
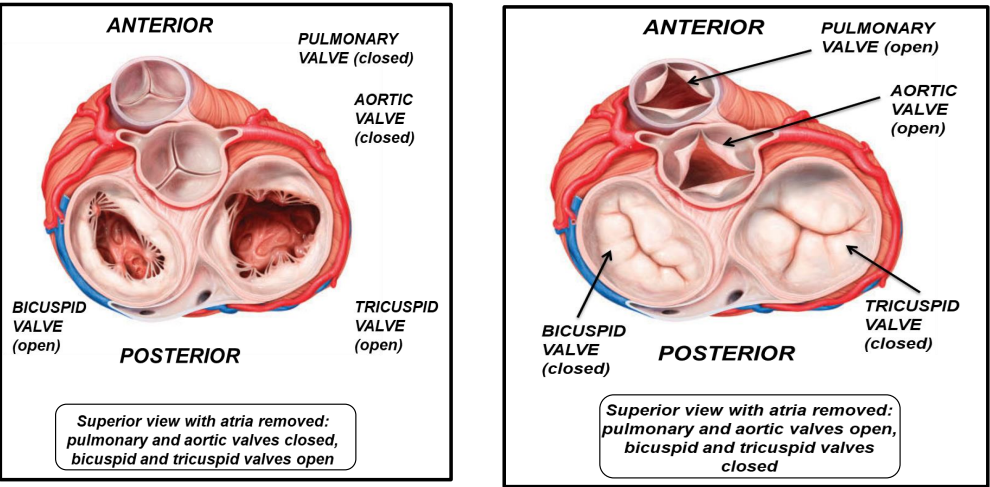
What are the valves of the heart?
right atrioventricular → tricuspid valve
left atrioventricular → bicuspid (Mitral) valve
pulmonary valve
aortic valve
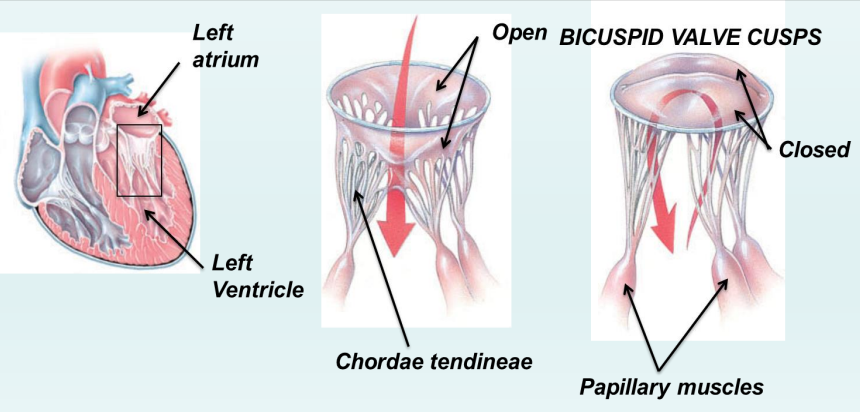
How are the cuspid valves attached to papillary muscle?
chordae tendineae
Where are the 2 great vessels valves (semilunar) valves?
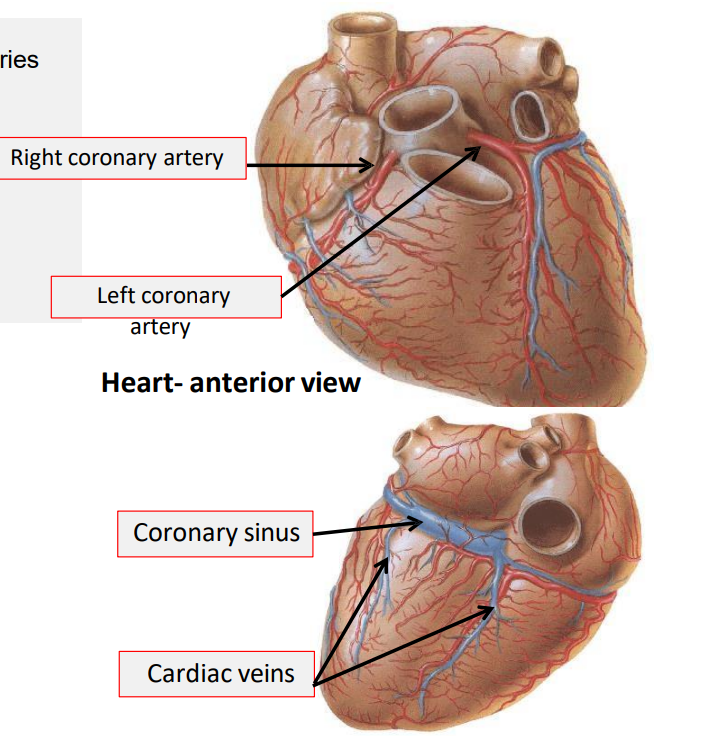
What is the blood supply of the heart?
supplied by two coronary arteries
right coronary artery
left coronary artery
drained by cardiac veins and coronary sinus
How is the heart innervated?
sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves which form cardiac plexus (superficial and deep cardiac plexus)