1.05 Ciliary body, aqueous humour and IOP
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Ciliary body function
Produce aqueous
Contains ciliary muscle to change shape of the lens (via zonules)
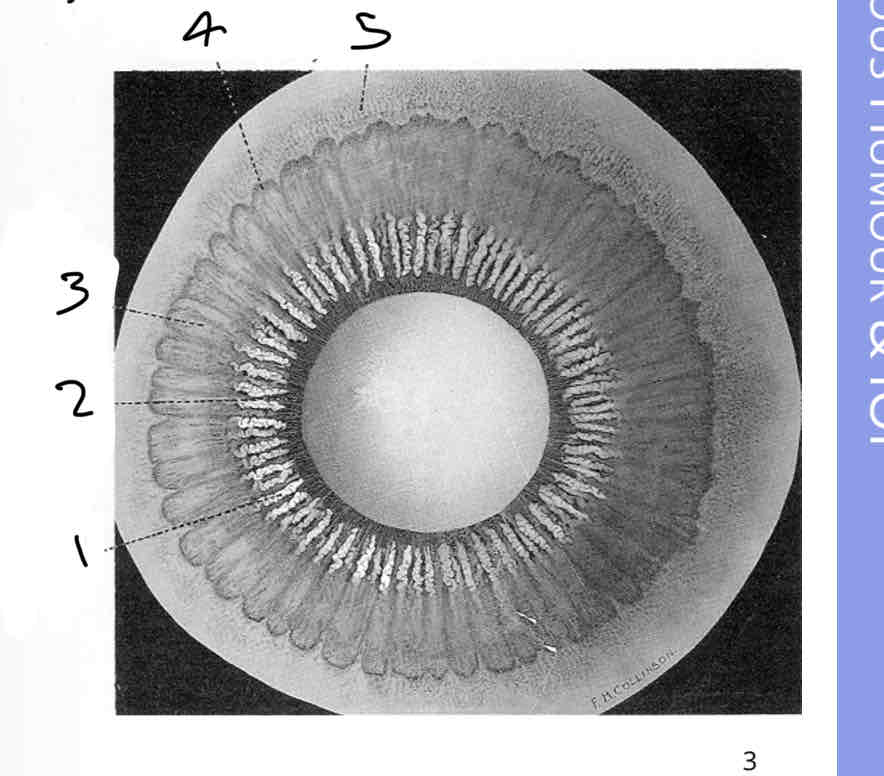
Label the posterior iris
Ciliary processes
Fibres of suspensory ligaments
Striae in pars plana
Ora serrata
Peripheral cystic degeneration
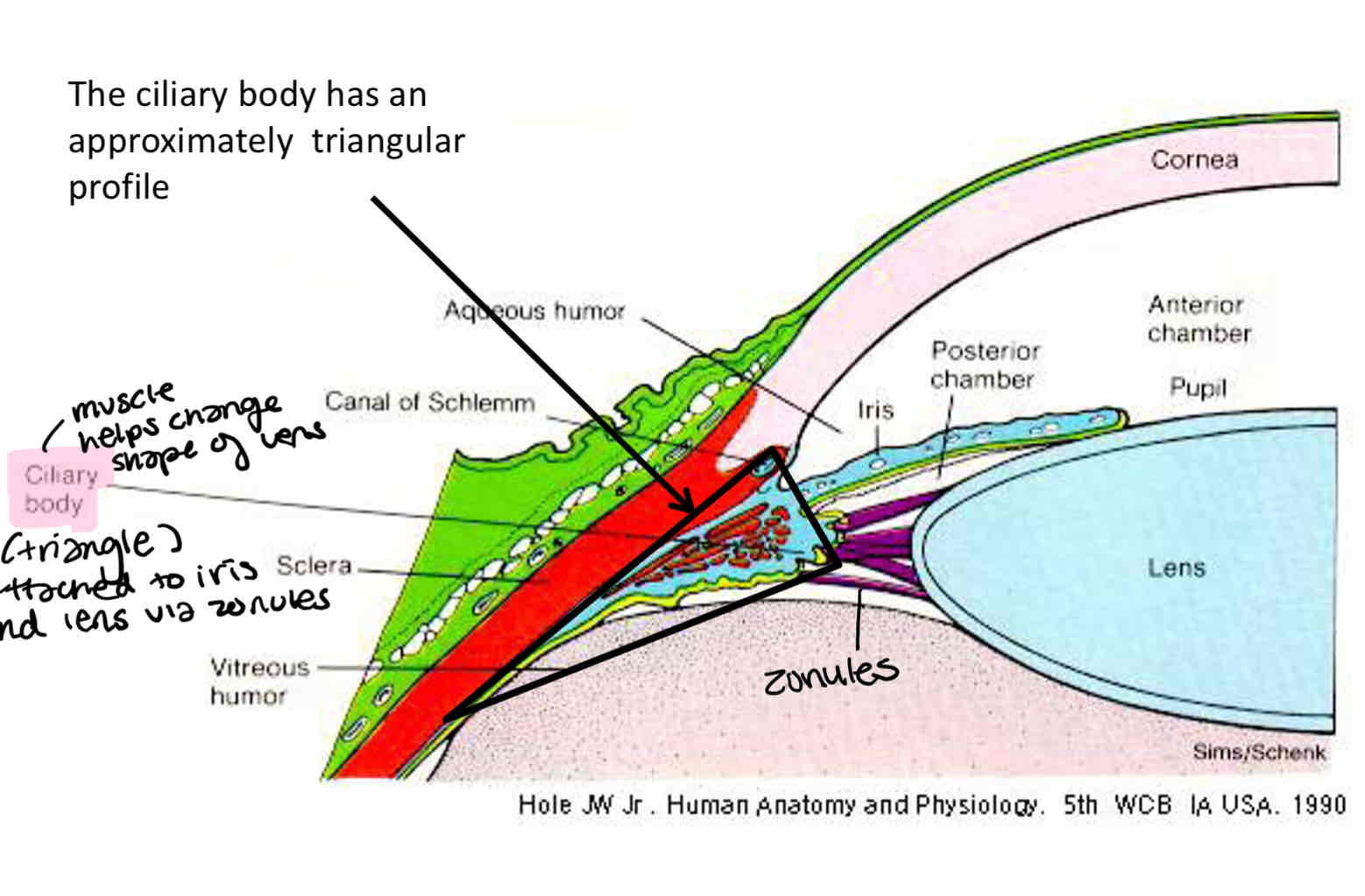
How is the ciliary body attached to the iris and lens
Via zonules
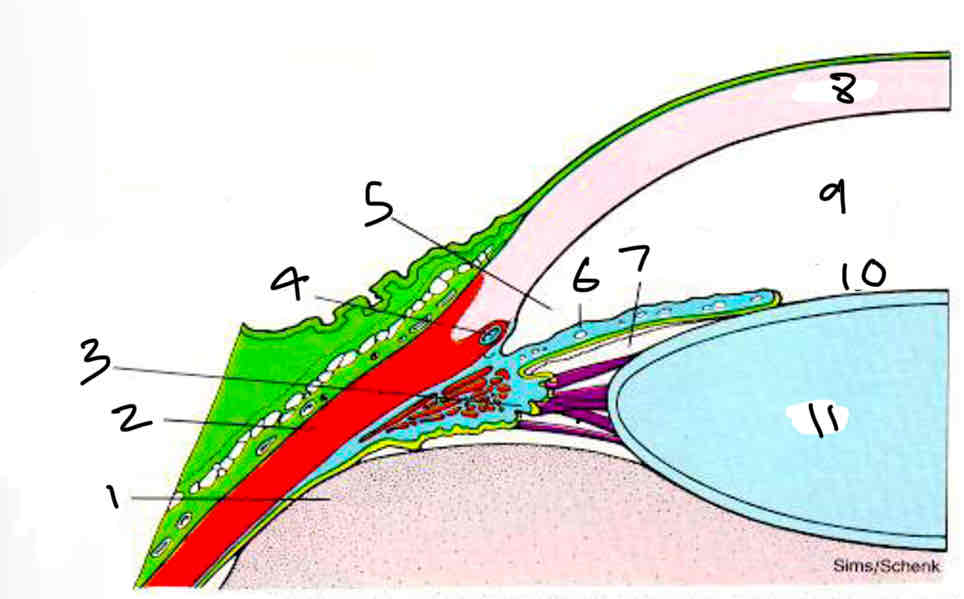
Label
Vitreous humor
Sclera
Ciliary body
Canal of schlemm
Aqueous humor
Iris
Posterior chamber
Corne
Anterior chamber
Pupil
Lens
What is the thickest part of the ciliary body
Anterior pars plicta (closest to lens)
This gets thinner as you get more posterior
Where is the pars plana
Runs up to the edge of the retina
Where is the ora serrata
Edge of the retina
What are the two part of the ciliary body and how do they differ
Pars plicata - wider, naterior portion containing the ciliary processes
Pars plana - flatter region. It extends from the posterior of the pars plicata to the ora serrata (which is the transition between ciliary body and choroid)
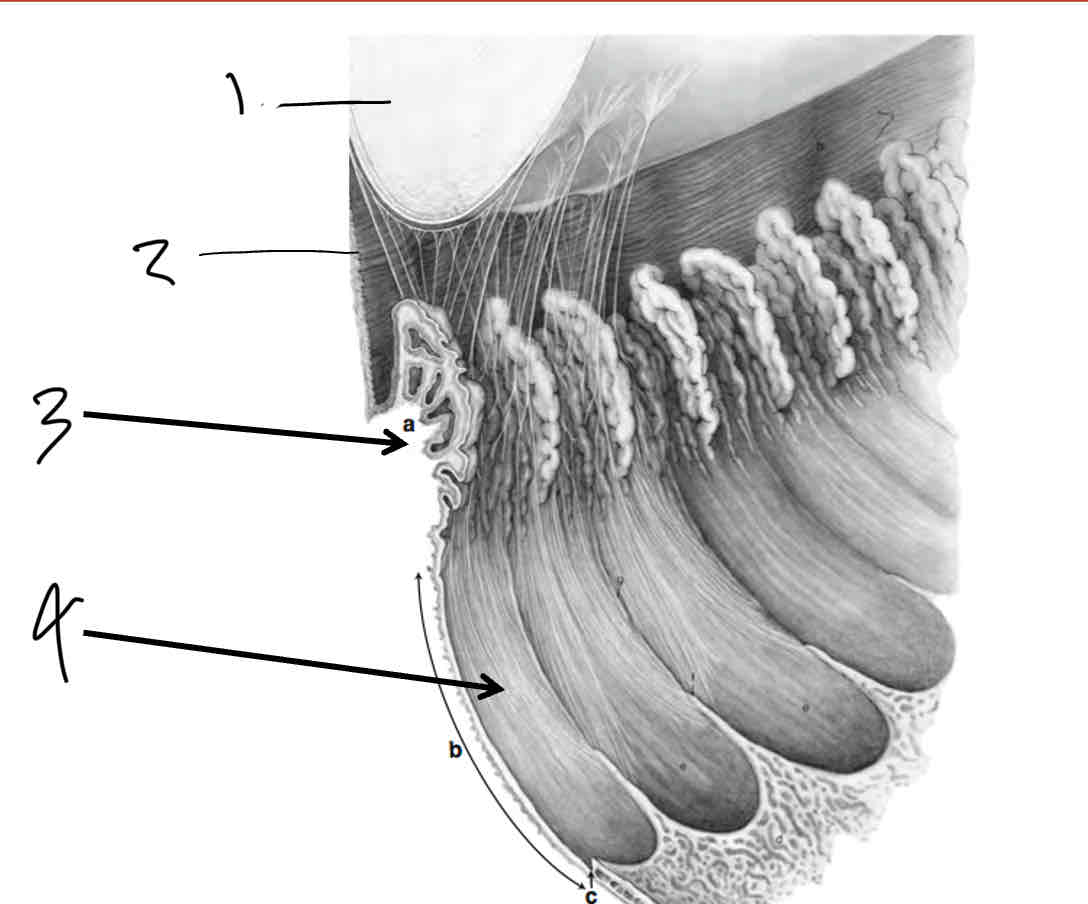
Label
Lens
Zonules
Pars plicata
Pars plana
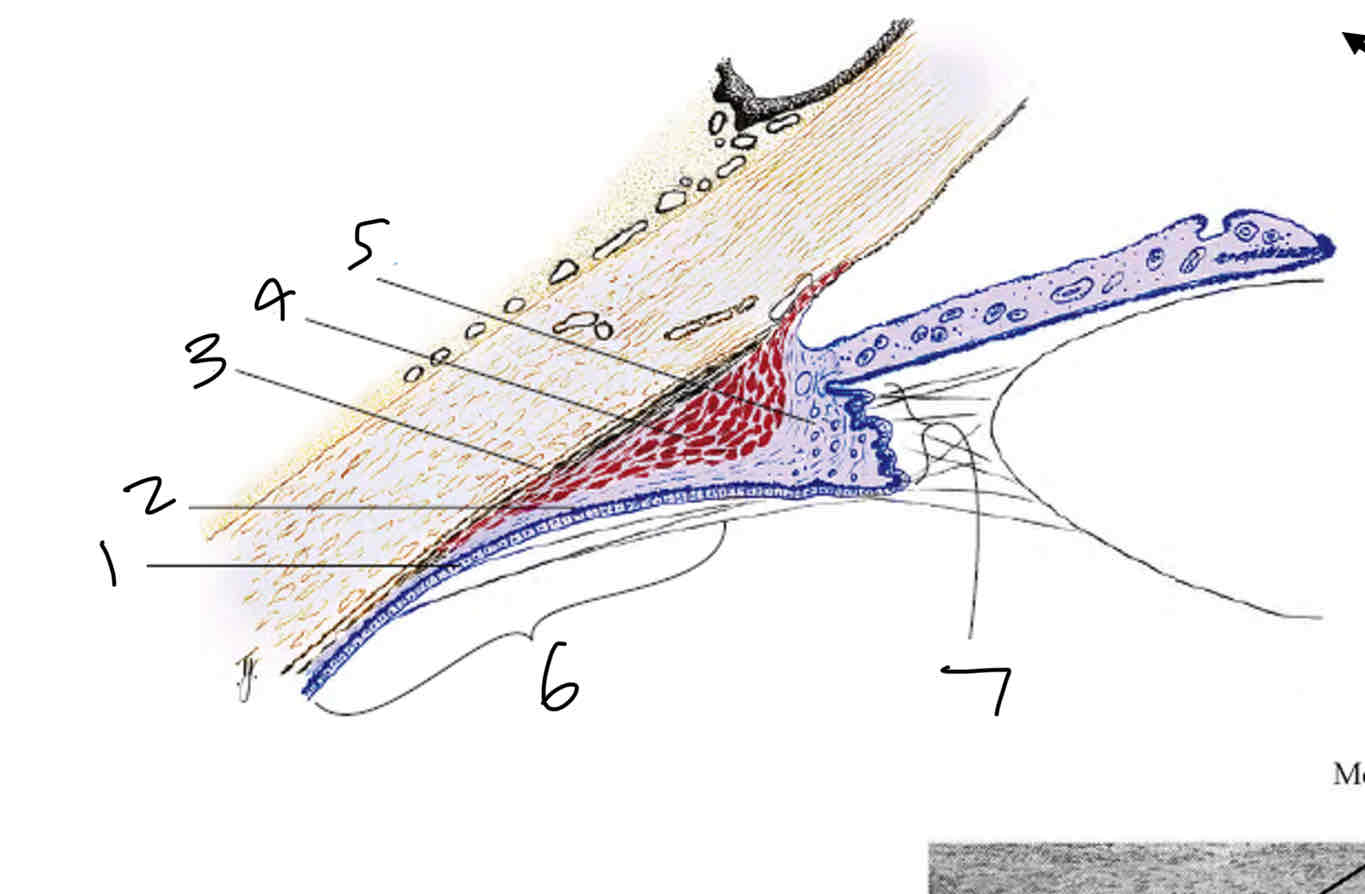
Label
Non pigmented epithelium
Pigmented epithelium
Supraciliaris
Ciliary muscle
Ciliary stroma
Pars plana
Pars plicata
Label the ciliary muscle
Meridional portion
Radial portion
Circular portion
Layers of the ciliary body

Label the layers of the ciliary body
Supraciliaris
Ciliary muscle
Ciliary stroma/pigmented epithelium
Non pigmented epithelium
Supraciliaris
tissue
Type
Function
tissue - connective (collagen)
Type - loose/ fibroblasts and melanocytes
Function - loose interface with sclera - passage of nerves and blood vessels
Ciliary muscle
tissue
Type
Function
tissue - muscle
Type - smooth muscle (involuntary)
Function - controls accomodation
Ciliary stroma
tissue
Type
Function
tissue - connective
Type - loose
Function - supporting framework for muscle and blood vessels
Ciliary epithelium pigmented
tissue
Type
Function
tissue - inner epithelium
Type - pigmented, simple, cuboidal
Function - light absorption in posterior cavity, helps the production of aqueous humor
Ciliary epithelium unpigmented
tissue
Type
Function
tissue - epithelium
Type - unpigmented simple
Pars plicata - cuboidal
Pars plana - columnar
Function - secrete aqueous humor, blood aqueous barrier, attachment of lens zonules
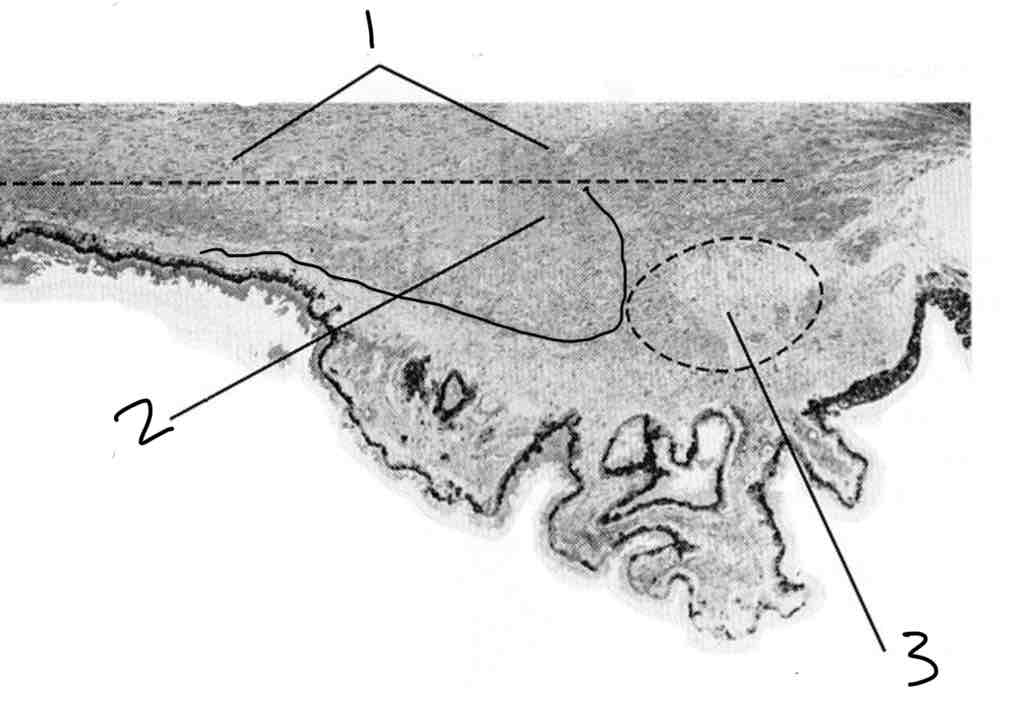
Label pars plana
Medial rectus
Sclera
Supraciliaris
Ciliary muscle
Stroma
Pigment layer
Epithelium
Where is the medial rectus muscle inserted
Inserted into the sclera
Inserted around the pars plana
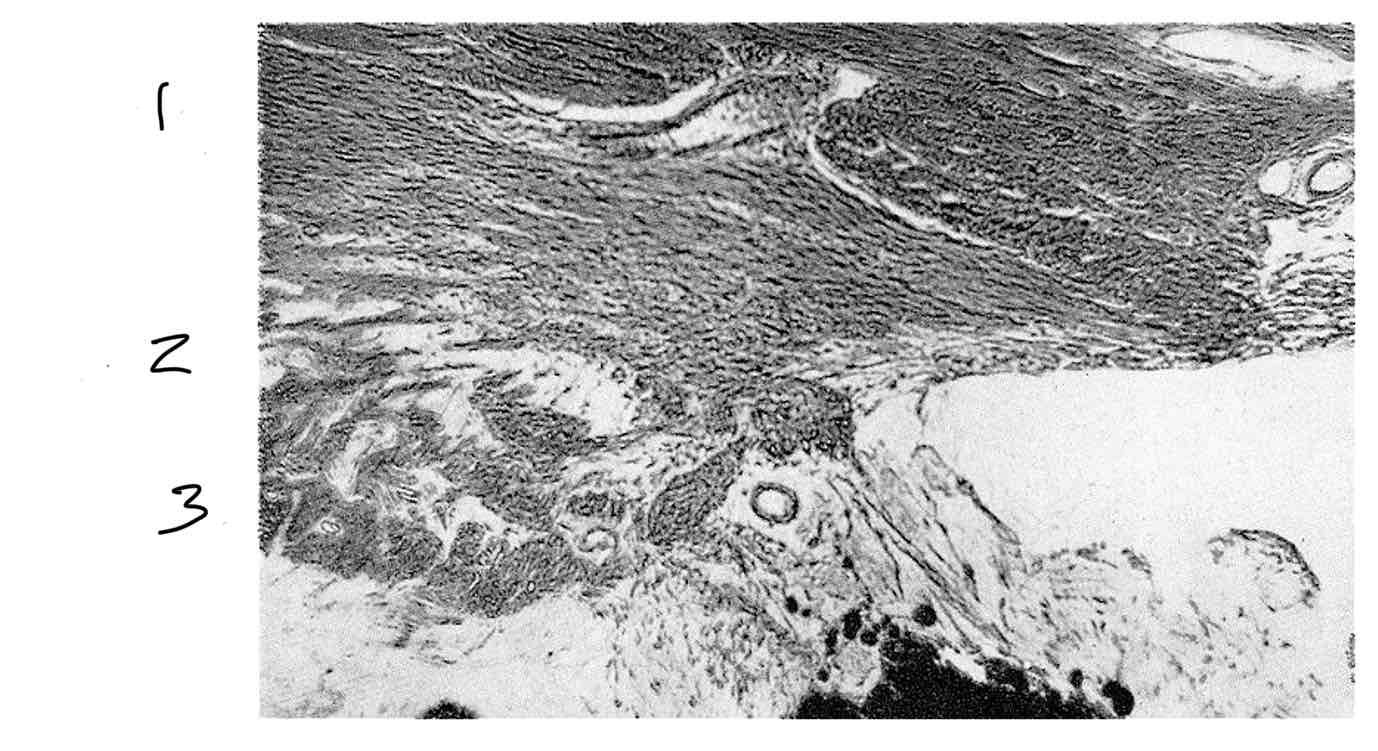
Label pars plicata muscle fibres
Meridional/longitudial fibres
Radial/oblique fibres
Circular/sphincteric fibres
Describe meridional/longitudinal ciliary muscle fibres
Most anterior
Goes to edge of pars plana
Long and thin
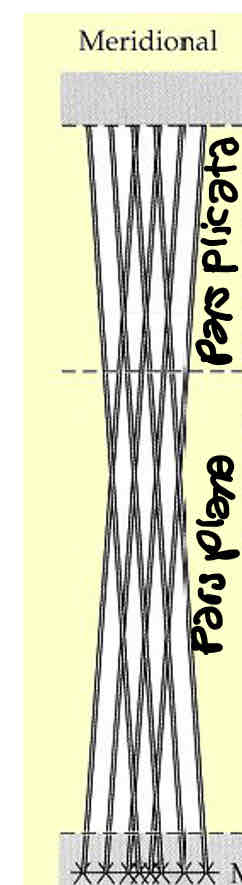
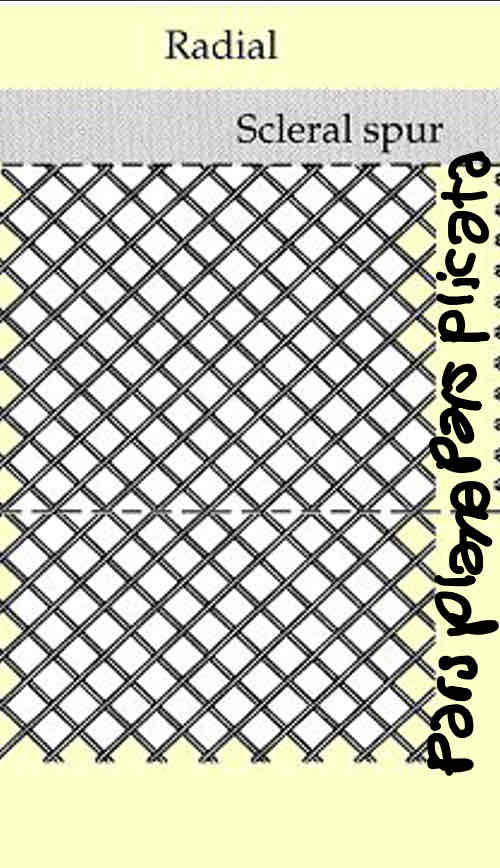
Describe radial/oblique ciliary muscle fibres
In the middle (between meridional and circular)
Run from centre to outside of ciliary body
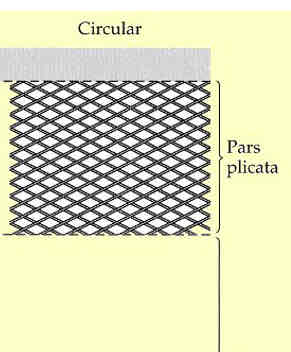
Describe circular/sphincteric ciliary muscle fibres
Internal/posterior
Ring shaped
What do conjunctival capillary loops supply
The limbus
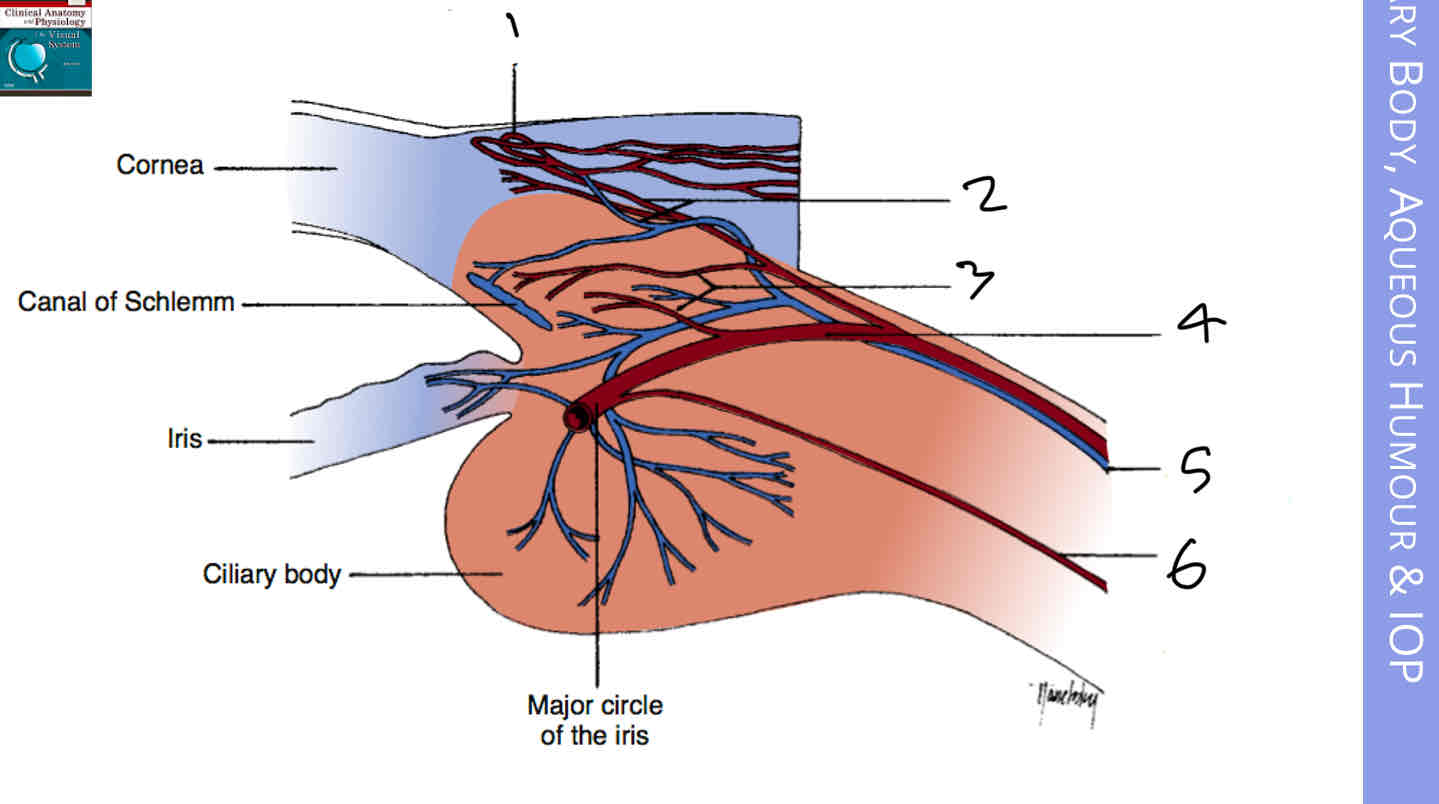
Label the blood vessels of the anterior eye
Conjunctival capillary loops
Conjunctival plexus
Episcleral plexus
Anterior ciliary artery
Anterior ciliary vein
Long posterior ciliary artery
What are ciliary processes and their function
Lumpy bits of the pars plicata
Ciliary processes attach to zonules
Have a rich vascular blood supply
Produce aqueous
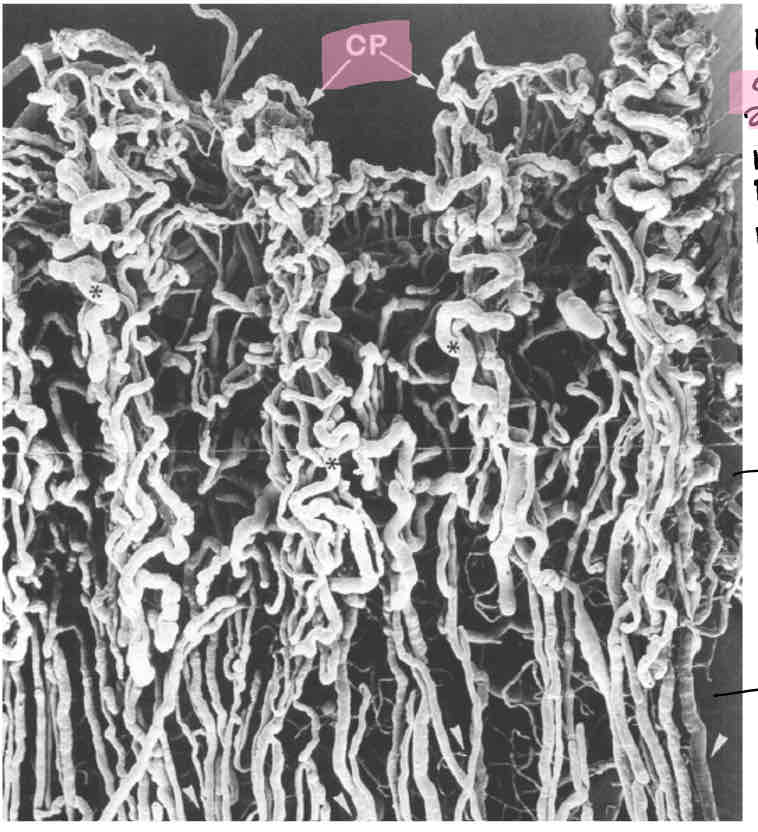

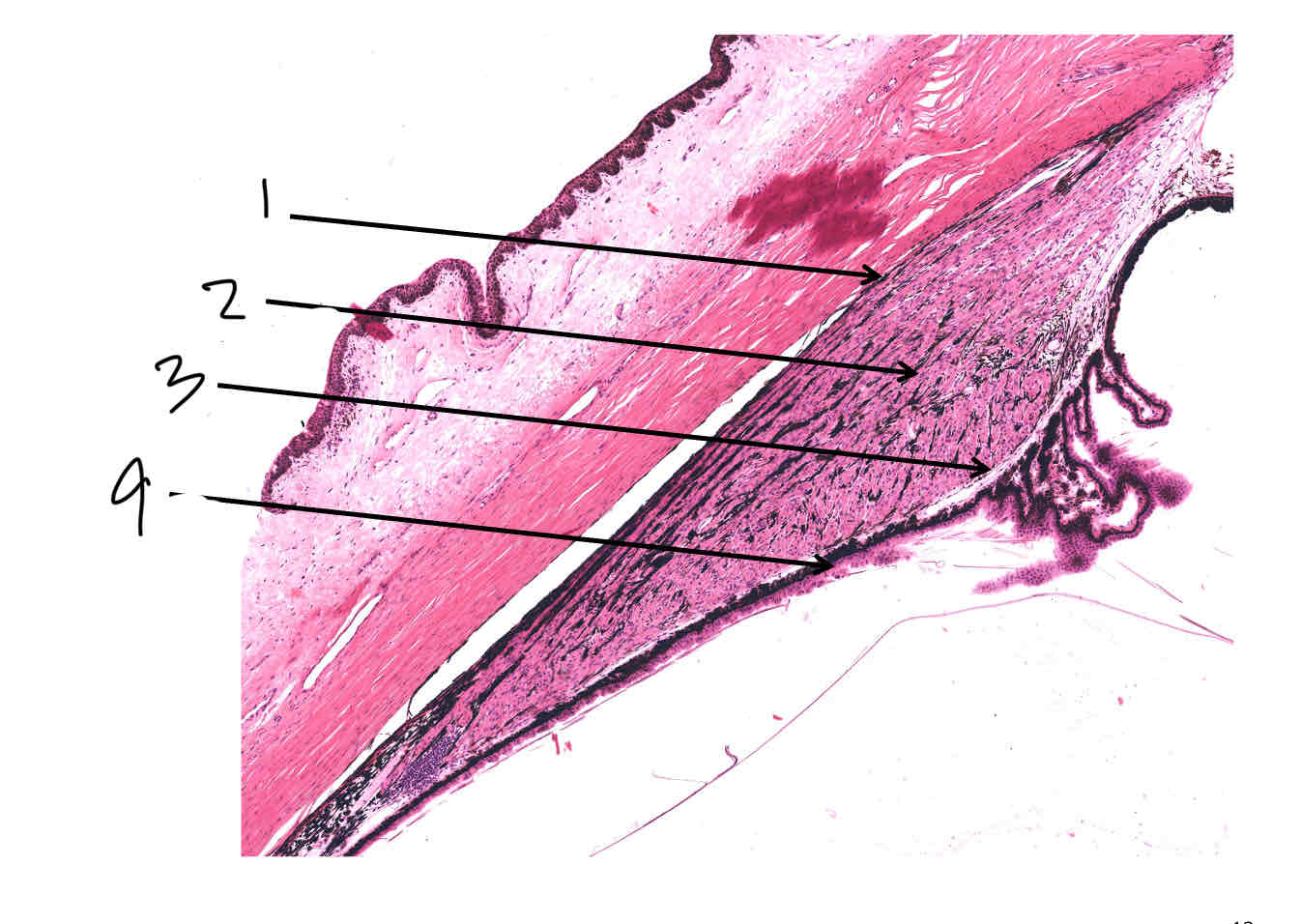
Label the ciliary process
Stroma
Pigmented epithelium
Non pigmented epithelium
Is the non pigmented epithelium outer or inner
Inner - in contact with vitreous and closer to middle/inner of the eye
However it is on the outside of the ciliary process
Unpigmented epithelium function
Produce aqueous
It comes out of the pores in between unpigmented epithelium
Why does the stroma of ciliary processes need a good blood supply
Aquous is produced by unpigmented epithelium
How is aqueous humor produced
From blood in the capillaries of the ciliary processes and trasported to anterior chamber via ciliary epithelium
Pathway of aqueous humor
Formed in ciliary body by ciliary processes by unpigmented epithelium
Moves around the lens and behind the iris to the front of the lens
Flows through the pupil,
Out the anterior chamber through trabecular meshwork into shlemms canal and then to episcleral vessels (anterior angle)
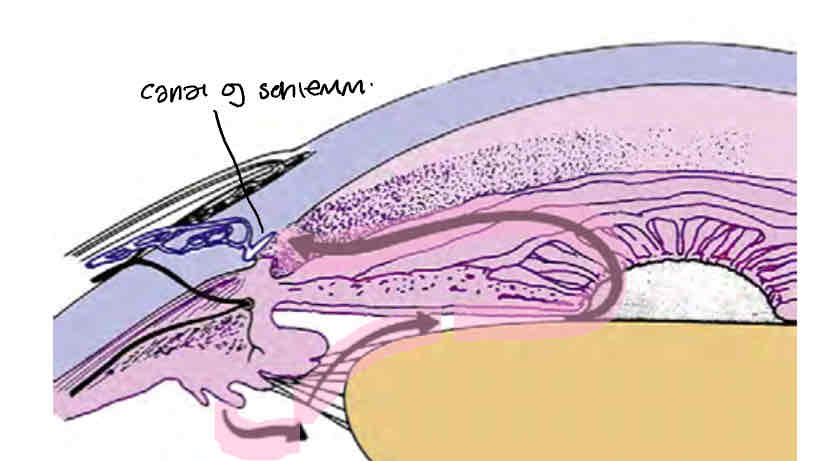
What does pigmented epithelium turn into anteriorly
Anteiror iris epithelium
What does pigmented epithelium turn into posteriorly
Retinal pigment epithelium
What attaches the pigment epithelium to the stroma
Basement membrane (acts as a barrier)
What does non pigmented epithelium turn into anteriorly
Posterior iris epithelium
What does non pigmented epithelium turn into posteriorly
Ora serrata and becomes neural retina
What is aqueous humor and where is it mainly found
A clear fluid found in the anterior and posterior chambers of the eye
What is the rate that aqueous humor is produced
2.75 (+/- 0.63) microlitres per min
Functions of aqueous humor
Provide nutrion to cornea and lens (as theyre avascular)
Removes excretory products from cornea and lens (eg urea,co2)
Contribues to the maintenance of the intraocular pressure of the eye
Which mechanisms is aqueous produced by and describe them
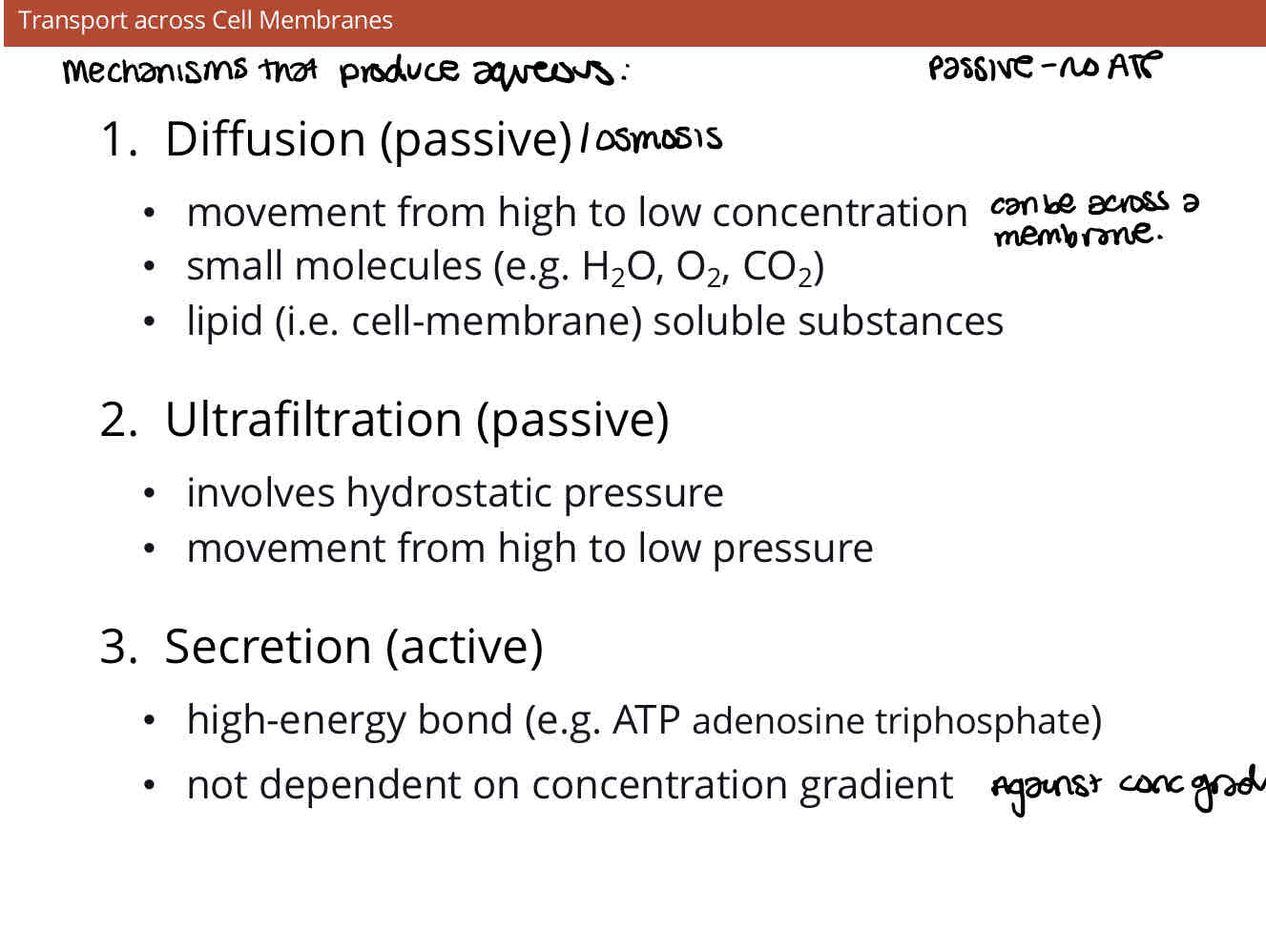
What % of phospholipid bilayer do lipids, protiens and carbohydrates account for
Lipid - 42%
Protien - 55%
Carbohydrates - 3%
Which mechanism is most important in the production of aqueous humor
Osmosis
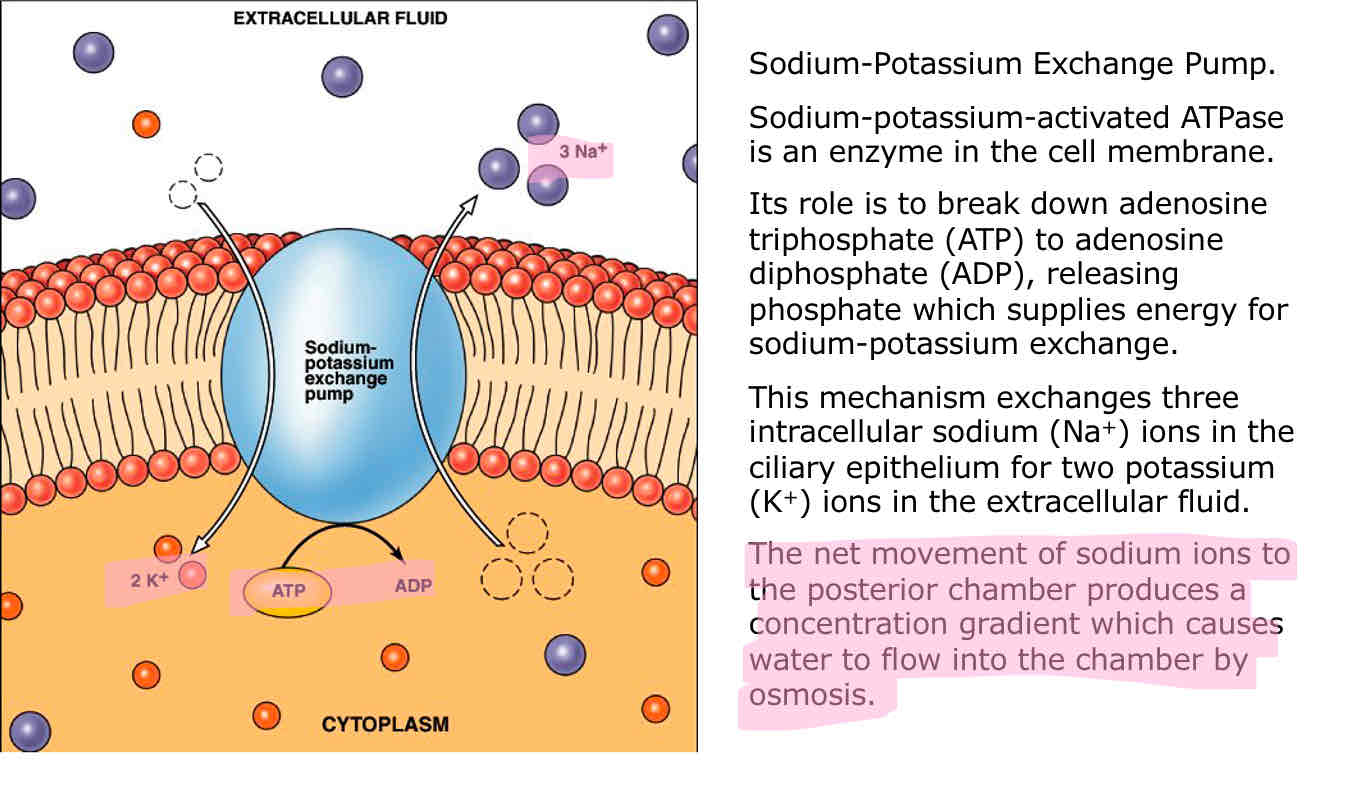
Role of active transport in the production of aqueous humor
Sodium potassium pump
Flow of Na+, Cl-, HCO3- from unpigmented epithelial cells
Hith concentration of ions causes osmosis of water into intercellular space
What does IOP rely on
The balance between
Secretion of aqueous humour from ciliary body
Outflow resistance in the trabecular meshwork
(Production and drainage)
Healthy range of IOP
11-21 mmHg
Decreased production of aqueous risks
Low IOP
retinal detachment /Oedema risk
Increased production of aqueous risk
Increased IOP
Glaucoma risk
Normal productiom but less outflow (more resistance to outflow) risks
High IOP
Risk of glaucoma