Topic 1: Classification & Characteristics of Living Organisms
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Define sensibility.
The ability to detect and respond to changes in an environment.
Define respiration.
A process by which living organisms release energy stored in food.
Define movement.
The action by a living organism to change one position of a part or the whole organism.
Define growth.
A permanent increase in size and dry mass, seen in all organisms as they produce new cells.
Define development.
Increase in the complexity of a cell or organism.
Define reproduction.
The process that makes more of the same organism/species.
Define excretion.
The process of removing waste products and excess substances, like extra water, from the organism.
Define nutrition.
The process by which living organisms make or take in food substances needed for energy, growth, and development.
Define species.
A group of organisms that can reproduce to produce fertile offspring.
How can organisms be classified into groups?
By the features that they share.
What is the binomial system for naming species?
An internationally agreed system in which the scientific name of an organism is made up of two parts, showing the genus and species.
How do classification systems aim to reflect evolutionary relationships?
By grouping organisms that share a common ancestor. Traditional systems used physical features, but now we use DNA and molecular evidence, which is more accurate.
How are the sequences of bases in DNA used as a means of classification?
Organisms with more similar DNA base sequences are more closely related, so DNA is used to classify them based on their evolutionary relationships.
What are the 5 Kingdoms?
Animal, Plant, Fungus, Prokaryote, Protoctist
What are the main features of the Animal Kingdom?
They are multicellular, their cells contain a nucleus but no cell walls or chloroplasts, and they feed on organic substances made by other living things.
What are the main features of the Plant Kingdom?
They are multicellular, their cells contain a nucleus, chloroplasts and cellulose cell walls, and they all feed by photosynthesis.
What are verterbrates?
Organisms with a backbone.
What are Invertebrates?
Organisms without a backbone.
What are the 5 classes of vertebrates?
Mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish.
What are the 4 classes of Invertebrates or Athropods?
Myriapods, Insects, Arachnids, Crustaceans

What are the main features of mammals?
They have fur/hair on their skin, they have a placenta, their young feed on milk from mammary glands, their external ears (pinna) are visible, and are endothermic.
What are some examples of mammals?
Horse, Dog, Lion, Tiger

What are the main features of birds?
Their skin is covered in feathers, they have 2 legs & 2 wings instead of forelimbs, they lay eggs with hard shells on land, they have a beak, and are endothermic.
What are some examples of birds?
Parrot, Robin, Eagle

What are the main features of reptiles?
They have dry, fixed scales on their skin and can lay eggs with rubbery shells on land.
What are some examples of reptiles?
Snake, Turtle, Iguana

What are the main features of amphibians?
They have smooth moist skin, larvae live in water so they have gills while adults live on land so they have lungs, they lay eggs without shells in water.
What are the examples of amphibians?
Frog, Toad, Newt

What are the main features of fish?
They have loose wet scales on skin, they have gills to breathe, and lay eggs without shells in the water.
What are some examples of fish?
Flounder & Grouper

What are the main features of myriapods?
Their body consists of many segments, each segment contains at least 1 pair of jointed legs, more than 4 pairs of legs, and 1 pair of antennae.
What are some examples of myriapods?
Centipede

What are the main features of insects?
They have 3 body parts: head, thorax, and abdomen, they have 3 pairs of jointed legs, 2 pairs of wings, and 1 pair of antennae.
What are some examples of insects?
Butterfly, bees, flies, ants
What are the main features of arachnids?
They have 2 body parts: the cephalothorax & abdomen, 4 pairs of jointed legs, and no antennae.
What are some examples of arachnids?
Spider, Scorpion, Tick
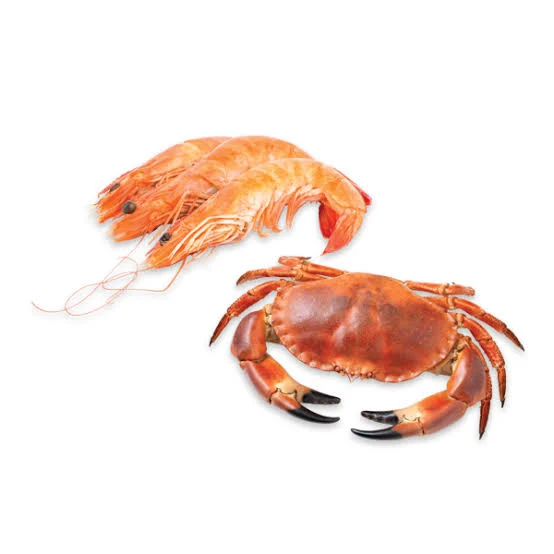

What are the main features of crustaceans?
They have more than 4 pairs of jointed legs, a chalky exoskeleton formed from calcium, they can breathe through gills, and have 2 pairs of antennae.
What are some examples of crustaceans?
Crab, Lobsters, Shrimp,
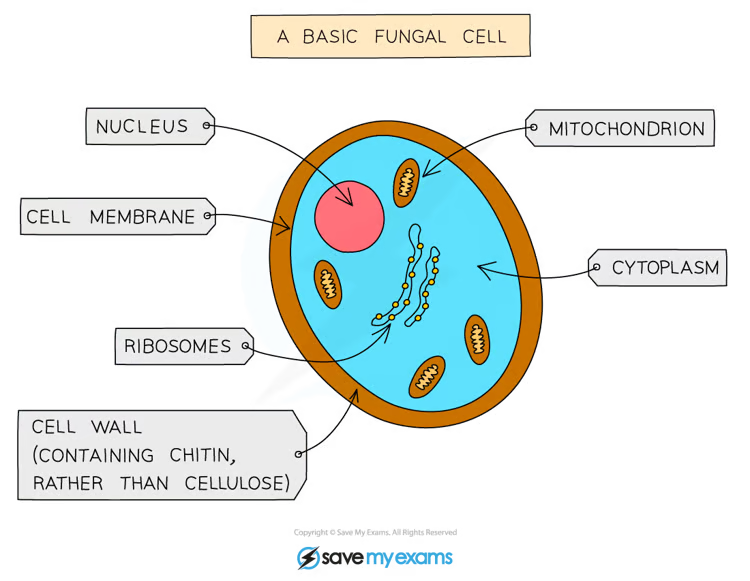
What are the main features of fungi?
They are usually multicellular, cells have nuclei and cell walls not made from cellulose, they do not photosynthesize but feed by saprophytic (on dead or decaying material) or parasitic (on live material) nutrition.

What are some examples of fungi?
Mushroom, yeast, molds, & mildews
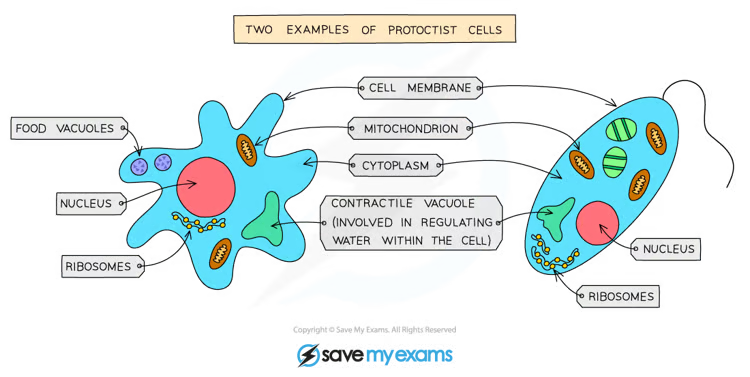
What are the main features of protoctists?
Most are unicellular but some are multicellular, they all have a nucleus, some may have cell walls and chloroplasts, some photosynthesize and some feed on organic substances made by other living things.
What are some examples of protoctists?
Amoeba, Paramecium, Plasmodium
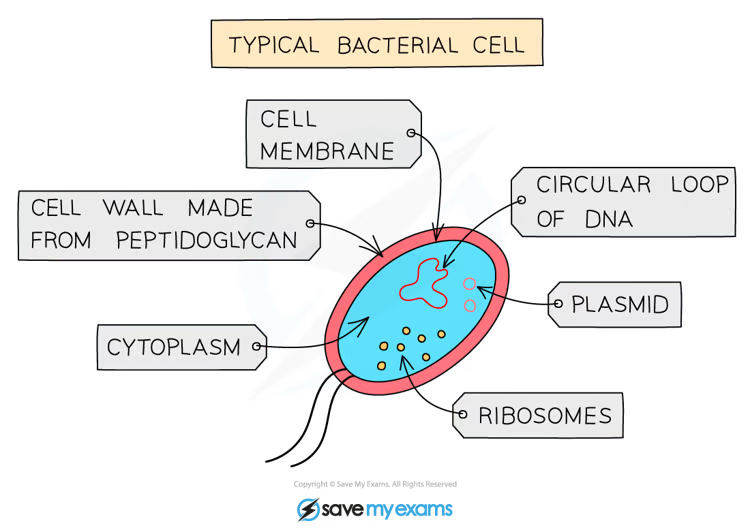
What are the main features of prokaryotes?
They are often unicellular, their cells have cell walls made of peptidoglycan (not made of cellulose) and cytoplasm but no nucleus or mitochondria.
What are some examples of prokaryotes?
Bacteria & blue-green algae
The Plant Kingdom can be divided into two groups: What are they?
Monocotyledons & Dicotyledons
What are the main features of ferns?
They have leaves called fronds and do not produce by flowers but instead reproduce by spores produced on the underside of fronds.
What are the main features of flowering plants?
They reproduce sexually by means of flowers and seeds. Their seeds are produced inside the ovary found at the base of the flower.
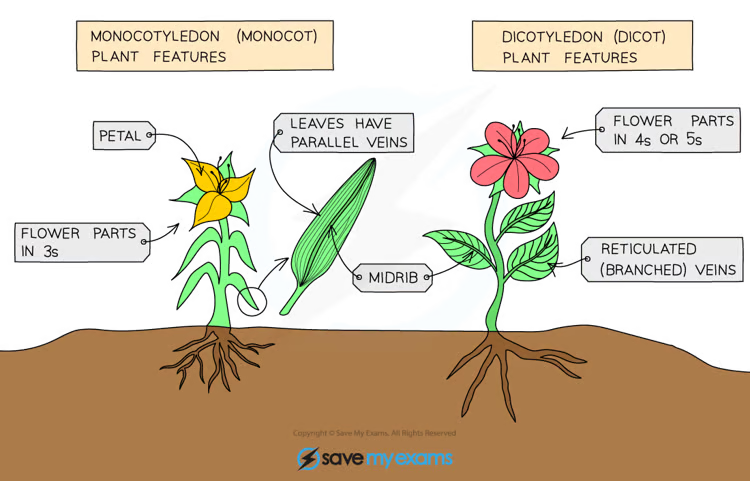
What are the features of monocotyledons?
Flowers contain petals in multiples of 3, their leaves have parallel veins and are narrow and grass-like.
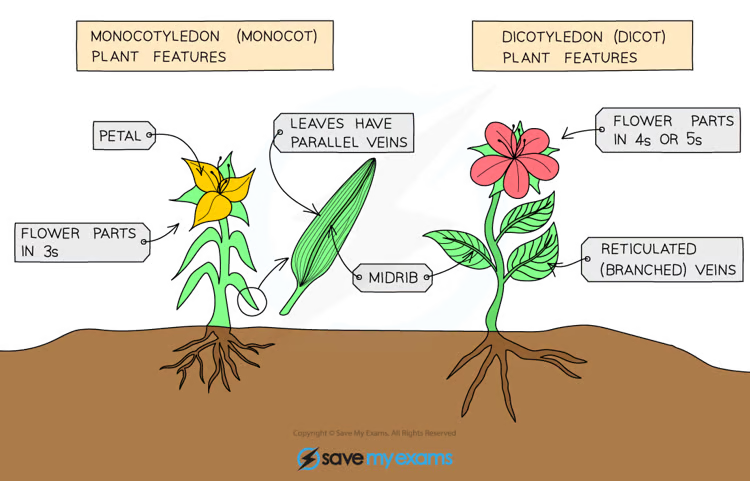
What are the features of dicotyledons?
Flowers contain petals in multiples of 4 or 5, leaves have reticulated veins (a web-like network) and are broader.
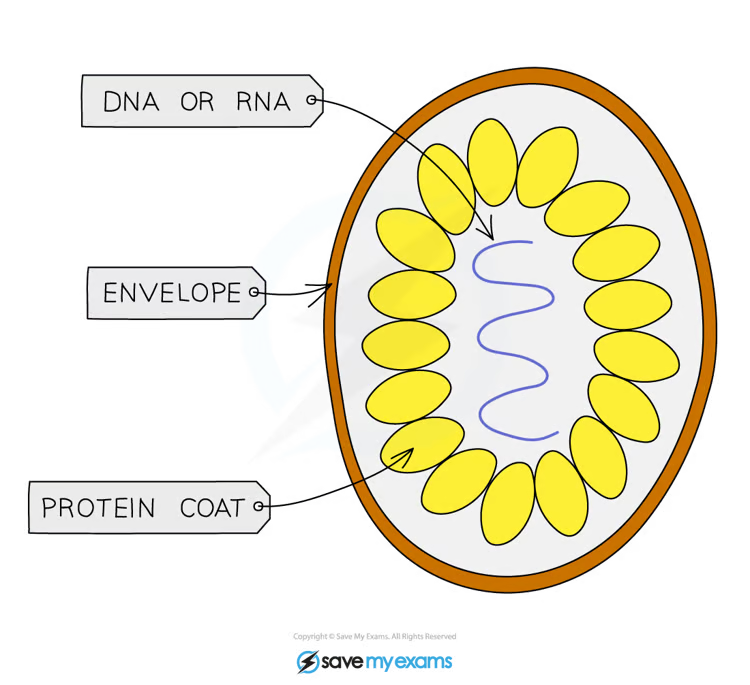
What are the main features of viruses?
A protein coat that protects the virus, and their structure is made of Genetic material (either DNA or RNA, but not both).