Kinematics and Kinetics in Biomechanics
1/145
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
Uniaxial joints
Joints allowing movement around one axis only.
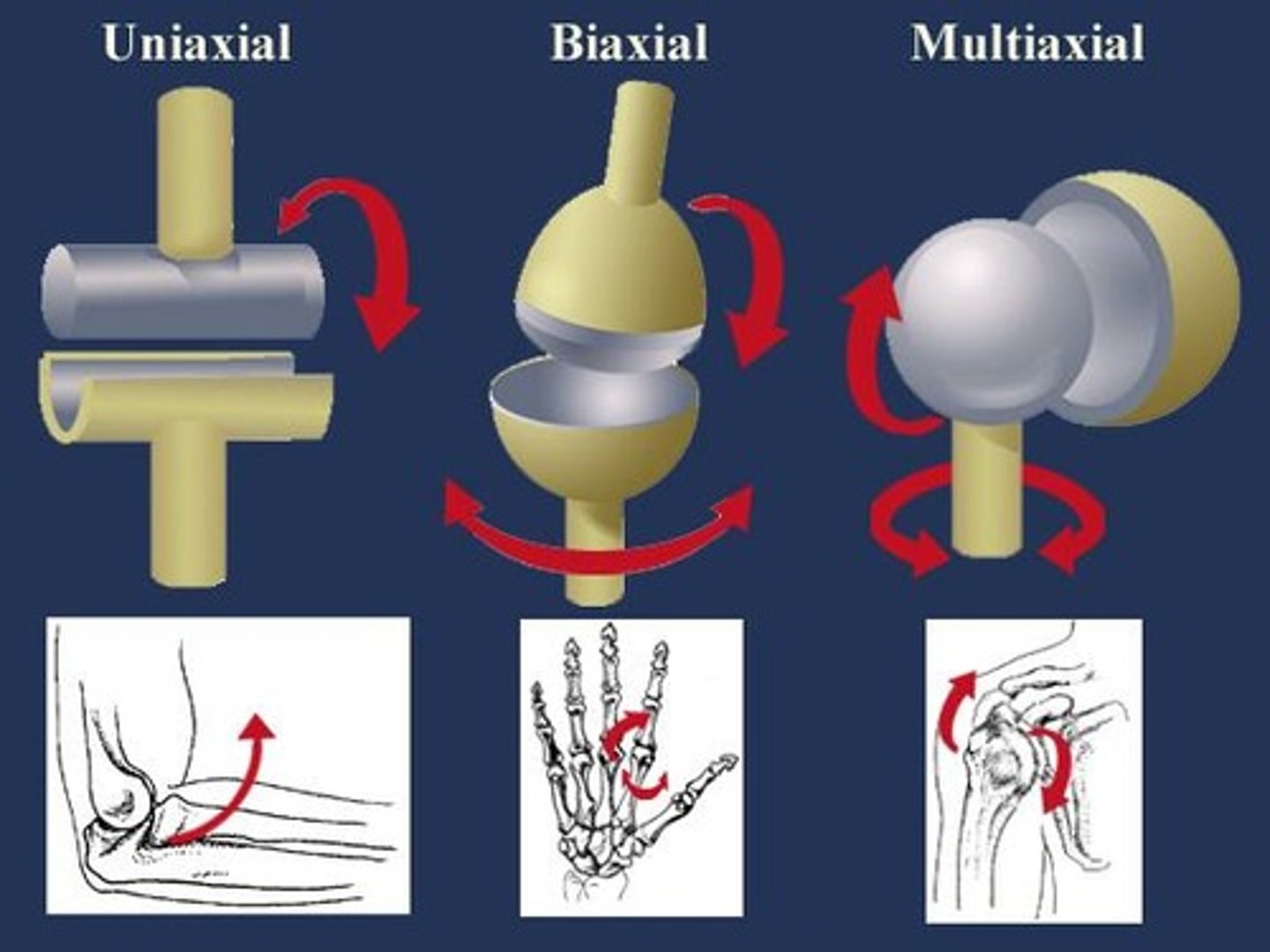
Biaxial joints
Joints permitting movement around two axes.
Tri-/Multi-axial joints
Joints enabling movement around multiple axes.
Osteokinematics
Study of bone movement in joints.
Arthrokinematics
Movement between joint surfaces during motion.
Close-packed position
Joint position with maximal surface contact.
Open-packed position
Joint position with minimal surface contact.
Kinematic chain
Sequence of linked body segments in motion.
Open kinematic chain
Distal segment free to move independently.
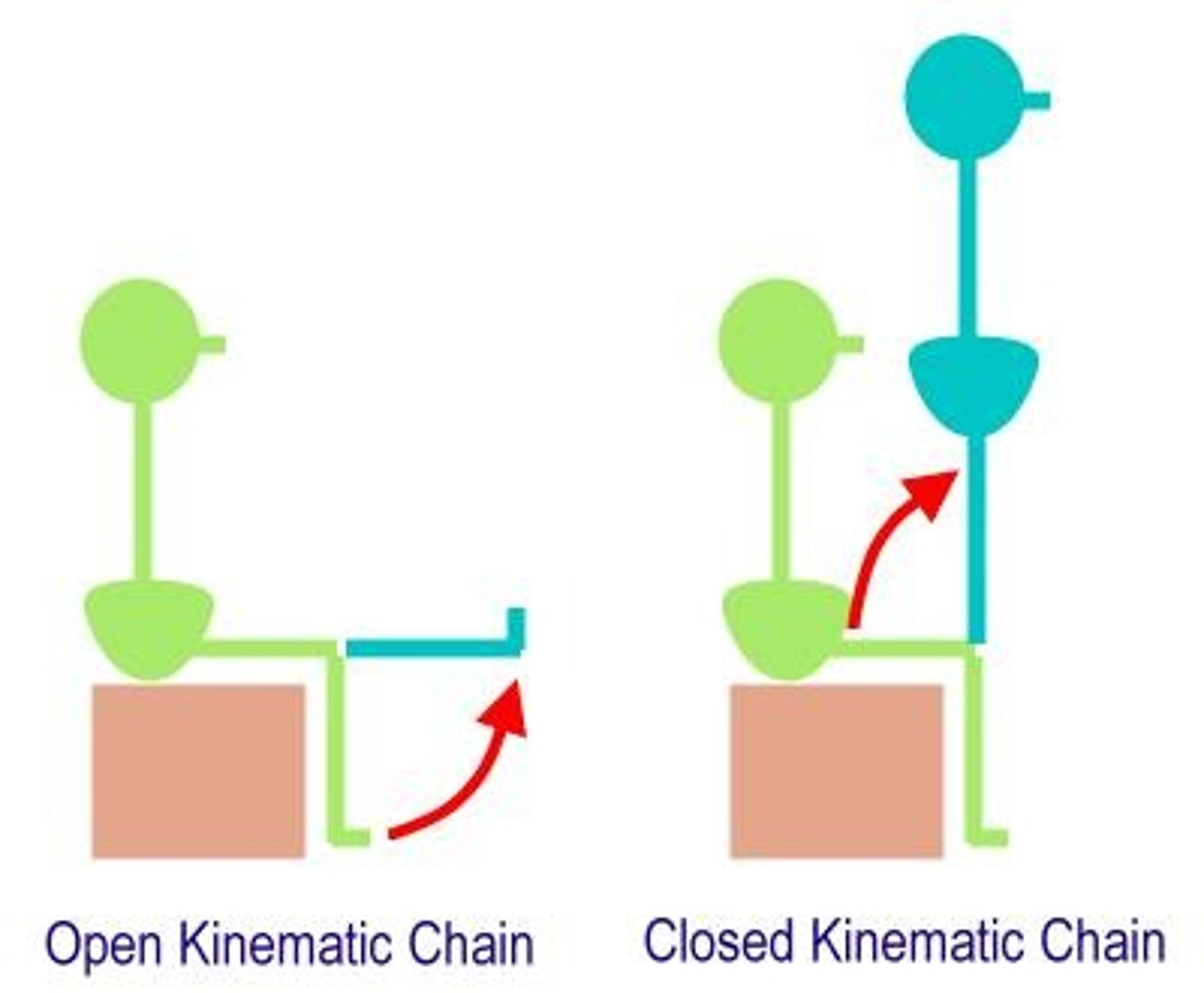
Closed kinematic chain
Distal segment fixed, proximal segments move.
Kinematics
Study of motion without considering forces.
Translatory motion
Movement in a straight line.
Rotary motion
Movement around an axis.
Velocity in rotary motion
Speed of points varies with distance from axis.
Degrees of Freedom
Number of planes a joint can move in.
One Degree of Freedom
Joint movement in one plane only.
Two Degrees of Freedom
Joint movement in two planes.
Three Degrees of Freedom
Joint movement in three planes.
Accessory Motion
Movement not primarily intended, e.g., joint play.
Instantaneous Axis of Rotation
Axis around which rotation occurs at a moment.
Convex-Concave Rule
Describes joint surface interactions during movement.
Open-Packed Position
Joint surfaces maximally separated, less stable.
Closed-Packed Position
Joint surfaces maximally congruent, more stable.
Open Kinematic Chain
Distal segment moves against fixed proximal segment.
Closed Kinematic Chain
Proximal segment moves against fixed distal segment.
Ligaments
Connect bone to bone, providing stability.
Tendons
Connect muscle to bone, facilitating movement.
Bursa
Fluid-filled sacs reducing friction in joints.
Cartilage
Smooth tissue covering joint surfaces, reducing friction.
Fibrocartilage
Tough cartilage providing support and cushioning.
Elastic Cartilage
Flexible cartilage allowing shape retention.
Hyaline Cartilage
Smooth cartilage at joint surfaces for movement.
Isotropic Material
Exhibits uniform mechanical properties in all directions.
Anisotropic Material
Mechanical properties vary with direction of force.
Load/Force
External force applied to a material or structure.
Stress
Force per unit area within materials.
Strain
Deformation resulting from applied stress.
Viscoelasticity
Material property exhibiting both viscous and elastic characteristics.
Viscoelasticity
Material property showing time-dependent strain response.
Creep
Gradual deformation under constant force application.
Stress-relaxation
Decreasing force needed under maintained stretch.
Hysteresis
Different load-deformation paths for loading and unloading.
Strain-rate sensitivity
Energy requirement varies with loading speed.
Uniaxial joints
Joints allowing movement in one plane.
Biaxial joints
Joints allowing movement in two planes.
Triaxial joints
Joints allowing movement in three planes.
Hinge joint
Allows flexion and extension, e.g., elbow.
Pivot joint
Allows rotational movement, e.g., atlantoaxial.
Condyloid joint
Allows movement with two degrees of freedom.
Ellipsoidal joint
Similar to condyloid, e.g., radiocarpal.
Saddle joint
Allows movement in two planes, e.g., thumb.
Plane joint
Allows gliding movements, e.g., carpal bones.
Ball and socket joint
Allows multi-directional movement, e.g., shoulder.
Displacement
Distance moved in a specific direction.
Velocity
Rate of change of displacement over time.
Acceleration
Rate of change of velocity over time.
Force
Push or pull acting on an object.
Inertia
Resistance to change in motion state.
Torque
Rotational force around an axis.
Impulse
Change in momentum due to force application.
Friction
Resistance force opposing motion between surfaces.
Inertia
Resistance of an object to change its state.
Mass (m)
Amount of matter in an object, measured in kg.
Weight (wt)
Force of gravity acting on an object.
Pressure (P)
Force distributed over a given area (P=F/A).
Volume
Amount of space occupied by an object.
Density (ρ)
Mass per unit volume (ρ=mass/volume).
Torque (τ)
Rotary effect of a force (τ=Fd).
Impulse (J)
Product of force and time (J=Ft).
Force
A push or pull acting on an object.
Unit of Force
Metric unit is Newton (N).
Unit of Mass
Metric unit is kilogram (kg).
Unit of Weight
Metric unit is Newton (N).
Unit of Pressure
Metric unit is Pascal (Pa).
Unit of Volume
Metric unit is cubic meters (m³).
Unit of Density
Metric unit is kg/m³.
Specific Weight (γ)
Weight per unit volume (γ=wt/volume).
Collinear Forces
All forces lie on the same line.
Coplanar Forces
All forces lie on the same plane.
Concurrent Forces
Forces meet at the same point.
Force Vector
A vector quantity representing force magnitude and direction.
Free Body Diagram
Simplified drawing showing forces acting on a body.
C2
Law of Cosines formula for triangles.
Force of Gravity
Attraction between two masses due to gravity.
Center of Gravity (CoG)
Point where weight is equally balanced.
Center of Mass (CoM)
Point representing average position of mass.
Line of Gravity (LoG)
Imaginary line through CoG to ground.
Segmental CoM
CoM for individual body segments.
Base of Support (BoS)
Area beneath an object supporting its weight.
Newton's First Law
Object remains at rest or uniform motion unless acted on.
Inertia
Resistance of an object to change its state of motion.
Static Equilibrium
Balanced forces result in no motion.
Dynamic Equilibrium
Balanced forces result in constant velocity.
ΣF = 0
Sum of forces equals zero in equilibrium.
Στ = 0
Sum of torques equals zero in equilibrium.
Anatomic Location - Head
CoG located at sphenoid sinus.
Anatomic Location - Arm
CoG at medial head of triceps.
Anatomic Location - Hand
CoG at 3rd metacarpal.
Anatomic Location - Thigh
CoG at adductor brevis or magnus.
Anatomic Location - Whole Body
CoG one inch anterior to S2.