Introduction to tissue mechanics, mechanotransduction & fibrosis
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
the order of soft tissue elasticity
brain
fat
muscle
cartilage
precalcified bone
the young modulus (E)
measure of stiffness or elasticity
E = stress/strain
what is the most common protein in the body
ECM proteins such as collagen
how is decellularisation of liver achieved
soap solution is perfused throughout, cells are washed out, leaving extracellular matrix behind
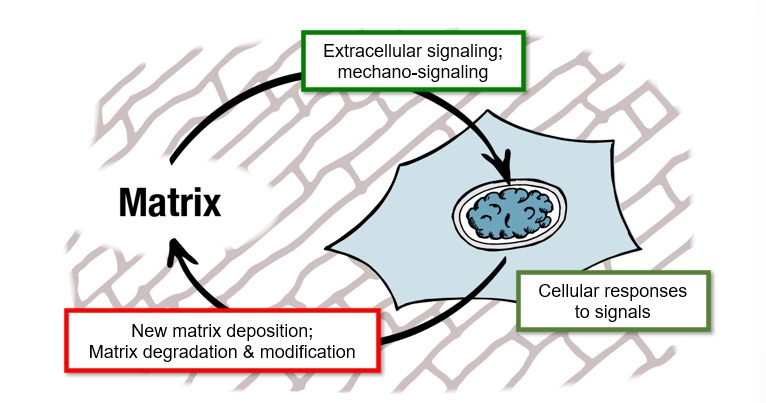
cell signalling to matrix general cycle
extracellular signalling - mechano signalling
cellular responses to signals
new matrix deposition; matrix degradation and modification
which cell behaviours can be controlled by stiffness
Cell morphology (e.g., spreading and shape)
Contractility (how hard cells pull on their surroundings)
Propagation rate and apoptosis
Cell movement
Differentiation (commitment to lineage)
hydrogel
synthetic polymer where cells can be cultured
stiffness depends on density of crosslinks
stiff gel causes cells to spread
soft hydrogel causes cells to be more compact
how can cells sense stiffness
deforming their surroundings
cells pull harder on stiffer substrates
how do cells act on stiffer substances - proliferation and apoptosis
cells grow faster on stiffer substrates
apoptosis is lower
durotaxis
cells move in response to gradients in the mechanical stiffness of their surroundings
typically towards a stiffer substrate
how does soft and stiff substrates affect differentiation
soft substrates drive differentiation to soft tissue types eg fats
stiff substrates drive differentiation to stiff tissue types eg bone
mechanotransduction
conversion of mechanical input into biochemical signal
integrins
membrane proteins that form focal adhesion complexes that tether the cytoskeleton to the matrix
actin
polymeric filaments; major component of the cytoskeleton; growth of filaments drives cell spreading
myosins
‘molecular motors’ pull against actin filaments, causing contractility
talin
a protein that deforms when pulled on, activating a signaling cascade (conversion into biochemical signal)
retrograde flow
actin is polymerised at the edge of the cell and pulled by myosin II, pushing and pulling
what happens if cell is attached to stiff substrate
talin will be deformed
activates MAPK and RhoA pathway
increased expression of actin and integrins to form contractility
LINC complex
nesprins protiens and SUN proteins
sun proteins of LINC complex binds to the nuclear lamina and lamin proteins
tether the cytoskeleton across the nuclear membrane to chromatin
YAP1
transcription factor
nuclear localisation of YAP1 drives osteogenic differentiation by activating genetic programmes
fibrosis
misregulation of feedback and loss of haemostasis causes cells to deposit too much matrix
makes tissues stiffer
mechanical properties are no longer matched to function
myofibroblasts
fibroblasts move to site of injury
activated to make myofibroblasts
more contractile and secrete more ECM
2 fibrotic diseases
severe atherosclerosis
COPD
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
area of fibrosis in lung alternate with normal lung
clustered cystic air spaces - honeycomb
dec gas exchange, lead to lung failure
symptoms of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
shortness of breath, finger clubbing, chronic dry cough
risk factors for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
smoking, chronic viral infections, abnormal acid reflux, family history
what does lung slide show for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
inc number of myofibroblasts
recruited by damaged cells
at leading edge of the disease region produce too much matrix
tight junctions
protein complexes anchored to the actomyosin skeleton
gap junctions
connexon channels that allow ion exchange
desmosomes
link intermediate filaments through adhesion plaques
nesprins
tether the nucleus with the actomyosin cytoskeleton
focal adhesion
large protein complexes that anchor cells to the extracellular matrix, connect actin to external
how are traction forces generated and where are they transmitted to
head of myosin ii pulls on actin filaments to generate traction forces, then transmitted to focal adhesions to deform the ECM
when are ecm bound growth factors activated and released
mechanical forces which trigger cellular signaling
which protein domains are unfolded with force
talin, paxilin
this leads to stabilisation of nascent adhesions
adherens junctions
link cytoskeletons of adjacent cells via clusters of cadherins