Chatper 3 - Water and Life
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
https://youtu.be/Jm0kFK5IiGo?si=Pv9Xx_d6yVg_l0xE(H+ vs H30+)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Water (H₂O)
A polar molecule essential for life, composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
Polar Covalent Bond
A chemical bond where electrons are shared unequally between atoms, creating partial charges ().
Polar Molecule
A molecule with an uneven distribution of charge which has a partial positive charge on hydrogen and a partial negative charge on oxygen.
Hydrogen Bond
A weak attraction between a hydrogen atom (δ⁺) and an electronegative atom (δ⁻), such as oxygen or nitrogen. In water, hydrogen bonds form between adjacent water molecules.
Cohesion
The attraction between water molecules due to hydrogen bonding
Adhesion
The attraction between water molecules and other substances
Surface Tension
A measure of how difficult it is to break the surface of a liquid
What causes water's high surface tension?
Hydrogen bonding at the air-water interface.
What is air-water interface?
The boundary where liquid water meets air.

Specific Heat
How much energy a material can absorb before its temperature changes
What is the specific heat of water?
Water has a high specific heat (1 cal/g·°C
Why does water resist changing its temperature?
Because of its high specific heat
FILL: Heat is absorbed when hydrogen bonds _____; Heat is released when hydrogen bonds ____
Break, form
Heat of Vaporization
The amount of heat required to convert 1 gram of a liquid into a gas.
What does evaporative cooling do?
Helps stabilize temperatures in organisms and bodies of water
Evaporative Cooling
The process by which a liquid cools as it evaporates.
Why does ice float on water?
Ice is less dense than water
Expansion Upon Freezing
Water expands when it freezes because hydrogen bonds in ice form a crystalline structure
Water reaches its greatest density at...
4°C
What is the universal solvent?
Water is the universal solvent
What is a solution?
A homogeneous mixture of two or more substances
S
Solvent
A substance capable of dissolving other substances.
Aqueous Solution
A solution in which water is the solvent.
Kinetic Energy
The energy of motion.
Thermal Energy
The total kinetic energy of atoms or molecules in a substance.
Temperature
A measure of the average kinetic energy of molecules in a substance.
Heat
Thermal energy transferred from one body of matter to another.
Calorie (cal)
The amount of heat needed to increase or decrease the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius.
Joule (J)
A unit of energy; 1 cal = 4.184 J.
What are food calories?
Kilocalories (kcal)
How many regular calories is one food calorie?
1,000 cal.
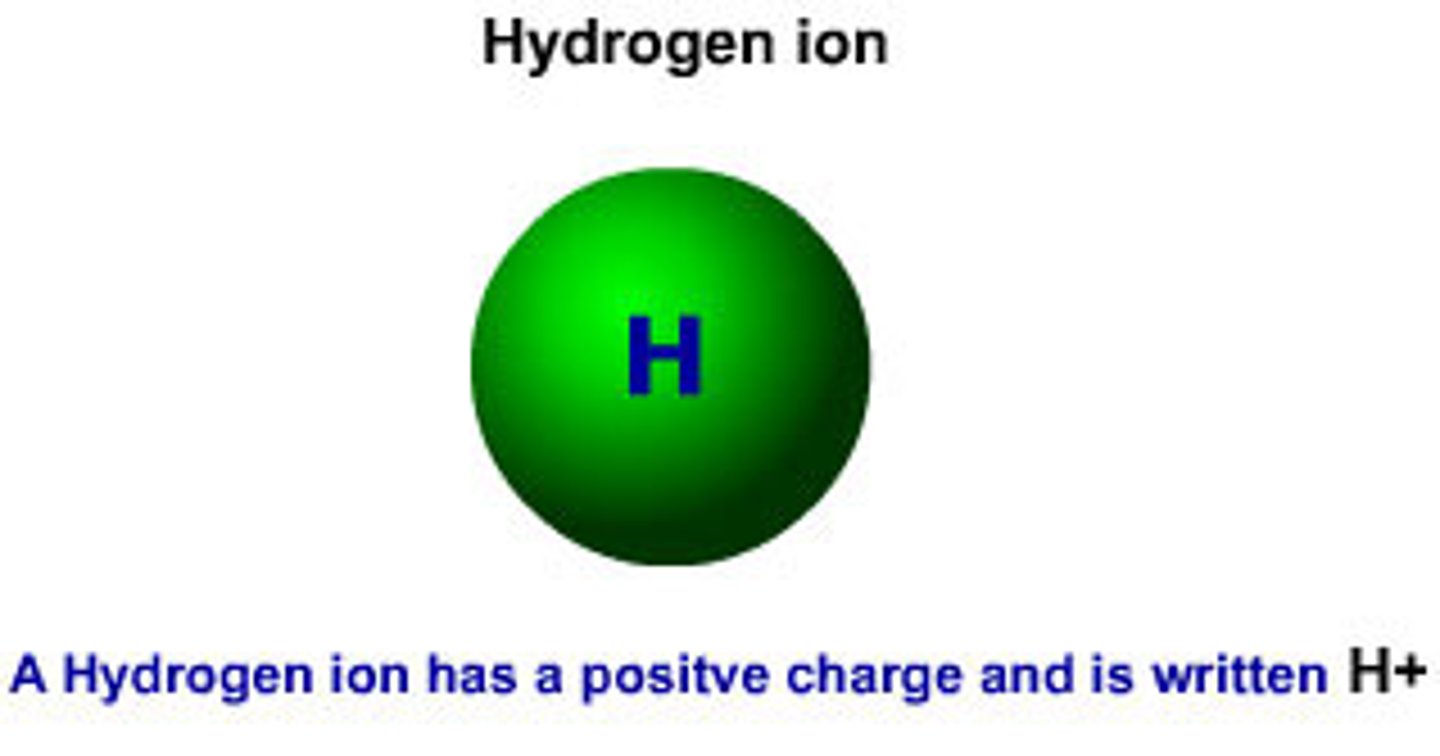
Hydrogen Ion (H⁺)
A proton atom when a hydrogen atom loses its electron.
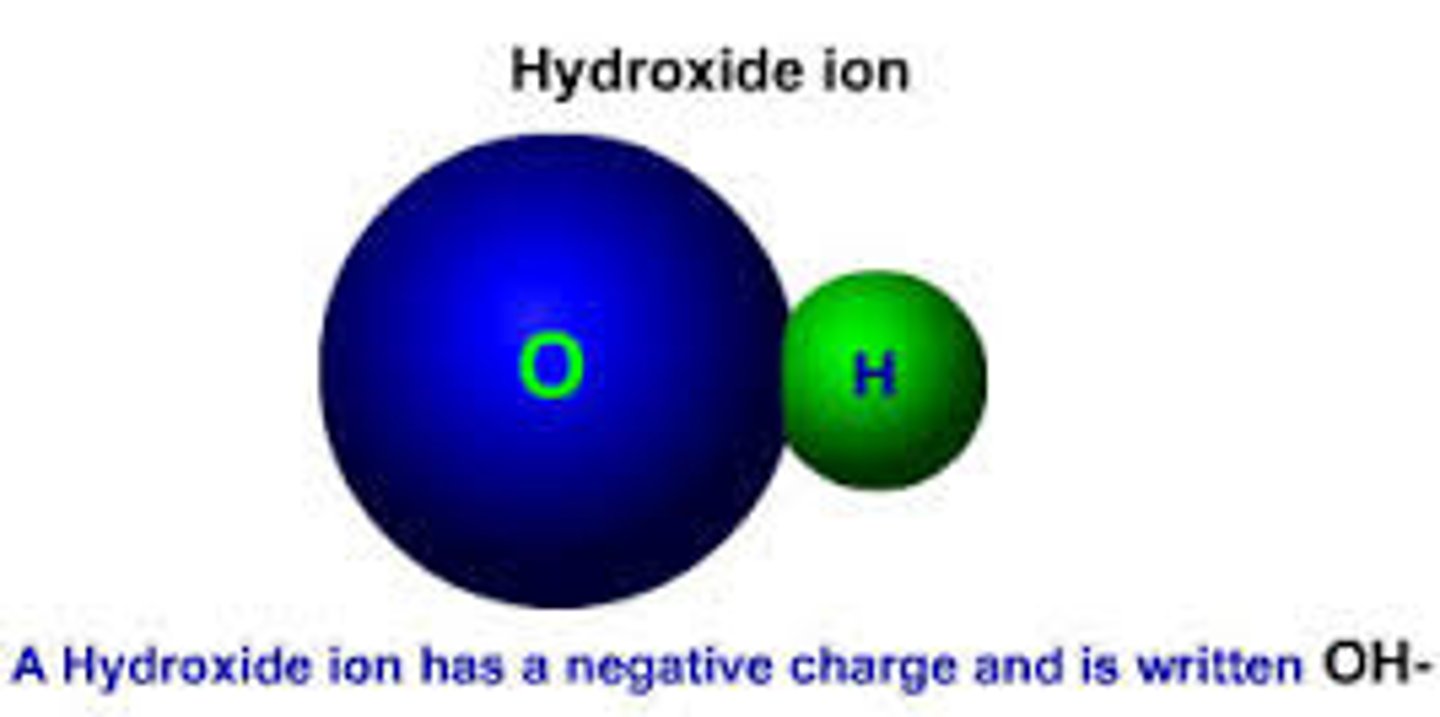
Hydroxide Ion (OH⁻)
A negatively charged ion formed when a water molecule loses a hydrogen ion.
Hydronium Ion (H₃O⁺)
A water molecule with an extra hydrogen ion, often represented as H⁺.
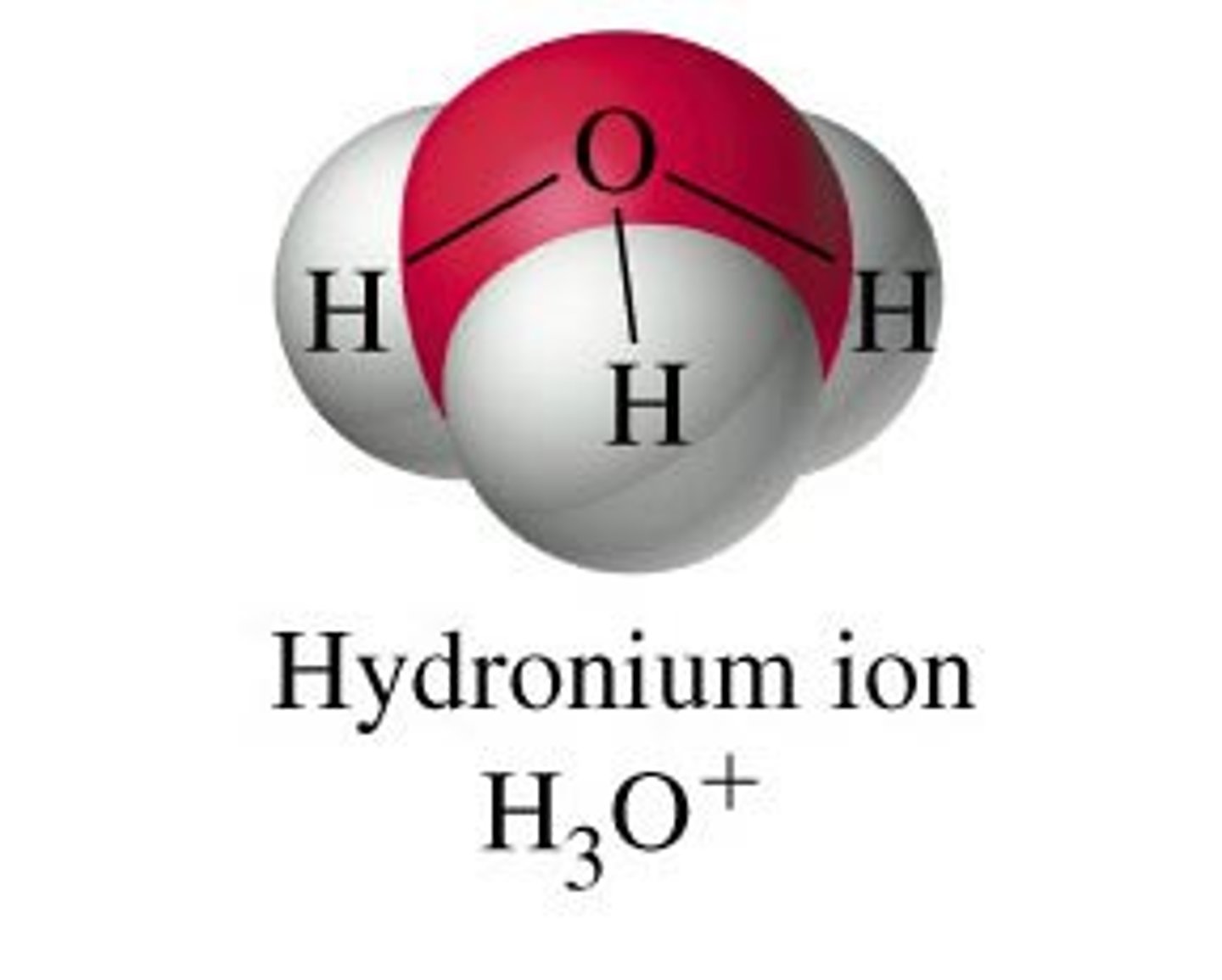
Hydronium
H₃O⁺ or often represented as H⁺(water molecule)
Acid
A substance that increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H⁺) in a solution.
Base
A substance that reduces the concentration of hydrogen ions (H⁺) in a solution.
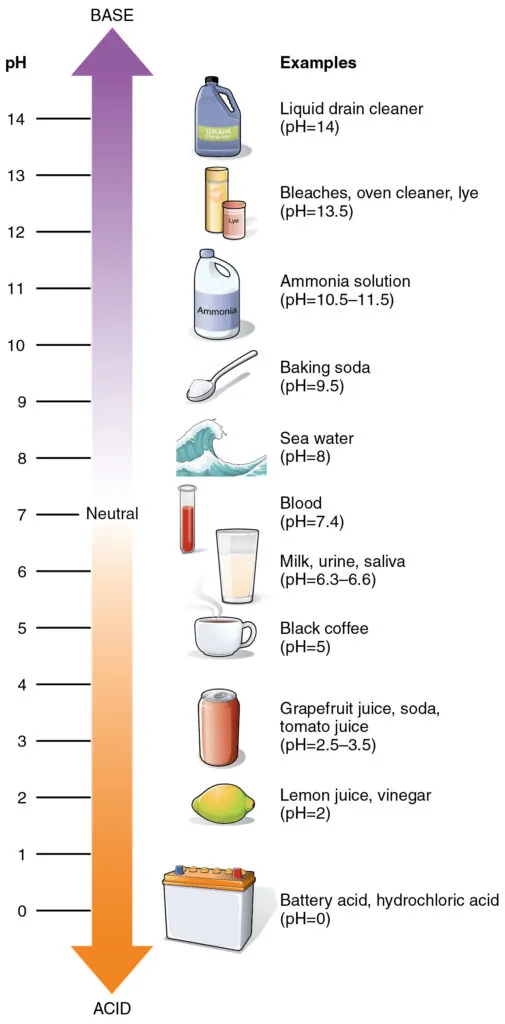
pH Scale
A logarithmic scale used to measure the acidity or basicity of a solution. pH = -log[H⁺].
Neutral Solution
pH = 7 (equal concentrations of H⁺ and OH⁻).
Acidic Solution
pH < 7 (higher concentration of H⁺).
Basic Solution
pH > 7 (higher concentration of OH⁻).
The higher the hydrogen ions concentration results in what?
The smaller value on the pH scale
What does pH mean?
Potential hydrogen
Buffer
A substance that minimizes changes in pH by accepting or donating H⁺ ions.(maintain pH)
Hydrophilic
Substances that have an affinity or likes water, typically polar or ionic molecules.
Hydrophobic
Substances that do not have an affinity for water, typically nonpolar molecules like oils and fats.
Ocean Acidification
The process by which CO₂ dissolves in seawater, forming carbonic acid (H₂CO₃), which lowers the pH of the ocean.
Carbonic Acid (H₂CO₃)
A weak acid formed when CO₂ reacts with water.
Bicarbonate Ion (HCO₃⁻)
An ion formed when carbonic acid dissociates, releasing H⁺ ions.
Carbonate Ion (CO₃²⁻)
An ion required by marine organisms for calcification (e.g., coral reefs).
Global Warming
The increase in Earth's average temperature due to the accumulation of greenhouse gases like CO₂.
Arctic Sea Ice
Ice that forms in the Arctic Ocean, which is melting at an accelerated rate due to global warming.
Glaciers
Large masses of ice that are shrinking due to rising global temperatures.
Extraterrestrial Life
Life that may exist outside of Earth, often searched for by looking for water or water vapor.
Mars
A planet in our solar system that has been found to contain water, making it a target for the search for extraterrestrial life.
Solution
A homogeneous mixture of two or more substances.
Solute
The substance that is dissolved in a solution.
Pure water
Concentrations of H+ and OH- are equal
Hydration Shell
A sphere of water molecules surrounding an ion in an aqueous solution.
Dynamic Equilibrium
A state in which the rate of a forward process (e.g., water dissociation) equals the rate of the reverse process (e.g., water reformation).
What makes life on Earth possible?
Water
What are the four properties of water that facilitate an environments for life?
1. Cohesion
2. Ability to moderate temperature
3. Expansion
4. Versatility as a Solvent
How does cohesion help plants?
Allows water to move against gravity in plants
What is an example of adhesion in plants?
Water and plant cell walls
FILL: What are the sticking properties shown in this diagram (top to bottom)
Adhesion (sticking to something else)
Cohesion (sticking to each other)
Water has many exceptional and useful properties. Which is the rarest property among compounds?
A. Water is a solvent.
B. Water has a high heat capacity.
C. Solid water is less dense than liquid water.
D. Water has surface tension.
C. Solid water is less dense than liquid water.
In a single molecule of water, two hydrogen atoms are bonded to a single oxygen atom by ________.
polar covalent bonds
Why does ice float in liquid water?
Hydrogen bonds stabilize and keep the molecules of ice farther apart than the water molecules of liquid water.
Hydrophobic substances such as vegetable oil are ________.
nonpolar substances that repel water molecules
Melting of ice and thus reduced feeding opportunities for polar bears is occurring because of the ________.
The partial negative charge at one end of a water molecule is attracted to the partial positive charge of another water molecule. What is this attraction called?
A. a van der Waals interaction
B. a hydrogen bond
C. an ionic bond
D. a covalent bond
B. a hydrogen bond
The partial negative charge in a molecule of water occurs because ________.
the electrons shared between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms spend more time around the oxygen atom nucleus than around the hydrogen atom nucleus
Rank, from low to high, the pH of blood, stomach acid, and urine.
A. stomach acid, urine, blood
B. blood, urine, and stomach acid
C. urine, blood, stomach acid
D. stomach acid, blood, and urine
A. stomach acid, urine, blood
A solution with a pH of 2 has how many more protons in it than a solution with a pH of 4?
1000 times more
pH scale
How would acidification of seawater affect marine organisms? Acidification of seawater would ________.
A. increase dissolved carbonate concentrations and hinder growth of corals and shell-building animals
B. decrease dissolved carbonate concentrations and hinder growth of corals and shell-building animals
C. increase dissolved carbonate concentrations and promote faster growth of corals and shell-building animals
D. decrease dissolved carbonate concentrations and promote faster growth of corals and shell-building animals
B. decrease dissolved carbonate concentrations and hinder growth of corals and shell-building animals
Water molecules can form hydrogen bonds with ________.
A. oxygen gas (O2) molecules
B. compounds that have polar covalent bonds
C. chloride ions
D. oils
B. compounds that have polar covalent bonds