4.3- Enzyme Efficiency and Regulation Biothermodynamics
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Denature protein has lost…
all structure except its primary structure and is non-functional.
Higher temperatures increase enzyme activity up to a…
threshold, past which enzyme activity decreases.
4 Levels of enzyme regulation:
Genetic Level
Physical Level
Enzyme Level
Negative Feedback/ Feedback Inhibition Level
Genetic Level:
genes producing enzymes can be activated or disabled (e.g.: lac operon).
Physical Level
enzymes can be stored in vesicles and only released as needed.
Enzyme Level
enzymes can be activated/disabled via chemical modification (like phosphorylation)
Ex: enzymes can be cleaved (inactive form → active form) via chemical modification
Can also be modified by having another molecule bind them, altering their level of activity
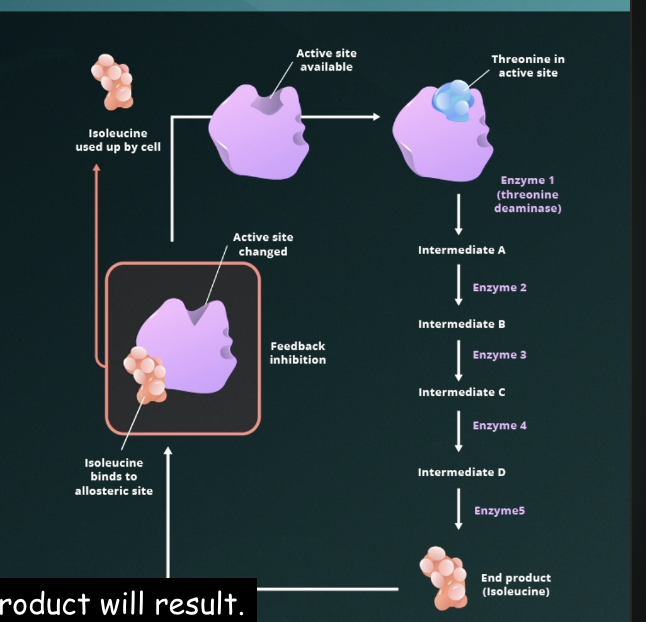
Negative Feedback/Feedback Inhibition
When the product of a reaction binds to and inhibits that reaction, preventing excess product production.
Primary way the body maintains homeostasis.
Positive Feedback
A product of an enzyme triggers even more of its own production
This creates a loop that increases in magnitude
Ex: Labor contractions in birth (head of fetus pushes against the cervix, stimulating the brain to release oxytocin, pushing the fetus more towards cervix)