Week 5 Pt. 2 (Cervical/Thoracolumbar Neurosurgery)
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Brain disease can look similar to what other disease processes?
- Cervical spinal disease
What are clinical signs of brain disease?
- Mentation changes
- Seizures Headaches
- Hemi-neglect (Can still see on one side, but not processing the info)
- Big circles
- Hemi or tetra ataxia
- Hemi or tetra paresis
- Stiff neck
- VERTICAL nystagmus
What are the most common surgical diseases of the brain?
- Tumors
- Hydrocephalus
- Chiari- like syndrome
- Maxillary/ Zygoma Skull Fractures
What are some potential neurologic exam findings for spinal segments C1-C5?
- +/- stiff or painful neck, +/- spontaneous screaming
- Tetra-ataxia
- Ambulatory or non ambulatory tetraparesis
- Tetraplegia is rarely possible =respiratory paralysis= death
- Muscle tone normal or increased
- Myotactic reflexes intact or UMN in all 4 limbs
- Withdrawal reflexes intact in all 4 limbs
- Upper motor neuron bladder and anal sphincter
What are some potential neurologic exam findings for spinal segments C6-T2?
- +/- stiff or painful neck, +/- spontaneous screaming
- Thoracic limb lameness/weakness or nerve root signature lameness (Shoot pain down neck into limb)
- Tetra-ataxia (often worse in hind limbs)
- Ambulatory or non-ambulatory tetraparesis
- Tetraplegia is rarely possible = Respiratory paralysis = Death
- Muscle tone may be decreased in front legs, and normal or increased in back legs
- Myotactic reflexes decreased in front limbs
- Myotactic reflexes intact or UMN in hind limbs
- Withdrwawal reflexes decreased in front limbs, intact in hind limbs
- UMN bladder and anal sphincter
What are some surgical C1-C5 Ddx?
1. Hansen's Type 1 (chondroid) Disk Disease
2. Wobblers (disk or osseous associated)
3. Atlantoaxial subluxation/ luxation
4. Spinal Tumor
5. Trauma (fractures, luxations, hematoma,
- Cats: Trauma, bb air-gun pellets, falls, etc.
What are some medical C1-C5 Ddx?
- Autoimmune meningitis: Granulomatous meningoencephalomyelitis, Steroid Responsive Meningitis, Pug Dog Meningitis
- Inflammatory/ infectious
- Fibrocartilaginous Embolism
- Syringohydromyelia (fluid in the spinal cord) itself)
- Discospondylitis
- CATS: Lymphoma and Feline Infectious Peritonitis
What are some surgical C6-T2 Ddx?
1) Wobblers (disk or osseous associated)
2) Hansens Type 1 (chondroid) Disk Disease
3) Spinal Tumor- NERVE SHEATH TUMOR
4) Trauma (fractures, luxations, hematoma, gunshot)
- Cats: Trauma, bb air-gun pellets, falls, etc.
What are some medical C6-T2 Ddx?
- Autoimmune meningitis: Granulomatous meningoencephalomyelitis, Steroid Responsive Meningitis, Pug Dog Meningitis
- Inflammatory/ infectious
- Fibrocartilaginous Embolism
- Syringohydromyelia (fluid in the spinal cord) itself)
- Discospondylitis
- CATS: Lymphoma and Feline Infectious Peritonitis
Paralysis of all 4 limbs = paralysis of ____________.
- Breathing
What are early signs of respiratory paralysis?
- Abdominal breathing patterns
- Panting
- Decreased ribcage excursions
The cervical spinal canal has more space relative to size of the spinal cord for mobility. What does this mean for pathology?
- By the time there is neurologic deficits = Severe compression
- Any deficits localized to cervical spinal cord -> Emergency
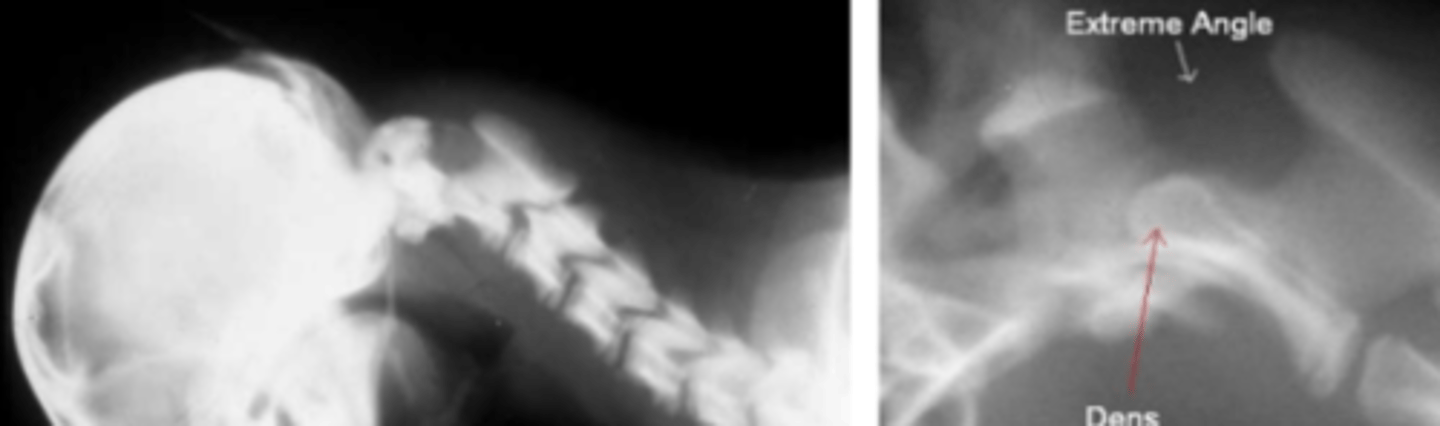
What is the pathogenesis of AA luxation?
- Hypoplastic dens/stabilizing ligaments of the atlantoaxial joint
What animals are commonly affected by AA luxation?
- Toy breed dogs
Describe the typical clinical presentation of AA luxation.
- Low head carriage
- Tetra paresis and tetra ataxia in all four legs
- Inability to stand or move the legs
- Difficulty breathing
What dogs with AA have a better prognosis?
- Dogs with shorter duration of signs
How is AA repaired?
- Screws and PMMA cement work best
What are some complications of AA repair?
- Breathing difficult
- Pneumonia
- Implant migration
- Collapsing trachea
- Hemorrhage (Blood vessels running through vertebrae)
Dogs with untreated AA die from...
- Can get kinking and edema of brain stem -> Death
What animals are commonly affected by cervical IVDD?
- Small breed dogs
- Chondrodystrophoid dogs
- Beagles, Whippets and French bulldogs; Labs, Dalmations
How do patients with cervical IVDD present?
- 50% present with acute signs
- 50% present with slow onset, chronic signs
What are some clinical signs associated with cervical IVDD?
- Severe and unrelenting neck pain and unable to move neck (90% pts)
- Nerve root signature lameness (25-50%) - Weakness or paralysis in the limb innervated by the pinched nerve root
- Ambulatory tetraparetic (42%); Very bad -> Next stop is respiratory paralysis
How is cervical IVDD diagnosed?
- Radiographs (35% accurate)
- CT (small breed dogs, often have mineralized disk which can be seen on CT)
- MRI (large breed dogs - Don't have mineralized discs)
How can cervical IVDD be managed medically?
- Strict cage rest x 4-6 weeks
- NSAIDS or steroids, Gabapentin, fentanyl patch, codeine
- Muscle relaxants: methocarbamol
When can medical management be attempted for cervical IVDD?
- Mild to moderate pain only
- No neurologic deficits
In what cases of cervical IVDD is advanced imaging and surgery essential to recommend?
- Severe unrelenting pain
- In more comfortable patients, if pain does not diminish with meds and rest
- Any neurologic deficits
According to the ACVIM, in what cases are steroids indicated for cervical IVDD?
- Corticosteroids are not recommended for routine use in medical management of the acute phase of presumptive TL-IVDE
- In the chronic phase, a short course of anti-inflammatory doses of corticosteroids may be of benefit for some dogs
What approach is used for surgical repair of cervical IVDD?
- Ventral slot
What are indications for a ventral slot surgery?
- Decompression of Hansen's type 1 disk disease
- Disk associated Wobblers -> Do in combination with fusion surgery
What are some structures encountered on the approach for a ventral slot surgery?
- Trachea
- Esophagus
- Vagosympathetic trunk
- Carotid
- Recurrent laryngeal nerve -> Laryngeal paralysis, disphonation
- Sympathetic nerve branch to eye -> Horners
- Other small nerve branches involved with pharyngeal sensation and motor function
What post-op care is needed for ventral slot surgeries?
- Strict cage rest x 8 weeks
- NSAIDS, Gabapentin, fentanyl patch, codeine
- Muscle relaxants: methocarbamol
- Icing
- Physical therapy
What are some potential complications for a ventral slot surgery?
- Bleeding
- Respiratory paralysis (Injury to recurrent laryngeal nerve or spinal cord edema affected brainstem/respiratory centers)
- Laryngeal paralysis
- Arrhythmias
- Residual disk
- Horner's Syndrome
- Spinal Subluxation
- Pneumonia
- Neurologic deterioration despite best efforts (chronic cases)
True or false: Patients with cervical IVDD (Type 1) and caudal cervical spondylomyelopathy present very similarly.
- False; Wobblers presents with more chronic signs and mild ataxia (Only ~15% present for pain)
What are the two flavors of Wobblers?
1) Osseous associated
2) Disc associated
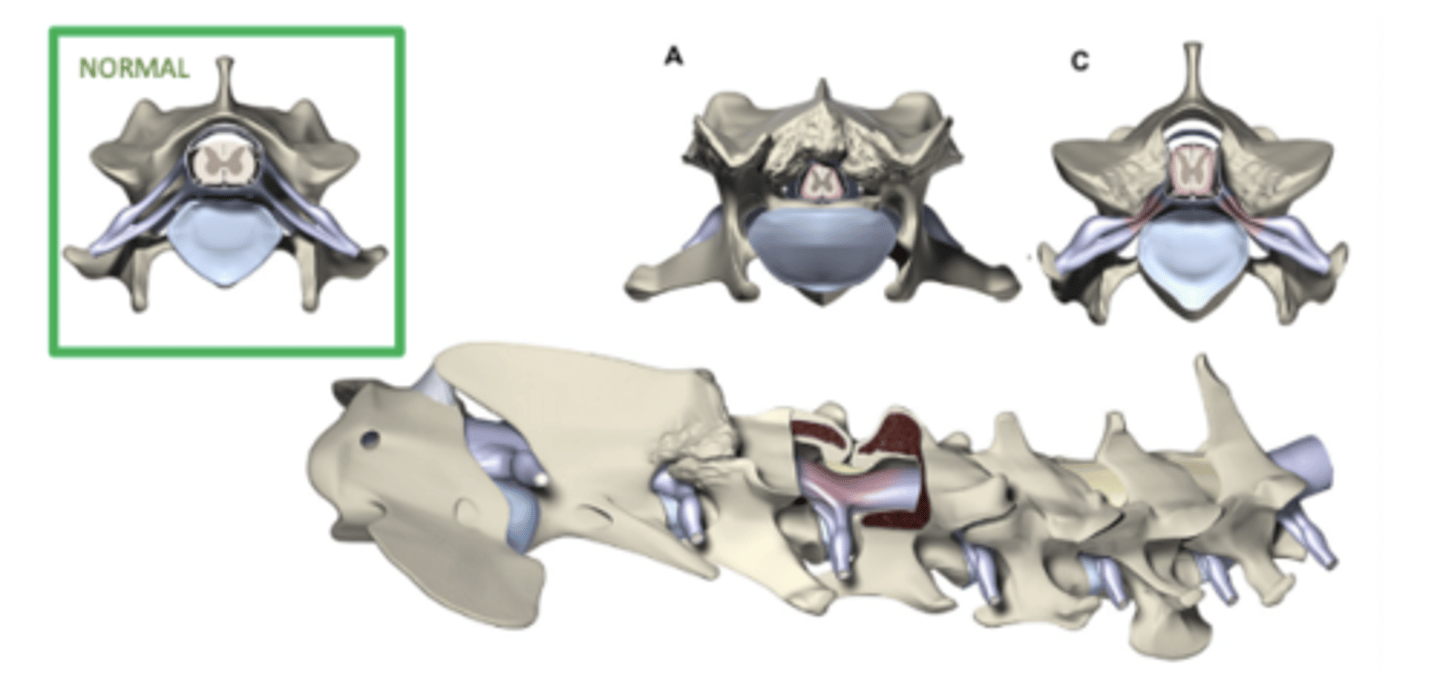
Describe the pathogenesis of osseous associated wobblers.
- Spinal canal is more square/rectangular in shape or even hourglass -> Lateral aspect of spinal cord is pinched -> Ataxia
- As patients age, they start getting facet OA -> Dorsolateral pressure on spinal cord -> Proprioceptive tract pressure -> More ataxia
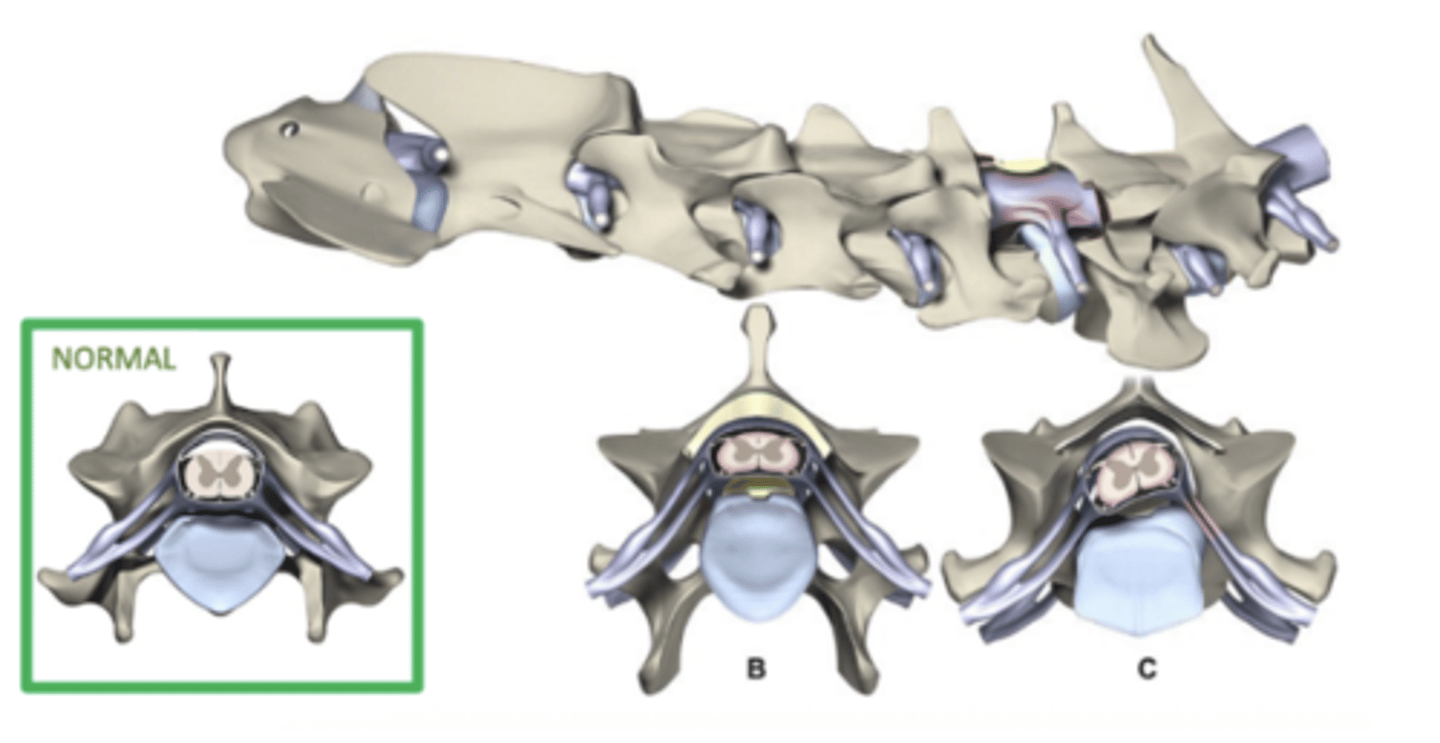
Describe the pathogenesis of disc associated wobblers.
- Instability of caudal cervical vertebrae and Disc starts to bulge (chicken and the egg with past two) -> Vertebrae subluxate past each other as patient move -> Frequent micropressure on disc -> Disc bulging -> Spinal cord compression -> Ataxia
How is wobbler's treated?
1) Osseous associated -> Dorsal laminectomy +/- fusion
2) Disc associated -> Ventral slot + distraction + fusion; disc arthroplasty
What are possible complications of surgical correction of Wobblers?
- Domino effect
- Neurologic deterioration
- Implant failure
- Laminectomy membrane
- Foraminal collapse
- Pneumonia
- Insufficient decompression (large dogs)
What is the prognosis of Wobblers with surgical correction?
- 80% good prognosis with 25% reoccurrence
What post-op nursing care is needed for cervical spine patients?
- The more severely affected the more intense the nursing care
- Ventilator support
- Decubitus ulcers (toes, hips, elbows) -> Padding and recumbency change
- Urinary retention -> Ucath
Why are cervical spine patients prone to atelectasis and pneumonia?
- Can't cough or sigh
Which type of fibers are most susceptible to damage?
- Superficial, larger, and myelinated fibers
What are some potential neurologic exam findings for a lesion between T3 and L3?
- +/- stiff or painful back- can look like abdominal pain
- Normal forelimbs (Except if Schiff-Sherington posture for cranial lumbar lesions)
- Para-ataxia
- Ambulatory or non-ambulatory paraparesis
- Paraplegic
- Muscle tone to hind limbs normal or increased
- Myotactic reflexes intact or UMN in hind limbs
- Withdrawal reflexes intact or exaggerated in hind limbs
- UMN Bladder: Can't pass urine due to spastic sphincters
- UMN anal sphincter: Formed stool with intermittent solid fecal balls falling out
What are some potential neurologic exam findings for a lesion between L4 and S2/3?
- Hunched/ flexed rump/ +/-painful tail jack+/- stiff or painful lumbar spine, +/- nerve root signature lameness
- Normal forelimbs
- Para-ataxia
- Ambulatory or non-ambulatory paraparesis
- Paraplegic
- Muscle tone to hind limbs decreased to absent, flacid
- Myotactic reflexes decreased to absent
- Withdrawal reflexes decreased/incomplete toe or hock flexion/absent
- LMN bladder (flaccid/leaking/difficult to express)
- LMN anal sphincter (open/no wink/leaking liquid feces)
What is the most likely cause of thoracolumbar spinal disease?
- Degenerative Diseases (IVDD if over 1 YO, degenerative instability/stenoses, degenerative myelopathy)
What are some non-surgical DDx for thoracolumbar spinal disease?
- FCE (large breed dogs)
- Auto-immune meningits (small breed dogs)
What are the goals of neurologic surgery?
- Decompression CNS
- Maintain or return stability/bony protection of CNS
- Relieve pain
- Allow CNS to heal if possible
For every day a patient is down in the rear prior to surgery equates to how long being down post-op?
- 1 day prior = 1 week post-op
With thoracolumbar disease, one expects _________ signs to the hind limbs. Will the bladder be expressable?
- UMN
- Difficult to express bladder because sphincter cannot relax (May be able to elicit detrusor reflex if meds are on board)
Will a patient with thoracolumbar disease be fecally incontinent?
- Expect UMN fecal incontinence (abdominal press may cause a poop to fall out)
What are some common surgical Ddx for thoracolumbar disease?
1) Hansen's Type 1 (chondroid) DIsk Disease
2) Trauma (Fractures, luxations, hematoma, gunshot)
3) Congenital deformity
- Cats: Trauma: Bb air gun, pelletes, falls, disks
What are some common medical Ddx for thoracolumbar disease?
- Hansens Type 2 Disk Disease
- Fibrocartilaginous Embolism
- Degenerative myelopathy
- Spinal tumor
- Congenital deformity
- Discospondylitis
- Autoimmune meningitis: Granulomatous meningoencephalomyelitis, Steroid Responsive Meningitis, Pug Dog Meningitis
- Inflammatory/ infectious
Syringohydromyelia (fluid in the spinal cord itself)
- CATS: Lymphoma and Feline Infectious Peritonitis
What is the typical function of the nucleus pulposus?
- Handles disk compressive forces
Describe the pathophysiology of Hansen Type 1 IVDD.
- "pew pew" - Dr. Ihms
- The disc degenerates due to FGF4 retrogene insertion (in chondrodystrophic breeds) which results in dysplastic, shortened long bones and premature degeneration/calcification of the IVD nucleus pulposus
- Dehydrated, chunky nucleus can't handle normal compressive forces and it can explosively rupture with the slightest provocation
What are some chrondrodystrophic breeds?
- Dachshund
- Pekingese
- Corgi
- Beagle
- Lhasa apso
- Mini poodle
- Maltese
- Chihuahua
IVDD is most common at which intervertebral disc spaces in chondrodystrophic breeds?
- T12-13 through L1-2 most common (Keystone in the spinal arch under the most compression)
Which non-chondrodystrophic breeds are predisposed to Hansen type 1 IVDD?
- Dobermans
- Labradors
- Tollers
IVDD is most common at which intervertebral disc spaces in non-chondrodystrophic breeds?
- L1 to L2
What is the typical age of onset for type I hansen IVDD?
- Chrondrodystrophic breeds: Age 1-10 years, peaks at 3-6 years of age
- Non-chondrodystrophic breeds: Age 6-8 years
Onset of signs associated with type I IVDD are usually ____________.
- Sudden (can progress rapidly)
If a patient presents w/o neurologic deficits, but with back pain upon spinal palpation, what should you do?
Offer referral, if owners decline:
- STRICT CAGE REST x 4 WEEKS
- NSAIDS (Steroids prevent Glu from getting into cells and inhibit protein synthesis - not good for this)
- GABApentin (pregabalin is better)
- Opioid
- +/- methocarbamol
- OFFER OVERNIGHT STAY FOR OBSERVATION, PAIN MEDS, IV FLUIDS
If owners decline all this -> Recheck exam in 24 hours and check in with O at end of day
- Make sure O is educated that they could wake up the next AM to a paralyzed pet and this could turn into a surgical ER at any time
When a patient presents with neurologic deficits and back pain upon spinal palpation, what should you do?
- Referal ASAP for advanced imaging and surgery
- Diagnosis: CT, MRI, (Myelogram - no longer standard of care)
What are indications for surgery in cases of Type I IVDD?
- Persistent pain (even without neuro deficits) despite rest and meds
- Cervical cases with ANY neuro deficits -> ER
- Large disk ruptures causing cord compression on advanced imaging
- Neurologic deficits, especially motor deficits (Once a pt starts losing motor or pain sensation, surgical decompression is needed ASAP)
What surgery is performed for decompression of IVDD in the thoracolumbar region?
- Hemilaminectomy
What is the prognosis for hemilaminectomies?
- As long as deep pain sensation is present, 85-97% of cases will make a complete recovery