Bio 1A - Chapter 28: Protists
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Protists
Eukaryotes with fossils dating back 2.1 billion years; 'chemical signatures' date back 2.7 billion years
Endosymbiosis
A hypothesis explaining the origin of eukaryotic cells through the engulfment of prokaryotic cells.
Protists
The most diverse group of eukaryotes, including unicellular, colonial, and multicellular organisms.
Protist Habitats
Freshwater and marine environments.
Photoautotrophs
Organisms that obtain energy from photosynthesis.
Heterotrophs
Organisms that obtain energy by absorbing organic molecules or ingesting food particles.
Mixotrophs
Organisms that combine photosynthesis and heterotrophic nutrition.
Diplomonadida
Major clade of protists with two equal-sized nuclei and modified mitochondria.
Parabasala
Major clade of protists with an undulating membrane and modified mitochondria.
Euglenozoa
Major clade of protists with a spiral or crystalline rod inside their flagella.
Alveolata
Clade of protists characterized by alveoli (membrane-bound cavities) beneath the plasma membrane.
Stramenopila
Clade of protists with hairy and smooth flagella.
Amoebozoa
Clade of protists with amoeboid movement using lobe-shaped pseudopodia.
Rhodophyta/Chlorophyta
Clade of protists including red algae and green algae, closely related to land plants.
Secondary Endosymbiosis
The process by which red and green algae were themselves ingested by other eukaryotes.
Mitosomes
Modified mitochondria found in diplomonads that lack functional electron transport chains.
Giardia lamblia
A common diplomonad parasite that infects the human intestine.
Trichomonas vaginalis
A parabasalid that is a common inhabitant of the human vagina.
Ciliates
Protists named for their use of cilia for movement and feeding.
Dinoflagellates
A diverse group of aquatic photoautotrophs and heterotrophs, often causing 'red tides'.
Plasmodium
Parasites of animals, including the causative agent of malaria.
Diatoms
Unicellular algae with unique glass-like walls composed of silica.
Oomycetes
A group including water molds, white rusts, and downy mildews, once considered fungi.
Brown Algae
The largest and most complex algae, all multicellular and mostly marine.
Euglenozoa
Predatory heterotrophs, photosynthetic autotrophs, and pathogenic parasites with spiral or crystalline rods inside their flagella.
Trypanosoma
A genus of euglenozoans that causes sleeping sickness (trypanosomiasis).
Euglena
An example of Euglenozoa found only in fresh water, that can be autotrophic or heterotrophic.
Gymnamoebas
Heterotrophic amoebozoans found in soil, freshwater, and marine environments.
Entamoebas
Parasites of vertebrates and some invertebrates; Entamoeba histolytica causes amebic dysentery in humans.
Slime Molds
Also known as mycetozoans, slime molds are now placed in the clade Amoebozoa.
Rhodophyta (Red Algae)
Algae containing reddish pigment (phycoerythrin), mostly marine, and usually multicellular.
Green Algae
Algae named for their grass-green chloroplasts, divided into chlorophytes and charophyceans, closely related to land plants.
Chlorophytes
Green algae which include unicellular, colonial, and multicellular forms
The placement of all protists in one kingdom caused dissatisfaction among taxonomists mainly because…
various pieces of evidence indicate that the kingdom Protista cannot be monophyletic
Which of the following is one of the main weaknesses of the proposed classification scheme in which all eukaryotes are divided into four supergroups?
It shows all four supergroups diverging simultaneously from a common ancestor. Because the origin of eukaryotes is not yet known, it is impossible to accurately portray the branch points in eukaryotic lineages. This results in a lack of clarity regarding evolutionary relationships.
Diplomonads
a group of flagellates, most of which are parasitic.
Parabasalids
a group of flagellated protists within the supergroup Excavata. Most of these eukaryotic organisms form a symbiotic relationship in animals.
Which example below is a characteristic shared by diplomonads and parabasalids?
Both lack plastids.
How do trypanosomes withstand the attack of a host's immune system?
The molecular composition of their surface changes continually.
Which of these groups includes photosynthetic unicellular organisms with flagella and contractile vacuoles?
Euglenids
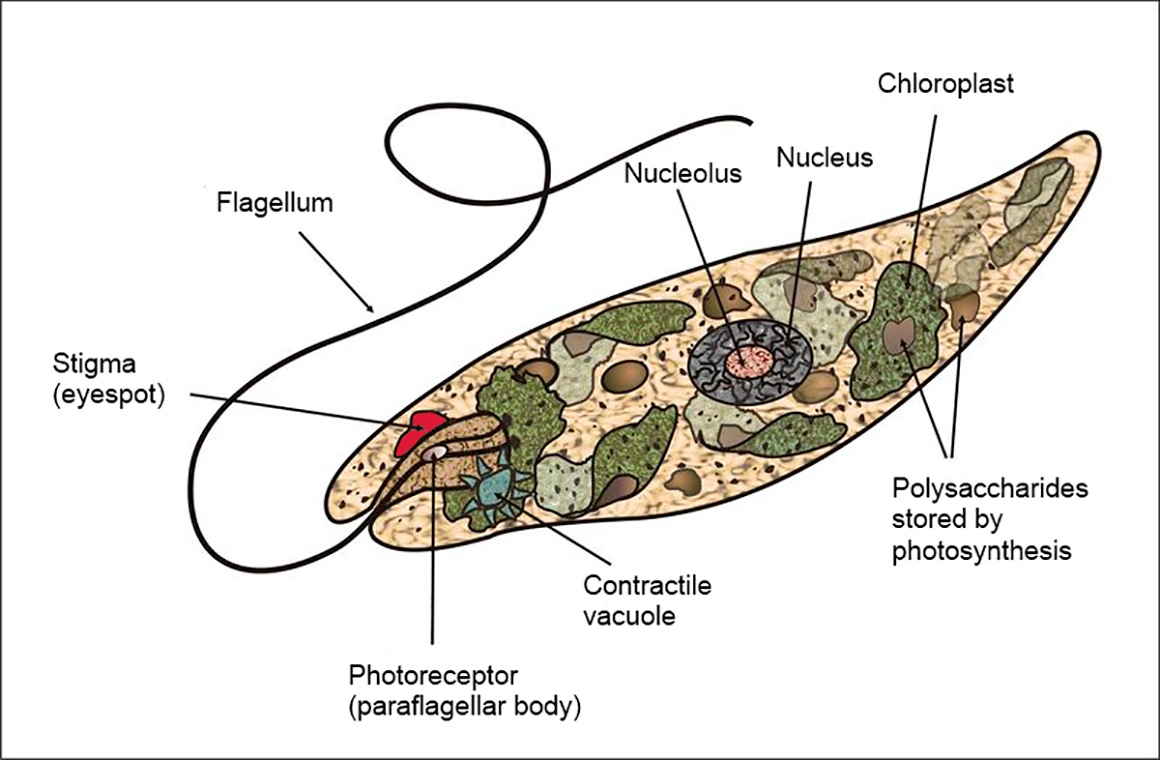
Contractile vacuoles
Specialized organelles, primarily found in single-celled organisms like protists, that regulate water balance within the cell
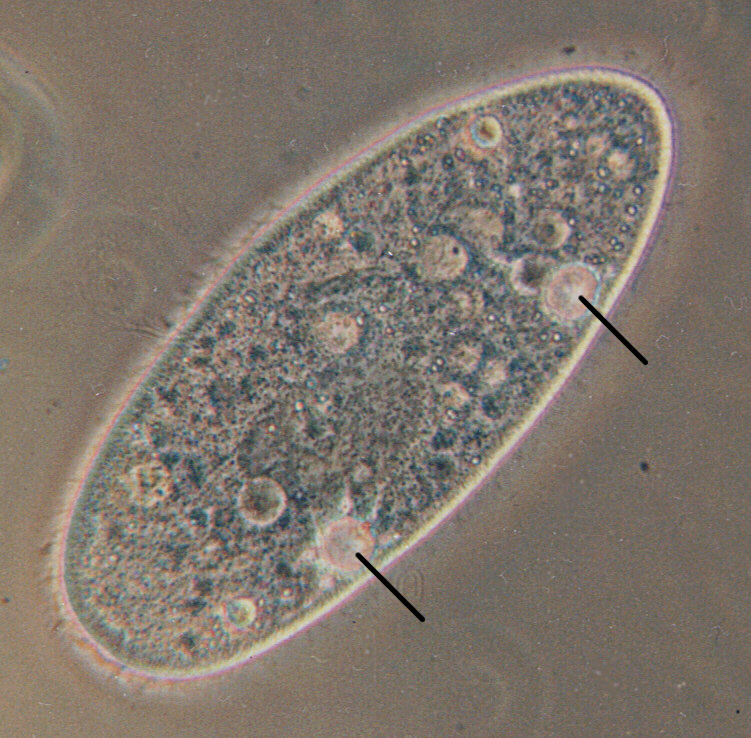
Apicomplexans are currently assigned to the SAR clade because…
the apicoplast, a modified plastid, appears to be of red algal origin.
SAR clade
a highly diverse clade of eukaryotes, often considered a supergroup, that includes stramenopiles, alveolates, and rhizarians
What do a carnivorous dinoflagellate, a parasitic apicomplexan, and a ciliate have in common?
All three have sacs known as alveoli just beneath their plasma membranes. This is one characteristic that unites these three distinct types of protists into a group called alveolates.
Which organisms are capable of producing a "red tide"?
Dinoflagellates
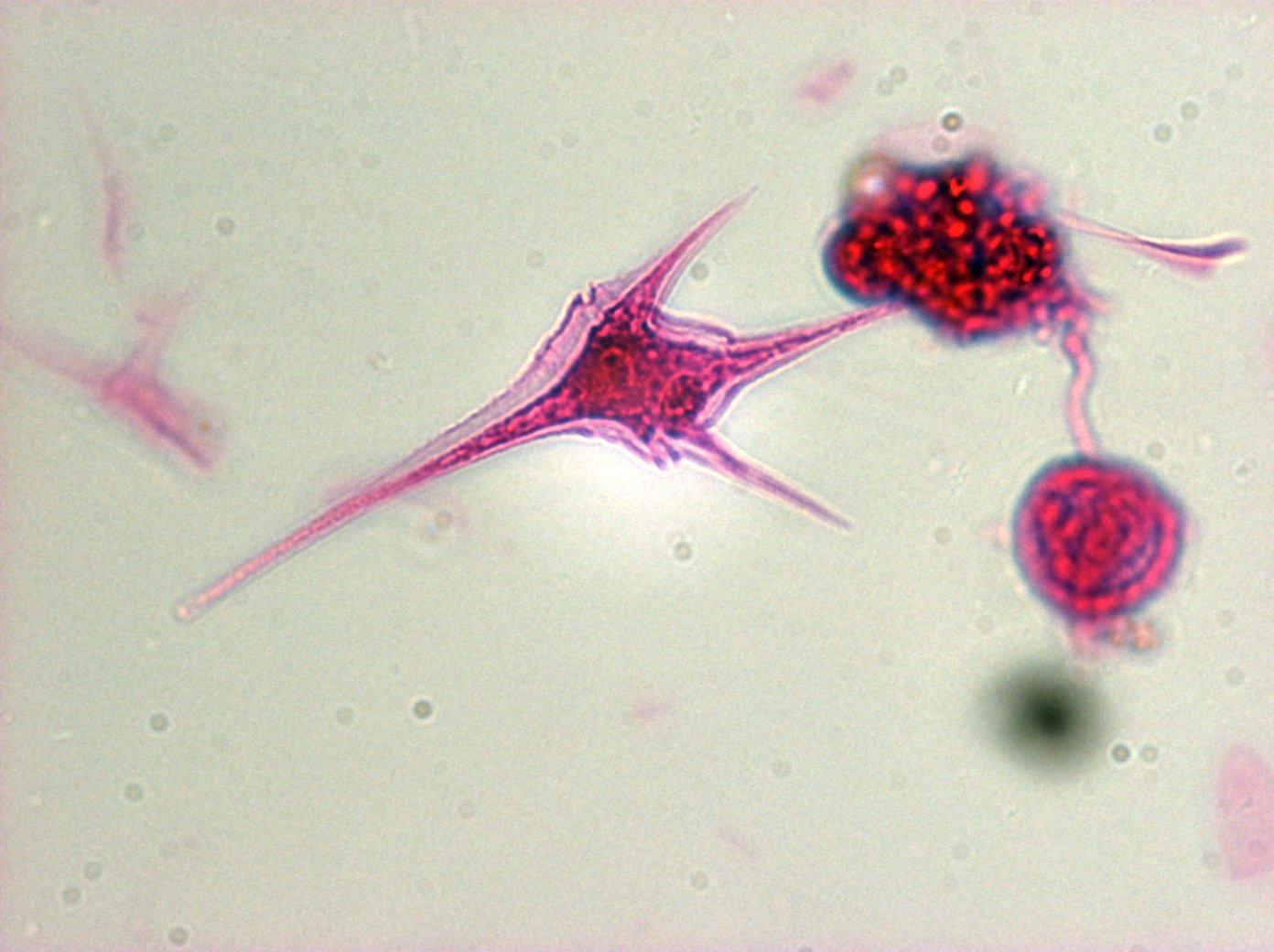
Which of these groups includes parasitic unicellular organisms with a complex of organelles specialized for penetrating host cells and tissues?
Apicomplexans
Which of these groups is characterized by cells that have more than one nucleus?
Ciliates
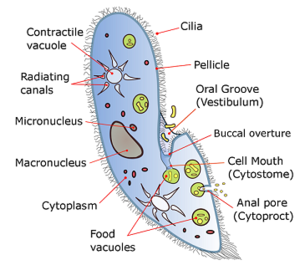
How do ciliates generate genetic variation?
Conjugation: a sexual process in which two individuals exchange haploid micronuclei.
Which of these groups includes unicellular organisms that, due to the structure of their cell walls, can withstand pressures equal to the pressure under each leg of a table supporting an elephant?
Diatoms

Which characteristic is/are shared by most diatoms, golden algae, and brown algae at least at some stage of their life cycles?
All are autotrophs. They all have flagella with numerous fine, hairlike projections. All are stramenopiles (protists distinguished by the presence of stiff tripartite external hairs)
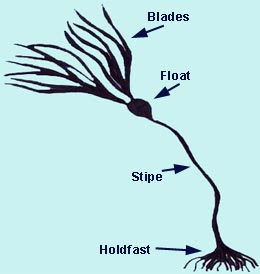
What is the purpose of the "floats" in some brown algae?
Facilitating photosynthesis
Which of the following organisms is commercially harvested to extract algin from their cell walls?
Brown algae
What role do diatoms play in the global carbon balance affecting global warming?
During a bloom, diatom populations may increase rapidly. If many diatoms die and sink to the bottom without being eaten, they effectively pump carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere.
On some areas of the seafloor, one could observe an "ooze" that is hundreds of meters thick. What creates this ooze?
The tests of dead radiolarians
Many species of red algae are adapted to deeper water due to the fact that __________.
Their photosynthetic pigments efficiently absorb blue and green light
Which of the groups of algae is/are most closely related to land plants?
Green algae.
In lab class, a plasmodial slime mold is used as a demonstration organism. One of the students does not understand why this organism is not considered multicellular. How would you explain it to her?
The plasmodium is undivided by membranes and contains many diploid nuclei; therefore, it is not technically multicellular.
To which of the four eukaryotic supergroups do amoebas belong?
None, organisms that move by pseudopodia are found in more than one supergroup. They are not monophyletic.
The red algae are characterized by
diverse life cycles, including alternation of generations.
What percentage of the world's photosynthesis is carried out by protists?
about 30%
_____ is a protist that causes late blight of potatoes and was responsible for the Irish potato famine of the 19th century.
Phytophthora infestans
Hypermastigotes are important endosymbionts that live in the guts of…
termites.