Embalming II Terms & Definitions - Lesson 5 Biology
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
cavity embalming
second major procedure in the sanitation and temporary preservation of human remains; the other half of a standard embalming process for a normal case
cavity embalming
direct treatment of the contents of the body cavities and the lumina of the hollow viscera
- aspiration
- injection of chemicals using a tracer
cavity embalming is usually accomplished by:
- to supplement vascular (arterial) embalming (by treating the contents of the hollow viscera and area between organs)
- to reduce putrefactive changes caused by areas not receiving arterial solution
what is the purpose of cavity embalming?
- the 9-region method
- the quadrant method
to simplify the process and ensure all areas are treated in an orderly way, the torso (technically the abdomen) is divided into sections using one of two systems:
9-region method
extend two vertical lines upward from a point midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the symphysis pubis; use two horizontal lines; one at the inferior margin of the 10th costal cartilage and the other at the tubercles on the iliac crests
9-region method
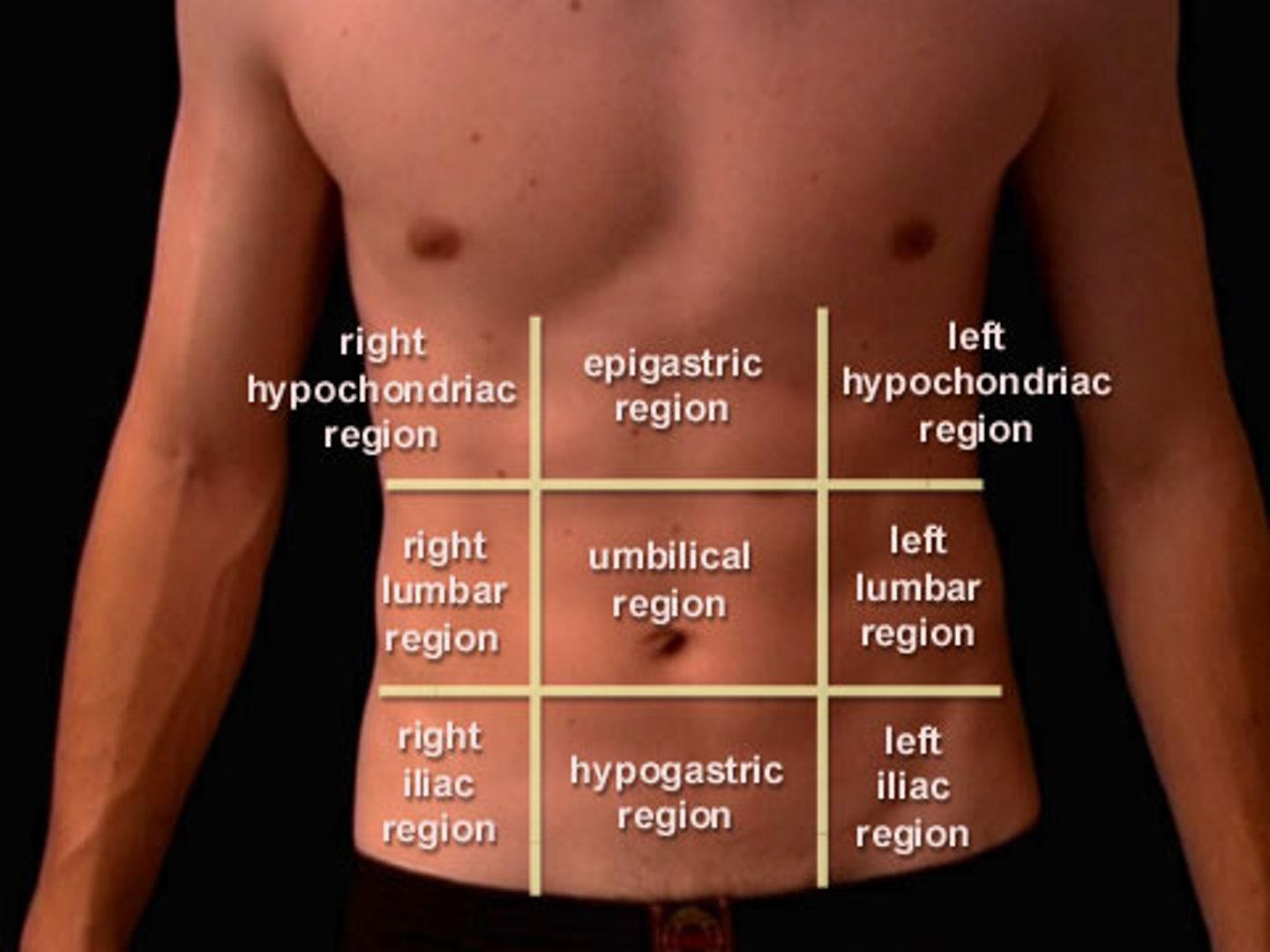
- upper regions (right hypochondriac, epigastric, left hypochondriac)
- middle regions (right lumbar, umbilical, left lumbar)
- lower regions (right inguinal/iliac, hypogastric, left inguinal/iliac)
the 9-region method is comprised of:
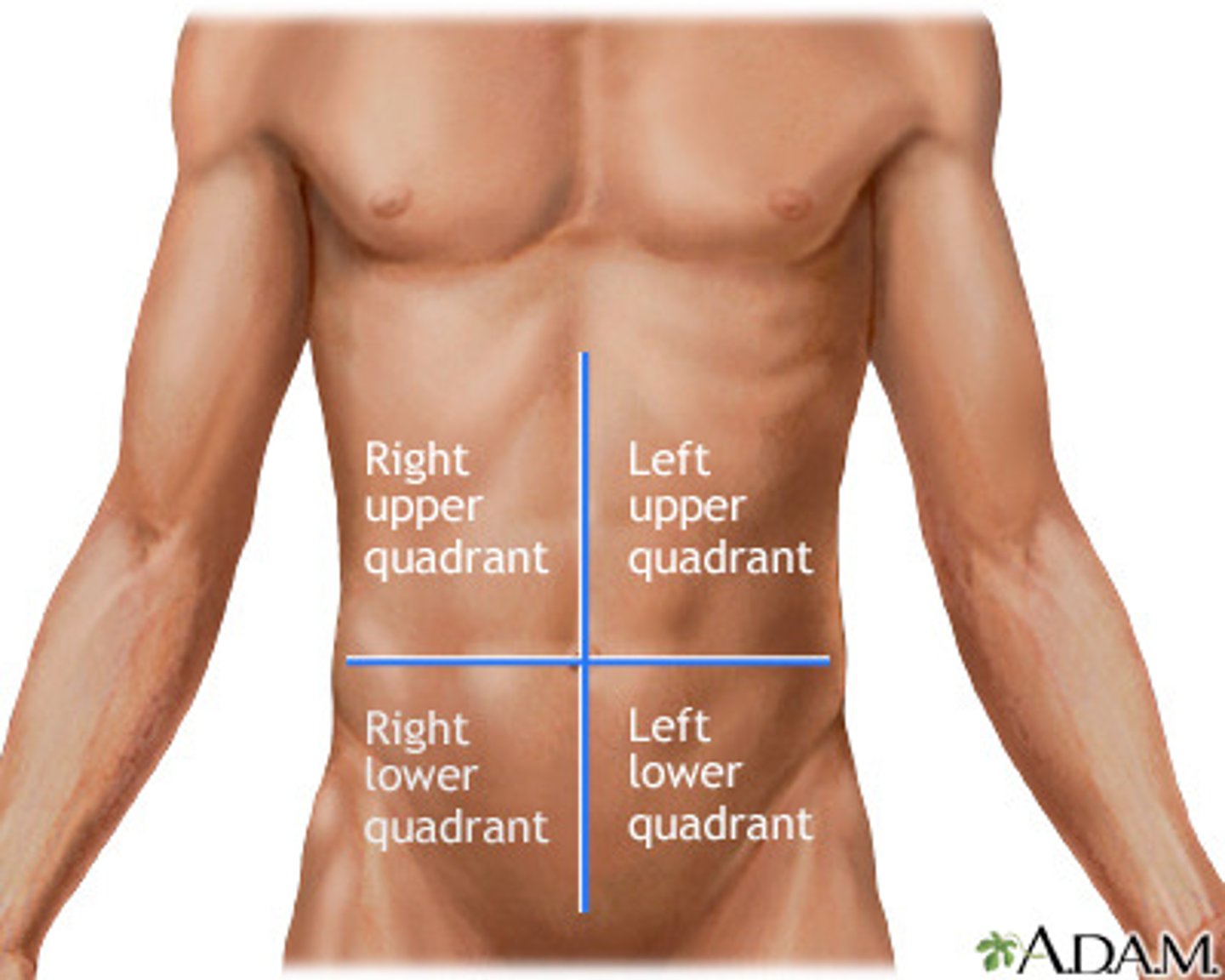
quadrant method
draw a horizontal line through the umbilicus and draw a vertical line down the midline of the body
- right upper quadrant
- left upper quadrant
- right lower quadrant
- left lower quadrant
the four quadrants in the quadrant method:
quadrant method
- gases
- liquids
- semi-solids
all materials needing to be aspirated can be simplified into 3 main categories:
left; umbilicus
The trocar is inserted two inches superior and two inches to the _______ of the subject's _____________. [HINT: their left]
trocar guide for the stomach
direct the trocar point toward the intersection of the 5th intercostal space and the left mid-axillary line; continue until the trocar enters the stomach
trocar guide for the cecum
direct the trocar toward a point ¼ of the distance from the right anterior superior iliac spine to the pubis symphysis; keep the point of the trocar close to the abdominal wall until within 2-4 inches of the right anterior superior iliac spine; dip trocar 2 inches and insert
trocar guide for the urinary bladder
direct the trocar toward the intersection of the median line and the pubic bone(symphysis pubis); keeping it toward the surface until it touches the pubic bone; withdraw it slightly (1/2 inch), dip the point slightly, and insert into the bladder
trocar guide for the heart
direct the trocar along a line from the left anterior superior iliac spine to the lobe of the right ear; keep the trocar point close to the surface of the abdominal wall until it pierces the diaphragm, and then dip the point downward and into the right side (key side)
hydrochloric acid, gases, undigested food, blood
materials needing aspiration from the stomach:
gases, undigested foods, partially digested foods, blood, fecal matter
materials needing aspiration from the cecum:
urine, pustular material, blood
materials needing aspiration from the urinary bladder:
blood
materials needing to be aspirated from the heart:
- cecum
- stomach
- heart
- urinary bladder
the four organs that have guides to allow for the embalmer to direct the trocar:
false
there is a specific order to aspiration (t/f)
true
several passages can be made through each organ (t/f)
true
all organs and the spaces between them need to be aspirated (t/f)
true
concentrated (undiluted) cavity fluid is always used (t/f)
16 oz; 2 total bottles
the rule of thumb is ____ oz. in each the thoracic and abdominal cavities. (___ total bottles)
- gravity injection (most common)
- machine injected
undiluted cavity fluid may be injected by two methods:
mass of tissue
the volume of chemical is determined by the ________ of __________ to be treated
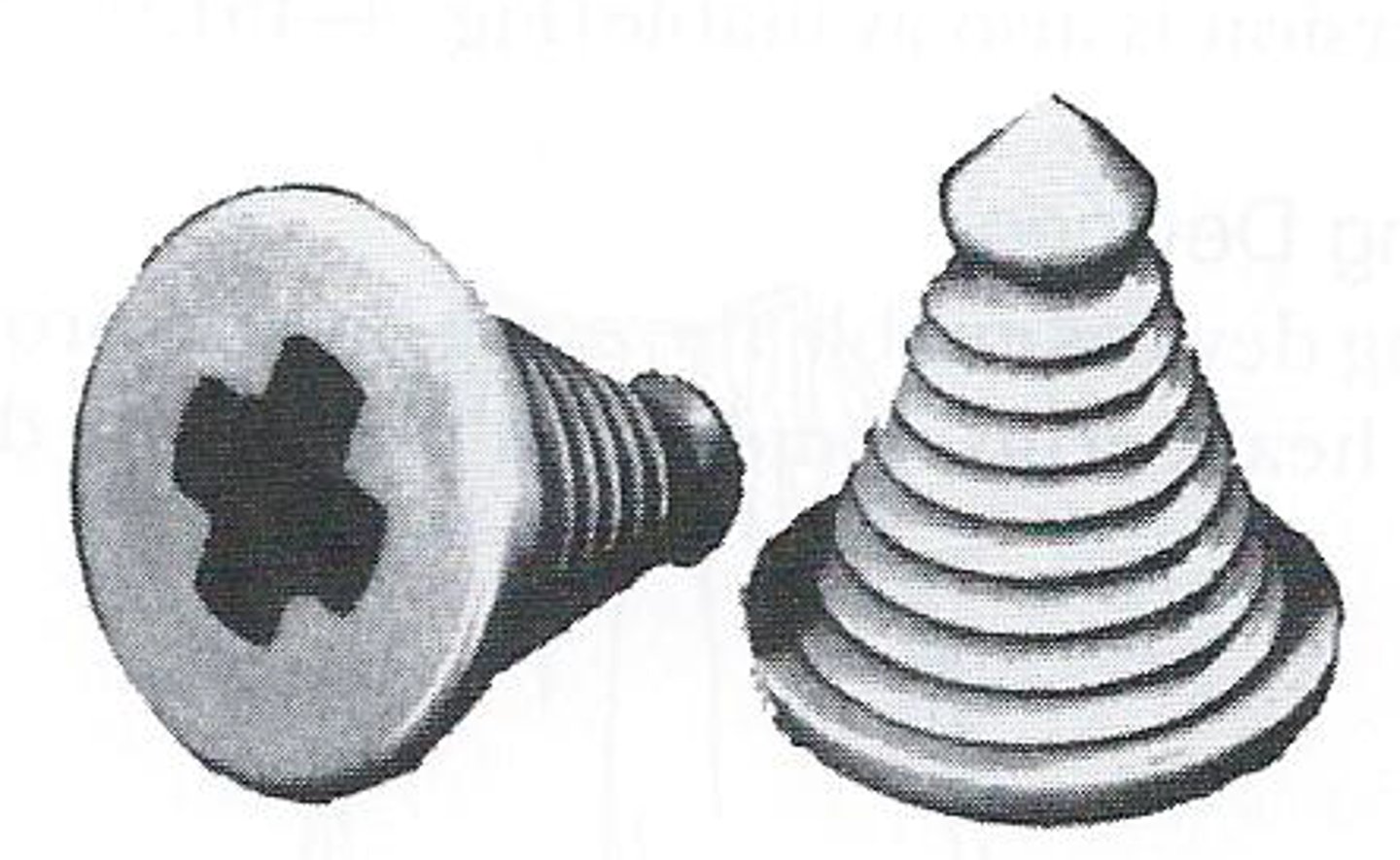
trocar button
provides complete closure and is easily removed if further aspiration and/or re-injection is necessary
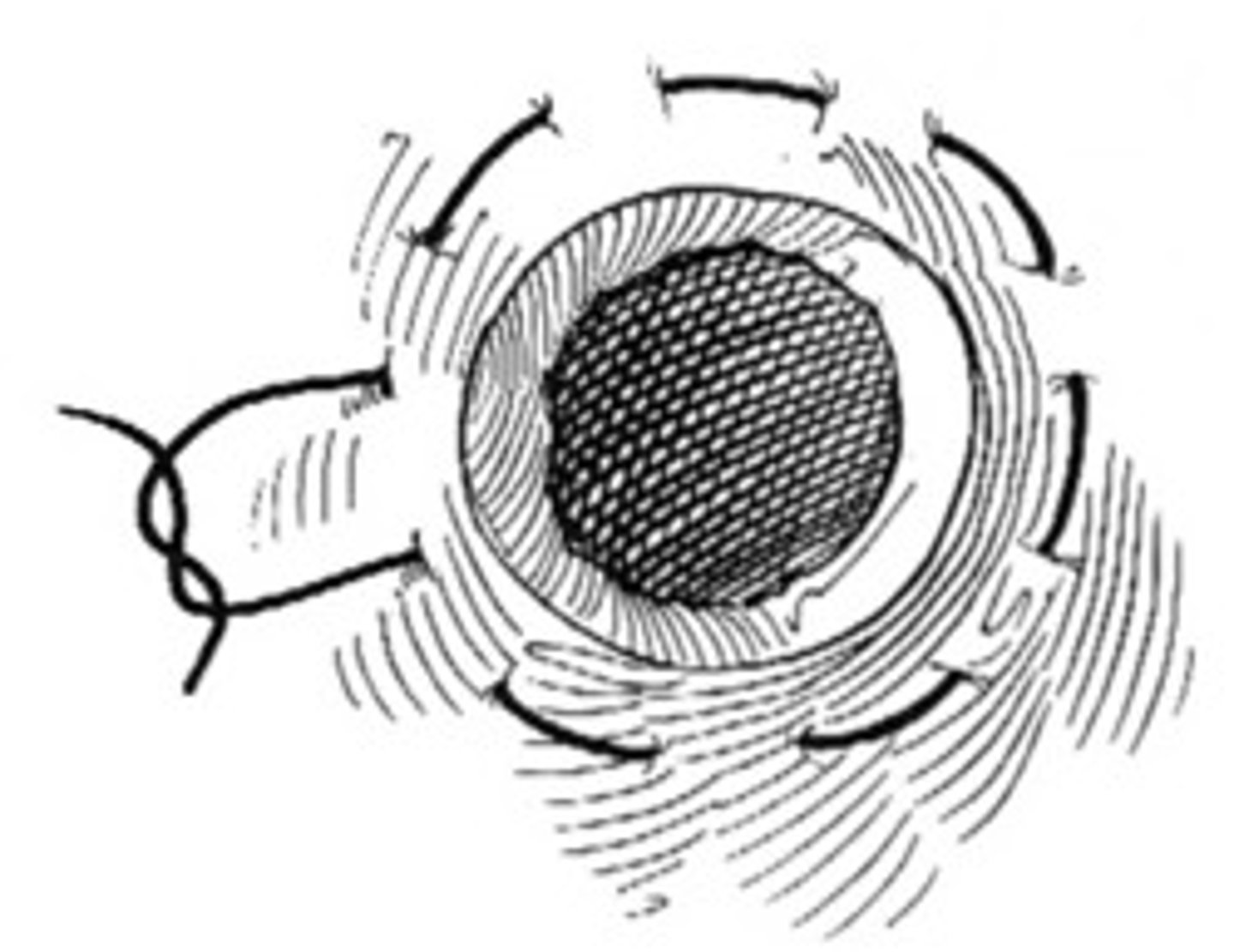
purse string suture
offers a complete closure; stitches are made around the opening, and the loose ends are pulled tightly when complete; a bow may be used to tie it; enabling re-opening if needed
• those in which gas formation causes distention or purge
• ship-out cases
• cases with advanced decomposition
• obese cases
• cases in which death occurred due to infectious disease
• cases with ascites present
cases for which reaspiration is common and recommended:
• diseases of the brain
• cerebral hemorrhage
• gas within the cranium
• trauma to the cranial cavity
• infant cases (remember: the infant brain has a tendency to decompose first)
examples of conditions requiring cranial cavity treatment include:
purge
the postmortem evacuation of any substance from an external orifice of the body due to pressure