Extensive Direct restorations and foundations
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Direct restorations definition?
ideal prep with minimal tooth structure involvement, amalgam, resin, GI
what is a complex prep design?
large amounts of tooth structure is missing due to
-caries
-previously placed material
-fractured tooth
what are the advantages of complex direct restorations?
-conservation of tooth structure
-one visit
- no extra lab fees
-reduction of weak cusp= increase in resistance form
definition of resistance forms?
the ability of the tooth and material to withstand forces directed along the long axis of the tooth
properties of the resistance form?
flat pulpal floors
cavity walls parallel to long axis
rounded internal line angles
adequate thickness of restorative material
reduction of cusps
preservation of cusps and marginal ridges when possible
what is retention definition?
ability of the tooth to retain the restoration when tipping or lifting forces are applied
-converging occlusal walls
-grooves, slots, boxes, pins
-adhesive system that bond restoration to tooth structure
how are resin composite restorations primarily retained in the tooth?
by micro mechanical bonding that is established between the restoration and the tooth structure
what does adhesive bonding allow for?
-more conservative tooth preps
-less removal of unsupported enamel
-depends on micromechanical
-less reliant on macromechanical
In direct restorations is the material completed during the visit?
yes.
prep will be completed and restoration is placed immediately
-light/chemical cure
-pt leaves with final restoration
what is the definition of an indirect restoration?
the prep is completed but the restoration is constructed outside the mouth
-restoration is cemented into prep: inlay, onlay, crown
-multiple appointments
indirect restorations designs: inlays def?
a restoration in which the cavity prep includes intracoronal preparation only, but is fabricated outside of the mouth and then cemented or bonded to the prep
indirect restorations designs: onlays def?
a restoration in which the cavity prep includes intracoronal prep with cuspal reduction but is fabricated outside of the mouth and cemented or bonded to the prep
indirect restorations designs: crowns def?
a restoration in which the cavity prep includes extracoronal prep and is fabricated outside of the mouth and then cemented or bonded to the prep
what does the prepped tooth need while the final restoration is being fabricated?
provisional or interim restoration
what material do we use for provisionals?
Protemp plus
what is a foundation or core build-up?
supporting direction restoration that will provide resistance and retention form to a broken down tooth so that it may accept a final indirect restoration such as a crown
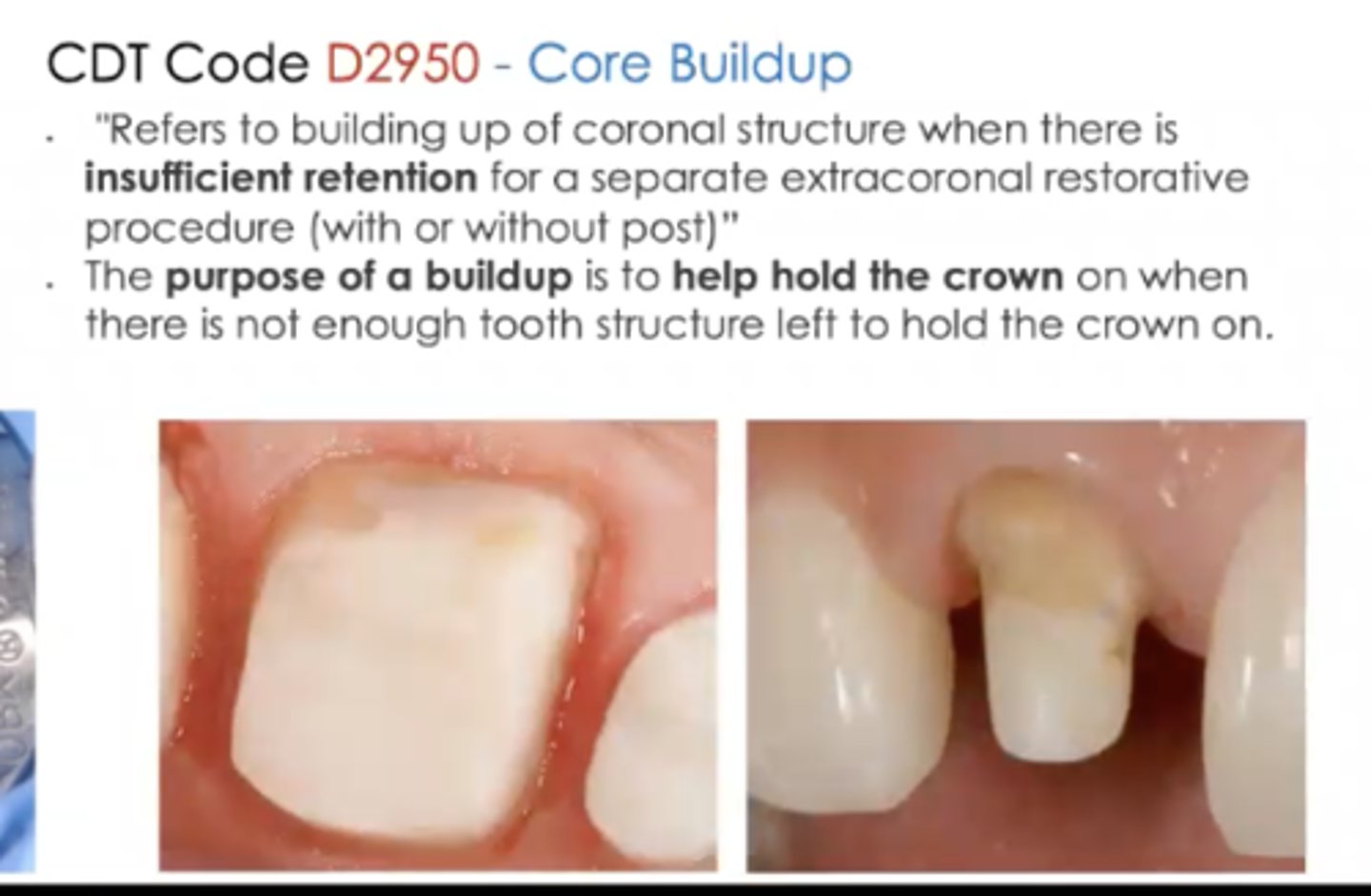
what are indications for foundations or core buildups for indirect restorations?
large amounts of tooth structure missing
tooth lacks resistance and retention for a indirect restoration
what does the foundation serve as?
in place of the missing tooth structure allowing for resistance and retention
-resin, amalgam, cast metal
should a core build-up be compromised with subsequent tooth prep for indirect restoration?
no. should not be compromised
when should a cusp be kept and when should it be removed?
decision to reduce a cusp should be approached judiciously
what is the most important aspect in evaluation of a wakened cusp?
remaining dentin support
-weakened and friable tooth structure should always be removed
if you increase the occlusal load, what happens to the potential future fracture?
it increases
the more posterior the tooth is, the higher the occlusal load
when should a cusp tip be kept vs removed?
1/2-2/3: consider reduction
2/3 or more: recommend reduction
what is the exception to reducing a cusp?
where the extension has been two thirds from a primary groove toward the cusp tip, is where there is adequate dentin support
what are types of auxiliary retention?
grooves, boxes, slots, pulp chambers, pins
what is a dentin slot?
horizontal areas where no vertical walls remain
-length varies
-1mm wide and deep
-inverted cone bur
-0.5-1mm from DEJ
what is pulp chamber retention?
in multirooted, endodontically treated teeth
-2-4 mm extension of the foundation into canal spaces
what is a post?
cemented into canals of endodontically treated teeth can also be used
when are pins used?
in amalgam build-ups
components of the self threading pin systems
-depth limiting drill: used to cut the pin channel
-TMS link PLus pin
what should the angulation of the pin channel for a threaded pin be?
parallel to the nearest external tooth surface to avoid external perforation of the tooth
Pin is placed in a _______ and _________ is activated until pin shears
hole
handpiece
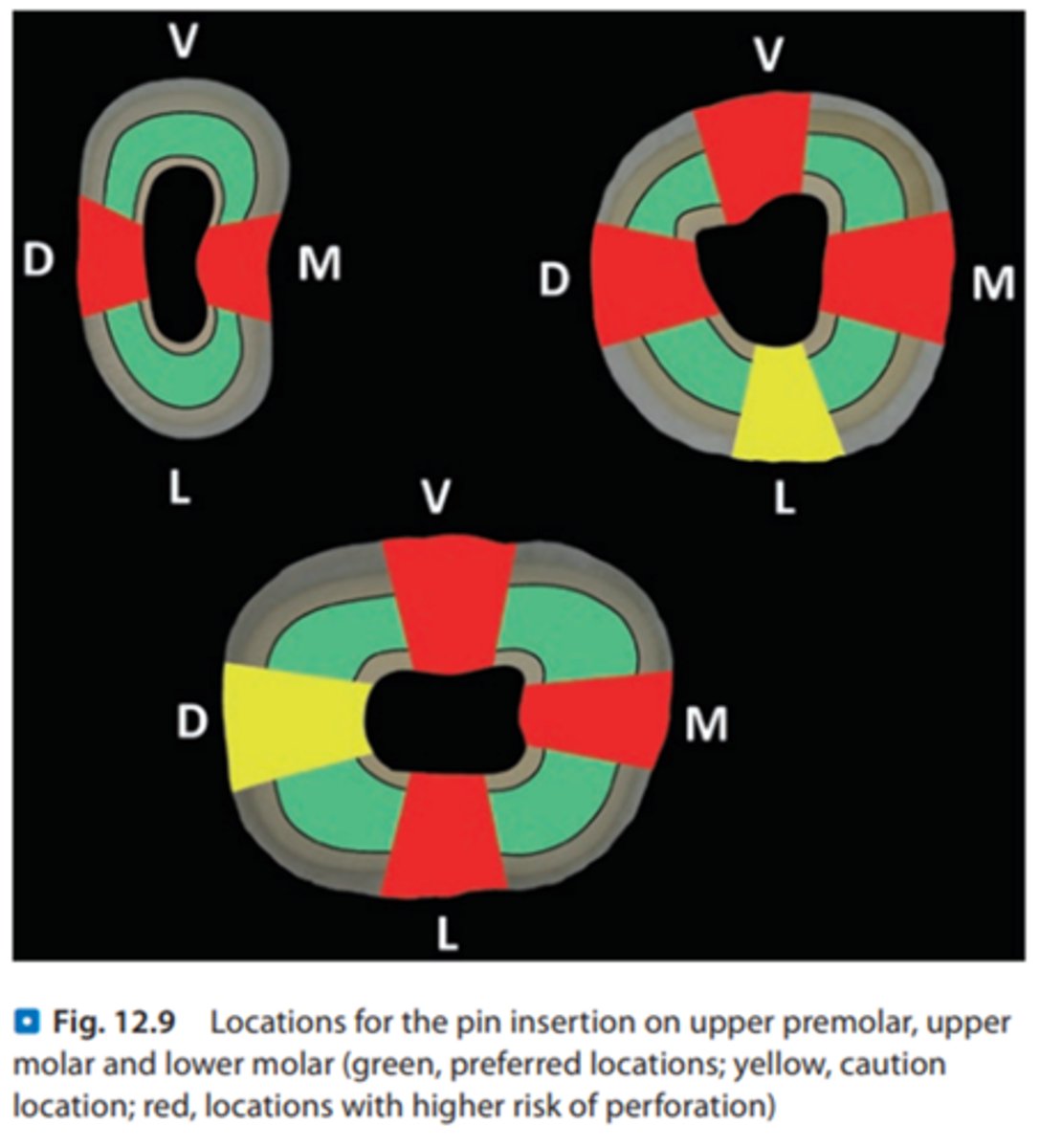
where to place pins?
Yellow, not the best: distal of mandibular and Lingual of maxillary
avoid the areas in red: L,M,B of mandibular and DMB of maxillary
good: in btwn these areas