Ch 26 Bacteria and Archaea (Prokaryotes)
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What are prokaryotes?
Organisms that do not have a membrane bound nucleus
True or False: Most Prokaryotes are unicellular
True
What are the 2 main domains of prokaryotes?
Archaea and bacteria
Fill on the Blank: Archaea and Bacteria lack a _______ _____ but both have a _______ ______
Nuclear Envelope
Plasma Membrane
What is microbiology?
The study of organisms that can be seen only w/ the aid of a microscope
Fill in the Blank: Some Prokaryotes thrive in extreme environments; they are known as _______
Extremophiles – bacteria or archaea that live in high-salt, high-temp/low-temp, or high-pressure habitats
True or False: We can’t find much information on prokaryotes to help us understand the past.
False: Studying them have been helpful for understanding the tree of life, developing industrial applications, and exploring the structure and function of enzymes
What are the ways that studying prokaryotes have helped us?
Origin of Life – the first forms of life prolly lived in extreme conditions so it could help explain the beginning of life
Extraterrestrial life – if other prokaryotic cells can thrive in extreme habitats
Commercial Applications – bc enzymes that function at extreme temps and pressures are useful in many industrial processes, they are of commercial interest
Medical Importance - Thousands of bacteria species live in and on the body, but only a small faction can disrupt the body’s function enough to cause illness
What are pathogens?
Bacteria that cause disease
How do we characterize prokaryote diversity?
Genetic, physiological, morphological, molecular characteristics
Fill in the Blank: Bacteria can be shaped like ____ (bacilli), _____ (Cocci), and______ (helical)
Rods
Spirals
Helical
Bacteria can swim, but how? Bacteria can glide, but how?
Bacteria can swim with rotating flagella
Bacteria can glide, but we don’t know how yet
In what ways can we test prokaryote diversity?
Enrichment Culture - a method of detecting and obtaining cells w/ specific characteristics by placing a sample, containing many types of cells under a specific set of conditions and isolating those cells that grow rapidly in response
Metagenomics - method to catalog all the genes present in a mixed community of prokaryotes by extracting and sequencing DNA from an environmental sample that contains numerous unknown species
Direct Sequencing - a technique based on isolating and sequencing a specific gene from organisms found in a particular habitat
What is bioinformatics?
A discipline concerned w/ the storage, analysis, and presentation of biological data
In what ways can we find the differences between Bacteria and Archaea?
Cell membranes, cell walls, metabolic diversity, genetic machinery for making proteins
Bacteria and Archaea have different plasma membranes but why?
Bacteria - plasma membranes that contain phospholipids w/ ester bonds
Archaea - plasma membranes that have unique lipids that cotain ether bonds
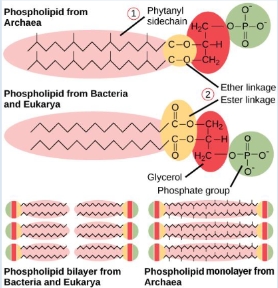
True or False: Ether bonds in Archaea are more stable which allows it to survive in extreme conditions
True
What are the differences in cell wall of Bacteria and Archaea?
Bacteria - presence of peptidoglycans
Archaea - no peptidoglycans, but still cell walls
True or False: The presence of peptidoglycans affects the response to external environements
True
What is a grain stain?
how biologists distinguish bacteria using a dyeing system that relies on the presence of peptidoglycan in the cell walls
What are the two types of results that come from a grain stain?
Gram-Positive (purple) – cells that have a plasma membrane surrounded by a cell wall w/ extensive peptidoglycan
Gram-negative (pink) – have a plasma membrane surrounded by a cell wall that has two components a thin layer containing peptidoglycan and an outer phospholipid layer
How can we use genetic machinery for making proteins to differentiate between archaea and bacteria?
RNA Polymerase - Archaea have a single type w/ 13 subunits, bacteria have a simpler type w/ only 5 subunits
First Amino Acid in Translation during protein synthesis - Bacteria starts w/ formyimethionie and archaea starts w/ methionione
Histones - Archaea have histones associated w/ their DNA but bacteria do not
Why is protein important?
Protein leads to potential growth and reproduction
Why are bacteria and archaea masters of metabolism?
Bc they can subsist on almost anything
How do both domains acquire energy to produce ATP in 3 ways?
Phototrophs “light feeders” - use light energy to excite electrons so ATP is produced by photophosphorylation
Chemoorganotrophs “chemical-carbon-feeders" - oxidize organic molecules w/ high potential energy like sugars, and ATP may be produced by cellular respiration w/ sugars serving as electron donors or via fermentation pathways
Chemolithotrophs “chemical-rock-feeders" - oxidize inorganic molecules w/ high potential energy, so ATP is produced by cellular respiration and inorganic compounds serve as the electron donor
What are the 2 ways do bacteria and archaea obtain building-block compounds?
Autotrophs “self-feeders” - synthesize their own compounds from simple starting materials such as carbon dioxide and methane
Heterotrophs “other-feeders” - absorb ready-to-use organic compounds (building-block compounds) produced by other organisms in their environment
True or False: Lateral gene transfer is central to the evolution of bacteria and archaea bc prokaryotes can acquire diverse traits
True
What is the process of lateral gene transfer in bacteria and archea?
Transformation – when bacteria or archaea naturally take up DNA from the environment that has been released by cell lysis or secreted
Transduction – when viruses pick up DNA from one prokaryotic cell and transfer it to another cell
Conjugation – when genetic info is transferred by direct cell-to-cell contact
How can conjugation happen?
Plasmid – a small circular piece of DNA that is copied in once cell and transferred to the other cell
Can result in genetic recombination when a plasmid that has become integrated into the main bacterial chromosome is copied and transferred, along w/ the genes from the main bacterial chromosome, to a recipient cell
True or Fals: Sexual reproduction happens in prokaryotes
False; it doesn’t happen bc they are haploid throughout their lives
True or false: Genes can move from one individual to another via conjugation
True
What is true about Archaea?
No pathogens/parasites
Some are symbiont (mutualistic +/+ relationship)
Primarily Exdtremeophiles
What are teh 4 types of Archaea?
Thermophiles
Acidophiles
Halophiles
Methanogens
Archaea: What are thermophiles and their conditions?
Live in extremely high temps (140 – 175 degrees farenheight or 60 to 80 degrees celsius)
Ex: Hot springs, geysers, hydrothermal vents (oceanic)
Heat stable enzymes allow for organisms to have normal metabolism/growth/and reproduction in high temps
Archaea Types: Acidophiles
Live in extremely low pH (Acidic; pH less than 2)
Naturally acid environments like pine forests, bogs, not natural but still acid mine drainage (AMD)
Food: Sour cream, yogurt, buttermilk
Archaea Types: Halophiles
Live in extremely high salinity
35-40% of salinity
Natural Saline Habitats – great salt lake, dead sea
Foods: Soy sauce, sauerkraut, kimchi
Archaea Types: Methanogens
Produce Methane, which is a atmospheric greenhouse gas
Methane Production
Natural sources (36%): wetlands, ocean archaea, termite guts
Human Driven (64%): Livestock digestive tract which are loaded w/ archaea that helps w/ digestion of plant matter, landfills and dumps create biogas energy
Number 1 Source of Methane production (not associated w/ archaea) is Fossil Fuel Combustion
Bacteria types: Phylum Actinobacteria
Gram positive
Filamentous, forming branching species
Important agriculture, human health, forest areas bc they are abundant in soil and are important decomposers of dead plant and animal material
Free living Actinobacteria: Organic Matter Decomposition (Soils) and Nutrient Cycling
Mutualist (+/+)
Forms Biofilms - when bacteria secrete polysaccharide matrix and other organisms colonize on it (dental plaques)
Used in Bioremediation - process to clean up soil/water contamination from heavy metal
Bacteria Types: Phylum Cyanobacteria
Gram negative
Found as independent cells, in chains that form filaments, or in loose aggregation of individual cells called colonies
Most abundant
“Blue Green Algae”
Photosynthetic Bacteria – they produce much of the oxygen, nitrogen, and organic compounds that feed organisms living in freshwater and marine environments
Strongly associated w/ algal blooms and poor water quality
Abundant where N and P at High Levels (Eutrophication)
Bacteria types: Phylum Firmicutes
Gram-positive
Extremely common in intestine where they live in symbiotic mutualism, aiding the digestive process
Many used in biological control
Used to control/kill another type of organism (Bacillus Thuringiensis (Bt))
Respiratory (Streptococcus Pneumoniae)
Cheeses, yogurt (Streptococcus Thermophilus)
Skin Infections (Streptococcus Aureus)
Bacteria Trypes: (Phylum) Proteobacteria
Gram negative
Diverse in morphology and metabolism
Geobacter Netallireducens (cleans up uranium)
E Coli (Critical to digestive processes in mammals, common in sewage water pollution)
Yersinia Pestis (causes disease like bubonic, black plague, pneumonic (respiratory infection)
Used in Bioremediation