Comprehensive Review of Atmosphere, Water Cycle, and Earth Mechanics
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
What is the definition of weather?
The state of the atmosphere at a given time and place, including temperature, air pressure, humidity, cloudiness, and wind speed and direction.
How is climate defined?
The average weather over a long period of time.
Why is water important in the Earth's system?
Water covers 70% of the Earth's surface, is a powerful greenhouse gas, and can exist in three phases (solid, liquid, gas) at the same temperature.
What is sensible heat?
The transfer of energy resulting in a change of temperature.
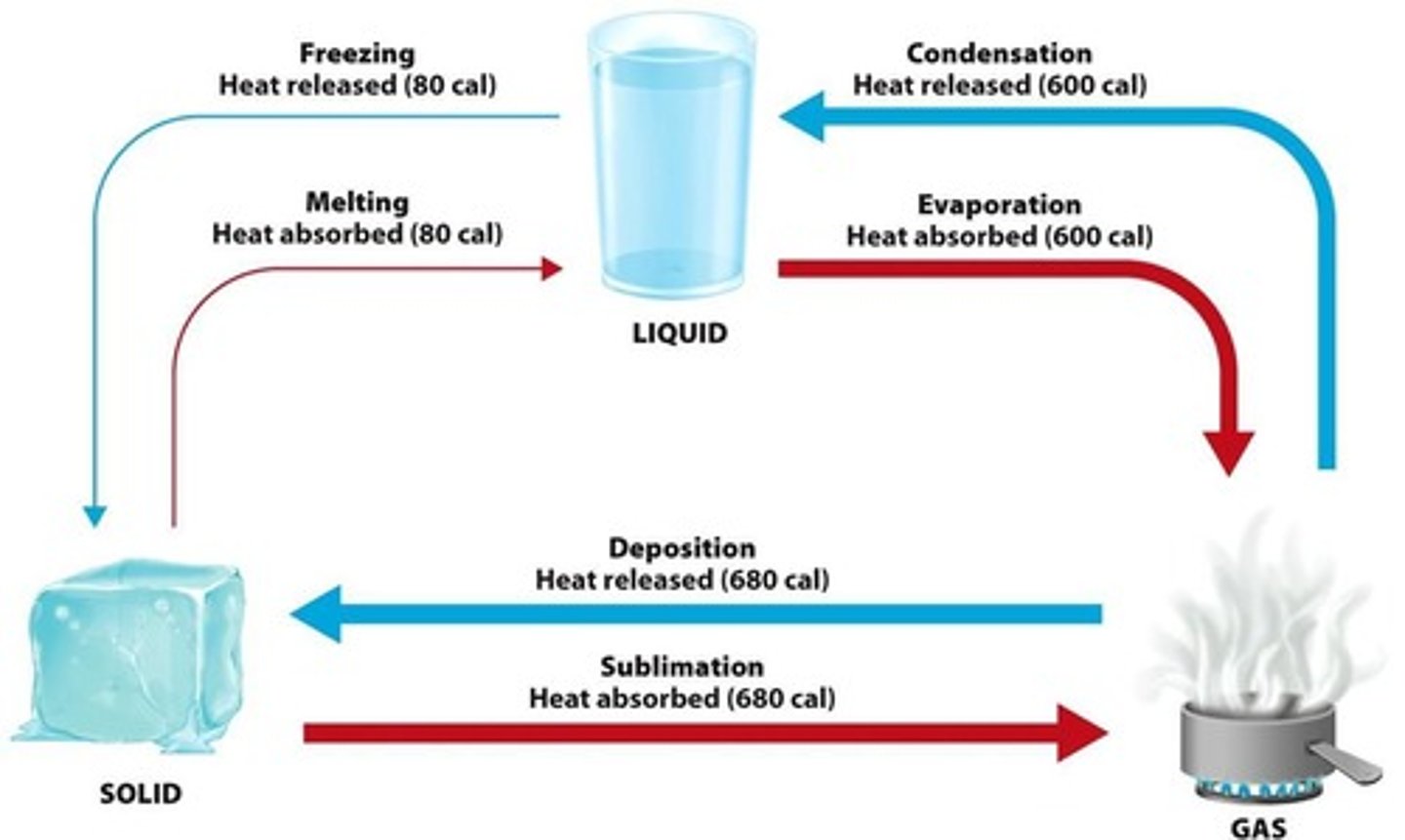
What is latent heat?
Energy required or released to change the phase of a substance without changing its temperature.
What are the three methods of heat transfer on Earth?
1. Radiation - energy moving between two points without requiring material. 2. Conduction - energy moves but the material itself does not. 3. Convection - energy moves with material.
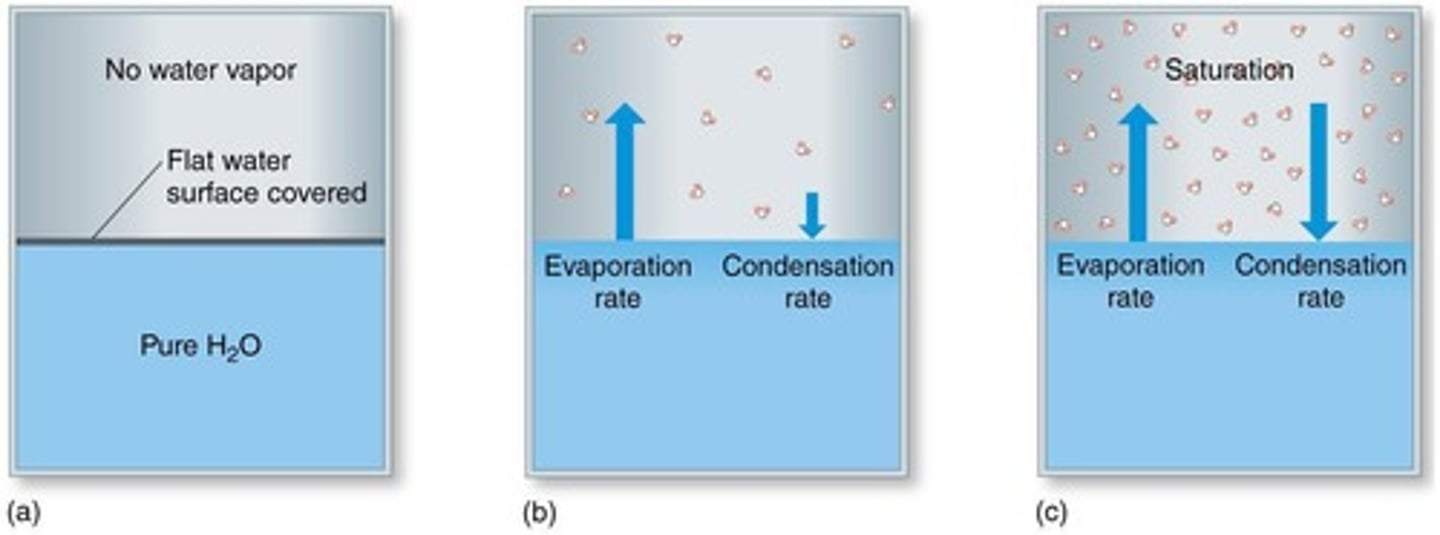
What is vapour pressure?
The pressure of a gas above a liquid.
What is equilibrium in the context of evaporation and condensation?
The rate of evaporation equals the rate of condensation.
What is saturation in atmospheric moisture?
The maximum amount of water in the gaseous phase at a given temperature.
What does relative humidity measure?
The amount of water in the air expressed as a percentage of the maximum amount possible.
How do you calculate relative humidity?
Relative Humidity = (actual vapour pressure / saturation vapour pressure) x 100%.
What happens to vapour pressure when temperature increases?
The air becomes undersaturated, allowing more evaporation if water is available.
What occurs when air is supersaturated?
Condensation will take place until the air reaches saturation.
What is the adiabatic lapse rate for unsaturated air?
The temperature drops at a rate of 10°C per kilometer as the air rises.
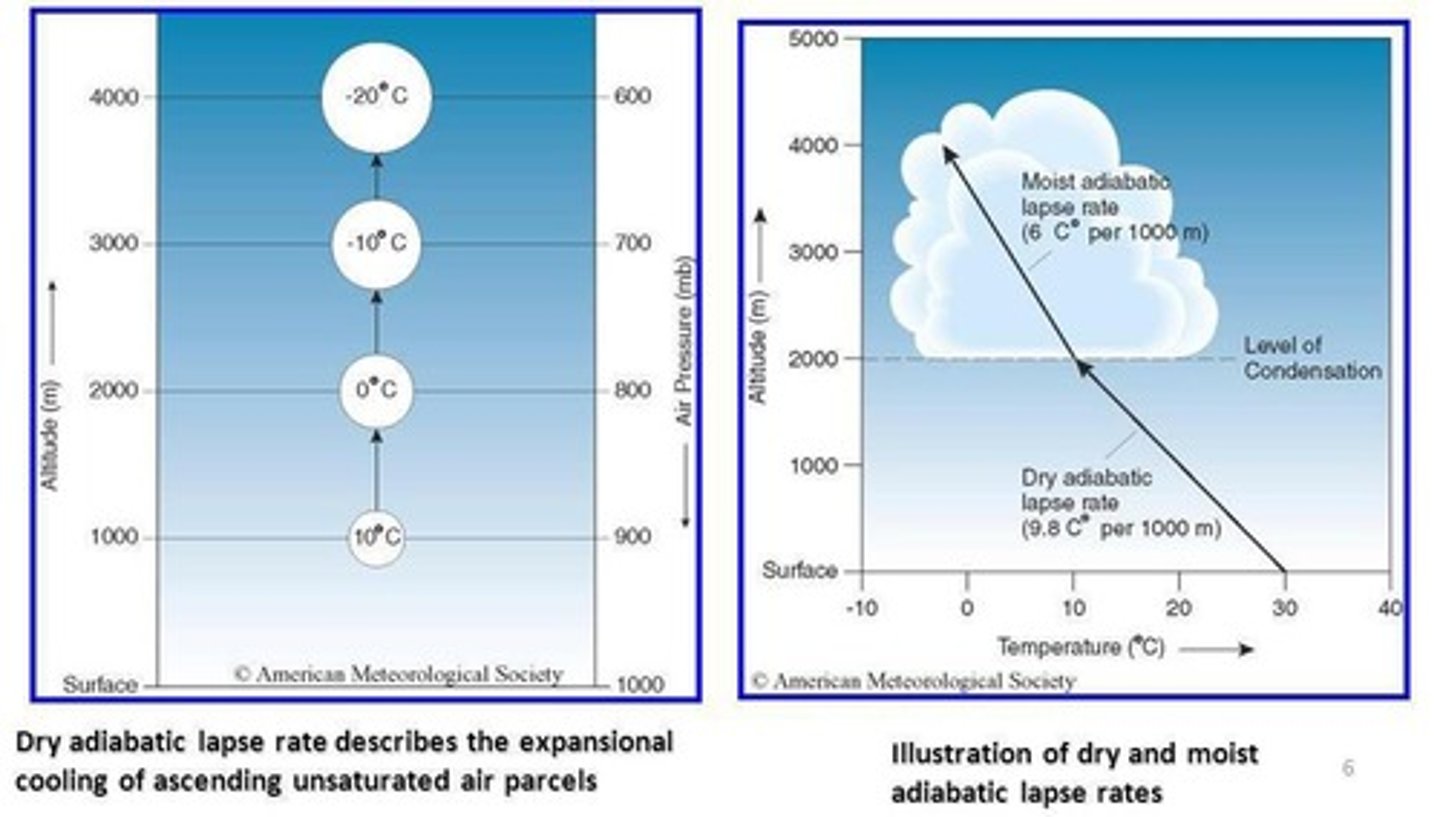
What is the adiabatic lapse rate for saturated air?
The temperature drops at a rate of 6°C per kilometer as the air rises.
What happens to air as it rises and cools?
The temperature drops, relative humidity rises, and condensation starts at the dew point.
What is the role of latent heat during condensation?
Latent heat is released
What are diabatic processes?
Processes where energy is removed from or added to a system, affecting temperature.
What are adiabatic processes?
Processes that do not involve the addition or removal of energy, focusing on changes in pressure.
What is the significance of the solar constant?
It represents the amount of solar energy received per unit area at the top of the atmosphere.
What is the relationship between temperature and saturation vapour pressure?
Saturation vapour pressure increases with temperature.
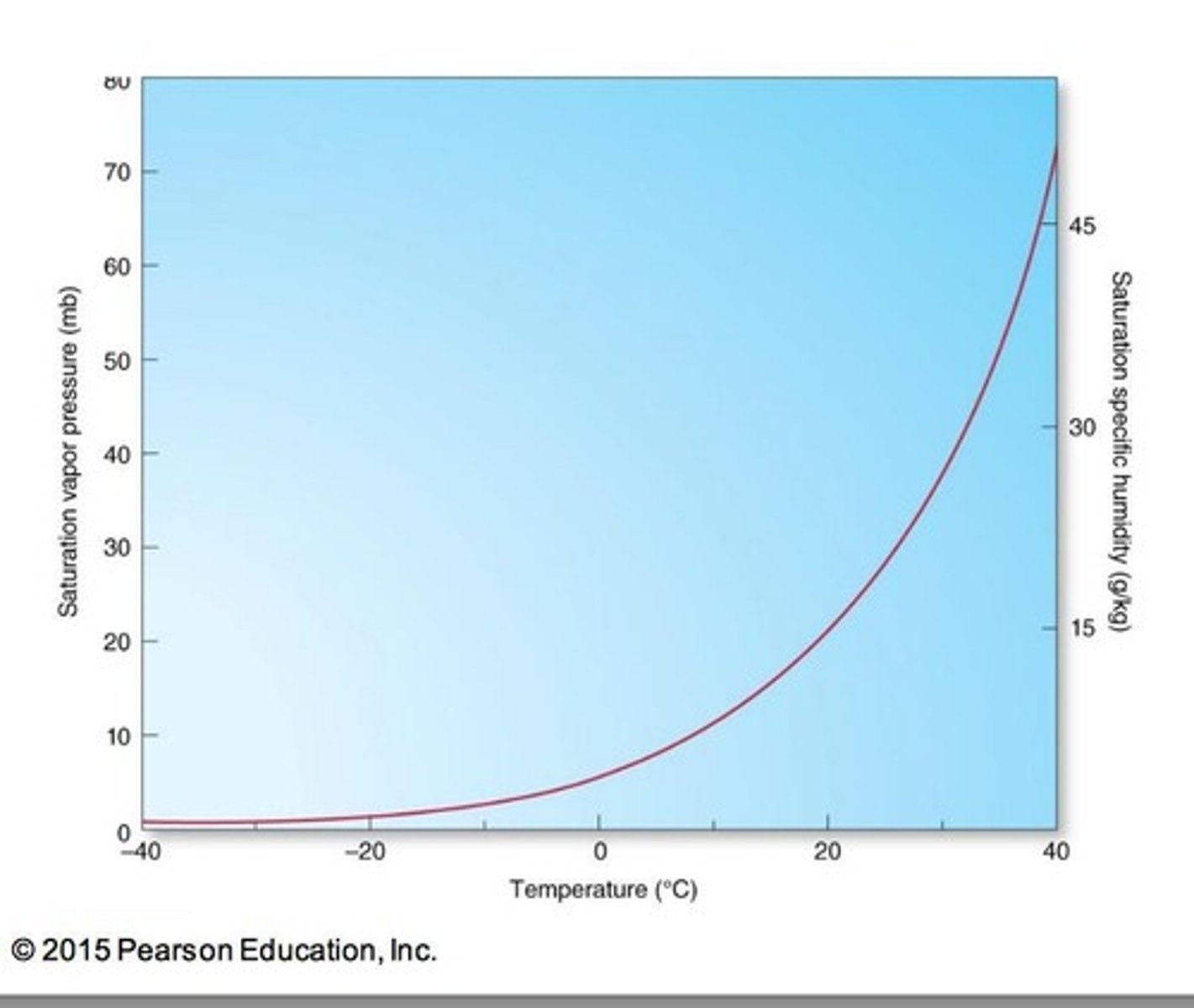
How can air be saturated with water vapour?
By adding water vapour to the air or decreasing the air temperature.
What is the specific heat capacity of water?
The energy required to raise 1 gram of water by 1°C is 4190 J/kg/K.
What is the latent heat of vaporization for water?
The energy required to vaporize water is 2,500,000 J/kg.
What happens when warm and cold air mix?
It can lead to changes in temperature and humidity, affecting weather patterns.
What is the dew point temperature?
The temperature at which air becomes saturated with moisture, leading to condensation.
What happens to temperature as unsaturated air rises?
Temperature drops
What occurs when rising air reaches its dew point?
Condensation starts
What is released during condensation?
Latent heat
How does latent heat affect the rate of cooling?
It decreases the rate of cooling
What is the definition of climate?
The long-term average of weather patterns
What is the solar constant?
The nearly constant amount of solar energy reaching Earth's upper atmosphere
What are the three main mechanics of Earth's orbit affecting seasons?
Revolution, rotation, and tilt
What is the tilt of the Earth that causes seasons?
23.5 degrees
How does the tilt of the Earth affect solar energy?
It influences the period of daylight, solar angle, and atmospheric beam depletion
What is the dry adiabatic lapse rate?
The temperature change of unsaturated air as it rises
What is the moist adiabatic lapse rate?
The temperature change of saturated air as it rises after condensation
What is relative humidity?
The ratio of actual vapour pressure to saturation vapour pressure, expressed as a percentage
What happens to clouds when air reaches saturation?
Clouds form as water vapour condenses
What is the effect of high clouds on Earth's temperature?
They trap heat and warm the Earth
What is the effect of low clouds on Earth's temperature?
They reflect sunlight and cool the Earth
What is the significance of water vapour in the atmosphere?
It is a powerful greenhouse gas influencing global climate
What is the relationship between cloud cover and albedo?
Cloud cover influences albedo, which affects radiation balance and temperature regulation
What is the process of convection in the atmosphere?
Heat transfer by the movement of air or fluid
What is conduction in the context of atmospheric energy transfer?
Heat transfer through direct contact
What is radiation in the context of atmospheric energy transfer?
Transfer of energy through space, such as sunlight
What is latent heat flux?
Energy used in phase changes, stored without changing temperature
How does Earth's revolution affect sunlight?
It causes seasonal and daily variations in sunlight
What three mechanics of Earth affect the experience of day/night and seasons?
Revolution, rotation, and tilt.
What is the angle of Earth's tilt?
23.5 degrees.
How does Earth's tilt affect solar energy distribution?
It influences the period of daylight, solar angle and beam spreading, and atmospheric beam depletion.

What is beam spreading?
The way a light beam covers a larger area when it hits a surface at an angle.
What happens to solar energy during atmospheric beam depletion?
Less direct sunlight passes through more of the atmosphere, resulting in energy loss.
What are the five major reservoirs of Earth?
Atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, and anthroposphere.
What percentage of Earth's surface is covered by water?
71%.
What is the hydrological cycle?
The fixed amount of water that circulates between the atmosphere, ocean, cryosphere, pedosphere, and biosphere.
What defines a stream?
Water that flows downslope in a clearly defined and natural passageway or channel.
What is runoff?
Precipitation or snowmelt that does not infiltrate the ground and travels downslope until it enters a stream.
What is a drainage basin?
The total area that contributes water to a stream.
How do plate tectonics and topography influence drainage regions?
They create drainage basins.
What is the significance of the cryosphere in freshwater distribution?
It plays a role in the proportions of fresh versus saline water, especially during ice ages.
What is the main cause of the seasons on Earth?
Earth's tilt affects the amount of solar energy reaching different locations throughout the year.
What is the relationship between solar angle and beam spreading?
A smaller angle with the horizon results in more beam spreading and less concentrated solar energy.
What is the role of gravity in the hydrological cycle?
It helps in the movement of water through various reservoirs.
What is the biosphere?
All of Earth's organisms and any organic matter that has not decomposed.
What is the pedosphere?
The layer of aggregated and decomposed (weathered) rock debris at the surface of exposed landmasses.
What is the geosphere?
The solid Earth, including the lithosphere, mantle, and core.
What is the anthroposphere?
The part of the environment made or modified by humans.
What is the significance of the Earth's surface distribution of water?
It highlights that water covers 71% of the surface while land covers 29%.
What is a river delta?
A landform created where a stream enters a standing water body, losing energy and depositing its load.
What factors control stream behavior?
1. Average width and depth of the channel 2. Channel gradient 3. Average velocity 4. Discharge 5. Sediment load
How is channel gradient defined?
It is the vertical distance the channel descends per horizontal distance traveled, indicating how steep the channel is.
What is discharge in the context of streams?
The volume of water flowing per second, calculated as discharge = velocity × width × depth.
What are the three types of sediment load in streams?
1. Bed load (large particles along the stream bed) 2. Suspended load (fine particles in the water) 3. Dissolved load (dissolved materials in water)
What is the Hjulström curve?
A graph that illustrates the relationship between flow energy and the erosion, transport, and deposition of different grain sizes.
Where is stream velocity typically fastest?
In the middle of the channel, away from the banks, due to reduced friction.
What is the importance of sediment load in streams?
Sediment load redistributes material and affects the stream's behavior and ecology.
What is the relationship between stream velocity and friction?
Increased friction slows the stream, while reduced friction allows for faster flow.
What defines a drainage basin?
The land area that feeds a stream, with divides marking the boundaries.
What happens to rainfall in a hydrologic cycle?
Rainfall partitions into runoff, infiltration, subsurface flow, evapotranspiration, and, in cold regions, snow/ice storage.
How does vegetation affect infiltration capacity?
Infiltration capacity rises with vegetation and soil biota, and decreases with bare or compacted soils.
What are braided streams characterized by?
Steep gradients, highly variable flows, and abundant coarse sediment, often found near glaciers.
What are meandering streams known for?
Transporting finer sediment and alternating between riffles (shallow areas) and pools (deep areas).
What is lithification?
The process of compaction and cementation that turns sediments into sedimentary rocks.
What is the significance of the solar constant in Earth's climate?
It is roughly steady and influences seasons through Earth's revolution, rotation, and axial tilt.
What does the term 'hydrologic budget' refer to?
The balance of inflow and outflow of water in a given area, considered steady when ΔStorage is approximately zero.
What is the role of the channel width and depth in stream behavior?
They influence the average velocity and discharge of the stream.
What happens to sediment when a stream enters standing water?
The stream loses energy, slows down, and deposits its sediment load, forming a delta.
What is the impact of impervious surfaces on infiltration?
Impervious surfaces, like roads, decrease infiltration capacity, leading to increased runoff.