Understanding Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What are the characteristics of neurodegenerative diseases?
They are usually progressive, can eventually be fatal, and each has its own pattern of illness.
Who first documented Alzheimer's Disease and when?
Alois Alzheimer described the first documented case on 3rd November 1906.
What are the primary symptoms of Alzheimer's Disease in Stage I?
Impaired short-term memory, spatial perception, concentration, and personality changes.
What are the symptoms of Alzheimer's Disease in Stage II?
Progressive decline in memory, intellectual decline, fatigue, disorientation, and blunting of emotion.
What is the mean survival rate after detection of Alzheimer's Disease?
7 years.
What brain structures are particularly at risk in Alzheimer's Disease?
Cerebral Cortex, Basal forebrain, and Hippocampus.
What role does the Basal forebrain play in Alzheimer's Disease?
It contains large numbers of neurons with acetylcholine, which is important for memory and learning.
What is the significance of the hippocampus in Alzheimer's Disease?
It is essential for memory storage and shows reduced volume in Alzheimer's Disease.
What changes occur in cholinergic pathways in Alzheimer's Disease?
There is a correlation between cognitive deficit and cholinergic loss, leading to reduced acetylcholine synthesis.
What is the impact of lesions in cholinergic innervation of the hippocampus?
They lead to learning and memory deficits.
How can memory deficits caused by cholinergic loss be restored?
By using drugs that enhance cholinergic transmission.
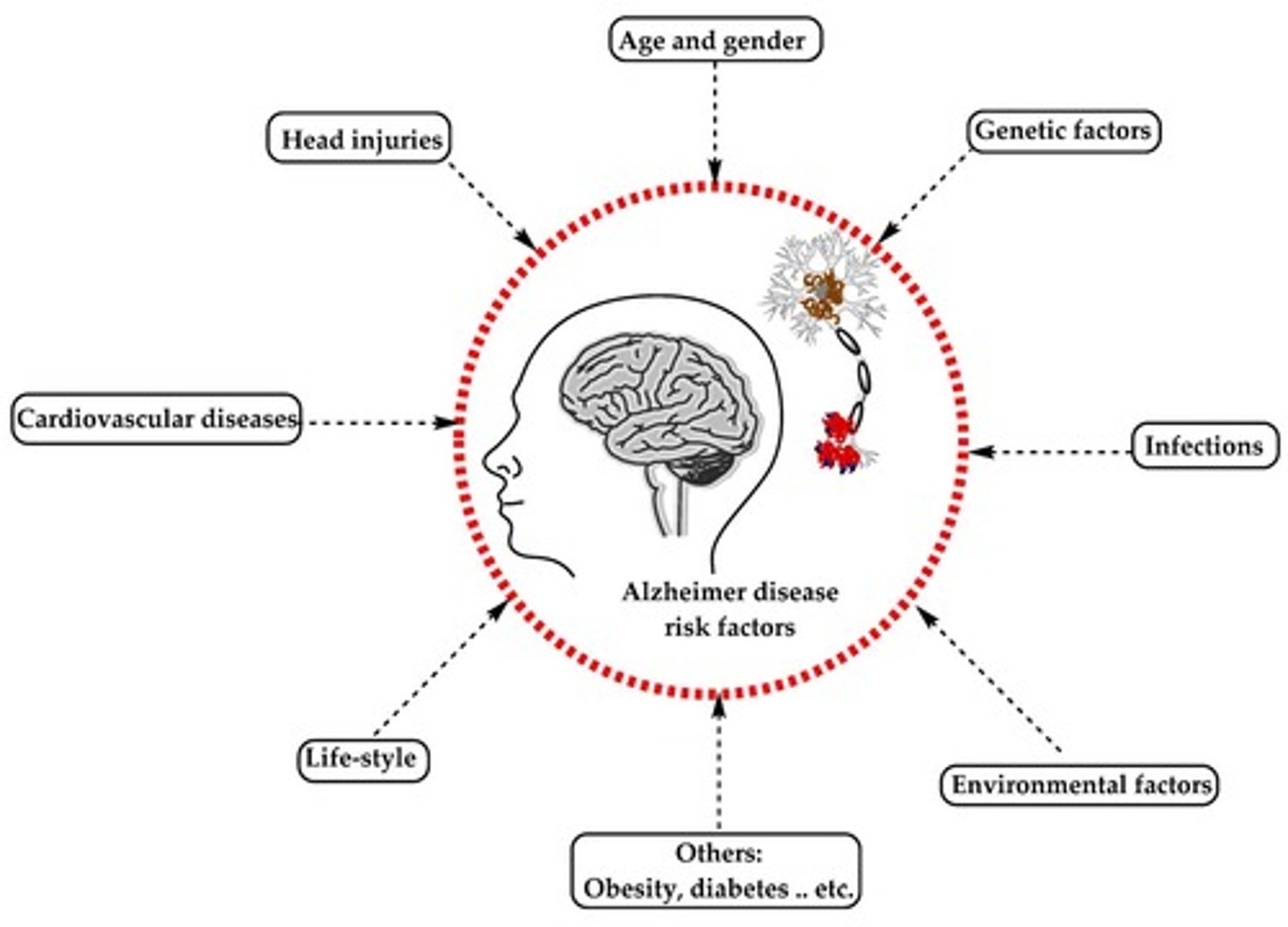
What are some risk factors associated with Alzheimer's Disease?
Poor cerebral perfusion, head trauma, female gender, environmental factors, and genetic predispositions.
What is the relationship between Alzheimer's Disease and brain metabolism changes?
Changes in brain metabolism can be observed through techniques like positron emission tomography (PET scan).
What does a PET scan reveal in an Alzheimer's brain compared to a normal brain?
Dark colors denote inactive areas, indicating cortical degeneration.
What percentage of brain weight loss is associated with Alzheimer's Disease?
30-40% loss of brain weight, including neurons, synapses, and fibers.
What are common cognitive deficits associated with Alzheimer's Disease?
Amnesia and confusion.
What is the role of acetyltransferase (ChAT) in Alzheimer's Disease?
Reduced ChAT activity results in decreased acetylcholine synthesis, impacting memory.
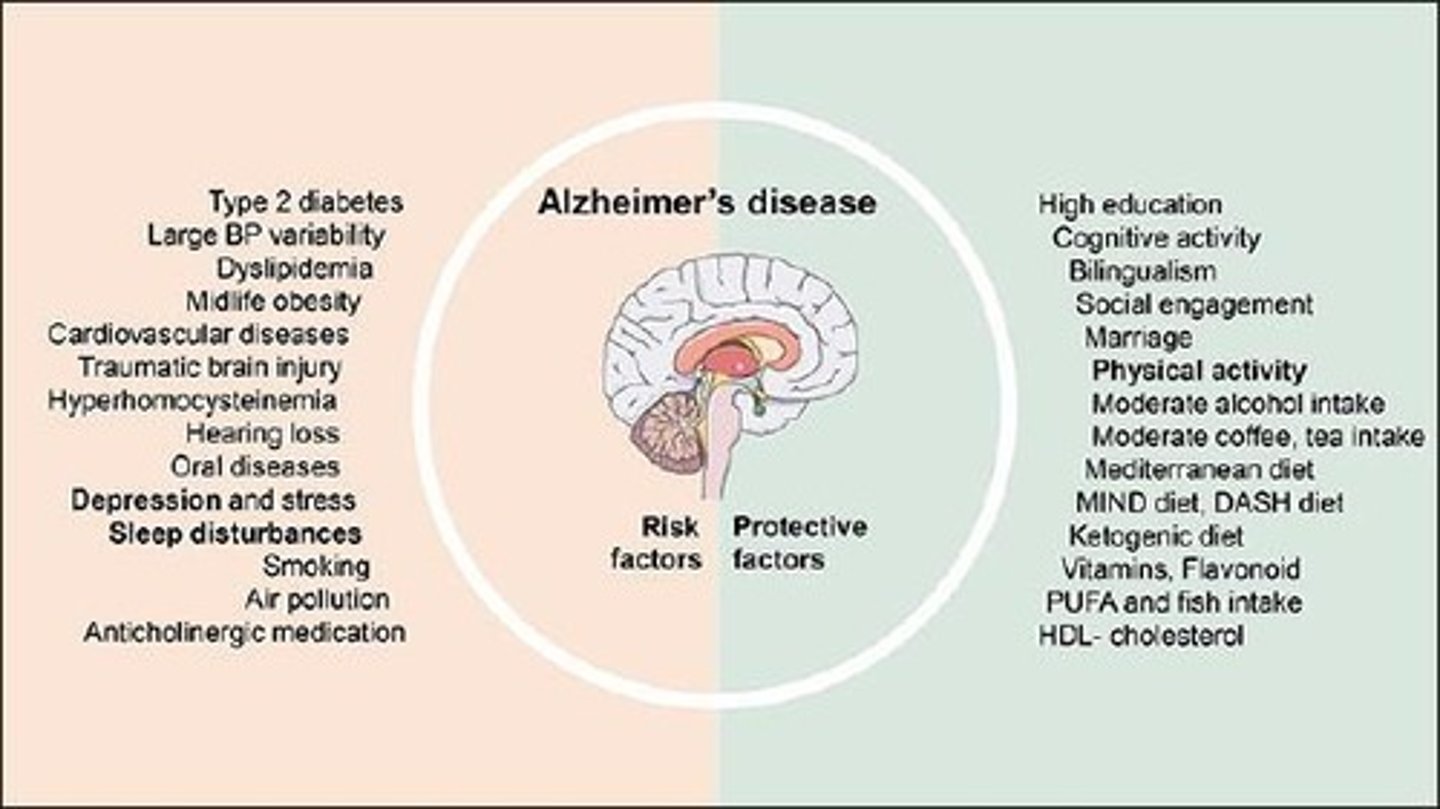
What environmental factors are considered risk factors for Alzheimer's Disease?
Aluminum, zinc, food-borne poisons, viruses, and bacterial infections.
What is the significance of the enlarged ventricles in Alzheimer's Disease?
They indicate a loss of neuronal tissue and are a hallmark of the disease.
What is the typical progression of symptoms in Alzheimer's Disease?
It starts with memory failure and cognitive decline, leading to severe intellectual disturbance and vegetative state.
What are senile plaques in the context of Alzheimer's Disease?
Focal collections of degenerating nerve endings surrounding a core of amyloid protein.
What is the core composition of an amyloid plaque?
Aggregated protein core of β-amyloid (40-42) at the center of degenerating nerve endings.
What genetic mutation is associated with Alzheimer's Disease?
Mutation in the gene coding for amyloid precursor proteins (APP) on chromosome 21.
What are neurofibrillary tangles?
Masses of paired helical filaments filled in nerve cell bodies, arising from hyperphosphorylation of tau protein.
What is the role of tau protein in neurons?
Tau protein stabilizes axonal microtubules, but hyperphosphorylation leads to disruption of transport.
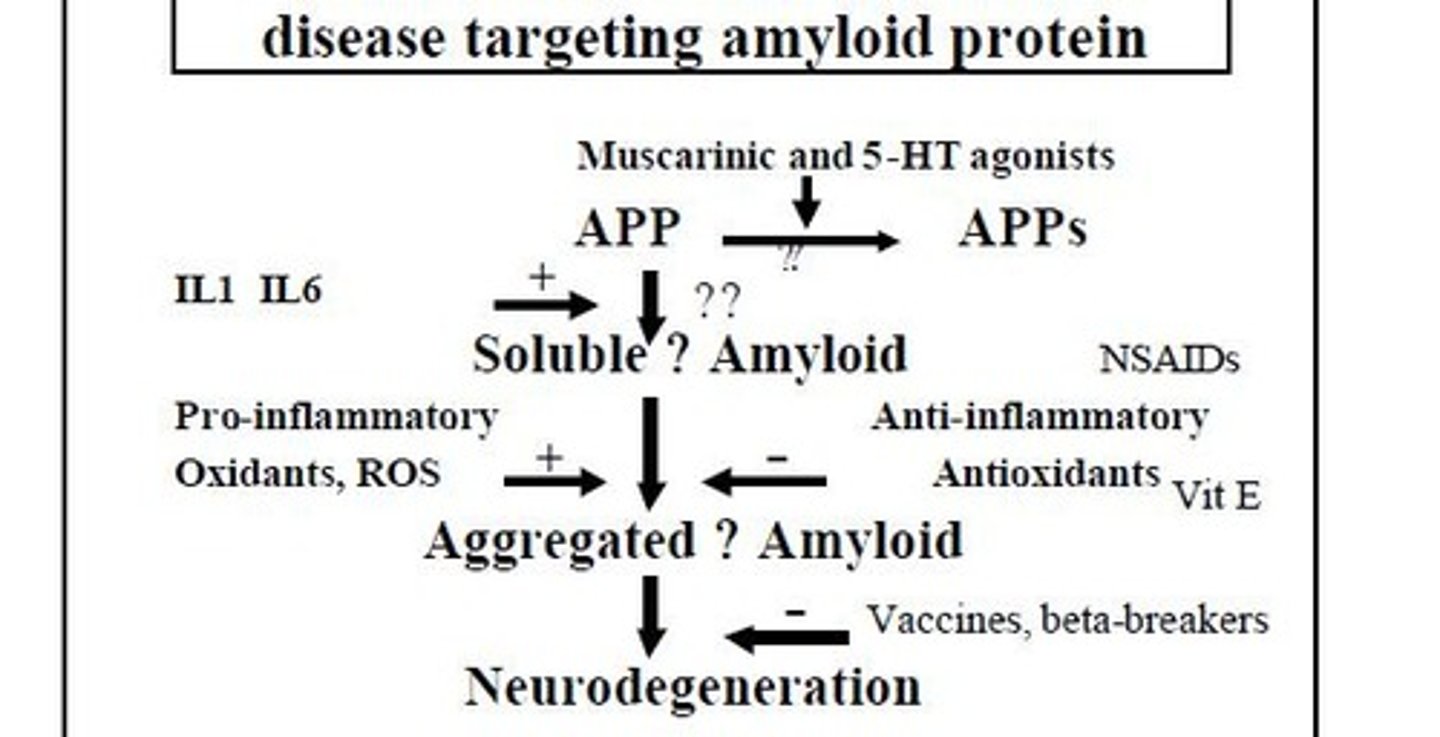
What is the amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's Disease?
Most genetic and environmental risk factors affect the metabolism of amyloid precursor protein, leading to deposition of beta-amyloid in plaques.
How do plaques and tangles relate in Alzheimer's Disease progression?
The presence of plaques may precede the formation of tangles.
What is the significance of β-amyloid in Alzheimer's Disease?
Production of β-amyloid is central to the disorder.
What is the β + γ secretase pathway?
A toxic, amyloidogenic pathway that produces excess β-amyloid.
What is the α secretase pathway?
A normal pathway that leads to the release of soluble APP.
What is the process of Aβ generation in Alzheimer's Disease?
Aβ is generated by APP cleavage in acidified compartments like late endosomes and subsequently released from neurons.
What are the stages of Aβ aggregation?
Extracellular Aβ assembles into oligomer aggregates, fibrils, and ultimately amyloid plaques.
How does Aβ affect synaptic function?
Oligomeric Aβ can disrupt synaptic function through long-term potentiation (LTP) impairment and long-term depression (LTD) enhancement.
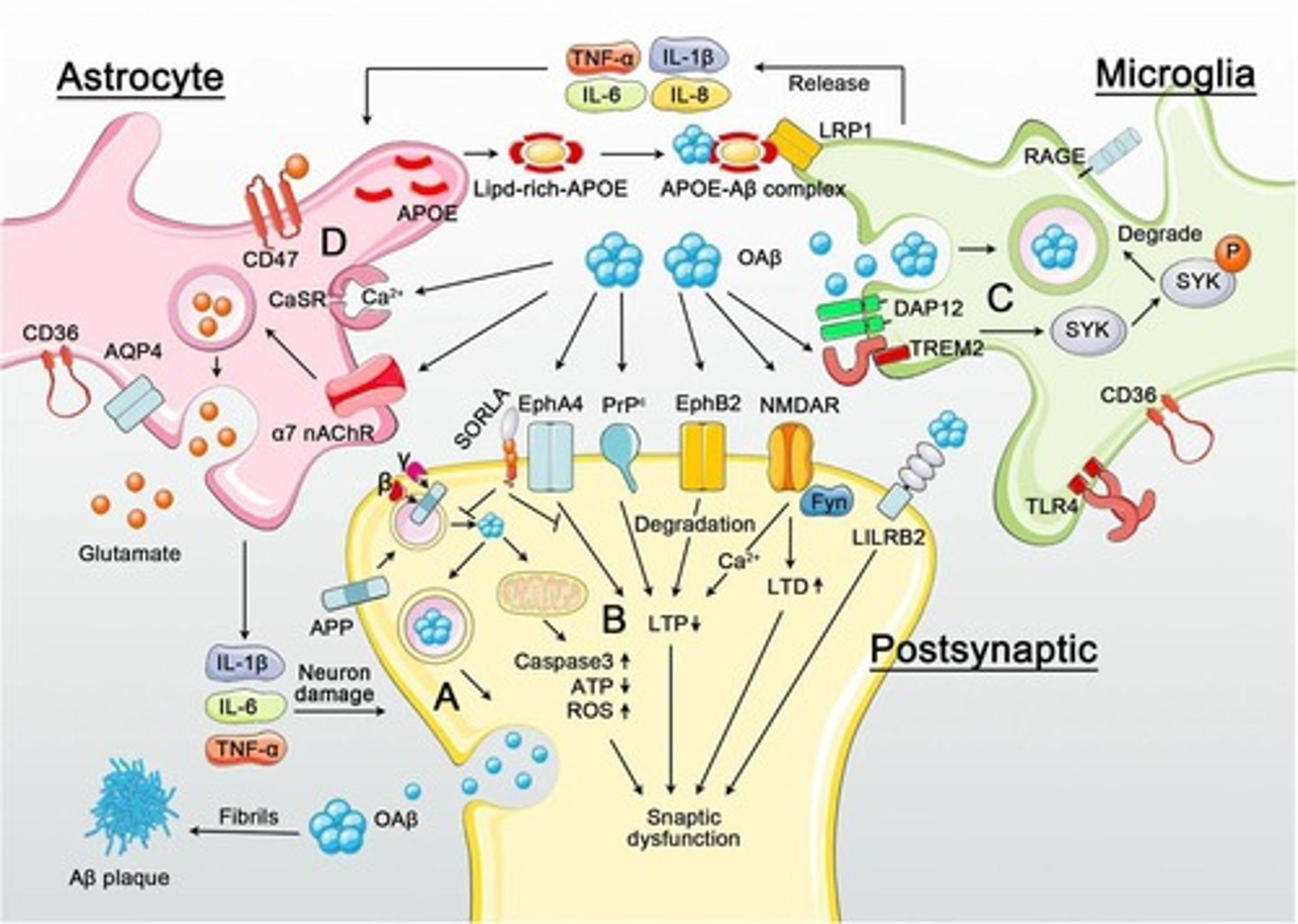
What receptors are involved in Aβ-mediated synaptotoxicity?
Potential receptors include EphA4, PrPc, EphB2, NMDAR, and LiLRB2.
What role does SORLA play in Alzheimer's Disease?
SORLA can inhibit EphA4-mediated synaptic and cognitive dysfunction in the presence of oligomeric Aβ.
What is the impact of oligomeric Aβ on mitochondrial function?
It induces caspase-3 activation, ATP reduction, and ROS upregulation, aggravating synaptic dysfunction.
How can microglia be activated by Aβ?
Oligomeric Aβ may activate microglia through binding to receptors such as TREM2, LRP1, RAGE, TLR4, and CD36.
What is the effect of Aβ binding to TREM2?
It activates the SYK pathway through DAP12, leading to the degradation of Aβ.
What pro-inflammatory cytokines do activated microglia release?
TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8.
How does APOE interact with Aβ in Alzheimer's Disease?
APOE released from astrocytes binds Aβ, enhancing Aβ/APOE interactions with LRP1.
What are potential direct activation pathways for astrocytes by oligomeric Aβ?
Activation can occur through α7-nAchR, CaSR, CD36, CD47, and AQP4.
What may activated astrocytes damage neurons through?
Extracellular glutamate dyshomeostasis/excitotoxicity, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6.
What is the cholinergic treatment hypothesis in Alzheimer's disease?
It involves using drugs that enhance cholinergic transmission.
Name three reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitors used in Alzheimer's treatment.
Donepezil (Aricept), Rivastigmine (Exelon), and Galantamine (Reminyl).

What are some typical cholinergic side effects of anticholinesterases?
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, gastric ulcers, breathlessness, bradycardia, headache, dizziness, fatigue, hallucinations, and anorexia.
What factors affect the selection of anticholinesterase treatment in Alzheimer's patients?
Existing cardiac dysrhythmias, gastric and duodenal ulcers, asthma/COPD, renal impairment, and hepatic impairment.
What is Memantine and its role in Alzheimer's treatment?
Memantine (Ebixa) is an NMDA receptor antagonist that may be neuroprotective and has shown efficacy in stabilizing or improving patients.
What were the results of the US and UK studies on Memantine?
In the US study, 29% of patients stabilized or improved vs. 10% on placebo; in the UK study, 61.3% stabilized or improved vs. 31.6% on placebo.
What caution should be taken when using antipsychotics in Alzheimer's patients?
They should be used cautiously as they can increase the risk of strokes and may be associated with an increased risk of death.
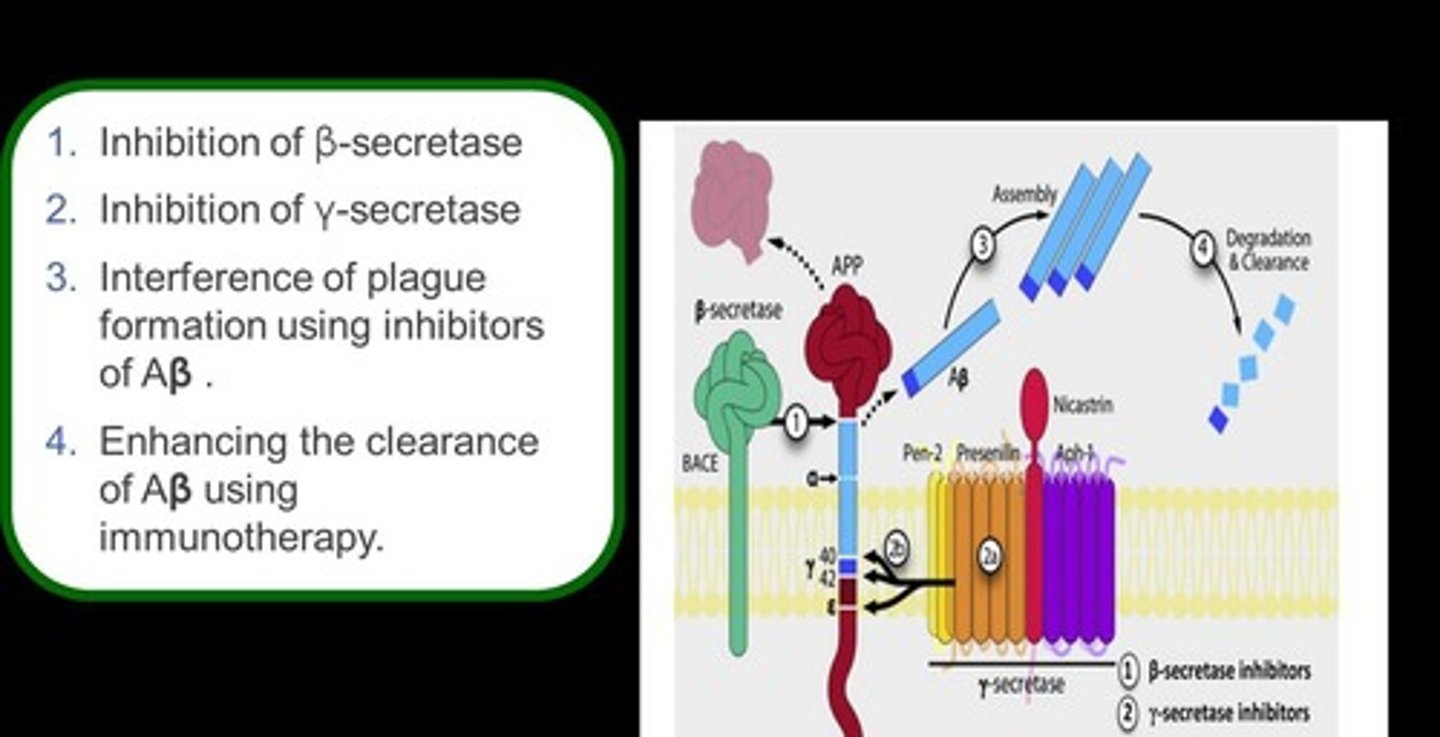
What is the role of α-secretase in Alzheimer's disease?
The protein responsible for α-secretase activity is ADAM-10, and the aim is to boost its activity.
What is the function of β-secretase in Alzheimer's pathology?
β-secretase activity is mediated by BACE, and the aim is to decrease its activity.
What is the significance of γ-secretase in Alzheimer's disease?
γ-secretase is a complex that aims to decrease activity, but non-selective inhibitors can prevent Notch signaling and affect cell differentiation.
What is Tarenflurbil and its impact on Alzheimer's treatment?
Tarenflurbil shifts cleavage of APP away from the 42 site to the 38 site, which is less toxic and more soluble, and is well tolerated with a 50-60% reduction in deterioration rate.
What is the purpose of the Phase 1 study testing a skin patch for Donepezil?
To evaluate if transdermal delivery of Donepezil is as effective as the oral form.
What is AADvac1 and its purpose in Alzheimer's treatment?
AADvac1 is a vaccine against tau that aims to induce the immune system to produce antibodies against abnormal tau forms to protect neurons from degeneration.
What are the results of the Phase 1 study for AADvac1?
It showed therapeutic potential in Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal dementia.
What are the potential side effects of anticholinesterase inhibitors?
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, gastric ulcers, breathlessness, bradycardia, headache, dizziness, fatigue, hallucinations, and anorexia.
What should be monitored closely when treating Alzheimer's with anticholinesterases?
The effects of treatment due to potential side effects.
What is the relationship between acetylcholine and asthma/COPD in Alzheimer's treatment?
Increased ACh can worsen breathing in asthma/COPD patients, who are often treated with antimuscarinics.
What is the caution regarding renal impairment when using Alzheimer's medications?
Galantamine and Rivastigmine should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment.
What is the caution regarding hepatic impairment when using Alzheimer's medications?
Rivastigmine and Galantamine should be used with caution and avoided if hepatic impairment is severe.
What is the goal of boosting α-secretase activity in Alzheimer's treatment?
To potentially reduce amyloid plaque formation.
What is the challenge with β-secretase inhibitors in Alzheimer's treatment?
Limited progress has been made, and BACE deficient mice exhibit learning difficulties.