The pH of weak acids
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
When a strong monobasic acid, HA, completely dissociates what is [H+] equal to?
[H+] = [HA]
When HA molecules dissociate H+ and A- ions are what?
H+ and A- ions are formed in equal quantities
What is the first approximation for the Ka?
The dissociation of water is negligible
[H+]eqm = [A-]eqm
What is the second assumption for the Ka of water?
the concentration of acid is much greater than the H+ concentration at equilibrium
[HA]eqm = [HA]start
Because of the approximations, the Ka can be simplified to what? When is this applicable?
ONLY for aqueous solution of a weak acid
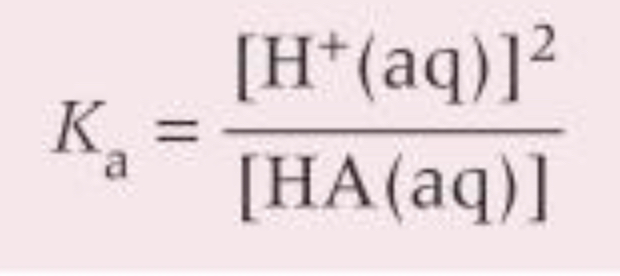
How can you determine the Ka for a weak acid experimentally?
by preparing a standard solution of the weak acid of a known concentration
By measuring the pH of the standard solution using a pH meter
How do you calculate percentage dissociation?
[H+] / [concentration of acid]