Roman Art + Archaeology
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lectures 11-22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
The Triumph
procession through the city of Rome
celebrate a great victory of the State
display of success and spoils taken for the glory of Rome
general “King for a Day”
Who Received a Triumph
a general with Imperium (Commander)
triumphator ‘man of triumph’
Components of a triumphal
spoils (anything taken from conquered peoples) (Including foreign leaders)
general (Triumphator ‘man of triumph’)
soldiers (of victorious army)
Fasti Triumphales
Calendar of Roman magistrates granted a triumph from Roman monarchy to 19 BCE
Pomerium
The boundary of Rome
marked the city limits and where military triumphs were traditionally celebrated
would have changed over time
Via Triumphalis
Triumphal Way (route)

Temple to Divus Iulius
Dedicated to Julius Caesar in 29 BC
commissioned by Augustus
Located in the Roman Forum
converted into the Rostra lulia (speakers podium for orators/politicians)

Arch of Septimuis Severus
located along the Via Sacra
built after the triumphal celebration of Septimuis’s Parthian victories
triple fornix (arches)
scenes from the Parthian campaigns on it
Damnatio memoriae
condemnation of memory
easer of their memory
Contrapposto
a sculptural position
weight is shifted to one leg, while the other leg is bent
has movement
tablinum
a office/reception area for the head of the household
ancestor bust placed here
a room situated on one side of the atrium and opposite to the entrance
What are the four gens in order
Julio-Claudian
Flavian
Nerva-Antonine
Severan

Verism
republican portraiture
“warts and all”
hyper-realistic
individual features and imperfections, wrinkles, and asymmetry

Julio-Claudian Portraiture
Augustus (27 BCE - 14 CE)
Idealism
serene, youth, less emotion
‘classicizing’
athleticism (bodies)
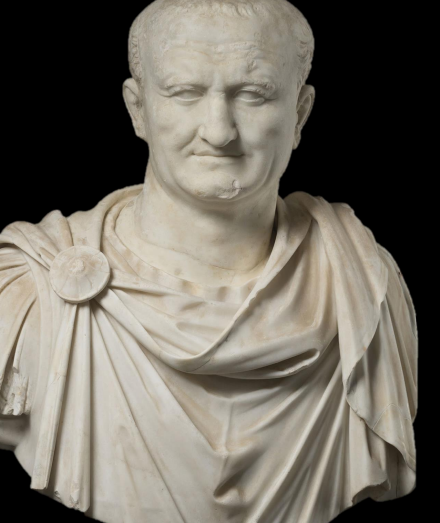

Flavian Portaiture
Vespasian (69-79 CE)
return to verism
Unidealized (not youthful, wise, experienced general)
used the drill
what was the drill and what was is used for
The drill was a sculpting tool
used in Roman portraiture
create intricate details, textures, and realistic features in stone, enhancing the lifelike quality of the sculptures.
curls, female hairstyles, military uniforms, pupils
slave/attendants would pull the string that pulls the drill
Nerva-Antonine Portraiture
Trajan (98-117 CE)
ageless
youthful yet mature
male hair is defined
nude upper torso
using the drill to create pupils is popular


Nerva-Antonine Portraiture pt. 2
Hadrian (117-138 CE)
Antoninus Pius (138-161 CE)
Marcus Aurelius (161-180 CE)
bearded wise
military garb
stoic

Severan Portaiture
Caracalla (198-217 CE)
Geta (209-211 CE)
return to Verism
militaristic hair style
mean (Expressive)
What is chiasmus
sculpture framing style
people leaning away from the center
the axis of the body is in a reversed s curve than a straight line
What is camaeus
a low-relief portrait
seen on Roman currencies
Die
used to create coin designs and impressions on obverse and reverse
Brockage
imperfectly minted coin
Polychromy
statues were painted in colours
what was a Libitinarius
they were a undertaker
took care of funerals and burial arrangements in ancient Rome.
they were prohibited from many places
what is Larve/larvae
silver skeleton model placed on tables during feast
representations of the dead in Roman funerary traditions.
spirits of the dead
what was a ustrinum
a building used for cremation in ancient Rome
cremated remains in niches
What Dis Manibus (D.M.)
to the manes gods
to the spirits of the dead and ancestors in Roman beliefs.

What was the Tomb of Eurysaces
outside Aurelian Walls
buried within the Aurelian Walls
Elite burial of a wealthy Roman baker
Freedman?

Pyramid Tomb of Cestius
Gaius Cestius (priest)
death 18-12 BCE
Tomb was in the city

Mausoleum of Augustus
Tumulus - burial mound
Campus Martius - burial site of the first emperor of Rome, Augustus, built in 28 BCE.
Res Gestae Divi Augusti - bronze panels with inscriptions detailing Augustus's achievements.
used to be outside of the city walls
was then incorporated into the city when it expanded

Mausoleum of Hadrian
re-claimed and turned into Castle St. Angelo
134-139 CE
Hadrian buried in 139 CE
final resting place of Sabina (wife), Lucius Aelius (son)
When did Mount Vesuvius erupt?
August/October 24th 79 CE
Pliny the Younger
letters to Tacitus describing the eruption of Mount Vesuvius and its effects on the people of Pompeii
What is a Lupinar
it is a brothel
it was the largest in Pompeii

Tintinnabulum
apotropaic device
hung in Roman homes or at entrances to ward off evil spirits.
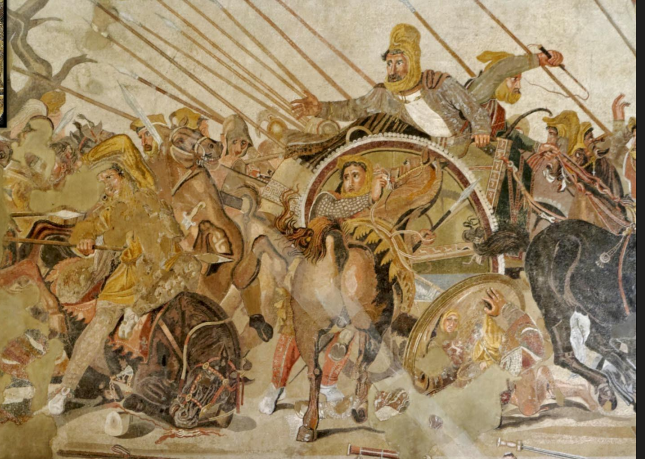

Battle of Issus Mosaic
located at House of the Faun, Pompeii
made with tesserae - small stones used in mosaics

1st Pompeian Style
Masonry (~200-80 BCE)
Stucco - plaster
mimic the appearance of stone
Identifying styles helps archaeologists date buildings

2nd Pompeian Style
Architectural style
1st c. BCE
illusion of Architecture
Identifying styles helps archaeologists date buildings

3rd Pompeian Style
Ornamental style
~20-10 BCE
Thin spindly lines
New age
unrealistic
creates a mock picture frame that shows scenes
Identifying styles helps archaeologists date buildings

4th Style Pompeian Style
Complex style
1st-2nd c. BCE
combines all the styles together
1st style stone work
2nd style architecture
3rd style narrative scenes
Identifying styles helps archaeologists date buildings
What is a domus
Roman house for the wealthy
small villa like structure in a city center
Villa urbana
luxurious countryside residence often used for relaxation and leisure by wealthy Romans.
Insula
smaller residence for the poor
typically apartments
Parts of a Domus
Vestibulum - foray
Atrium - grand entree way
Impluvium - small pool in the center of atrium
Tablinum - office space where portraits of ancestors would be kept
Cubiculum - rooms with beds
Peristyle - garden
Piscina - pool in the center of the cubiculum
Culina - kitchen
Triclinium - dinning room
Lectus - daybed or couch used for reclining during meals
Posticum - exit from the domus
Fauces - small hallways
Roman Insula
type of apartment building
12 story +
bottom level had shops
higher apartment = higher risk of death + cheaper rent
The rich could own and rent insula
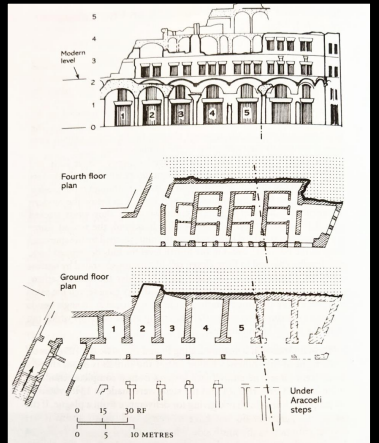
Insula, Aracoeli steps
2nd c. CE
located on Capitoline hill
5 stories high
first 3 levels were shops
4th level cell-like apartment rooms
cloaca maxima - ancient sewer system in Rome.
Villa suburbana
a country house or estate, typically located outside the city
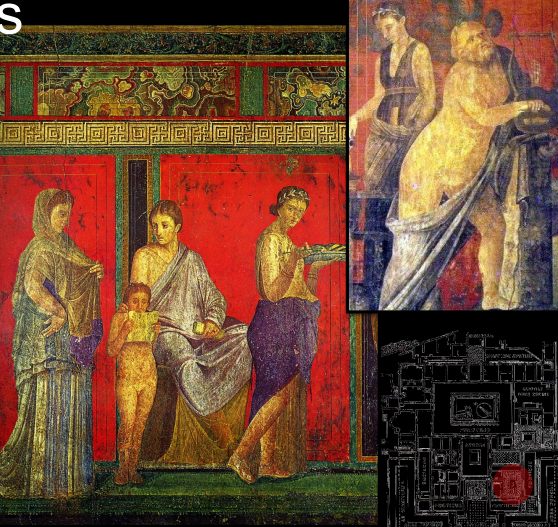
Villa of Mysteries
79 CE
frescos depicting rites being preformed
meeting place for a mystery cult?
depicting the God of wine (Bacchus)
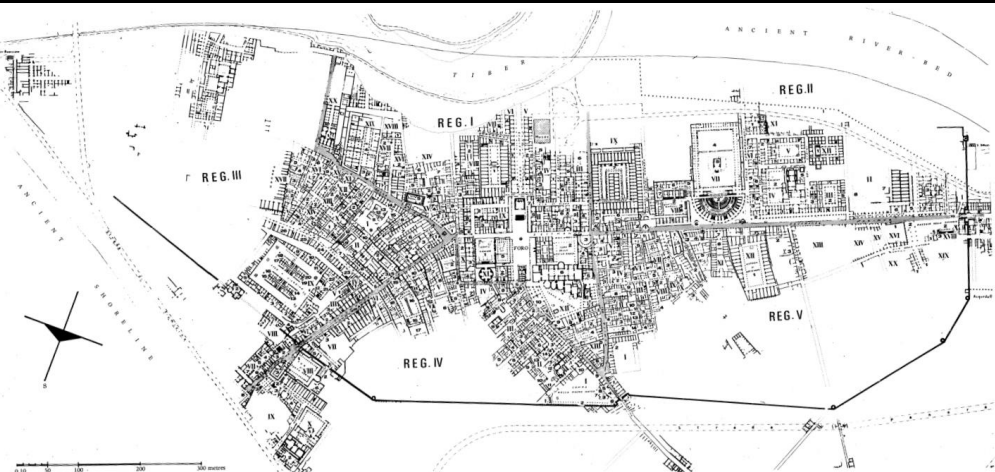
Ostia (Antica)
Port area for Rome

Athena Promachos
79 CE
found at Villa of Papyri
its is a reproduction of the on at Athens
Allows us to see how the original bronze statue at the Athenian Acropolis would have looked
Villa of Papyri
Villa Suburbana
Collectors villa
Held a Library of papyri
Pistrinum
Ancient Roman bakery where bread was produced, often featuring large ovens for baking.
Thermopolium
street food/live fires to cook food
they could be owned by the family who lived in the house the shop was in
likely rented out
imperial palace
Palatine hill
built between 81-92 CE (Domitian)
Built on top of the remains of earlier structures (Nero)
4 courts
public areas
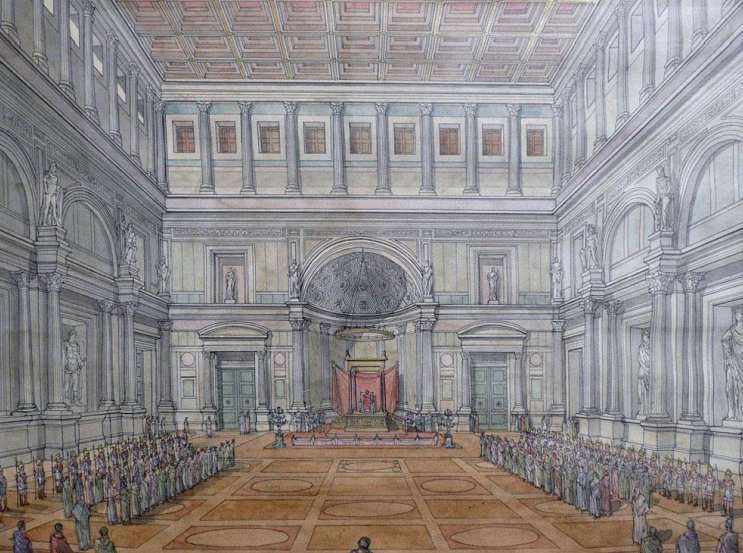
Aula Regia
audience hall/ ‘royal hall’, throne room
architect: Reberius
both Corinthian and ionic columns
Banquet Hall (triclinium)
built to rival the Jupiter Temple
interior colonnade, fountain courts
pink Egyptian granite (colourful)
hypocaustum
Hypocaustum
heated flooring
the wealthy and bath houses had these
Third Court
Piscina (pool)
Peltae (curvilinear ‘shields’)
upper level = receiving rooms
Lower levels = below ground level
island in center of pool
Hippodrome
Hippodrome
stadium used for horse and chariot racing
Hadrian’s Villa
rule: 117-138 CE
Built like a spa
30 buildings
Bathes, fountains, theatres, gardens, stadium, plaestra, peristyles
own fresh water supply

Augustus
27 BCE - 14 CE
Emperor and Pontifex maximus
imperial cult
Via Labincana Augustus
statute veiled for sacrifice
Augustus of Prima Porta
orator pose
Pontifex maximus
head of roman state (religious leader)
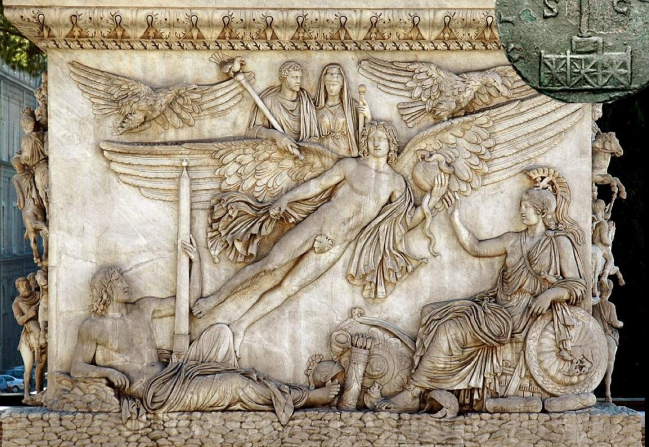

Column of Antoninus Pius
161 CE
A triumphal column in Rome commemorating Emperor Antoninus Pius and his wife Faustina.
post-mortem dedication
locations personified
Campus Martius
apotheosis - becoming a god after death

Marcus Aurelius
161-180 CE
Bronze statute
equestrian statue
Clementia pose - granting mercy

Commodus
177-192 CE
ended a century of stability
related himself to Hercules
son of Marcus Aurelius, known for his extravagant reign and gladiatorial combat.
Crisis of the Third Century
235-284 CE
A period of invasions, civil war, debasement of currency, economic collapse, plague
division of the Empire
Gallic, Palmyrene, Roman
25 people claimed they were the '“emperors” of Rome
Aurelian (emperor 270-275)
Unites the militaries throughout Rome
Defeats Palmyrene Empire 273
Defeats Gallic Empire 274
Marcus Claudius Tacitus (ruled 276-276)
Stability
Gaius Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus (Diocletian), 284- 305
Tetrarchy
Diocletian created
new governance
system dividing the Roman Empire into four regions, each ruled by a co-emperor to ensure better management and defense.
2 Augusti + 2 Ceasares

Porphyry Group
A group of Roman statues used to symbolize imperial power and wealth
What does provincio mean and how is it related to Rome
province
areas under roman control
Rome overs them protection
What does pax romana mean
Roman peace
What is terra sigillate and where is it found?
Roman pottery known for its red slip and intricate designs
it is found in Gaul and Italy
1st c. BCE/CE
indicates Roman presence
African Red Slip (ARS)
2nd and 3rd c. CE
large inclusions
brick colour

Faiyum portraits
realistic painted portraits on wooden panels or mummy wrappings
roman province 1st c. BCE
Hellenistic style
mixed cultural practices
Temple of Divine Hadrian
a temple dedicated to Emperor Hadrian
built-in 145 CE
Panels of the temple have personified geography/provinces on them
Therma/Thermae
public bathhouses in ancient Rome
featuring facilities for bathing, socializing, and exercising.
Apodyterium (baths)
dressing room
locker room
Palaestra (baths)
open courtyard used for exercise and training
Natatio (baths)
outdoors deep pool
a place for relaxation
Frigidarium (baths)
indoor cold pool
Tepidarium (baths)
heated baths
hypocaustum
Caldarium (baths)
Hot baths
like a sauna
heated with hypocaustum
has a Oculus to let light in
Latrines (baths)
shared toilets

Strigil/strigils (baths)
A curved tool used in baths for scraping dirt and sweat from the body after exercise or bathing
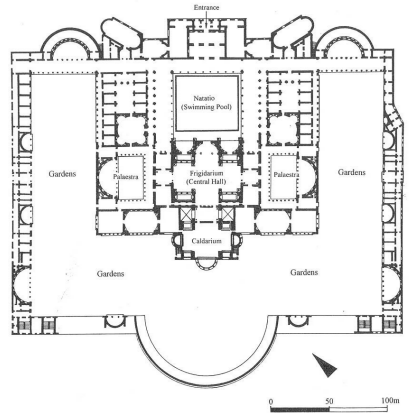
Baths of Trajan
Esquiline Hill, Rome
109 CE
2 palaestra
Ring of gardens
meeting rooms around the garden
blueprints for other imperial baths
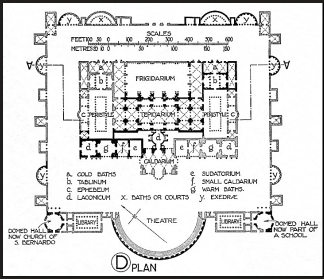
Baths of Diocletian
Near the Trian station, Rome
306 CE (4th c. CE)
Largest bath in Rome
Massive tepidarium
could hold 3000?
Bricks dated with stamps (helps with dating)
converted into a museum
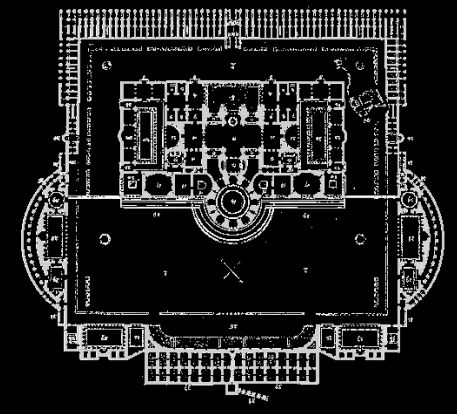
Baths of Caracalla
located next to the Coliseum, Rome
212-216 CE (3rd c. CE)
2nd largest imperial baths
Gardens, shops, pools, study rooms
Public libraries (Greek/Latin libraries)

Mithraeum
Baths of Caracalla, Rome
217-530 BCE
Fossa Sanguinis - Collecting basin for sacrifice
Celebration of the god Mithras
black and white mosaic tiled floor and benches
Tauroctony - sacrificing of a bull
Polytheism
the belief in or worship of multiple gods
common in ancient Rome
Monotheism
the belief in or worship of a single god
prevalent in later Roman history (Christianity)
ICHTHUS (fish)
an early Christian symbol representing Jesus Christ
The Greek word for fish
"ichthys” is an acronym for "Jesus Christ, Son of God, Savior."
Constantine
the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity
312 CE control of Western Empire
established the Edict of Milan - granted religious tolerance and for founding the city of Constantinople
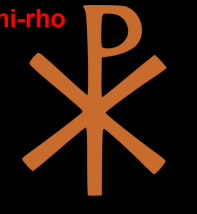
Chi-rho
Lactantius dreamt of the Chi-Rho symbol
Constantine put the symbol on his armies shields

Meta Sudans
a large circular public fountain in ancient Rome
turning point during a chariot race
The start of Via Scacara

Arch of Constantine
built in 4th CE
Spolia from other imperial monuments were used in its construction
Trajan, Hadrian, Marcus Aurelius, Constantine
Hadrianic roundels
and it commemorates Constantine's victory at the Battle of Milvian Bridge in 312 CE.
Spolia
architectural elements or materials from older buildings used in new constructions
roundels
circular relief sculptures used to depict figures or scenes in architectural settings.
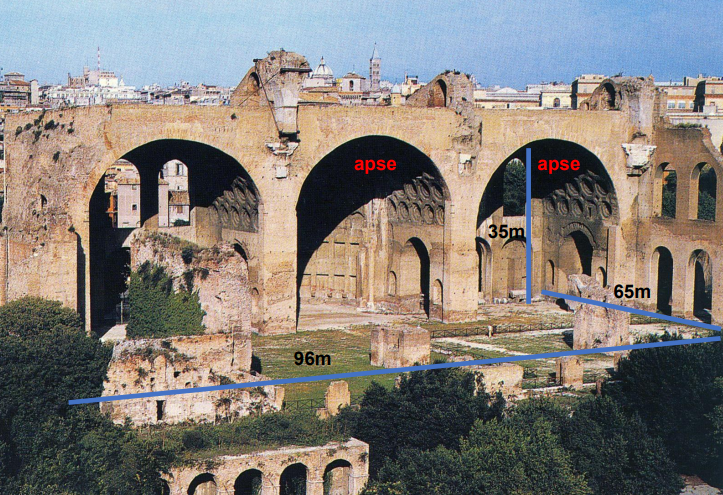

Basilica of Constantine
located in the Roman Forum next to the via sacra
built started by Emperor Maxentius 306 CE
completed by Constantine 313 CE
domed roofs
3 apes
‘flying buttress’
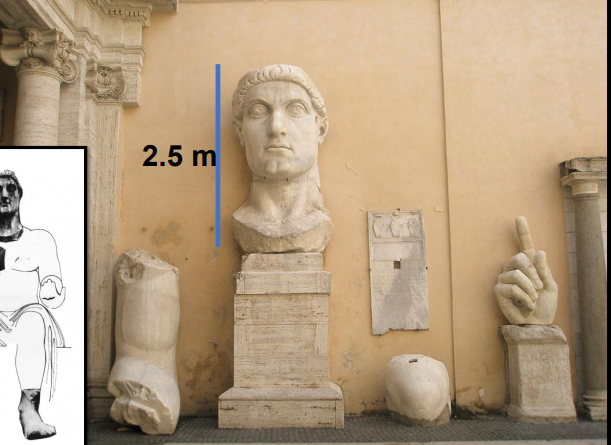

Colossal Constantine
statute of the emperor Constantine
legs, arms, and head made of white marble
the body made of brick core, wooden exterior, gilded bronze surface
held in the Palazzo dei Conservatori
Verism