M3L3: Data Privacy Act of 2012
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Republic Act 10173
Data Privacy Act of 2012
SECTION 1. Short Title.
“Data Privacy Act of 2012” or Republic Act 10173
An Act protecting individual personal information in information and communications systems in the government and the private sector, creating for this purpose a national privacy commission, and for other purposes
SECTION 2. Declaration of Policy.
“Data Privacy Act of 2012” or Republic Act 10173
It is the policy of the State to protect the fundamental human right of privacy, of communication while ensuring free flow of information to promote innovation and growth. The State recognizes the vital role of information and communications technology in nation-building and its inherent obligation to ensure that personal information in information and communications systems in the government and in the private sector are secured and protected.
SECTION 4. Scope of DPA
“Data Privacy Act of 2012” or Republic Act 10173
The DPA applies to the processing of all types of personal information and to any natural and juridical person, in the country and even abroad, subject to certain qualifications.
The National Privacy Commission
A commission created by this act which is mandated to administer and implement this law
SECTION 7. Functions of the National Privacy Commission
The National Privacy Commission
To administer and implement the provisions of this Act,
To monitor and ensure compliance of the country with international standards set for data protection
Rule-making, advisory, public education, investigations and complaints, and enforcement
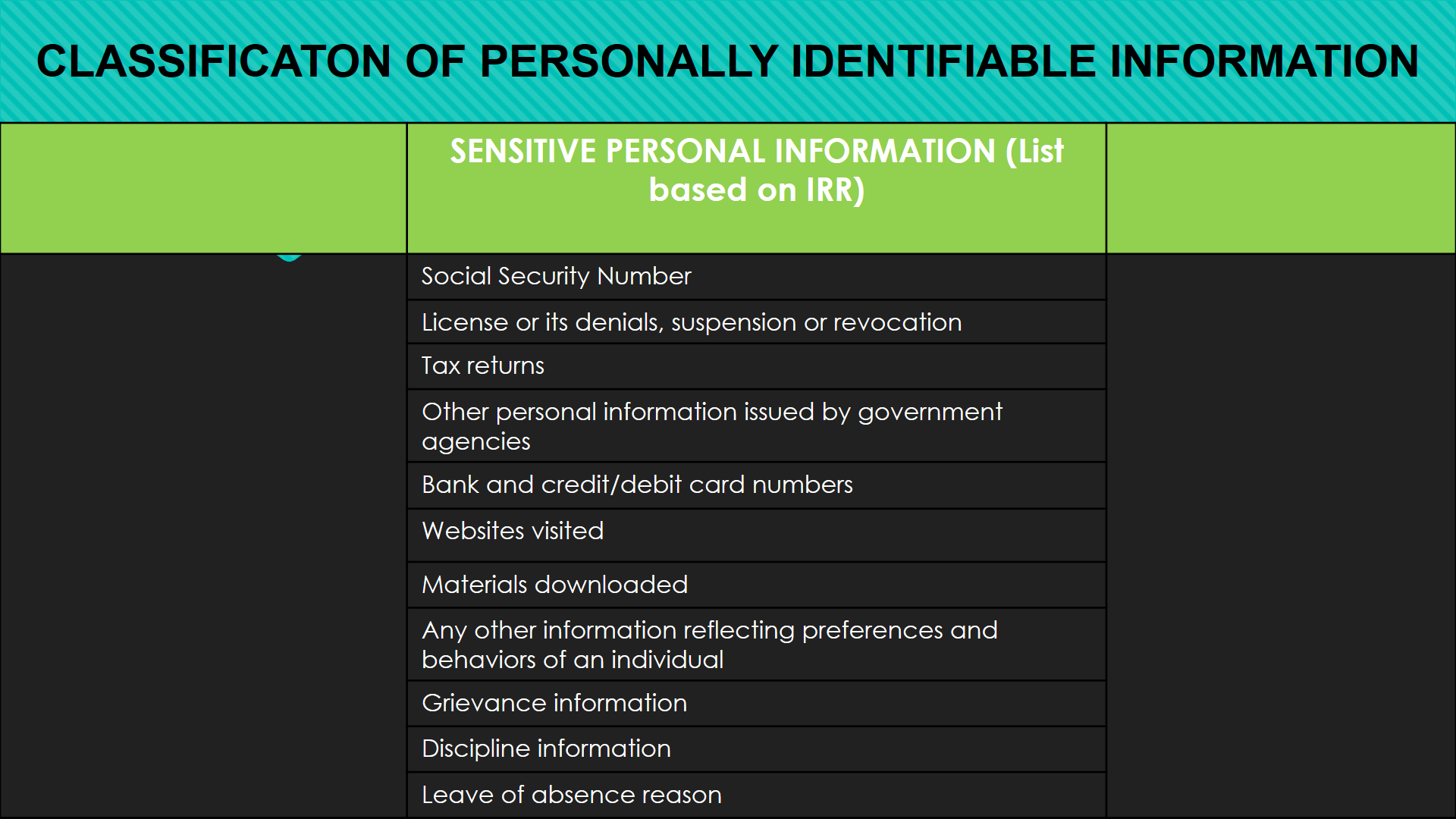
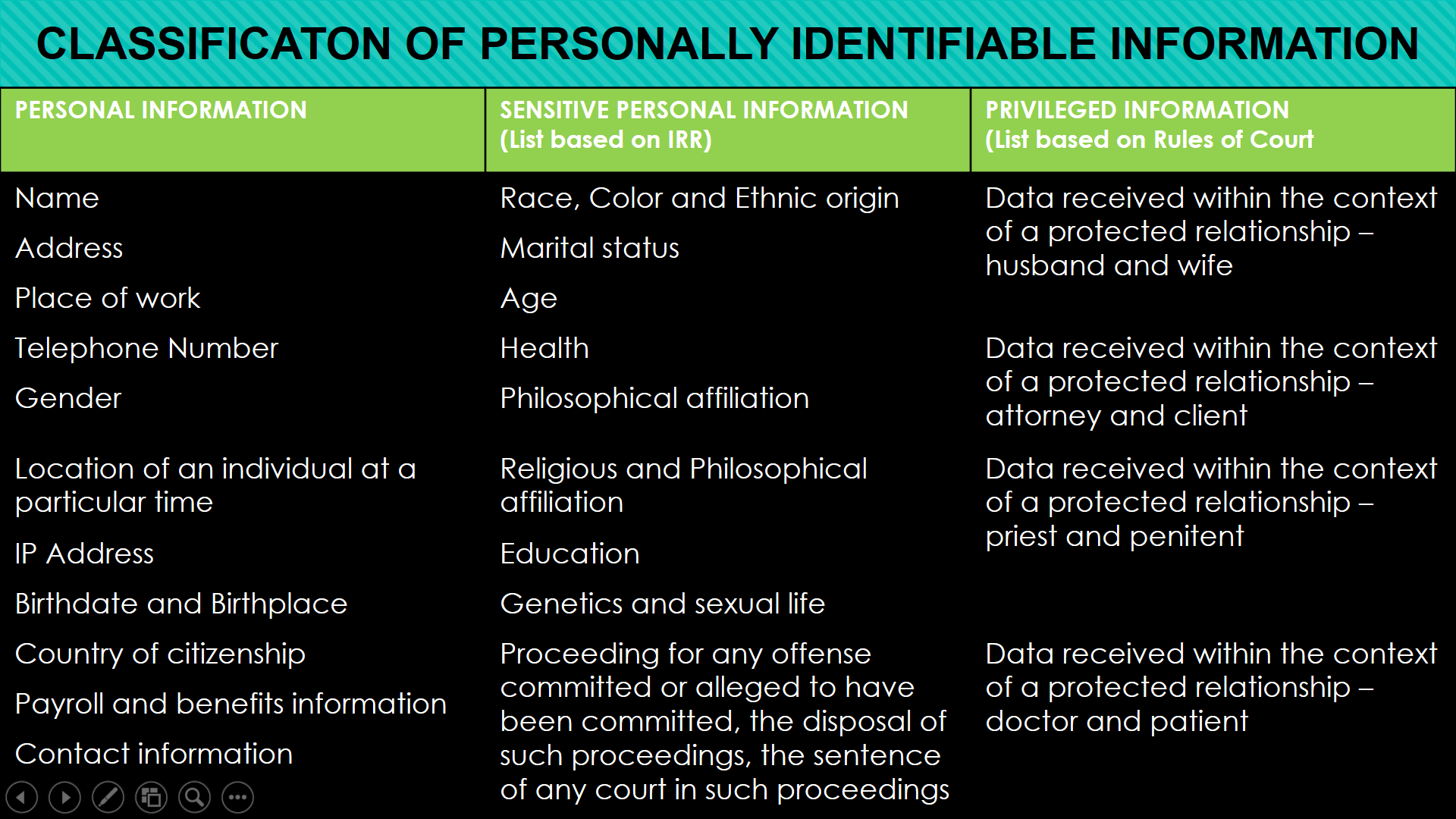
Data Subjects
(Data Privacy Act: Key Roles) Refers to an individual whose, sensitive, personal, or privileged information is processed personal
Personal Information Controller (PIC)
(Data Privacy Act: Key Roles) Controls the processing of personal data, or instructs another to process personal data on its behalf.
Personal Information Processor (PIP)
(Data Privacy Act: Key Roles) Organization or individual whom a personal information controller may outsource or instruct the processing of personal data pertaining to a data subject
Data Protection Officer (DPO)
(Data Privacy Act: Key Roles) Responsible for the overall management of compliance to DPA
National Privacy Commission
(Data Privacy Act: Key Roles) Independent body mandated to administer and implement the DPA of 2012, and to monitor and ensure compliance of the country with international standards set for personal data protection
Right to be informed
Right to object
Right to access
Right to data portability
Right to correct (rectification)
Right to file a complaint
Right to damages
Right to erasure or blocking
Transmissibility of Rights
Rights of the Data Subject (9)
Right to erasure or blocking
(Rights of the Data Subject) "The data subject shall have the right to suspend, withdraw or order the blocking, removal or destruction of his or her personal data from the personal information controller’s filing system." (DPA of 2012, IRR Sec. 34)
Transmissibility of Rights
(Rights of the Data Subject) "The lawful heirs and assigns of the data subject may invoke the rights of the data subject to which he or she is an heir or an assignee, at any time after the death of the data subject, or when the data subject is incapacitated or incapable of exercising the rights" (DPA of 2012, IRR Sec. 35)
(view image)
Classification of Personally Identifiable Information (view image)

(view image)
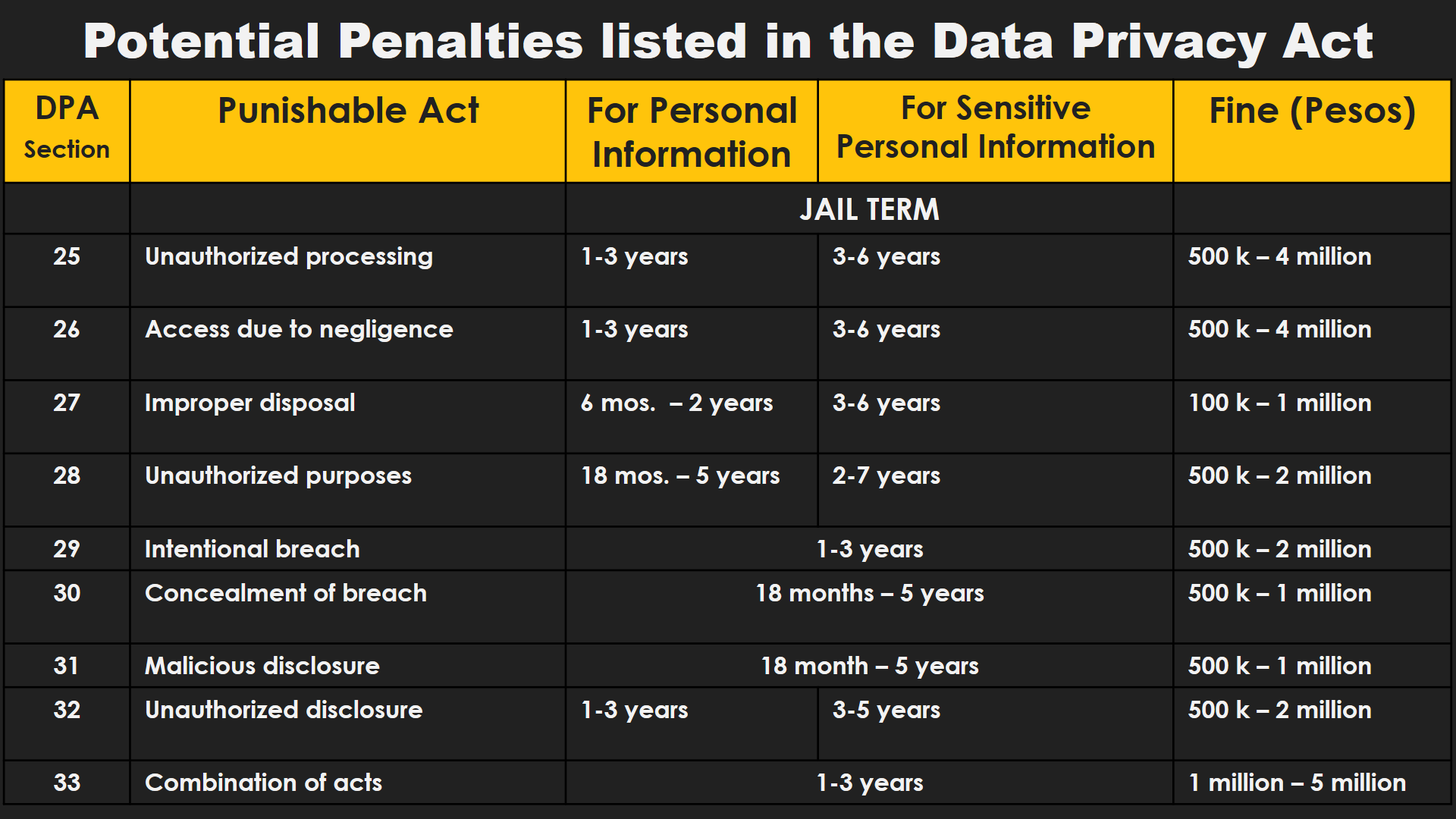
Potential Breaches and Security Incidents Involving Personal Information (view image)

(view image)
Access Control and Security Policy (view image)

Pillar 1: Appointment of Data Protection Officer (DPO)
(NPC’s Pillars of Compliance) Mandated by the NPC through the implementation of the Republic Act No. 10173 (Data Privacy Act of 2012)
Pillar 1: Appointment of Data Protection Officer (DPO)
(NPC’s Pillars of Compliance) A Data Protection Officer (DPO) is required to be appointed by the organization to ensure the protection of your personal data collection and processing.
Pillar 1: Appointment of Data Protection Officer (DPO)
(NPC’s Pillars of Compliance) A DPO is beneficial to your company due to the fact that all companies in the Philippines are now being mandated to comply with the said law.
Pillar 2: Conduct A Privacy Impact Assessment (PIA)
(NPC’s Pillars of Compliance) A Privacy Impact Assessment or PIA is a process used to assess and manage privacy impacts in planned or existing systems technology, programs, processes or activities.
Pillar 2: Conduct A Privacy Impact Assessment (PIA)
(NPC’s Pillars of Compliance) It is a tool for identifying and assessing privacy risks throughout the development life cycle of a program or system.
Pillar 2: Conduct A Privacy Impact Assessment (PIA)
(NPC’s Pillars of Compliance) A PIA states what personally identifiable information (PII) is collected and explains how that information is maintained, how it will be protected and how it will be shared.
Pillar 3: Write your Privacy Management Program and Privacy Manual
(NPC’s Pillars of Compliance) A PMP is a holistic approach to privacy and data security protection, important for all agencies, companies or other organization involved in processing of personal data.
Pillar 3: Write your Privacy Management Program and Privacy Manual
(NPC’s Pillars of Compliance) The PMP will reduce the risks of privacy breaches its impact to the organization. Effective implementation of the PMP will help you in identifying the root cause of the problems in relation to data privacy.
Pillar 4: Implement your Privacy Data Protection Measure
(NPC’s Pillars of Compliance) Implement your Privacy Data Protection (PDP) measures
Pillar 4: Implement your Privacy Data Protection Measure
(NPC’s Pillars of Compliance) Implementing data privacy governance to carry out identified security measures.
Pillar 5: Regularly Exercise your Breach Reporting Procedure
(NPC’s Pillars of Compliance) The Commission and affected data subjects shall be notified by the PIC within seventy-two (72) hours upon knowledge of, or when there is reasonable belief by the personal information controllers (PIC) or personal information processors (PIP) that, a personal data breach requiring notification has occurred.
Pillar 5: Regularly Exercise your Breach Reporting Procedure
(NPC’s Pillars of Compliance) There should be training and simulations, not just with the technical team but also with the data process owners.
Availability Breach
(NPC’s Pillars of Compliance: Types of Breach) Due to loss, accidental or unlawful destruction of personal data
Confidentiality Breach
(NPC’s Pillars of Compliance: Types of Breach) Due to the unauthorized disclosure of, or access to, personal data
Integrity Breach
(NPC’s Pillars of Compliance: Types of Breach) Due to alteration of personal data
Unlawful Processing/Violation of Privacy
(NPC’s Pillars of Compliance: Types of Breach) Unauthorized processing, processing for unauthorized purposes, violation of privacy rights

(view image)
Nurses Guidelines to Avoid Data Breach (view image)
