Neural crest and its derivative & formation of epidermal structures
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What does Neurotrophins (NT-3) do?
Helps neuron choose final target
True or false: neural crest cells do not dissociate from both epidermis and neural tubes?
false they do dissociate
Which part of the Semite does the trunk nRural crest cell migrate to?
Ventral path through anterior scerolome becomes ganglia
What is Ephrin and Eph? What does it do?
Ephrin (ligand) binds to Eph which is the receptor on the neural crest cell membrane and repel the cel migration
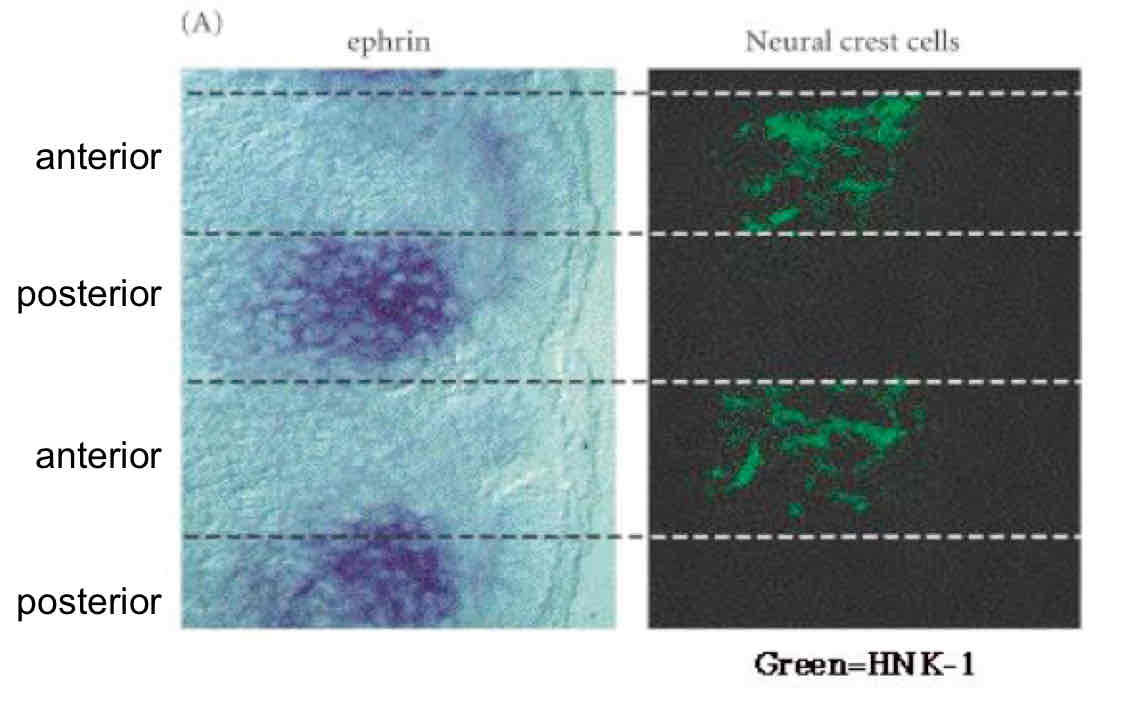
How do cells know when they have arrived }
Stop signals. Stem cell factor binds to Kit receptor
What happens when NC cells get implanted into another embryo?
They change their cell fate
What is the step right before melanoblSt becomes melanocytes
Neural crest cells invade stratum germinativum layer
Where does dermis come from in trunk and head?
In trunk: from somite
In head: from neural crest
Define heterotopic? And the tissue recombination
Change in location. Thigh dermis implanting therefore thigh wing feather is formed. Different morphology.
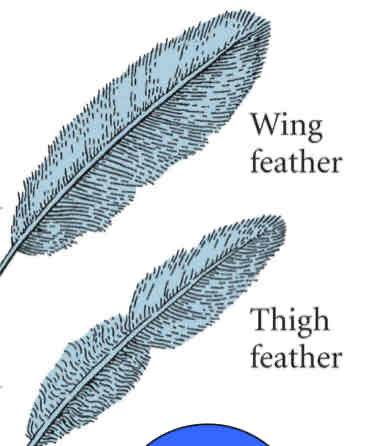
What induces ectoderm morphogenesis?
Neural crest mesenchymes
What is needed for tooth development?
interaction between oral epithelium and neural crest mesenchyme