Algebra II Final Part 3: Inverses and Logarithms (ASSUME ALL NUMBERS/ VARIABLES AFTER LOG NOT IN PARENTHESIS ARE THE BASEEEEEEE)
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Includes graphing an inverse function, creating an inverse equation, evaluating logarithms, and using tables with logarithms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
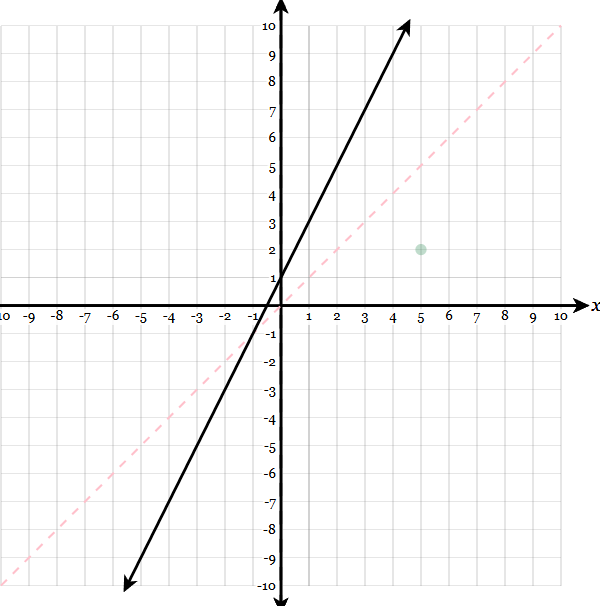
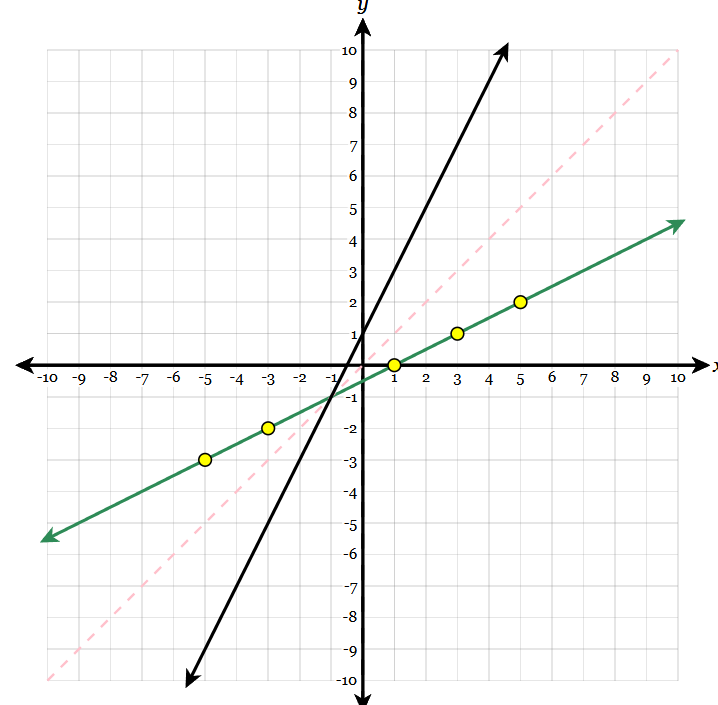
Graph the inverse given the initial graph and the line of y=x
Properties of log: Rewrite logb(xy)
logb(x)+logb(y)
Properties of log: logb(x^y)
ylogb(x)
Properties of log: logb(x/y)
logb(x)-logb(y)
Evaluate 6^log6(5)
5
(if the number and the log’s base are the same, the other number will be the answer)
Evaluate: log8(1/8)
-1
(rather than use the property of log here, rewrite 1/8 as its equivalent, 8^-1. Since the log base and the exponent base are now the same (8), we simply take the exponent as the answer, -1)
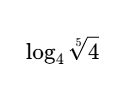
Evaluate:
1/5
(with radicals, we can take the top number in the radical (5 in this case) and use it as a numerator and use the exponent of the number inside (1 in this case) as the numerator, making 1/5. We rewrite everything as log4(4^1/5). As said before, if the log and exponent bases are the same, simply use the exponent as your answer).
If you are given a log without a base, what base is it assumed to be (in the U.S, at least)?
log10
If I wanted to do log15(20), but only had a log10 table, what could I do?
Do log10(20)/log10(15), as they are equivalent. This is also how you use the log button in your calculator. This method works with any log base, not just log10.