Disorders of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland - Clin Med
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What anterior pituitary hormone is the following
Target Organ
Mammary glands, ovaries
Key Function
Milk production, estrogen/progesterone secretion
Prolactin (PRL)
What anterior pituitary hormone is the following
Target Organ
Liver, adipose tissue
Key Function
Growth promotion
Growth Hormone (GH)
What anterior pituitary hormone is the following
Target Organ
Adrenal Gland
Key Function
Secretion of glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and sex corticoids
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
What anterior pituitary hormone is the following
Target Organ
Gonads
Key Function
Sex-hormone production
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
What anterior pituitary hormone is the following
Target Organ
Gonads
Key Function
Reproductive system growth (ovarian follicles growth, spermatogenesis)
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
What anterior pituitary hormone is the following
Target Organ
Thyroid gland
Key Function
Secretion of thyroid hormone
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
What posterior pituitary hormones is the following

Antidiuretic hormone (ADH; vasopressin)
What posterior pituitary hormone is the following (bottom one)

Oxytocin
What does this refer t
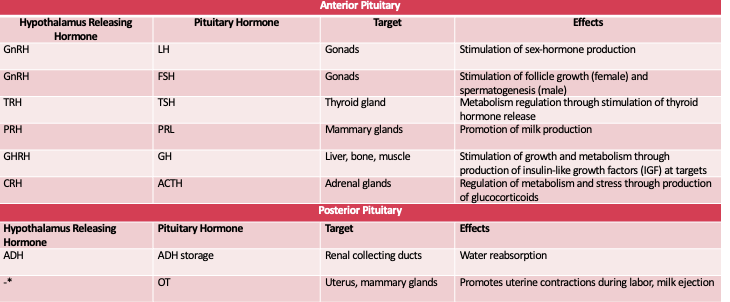
Hormone Axes and Effects
What does this refer to
A 45-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician for persistent thirst.
She has a past medical history of bipolar disorder and hypertension.
She reports that the thirst began 4 weeks ago, along with increased trips to the bathroom.
Her young cousin was recently diagnosed with diabetes after similar symptoms, and she is worried that she has diabetes.
On physical exam, she has dry mucous membranes.
A closer look at her medication list shows a new medication, lithium, started about 8 weeks ago.
Diabetes insipidus

What does this refer to
Classified as central diabetes insipidus (CDI) or nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
Absence of adequate ADH (decreased secretion or increased resistance) —> large volumes of very dilute urine
Diabetes Insipidus
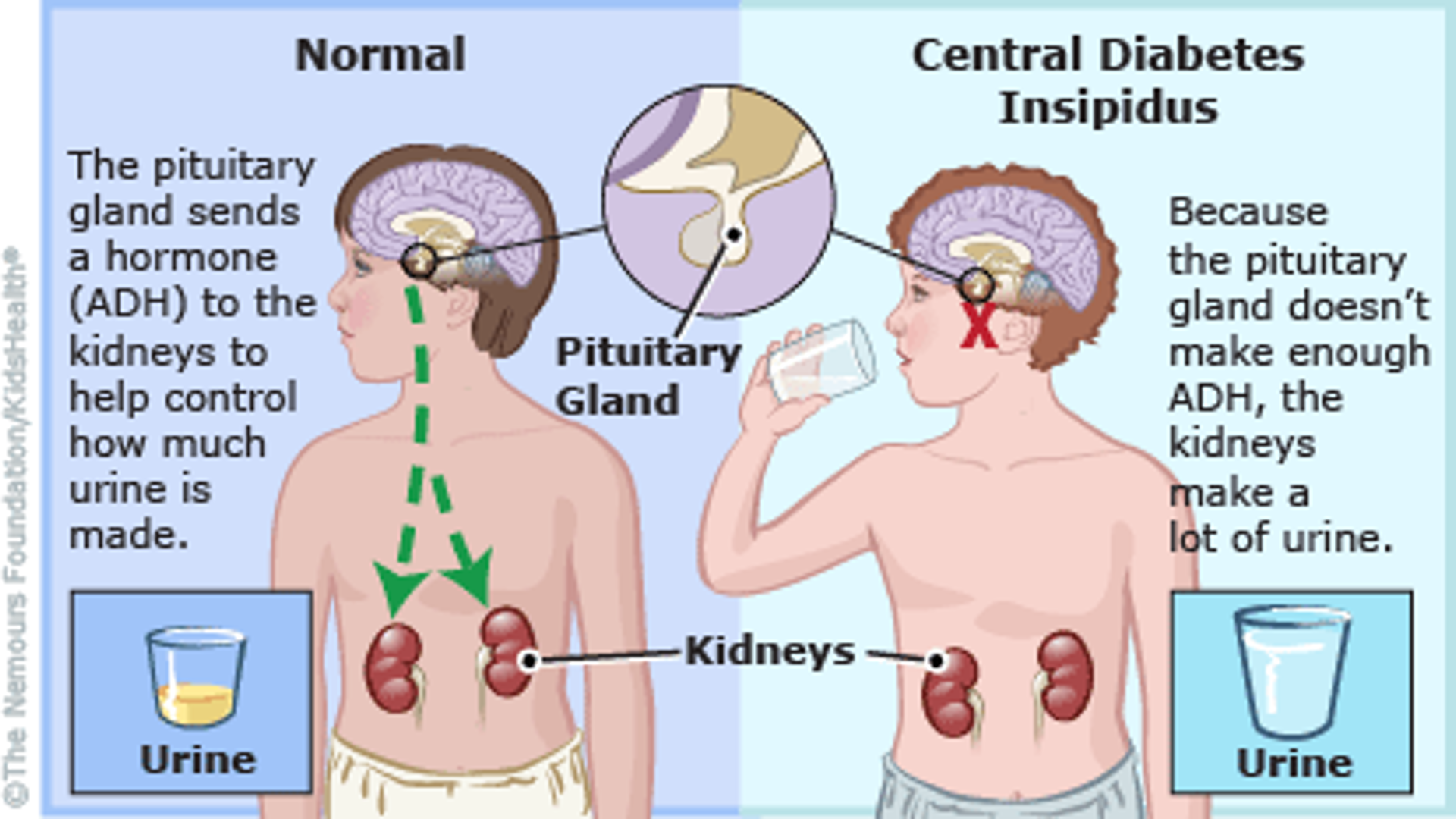
What does this refer to
History
Central diabetes insipidus (CDI): 50% have no known cause, during pregnancy have increased vasopressinase production
Nephrogenic DI: Usually result of increased ADH in collecting tubules
Presentation
Polyuria and polydipsia are the hallmark symptoms, nocturia and thirst
In infants, watch for heavy/excessively wet diapers
Clinical history of Diabetes Insipidus
What does this refer to
Dehydration
decreased weight
decreased skin turgor
increased capillary refill time
dry oral mucosa
orthostatic hypotension
tachycardia
Mental status is usually unaffected
Physical exam Diabetes Insipidus
What does this refer to
Primary polydipsia
Differential diagnosis for Diabetes Inspidus
What does this refer to

Workup Diabetes Insipidus
What does this refer to
Aimed at reducing symptoms of polyuria, polydipsia, and nocturia
CDI:
Desmopressin, typically taken before bed, is the preferred first-line treatment.
If excessive fluid intake continues, hyponatremia may result due to nonsuppressible ADH activity.
Serum sodium should be measured at 2 days after initiation and again at 4 days if normal.
Hydration
Clinical management Central Diabetes Insipidus
What does this refer to
Based on patient’s symptoms
Diet
low-sodium, low-protein diet in combination with NSAIDs and/or a thiazide diuretic.
If cause can be attributed to medication use, a medication change should be considered.
1st line tx options
HCTZ
Indomethacin
Amiloride
Lithium induced
Clinical management Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus
What does this refer to
A 25-year-old woman presents with her 4-day-old girl, born at full-term via spontaneous vaginal delivery complicated by postpartum hemorrhage, for a follow-up pediatric visit.
She reports that she has not been breastfeeding, as her milk never “came in.”
She has been feeding only with formula. (Sheehan syndrome)
Hypopituitarism
What does this refer to
Decreased secretion of pituitary hormone(s)
Universal decrease in function = panhypopituitarism
Sheehan syndrome: panhypopituitarism following postpartum hemorrhage
MC causes: pituitary adenoma or surgical resection of a portion of the pituitary gland
Hypopituitarism
What does this refer to
Given the relationship between the pituitary hormones and the function of the target organ
Clinical presentation of hypopituitarism typically mimics the clinical presentation of a decrease in the target organ function
Etiologies
Pituitary adenoma
Brain damage
Radiation therapy
Sheehan syndrome
History/Presentation Hypopituitarism
What does this refer t
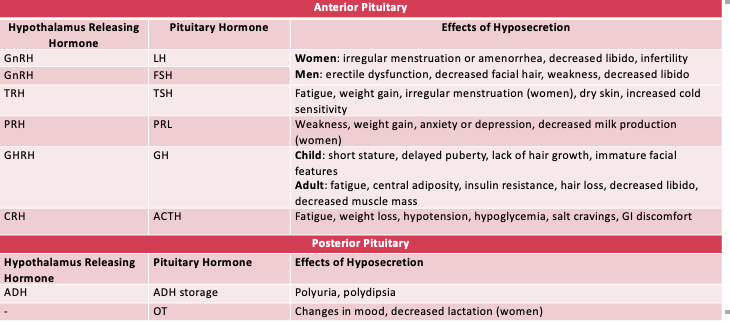
Hypopituitarism
What does this refer to
Physical Examination
Highly varied based on hormone deficiency
Physical exam Hypopituitarism
What does this refer to
Diagnostic Studies should be collected in the morning
Immunoassay of anterior pituitary hormones and their target hormones
Insulin-like growth factor
LH
FSH
Sex hormones (testosterone and estradiol)
TSH/free T4
Cortisol
ACTH
Prolactin
Workup Hypopituitarism
What does this refer t
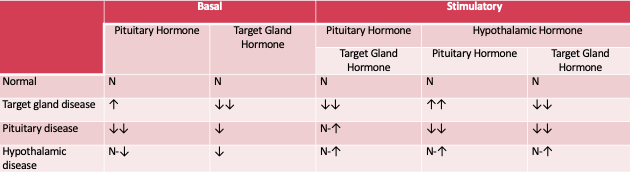
Diagnostic Evaluation of Hypopituitarism
What does this refer to
Varied based on individual hormones effected
Corticosteroids
Sex steroids
Growth hormone
Thyroxine
Clinical management Hypopituitarism
What does this refer to
Pituitary infarct due to postpartum hemorrhage → hypovolemic shock
Pregnancy causes increased pituitary size
Predisposes gland to hypoperfusion and ischemia
Sheehan Syndrome
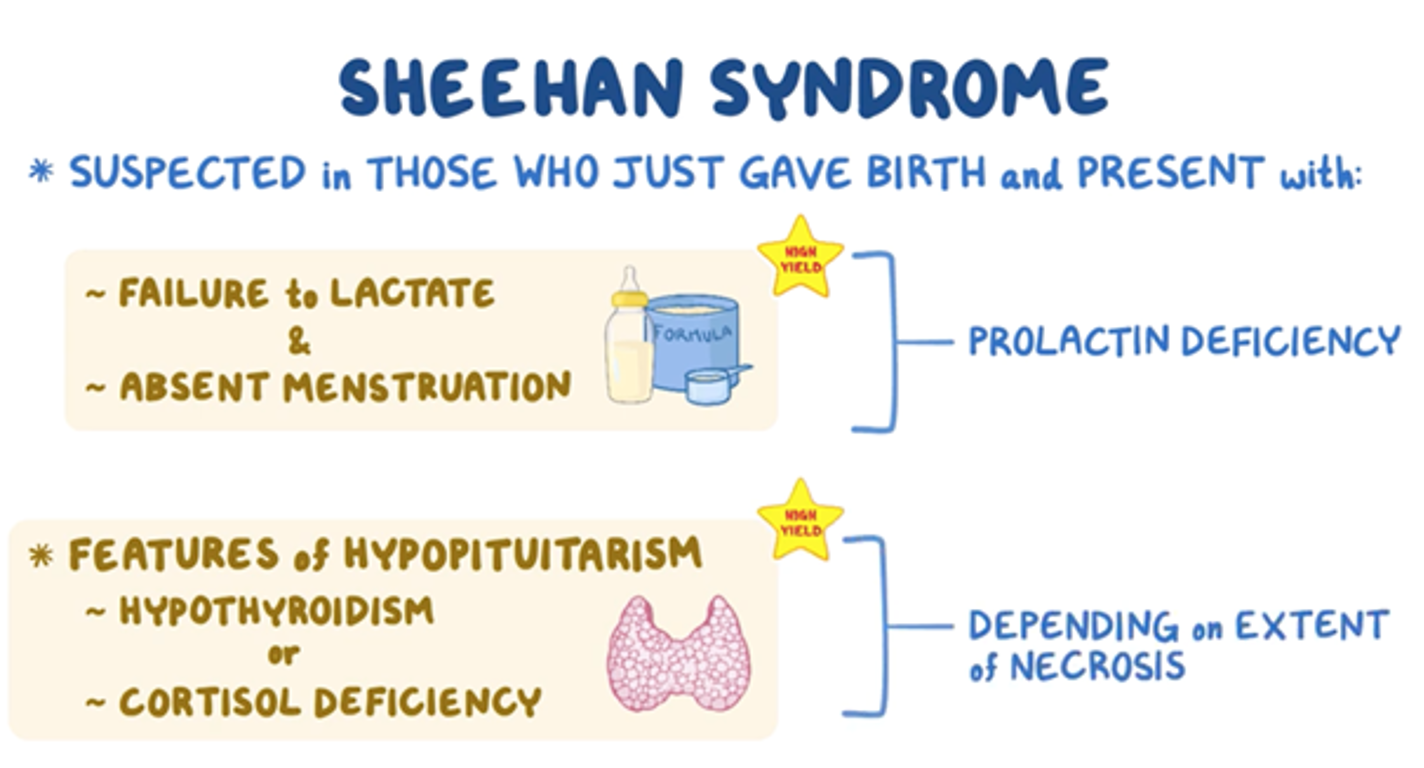
What does this refer to
Prolactin deficiency
Breast involution and failure to lactate
Amenorrhea
Hypothyroidism
Cold intolerance
Clinical history/presentation Sheehan Syndrome
What does this refer to
MRI brain
Infarction of the pituitary gland
Imaging Sheehan Syndrome
What does this refer to
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
Clinical Management Sheehan Syndrome
What does this refer to
A 43-year-old man complains of increased hat size and headaches when he wakes up in the morning.
Physical exam reveals mild hypertension, prominent jaw with spaces between the teeth, large hands and feet, and generalized muscle weakness.
Pituitary adenomas
What does this refer to
Excessive growth after skeletal epiphyseal closure
Due to ↑ growth hormone (GH)
Pituitary Adenoma
What does this refer to
Rare
Typically middle age at presentation
F = M
History
~90% of sellar masses in adults >30 years old are pituitary adenomas
May have a delay between symptom onset and seeking care
All visual field defects should be worked up for sellar mass
Epidemiology Pituitary Adenoma
What does this refer to
Not hereditary
Many have spontaneous mutation leading to persistent ↑cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) in somatotroph cells
Most are benign
Etiology Pituitary Adenoma
What does this refer to
HA
Sweating
Clothes/hat fitting tight
Amenorrhea or impotence
Deep voice & slow speech
Clinical history Pituitary Adenoma
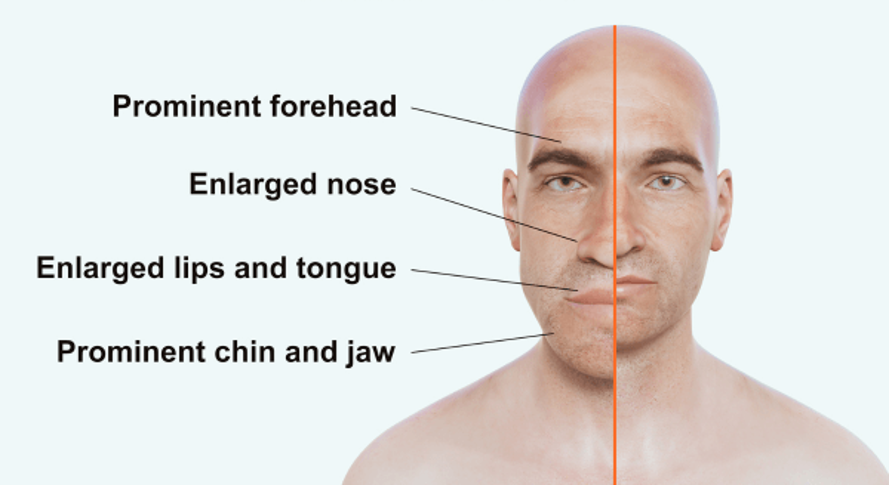
What does this refer to
Diaphoresis
Deep voice/slow speech
HTN
Mitral valve regurgitation
Enlarged head with frontal bossing + deepened facial folds
Enlarged jaw with increased teeth spacing
Enlarged fingers and feet
Skin tags
Skin feels “doughy”
Neuropathy
Muscle weakness
Physical exam Pituitary adenoma
What does this refer to
Gigantism
Pseudoacromegaly
Marfan syndrome
Prolactinoma
Differential Diagnosis Pituitary Adenoma
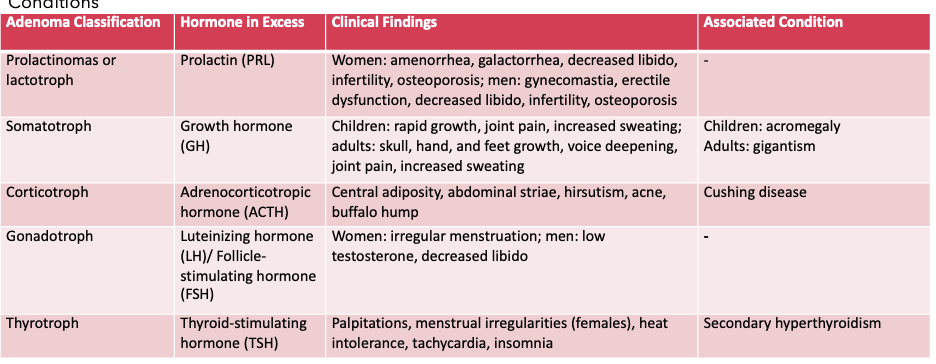
What does this refer t
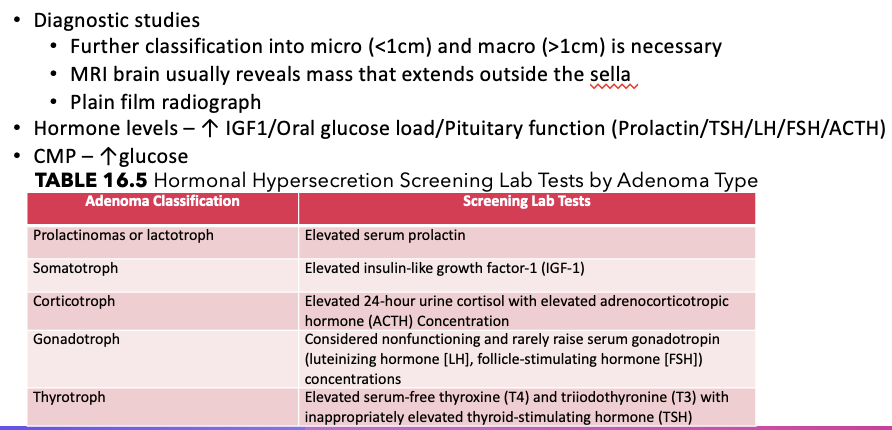
Workup Pituitary Adenoma
What does this refer to
Diagnostic studies (cont.)
If there is a primary disease (stemming from the target organ), the target organ hormone will be elevated but the stimulating hormone from the pituitary will be appropriately downregulated and appear low.
If there is secondary disease (stemming from the pituitary), both the target organ hormone and the pituitary stimulating hormone will remain elevated as the expected downregulation of the axis caused by excess circulating hormone is dysfunctional.
Hypothalamic releasing hormones can be used to distinguish tertiary disease from secondary disease.
Workup Pituitary Adenoma
What does this refer to
Asymptomatic incidentalomas do not typically require treatment, but monitoring should be continued.
Most pituitary adenomas require (surgical) transsphenoidal resection and is 1st line
resulting in hormonal insufficiency in approximately 7% to 20% of patients.
Medical management
Somatostatin analog 1st line medical mgmt (inhibits GH production, ↓ tumor size prior to surgery)
Octreotide or Lanreotide)
Dopamine agonist 2nd line
Bromocriptine or Cabergoline
Radiotherapy
Adjunct after resection
Clinical management Pituitary Adenoma
What does this refer t

Prognosis Pituitary Adenoma
What does this refer to
A 79-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department from home for altered mental status.
Her family reports that she is normally alert and oriented to person, place, and time, and very conversational.
On exam, she is confused, alert only to person, and appears anxious.
She has moist mucous membranes and normal skin turgor.
Pulmonary auscultation reveals localized crackles.
Laboratory tests are significant for serum sodium of 126 mEq/L.
SIADH
What does this refer to
Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH
Excessive free water retention and impaired water excretion
Results in dilutional hyponatremia
SIADH
What does this refer to
Common in patients who are hospitalized
Esp. those on mechanical ventilation
Risk Factors
Older age
Malignancy
Pulmonary disease
PNA
TB
Epidemiology SIADH
What does this refer t

Etiology SIADH
What does this refer to
Na+ levels 125 – 130 mEq/L (mild)
Nausea
Malaise
Na+ levels 115 – 125 mEq/L (moderate)
HA
Lethargy
Weakness
Na+ levels < 115mEq/L (severe)
Seizures
Coma
Respiratory arrest
Clinical history SIADH
What does this refer to
Euvolemia
No edema
Normal skin turgor
Physical exam SIADH
What does this refer to
Other causes of euvolemic hyponatremia
Hypothyroidism
Psychogenic polydipsia
Thiazide diuretic use
Differential diagnosis SIADH
What does this refer t

Workup SIADH
What does this refer to
Urine and serum osmolality are gold standard
Urine > serum
How’s it Diagnosed? SIADH
What does this refer t

Clinical management SIADH
What does this refer t

Morbidity/mortality SIADH
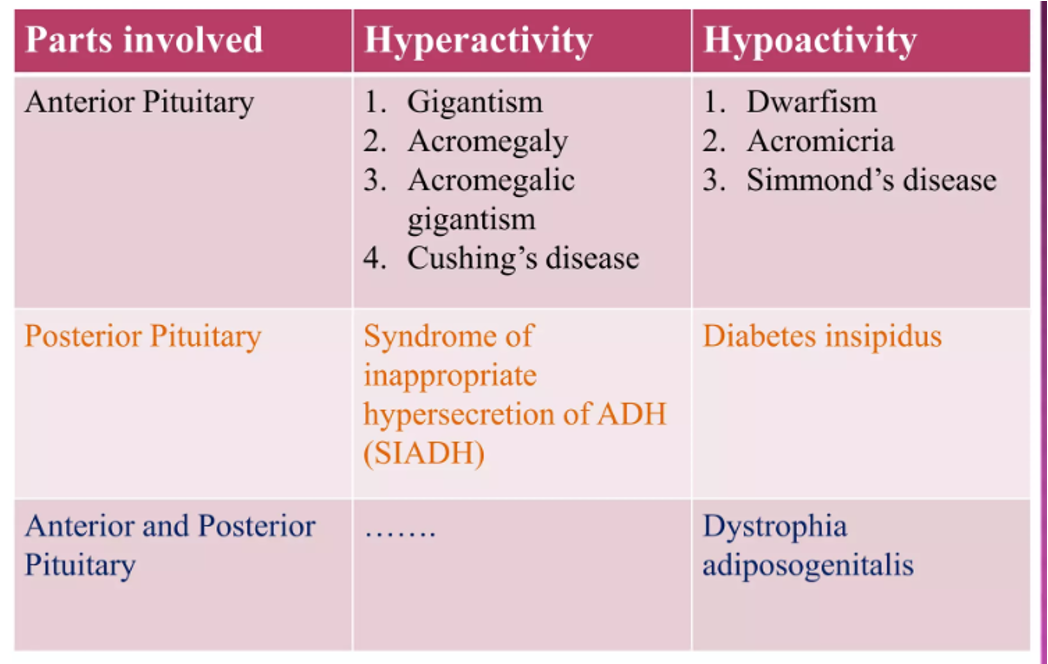
What does this refer to
Disorders of the Pituitary Gland