Chapter 4: Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/51
Last updated 1:13 AM on 1/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
1
New cards
Electrons can move as
Particles and Waves
2
New cards
Wave Nature
* Proposed by Louis de Broglie
* Electrons could be considered waves confined to the space around the NUCLEUS
* Only certain wavelengths and frequencies could exist
* Electrons could be considered waves confined to the space around the NUCLEUS
* Only certain wavelengths and frequencies could exist
3
New cards
A wave can be describes at
wavelength ( labda)
Frequency v (nv)
Energy: E
Frequency v (nv)
Energy: E
4
New cards
Wavelength
* Symbol: Lambda
* The distance between the crests of a wave
* UNITS: meters or nanometers
* 10^9nm = 1m
* The distance between the crests of a wave
* UNITS: meters or nanometers
* 10^9nm = 1m
5
New cards
Frequency
* Symbol: v (nv)
* The number of waves that pass/second
* UNITS: 1/sec = 1 hertz
* The number of waves that pass/second
* UNITS: 1/sec = 1 hertz
6
New cards
Speed of Light
* A constant
* Symbol: C
* fastest possible speed
* Symbol: C
* fastest possible speed
7
New cards
Speed of light equation
3\.00 x 10^8 meters/second
8
New cards
lambda and v are ….
inversely related
9
New cards
long wavelength =
low frequency
10
New cards
short wavelength =
long frequency
11
New cards
Electromagnetic Spectrum
350 nm = violet to 750 nm = red
12
New cards
Particle Nature of Light
Some properties of light cannot be explained by wave theory: white hot objects and the photoelectric effect
13
New cards
“White Hot” Objects
* When objects are heated they EMIT LIGHT
* Wave theory predicts that only UV LIGHT would be emitted but white, yellow, and orange light
* Wave theory predicts that only UV LIGHT would be emitted but white, yellow, and orange light
14
New cards
Photoelectric Effect
* Emission of electrons by certain metals when light shines on them
* The light must be of a certain energy/frequency to “knock” an electron from the surface
(Albert Einstein observed in 1905)
* The light must be of a certain energy/frequency to “knock” an electron from the surface
(Albert Einstein observed in 1905)
15
New cards
Quantum Energy
* MAX PLANCK
* White hot objects and the photoelectric effect both emit small, specific amount of energy call QUANTA or PHOTONS
* A specific amount “ bundle” of energy that can be gained or lost by an atom
* White hot objects and the photoelectric effect both emit small, specific amount of energy call QUANTA or PHOTONS
* A specific amount “ bundle” of energy that can be gained or lost by an atom
16
New cards
Energy of a Quantum
* An individual Quantum is known as a PHOTON of light and has evergy
17
New cards
Energy of a Quantum equation
* h = Plack’s constant
* h = 6.626 x 10 ^-34 joules x seconds
* E = hv
* h = 6.626 x 10 ^-34 joules x seconds
* E = hv
18
New cards
Energy + wavelength equation
E = hc/lambda
* inversely related
* inversely related
19
New cards
Wavelength of colors
750-625 nm - Red
625-590nm - Orange
590-565 nm - Yellow
565-520 nm - Green
520-435nm - Blue ( indigo)
435-350 nm - Purple
625-590nm - Orange
590-565 nm - Yellow
565-520 nm - Green
520-435nm - Blue ( indigo)
435-350 nm - Purple
20
New cards
Wavelengths ( highest to lowest)
Gamma Ray
X-Ray
Ultraviolet light
Visible
Infread
Microwave
Radio
X-Ray
Ultraviolet light
Visible
Infread
Microwave
Radio
21
New cards
Bohr Model
Why did Bohr study hydrogen?
Why did Bohr study hydrogen?
\- After observing the H line emission spectrum
* Simplest atom - only has one electron
* The electrons of the gas are easily excited by a current
* Simplest atom - only has one electron
* The electrons of the gas are easily excited by a current
22
New cards
1. How are the electrons moving
2. Where are the located
3. How much energy do they have
1. As particles with a definite circular path
2. In rings, or orbits around the nucleus
3. Th energy of an electron can be calculated
23
New cards
1. Electrons closer to the nucleus have …
2. At higher energy levels, the energy is …
1. Lower energy values
2. Higher
* each orbit is an energy lever designated by the variable n
* N =1 is the ground state
* N = infinity is when the electron has been removed from the atom
* Energy is quantized, meaning there are no levels in between the levels designated by n = 1,2,3,4, ect
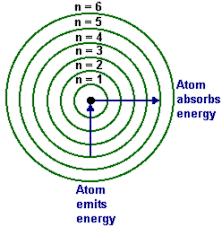
24
New cards
Spectroscopy
When atoms are excited by a outside energy source ( heat, flame, or electric current) the electrons can be promoted to higher energy states. However, this situation is highly unstable and the electron will eventually return to a lower energy state.
* when the electron returns to a lower energy level, energy is given off in the form of ( quanta), also known as a (photon of light)
* when the electron returns to a lower energy level, energy is given off in the form of ( quanta), also known as a (photon of light)
25
New cards
Energy input:
From LOWER levels to HIGHER level
26
New cards
Energy output:
From HIGHER levels to LOWER levels
27
New cards
Hyrogen produces lines in the
visible, ultraviolet, and infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum
28
New cards
Balmer series
visible
29
New cards
Lyman series
Uv
30
New cards
Paschen series
IR ( infread)
31
New cards
Energy at each level
E = -2.178 x 10^-18 J ( Z^2/ n^2)
Z = number of protons
n = energy level
* Calculation: deltaE = Efinal - Einital
* -2.178 x 10^-18 ( Z^2/n^2 (efinal) -Z^2/n^2 (einitial) )
Z = number of protons
n = energy level
* Calculation: deltaE = Efinal - Einital
* -2.178 x 10^-18 ( Z^2/n^2 (efinal) -Z^2/n^2 (einitial) )
32
New cards
Bohr’s Model ( hydrogen)
* Cannot successfully predict line spectra for an other element besides hydrogen
* Electrons must not be moving in circular orbits at set distances from the nucleus
* Electrons must not be moving in circular orbits at set distances from the nucleus
33
New cards
Electrons
* Moving as waves
* Not in orbits
* Located in Orbitals
* Areas of high probability based on the wave motion and energy of an electron
* Every orbital has an “address” given by a set of 4 Quantum numbers
* Energy: determined by h (like Bohr)
* Higher n= higher energy level = more energy = further from the nucleus
* Not in orbits
* Located in Orbitals
* Areas of high probability based on the wave motion and energy of an electron
* Every orbital has an “address” given by a set of 4 Quantum numbers
* Energy: determined by h (like Bohr)
* Higher n= higher energy level = more energy = further from the nucleus
34
New cards
* **Schrodinger**
Proposed a complex mathematical relationship to predict where e- is located
35
New cards
**DeBroglie**
* Proposed the particle to describe electron motion
36
New cards
**Heisenberg**
* Proposed the Heisenberg uncertainty
* The more you know about e- position, the less you know about it’s velocity (Inversely)
* The more you know about e- position, the less you know about it’s velocity (Inversely)
37
New cards
* **Pauli**
* Every electron in an atom must have a unique set of quantum numbers
* Electrons in the same orbital must have opposite spins
* Electrons in the same orbital must have opposite spins
38
New cards
**Hund’s**
* Electrons will fill an unoccupied within a sublevel before pairing up with another electron in an orbital
* This minimizes repulsion and leads to stability
* This minimizes repulsion and leads to stability
39
New cards
Principle Quantum Number
* n
* Tells what energy level the electron level is in
* Possible values: 1 to infinity
* Tells what energy level the electron level is in
* Possible values: 1 to infinity
40
New cards
* Orbital Quantum Number
* l
* Tells about the Shape of the orbital where the electron is housed
* Possible values: 0 to ( n-1)
* Tells about the Shape of the orbital where the electron is housed
* Possible values: 0 to ( n-1)
41
New cards
* Magnetic Quantum Number
* Ml
* Tells about the orientation of the orbital around the nucleus
* Possible values: -l to +l including 0
* Tells about the orientation of the orbital around the nucleus
* Possible values: -l to +l including 0
42
New cards
Spin Quantum Number
* Ms
* Tells the direction of the electron spin within an orbital
* Possible values: +1/2 and -1/2
* +1/2 : Clockwise spin
* -1/2 : Counterclockwise spin
* Tells the direction of the electron spin within an orbital
* Possible values: +1/2 and -1/2
* +1/2 : Clockwise spin
* -1/2 : Counterclockwise spin
43
New cards
S orbital:
* spherical ( l =0)
* 0
* 0
44
New cards
P orbital
* peanut shaped ( l =1)
* -1,0,1
* -1,0,1
45
New cards
D orbital:
* daisy shaped ( l =2)
* -2,-1,-0,1,2
* -2,-1,-0,1,2
46
New cards
F orbital
flower shaped ( l =3)
\-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3
\-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3
47
New cards
**Energy level Diagrams**
* A way to keep track of electrons
* Includes line boxes that represent Orbitals
* Also shows orbital types and energy levels
* Once filled, it is possible to find the quantum number set for any electron in the atom
* Includes line boxes that represent Orbitals
* Also shows orbital types and energy levels
* Once filled, it is possible to find the quantum number set for any electron in the atom
48
New cards
**Aufbau Principle**
* Meaning: Build up
* Electrons must be filled from the lowest energy to the highest energy
* Do not move to the next until the one below has been completely filled
* Electrons must be filled from the lowest energy to the highest energy
* Do not move to the next until the one below has been completely filled
49
New cards
**Hund’s Rule**
* Electrons will fill an unoccupied within a sublevel before pairing up with another electron in an orbital
* This minimizes repulsion and leads to stability
* This minimizes repulsion and leads to stability
50
New cards
Octet Rule
* Atoms become stable when their outermost energy level contains 8 electrons
* Noble gases have a full OCTET
* The outermost electrons are called Valance Electrons (except He)
* Noble gases have a full OCTET
* The outermost electrons are called Valance Electrons (except He)
51
New cards
**Electron Configuration**
* Shows every electron in the atom starting with the 1s orbital
* Valence electrons exist in the highest energy level listed
* Valence electrons exist in the highest energy level listed
52
New cards
**Noble Gas Configuration**
* Uses the preceding noble gas core to shorten the electron configuration
* Allows the valence electrons to be determined easily
* Allows the valence electrons to be determined easily