Sensory Receptors and Afferent Pathways
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Pacinian Corpuscle
Have a threshold
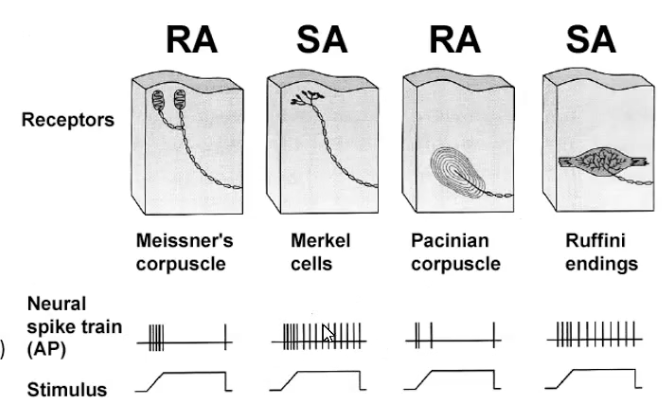
Rapidly adapting receptors
Meissner’s corpuscle responds instantaneously to change but stop firing after the stimulus has been there a while (fast adaption rate)
Pacinian corpuscles do the same thing

Slowly adapting receptors
Merkel cells respond to the change in stimulus but have a slower rate of adaption.
Detect continuous stimuli of the same strength
Where are the receptors found?
Nocicereceptors are free nerve endings
Merkel disks are at the base of the epidermis.
They are made of merkel cells
Light found in skin and mucosa
Meissner, ruffini, and pacinian corpuscles (Aβ) are encapsulated by cells or connective tissue to detect light pressure or vibration.
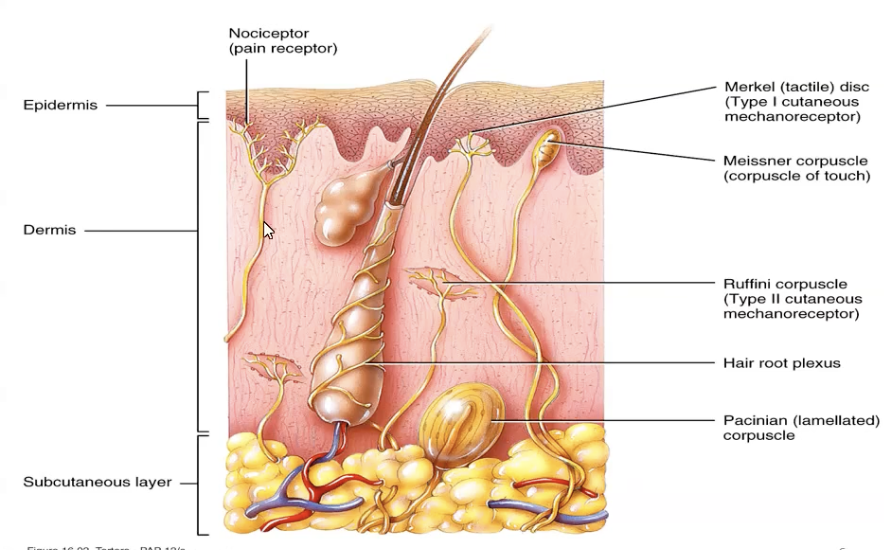
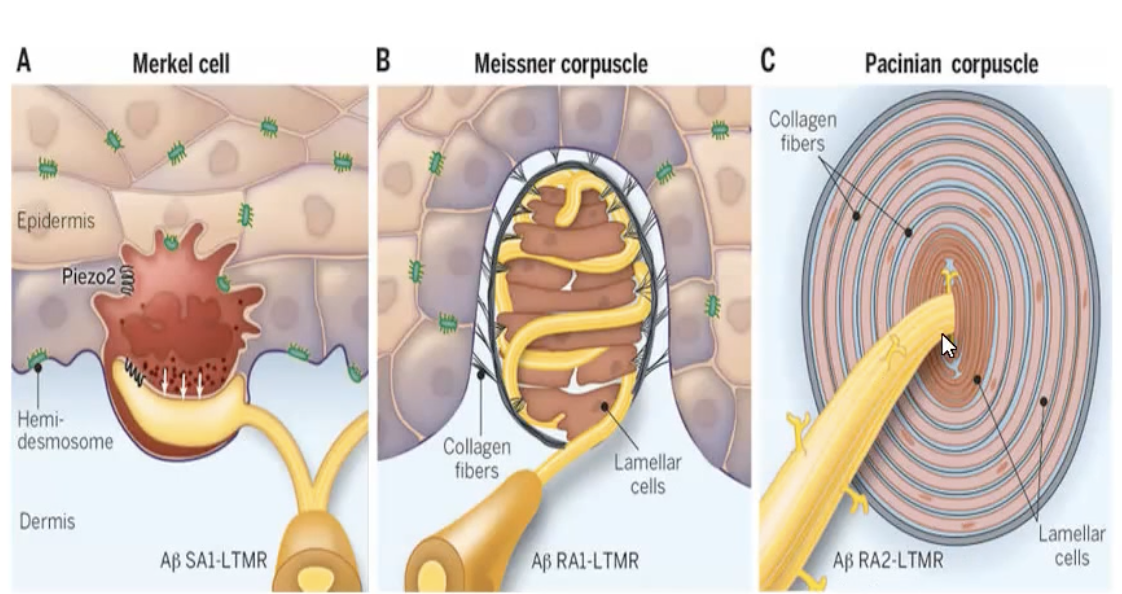
Meissner corpuscles
Fine touch and low frequency vibration
Hairless skin e.g. finger tips, palms and soles, eyelids, tip of tongue and lips
Ruffini Corpuscles
Stretch due to movement
Deep in the dermis (hands and soles), joint capsules, ligaments and tendons
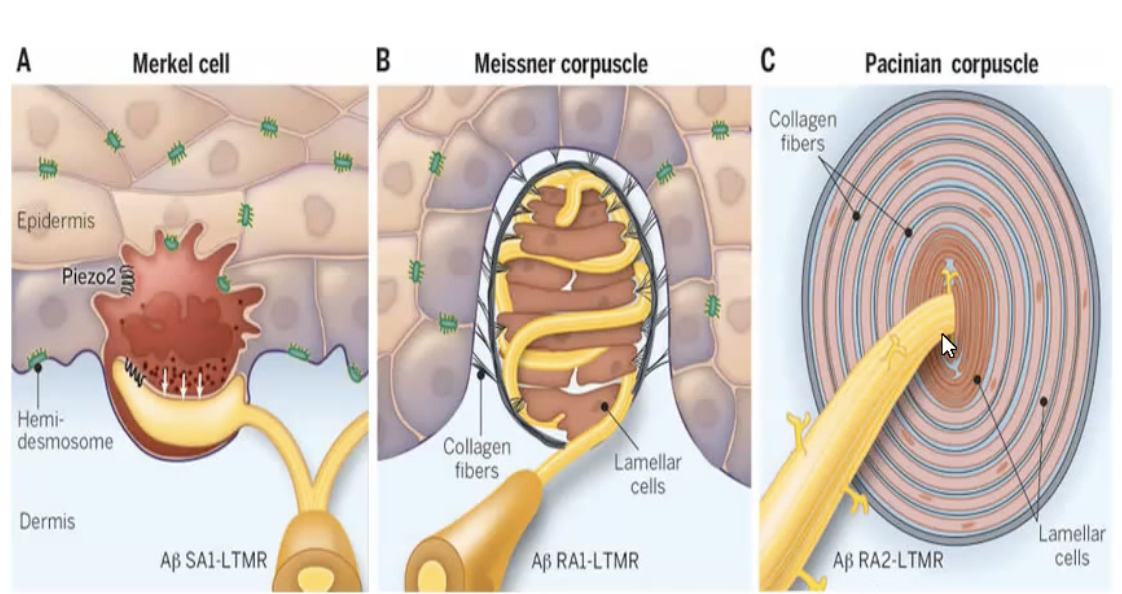
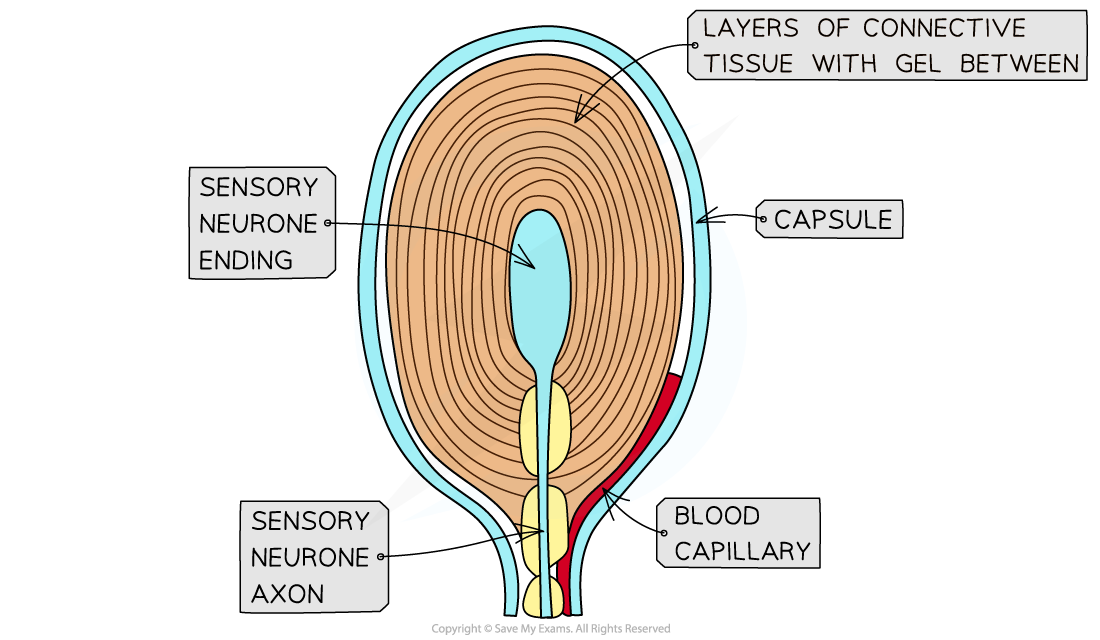
Pacinian Corpuscles
Responds to deep pressure and high frequency vibration
Deep in the dermis, around joint capsules, tendons, muscles, periosteum, mammary glands, external genitalia, pancreas, and bladder.

Exteroceptors
Receptors located near the skin
Respond to stimuli outside and on the surface of our body
Special senses
Proprioceptors
Movement in the skin, muscles, tendons, ligaments and joints
Body position awareness and kinaesthesia awareness of movement in the body
Meissners, merkel’s, ruffini, pacinian corpuscles, golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles and free nerve endings.
Interoceptors
Respond to stimuli in the body from visceral organs and blood vessels
Visceral nervous system
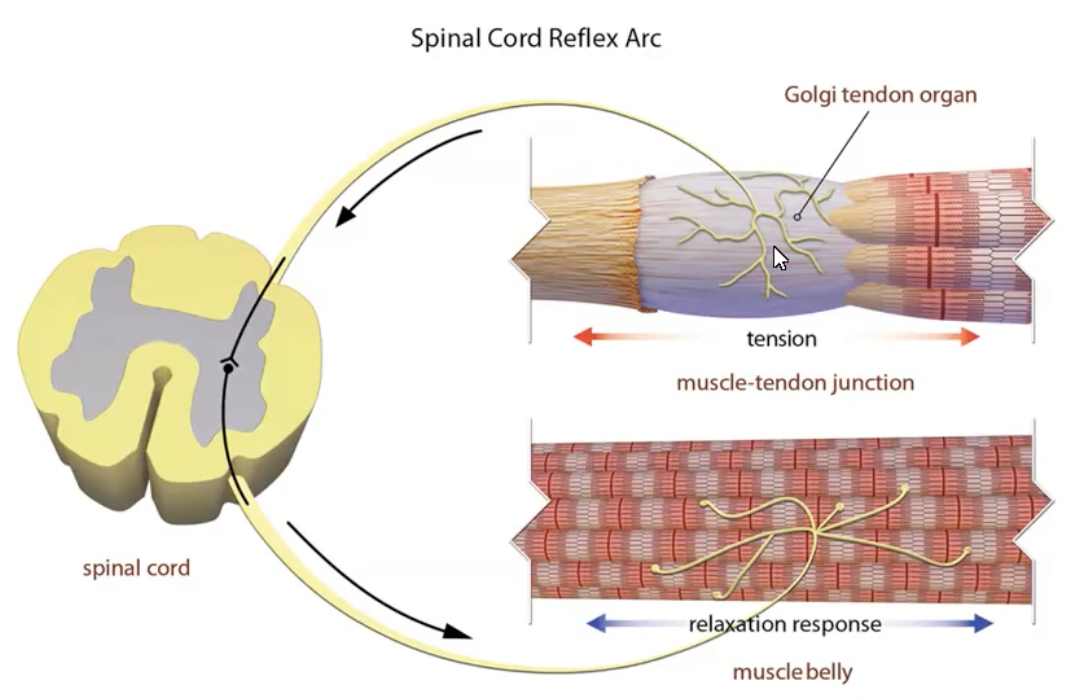
Golgi Tendon Organs
Junction between muscle and tendon
Detect tension in muscles
Sensory afferents (1b) detect tension and convey AP’s to inhibit alpha motor efferents causing the muscle to relax
Mostly moderators and make fine adjustments
Classification via Stimulus
Mechanoreceptors
Thermoreceptors respond to temp
Free nerve endings
Cold (epidermis 10-40)
Warm (dermis 32-48)
Below 10 and above 48 activates pain receptors
Nociceptors
Nociceptors
Mechanical receptors - A𝛿
Thermal-mechanical nociceptors (temo and strong mechanical stimuli) - A𝛿 (fast) or C (slow unmyleinated)
Group 1 (+48) and Group 2 (<10)
Polymodal receptors respond to strong mechanical thermal or chemical stimuli (K, ATP, histamine, bradykinin, pH, substance P, serotonin and ACh) - C
Slow burning pain
Trauma that has burst calls and contents have escaped these will be stimulates
Chemoreceptors
Special senses: Gustatory receptors in the taste buds and olfactory receptors in the nasal cavities.
Respirator chemoreceptors:
Digestive chemoreceptors: Sense macronutrients and non-nutrient constituents of food.
Osmoreceptors
Hypothalamus and kidneys
Detect changes in osmotic pressure
Control fluid balance in the body
Glucose receptors
Hypothalamus, liver, pancreas and gut
Detect changes in glucose concentrations
Spinal Tracts
Posterior columns (gracile and cuneate fasciculus) run up to the brainstem and carry fine touch, pressure, vibration and conscious touch.
Anterolateral tracks carry pain and temp, tickle, itch.
Pathway VS Fibre Tracts
Fibre tracts are nerve fibers bundled together in the CNS with a common function e.g. corticospinalis
A pathway refers to the entire neuronal circuit associated with the function of a tract
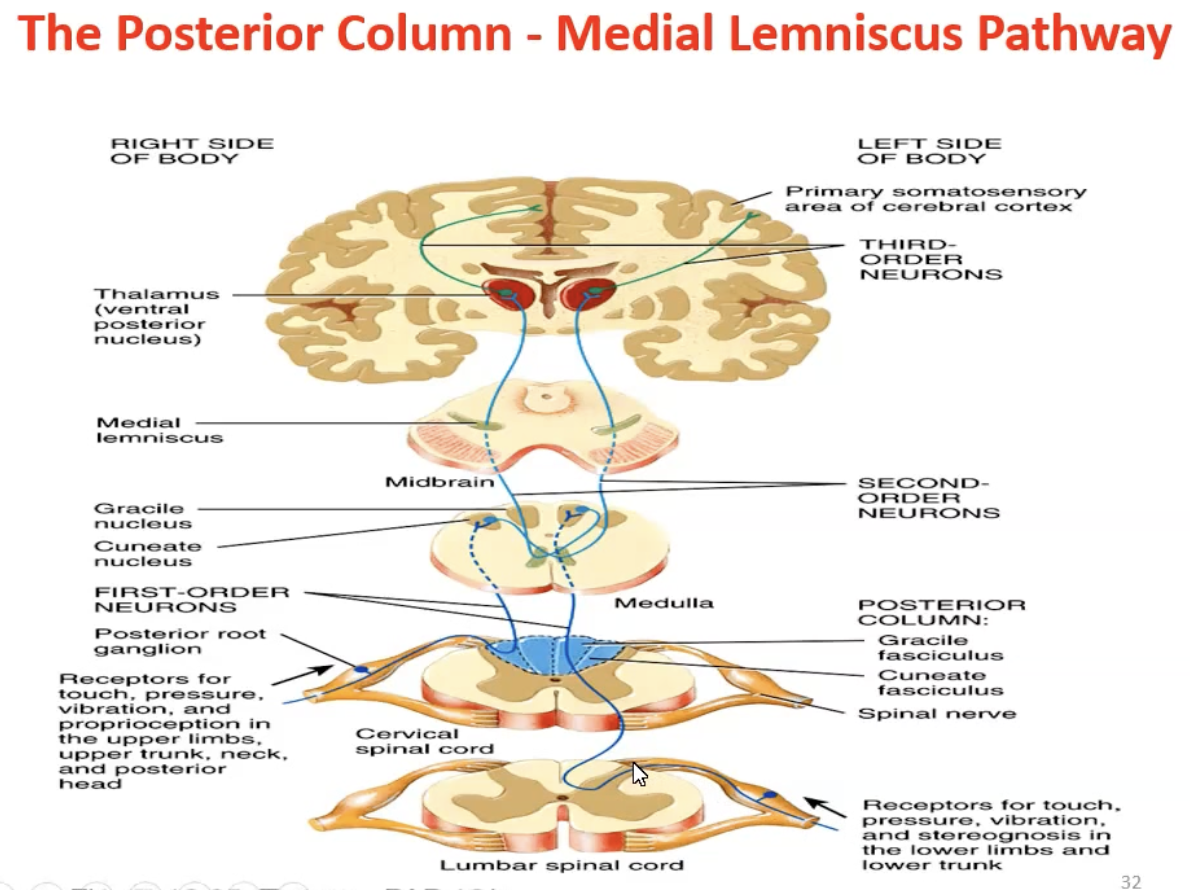
Posterior Funiculus (Part of the Posterior column Medial Lemniscus)
Gracile fasciculus: Fine touch, pressure vibration, conscious proprioception from lower limbs.
Cuneate fasciculus: Fine touch, pressure vibration, conscious proprioception from upper limbs (above T6).
Open Rostral Medulla
Pyramids - before decussation
Medial lemniscus on either side of the midline - medial medulla goes up and out
Inferior olivary nuclei go to inferior cerebellar peduncles
The 4th floor of the 4th ventricle, hypoglossal nuclei, dorsal motor nucleus and vestibular nuclei.
Posterior Column Medial Lemniscus Pathway
First order neurons run in the peripheral/spinal nerve
They run from receptor to the dorsal gray horn and enter the ipsilateral posterior column without synapsing.
The neurons from below T6 run in the gracile fascicles
The neurons from at and above T6 run in the cuneate fascicles
The first order neurons synapse on the cuneate or gracile nuclei in the medulla.
Second order neurons decussate and enter the medial lemniscus from the medulla to the VPL in the thalamus.
Third order neurons run from the thalamus to the somatosensory cerebral cortex.
Anteriolateral Pathways
Made of three pathways the
Spinothalamic pathway
Spinoreticular Pathways
Spinomesencephalic Pathway
Spinothalamic Pathway
First order neurons run in the peripheral/spinal nerve from receptor to the dorsal gray horn and synapse on second order neurons.
Second order neurons decussate in the ventral white commissure and send via the lateral and anterior spinothalamic tracts on the contralateral side
They continue through the medulla above the inferior olivary nuclei and form the spinal lemniscus.
They run from the VPL nucleus of the thalamus and synapse on third order neurons.
Third order neurons run to the somatosensory cortex for contralateral pain.
Lateral tracts carry fast and localised pain (A𝛿 fibres) and temp
Anterior tracts carry tickle itch and touch
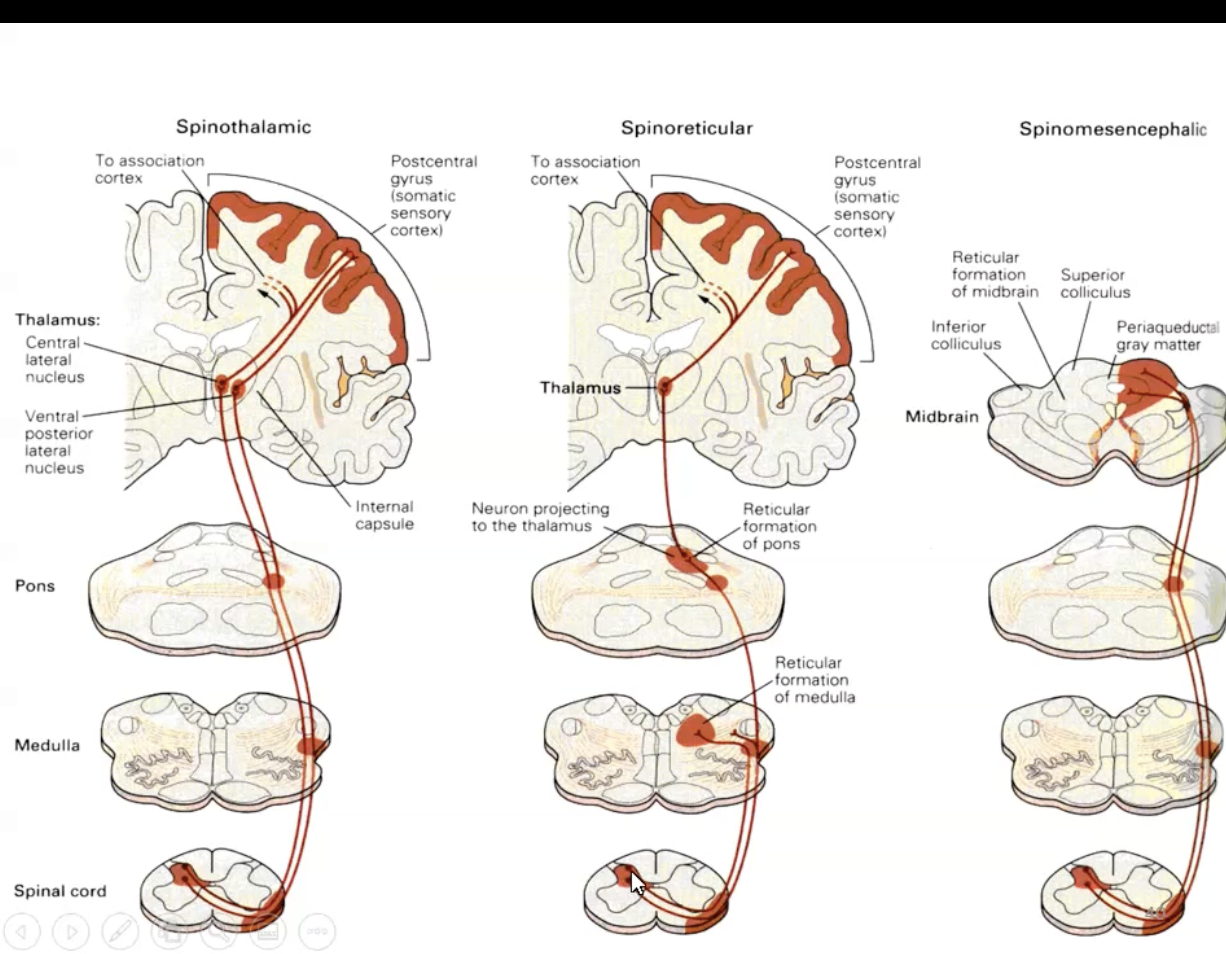
Spinoreticular Pathways
Carry dull, aching pain (C fibres)
First order neurons in spinal nerve synapse in dorsal gray horn onto second order neurons that decussate to contralateral side.
Second order neurons synapse at the brainstem reticular formation onto third order neurons.
Third order neurons run to the thalamus and synapse on fourth order neurons
Fourth order neurons run to the cerebral cortex.
Phylogenetically older and for general arousal to pain
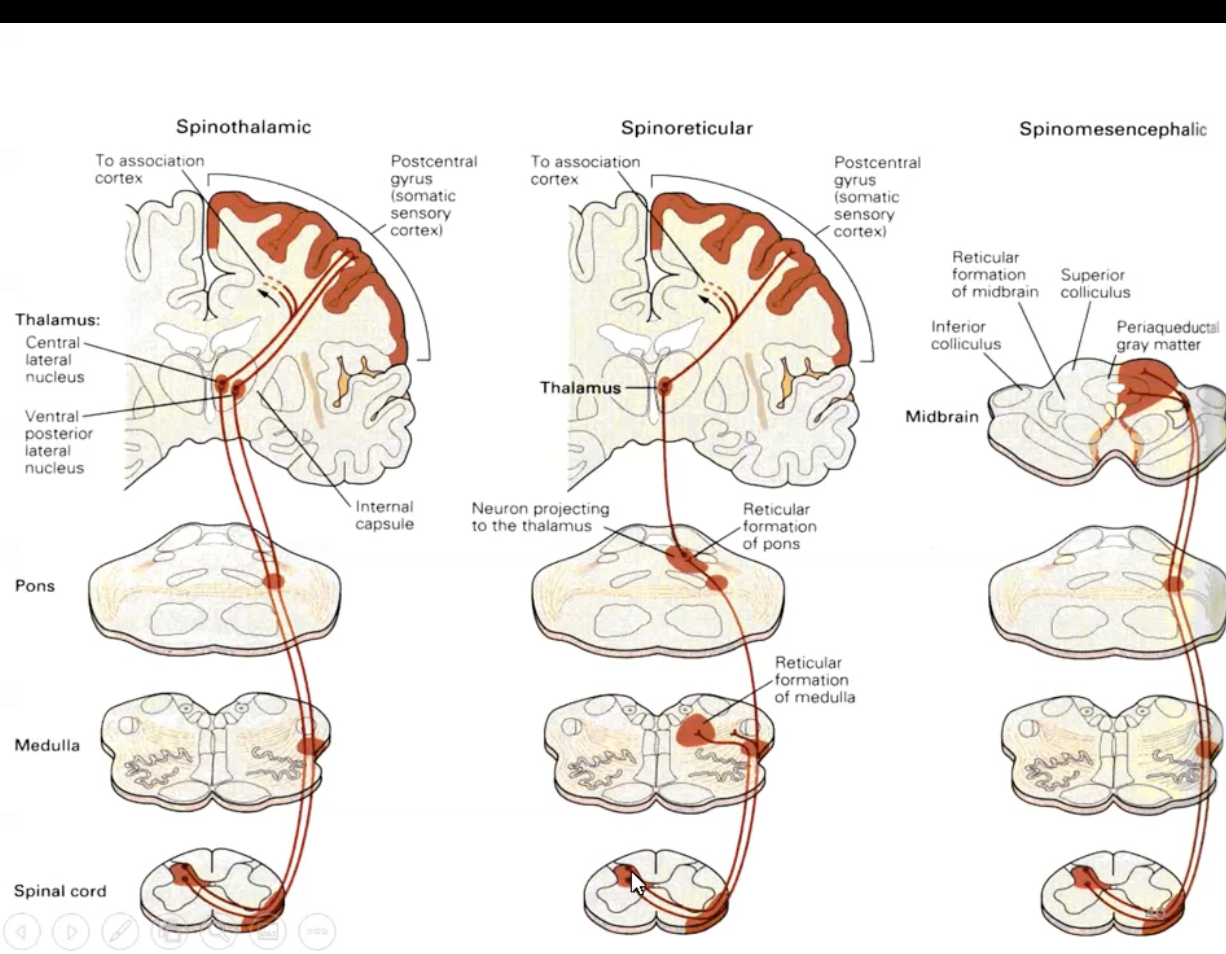
Spinomesencephalic Pathway
First order neurons in spinal nerves synapse on to second order neurons in the dorsal gray horn which decussate to the contralateral side
Second order neurons run up to the mesencephalic (midbrain) reticular formation and periaquaductal gray matter
These then connect to limbic system e.g. amygdala
Responsible for affective responses to pain
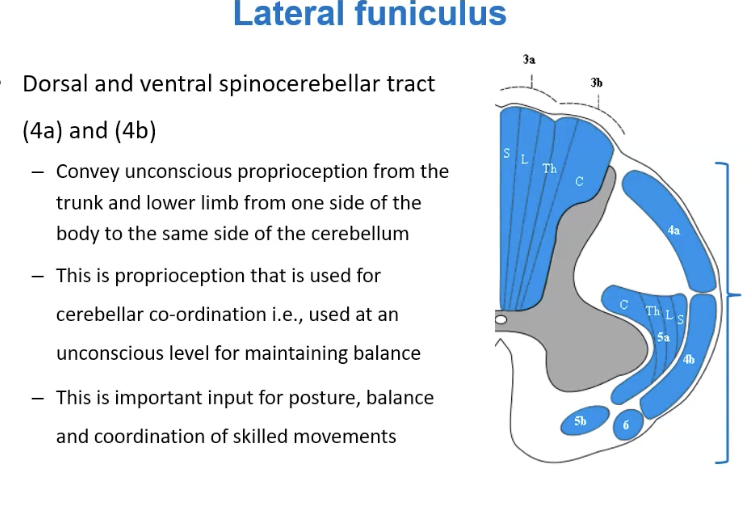
Spinocerebellar Pathways
Located in the lateral funiculus
Unconscious proprioception - awareness of body and how it is moving
Goes to cerebellum for learning
Inout for posture, balance and coordination and skilled movement
Only lower limbs and trunk and is ipsilateral
Posterior Spinocerebellar Pathway
First order neurons from the spinal nerves (trunk + lower limb) run through the dorsal gray horn and synapse on clarks nucleus.
Second order neurons enter the posterior spinocerebellar tracts ipsilateral.
They run up via the inferior cerebellar peduncles to the cerebellum.
Clarke’s nucleus does not exist caudal to L2
Below afferents ascend via the gracile fasciculus of the posterior column and synapse on clarke’s nucleus.
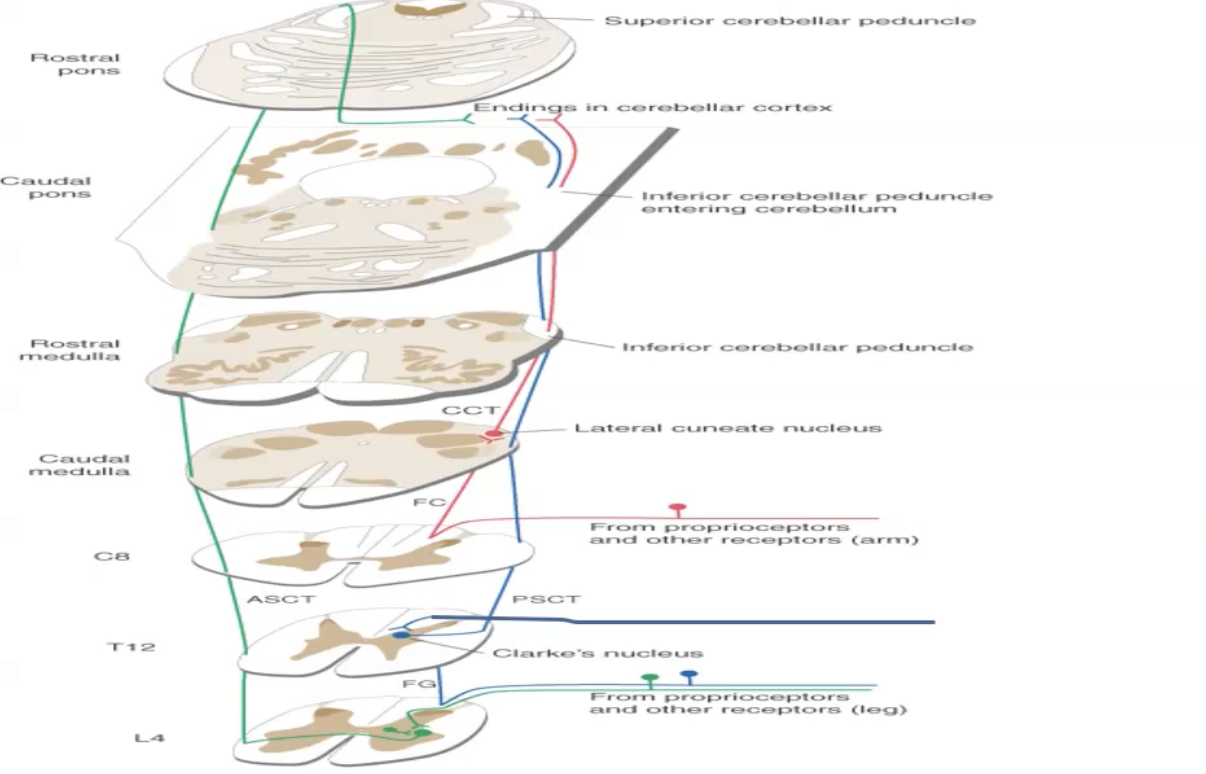
Cuneate Cerebellar Tract (CCT)
First order fibres from the arm enter at the dorsal gray horn and travel in the cuneate fasciculus of the posterior columns to the lateral cuneate nucleus in the medulla and synapse on second order neurons.
Second order neurons form the cuneocerebellar tract which projects to the ipsilateral cerebellum through the inferior cerebellar peduncles
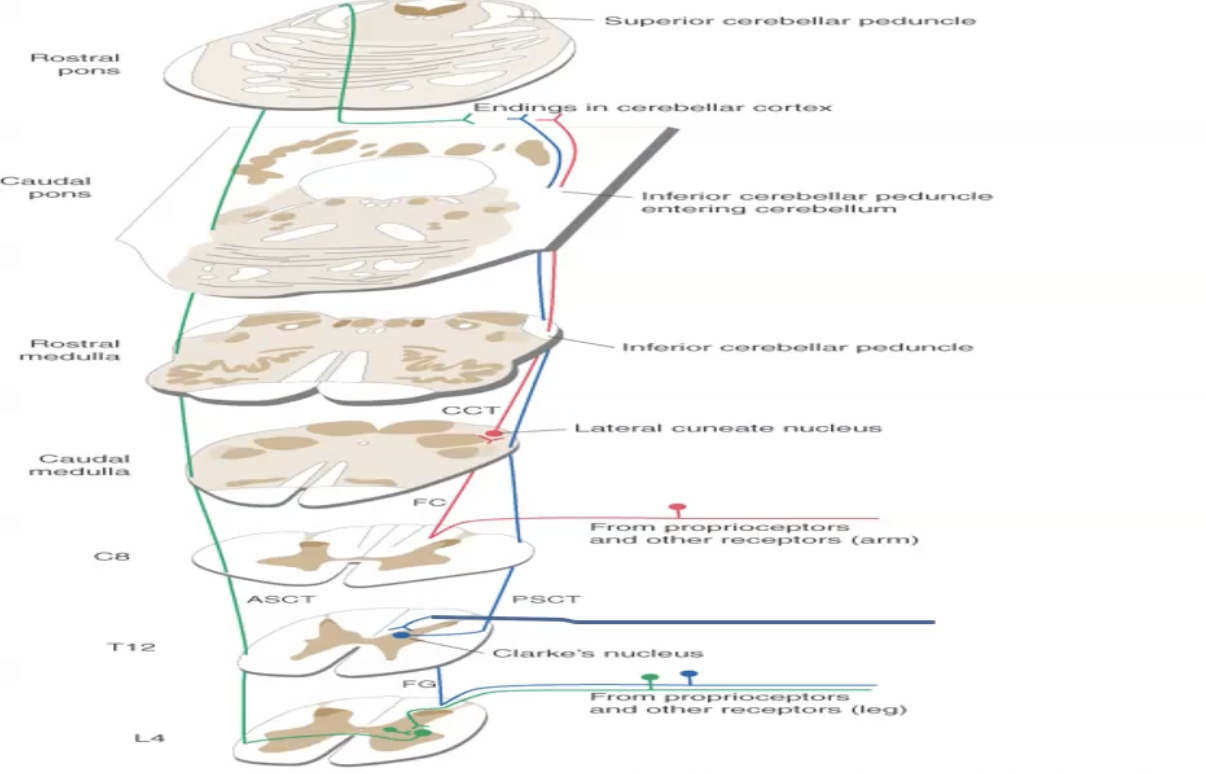
Anterior Spinocerebellar Pathways
Unconscious proprioceptive information (first order neurons are usually golgi tendons) enters through the dorsal grey horn onto second order neurons.
Second order neurons decussate onto the anterior spinocerebellar tracts.
Ascends to the pons and enter the cerebellum via the superior cerebellar peduncles where fibres cross again.
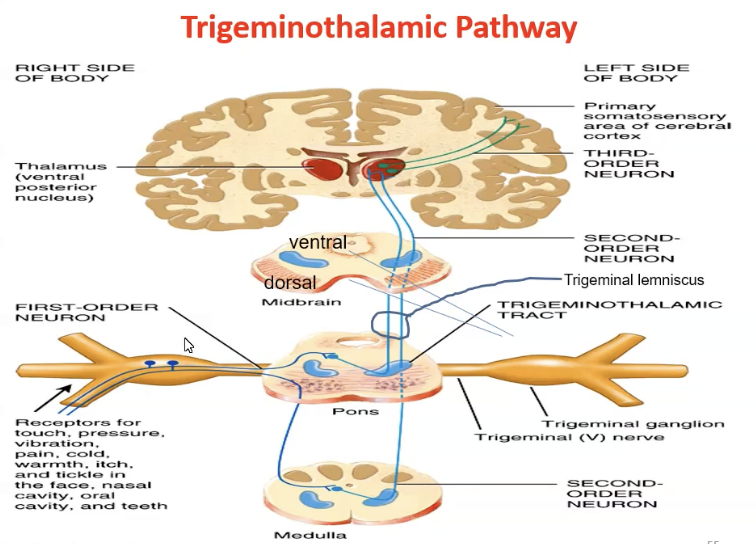
Trigeminothalamic Pathway
Facial information - touch, pain, pressure, tickle ect.
The first order neurons enter the principal nucleus in the pons.
Large diametre fibres (Aβ) for touch, pressure and vibration synapse here on second order neurons
The second order neurons decussate, then join the dorsal trigeminothalamic tract to the VPM nucleus in the thalamus where they synapse on third order neurons that run to the somatosensory cortex
Fine unmyelinated fibres for pain and temperature don’t synapse on the principal nucleus but turn caudally down the spinal nucleus of CNV.
These first order neurons synapse on second order neurons that decussate and run via the ventral trigeminothalamic tract to the VPM nucleus in the thalamus and synapse on third order neurons that run to the somatosensory cortex
The ventral and dorsal trigeminothalamic tracts together form the trigeminal lemniscus.
Fibres for proprioception don’t synapse on the principal nucleus but turn rostrally up to the mesencephalic nucleus (ganglion for nerve cell bodies) and then synapse on the motor nucleus of CNV – chewing reflex