LESSON 2: The Tissue Level of Organization
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
Tissues
these are a group of cells with a common embryonic origin that function together to carry out specialized activities.
They include various types, ranging from hard (bone) to semisolid (fat) to liquid (blood).
Histology
It is the study of the microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues – it is a branch of pathology.
Of the 10 trillion cells in our body, no single cell type can said to be “typical”. A trained histologist can recognize over 200 distinct human cell types under the microscope and is able to distinguish a cell from pancreatic tissue as opposed to a cell from the skin.
Each cell type has features particular to its function.
Epithelial tissues, Connective tissues, Muscular tissues, Nervous tissues
The 4 Basic Tissues
Of all the cells in the body, they combine to make only 4 basic tissue types: (what are those 4?)
Epithelial tissues
The 4 Basic Tissues
cover body surfaces and form glands and line hollow organs, body cavities, and ducts.
Connective tissues (C.T.)
The 4 Basic Tissues
protect, support, and bind organs.
Fat
is a type of C.T. that stores energy.
connective tissues
Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are all ___________ (what type of tissue?)
Muscular tissues
The 4 Basic Tissues
generate the physical force needed to make body structures move. They also generate heat used by the body.
Nervous tissues
The 4 Basic Tissues
detect changes in the body and respond by generating nerve impulses.
Endoderm, Mesoderm, Ectoderm
Tissues of the body develop from three primary germ layers: (what are those 3 layers?)
Epithelial tissues
what type of tissue is from all three germ layers
connective tissue, muscular tissue
what type of tissues (2) are derived from mesoderm?
Nervous tissue
what type of tissue is developed from ectoderm?
ectoderm
__________ develops into:
nervous tissue
outer skin layer (including hair and nails)
parts of:
sense organs
mouth
sinuses
teeth
endoderm
________ develops into parts of:
digestive tract
lungs and respiratory tract
bladder
mesoderm
__________ develops into
muscles
bones
cartilage
blood and vessels
lymph tissue
part of:
kidneys
gonads
Epithelium
___________ is used to line surfaces and form protective barriers.
__________ is also good at secreting things like mucous, hormones, and other substances.
All ________ have a free apical surface and an attached basal surface.
basal layer
The ___________ of the epithelium secretes a basal lamina; the underlying C.T. secretes a reticular lamina.
basal lamina
The basal layer of the epithelium secretes a __________; the underlying C.T. secretes a reticular lamina.
reticular lamina
The basal layer of the epithelium secretes a basal lamina; the underlying C.T. secretes a _________.
noncellular basement membrane
Together the basal lamina and the reticular lamina form a ___________________ on which the epithelium sits.
Epithelia
are named according to the shape of their cells, and the thickness or arrangement of their layers (of cells).
simple, pseudostratified, stratified
naming epithelium based on arrangement of layers
squamous, cuboidal, columnar
naming epithelium based on cell shape
squamous
Naming epithelia according to shape
Flat, wide “paving stone” cells
cuboidal
Naming epithelia according to shape
Cells as tall as they are wide
columnar
Naming epithelia according to shape
Cells taller than they are wide
simple
Naming epithelia according to arrangement
One layer. All cells in contact with basement membrane
pseudostratified
Naming epithelia according to arrangement
Appears to have layers, but in reality all cells go from the apex to the base
stratified
Naming epithelia according to arrangement
Two or more layers. Only basal layer in contact with basement membrane
Naming epithelia
Naming epithelia
Three different cell shapes x three different cell arrangements = nine possibilities. Two of these are not used. Add transitional (cells that change shape), and we’re back up to eight possible combinations.
If different shapes are present in layers of cells, the epithelium is always named by the shape of cells in the apical (outermost) layer.
Simple Squamous Epithelium
is composed of a single layer of flat cells found:
In the air sacs of lungs
In the lining of blood vessels, the heart, and lymphatic vessels
In all capillaries, including those of the kidney
As the major part of a serous membrane
function: for easy permeability & diffusion
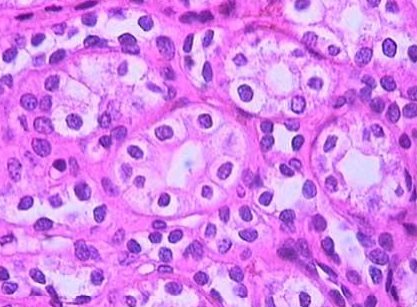
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
is composed of a single layer of cube shaped cells.
It is often found lining the tubules of the kidneys and many other glands.
function: for secretion
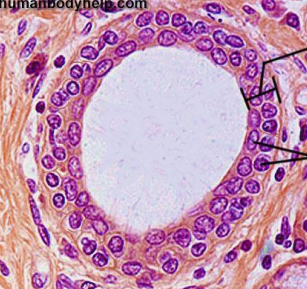
Simple Columnar Epithelium
forms a single layer of column-like cells, ± cilia, ± microvilli, ± mucous (goblet cells).
Goblet cells are simple columnar cells that have differentiated to acquire the ability to secrete mucous.
this is found in respiratory tract and digestive tract
functions:
goblet cells - for secretion of mucus
cilia - for protection & movement
simple cuboidal epithelium, kidney tubules
classify based on shape and number of layers, and what organ
free apical surface, attached basal surface
epithelia has two main parts, what are these?
basal lamina
what part of basement membrane is closely attached to the epithelium
reticular lamina
what part of basement membrane is next to the basal lamina
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
appears to have layers, due to nuclei which are at various depths. In reality, all cells are attached to the basement membrane in a single layer, but some do not extend to the apical surface.
Ciliated tissue has goblet cells that secrete mucous.
It is found in the upper respiratory tract
function: since its found in upper respiratory tract, it functions more in secretion of mucous, protecting upper respiratory from dust.
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
has an apical surface that is made up of squamous (flat) cells.
The other layers have different shapes, but the name is based on the apical layer.
The many layers are ideal for protection against strong friction forces.
function: for protection
found in skin
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
has an apical surface made up of two or more layers of cube-shaped cells.
Locations include the sweat glands and part of the ♂ (male) urethra
it is not very common
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
is very rare, and for our purposes, hardly worth mentioning.
Transitional Epithelium
The cells of _____________ change shape depending on the state of stretch in the tissue.
The apical “dome cells” of the top layer (seen here in relaxation) are an identifiable feature and signify an empty bladder.
In a full bladder, the cells are flattened.
maximum volume of urine that can be stored in urinary bladder is 700-800 ml
if urinary bladder is filled with urine, the epithelial lining is squamous (flat)
when it is empty or umihi ka na, the epithelial lining is either cuboidal or columnar
stratified cuboidal, found in male urethra and sweat glands, absorption & secretion
Classify epithelium based on shape and number of layer, location, and function
Stratified squamous epithelium
Although epithelia are found throughout the body, certain ones are associated with specific body locations.
____________ is a prominent feature of the outer layers of the skin.
Simple squamous
_______________ makes up epithelial membranes and lines the blood vessels.
Columnar
is common in the digestive tract.
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar
_____________________ is characteristic of the upper respiratory tract.
Transitional
____________ is found in the bladder.
Cuboidal
____________ lines ducts and sweat glands.
Endothelium
Covering and Lining Epithelium
is a specialized simple squamous epithelium that lines the entire circulatory system (including capillaries, blood vessels, veins, artery, and heart) from the heart to the smallest capillary – it is extremely important in reducing turbulence of flow of blood.
lines blood vessels and heart
Mesothelium
Covering and Lining Epithelium
is found in serous membranes such as the pericardium, pleura, and peritoneum.
Unlike other epithelial tissue, both are derived from embryonic mesoderm (the middle layer of the 3 primary germ layers of the embryo).
lines serous membrane
mesoderm
all epithelial tissue comes from 3 germ layers except for endothelium & mesothelium, which comes from the ___________
Connective Tissues
__________ are the most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body – they are also the most heterogeneous of the tissue groups.
They perform numerous functions:
Bind tissues together
Support and strengthen tissue
Protect and insulate internal organs
Compartmentalize and transport
Energy reserves and immune responses
Collagen
_____________ is the main protein of C.T. and the most abundant protein in the body, making up about 25% of total protein content.
Connective tissue
__________ is usually highly vascular and supplied with many nerves.
The exception is cartilage and tendon - both have little or no blood supply and no nerves.
connective tissues
Although they are a varied group, all ___________ share a common “theme”:
Sparse cells
Surrounded by an extracellular matrix
extracellular matrix
The __________ is a non-cellular material located between and around the cells.
It consists of protein fibers and ground substance (the ground substance may be fluid, semifluid, gelatinous, or calcified.)
protein fibers, ground substance
The extracellular matrix is a non-cellular material located between and around the cells.
It consists of _________ and __________ (the ground substance may be fluid, semifluid, gelatinous, or calcified.)
Fibroblasts
Common C.T. cells
are the most numerous cell of connective tissues. These cells secrete protein fibers (collagen, elastin, & reticular fibers) and a “ground substance” which varies from one C.T. to another.
Chondrocytes
Of the other common C.T. cells:
make the various cartilaginous C.T.
Adipocytes
Of the other common C.T. cells:
store triglycerides.
Osteocytes
Of the other common C.T. cells:
make bone.
White blood cells
Of the other common C.T. cells:
are part of the blood.
g-actin
most common protein in cytosol
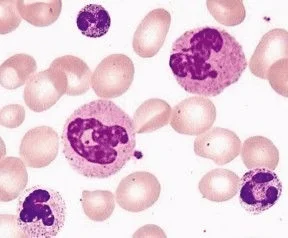
macrophages, neutrophils, mast cells, eosinophils, lymphocytes
There are 5 types of white blood cells (WBCs): (what are those?)
monocyte
largest WBC in peripheral blood and it is horse-shoe shape. this becomes macrophages
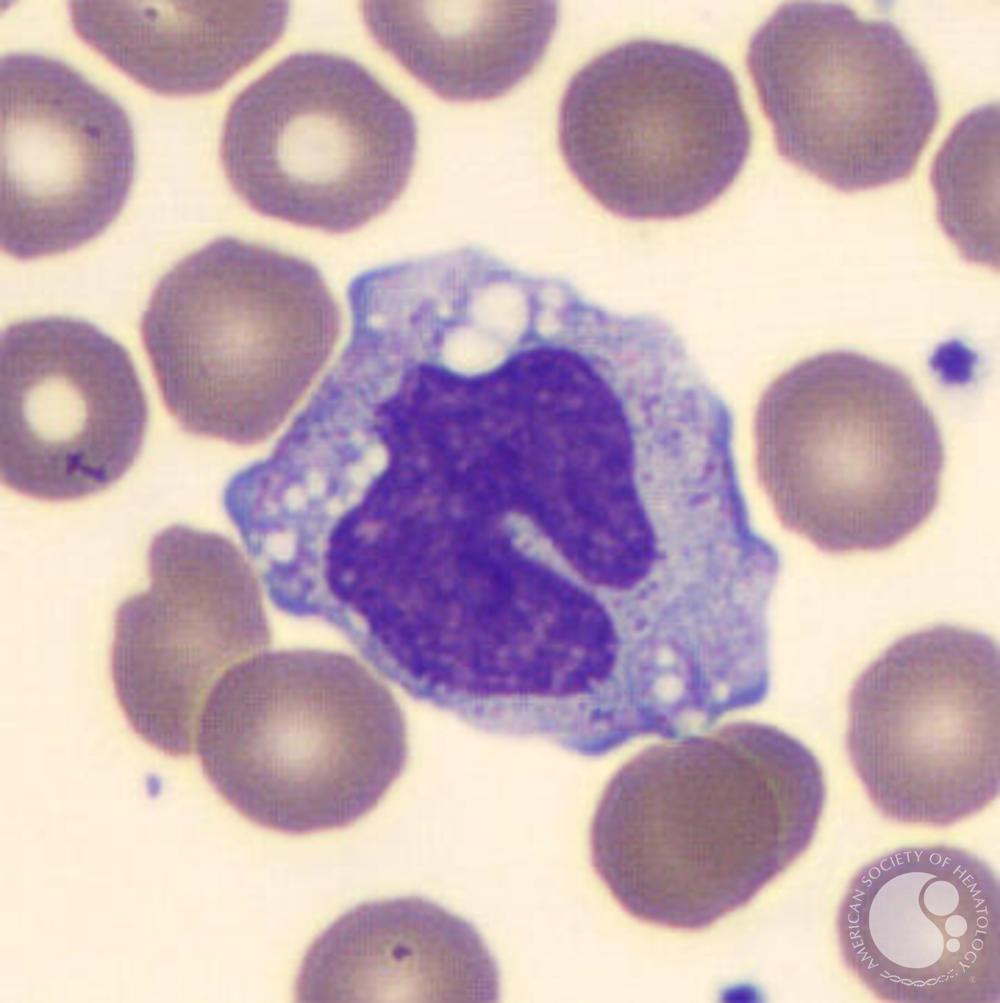
Macrophages
are the “big eaters” that swallow and destroy invaders or debris. They can be fixed or wandering.
Neutrophils
are also macrophages (“small eaters”) that are numerous in the blood.
increases when there is bacterial infection
w/ pinkish or lilac granules
Mast cells, Eosinophils
these two play an important role in inflammation
basophil
w/ purplish granules
nasa granules yung histamine
paglabas sa blood magiging mast cell
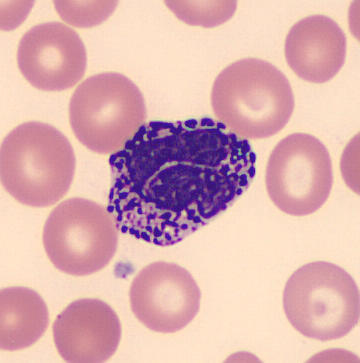
mast cells
it is called basophils when inside the blood
it has histamine
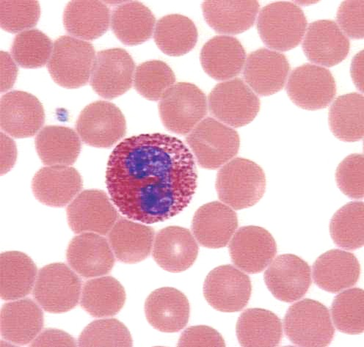
eosinophils
increases when there is allergy and parasitism
w/ orange granules
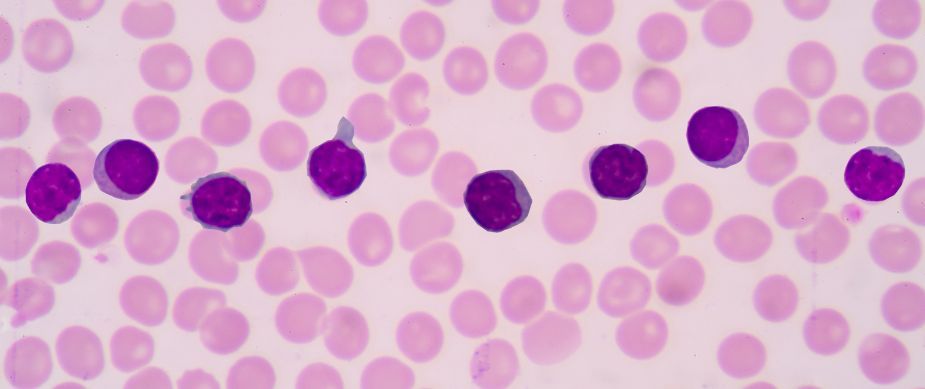
Lymphocytes
secrete antibody proteins and attack invaders.
appearance: almost occupying the whole cell
macrophage
_________ = outside the blood
monocyte = inside the blood
monocyte
macrophage = outside the blood
_________ = inside the blood
Langerhans cell
macrophage of skin
Kupffer cell
macrophage of liver
microglia
macrophage of nervous system
histiocyte
macrophage of connective tissue
osteoclast
macrophage of bone
dust cells
macrophage of lungs
T-lymphocyte
bone marrow → thymus → blood
for cellular immunity
T4 - helper
T8 - cytotoxic
T8 attacks virus, tumor, and transplanted cells
normal:
CD4 (T4) : CD8 (T8) = 2 : 1
person with HIV:
CD4 (T4) : CD8 (T8) = 1 : 2
B-lymphocyte
bone marrow → blood
for humoral immunity
produces antibodies
Collagen fibers, Elastin fibers, Reticular fibers
C.T. cells secrete 3 common fibers: (what are these?)
Embryonic connective tissue, Mature connective tissue
2 Connective Tissue Classification
Mesenchyme, Mucous connective tissue
There are 2 Embryonic Connective Tissues: (what are these?)
Mesenchyme
Embryonic Connective Tissue that gives rise to all other connective tissues.
mucous connective tissue
Embryonic Connective Tissue that (Wharton's Jelly) is a gelatinous substance within the umbilical cord and is a rich source of stem cells.
mesenchymal connective tissue
identify
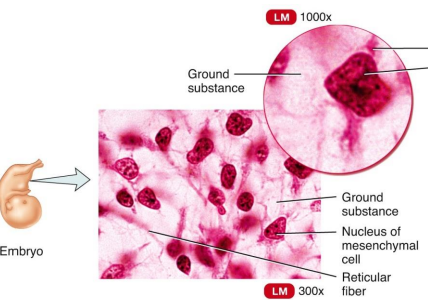
mucous connective tissue
identify
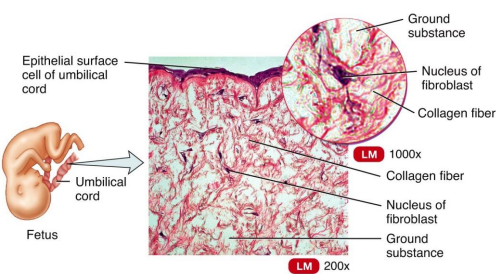
Areolar Connective Tissue
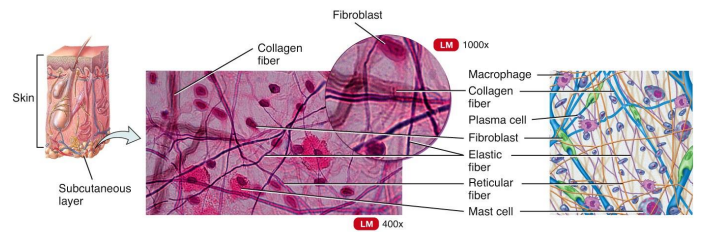
Loose Connective Tissues
is the most widely distributed in the body. It contains several types of cells and all three fiber types.
It is used to attach skin and underlying tissues, and as a packing between glands, muscles, and nerves.
most easily identified because it is widely distributed
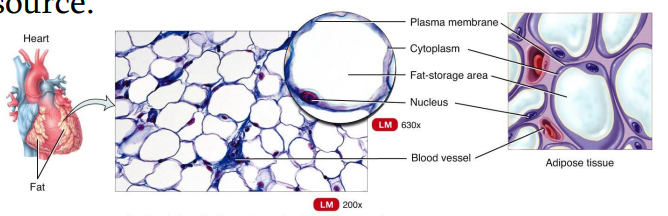
triglycerides
type of fat stored in adipose tissue
Adipose tissue
Loose Connective Tissues
is located in the subcutaneous layer deep to the skin and around organs and joints.
It reduces heat loss and serves as padding and as an energy source.
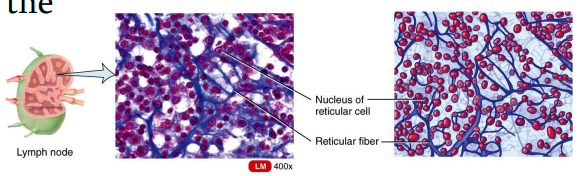
Reticular connective tissue
Loose Connective Tissues
is a network of interlacing reticular fibers and cells.
It forms a scaffolding used by cells of lymphoid tissues such as the spleen and lymph nodes.
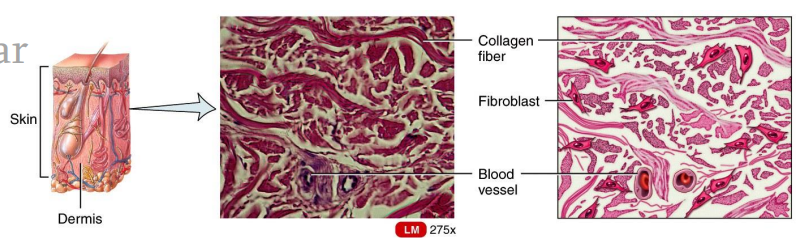
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Dense Connective Tissues
consists predominantly of fibroblasts and collagen fibers randomly arranged.
It provides strength when forces are pulling from many different directions.
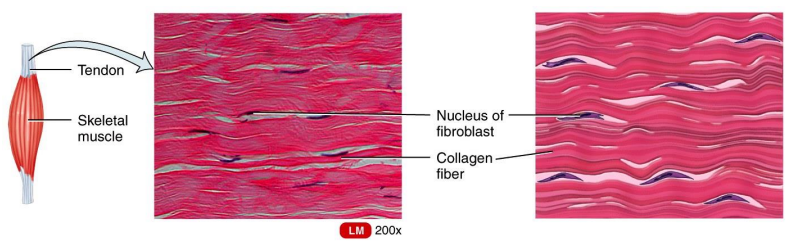
Dense regular Connective Tissue
Dense Connective Tissues
comprise tendons, ligaments, and other strong attachments where the need for strength along one axis is mandatory (a muscle pulling on a bone).
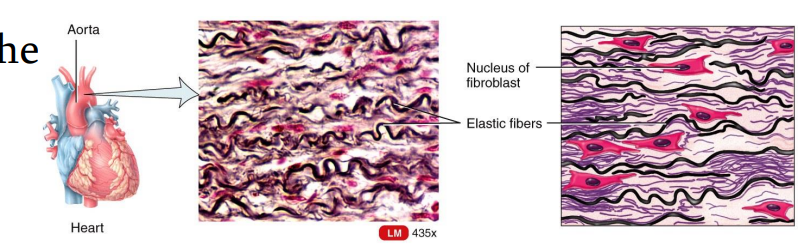
Elastic Connective Tissue
Dense Connective Tissues
consists predominantly of fibroblasts and freely branching elastic fibers.
It allows stretching of certain tissues like the elastic arteries (the aorta).
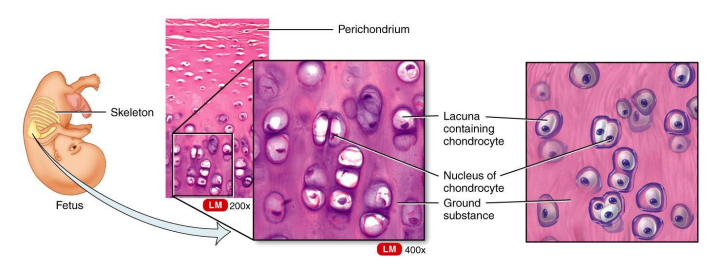
Cartilage
is a tissue with poor blood supply that grows slowly. When injured or inflamed, repair is slow.
Hyaline cartilage
cartilage
is the most abundant type of cartilage; it covers the ends of long bones and parts of the ribs, nose, trachea, bronchi, and larynx.
It provides a smooth surface for joint movement.