Cartilage and Bone - CTB Histo
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
firm connective tissue
cartilage and bone
hyaline cartilage
connective tissues of cartilage
chondrocytes
ECM
cartilage vascularity
avascular (receives nutrients by diffusion)
types of cartilage
hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage
all forms of cartilage contain isogenous groups of chodrocytes when they grow
which forms of cartilage contain isogenous groups of chodrocytes when they grow?
interstitial expansion
all forms of cartilage can grow by ______
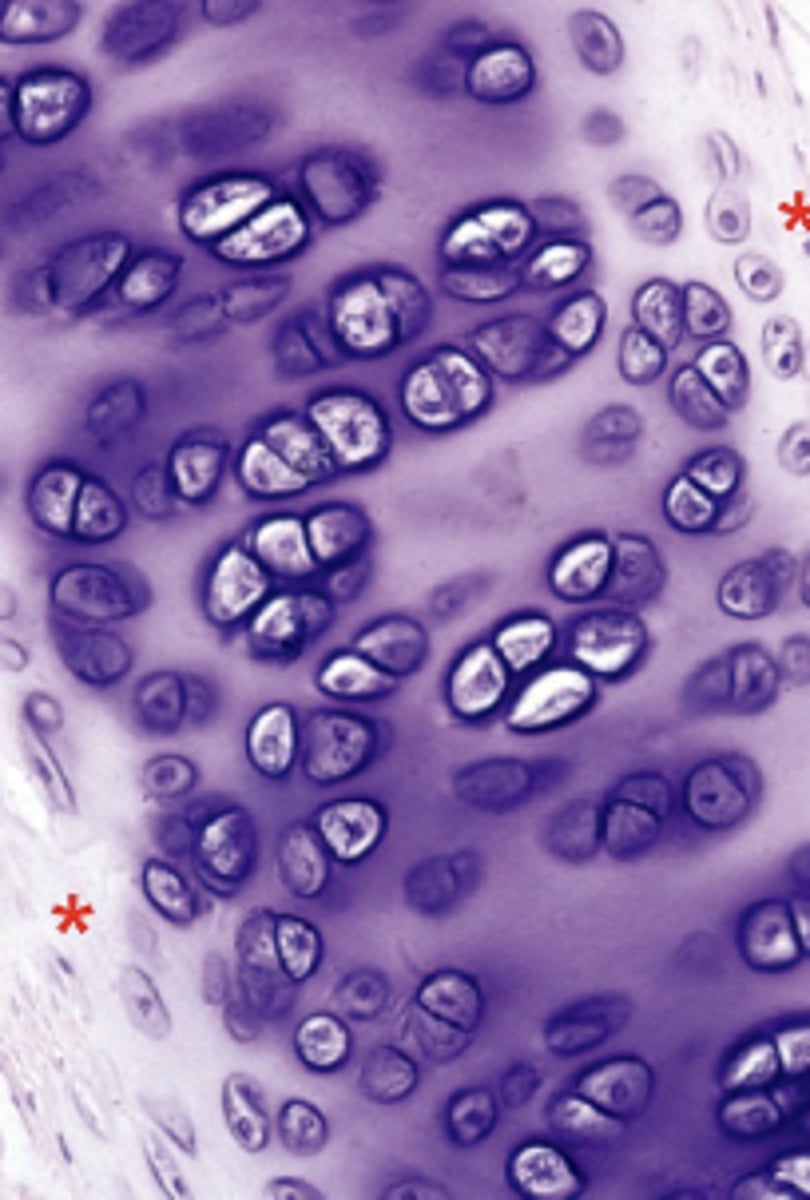
Hyaline cartilage
found in
Fetal, Articular Respiratory, Costal rib
Hyaline cartilage
Resist compression Cushioning
Hyaline cartilage
Collagen II Aggrecan
Hyaline cartilage
has perichondrium except for the articular cartilage
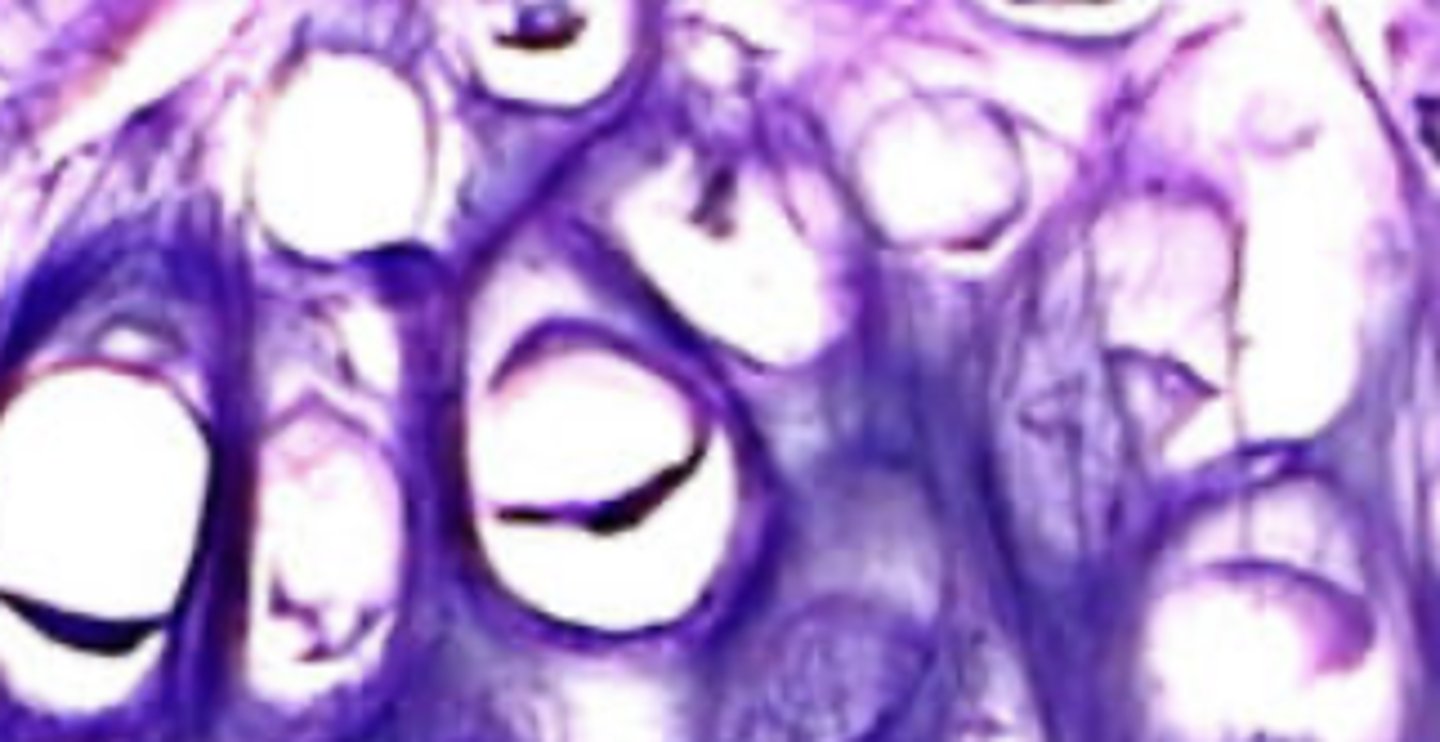
elastic cartilage
Hyaline cartilage
elastic cartilage
Ear, Larynx (epiglottis)
elastic cartilage
flexible support
elastic cartilage
Collagen II Aggrecan
Elastic fibers
elastic cartilage
has perichondrium
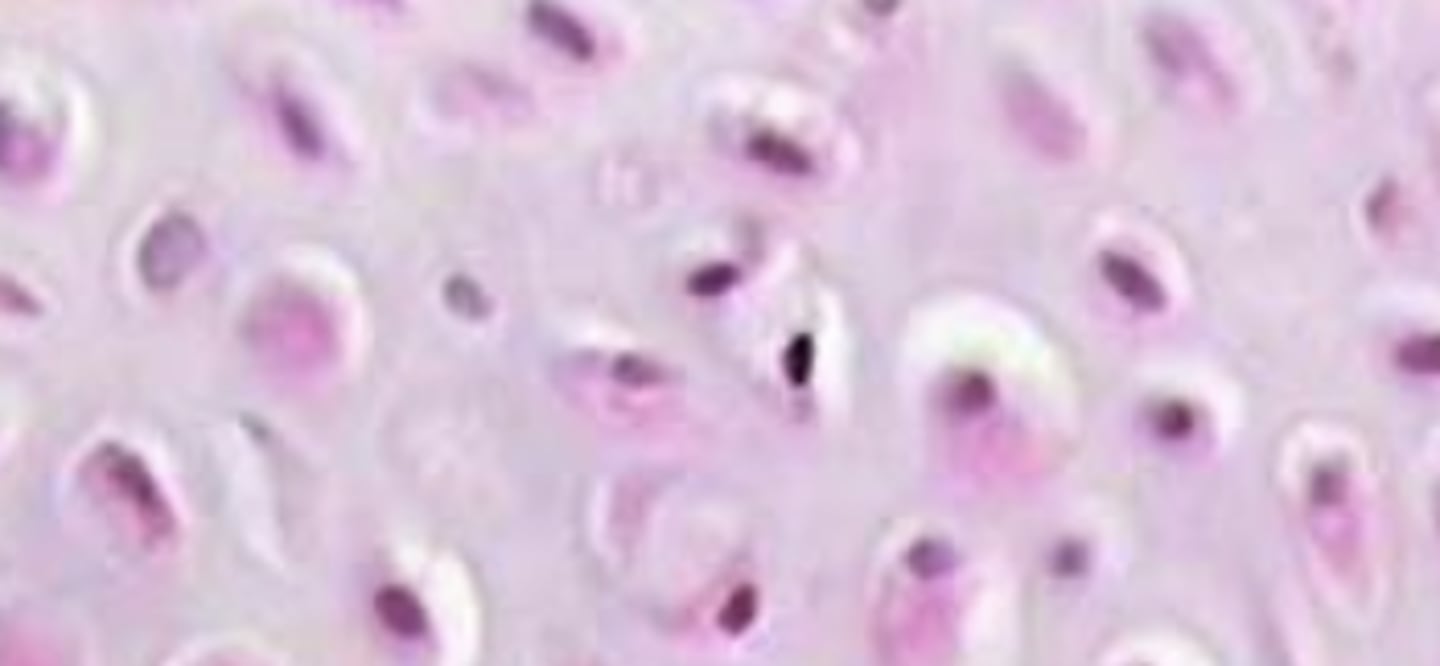
Fibrocartilage
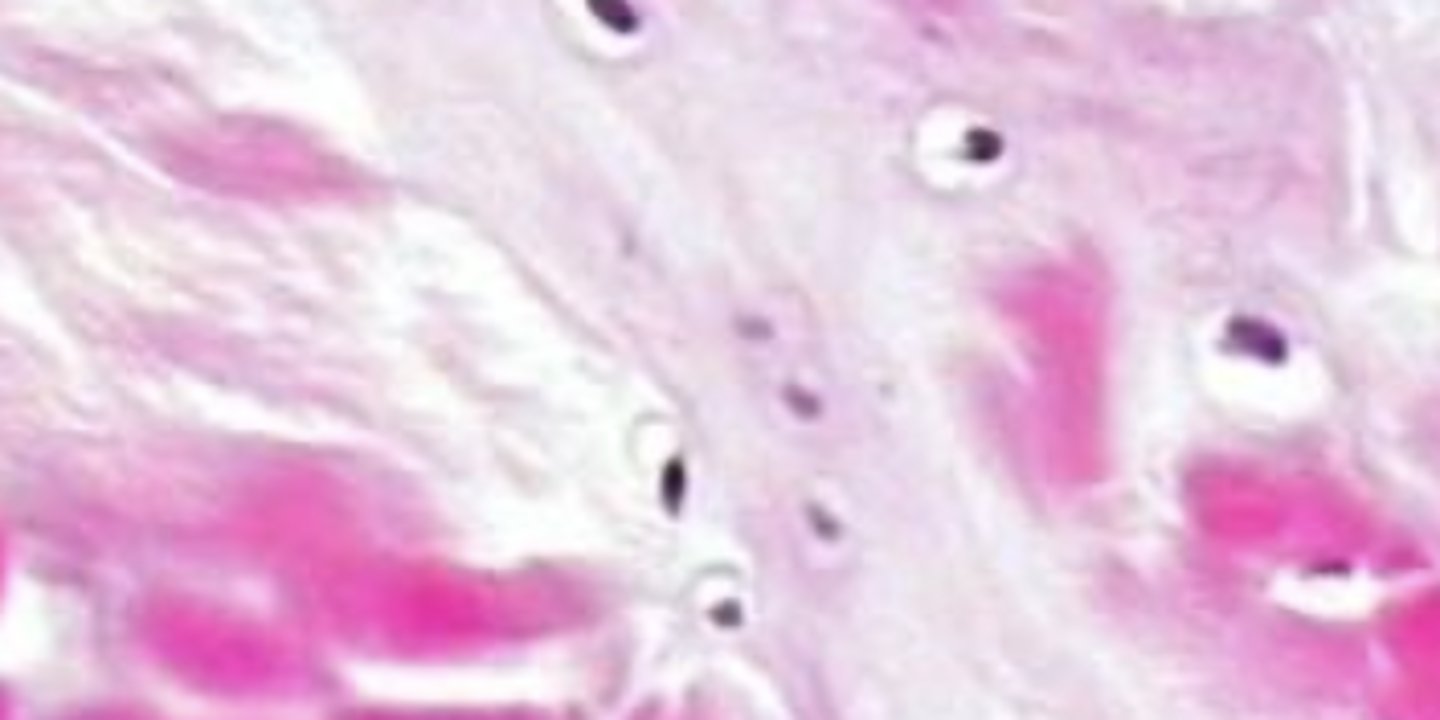
Fibrocartilage
IVD, meniscus,TMJ
Fibrocartilage
Resist compression Resist shearing forces
Fibrocartilage
Collagen II Collagen I
Versican, aggrecan
Fibrocartilage
does not have perichondrium
Appositional growth
from perichondrium, form at surface
Increases in girth
Interstitial growth
cell divisions within the matrix
increases in length and girth
fibrocartilage
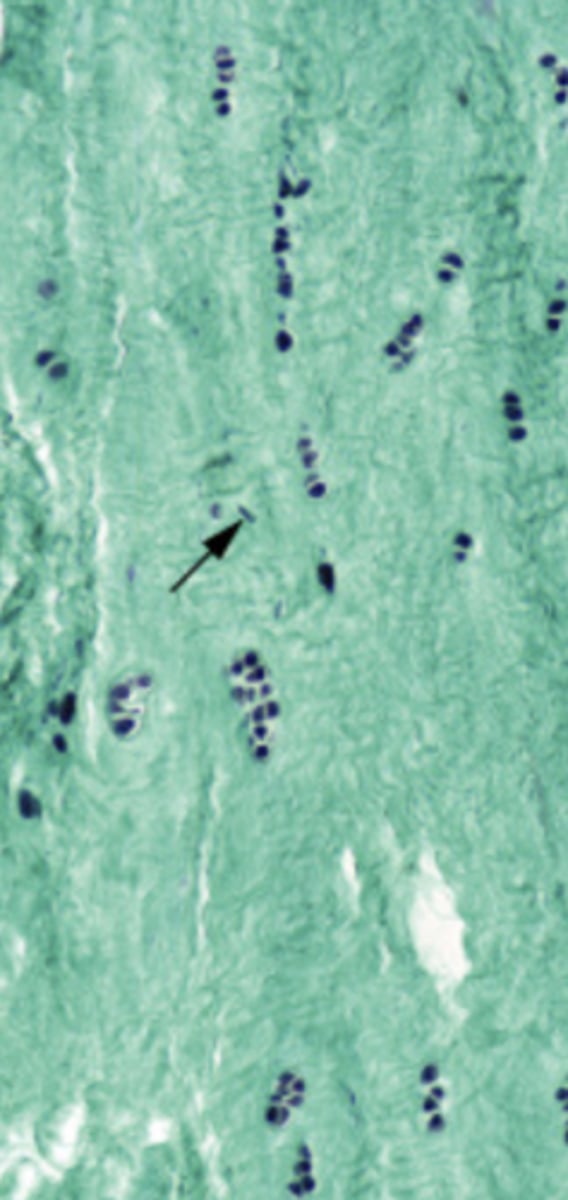
elastic cartilage
proteoglycan
cartilage matrix structure that is basophilic
collagen
cartilage matrix structure that is eosinophilic
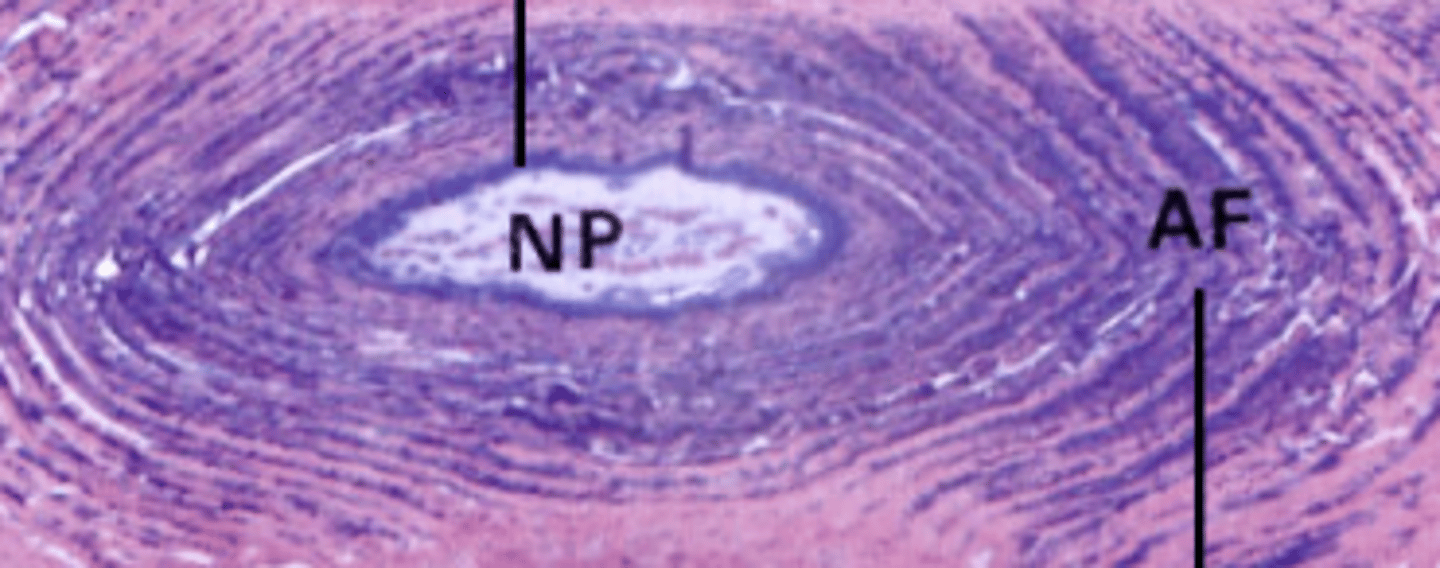
herniated disk
protrusion of a degenerated or fragmented intervertebral disk so that the nucleus pulposus protrudes, causing compression on the nerve root
herniated disk
rupture of annulus fibrosis
intervertebral disc
synovial joint
created where two bones articulate to permit a variety of motions
has articular cartilage between
synovial joint
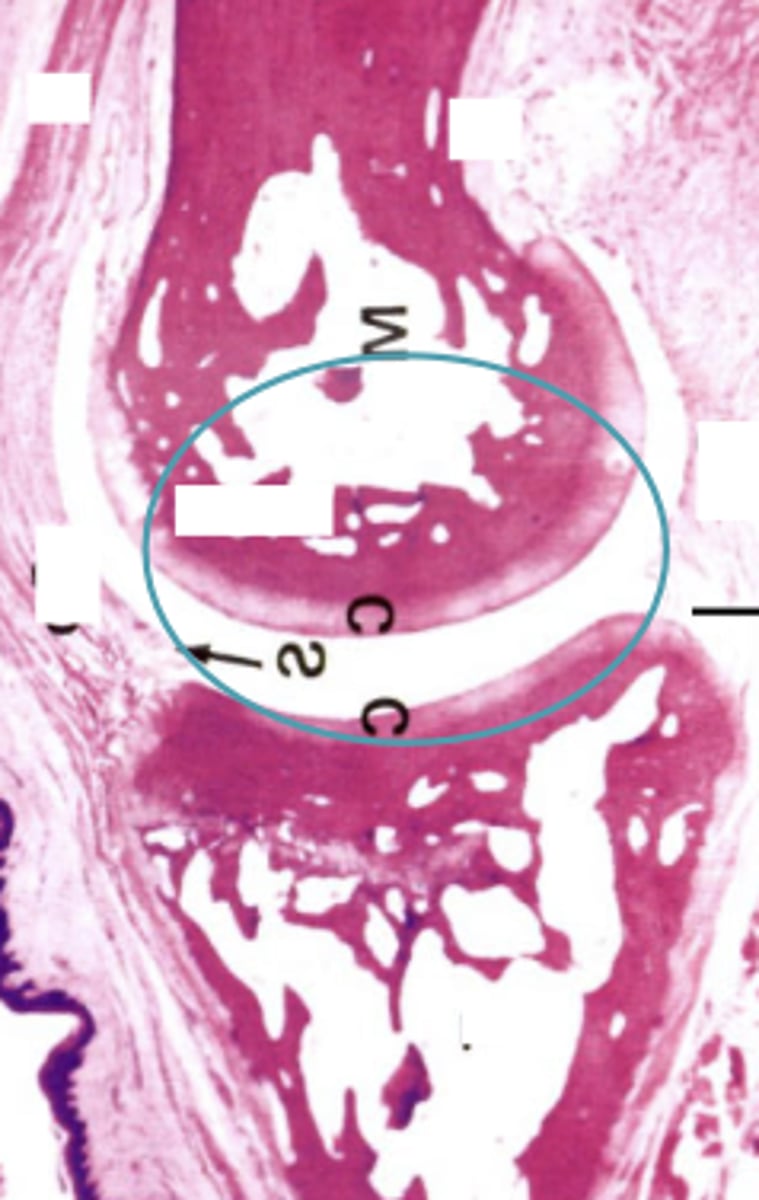
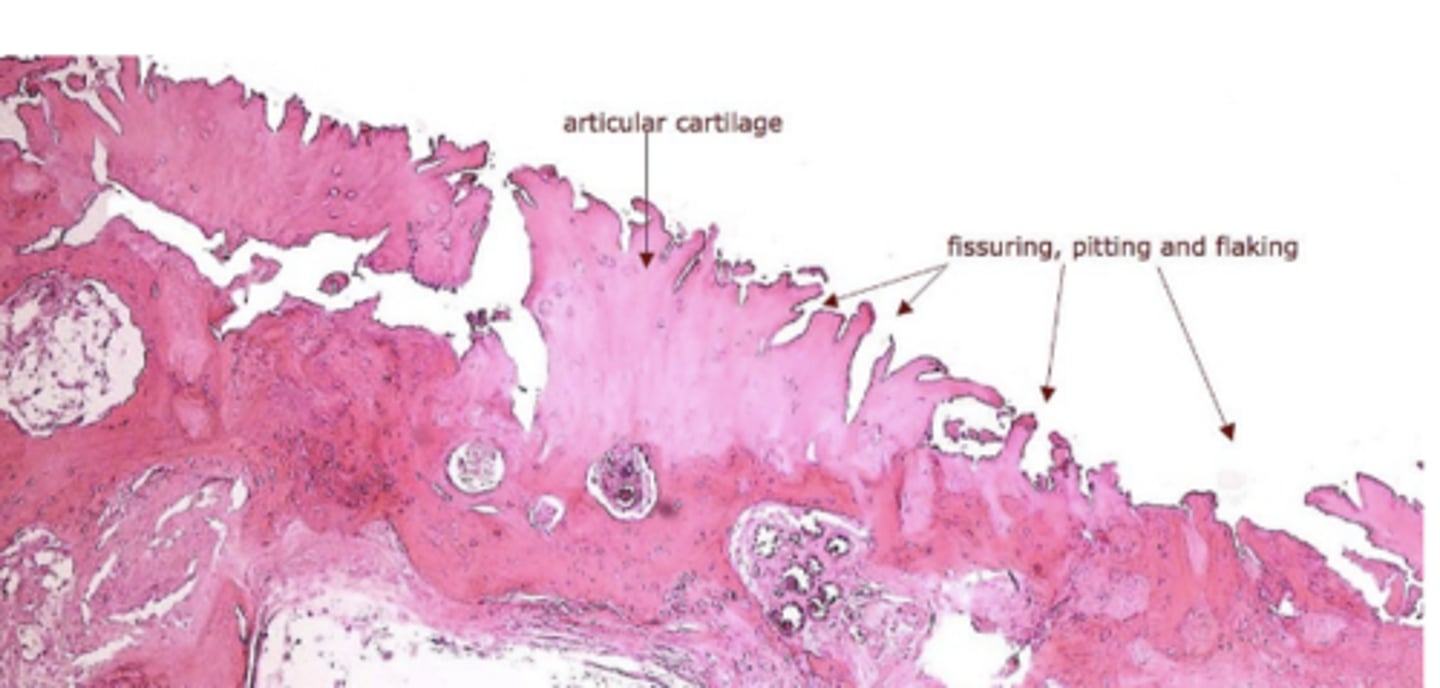
arthritis
caused by degradation of articular cartilage
Osteoarthritis risk factors
age (menopause)
joint injury
obesity
genetic (joint alignment, cartilage thickness)
cartilage ECM
not mineralized
cartilage growth
interstitial and appositional
bone growth
appositional
bone blood supply
vascular
bone function
support
calcium and phosphate storage
bone ECM
mineralized
bone organic fibers
collagen I
ground substance proteoglycan
bone inorganic matrix
hydroxyapetite
epiphysis
End of a long bone
metaphysis
where diaphysis and epiphysis meet
diaphysis
shaft of a long bone
periosteium
a dense layer of vascular connective tissue enveloping the bones except at the surfaces of the joints.
transverse canals
osteon / Haversion system
found in compact bones
spongey bone
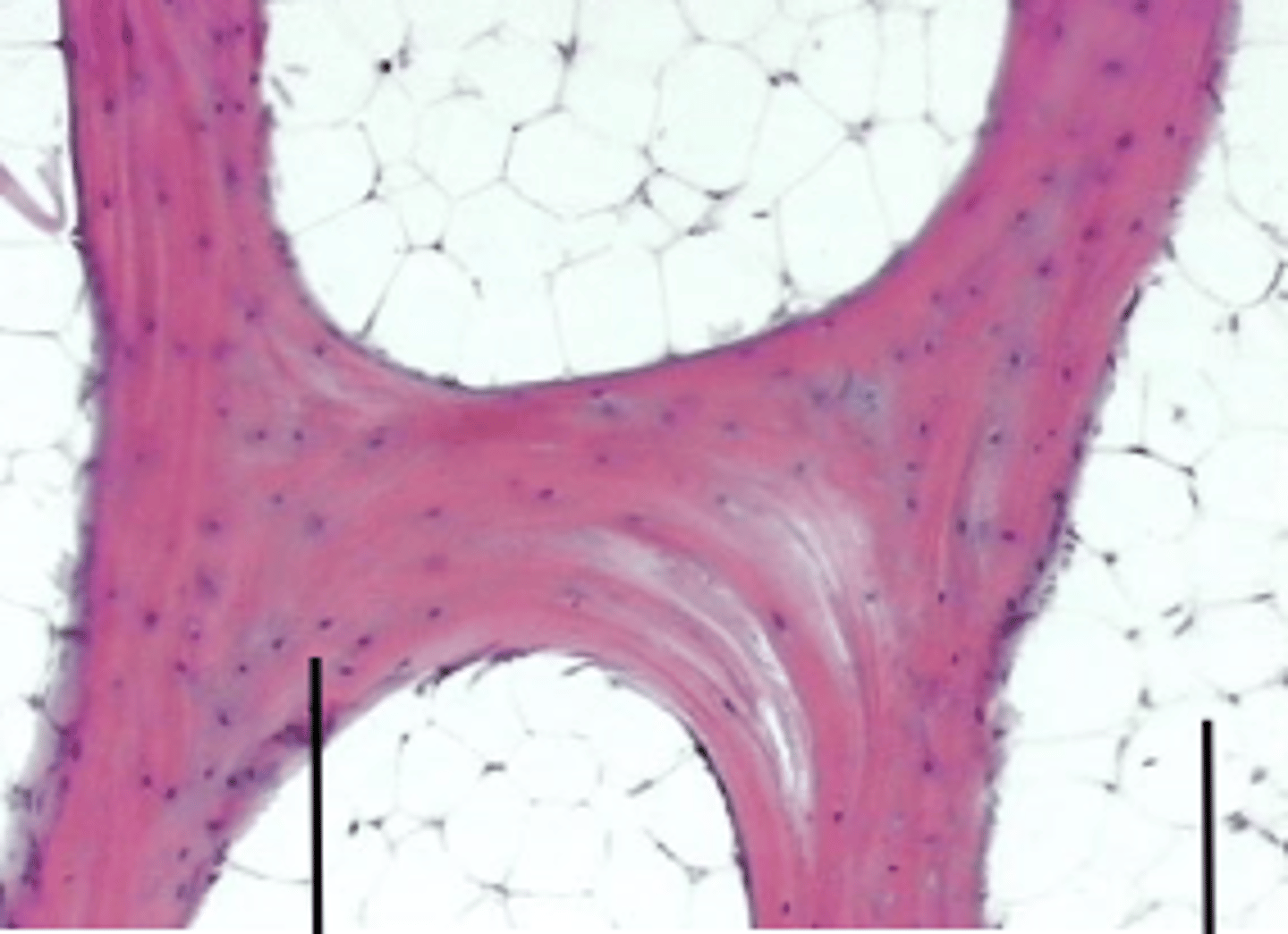
Cannaliculi
contain processes of osteocytes
to communicate with each other
concentric lamella
rings within osteon
intersticial lamella
rings between osteons
Volkmann's canal
transverse canal, perforating canal
Volkmann's canal
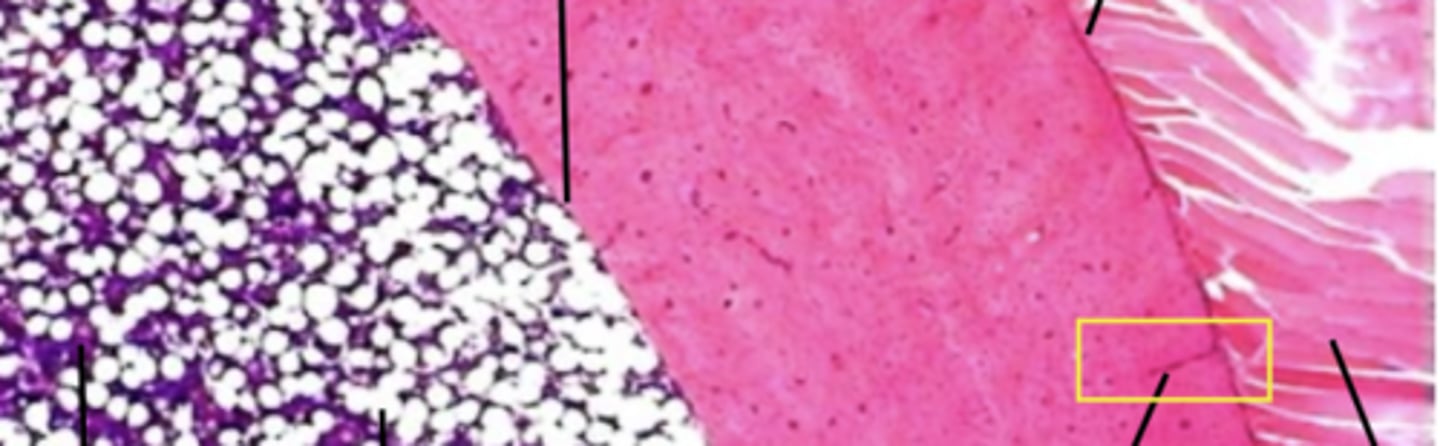
bone making
Osteoprogenitor cells
osteoblasts
osteocytes
Osteoprogenitor cells
periosteal cells and endosteal cells
osteoblasts
secrete bone matrix
not yet surrounded by matrix
osteocyte
Matrix deposition: maintains bone matrix
Surrounded by matrix
bone reabsorption
osteoclasts
osteoclasts
Large multinucleated cells
Derived from mononuclear hemopoietic cells
Phagocytotic
Howship's lacuna
space created by osteoclast resorption
Osteoclasts-mediated bone resorption
1. Decalcify through acidification
2. Degradation of bone matrix
3. Clean up: recycle
Decalcify through acidification
Pumping out proton (H+) (note cytoplasmic infolding)
Degradation of bone matrix
digestion by enzymes released from lysosomes
Clean up: recycle
endocytosis
Osteoporosis
characterized by low bone density
can be prevented by weight bearing exercises
caused by increase in osteoclasts and decreased osteoblasts
osteoporosis
Low bone mass, structure deterioration of bone tissue Bone fragility, and more susceptible to fracture
Osteopetrosis
Increased bone mass, due to defect osteoclast function
Bone fragility, and more susceptible to fracture; Unerrupted teeth
Paget disease
Increased bone remodeling, overactive osteoclast
Softer bone, more susceptible to fracture
Rheumatoid arthritis
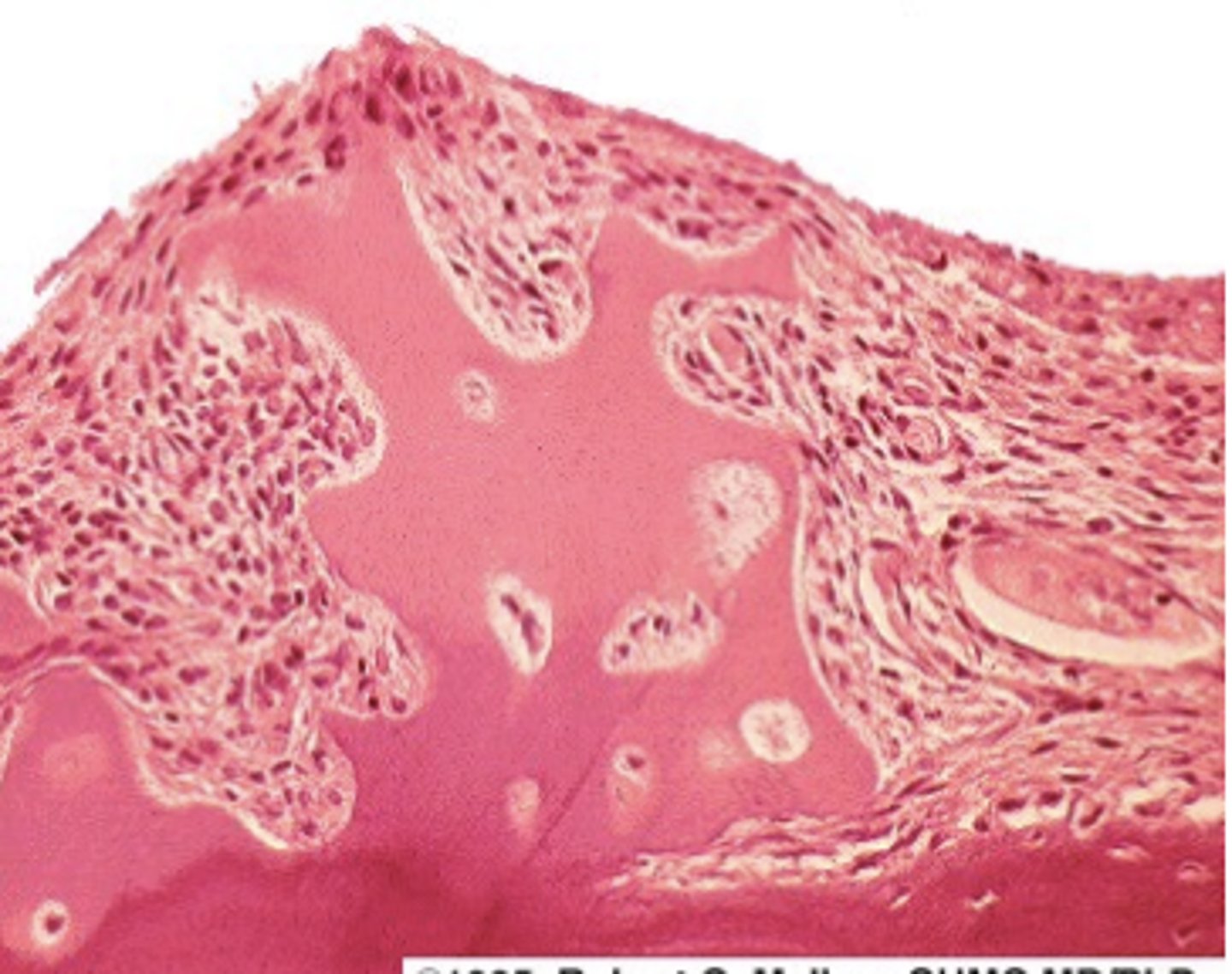
Osteoarthritis
elastic cartilage
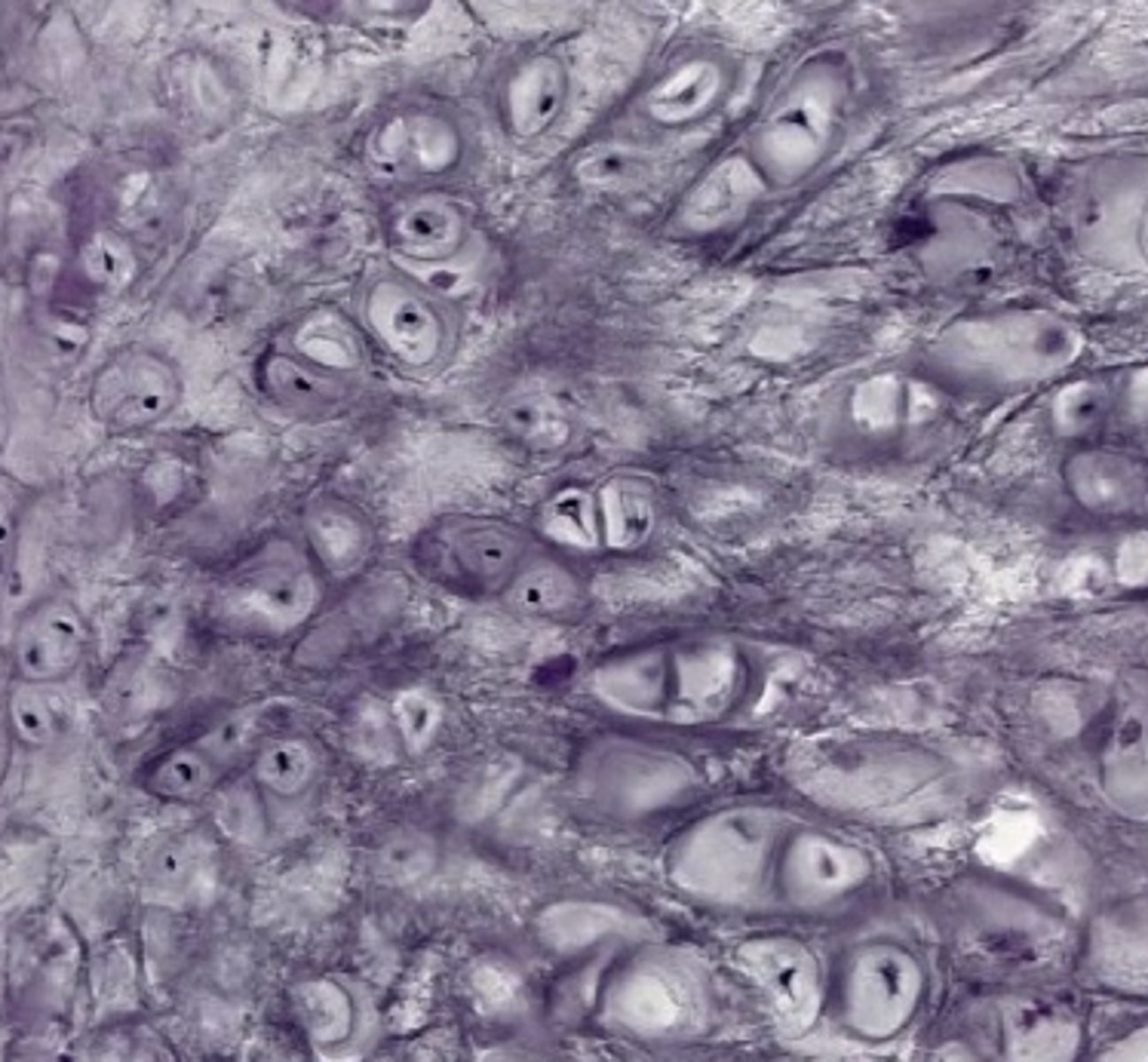
elastic cartilage
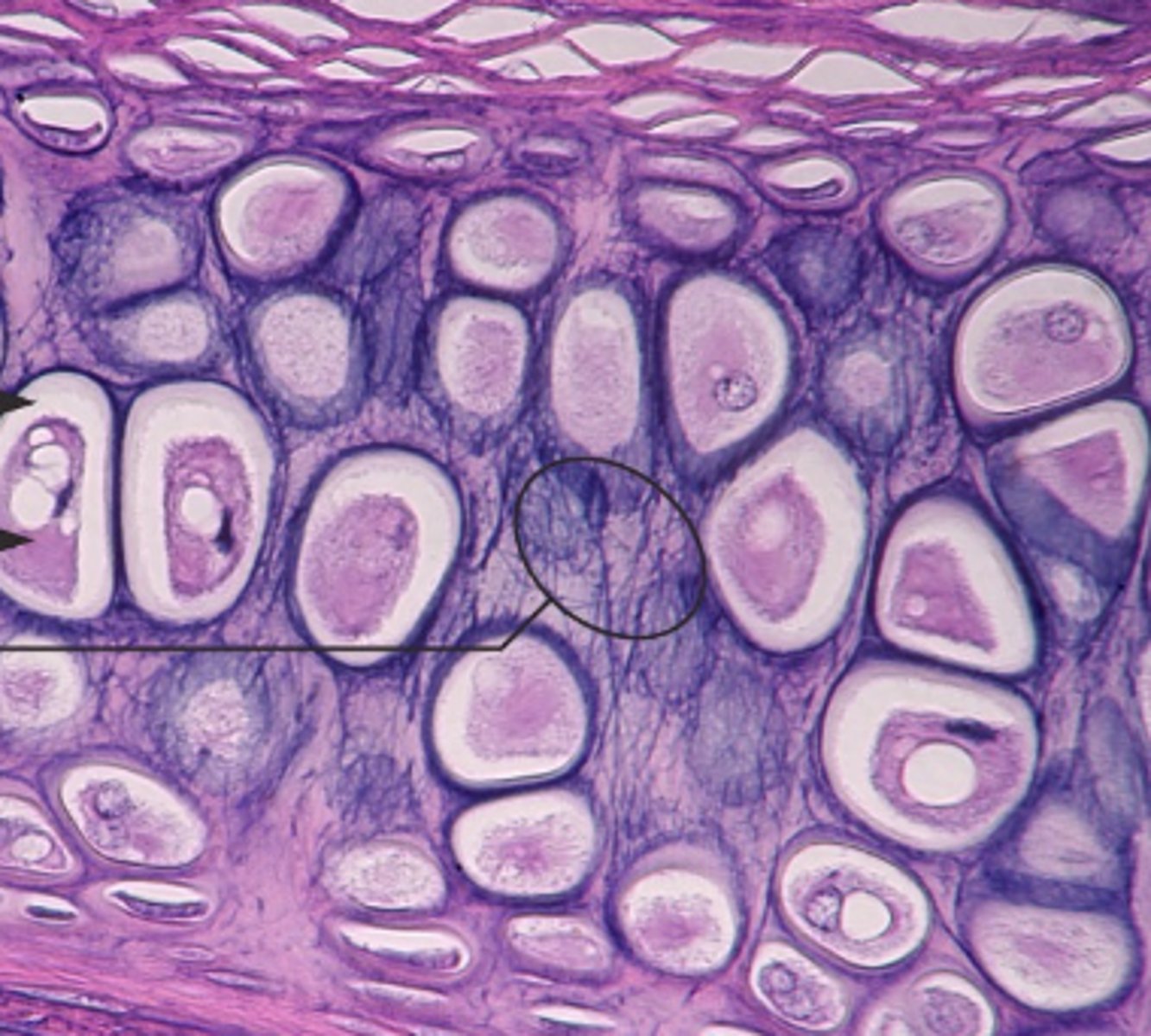
fibrocartilage
ground section
-no organic tissue
-air spaces (formerly organic)
are dark
-fine detail visible
decalcified section
-no mineralized tissue
-stains well with H&E
-fine detail less visible
interstitial lamellae
overlapping aversion canals
spongey bone
contains bone lamellae but no Haversian system
red
many mitochondria, myoglobin & oxidative enzymes (aerobic)
red
these can contract for long periods without fatigue
white
these are quick to fatigue
white
fewer mitochondria & oxidative enzymes (anaerobic)
red
slow twitch
white
fast twitch
Golgi tendon
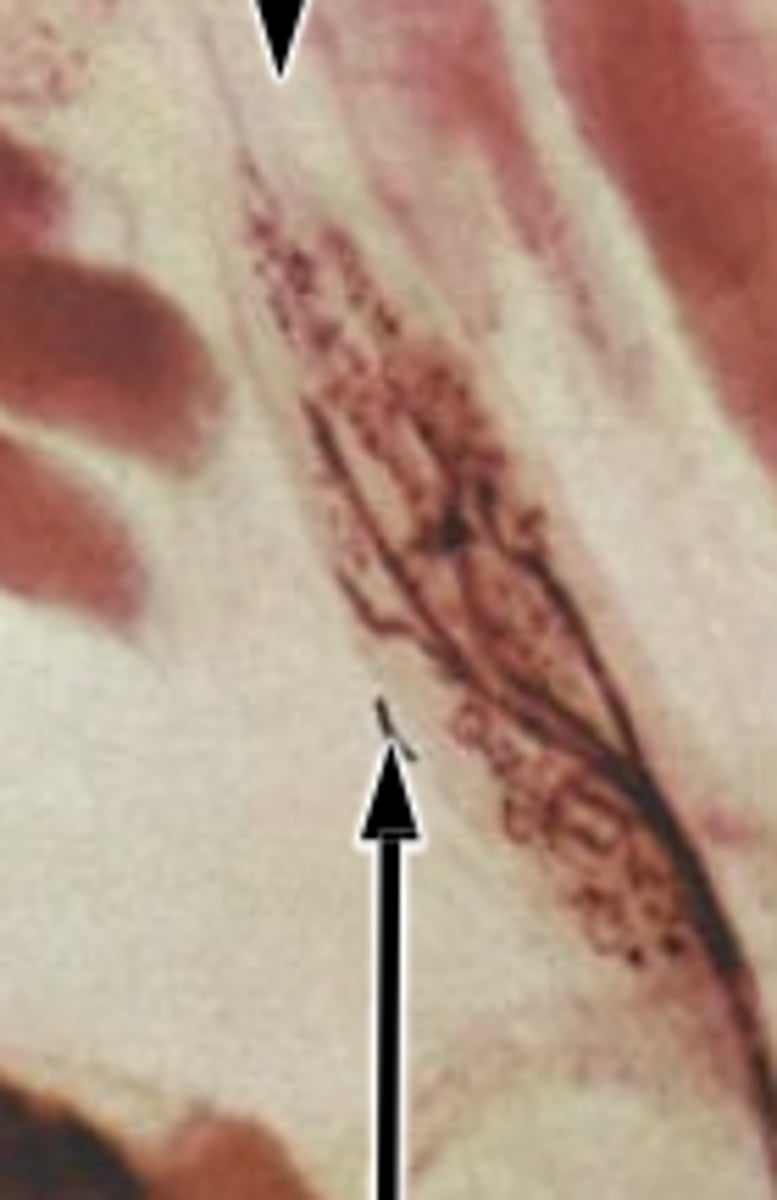
Dense bodies (Z disc equivalent in smooth muscle cells)
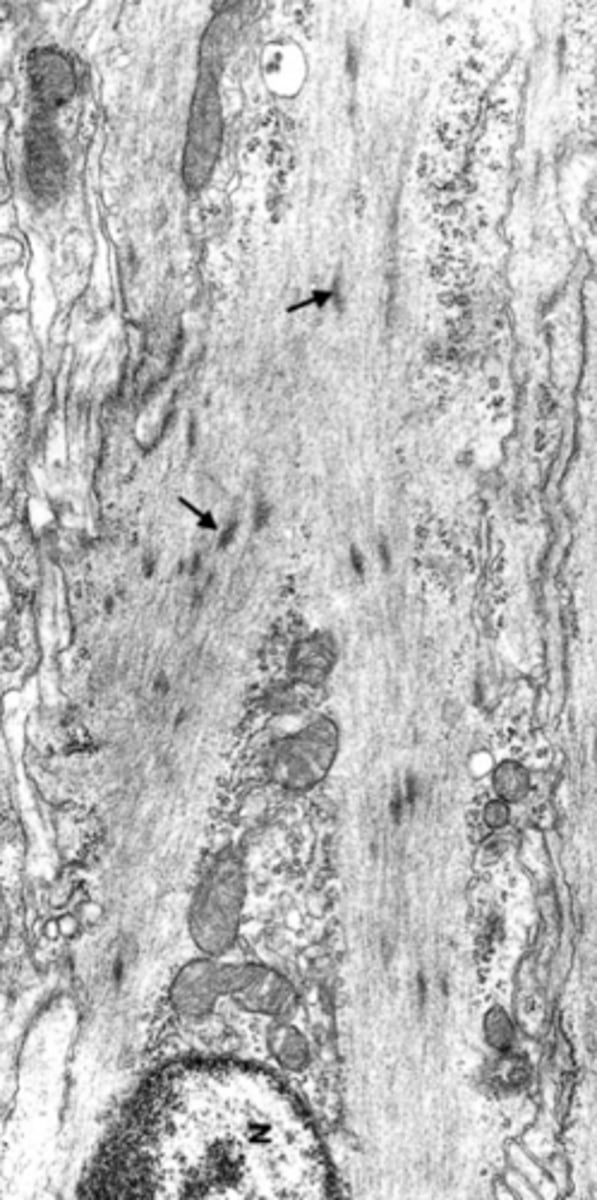
arrows pointing to