4.5 elements in Group 17
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
group 17 consists of elements of …
F, fluorine
Cl, chlorine
Br, bromine
I, iodine
At, astatine
Ts, tennessine
mnemonic …
first class biriyani in austria
f, cl, br, i, at, ts
elements in group 17 are known as …
halogens (exist as diatomic molecules)
physical properties of group 17 elements …
very low melting and boiling points
does not conduct electricity or heat
have pungent smell and are poisonous
low density
exist as diatomic molecules at low temperatures (F2, Cl2, Br2, I2, At2, Ts2)
why is the boiling point of group 17 elements low ?
the presence of very weak attraction force between particles (Van der Waals force). thus, only a small amount of heat is required to overcome the attraction force to separate halogen molecules.
the physical state of halogens at room temperature changes gradually…
from gas (fluorine, chlorine) → to liquid (bromine) → to solid (iodine, astatine)
going down the group …
the atomic radius or atomic size of elements increase
^^ due to the number of electrons and electron filled shells increasing
the melting and boiling points increase
when going down the group, the atomic radius or atomic size increases
the attraction force between molecules also increases
more heat energy is need to overcome the attraction force between molecules
the density of elements increase
increase in atomic mass is higher than increase of atomic radius
the existence of different physical states of elements at different room conditions
atomic size increases down the group, so does the force of attraction
the electronegativity of halogens decrease
the tendency to accept electrons to form negative ions decrease.
physical state of: chlorine gas at room temperature
molecular size of chlorine is small
therefore, the force of attraction between molecules is weak
this causes chlorine to exist as a greenish yellow gas at room temperature
physical state of: liquid bromine at room temperature
the molecular size of bromine is larger than chlorine
therefore, the force of attraction between molecules is stronger
this causes bromine to exist as a reddish brown liquid at room temperature
physical state of: solid iodine at room temperature
the molecular size of iodine is huge
therefore, the force of attraction between molecules is very strong
this causes iodine to exist as a purplish black solid
all halogens have …
7 valence electrons.
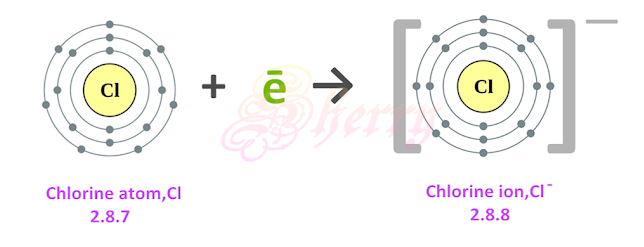
in chemical reactions, these atoms receive one electron and form ions with a -1 charge.
X + e- → X-
halogen elements such as chlorine, bromine and iodine exhibit …
the same chemical properties when reacting with …
water to produce two types of acids
iron to produce iron (III) halide
sodium hydroxide solution to produce sodium salt and water
chlorine, bromine and iodine have the same … but different …
chemical properties
reactivity
the reactivity of the reaction between halogens and water…
decrease when going down group 17
Cl2 Br2 I2
———————>
reactivity decreases
halogens react with water to form …
an acidic solution
reaction of chlorine with water
chlorine dissolves in water to form a mixture of hydrochloric acid and hypochlorous acid (bleaching agent). the light yellow solution is called chlorine water (chlorine solution)
Cl2 (g) + H2O (l) <—> HCl (aq) + HOCl (aq)
reaction of bromine with water
bromine dissolves in water to form a mixture of hydrobromic acid and hypobromous acid. the reddish brown solution is called bromine water (bromine solution)
Br2 (l) + H2O (l) <—> HBr (aq) + HOBr (aq)
bromine water is also a bleaching agent but is less effective than chlorine water.
reaction of iodine with water
iodine does not dissolve easily in cold water. it only dissolves slightly in hot water to produce a mixture of hydroiodic acid and hypoiodous acid. the resulting brownish yellow solution is called iodine water.
I2 (s) + H2O (l) <—> HI (aq) + HOI (aq)
halogens react with metal to form …
a metal halide.
halogens are very electronegative elements and tend to combine with other metals to form metal halides. all halogens show similar chemical properties in their reaction with iron.
reaction of chlorine with metal
chlorine gas reacts vigorously with iron to produce a brown solid of iron (III) chloride
2Fe (s) + 3Cl2 (g) —> 2FeCl3 (s)
sodium hydroxide solution is used to absorb excess chlorine gas.
reaction of bromine with metal
bromine vapour reacts with iron to produce a brown solid of iron (III) bromide
2Fe (s) + 3Br2 (g) —> 2FeBr3 (s)
sodium hydroxide solution is used to absorb excess bromine gas.
reaction of iodine with metal
iodine vapour reacts with iron to produce a brown solide of iron (III) iodide.
2Fe (s) + 3I2 (g) —> 2FeI3 (s)
when halogens react with an alkaline solution ,
a metal halide, a metal halate and water will be produced.
reaction of chlorine with sodium hydroxide solution
chlorine reacts vigorously with sodium hydroxide solution to produce sodium chloride solution, sodium hypochlorite (sodium chlorate (I)) solution and water.
Cl2 (g) + 2NaOH (aq) —> NaCl (aq) + NaOCl (aq) + H2O (l)
reaction of bromine with sodium hydroxide solution
bromine reacts less vigorously with sodium hydroxide solution to produce sodium bromide solution, sodium hypobromite (sodium bromate (I)) solution and water.
Br2 (l) + 2NaOH (aq) —> NaBr (aq) + NaOBr (aq) + H2O (l)
reaction of iodine with sodium hydroxide solution
iodine reacts slowly with sodium hydroxide solution to produce sodium iodide solution, sodium hypoiodite (sodium iodate(I)) solution and water.
l2 (s) + 2NaOH (aq) —> Nal (aq) + NaCl (aq) + H2O (l)
elements in group 17 have the same ….
chemical properties because they have the same number of valence electrons, which is 7.
during a chemical reaction …
these atoms accept one electron into the valence shell to achieve a stable octet arrangement. this reaction forms a negative ion, such as F, Cl, Br, I, At with a -1 charge.
draw a chlorine atom receiving an electron to achieve stability
…
explain the reactivity of halogens
the reactivity of halogens decreases down the group.
when going down the group, atomic size increases
the distance of the valence shell becomes further away from the nucleus
the force of attraction of the nucleus on the electrons in the valence shell become weaker
the tendency for atoms to accept one electron to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement decreases.
compare the reactivity of fluorine and chlorine.
chlorine atomic size is larger than fluorine atom.
the distance between the nucleus and the valence electrons of chlorine atom is larger
the force of attraction between the nucleus and the valence electrons becomes weaker for the chlorine atom,
thus, the tendency of chlorine atom to accept a valence electron is lower than that of fluorine atom.
F + e- —> F- (easier to happen)
Cl + e- —> Cl- (more difficult to happen)
reactivity of astatine
astatine is under iodine in group 17 . thus, it is expected to react with water, iron and sodium hydroxide solution in the same way as iodine but slower (less reactive) than iodine.
astatine is a rare radioactive element because it is not chemically stable.