Session 5: Lumbosacral Plexus and Knee
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What are the plexuses of the lower limb?
Lumbosacral plexus
- Lumbar plexus
- Sacral plexus
Lumbar Plexus arises from
Ventral rami of L1-L4
Sacral Plexus arises from
Ventral rami of L4-S4
Femoral nerve root
L2, L3, L4
Obturator nerve root
L2, L3, L4
Lumbosacral trunk root
L4, L5
Lateral cutaneous nerve root
L2, L3
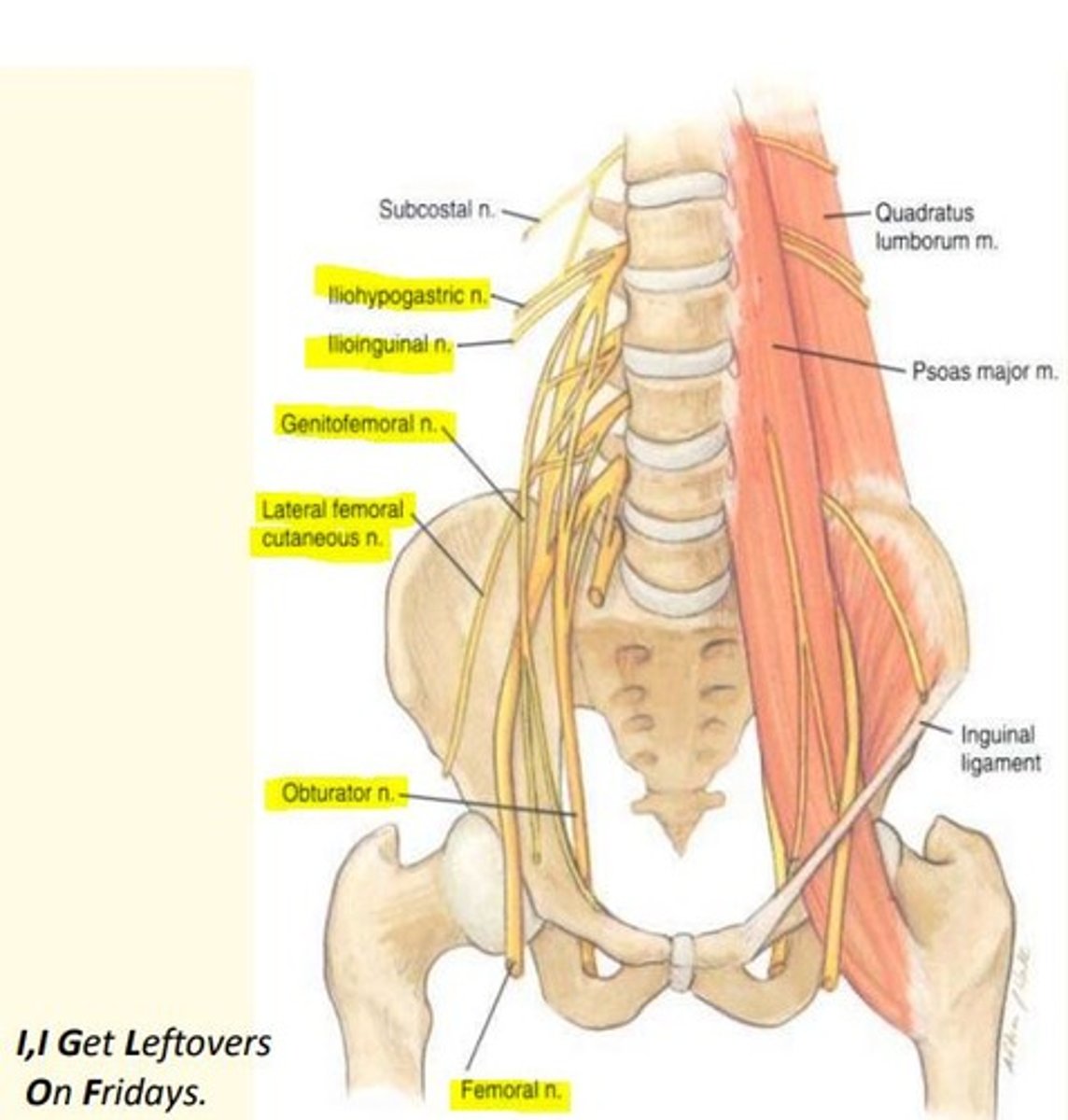
Lumbar plexus nerves (L1-L4)
I, I Get Leftovers On Fridays
Iliohypogastric
Ilioinguinal
Genitofemoral
Lateral cutaneous of the thigh (L2, 3)
Obturator (L2, 3, 4)
Femoral nerve (L2, 3, 4)
Branches of the sacral plexus
Some Irish Sailor Pesters Polly
Superior gluteal nerve (L4, 5, S1)
Inferior gluteal nerve (L5, S1, S2)
Sciatic nerve (L4 to S3)
Posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh (S1, 2, 3)
The pudendal nerve (S2, 3, 4)
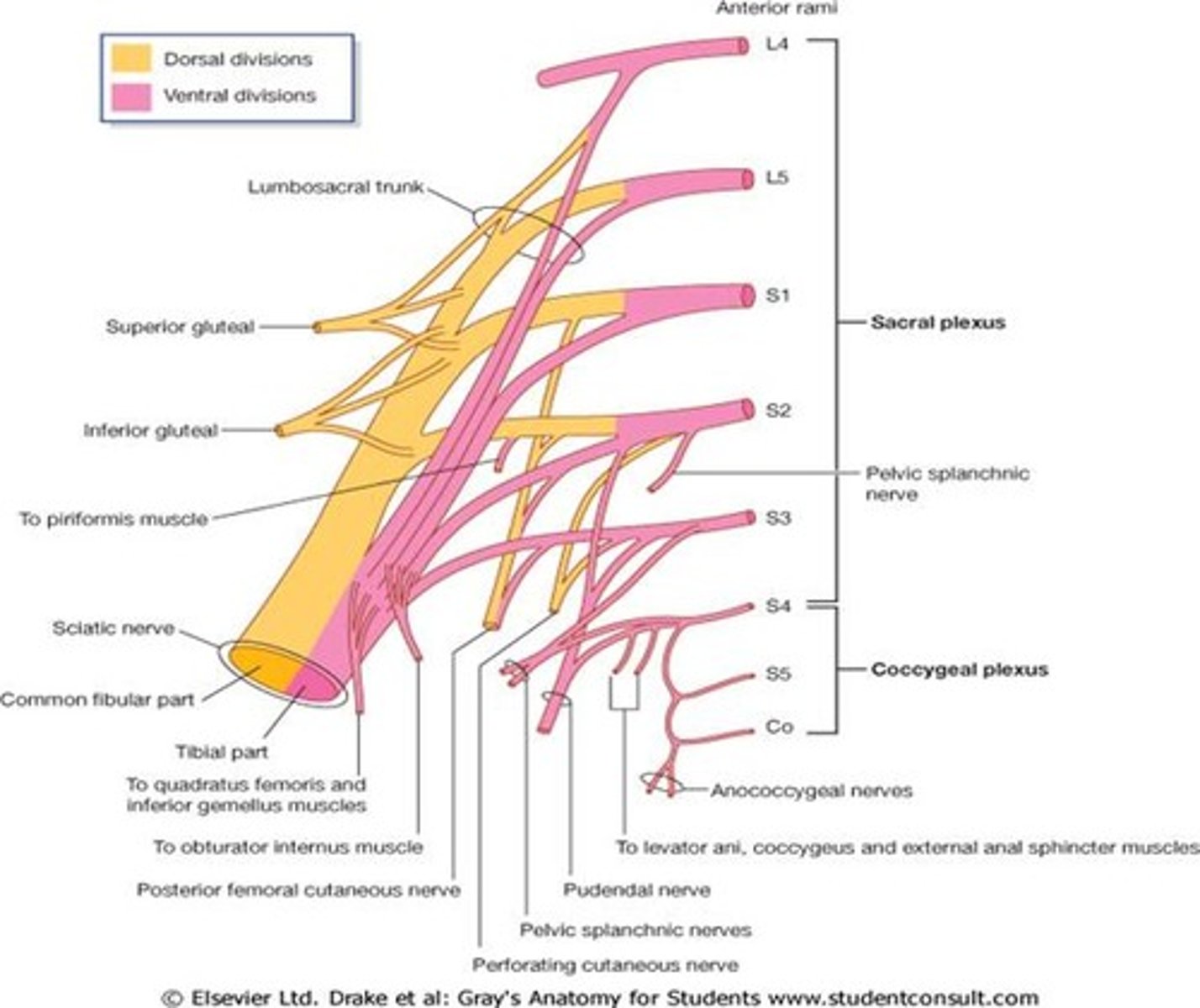
The sciatic nerve branches into...
Tibial nerve and common fibular nerve
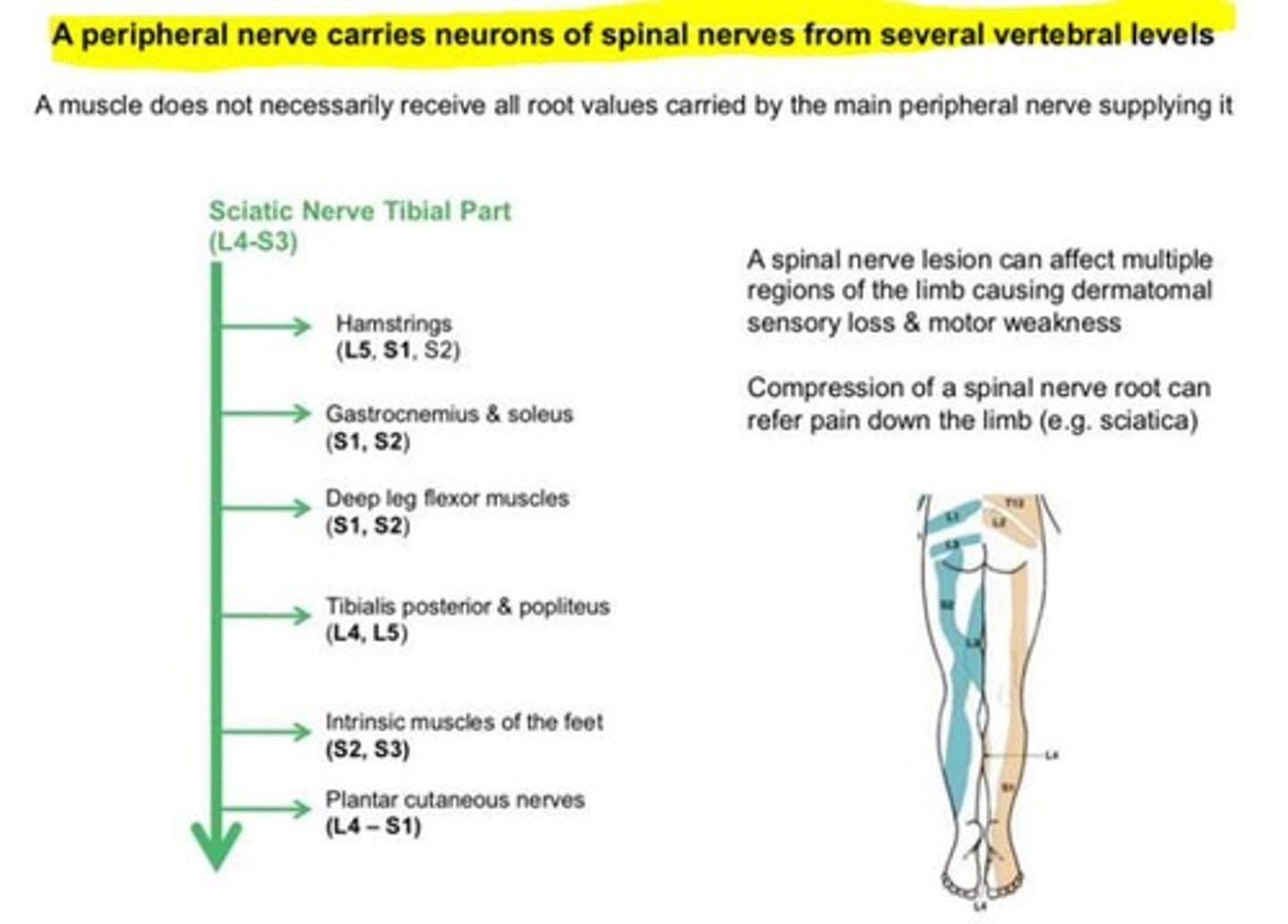
Why will injury to one spinal nerve not cause loss of function or sensation to a large area?
Most peripheral nerves will have contributions from multiple spinal nerves. Therefore, injury to one spinal nerve will NOT cause loss of function or sensation to a large area as the nerve will receive contributions from other spinal roots.
A peripheral nerve carries neurons of spinal nerves from several vertebral levels
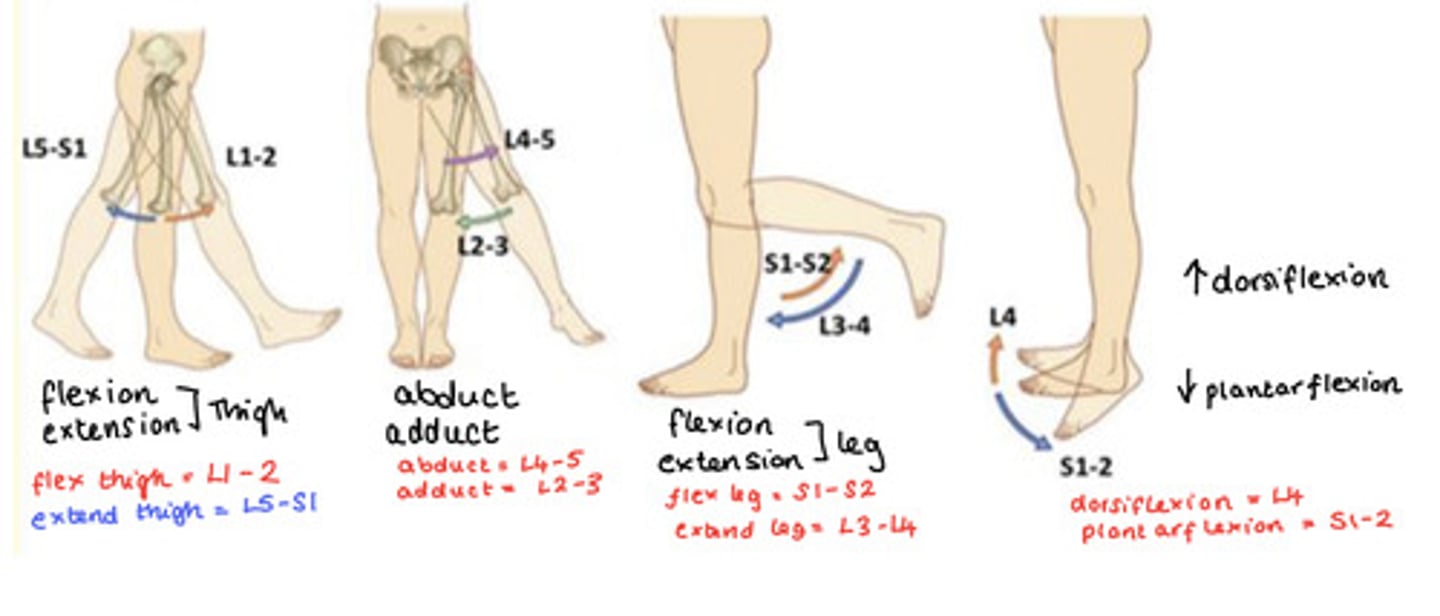
Root values for movements
Flexion & Extension of Thigh
Flexion = L1-2
Extension = L5-S1
Abduction & Adduction of Thigh
Abduct = L4-5
Adduct = L2-3
Flexion & Extension of Leg
Flexion = S1-2
Extension = L3-4
Dorsiflexion & Plantarflexion of Foot
Dorsi (up) = L4
Plantar (down) = S1-2
Root value of (ankle jerk reflex) achilles reflex
This occurs when Achilles tendon is tapped while the foot is dorsiflexed.
S1-2
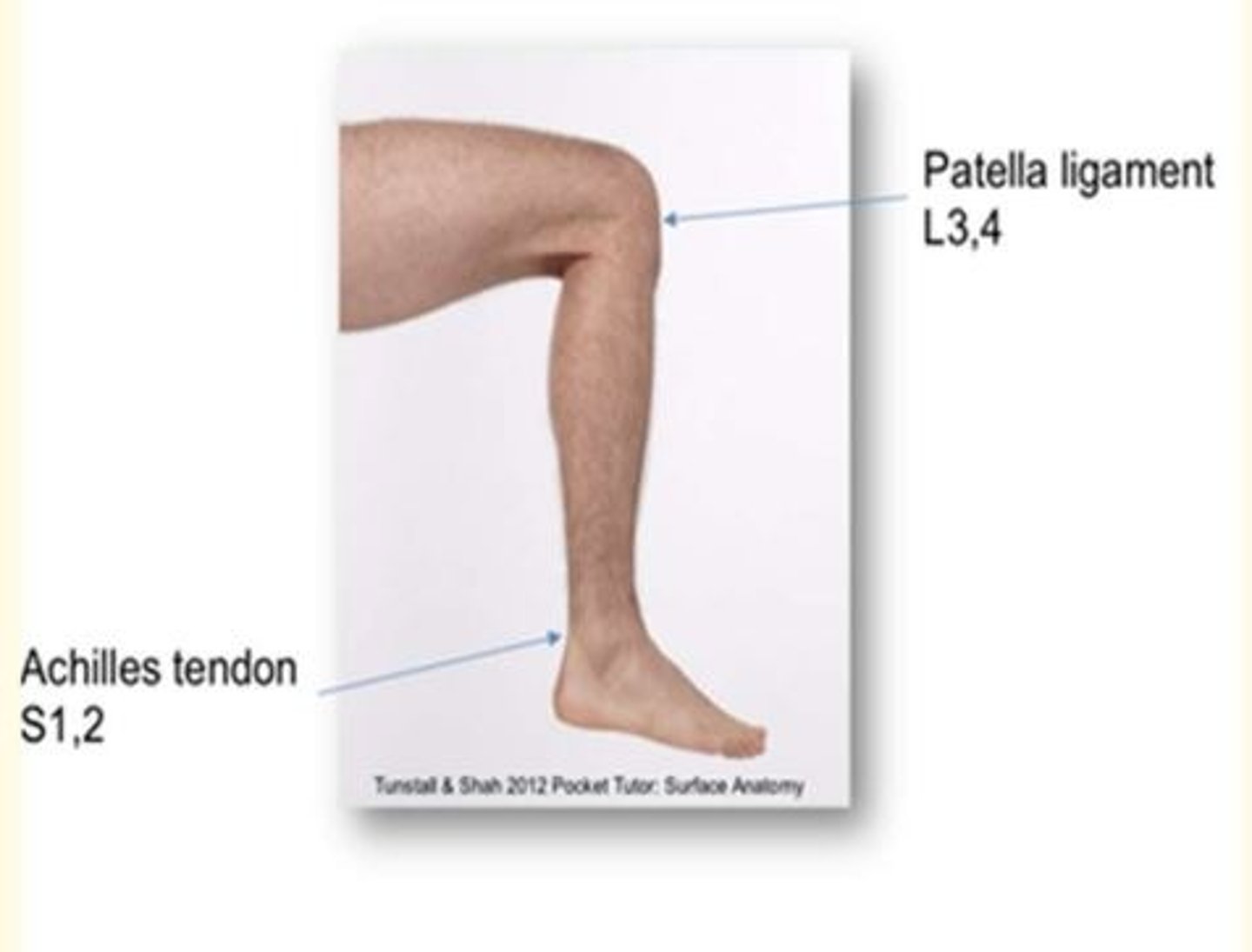
Root value of (knee reflex) patellar reflex
Stretch reflex when the patellar ligament is tapped.
L3-4
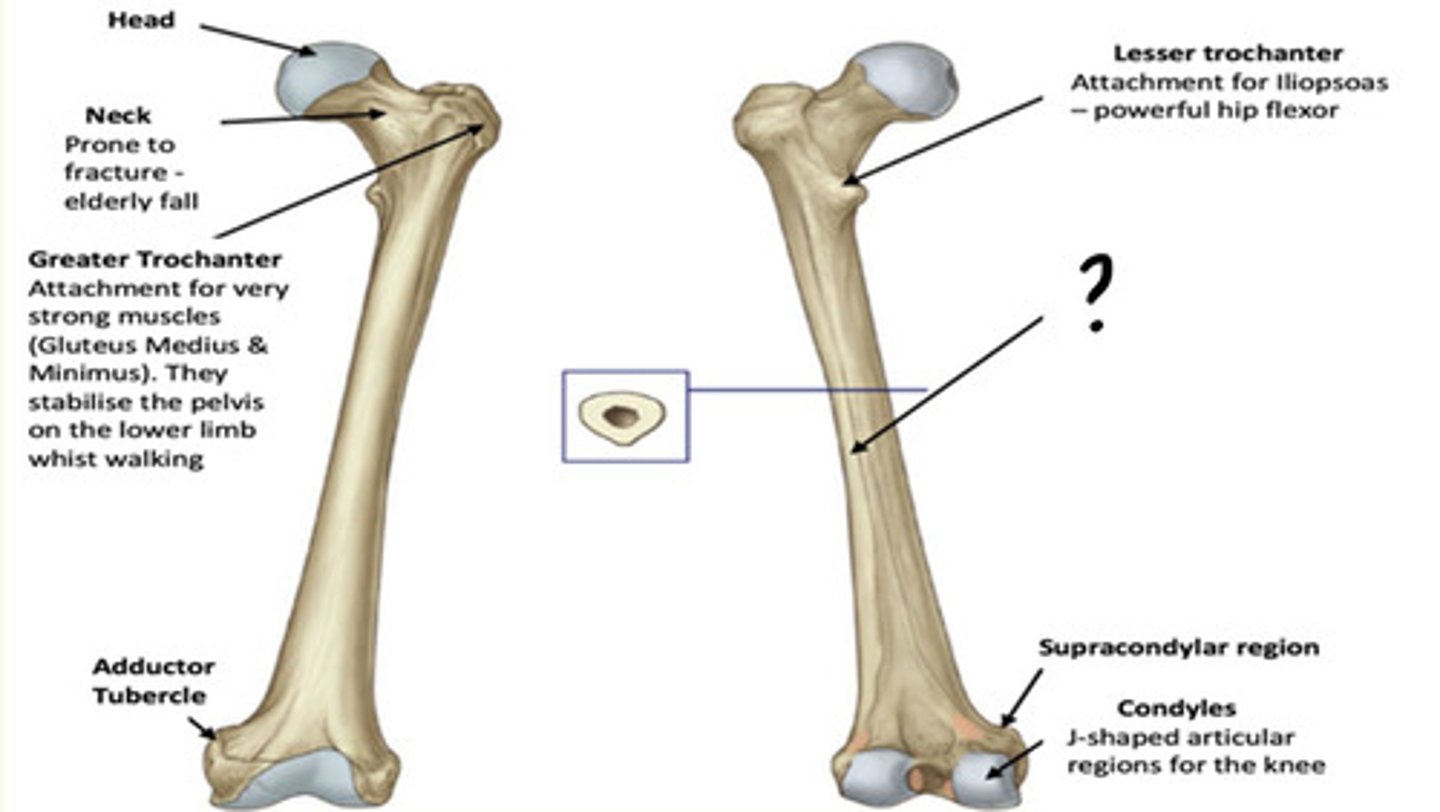
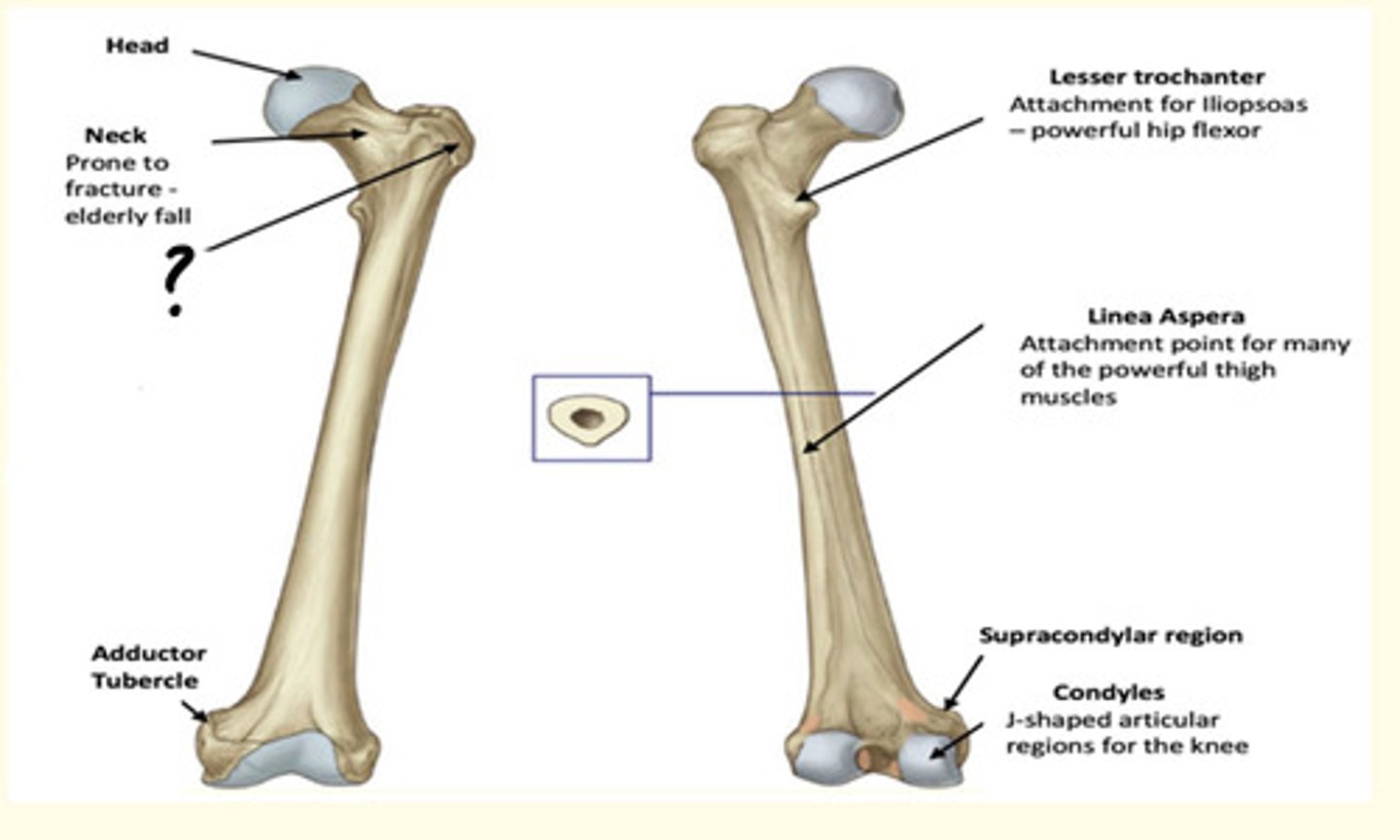
Osteology of the lower limb
Identify the region in the image labelled with a '?'
Lesser Trochanter
Attachment for Iliopsoas - powerful hip flexor
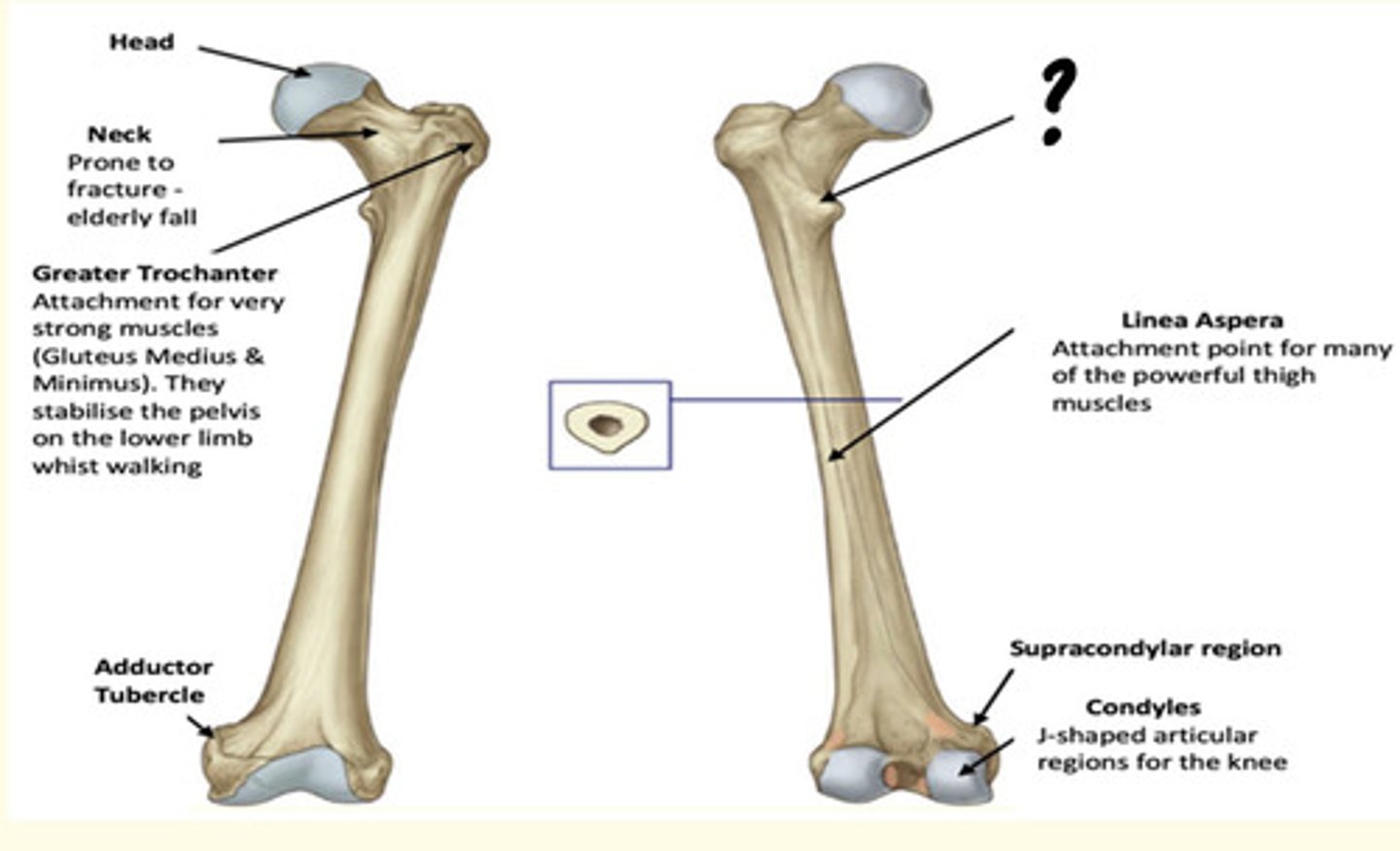
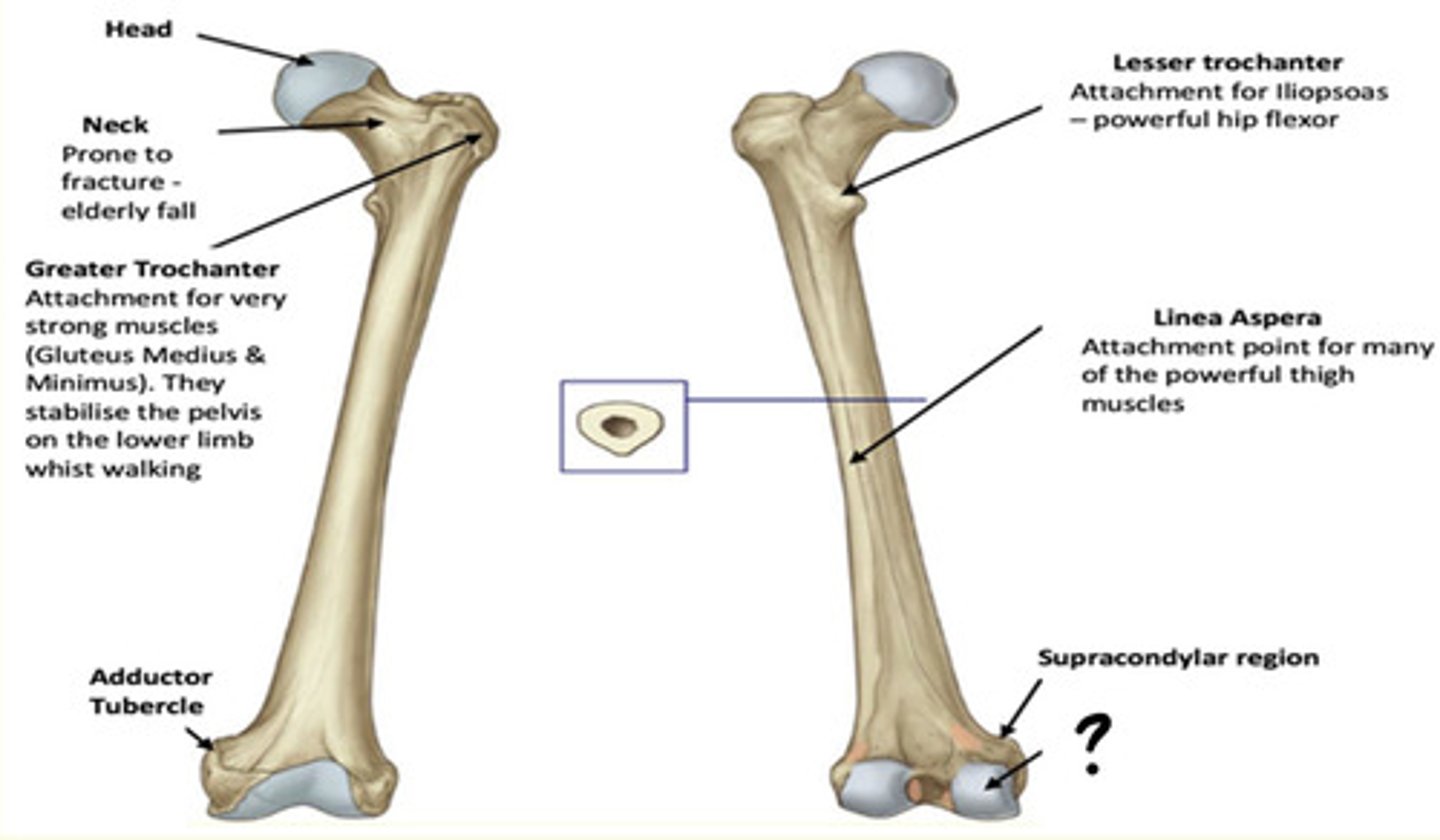
Osteology of the lower limb
Identify the region in the image labelled with a '?'
Linea Aspera
Attachment point for many of the powerful thigh muscles
Osteology of the lower limb
Identify the region in the image labelled with a '?'
Supracondylar region
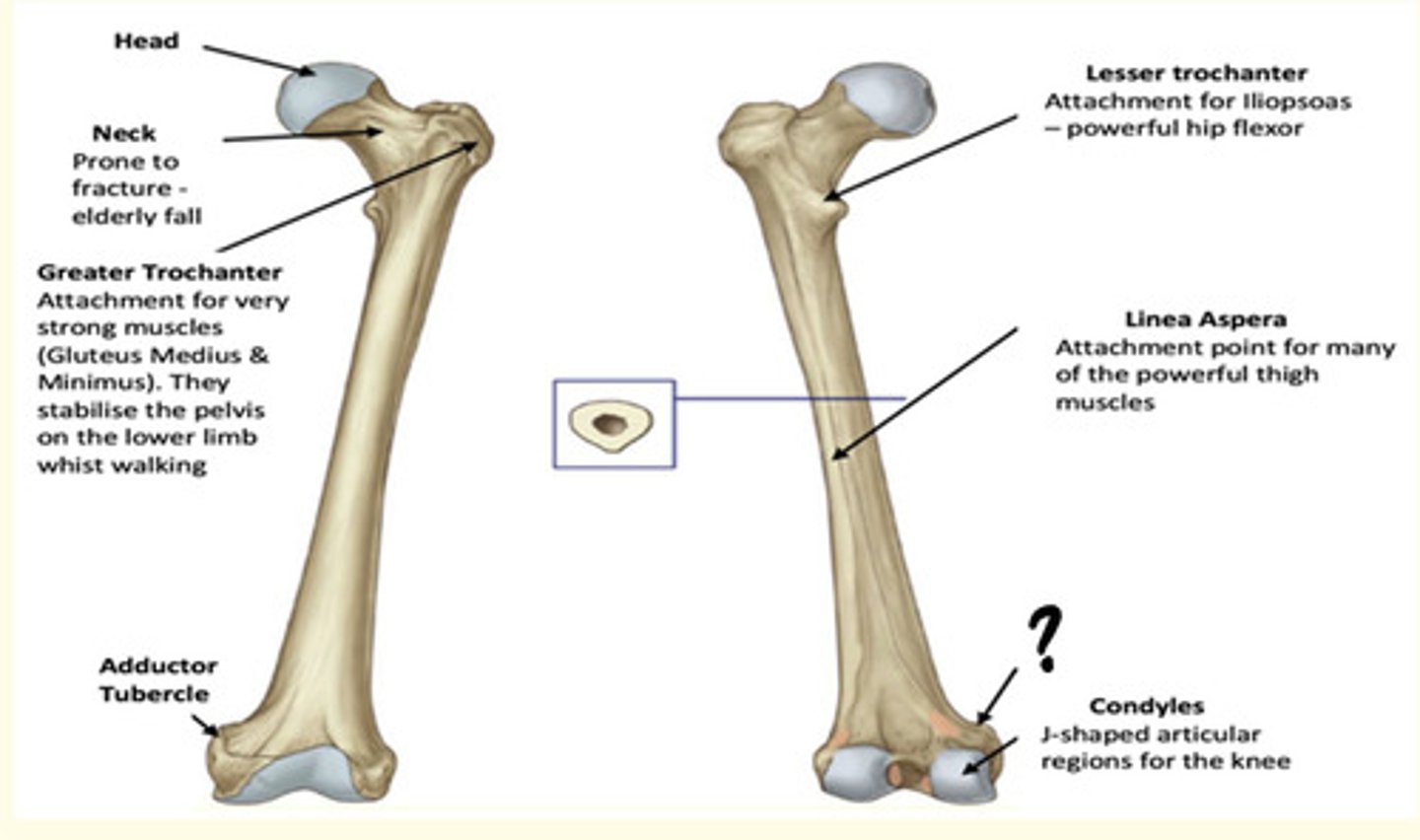
Osteology of the lower limb
Identify the region in the image labelled with a '?'
Condyles
J-shaped articular regions for the knee
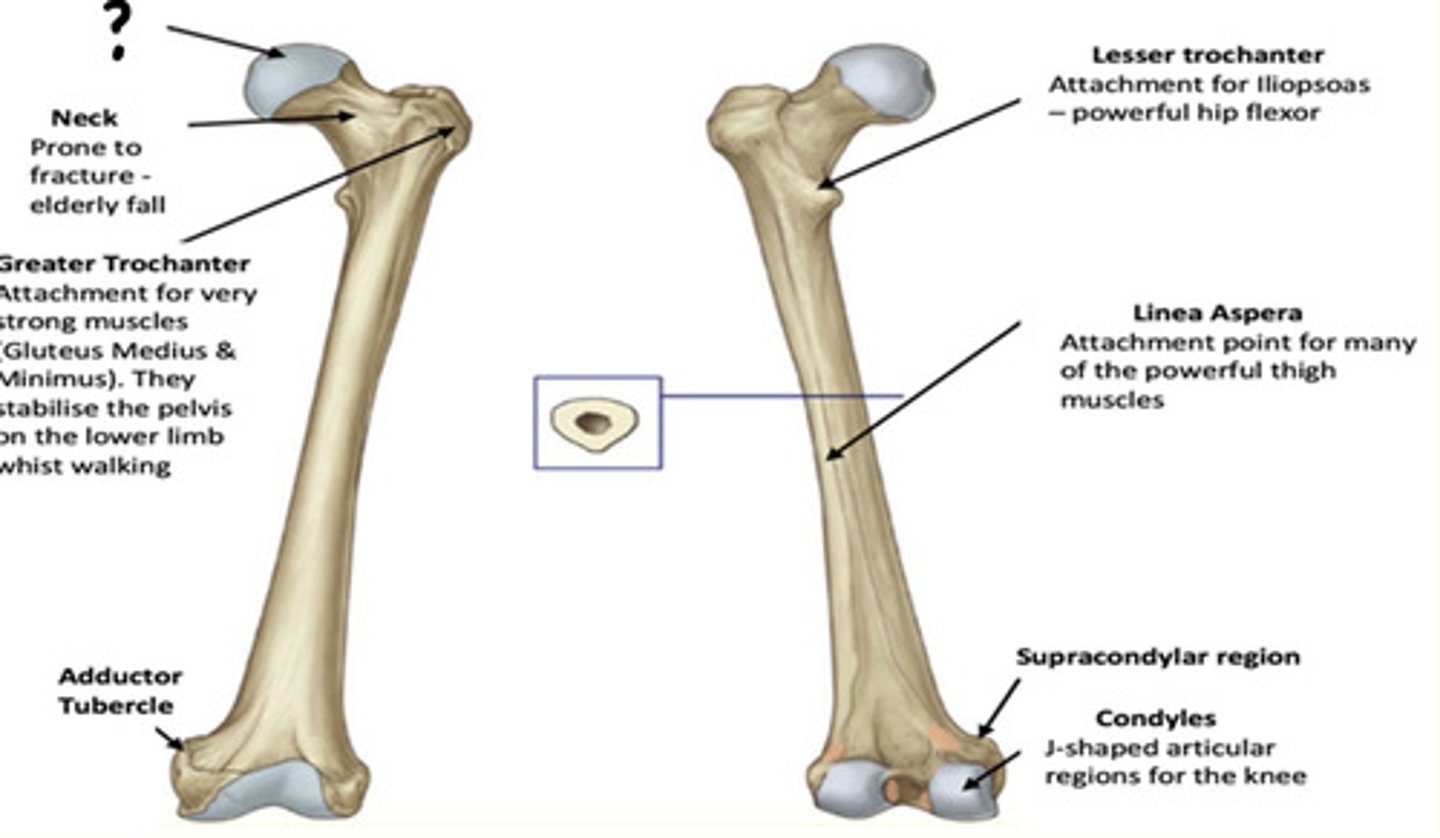
Osteology of the lower limb
Identify the region in the image labelled with a '?'
Head
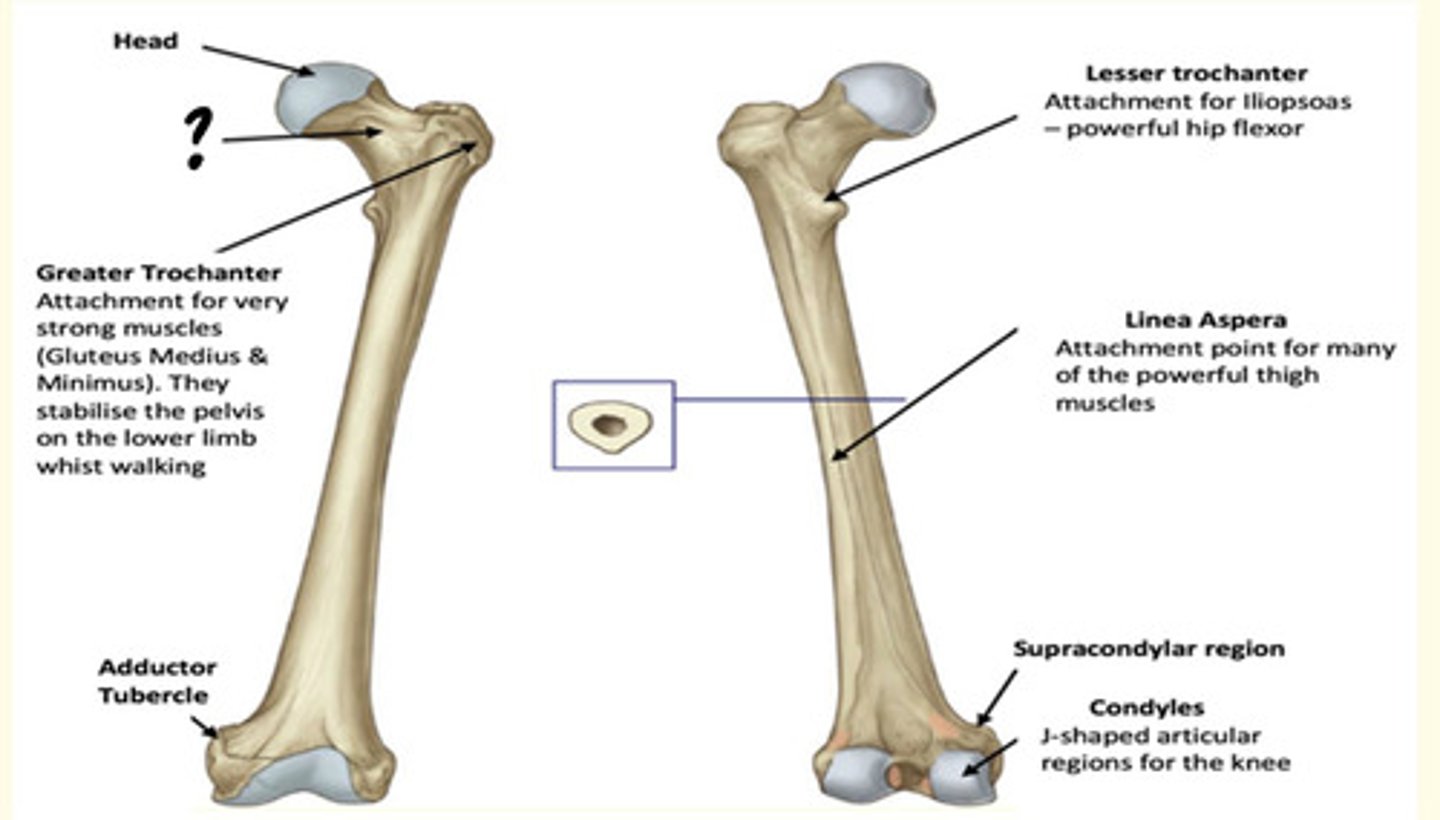
Osteology of the lower limb
Identify the region in the image labelled with a '?'
Neck
Prone to fracture - elderly fall
Osteology of the lower limb
Identify the region in the image labelled with a '?'
Greater Trochanter
Attachment for very strong muscles (Gluteus Medius & Minimus). They stabilise the pelvis on the lower limb whilst walking.
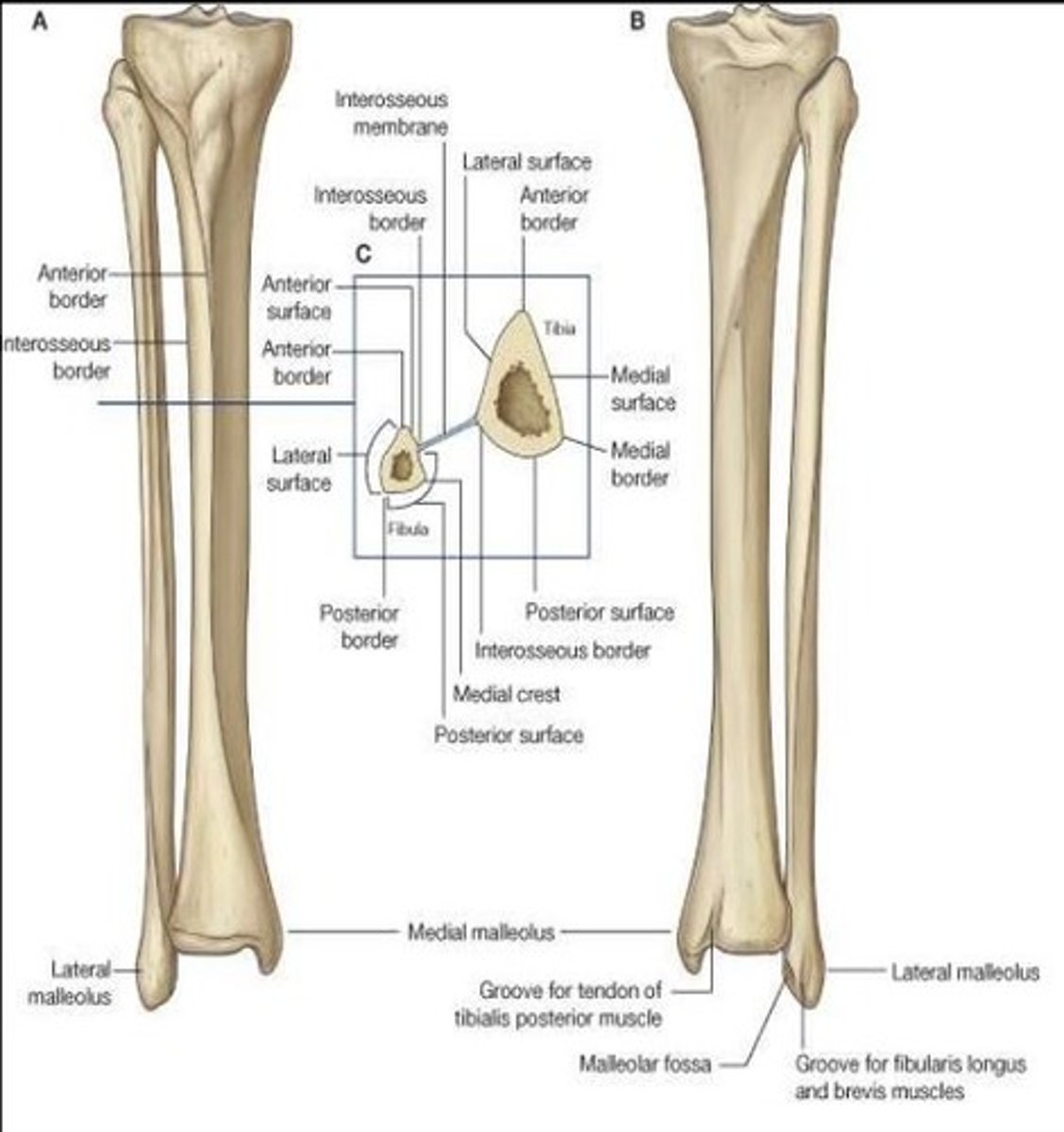
Bony components of the leg region
Tibia (on side of the toe)
Fibula
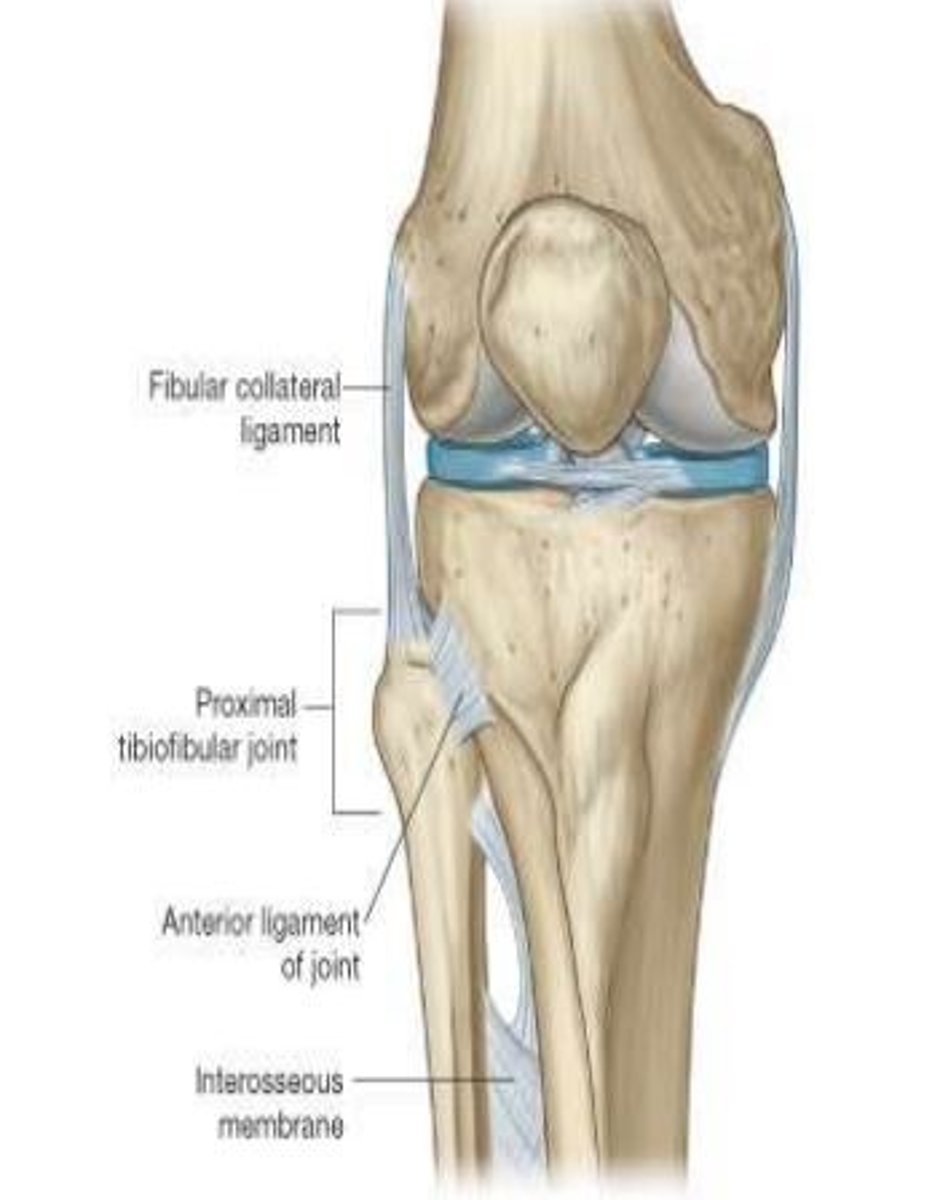
What type of joint is the knee?
Modified hinge joint (synovial)
Movements of the knee joint
Flexion, extension, some rotation when flexed

Patella bone type
Sesamoid bone
Articulates with femoral condyles
Contained within patellar ligament
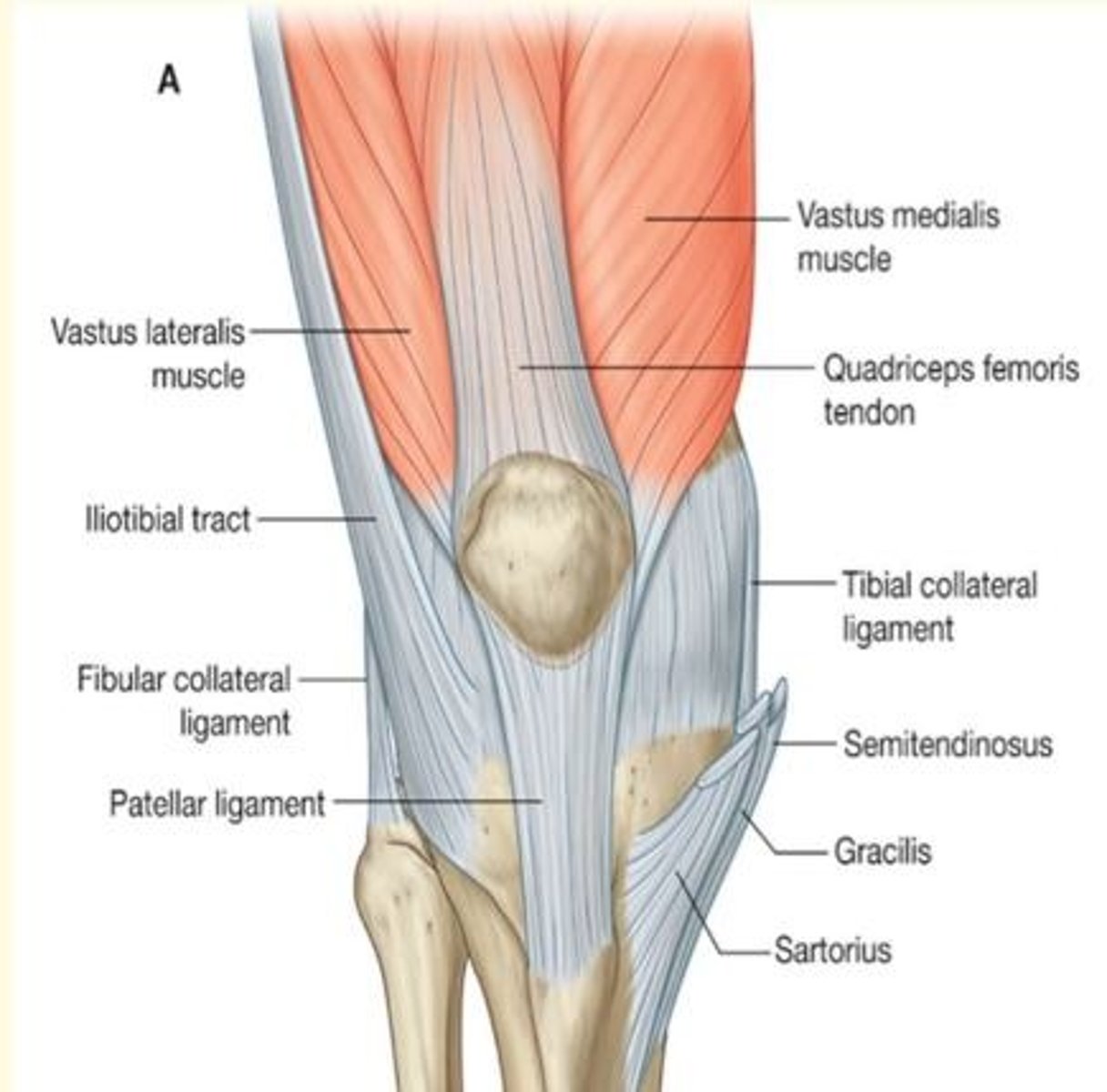
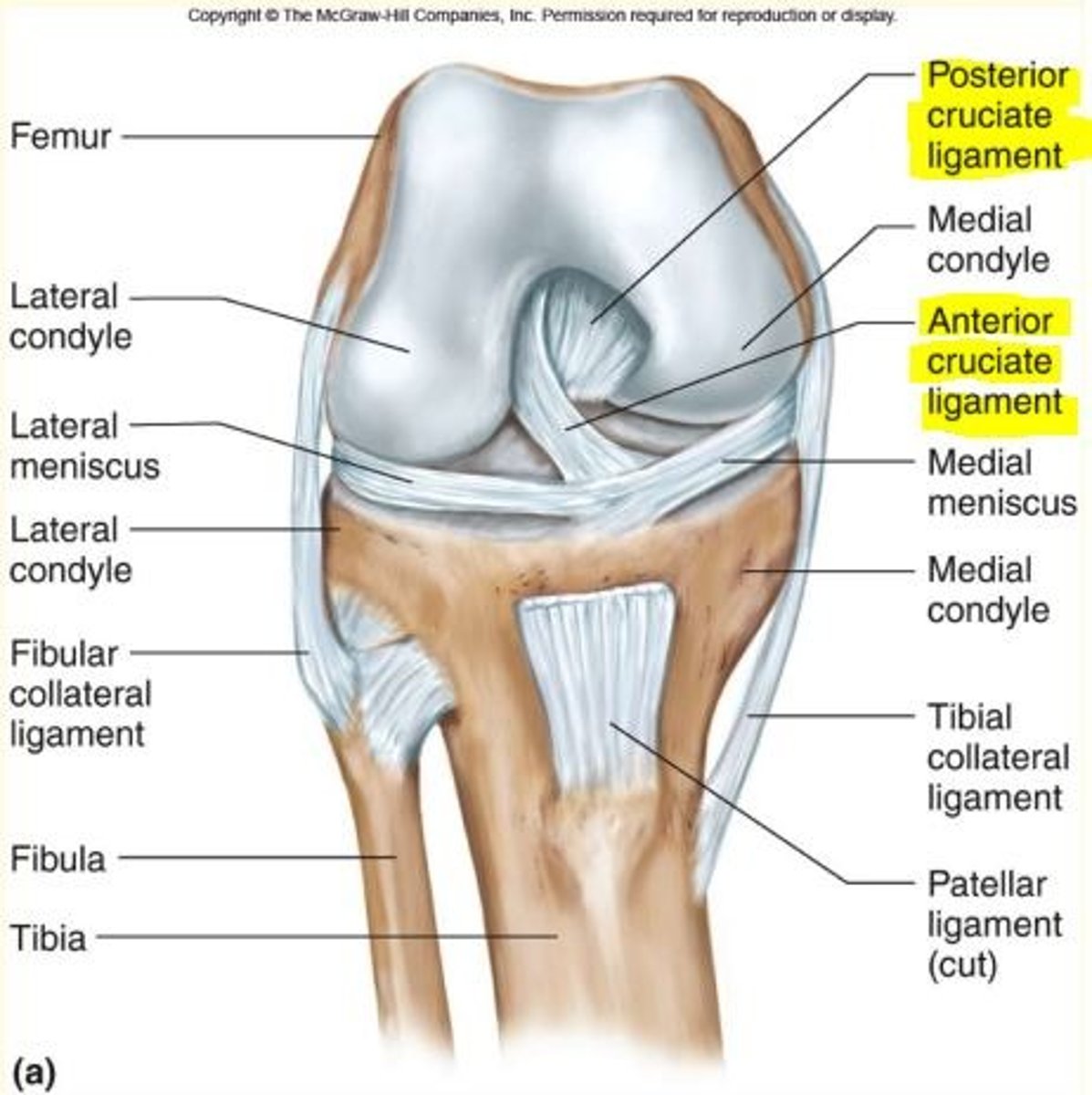
Ligaments of the knee are split into two groups
- Extra-articular ligaments
- Intra-articular ligaments
Name the extra-articular ligaments of the knee
Extra-articular ligaments
1) Fibular (lateral) collateral ligaments
2) Tibial (medial) collateral ligaments - middle fibers attached to medial meniscus
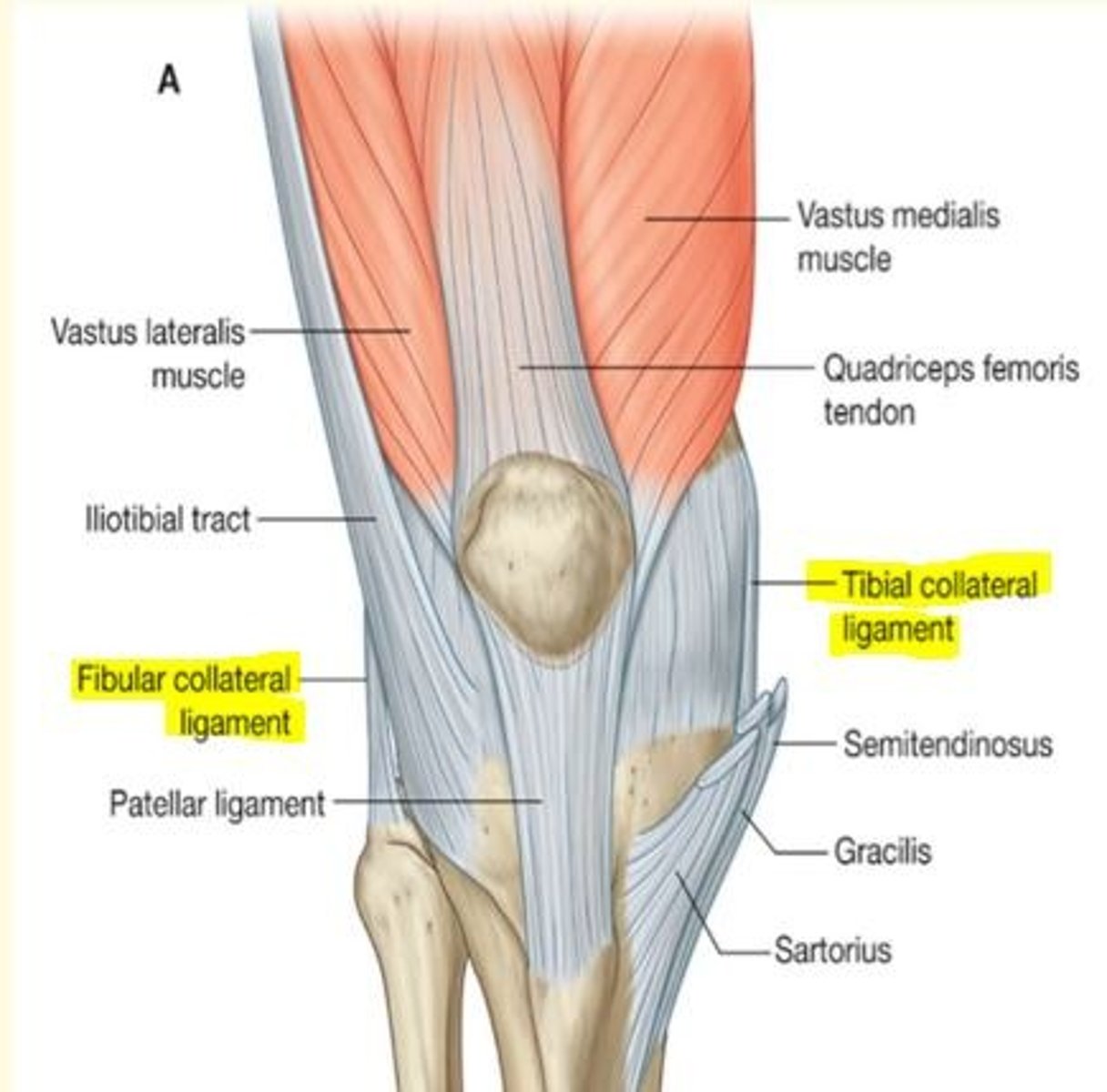
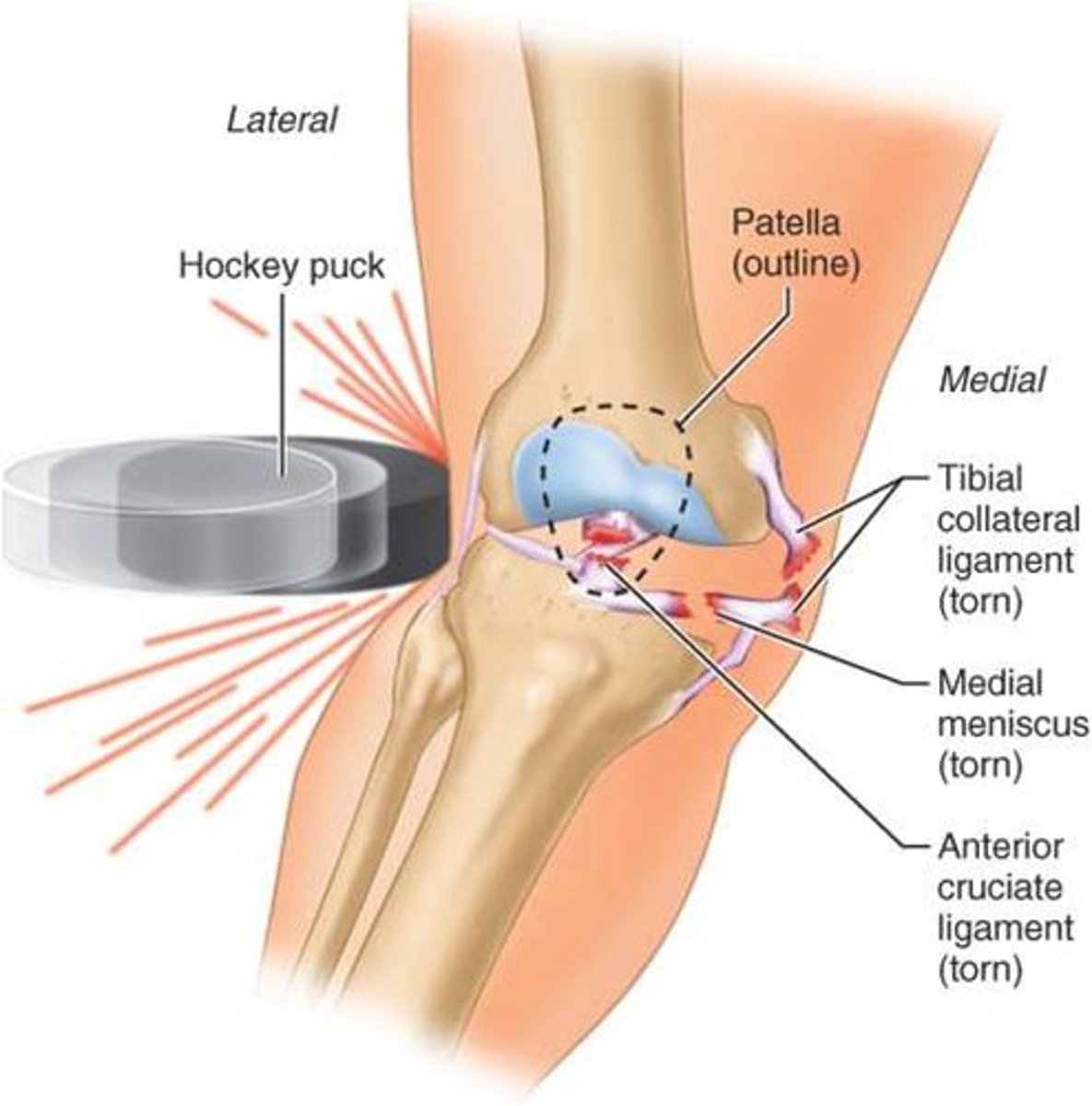
Injury of the tibial (medial) collateral ligament
Direct blow to the lateral aspect of the knee or twisting injury
Assessed by a valgus test
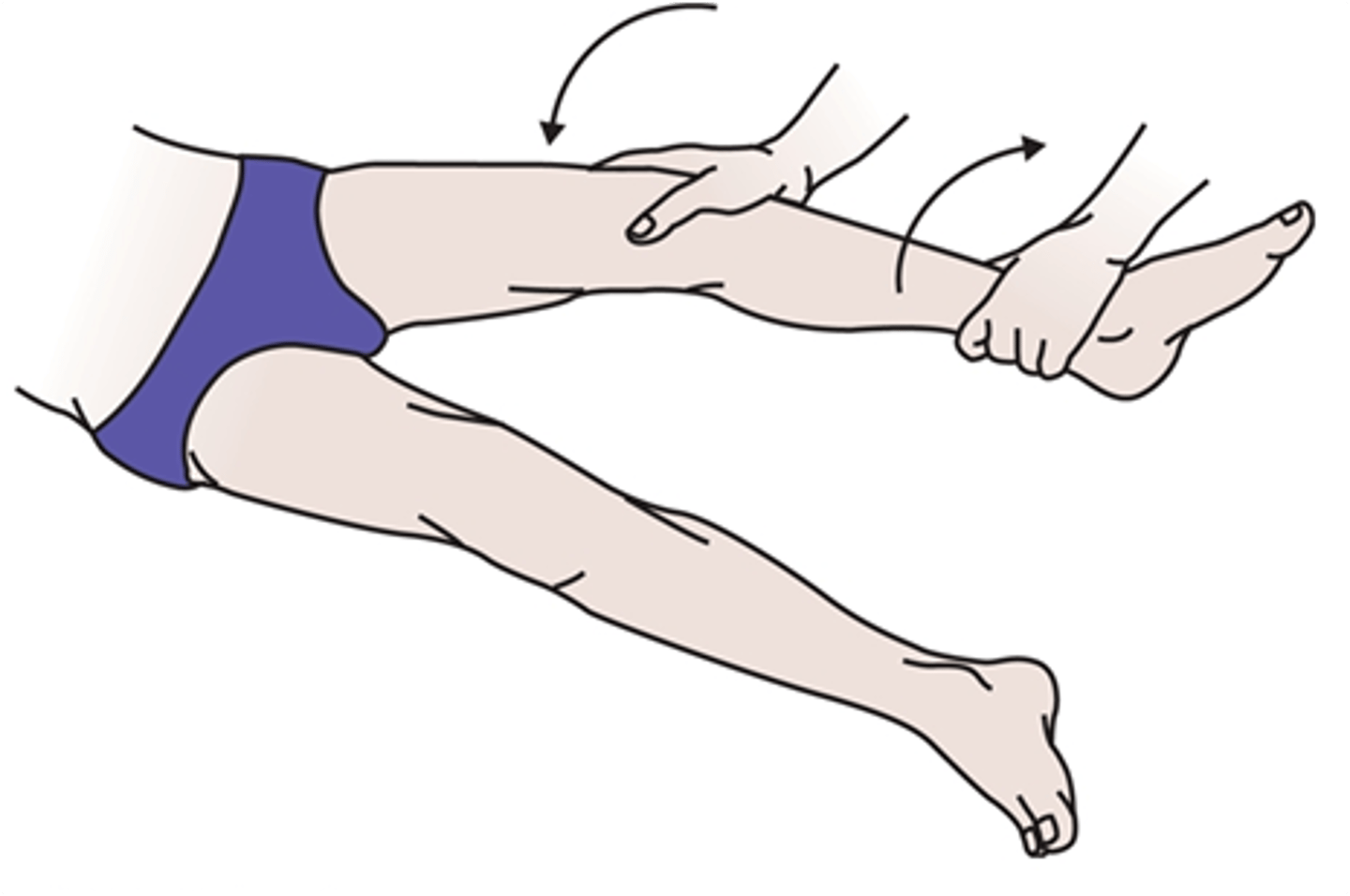
What test is used for injury to the extra-articular ligaments (MEDIAL/tibial collateral ligament)
Medial (tibial) collateral ligament testing is performed via the valgus stress test
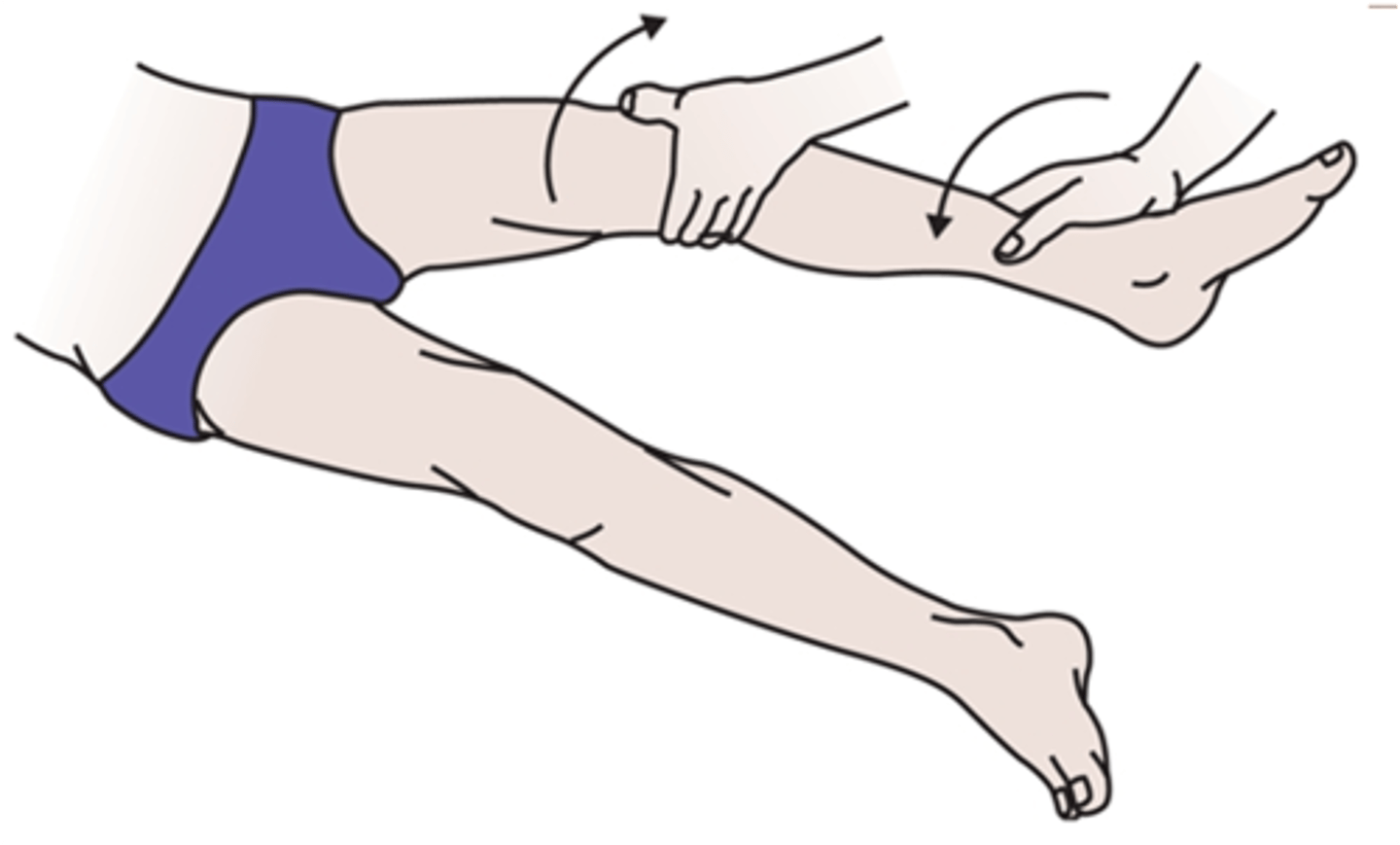
What test is used for injury to the extra-articular ligaments (LATERAL/fibular collateral ligament)
Lateral (fibular) collateral ligament testing is performed via the varus stress test
Ligaments of the knee are split into two groups
- Extra-articular ligaments
- Intra-articular ligaments
Name the intra-articular ligaments of the knee
Intra-articular ligaments
1) Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
2) Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)
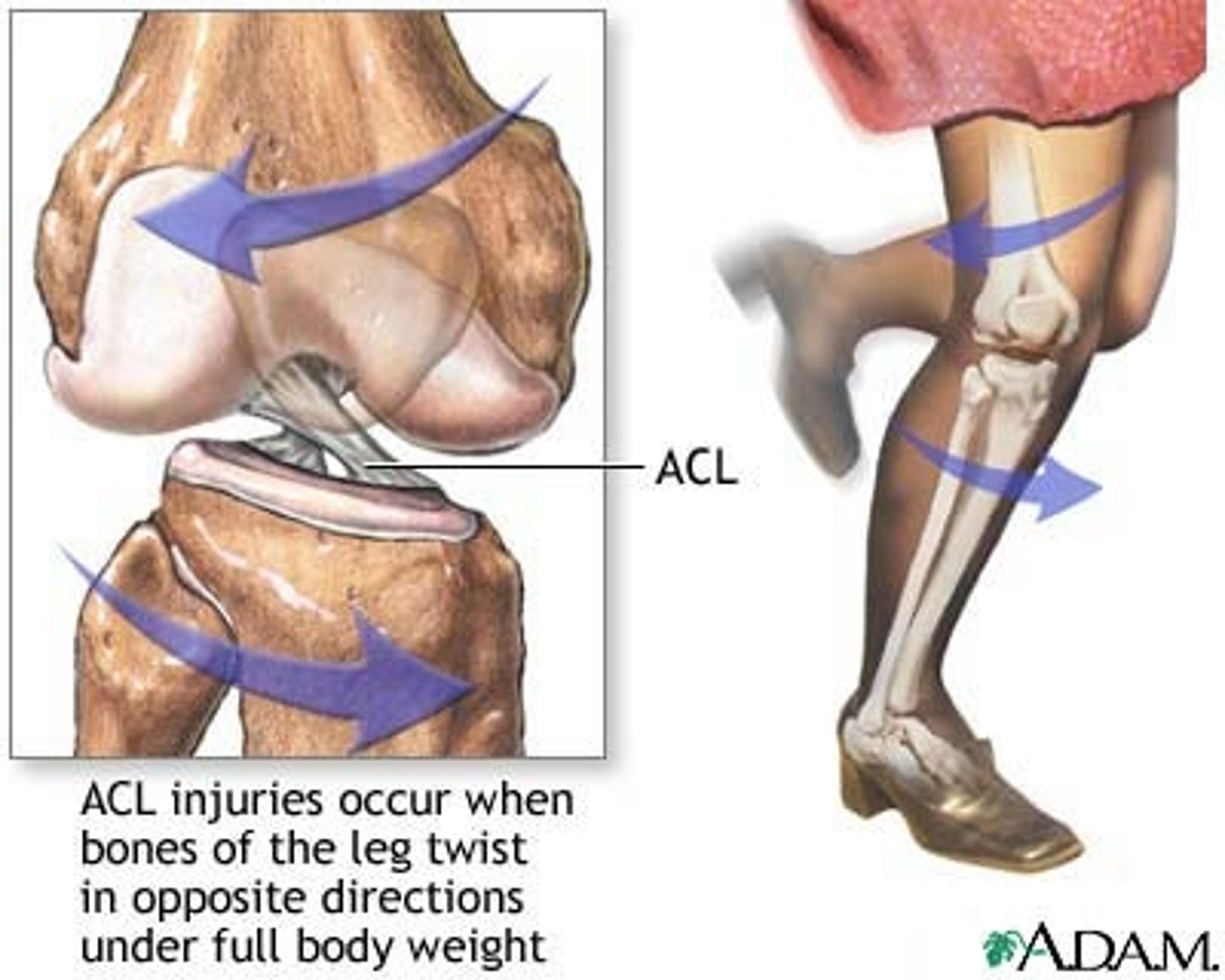
Injury of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
Usually caused when pivoting on a flexed knee
Often injured as athlete is attempting to change direction
Twisting of lower leg - popping sound
Injured during excessive hyperextension
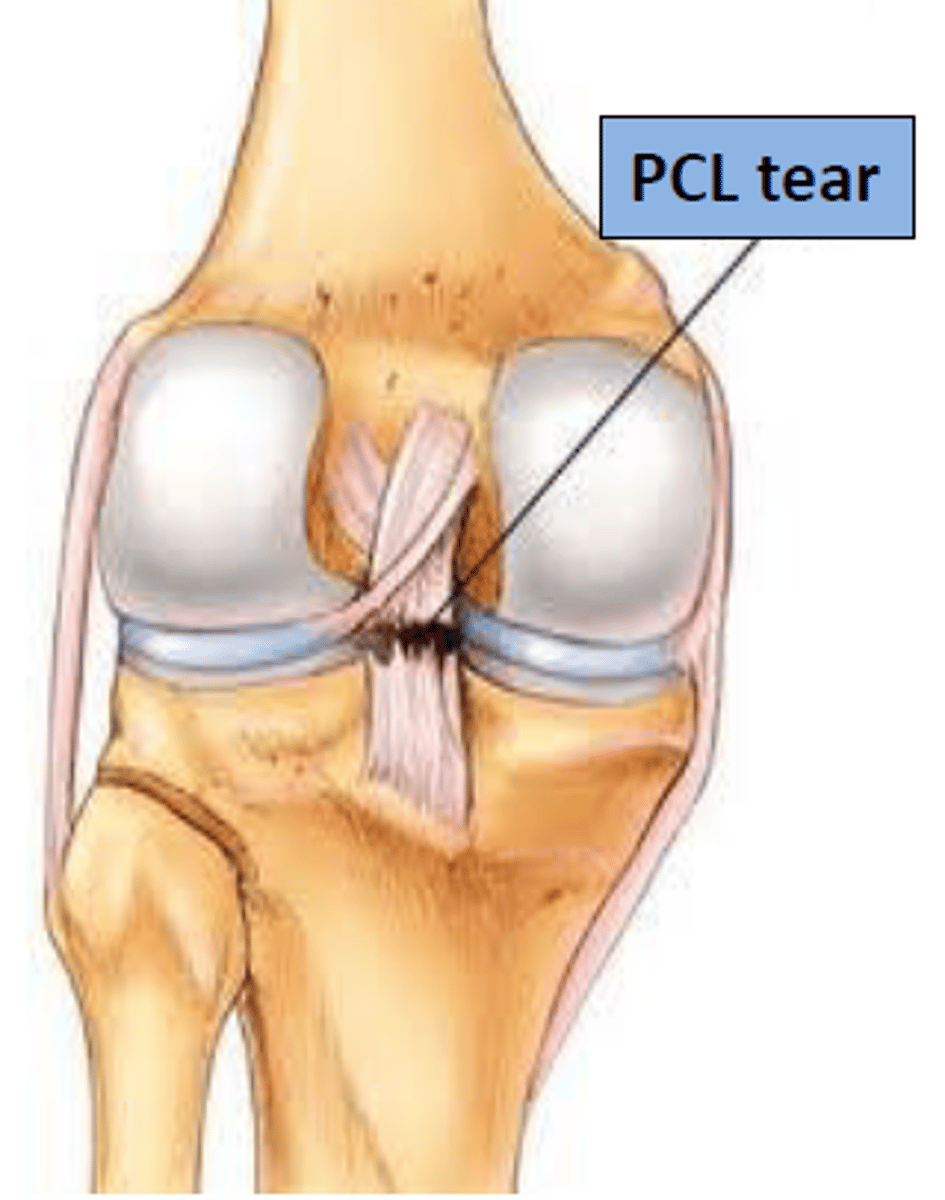
Injury of the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)
Damaged by hyperextension or impacts to the upper end of the tibial tuberosity
Tests for ACL damage
Lachman (20 degree flexion)
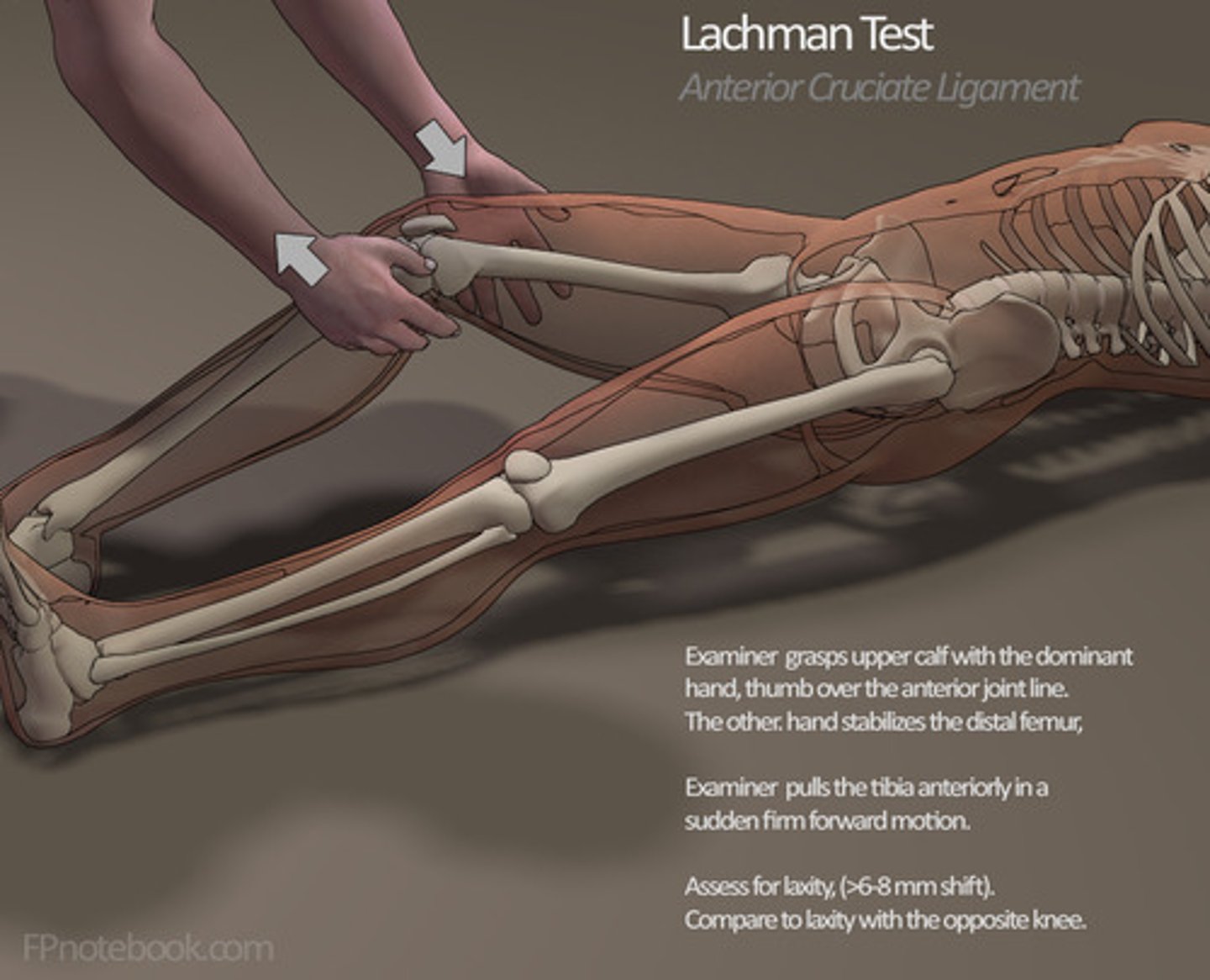
What test is used for injury of intra-articular ligaments
(Anterior cruciate ligament injury)
Lachman test (20 degree flexion) is the most sensitive test for ACL damage
What tests are used for testing for damage to the intra-articular CRUCIATE ligaments?
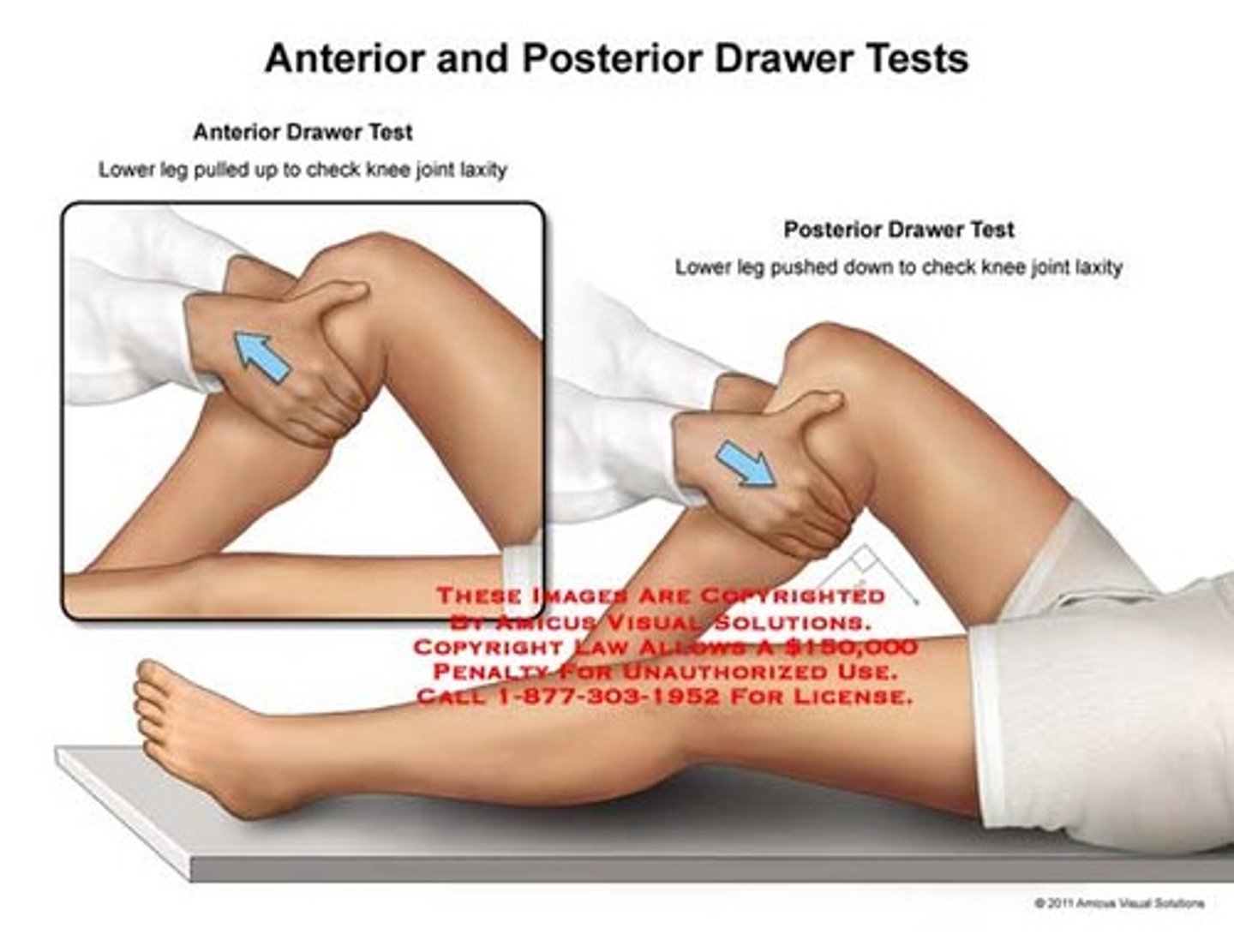
Anterior and posterior drawer tests
Testing ACL = pull tibia forward on femoral condyles (anterior drawer)
Testing PCL = push tibia backwards on femoral condyles (posterior drawer)
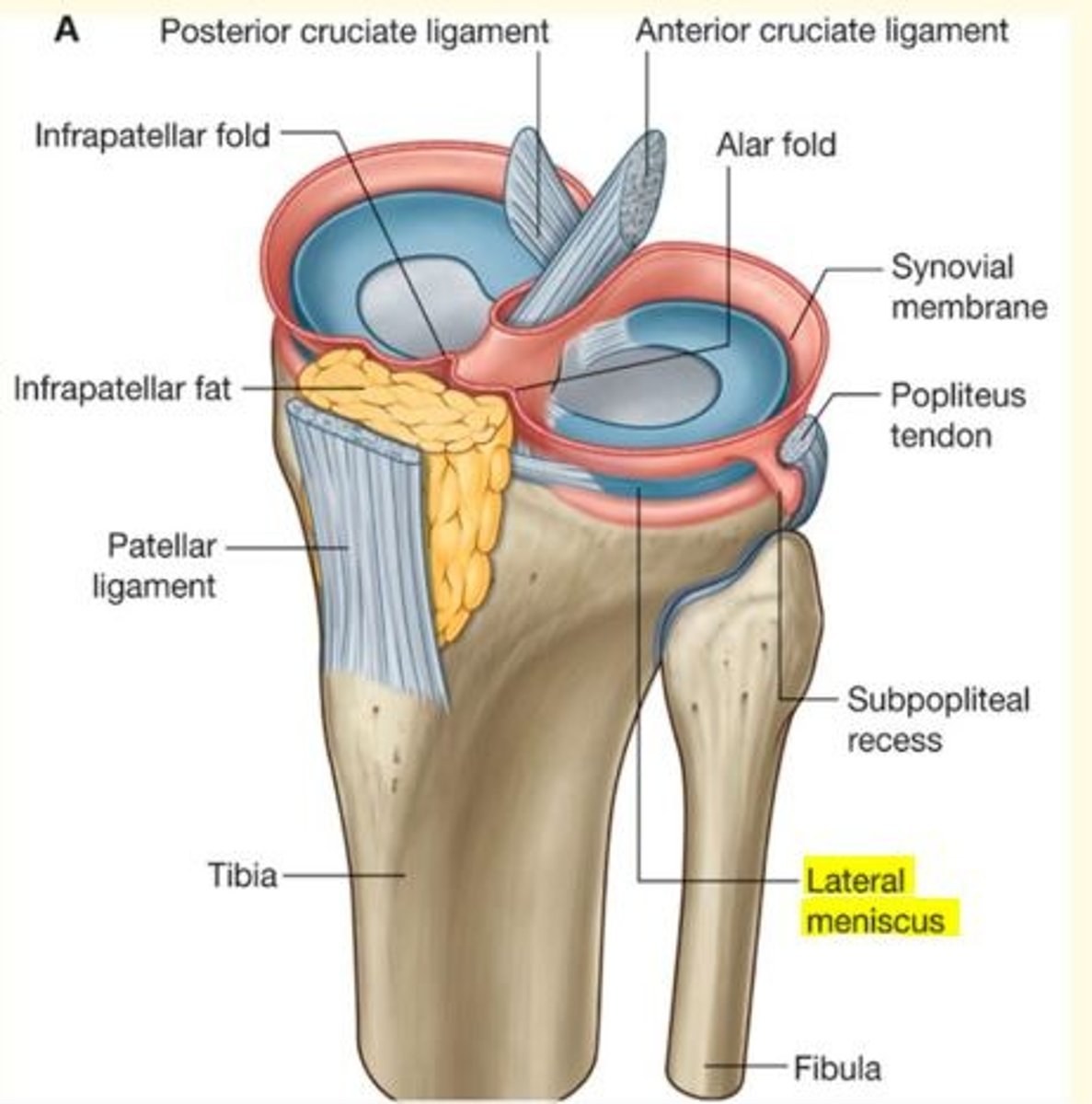
Menisci of the knee
Crescent-shaped fibrocartilage
Deepens the articular surface of tibia - gives stability
Functions as a shock absorber
1) Medial meniscus
2) Lateral meniscus
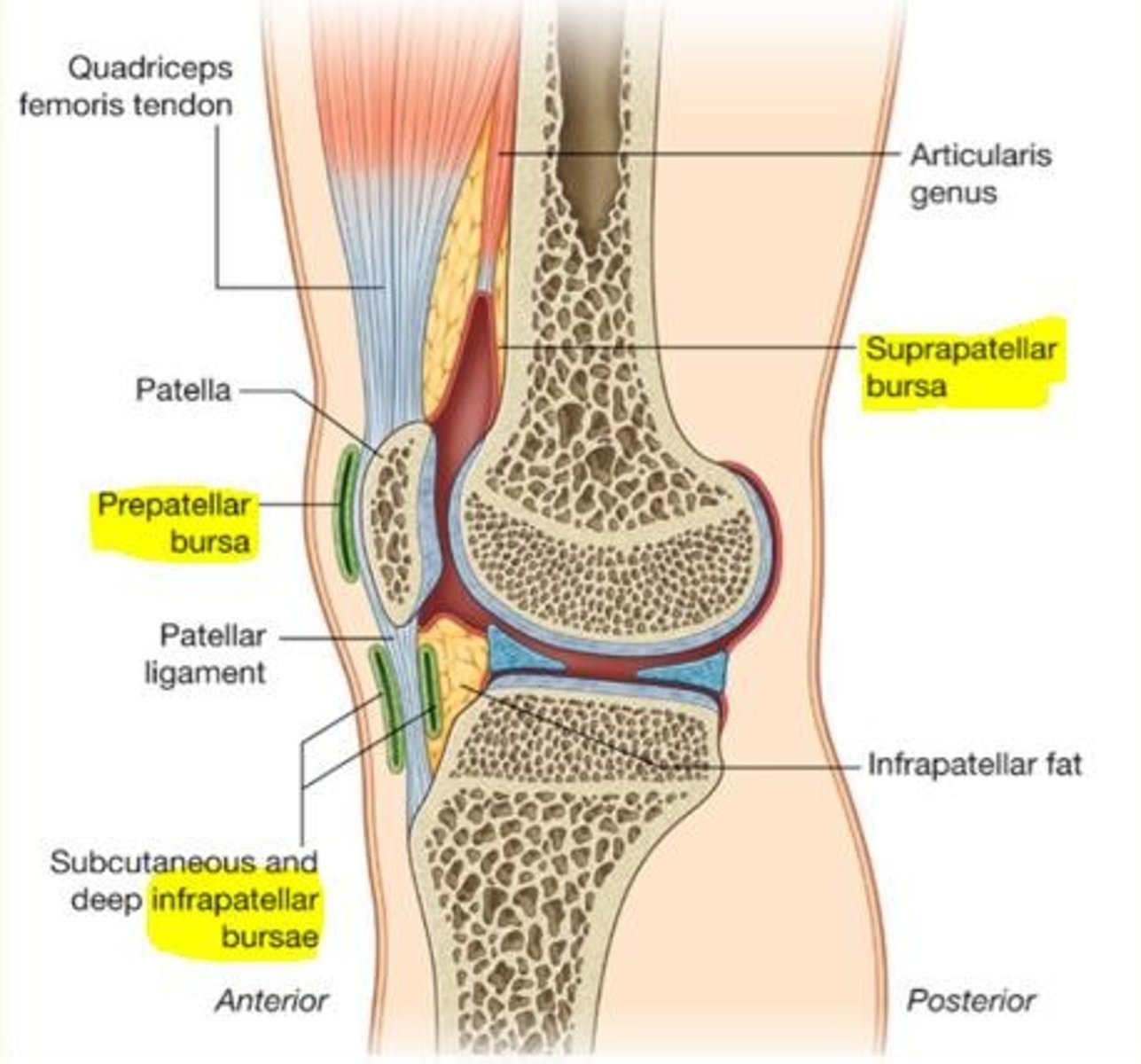
Four bursae of the knee
1) Suprapatellar bursa
2) Prepatellar bursa
3) Superficial infrapatellar bursa
4) Deep infrapatellar bursa
When bursa become swollen and inflamed...
Bursitis
These can be treated with aspiration & steroids if they don't settle
Bursa
Fluid-filled sac of synovium/synovial fluid that allows for easy movement of one part of a joint over another
Found in regions of friction/wear
Genu valgum
Knock-kneed; the knees are in close position and the space between the ankles is increased.
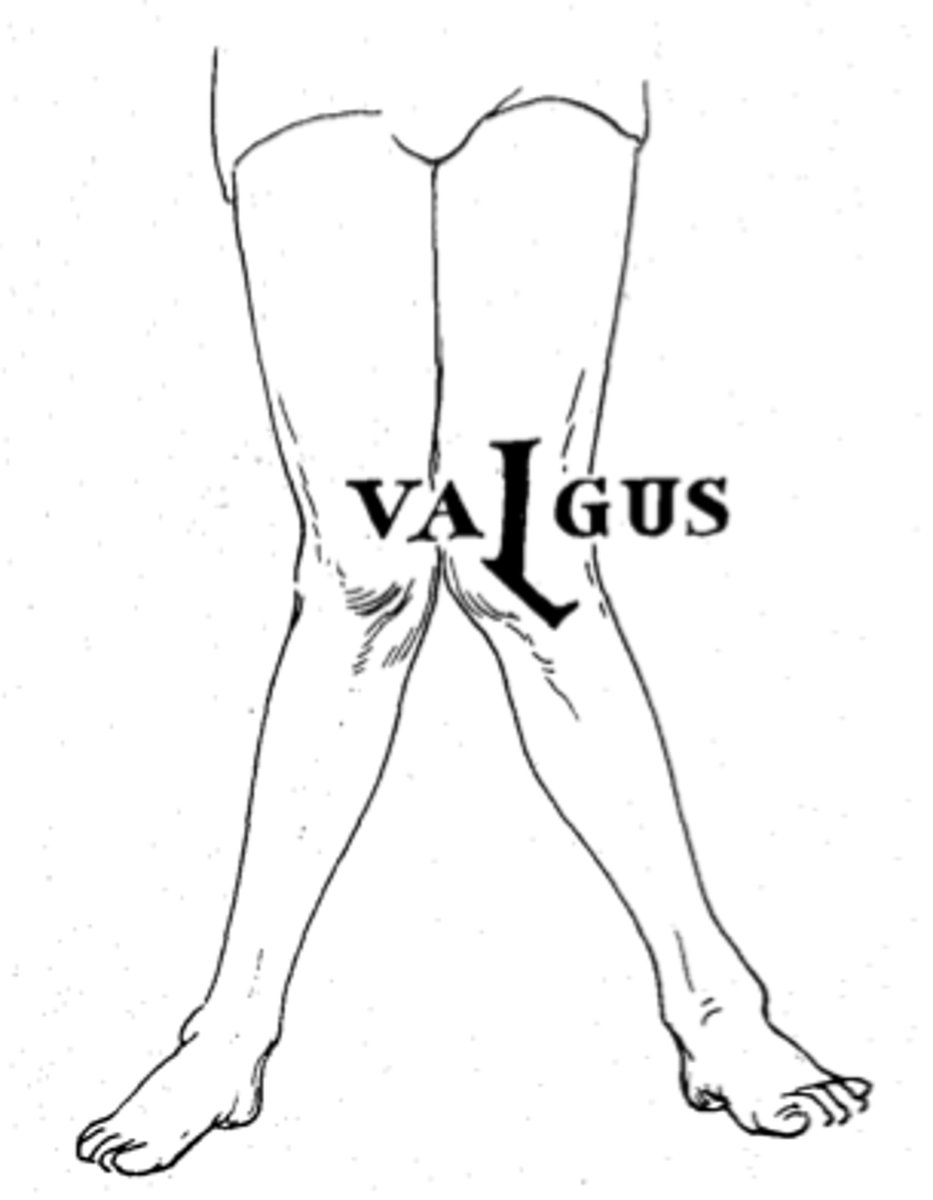
Genu vara
Bow-legged
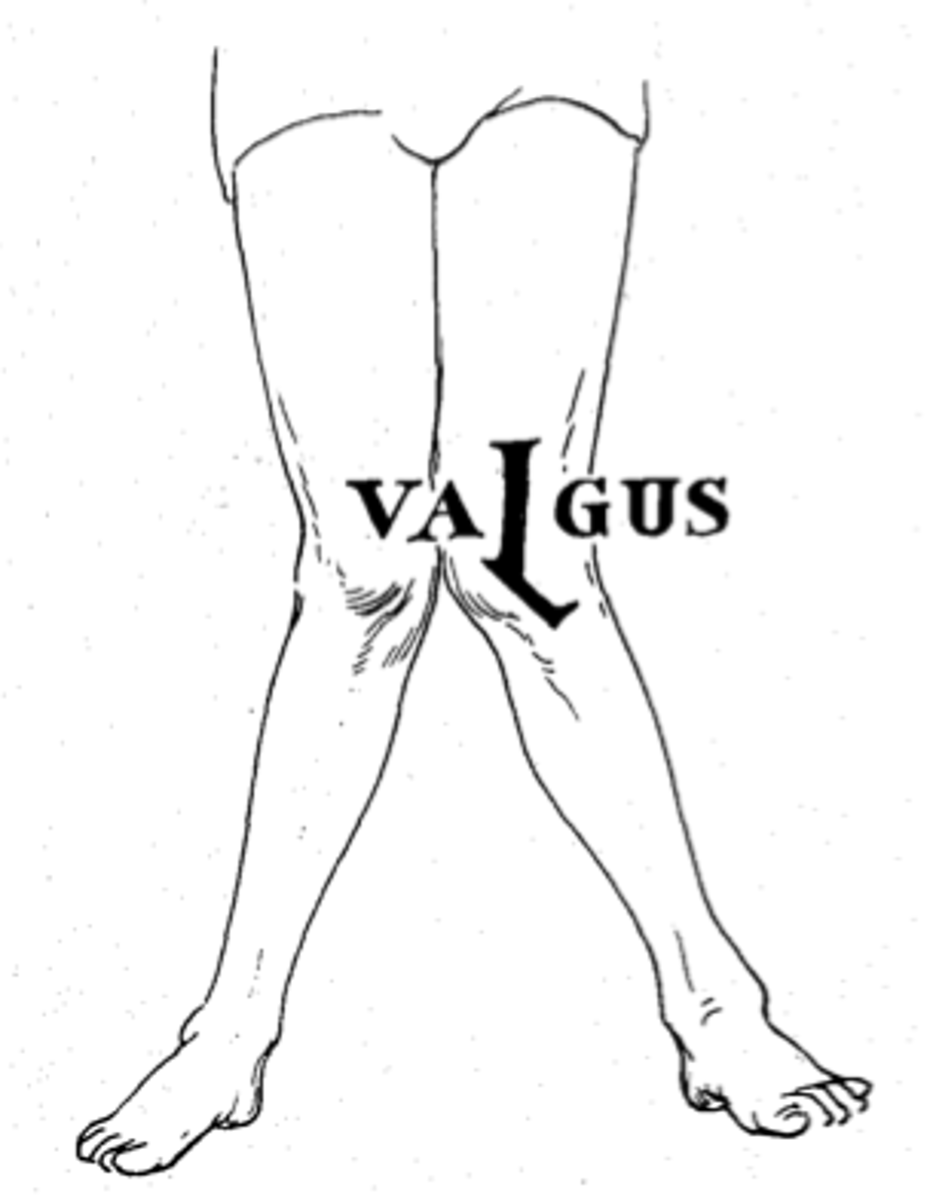
Valgus
Distal part of the bone is directed AWAY from the midline
Knock-kneed
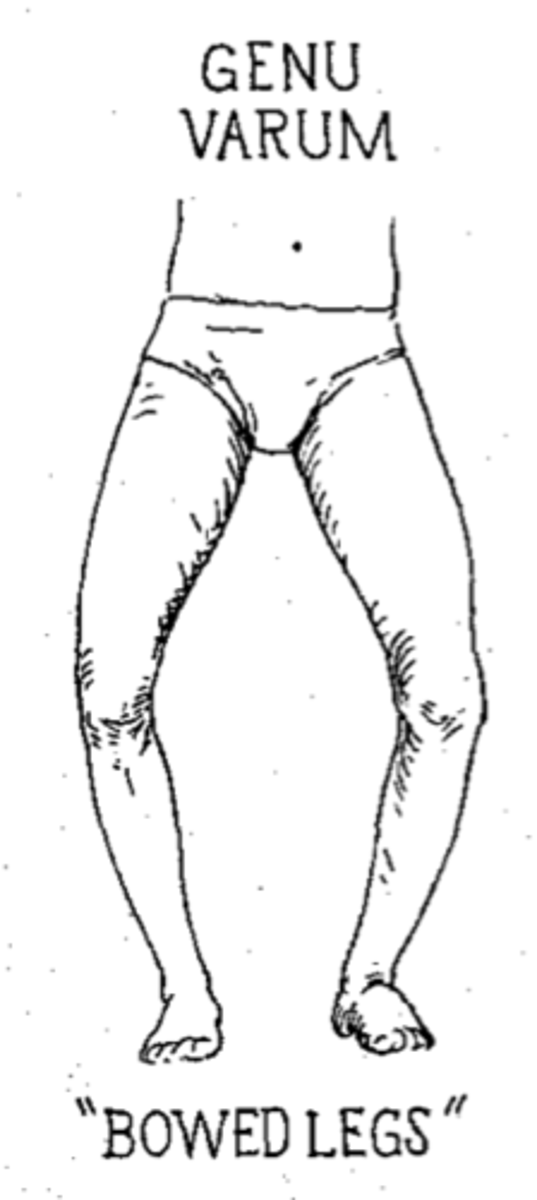
Varus
Distal part of the bone is directed TOWARDS the midline
Bow-legged
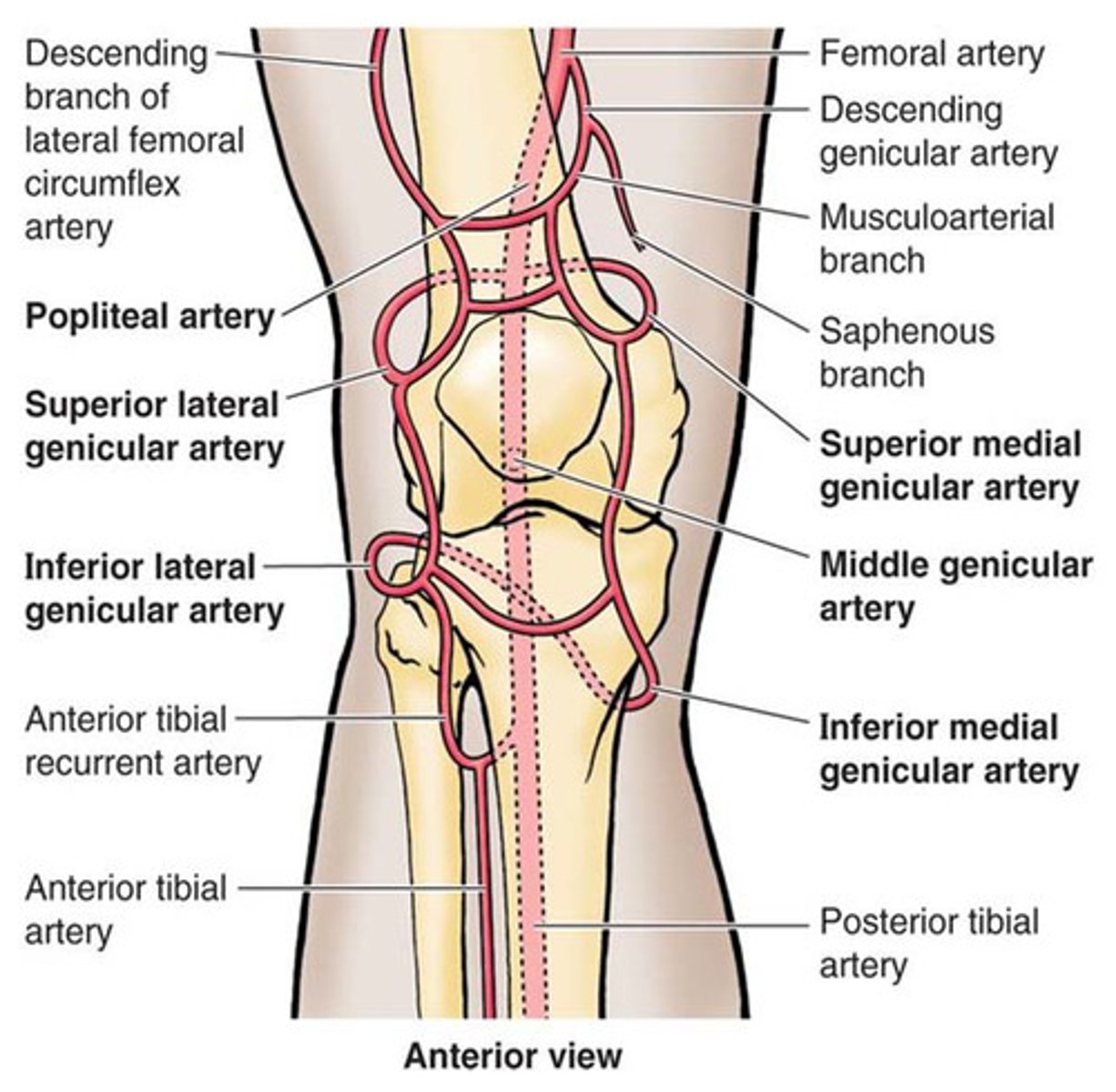
Blood supply to the knee
Genicular branches of the femoral and popliteal arteries to form a genicular popliteal anastomosis around the knee
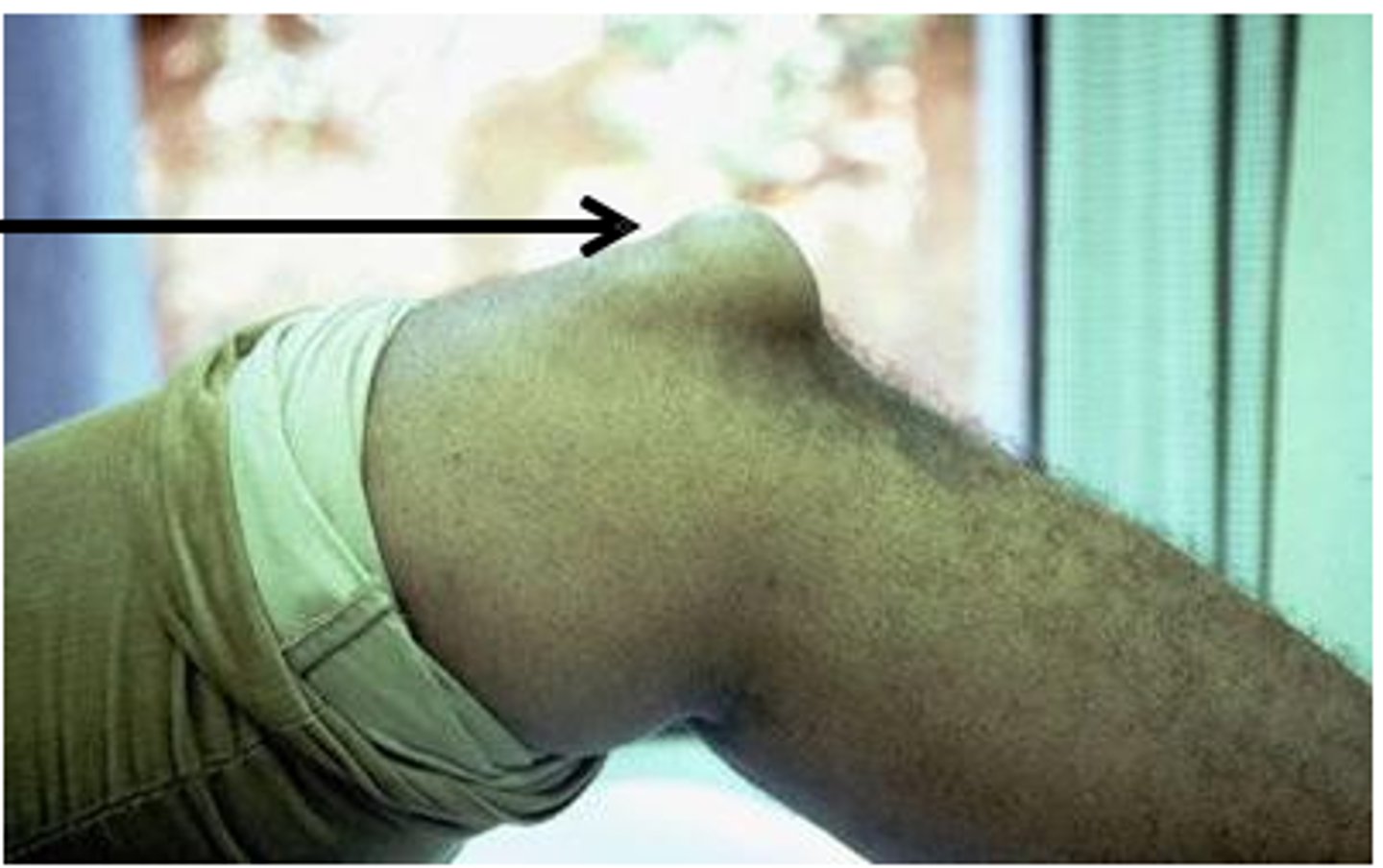
Housemaid's knee
Prepatellar bursitis after repetitive pressure on the knee
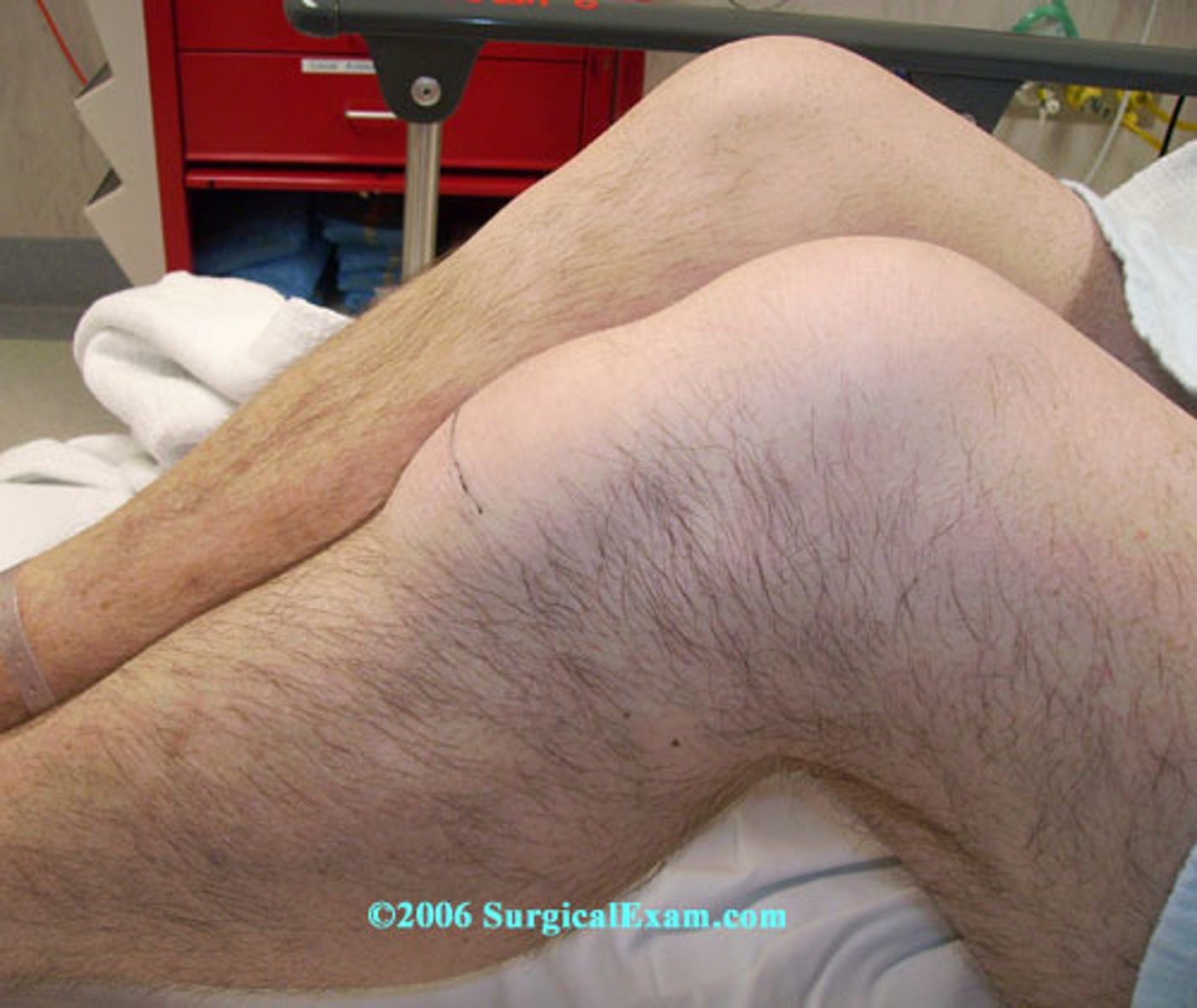
Clergyman's knee
Superficial infrapatellar bursitis
Which one of the following represents the innervation of the patellar tendon reflex?
a) L2, 3, 4
b) S1, 2, 3
c) L4, 5
d) L4, 5, S1, 2, 3
e) L1, 2, 3
a) L2, 3, 4
Which one of the following location / areas does not need / have a bursa?
a) Cartilage exposed to wear
b) Ligaments exposed to friction
c) Around blood vessels
d) Tendons exposed to friction
e) Beneath skin covering a bone
c) Around blood vessels
Which one of the following is not a characteristic of the sacroiliac joint (SIJ)?
a) The mechanics of this joint is typically disturbed by lifting heavy objects without bending the knees
b) Architectural changes with age result in SIJ dysfunction
c) It develops increased range of movement during late pregnancy
d) It resembles a typical synovial joint in an adult
e) It plays a role in supporting and transferring the body weight
d) It resembles a typical synovial joint in an adult
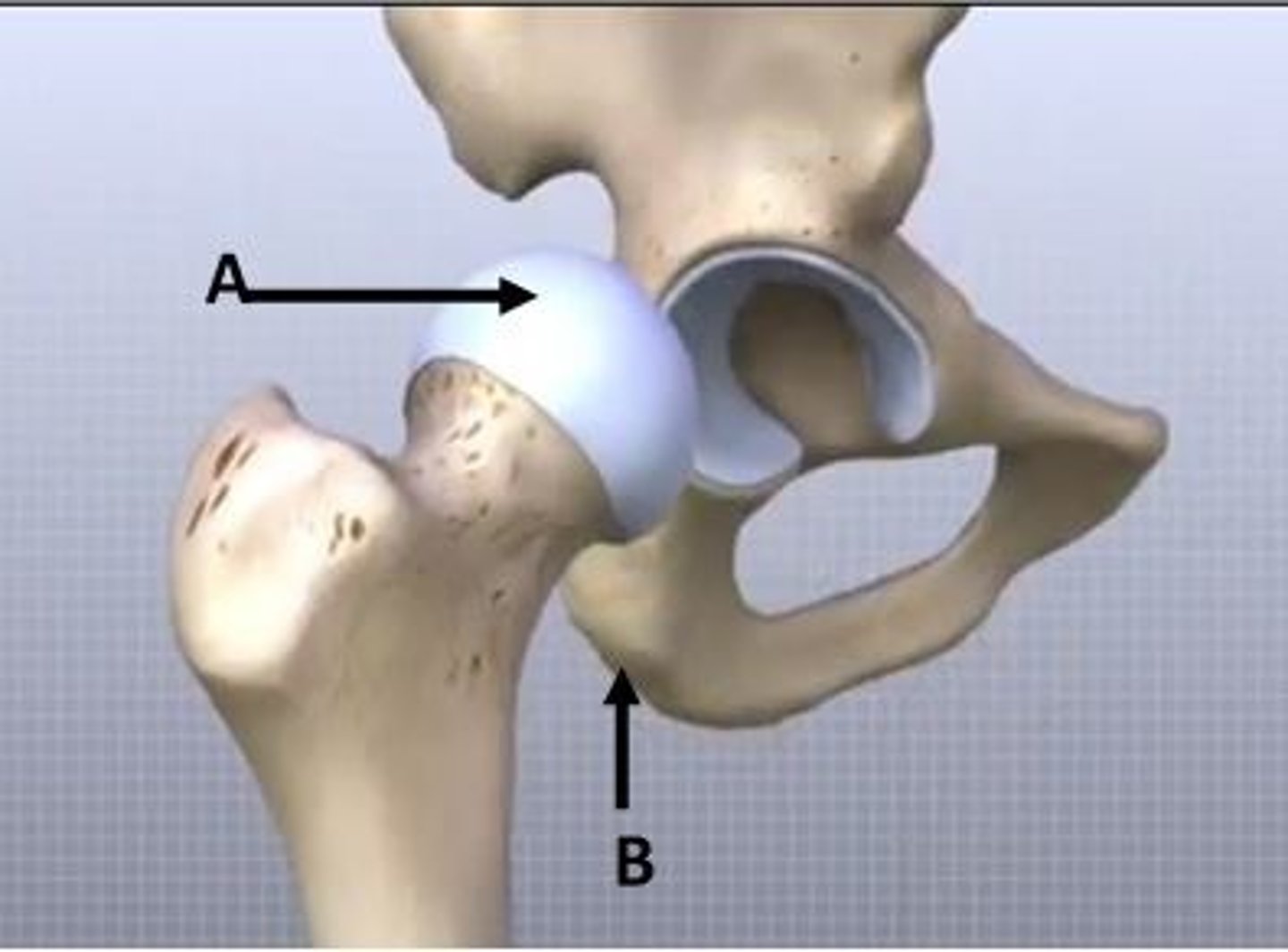
With respect to the image shown, ___ cartilage is indicated at A.
The landmark labelled B is called the ___. It is functionally significant in sitting position because it acts as a site for weight transmission.
With respect to the image shown, hyaline cartilage is indicated at A.
The landmark labelled B is called the ischial tuberosity. It is functionally significant in sitting position because it acts as a site for weight transmission.
Varus
Distal part of the bone is directed TOWARDS the midline of the body
Bow-legged
The most sensitive test for ACL damage
Lachman's test