All cells arise from other cells
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
1
New cards
what are the 3 stages of interphase?
G1- Cell grows in size and creates new biomass (whilst carrying out normal activity)
S- DNA replicates and doubles (semi conservation replication)
G2- Cell prepares to divide - the amount of ATP is increased to provide extra energy for the cell, organelles replicated etc.
S- DNA replicates and doubles (semi conservation replication)
G2- Cell prepares to divide - the amount of ATP is increased to provide extra energy for the cell, organelles replicated etc.
2
New cards
what is mitosis in terms of the cell cycle?
-When the eukaryotic cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells
-Each with identical copies of DNA produced by the parent cell during DNA replication
-Each with identical copies of DNA produced by the parent cell during DNA replication
3
New cards
what is cytokinesis?
division of the cytoplasm to form two cells
-a ring of protein filaments form around the equator of the cell - this then tightens and splits the cell into two
-a ring of protein filaments form around the equator of the cell - this then tightens and splits the cell into two
4
New cards
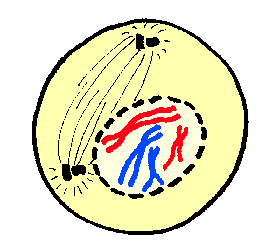
what occurs during prophase?
-Chromosomes will condense and get shorter, fatter and more visible
-Centrioles migrate to opposite ends of the cell and develop spindle fibres (spindle apparatus)
-Nuclear envelope breaks down and nucleolus disappears so chromosomes float freely in the cytoplasm
-Centrioles migrate to opposite ends of the cell and develop spindle fibres (spindle apparatus)
-Nuclear envelope breaks down and nucleolus disappears so chromosomes float freely in the cytoplasm
5
New cards
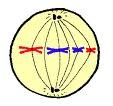
what occurs during metaphase?
-Chromosomes are drawn to the middle of the cell (the equator) by spindle fibres attached to the centromere and line up
-Centromeres attach to the metaphase plate
-Centromeres attach to the metaphase plate
6
New cards
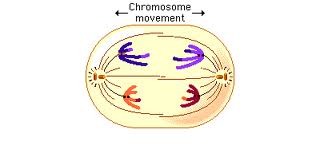
What occurs during anaphase?
-Centromeres divide and separate sister chromatids
-The spindle pulls the individual chromatids to opposite ends (poles) of the cell
-Chromatids will now appear V-shaped
-Now chromosomes
-The spindle pulls the individual chromatids to opposite ends (poles) of the cell
-Chromatids will now appear V-shaped
-Now chromosomes
7
New cards
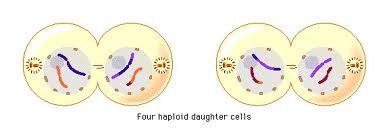
what occurs during telophase?
-Chromatids reach opposite poles and uncoil becoming longer and thinner (back into their chromatin state)
-Spindle apparatus breaks down
-Nuclear envelope forms around the chromosome forming two nuclei (and nucleolus reforms)
-Cytoplasm divides by cytokinesis
-Spindle apparatus breaks down
-Nuclear envelope forms around the chromosome forming two nuclei (and nucleolus reforms)
-Cytoplasm divides by cytokinesis
8
New cards
what 4 things is mitosis important for?
1) growth
2) replacement (of lost cells)
3) repair (replace damaged or killed cells)
4) asexual reproduction (in eukaryotic organisms)
2) replacement (of lost cells)
3) repair (replace damaged or killed cells)
4) asexual reproduction (in eukaryotic organisms)
9
New cards
what can uncontrolled cell division lead to?
the formation of tumours and cancers
10
New cards
how does cancer form?
-If a mutation occurs in the gene that controls cell division, the cell can divide out of control - cells may divide rapidly to form a tumour
-Cancer is a type of tumour that invade surrounding tissue - cancer forms tumours that are referred to a malignant
-Cancer is a type of tumour that invade surrounding tissue - cancer forms tumours that are referred to a malignant
11
New cards
how do cancer treatments work?
By disrupting the cell cycle - they will kill the tumour cells by limiting their rate of division
This is done by:
1) Preventing DNA from replicating
2) Inhibiting the metaphase stage of mitosis by interfering with spindle formation
This is done by:
1) Preventing DNA from replicating
2) Inhibiting the metaphase stage of mitosis by interfering with spindle formation
12
New cards
How does chemotherapy work?
-Disrupts cell growth and protein production
-Stops production of enzymes required for cell division
-The cell is unable to enter the S phase - forced to kill itself
-Stops production of enzymes required for cell division
-The cell is unable to enter the S phase - forced to kill itself
13
New cards
how does radiotherapy work?
-Inhibits DNA replication
Radiation can damage DNA at several points during the cell cycle
-The DNA is checked for damage
-If damage is detected the cell is forced to kill itself
Radiation can damage DNA at several points during the cell cycle
-The DNA is checked for damage
-If damage is detected the cell is forced to kill itself
14
New cards
How do viruses replicate?
-Viruses inject their nucleic acid into host cells
-They do this by binding to cells using their attachment proteins
-These 'hijacked' cells then create proteins and other compounds to assemble new viruses
-The new viruses burst out of the host cell
-This causes the cell to lyse (disintegration of a cell by rupture of the cell wall or membrane) and die
-They do this by binding to cells using their attachment proteins
-These 'hijacked' cells then create proteins and other compounds to assemble new viruses
-The new viruses burst out of the host cell
-This causes the cell to lyse (disintegration of a cell by rupture of the cell wall or membrane) and die
15
New cards
how do prokaryotic cells reproduce?
• cell increases in size and replication of the circular DNA and of plasmids occur
• division of the cytoplasm to produce two daughter cells, each with a single copy of the circular DNA and a variable number of copies of plasmids
• division of the cytoplasm to produce two daughter cells, each with a single copy of the circular DNA and a variable number of copies of plasmids