classics 10 pic id
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
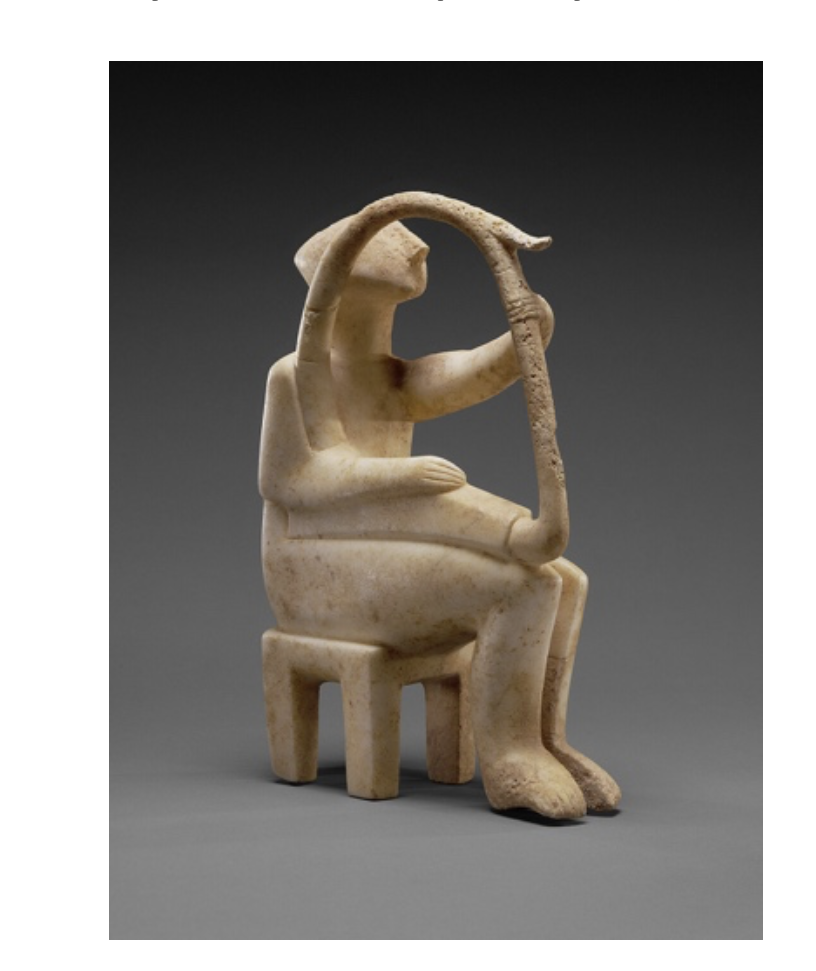

Cycladic Harp-Player (2700-2300BCE)
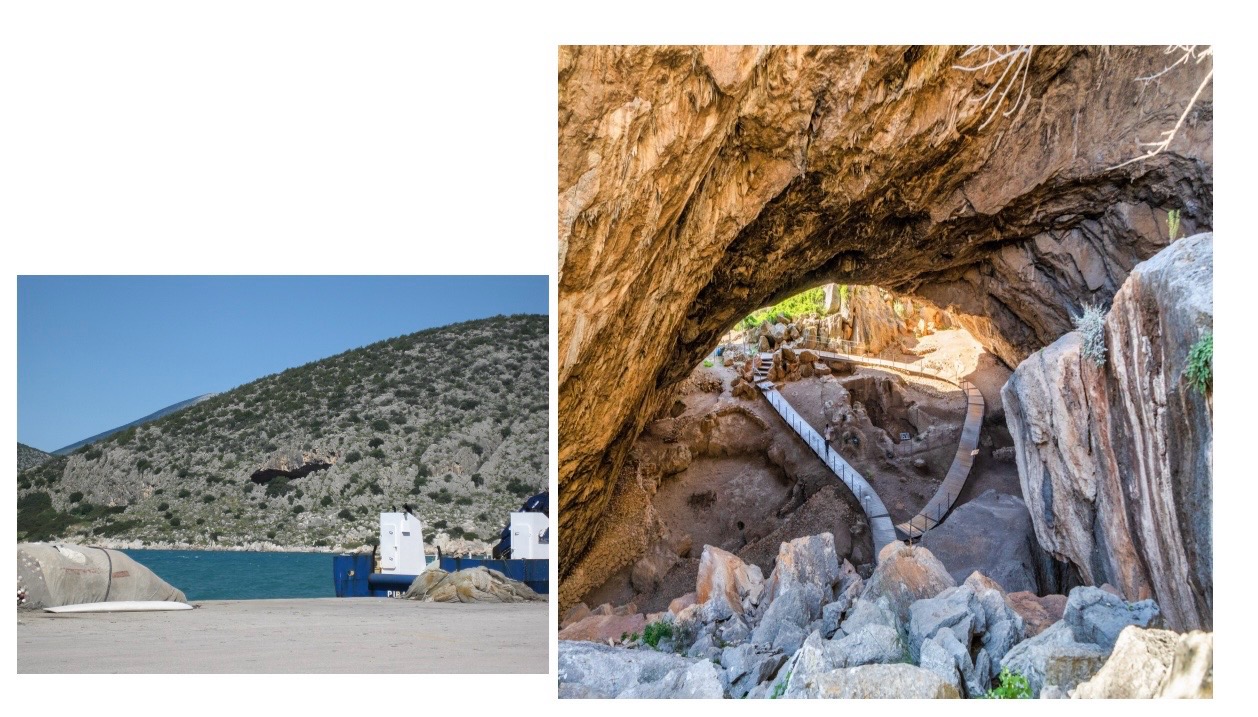

Paleolithic and Neolithic
Communities
The Franchthi Cave
18000BCE - 3200BCE,
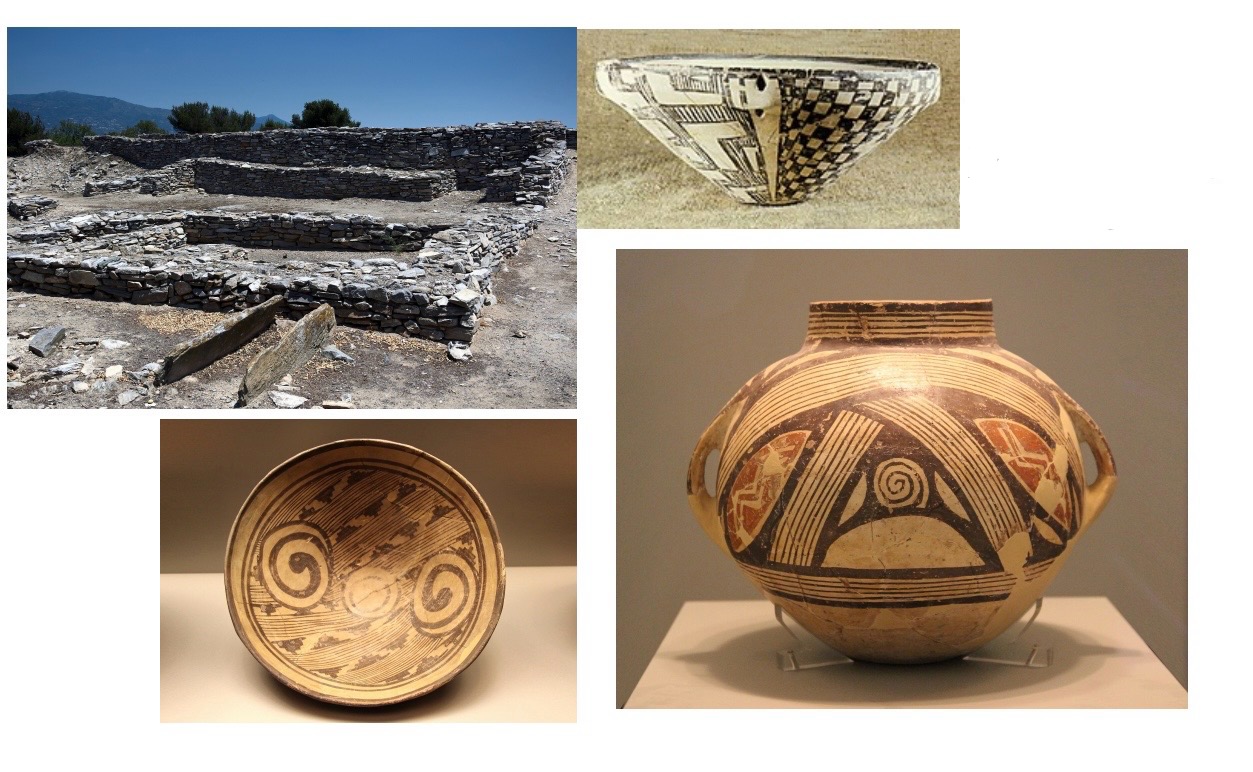

Pottery from
Neolithic
Dimini (5300-
3300BCE),

Early Helladic Cemetery at
Tsepi (3000 – 2000BCE),
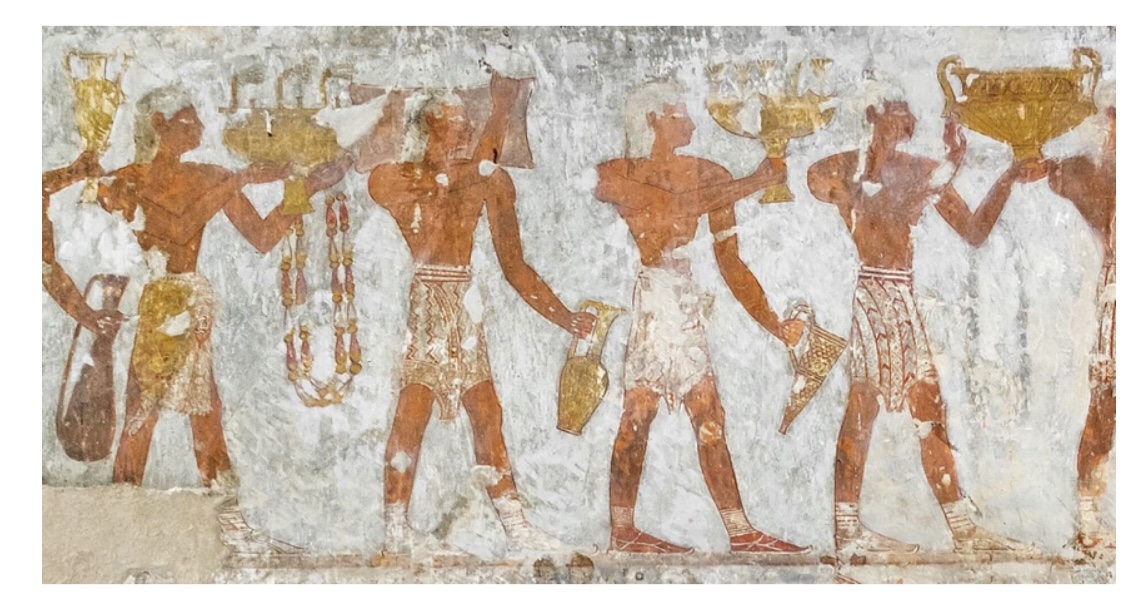

Rekhmire Tomb (ca.1400BCE) in Egypt,
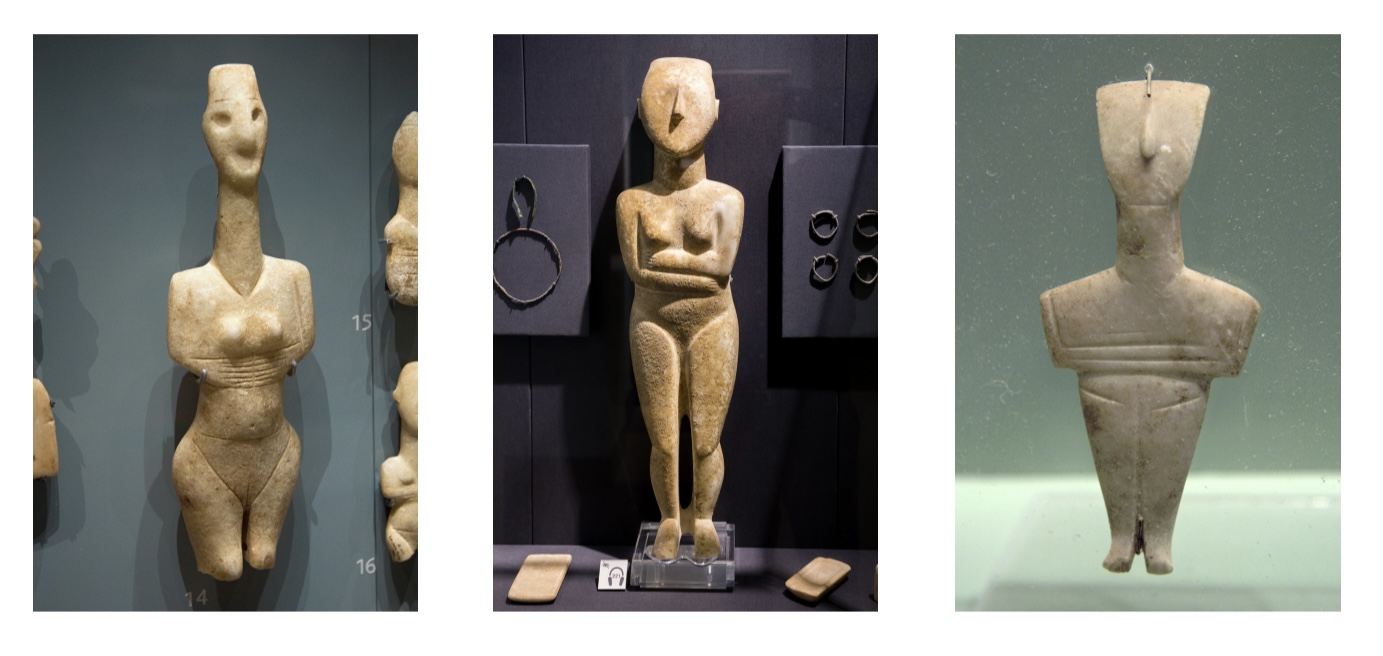

left ) Cycladic Figurine from Naxos, Plastiras Type,3200-2800BCE,
middle ) Cycladic Figurine, Spedos type, 2600-2500BCE
right ) Cycaldic Figurine from Crete, Koumasa Type, 2800-2200BCE,
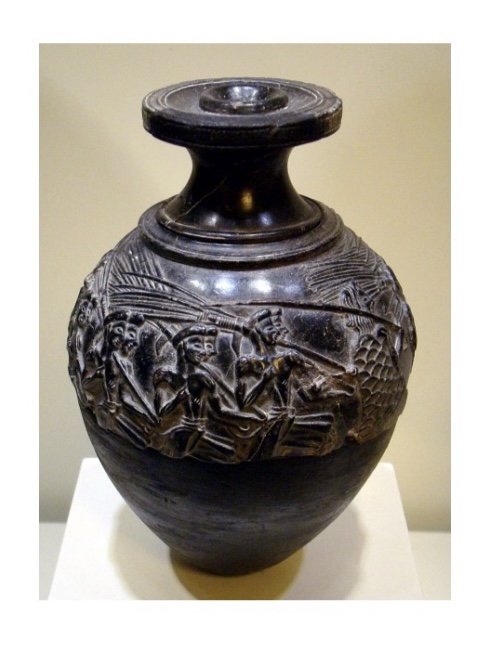

Harvester Vase,
Hagia Triada,
1500BCE,
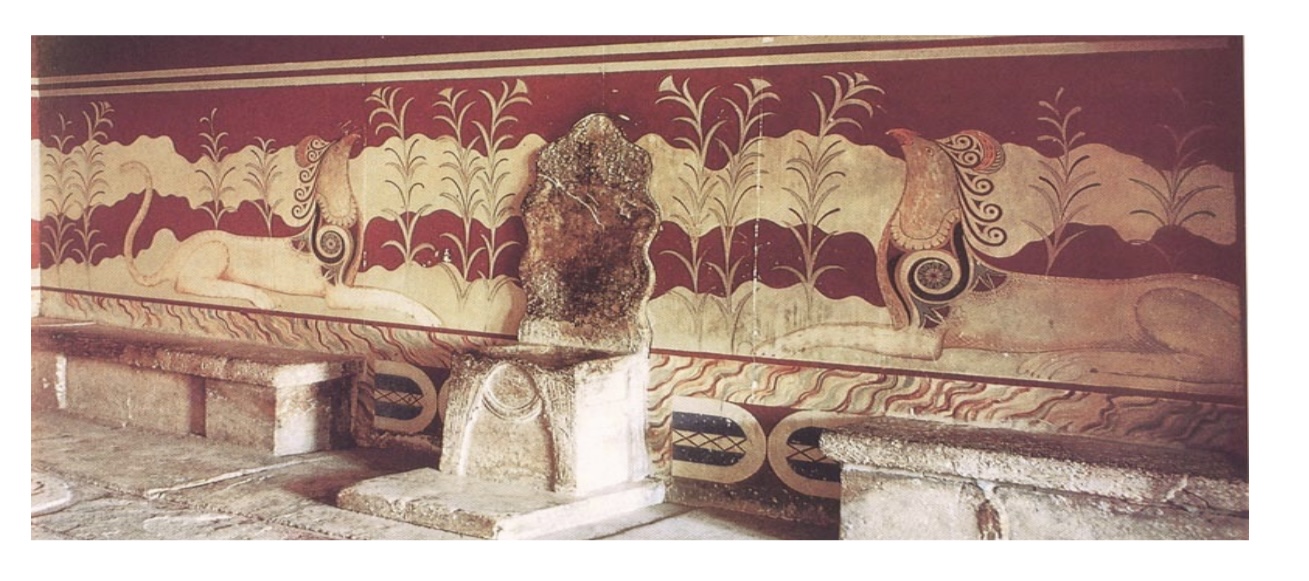

King’s Throne at Knossos - restored by Emile Gilliéron and Piet de Jong,
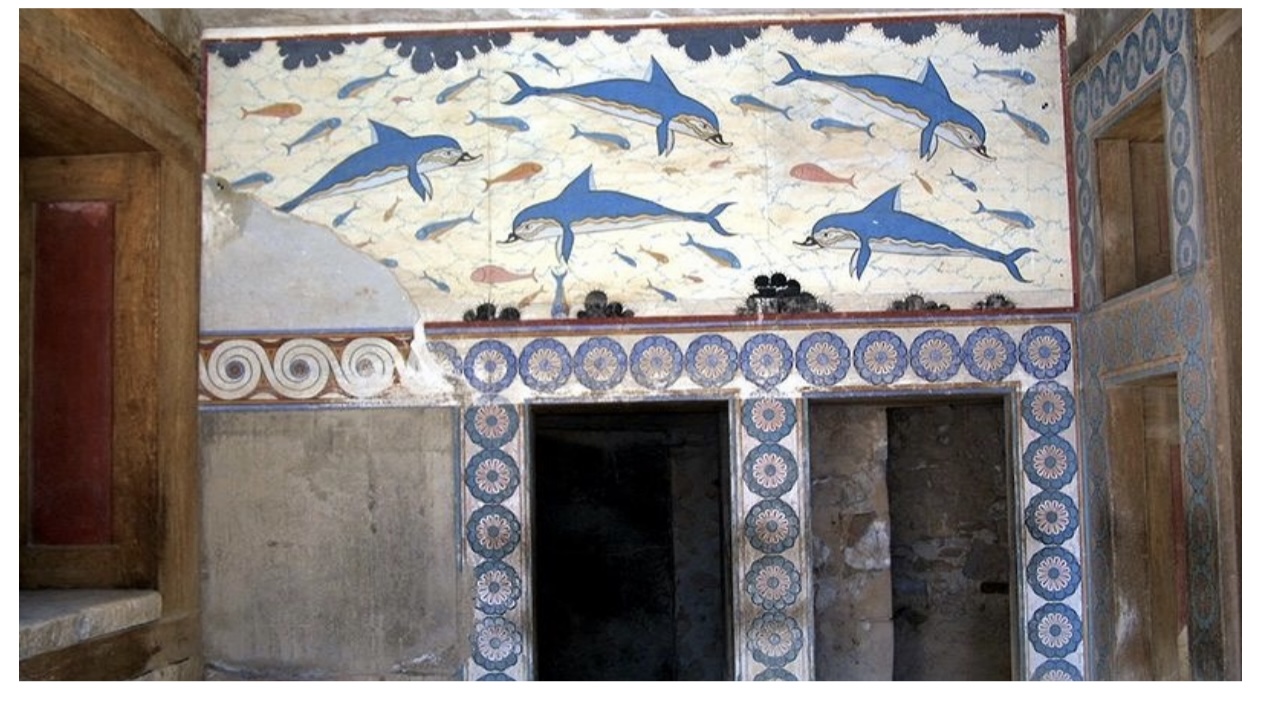

Fresco of the Dolphins, Knossos –
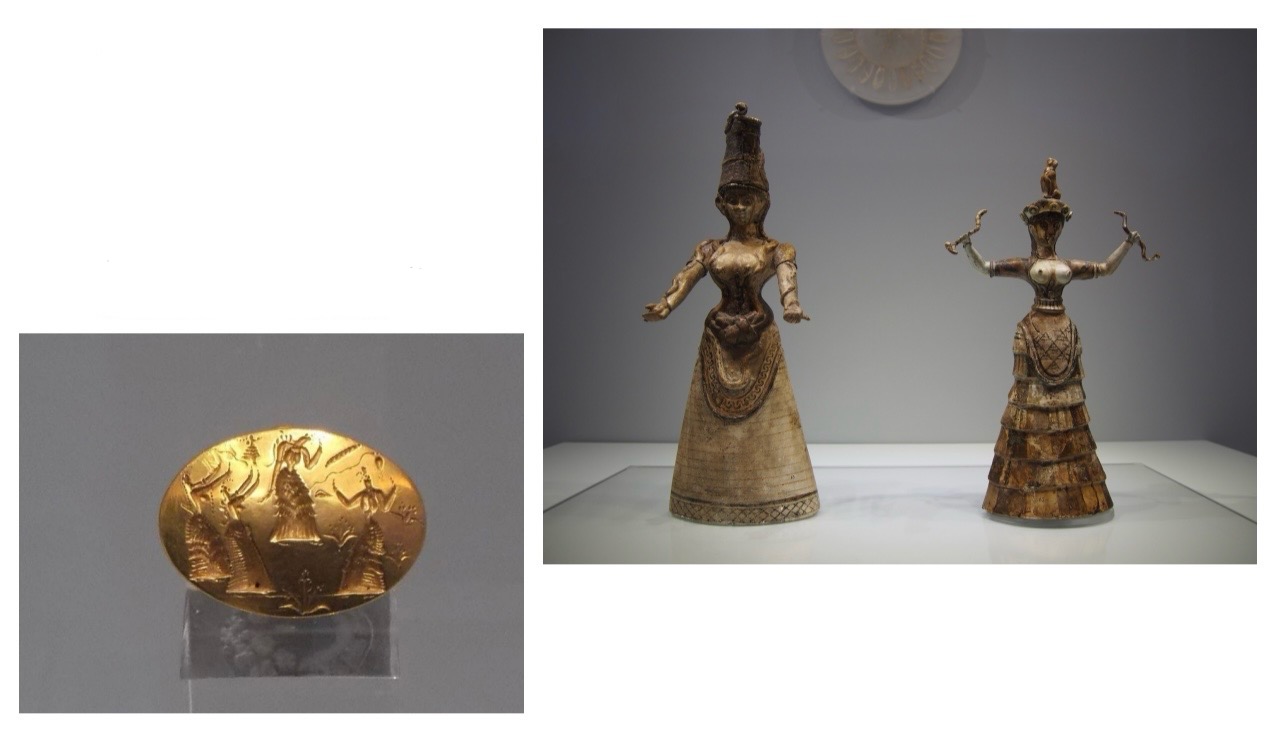

Minoan Religion
Snake Goddesses,
Crete, ca.1600BC.
Gold Signet ring from
Knossos, 1450BCE,
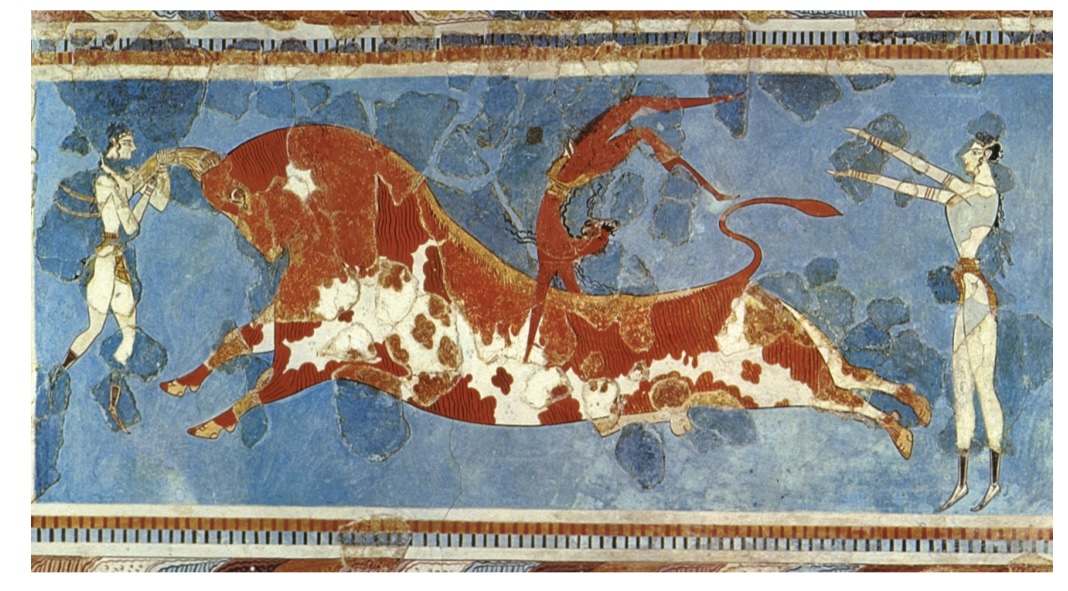

Bull-leaping Fresco, Knossos,
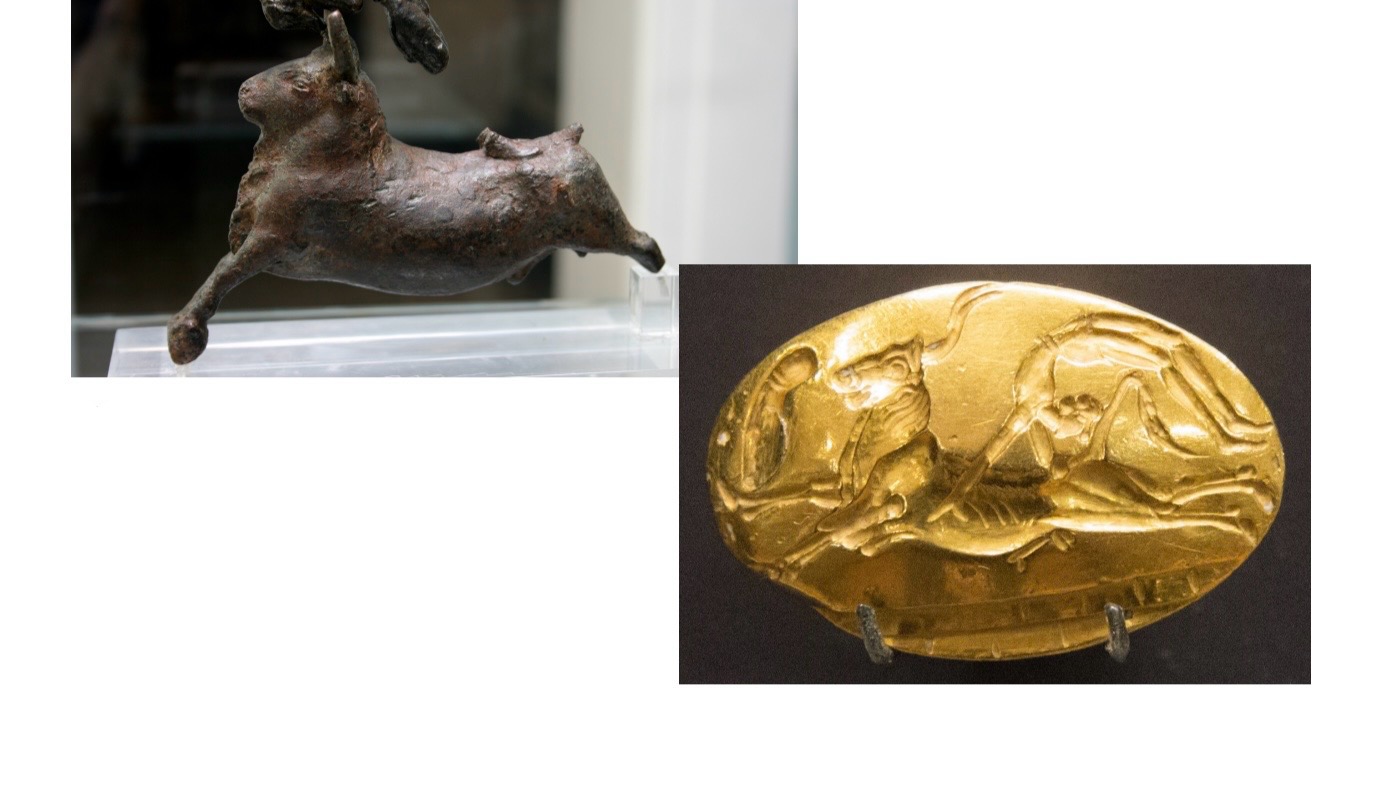

Minoan Bull Leapers
top ) Minoan Bull-Leaper1750-1400BCE Bronze, Knossos
botttom) Gold Ring with Minoan, Bull-Leaper, 1450-1375BCE, Knossos,
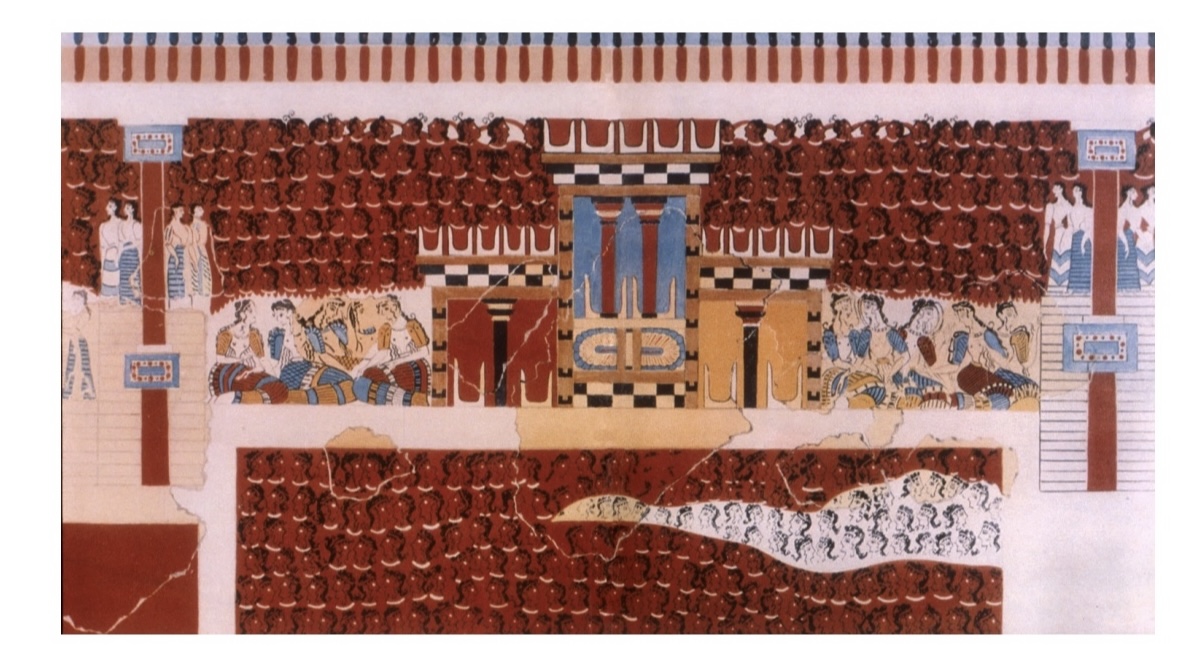

Grandstand Fresco at Knossos (ca. 1500BCE),
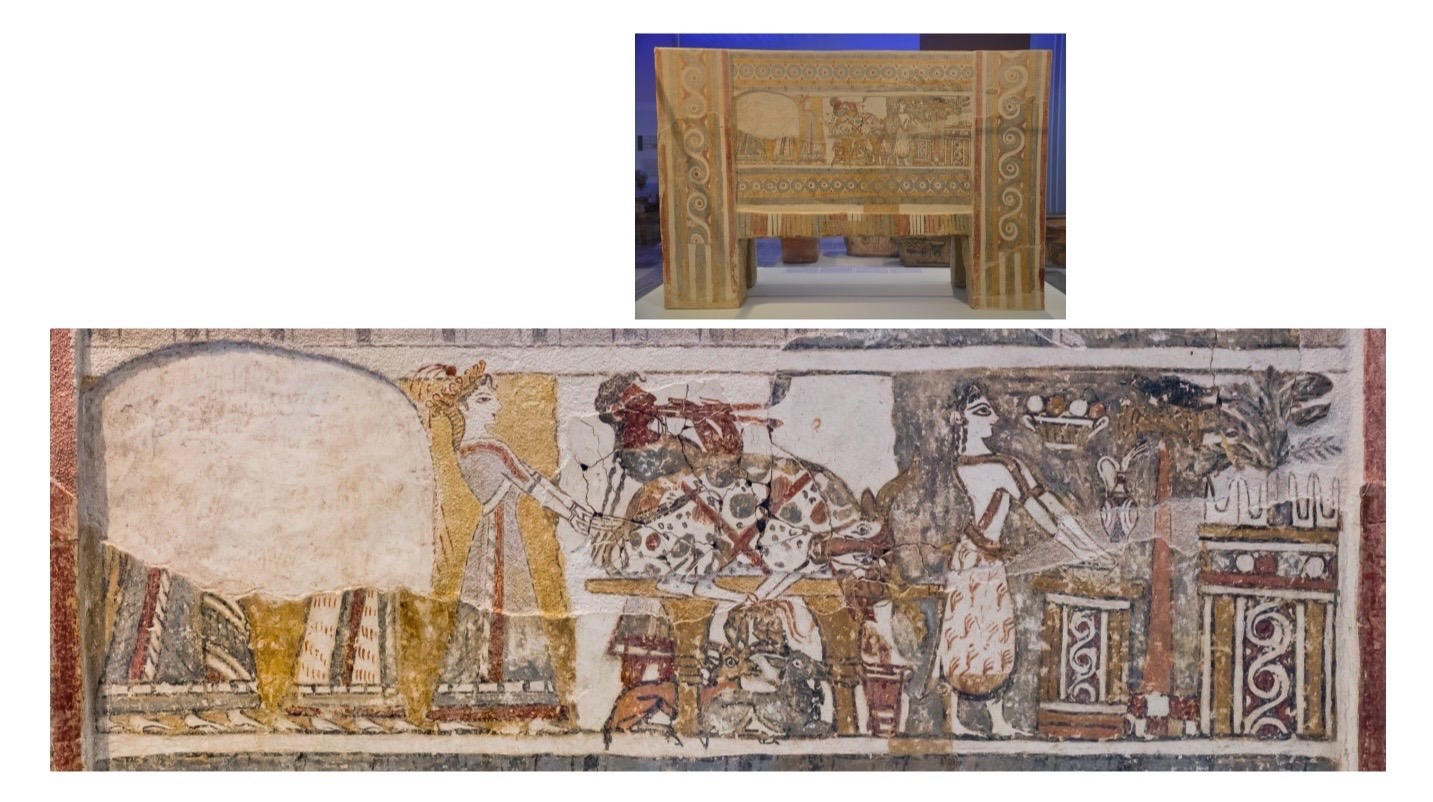

Hagia Triada
Sarcophagus
ca. 1400BCE,
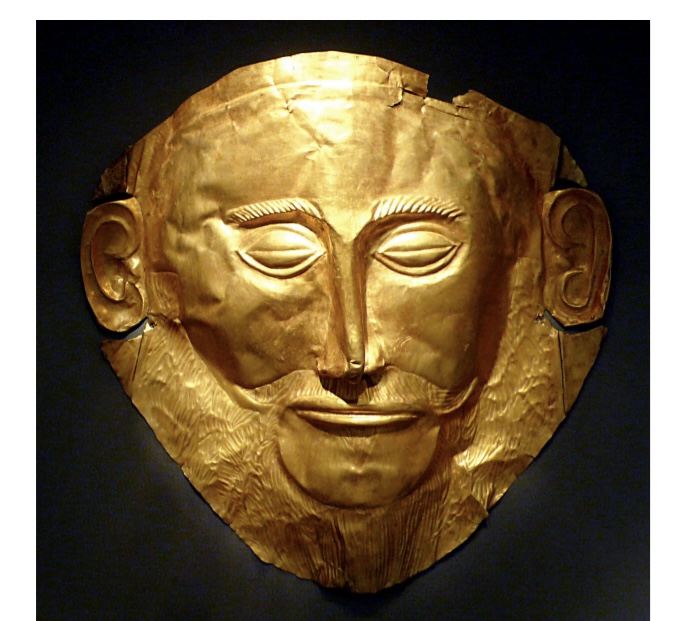

The ‘Mask of Agamemnon’, Gold, Mycenae, 1500BCE, ‘Mask of Agamemnon’ (Mycenae, 1500 BCE) —
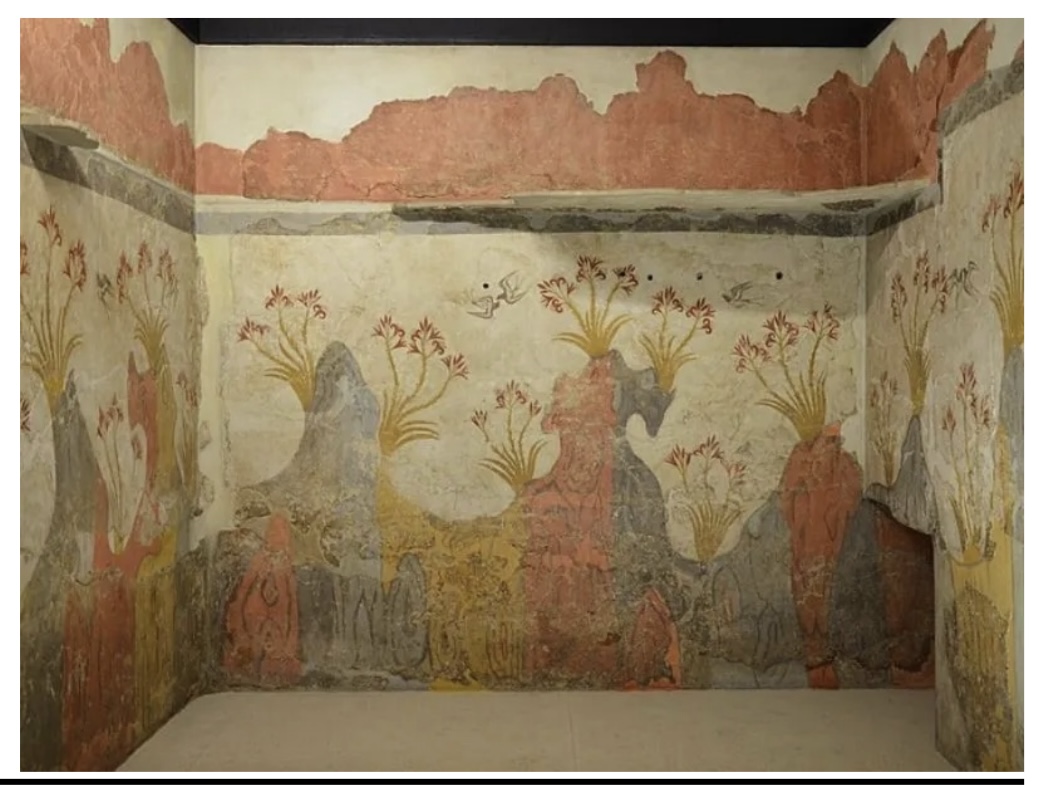

Spring
Fresco
Akrotiri,
ca. 1650BCE,
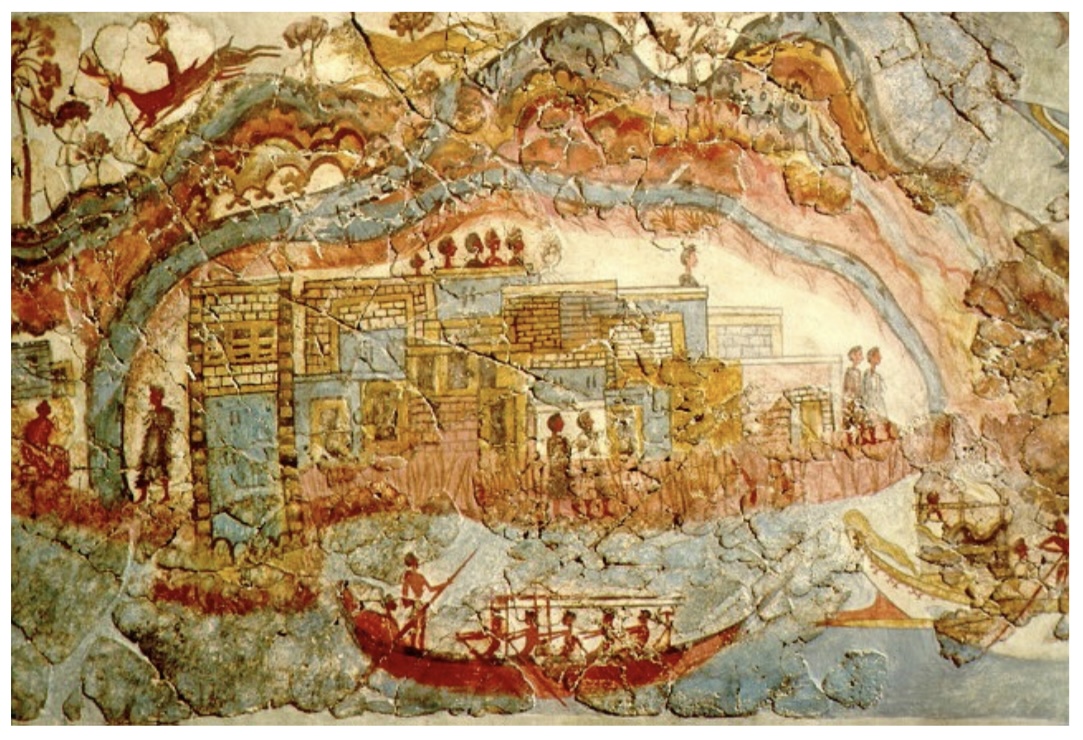

Flotilla
Fresco
detail from
Akrotiri,
ca.1650BC,

North Wall Frieze
from West House,
Akrotiri, ca.
1650BCE,
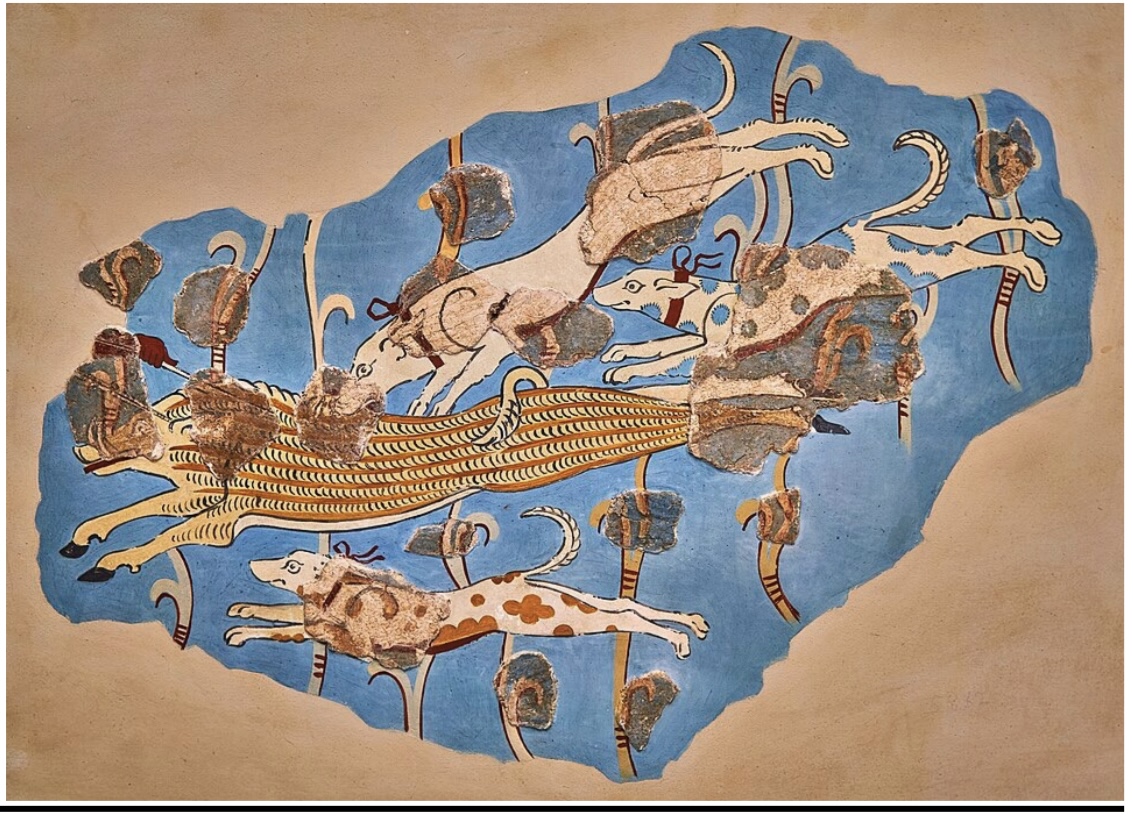

Boar Hunt
Fresco
Tiryns,
ca. 13th
century BCE,
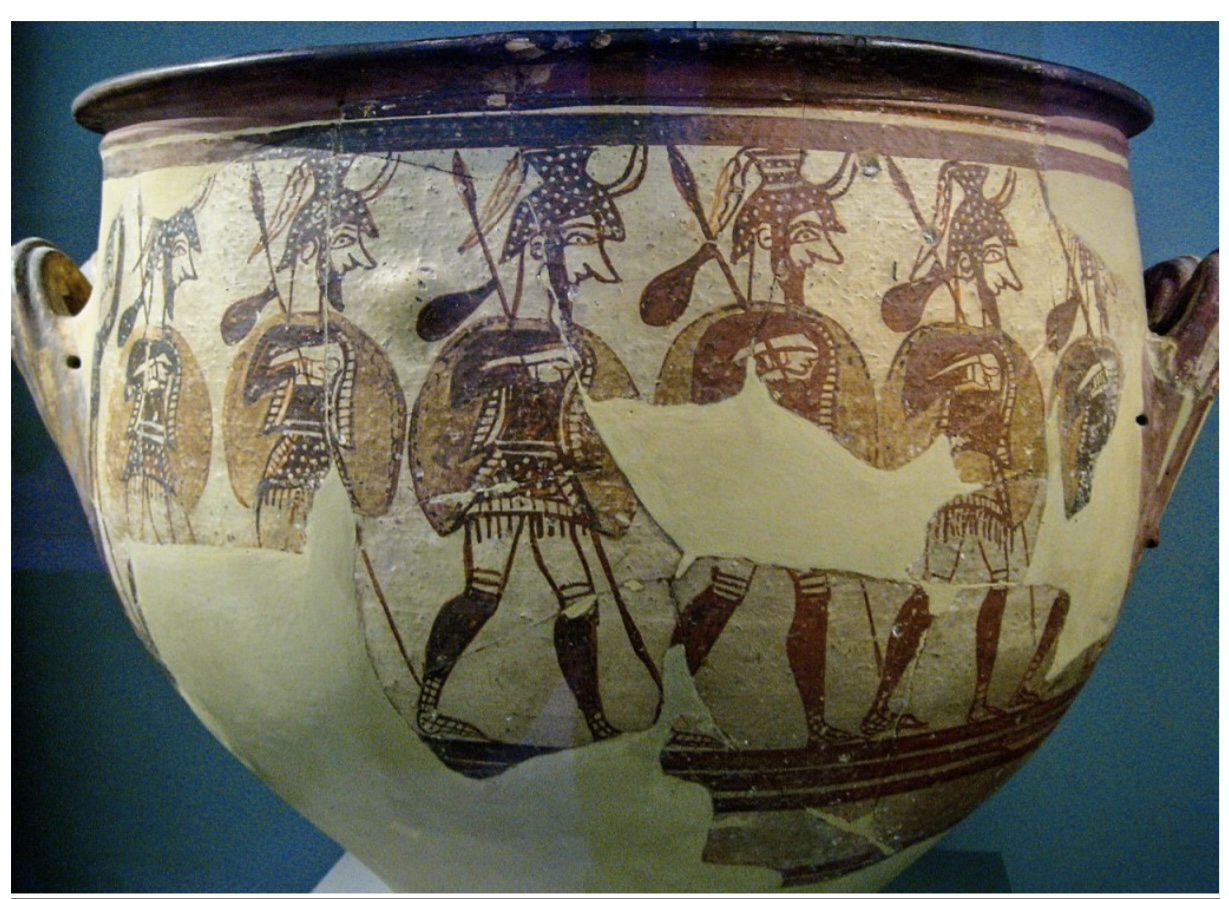

Mycenean Soldiers on the Warrior Vase ca.1200BCE,
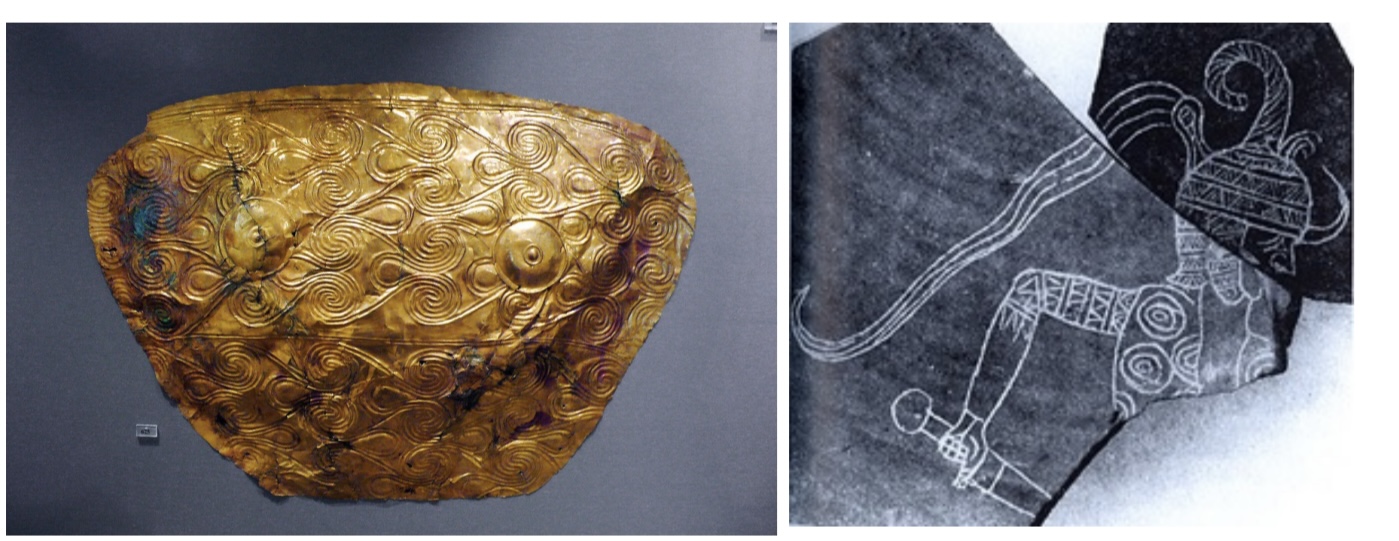
Mycenaean armor in Hittite art
left ) Mycenaean gold leaf breastplate, inimitation of bronze at Royal Shaft Grave V at Mycenae (ca.1500BC)
right ) Similar breast protection on this Mycenaean warrior inscribed on a Hittite clay vessel from ca. 1350BC found in Bogazkoy,
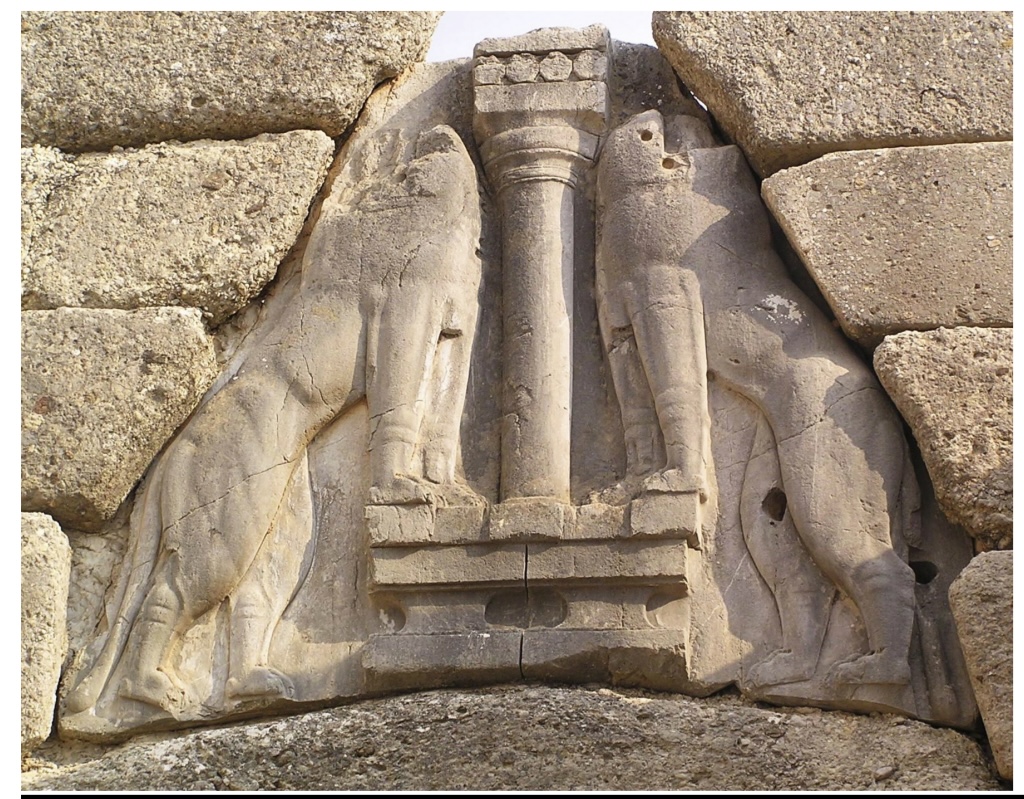

Lion Gate
Mycenae,
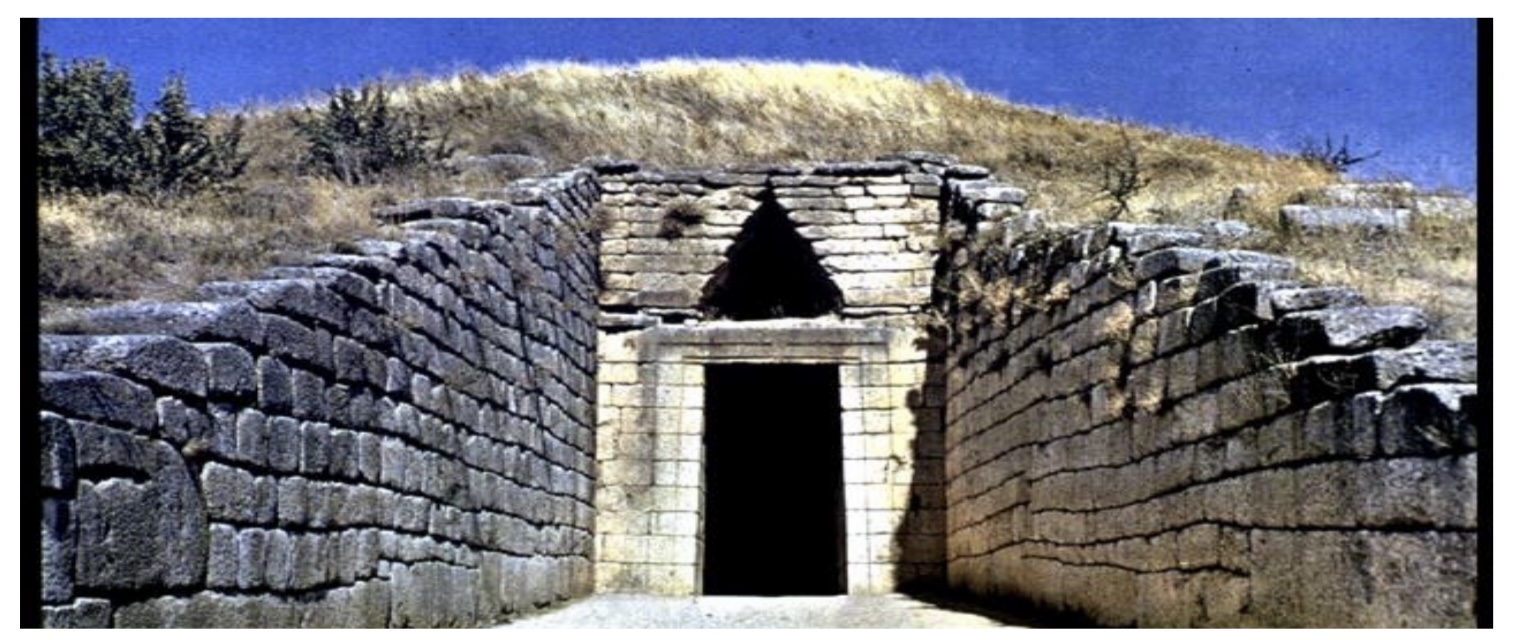

‘Treasury of Atreus’ Tholos Tomb (1300-1250BCE) at Mycenae,
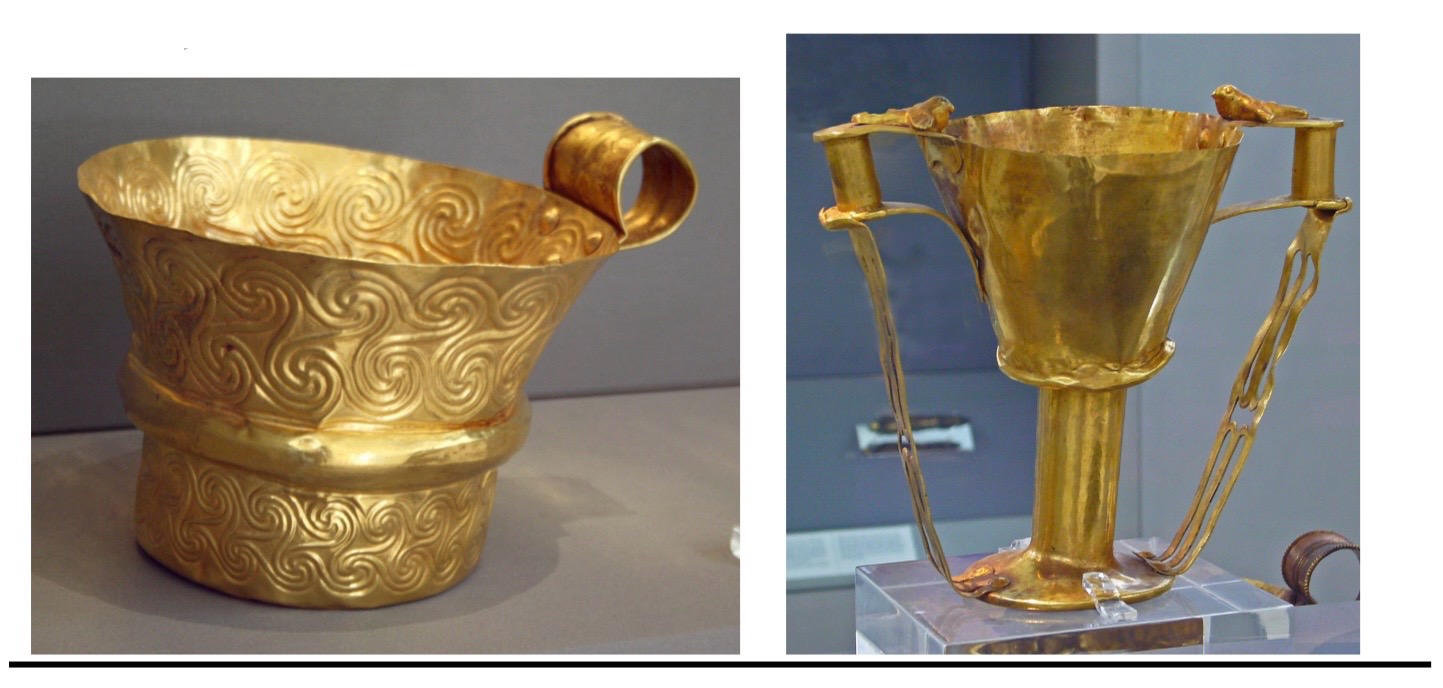

Mycenaean Wealth
Cups from Mycenae.
Ca., 1500BCE,

Mycenaean Wealth
Lion Hunt dagger from shaft grave IV,
Mycenae
1550-1500BCE,
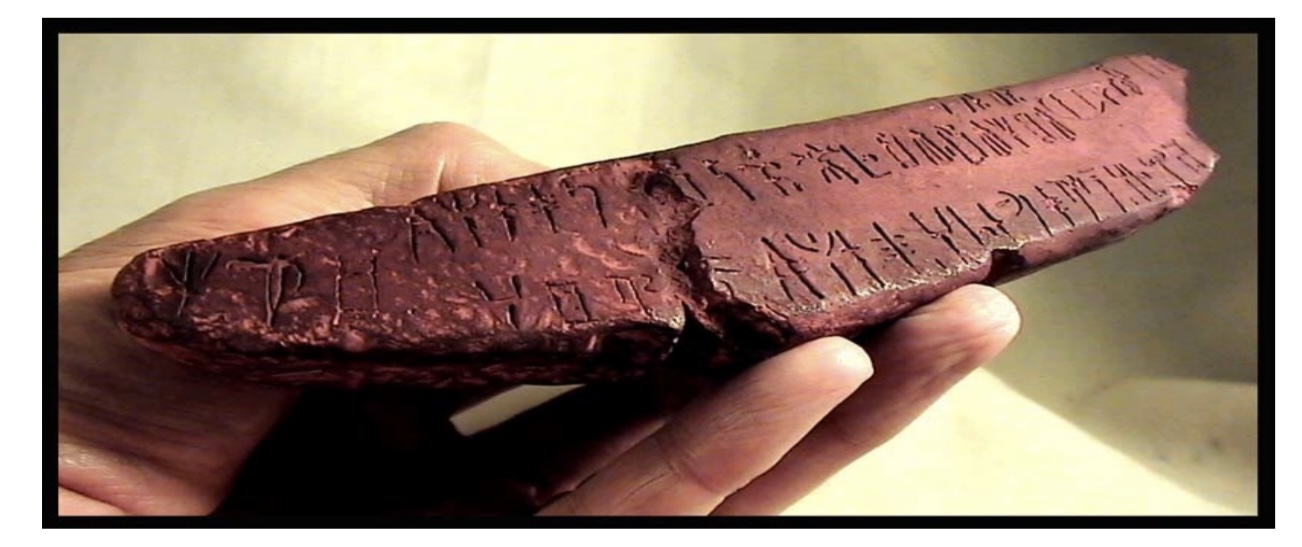

Mycenaean Writing
Linear B – Deciphered by Michael Ventris in 1952 (building on work
of Alice Kober),
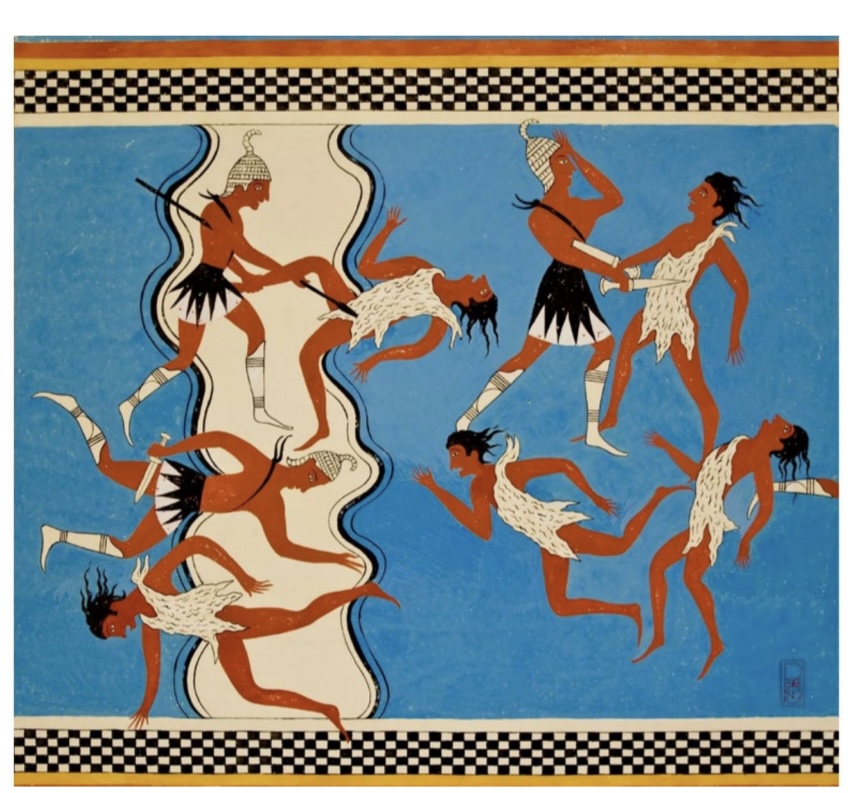

Warrior
Fresco
Pylos
ca. 1250BCE
Reconstruction
by Piet de Jong,
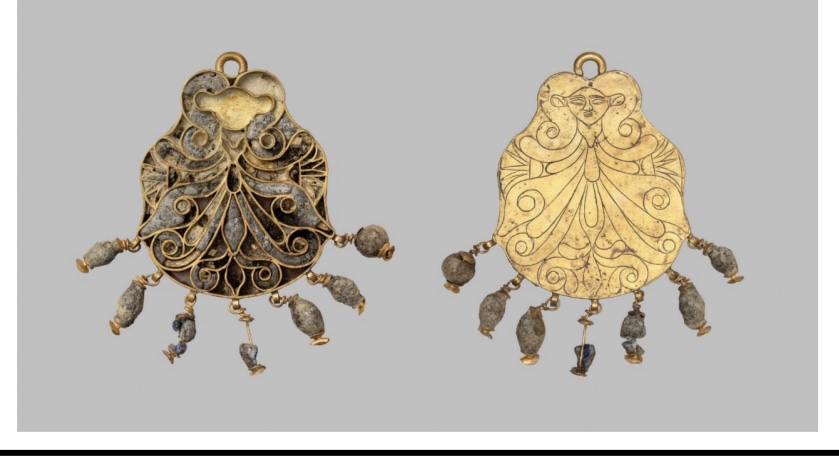

Pendants made of gold, lapis lazuli and glass
depict Egyptian goddess Hathor.
Palace of Nestor at Pylos, ca. 1400BCEm\,
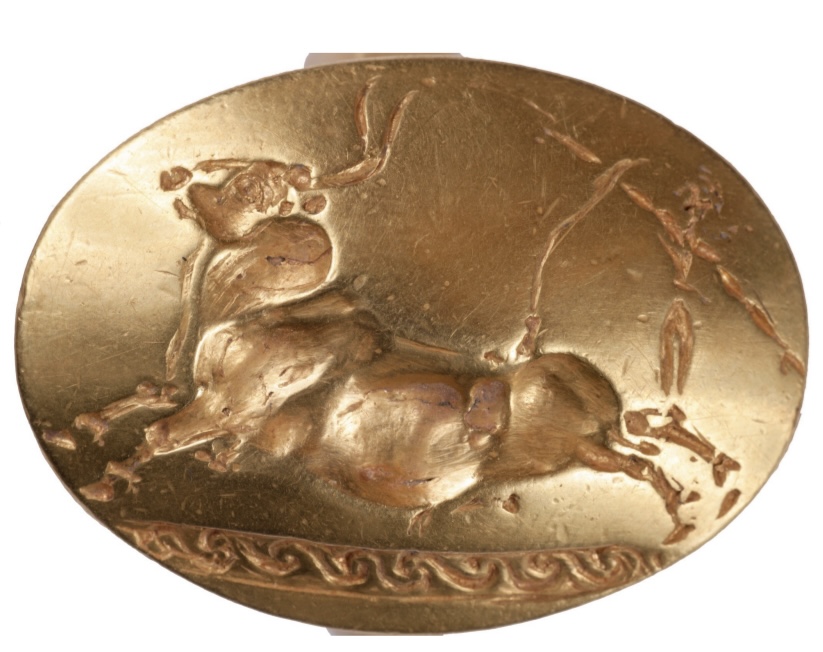

Tomb of the
Griffin Warrior
Gold ring
depicting bull-
leaping.
Ca., 1450BCE,
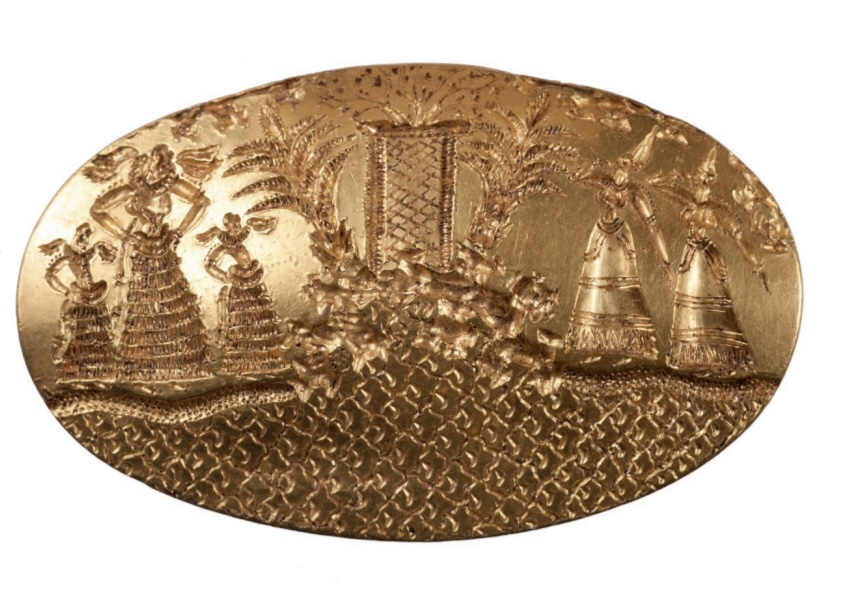

Tomb of the
Griffin
Warrior
Gold ring
depicting
women before
a shrine
ca. 1450BCE,
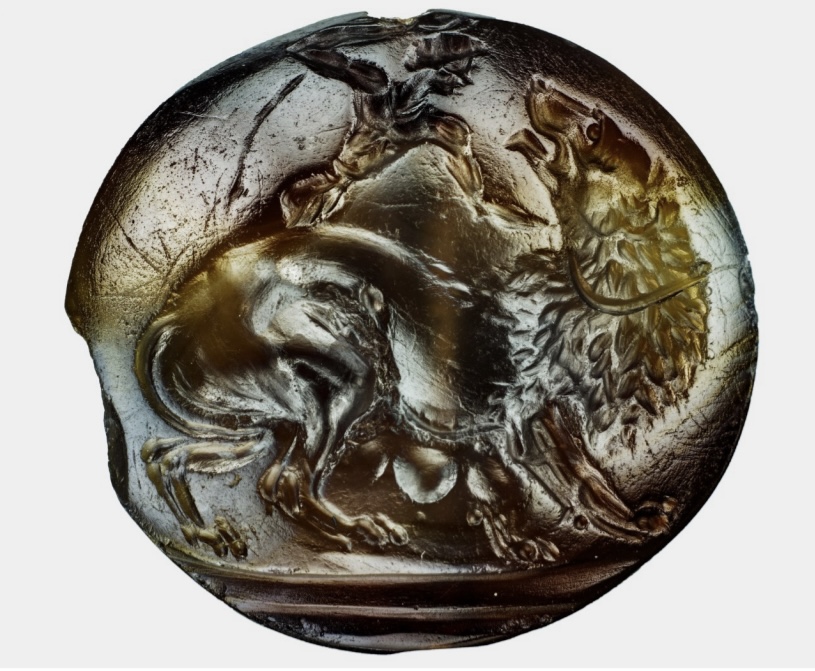

Tomb of the
Griffin Warrior
Agate stone from Pylos depicting a man looming over a lion.
Pylos.
Ca. 1630- 1440BCE,

Protogeometric Amphora from the Ceramicus cemetery in Athens, Ca. 975-950BCE,
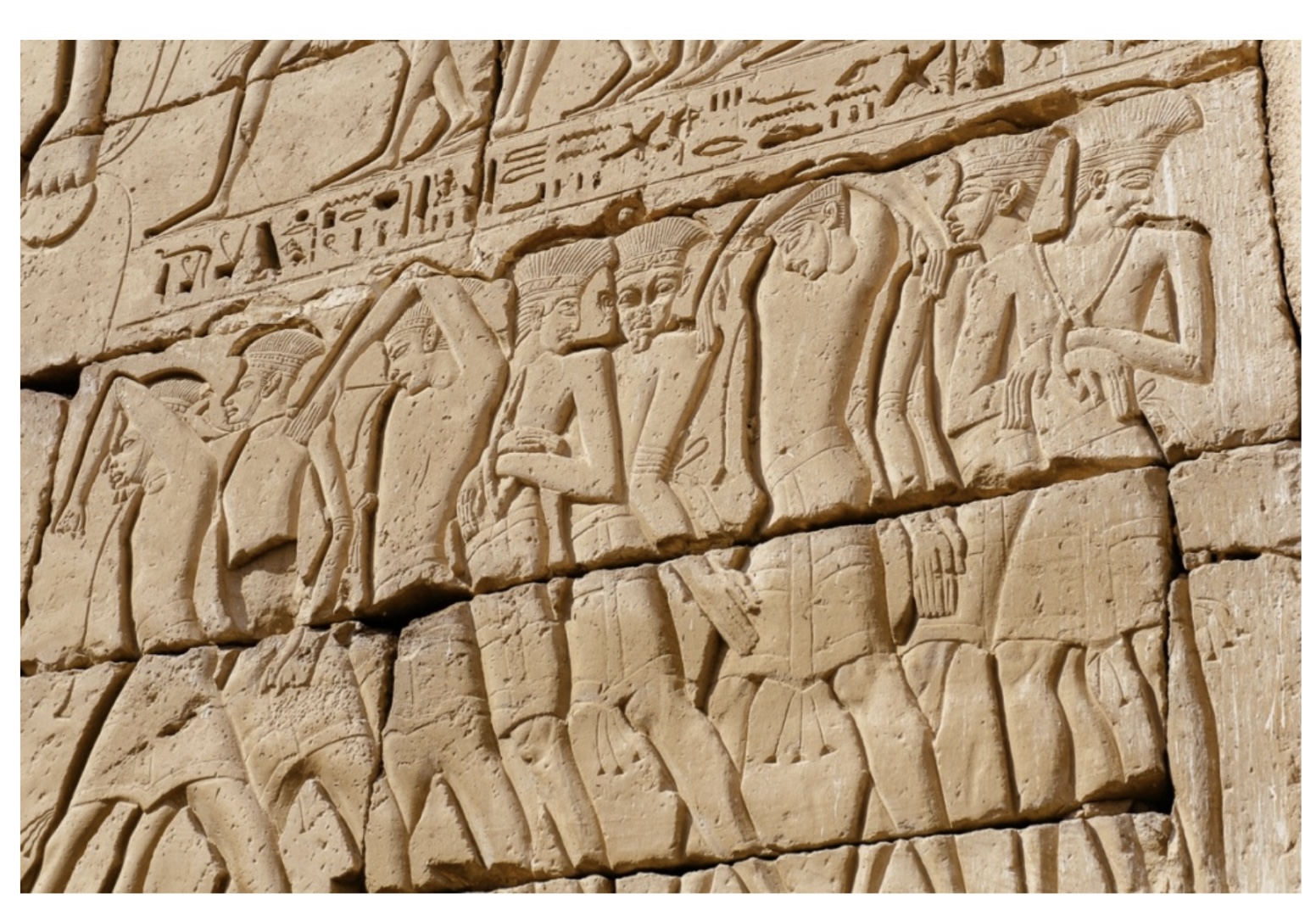

The Sea
Peoples
Peleset Prisoners – Stone relief at
Ramses III’s
temple at
Medinet Habu
(Egypt),
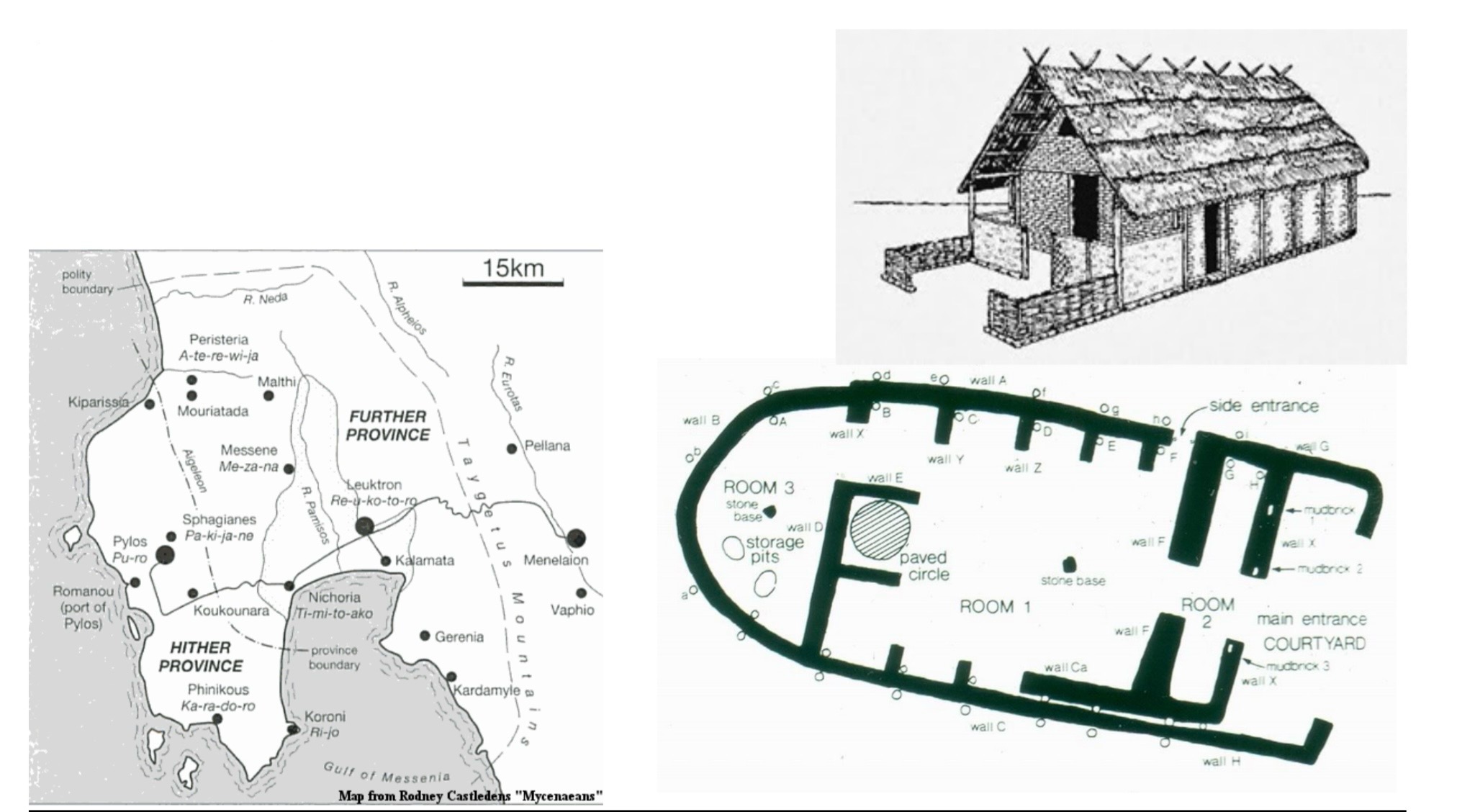
Early Iron Age sites
in Greece
a) Nichoria Chieftain’s House
ca. 1050BCE,
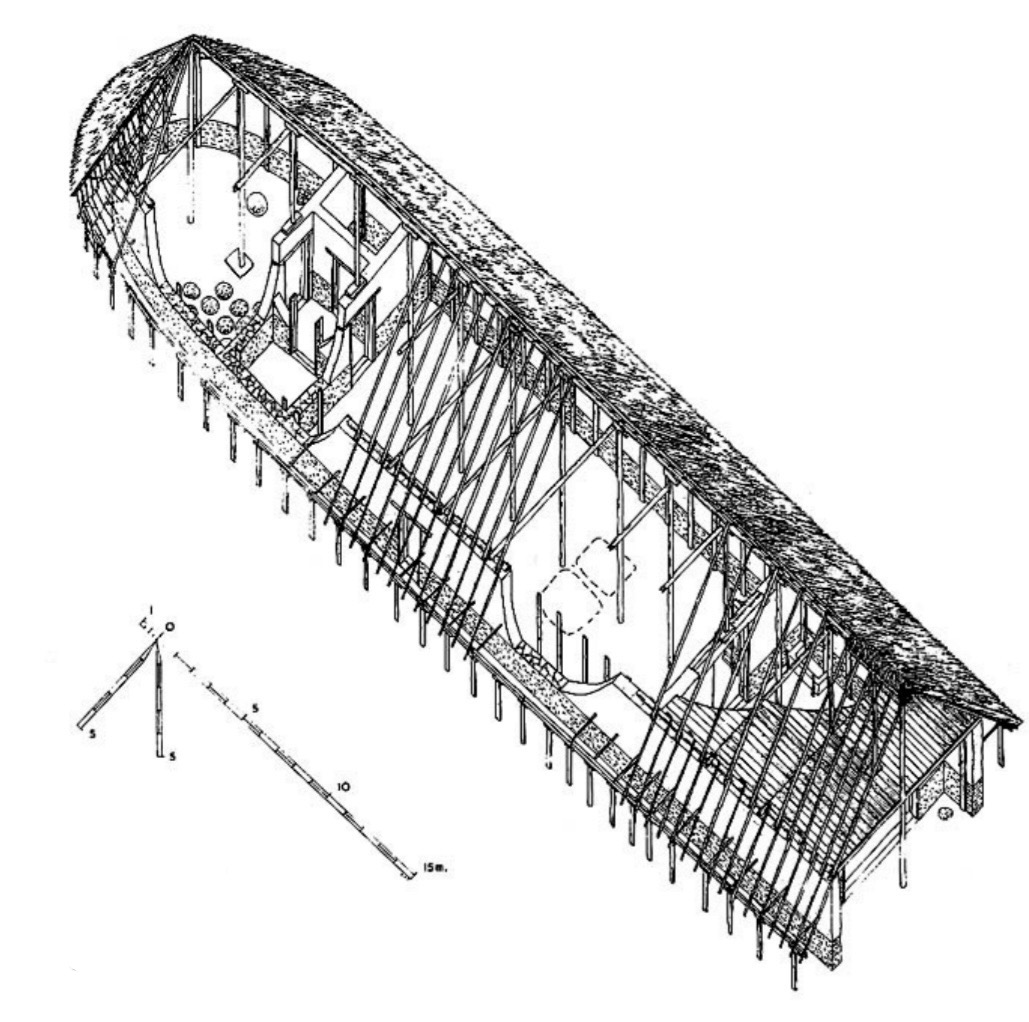
Iron Age sites in
Greece
b) Lefkandi
Heroön ca., 975BCE,
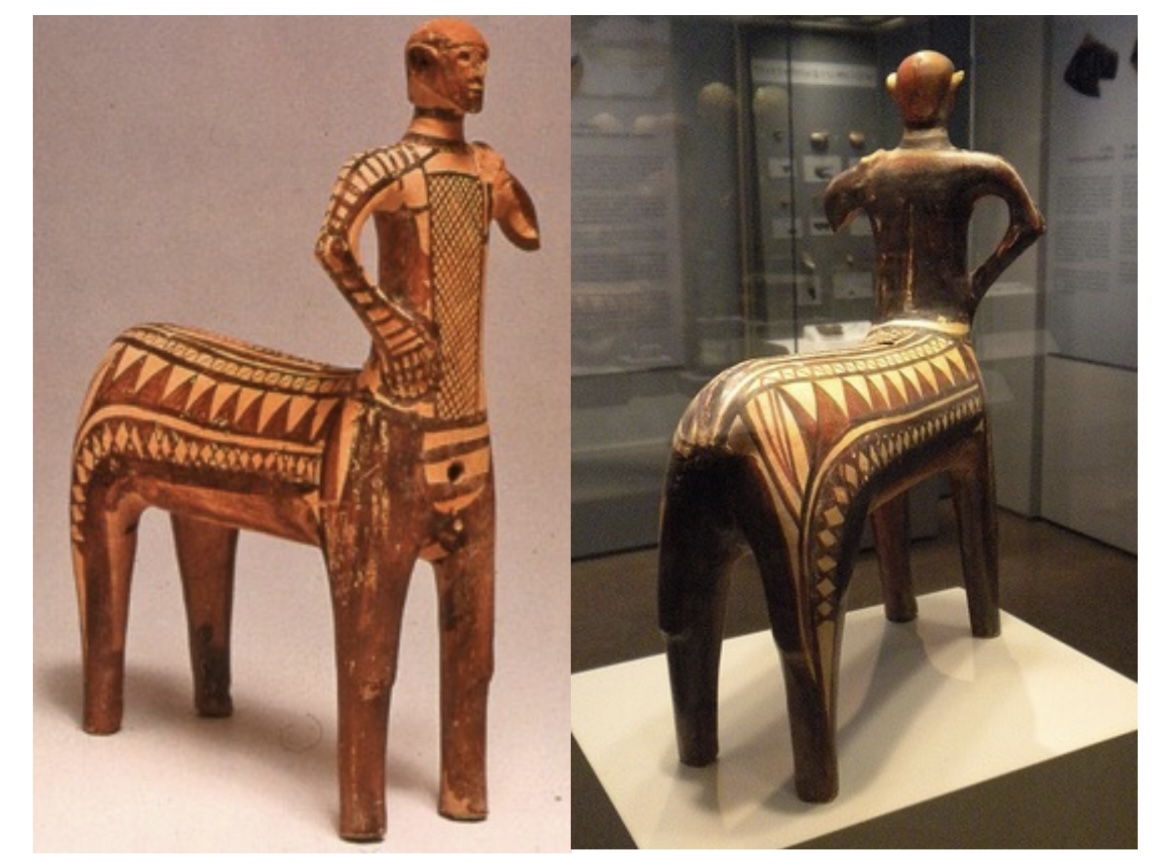

Lefkandi Centaur
(Cheiron?)
Found in grave site at
Lefkandi
– ca.900 BCE,

Nestor’s Cup - Found at Pithekoussai in Italy ca. 720 BCE
“I am the cup of Nestor good for drinking.
Whoever drinks from this cup, desire for beautifully
crowned Aphrodite will seize him instantly.”,
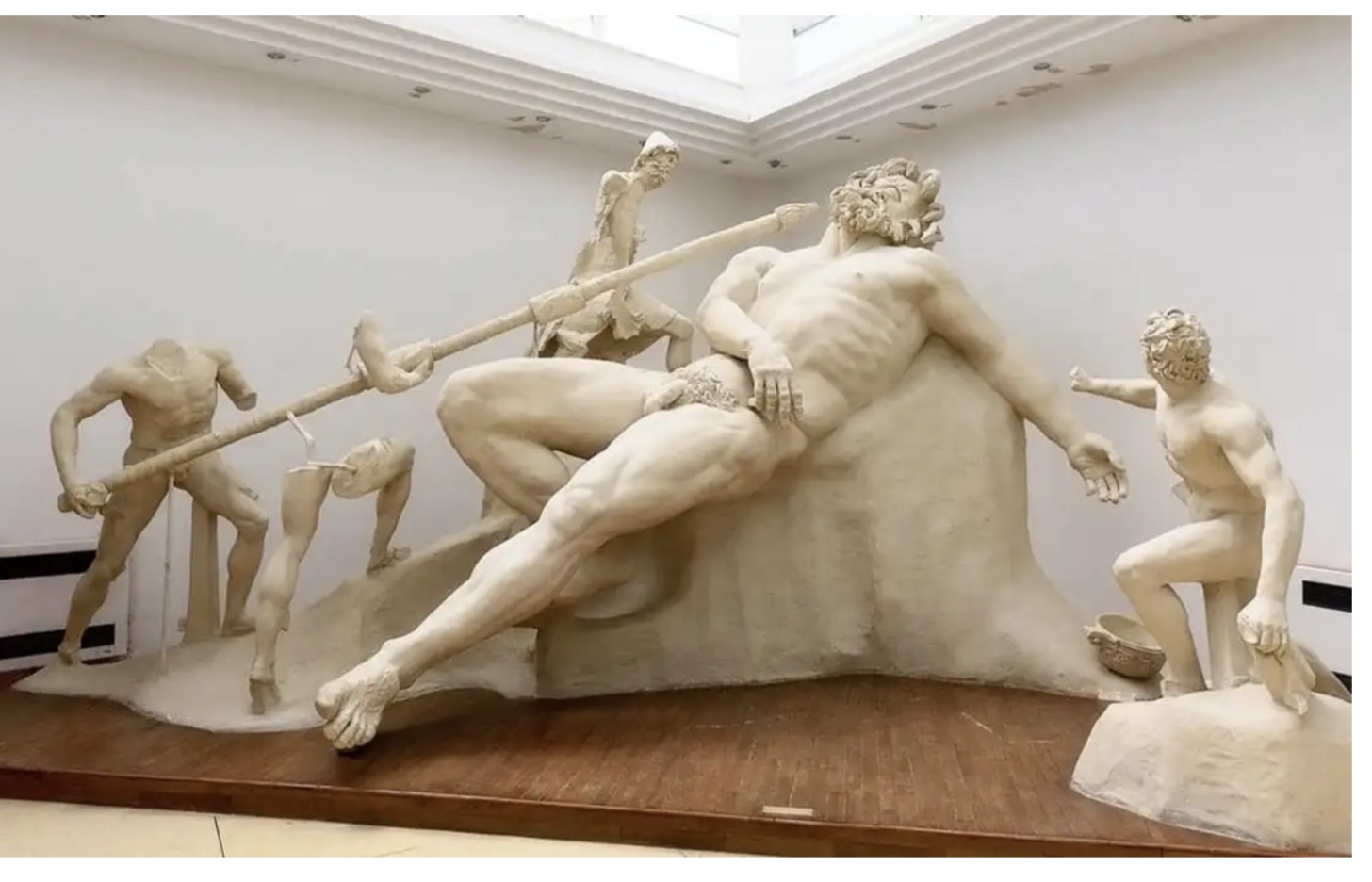

The Blinding
of the Cyclops
Sperlonga
Museum of
Archaeology.
Italy,

Tablet with instructions for the deceased in the Underworld. 350-300BCE,
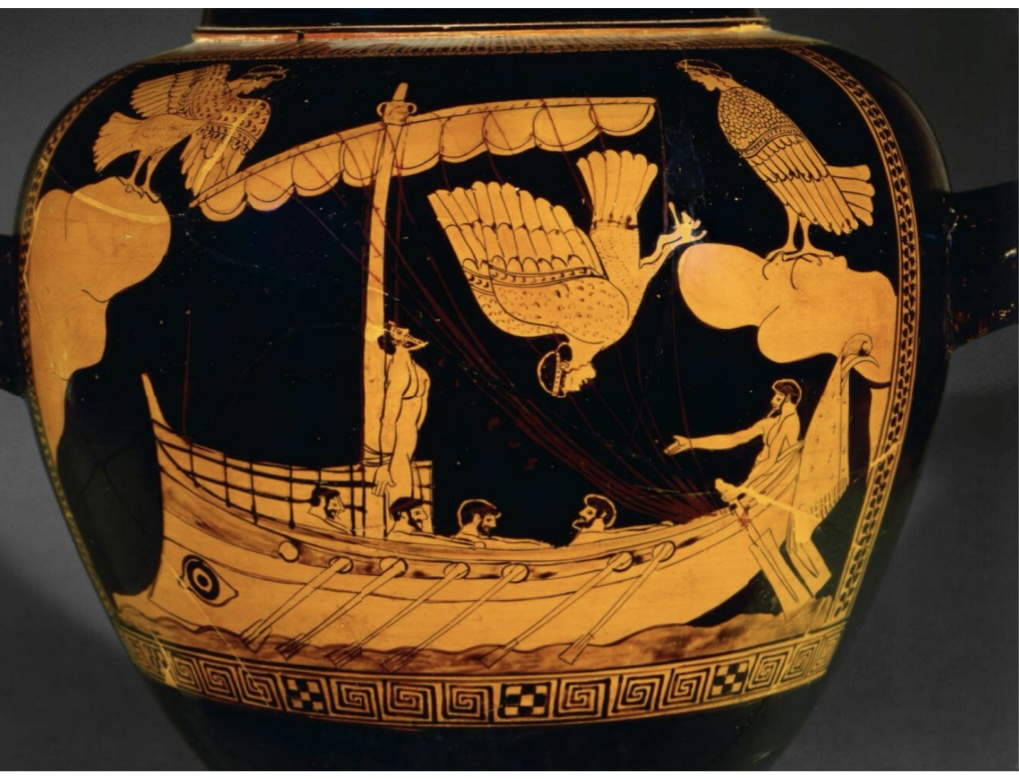

• Siren Vase:
Detail of Red-
Figure Stamnos.
480BCE.
• British Museum,
London.,

Athena born from the head of Zeus, with Eileithyia
(goddess of childbirth).Black-figured amphora.
550BCE. Louvre Museum, Paris,

Early 6th century BCE Black
Figure Kylix showing Eris
(=Strife),
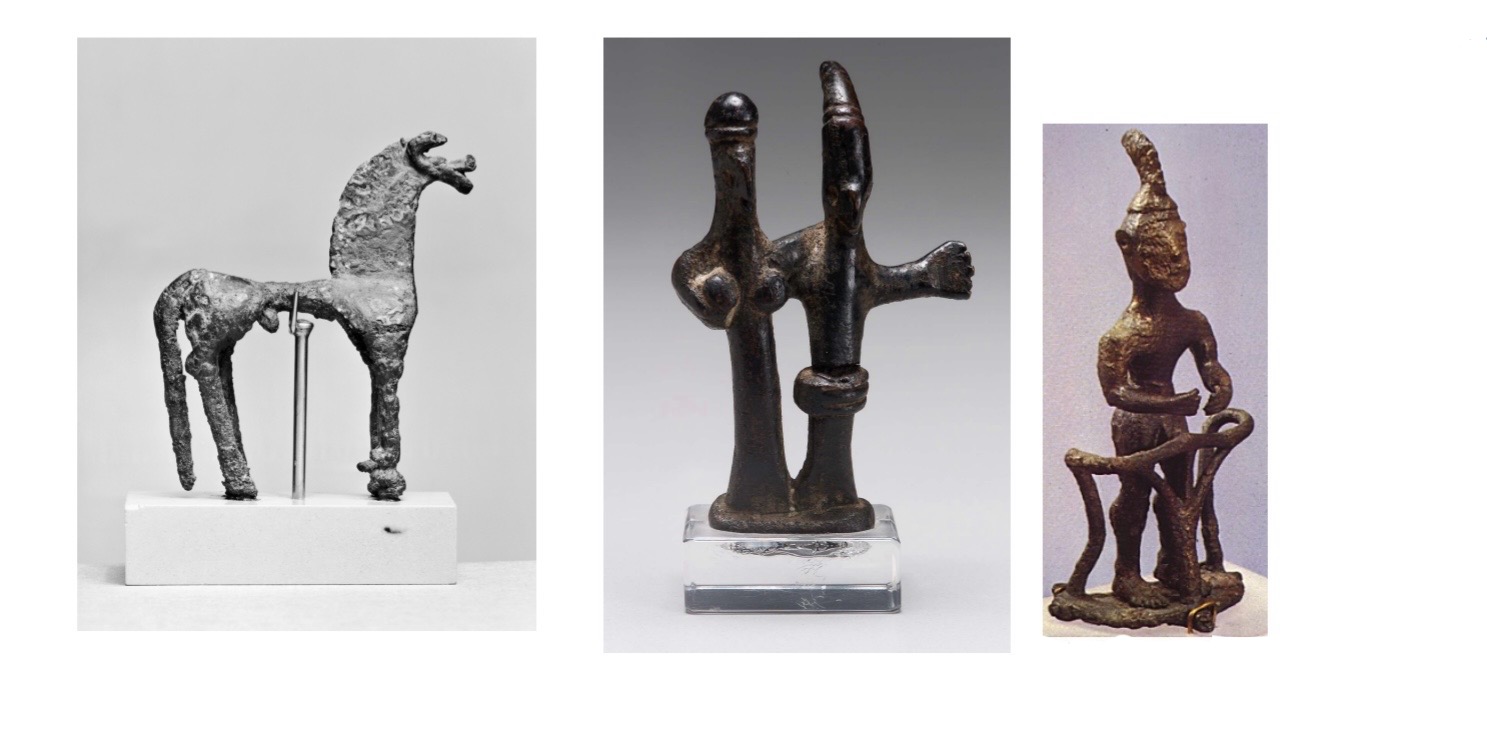

1. The Development of Pan-Hellenic Games
i) Early Olympia – Western Peloponnesian Rural Cult
Animal Figurines Dedicated at Olympia
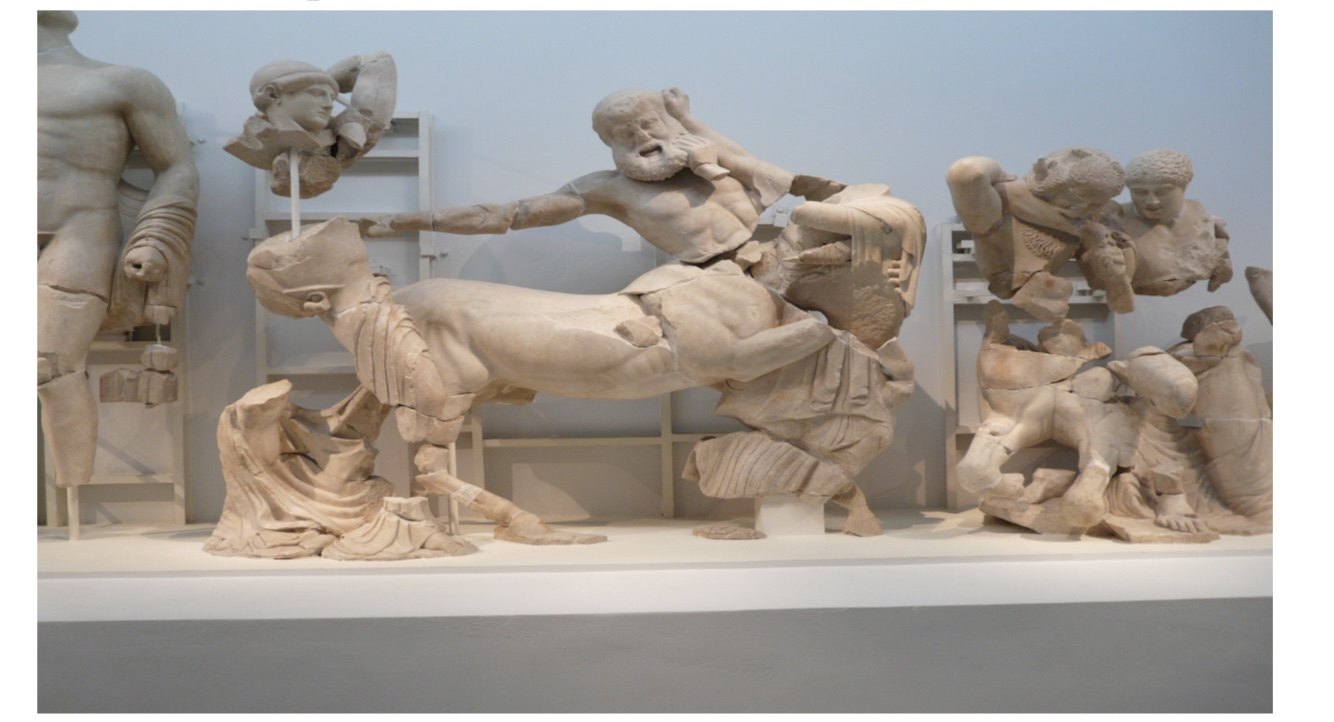

2. The Iconography of the Festival of Zeus
West Pediment - Lapiths and Centaurs,
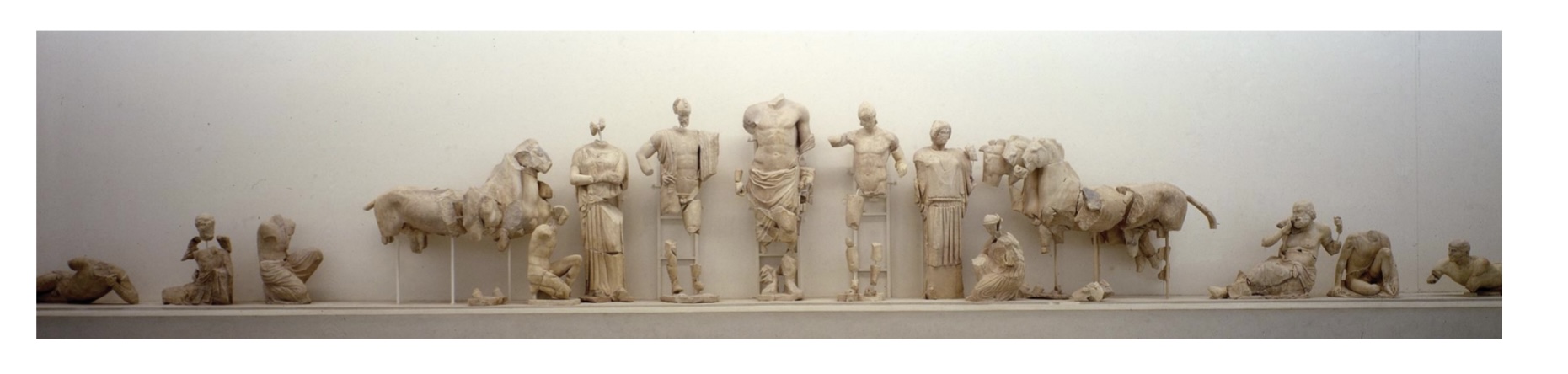

2. The Iconography of the Festival of Zeus
East Pediment - Zeus, Pelops and Oinomaos,
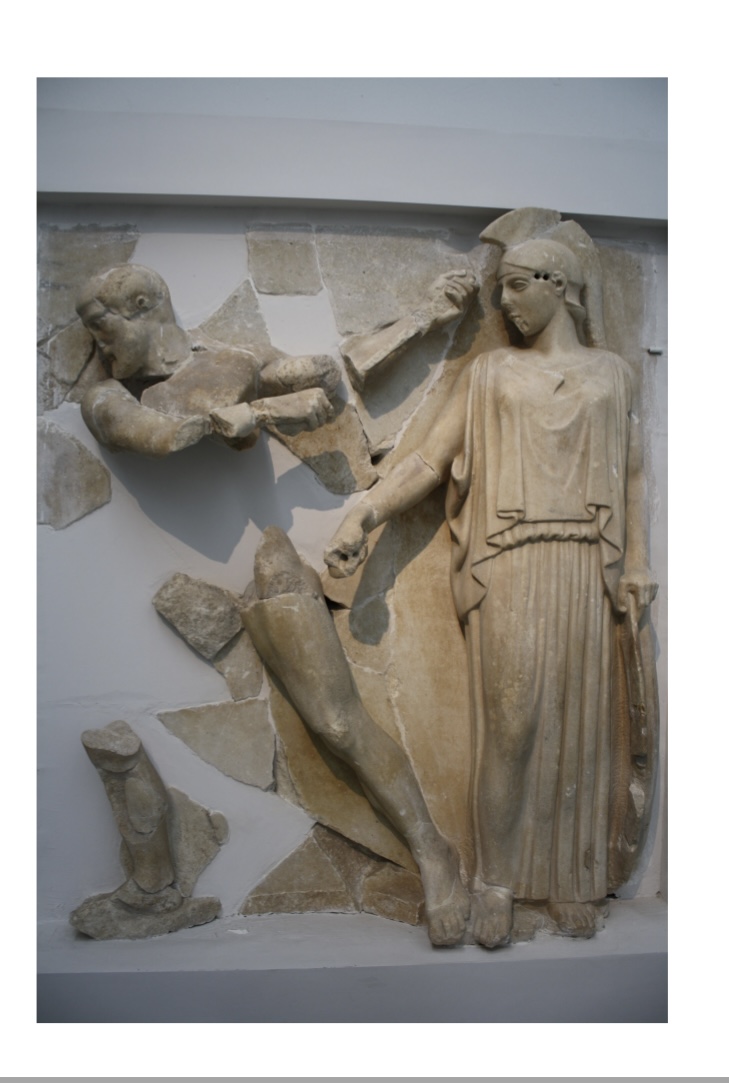

2. The Iconography of the
Festival of Zeus
Metopes – Heracles Cleaning the
Stables of Augeas (King of Elis),
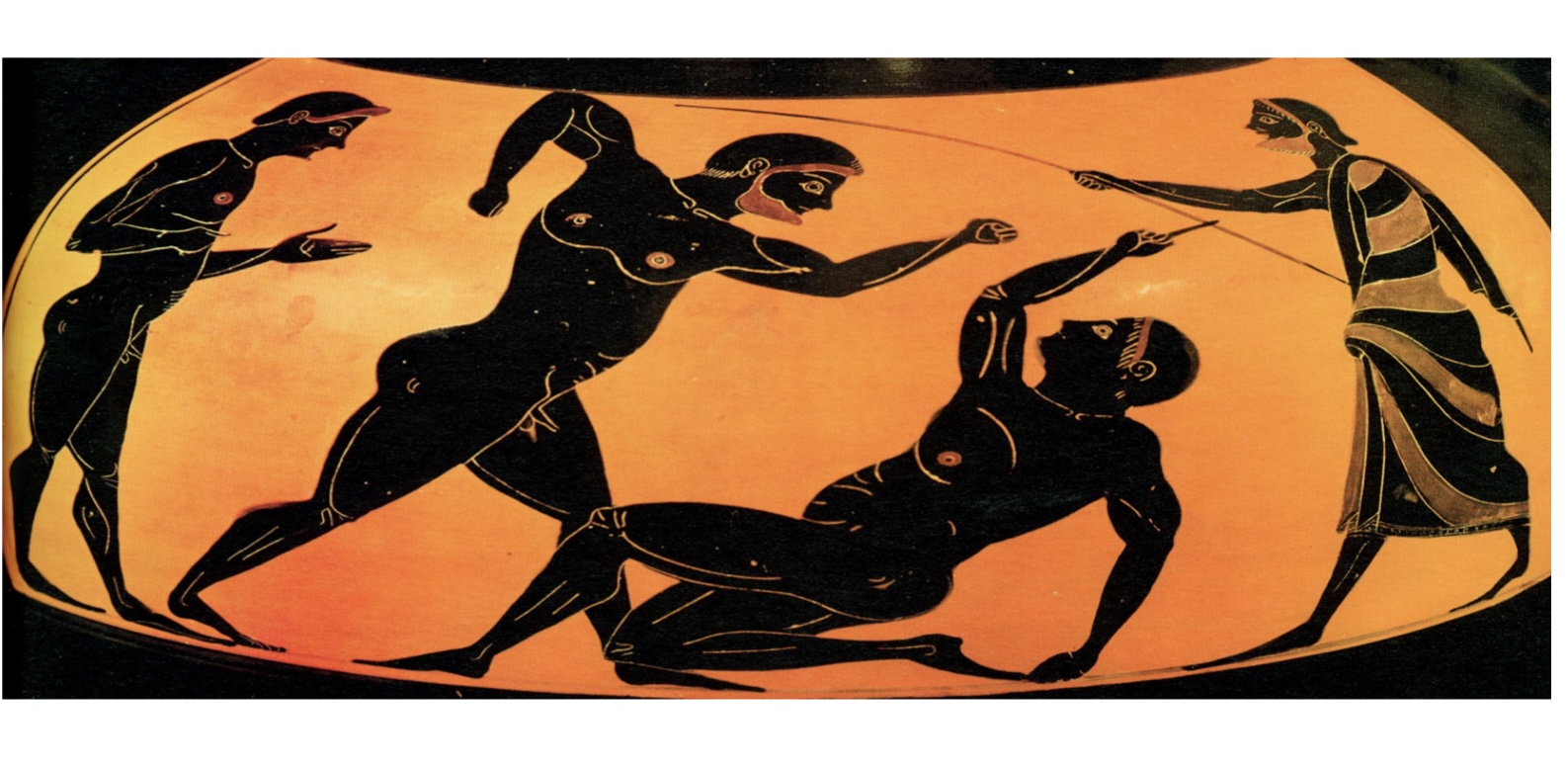

Isonomia – The Democratic Discourse of Equality
i) Rules and Objectivity,
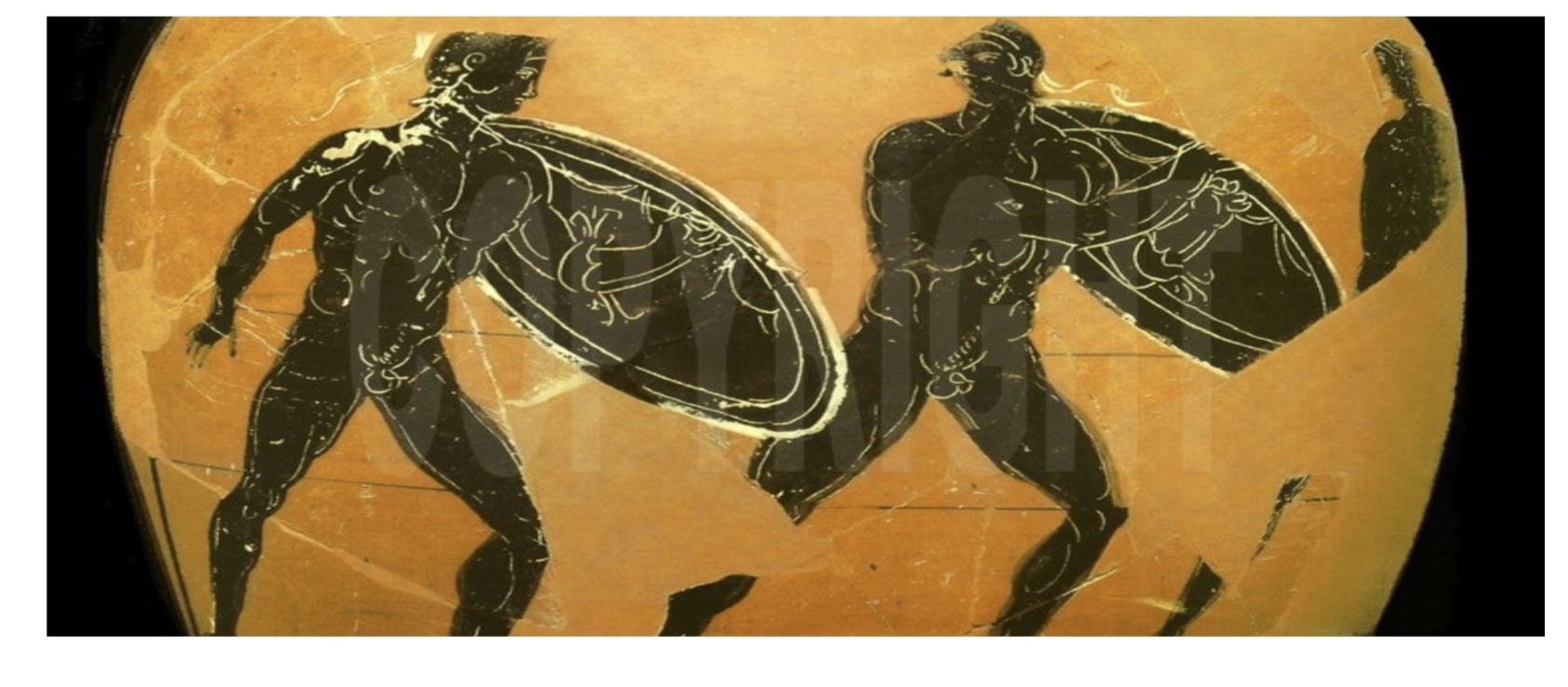

5. Isonomia – The Democratic Discourse of Equality
iii) The hysplex and the hoplitodromos
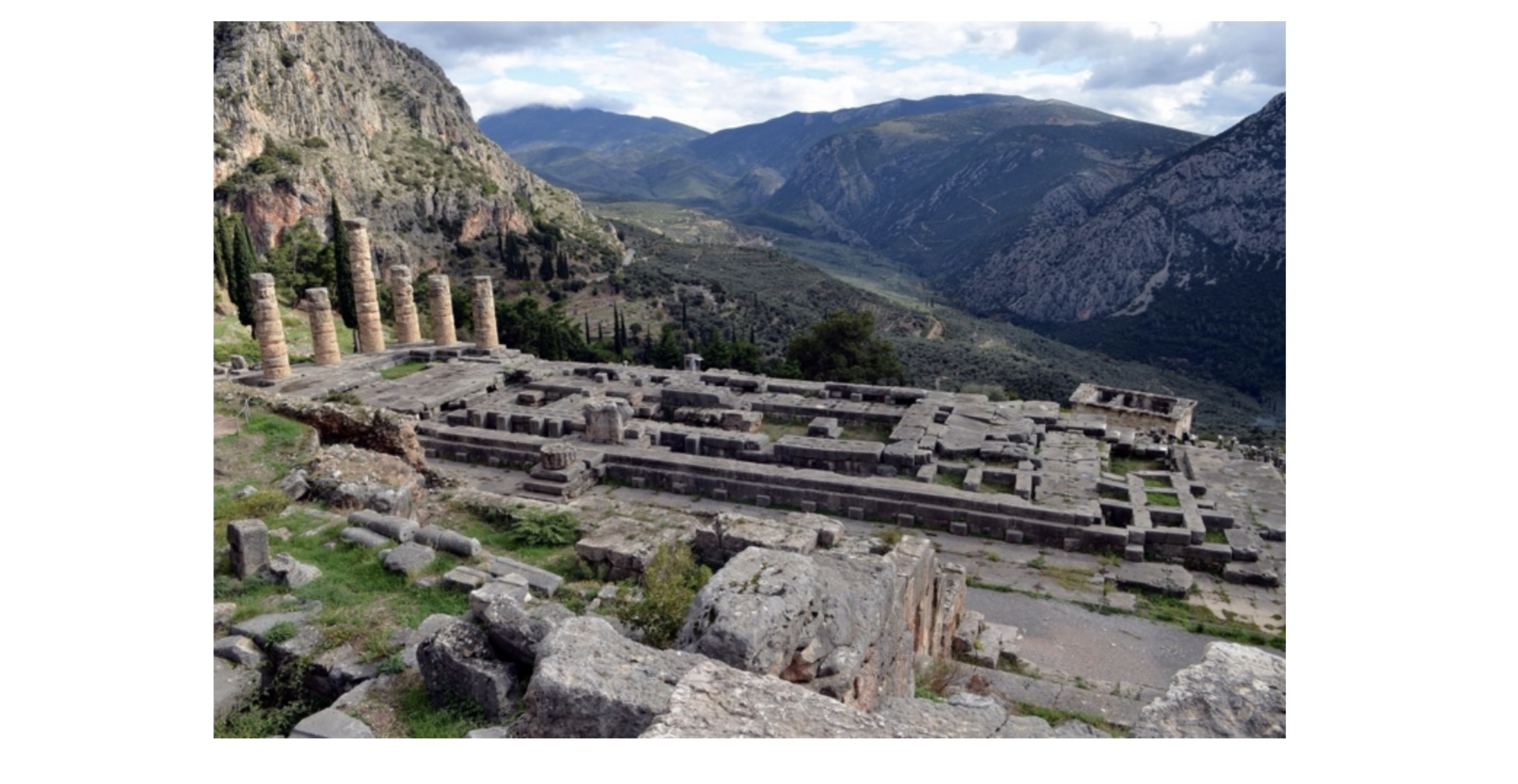

Temple of Apollo at Delphi,
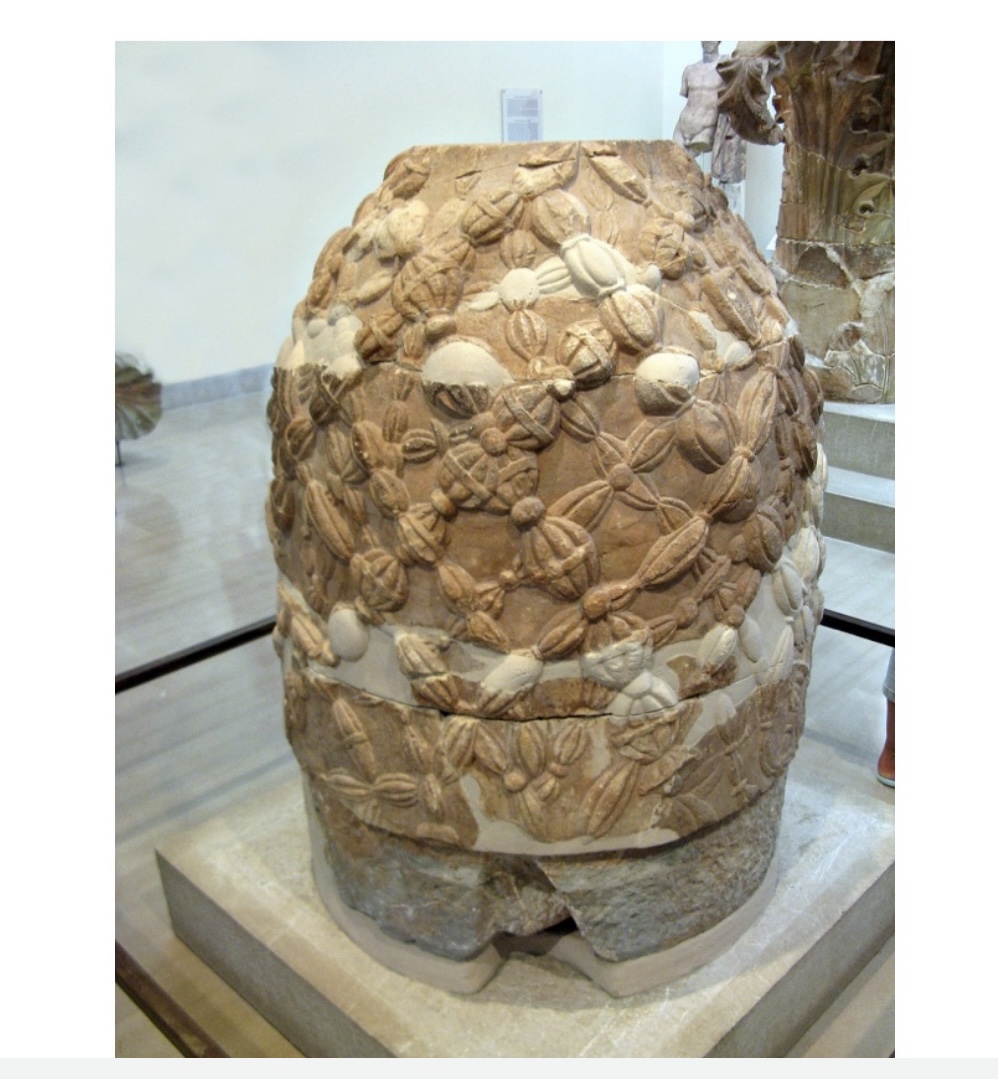

The Omphalos. Marble Late 1st century CE,
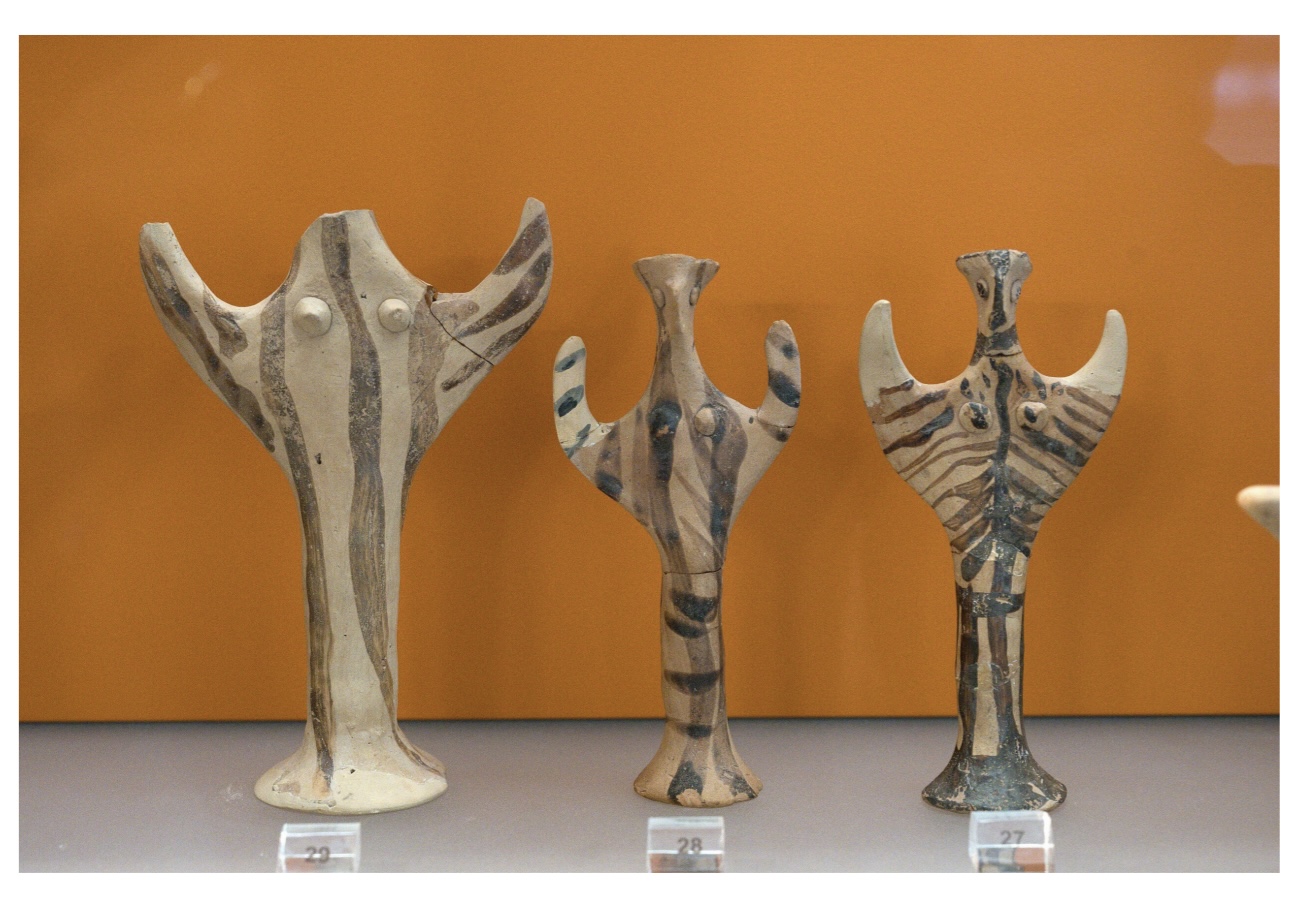

Early Cult Activity at Delphi (12c. BCE)
Late Myceanean
Terracotta Female
Figurines from the
sanctuary of Athena
Pronaia at Delphi.
Stylised clay grave
offerings from chamber
tombs in the sanctuary
repurposed and
dedicated when temple
of Athena built in 7th
century BCE,
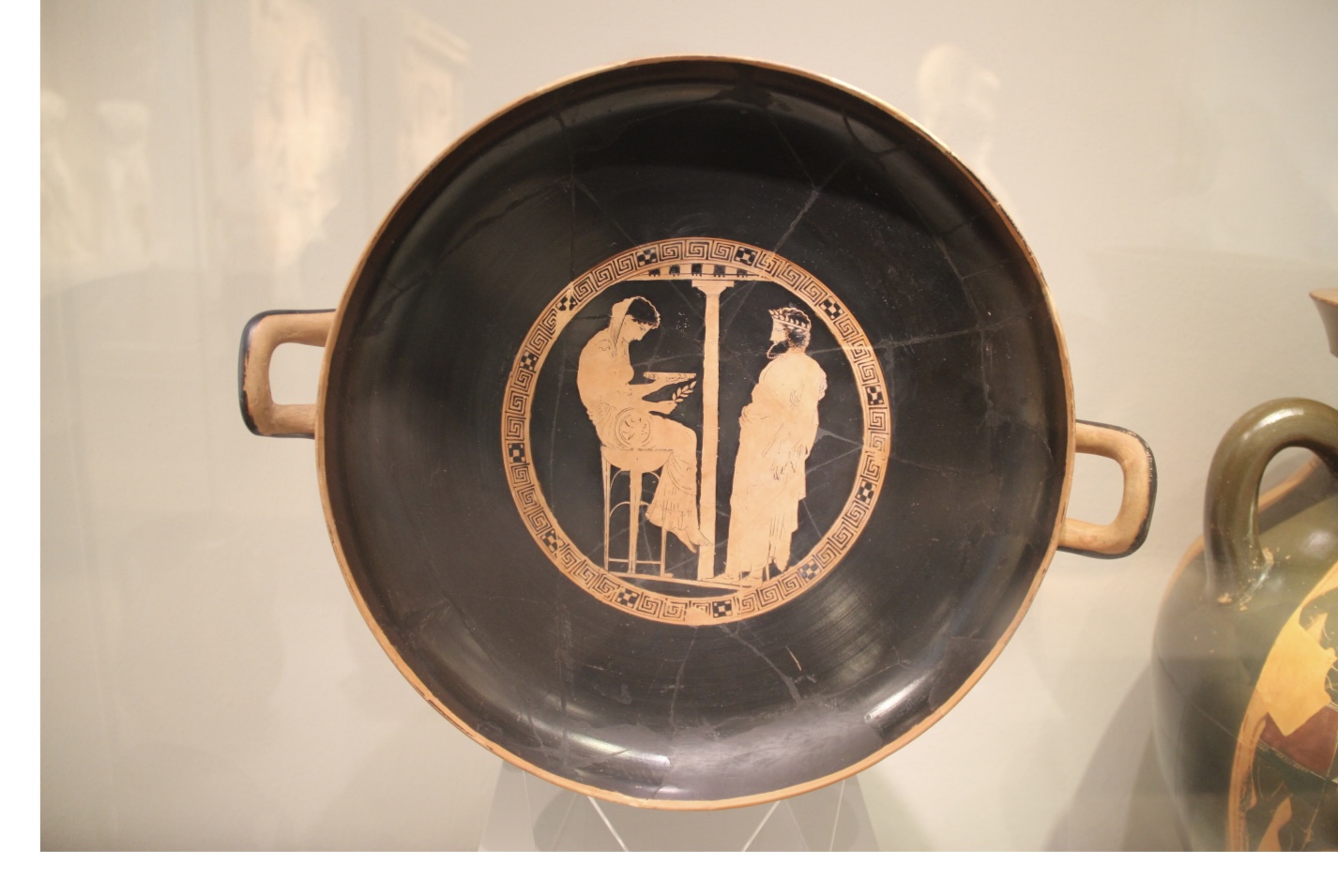

Aigeus, the mythical king of Athens, seeks an oracle from
Themis, seated on a tripod in the sanctuary at Delphi.
• Red figure Kylix by the Kodros
painter (ca 440 BE)

Cult of Apollo Pythios ca. 900BCE, with a
village established by 860BCE and cult
dedications increasingly thereafter.
Oracular dedications to Apollo increase
dramatically in 7th century BCE, with
dedications from around the Greek world
and beyond.,

• Apollo welcomes Dionysus at
Delphi, above the omphalos.
• Red figure krater by the Kadmos
Painter.
• Early 4th century BCE, visual play between order (Apollo) and ecstatic (Dionysus), showing religious complexity and tolerance for paradox.
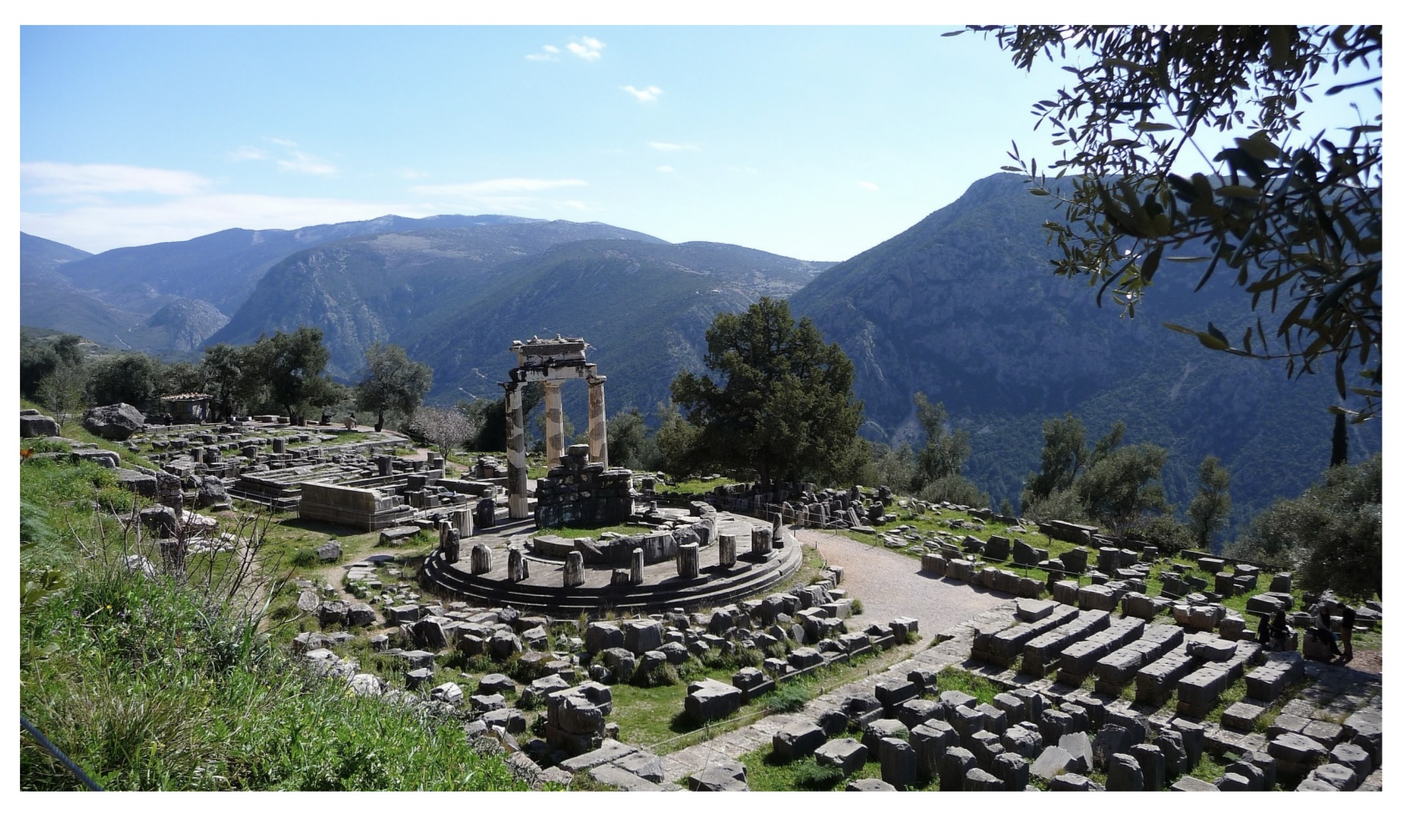

Tholos in the Sanctuary of Athena Pronaia,
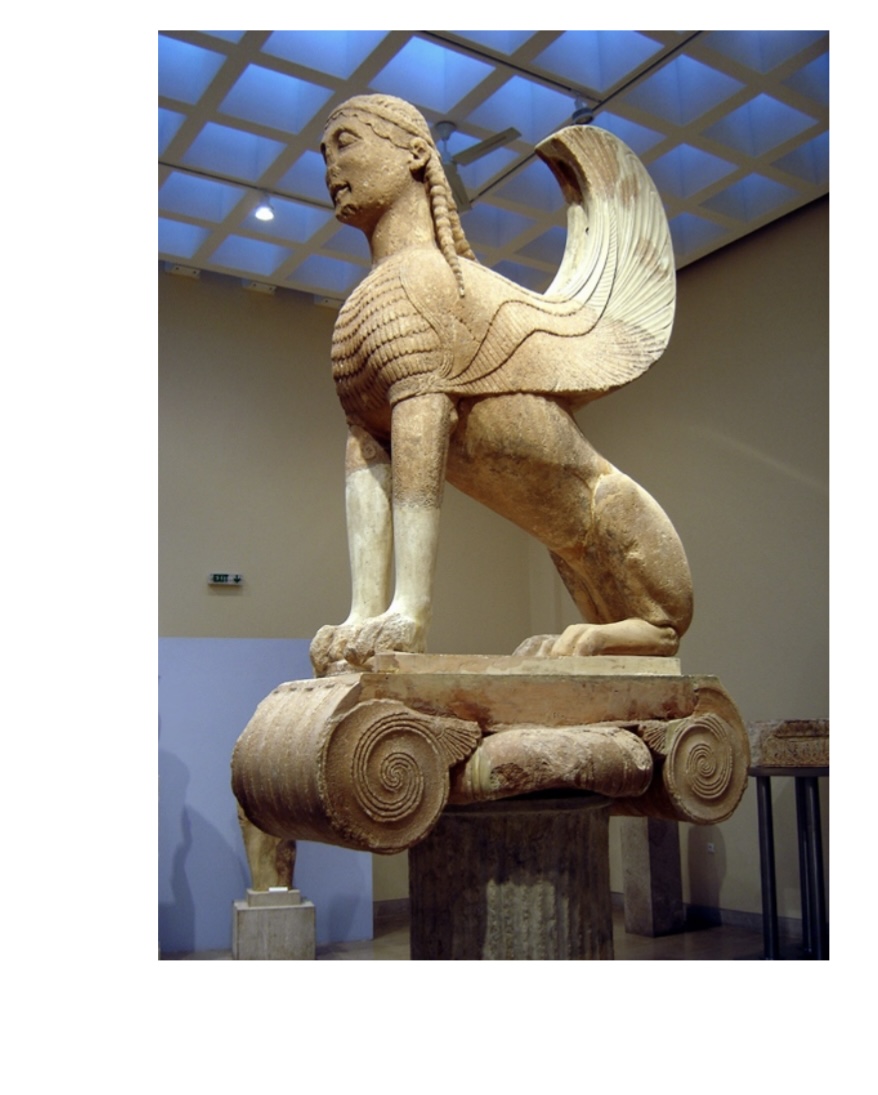

Sphinx of Naxians, originally atop a tall column. Dedicated to Sanctuary ca. 560BCE.,
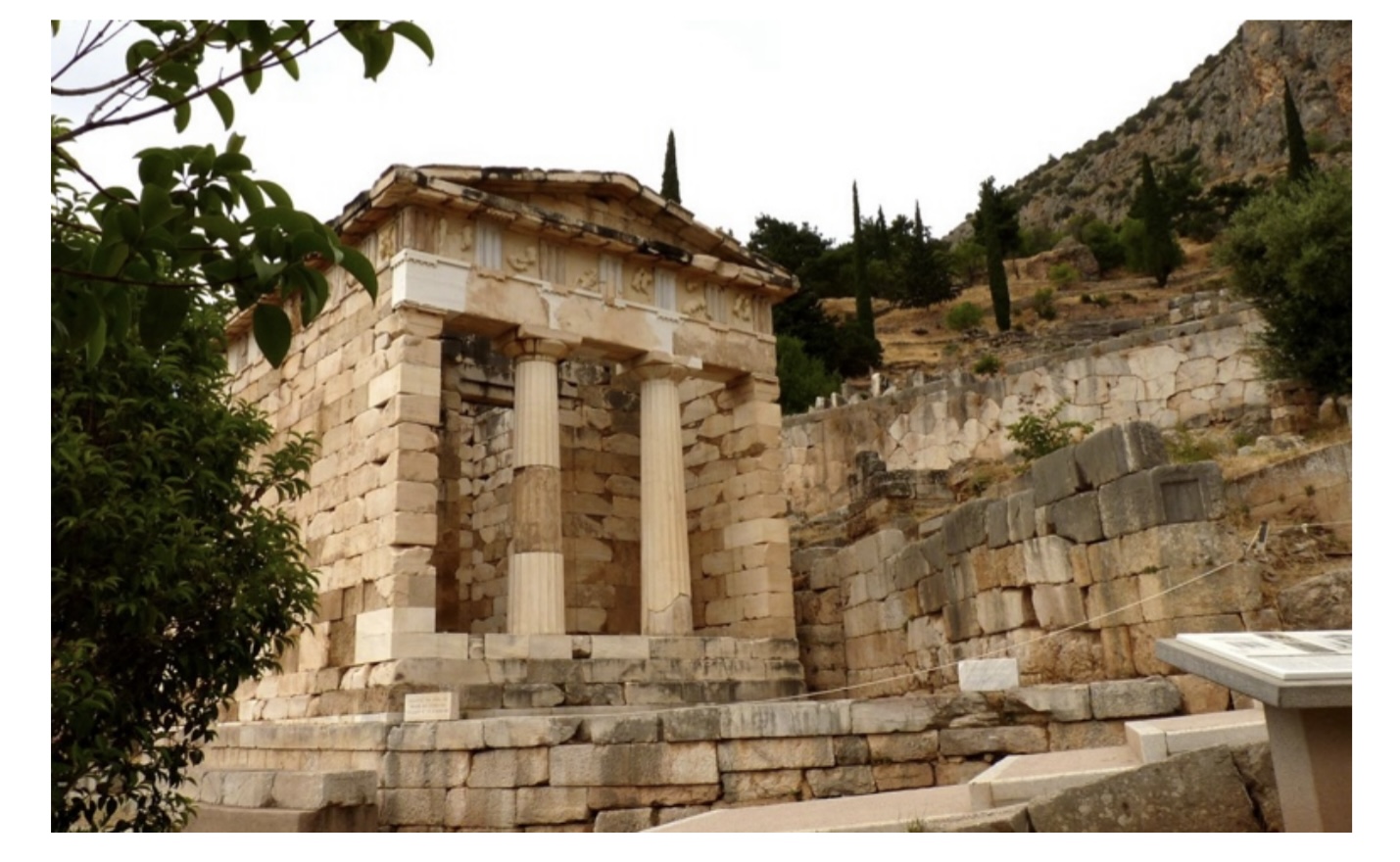

Athenian Treasury Delphi
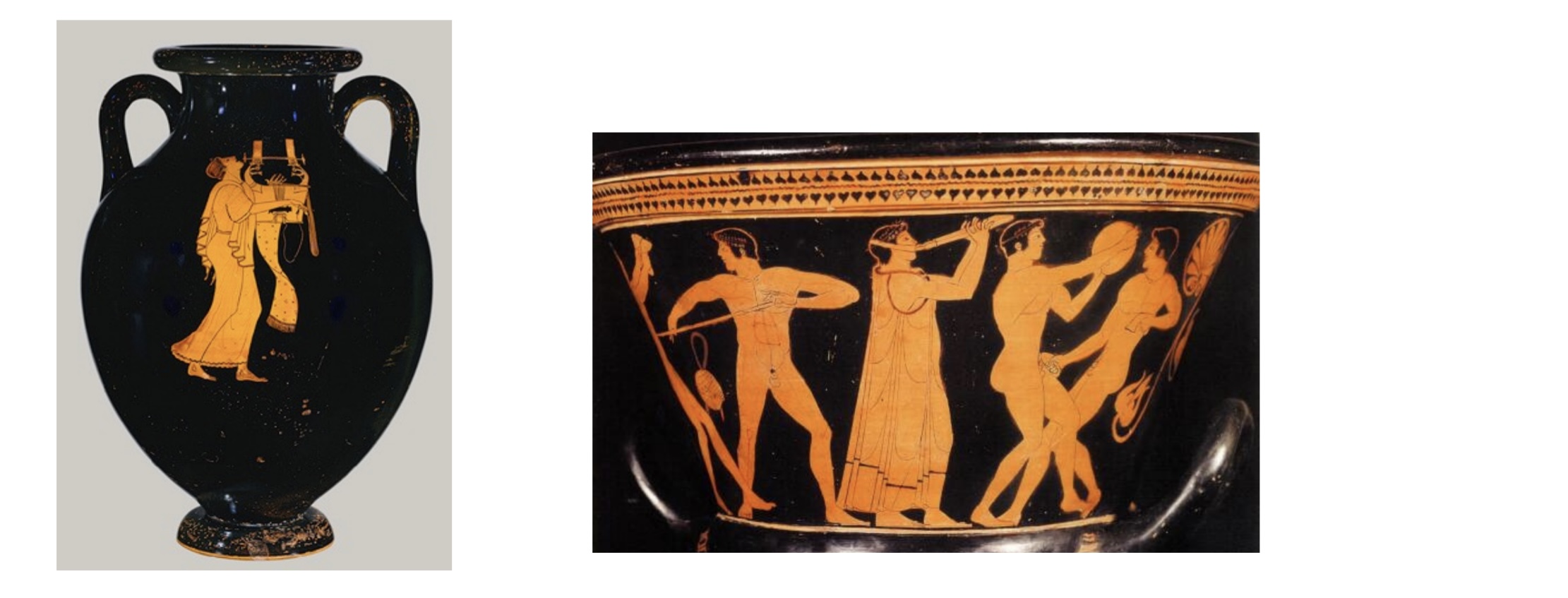

Delphi and the Pythian Games
Mousikoi Agones –
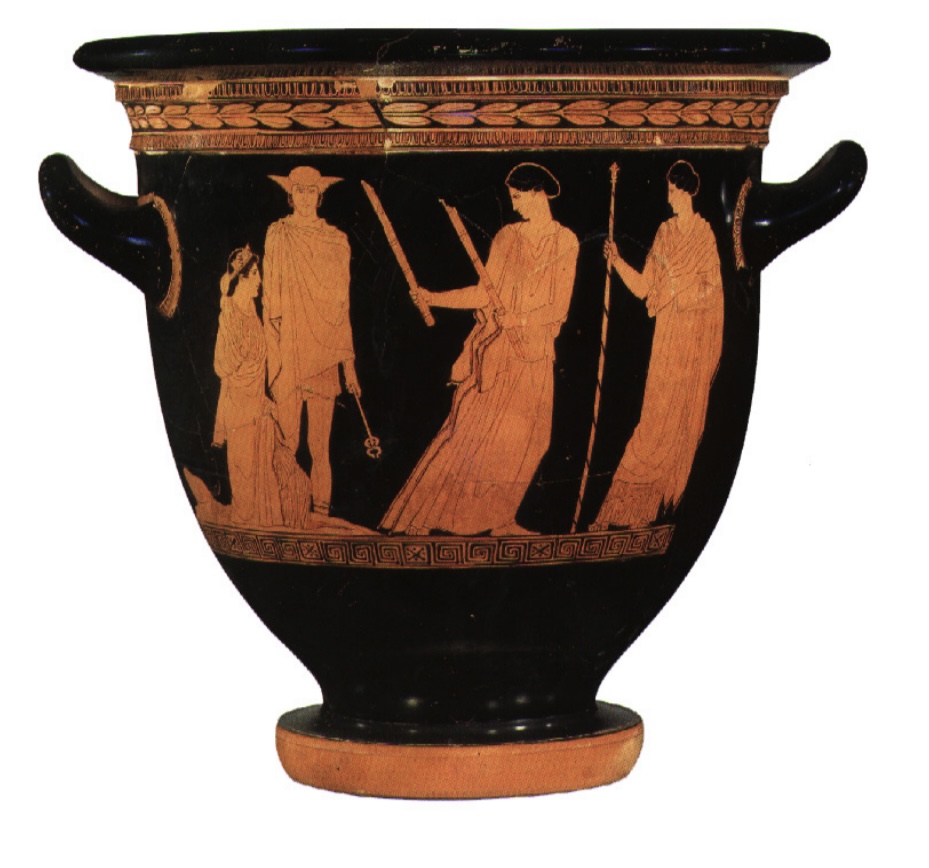

Attic Red Figure Krater. 5th century BCE. Hermes leads Persephone forth from the underworld to be greeted by Hekate and her mother Demeter,

Marble Votive Relief found at Eleusis – Showing (L-R) Demeter, Triptolemos and
Persephone. Date 440BCE
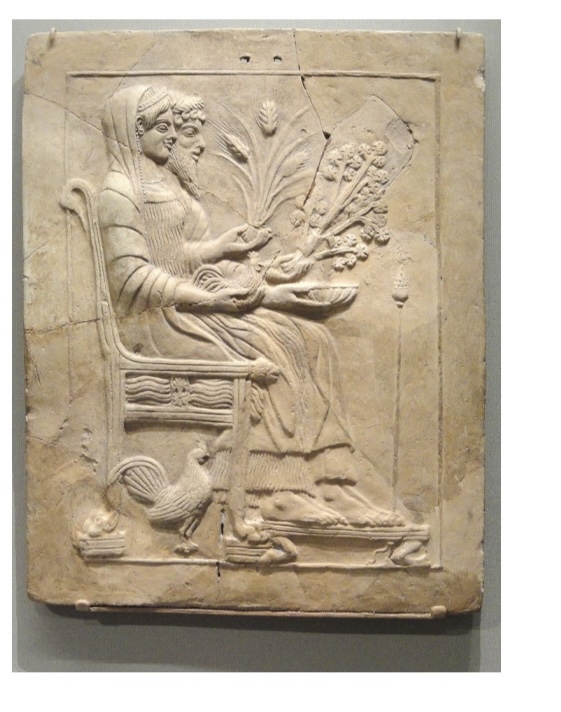

Marble Pinax of Persephone and Hades found in Sanctuary of Persephone in Locri, Sicily.
Early 5th century BCE,
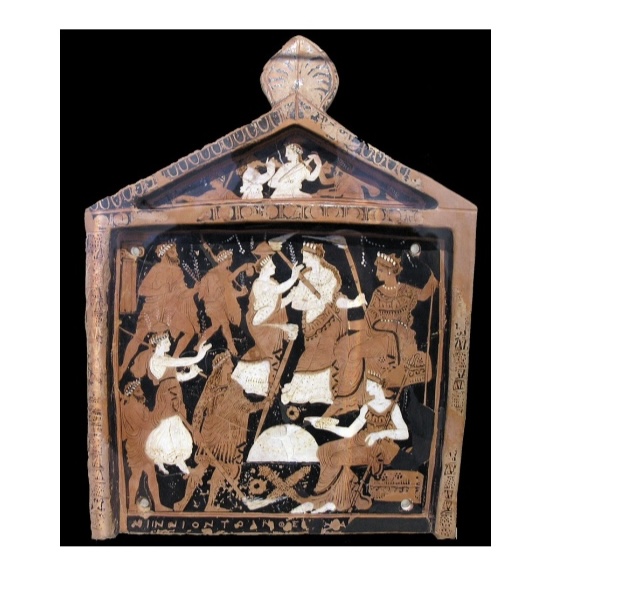

Ninnion Tablet. Red Clay. Circa 370BCE. Found at Eleusis – Only known represention of Eleusinian Procession and Initation Rites
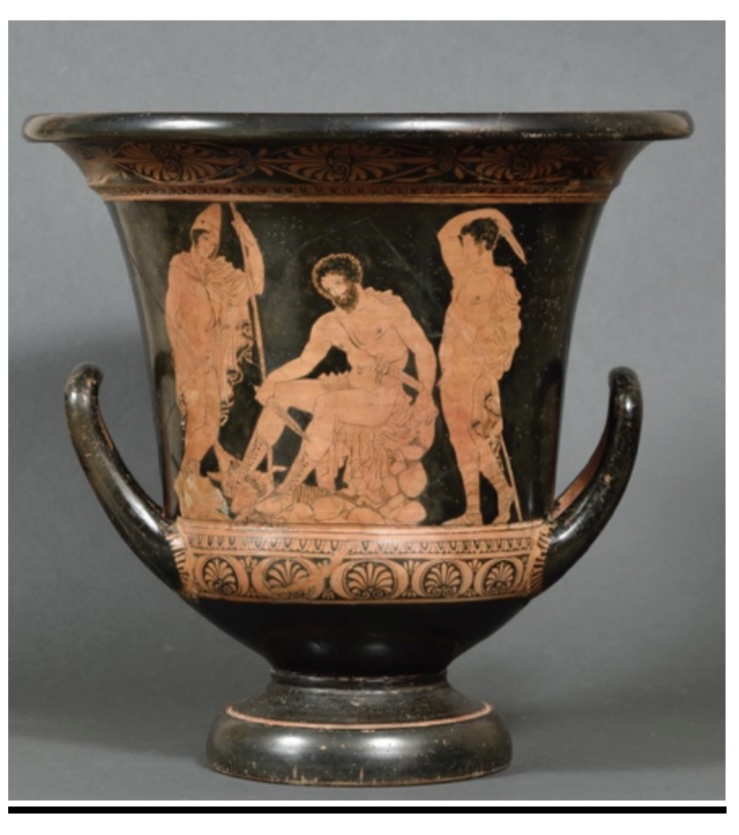

Odysseus summoning the shades. Lucanian Red-Figure Calyx-Crater. 390BCE.,