Water Treatment and Distribution Systems Overview
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Corrosion of non-ferrous pipes
Raising alkaline content by acidity, leading to rusting and clogging of steel pipes.
Hardness
Presence of magnesium and calcium salts causing clogging of pipes and impaired laundry and cooking.
Discoloration
Turbidity caused by silt or mud in surface or ground water, leading to bad taste.
Color
Presence of iron and manganese causing discoloration of fixtures and laundry.
Pollution
Contamination by organic matter or sewage leading to disease.
Ground Water Wells
Wells are holes in the earth from which a fluid may be withdrawn using manual or mechanical means.
Ground water
Water that flows into wells, coming from rain absorbed into the ground and filtered through different layers.
Water table
The level at which water stands in a well that is not being pumped.
Shallow Well
Also known as unconfined wells, completed in the uppermost saturated aquifer.
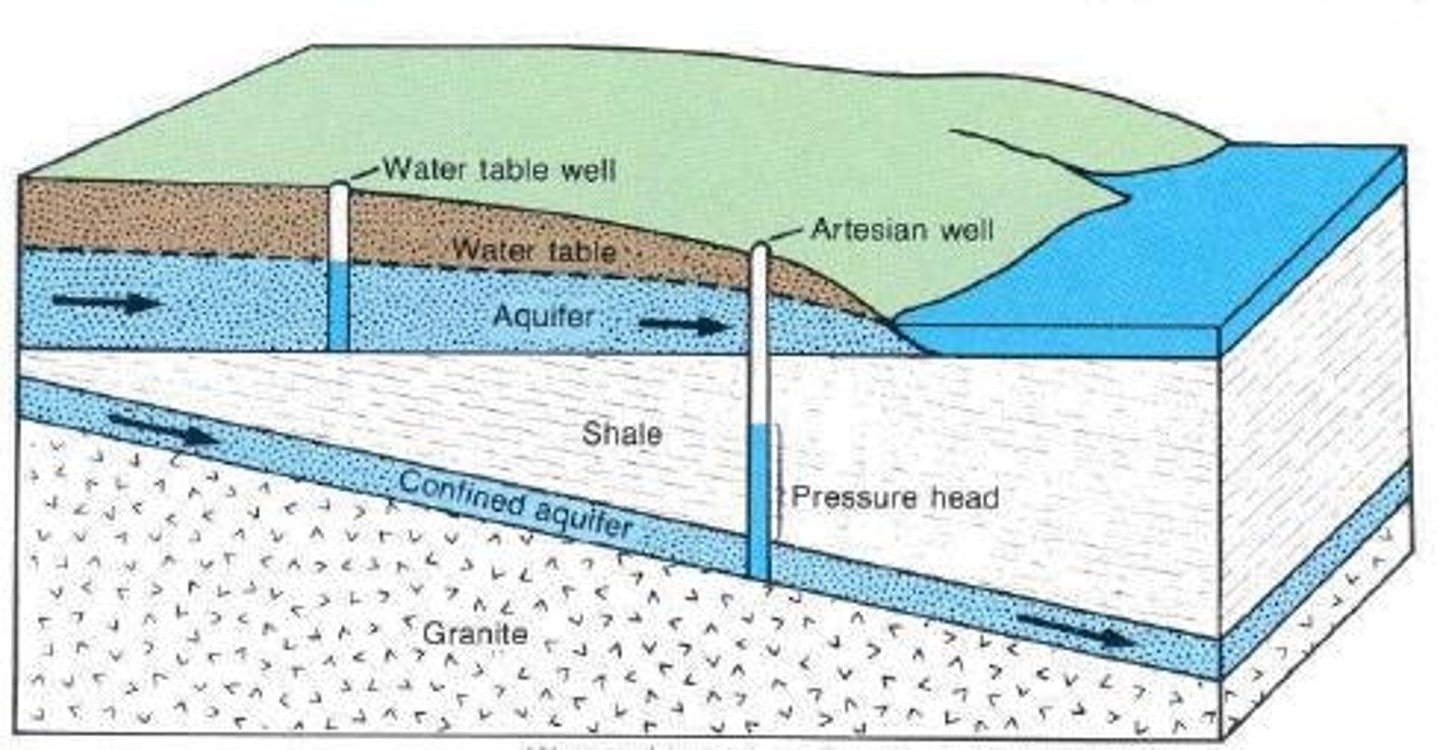
Deep Well
Also known as confined wells, sunk through an impermeable stratum into an aquifer sandwiched between two impermeable strata.
Dug Wells
Constructed with hand tools or power tools, can be dug to a depth of about 15 meters (50 feet).
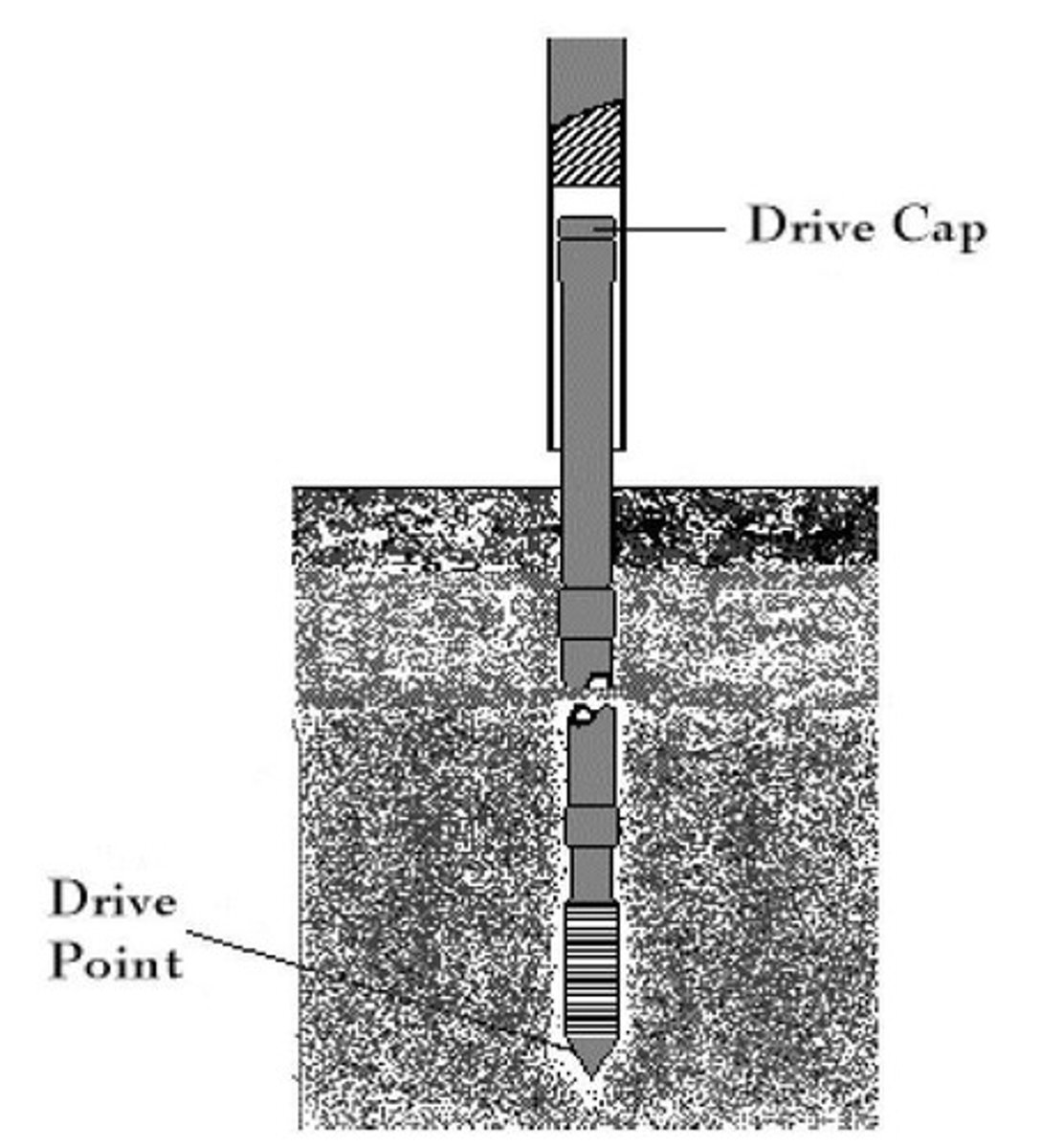
Driven Wells
The simplest and usually the least expensive, with a steel drive well point driven into the earth, up to 15 meters deep.
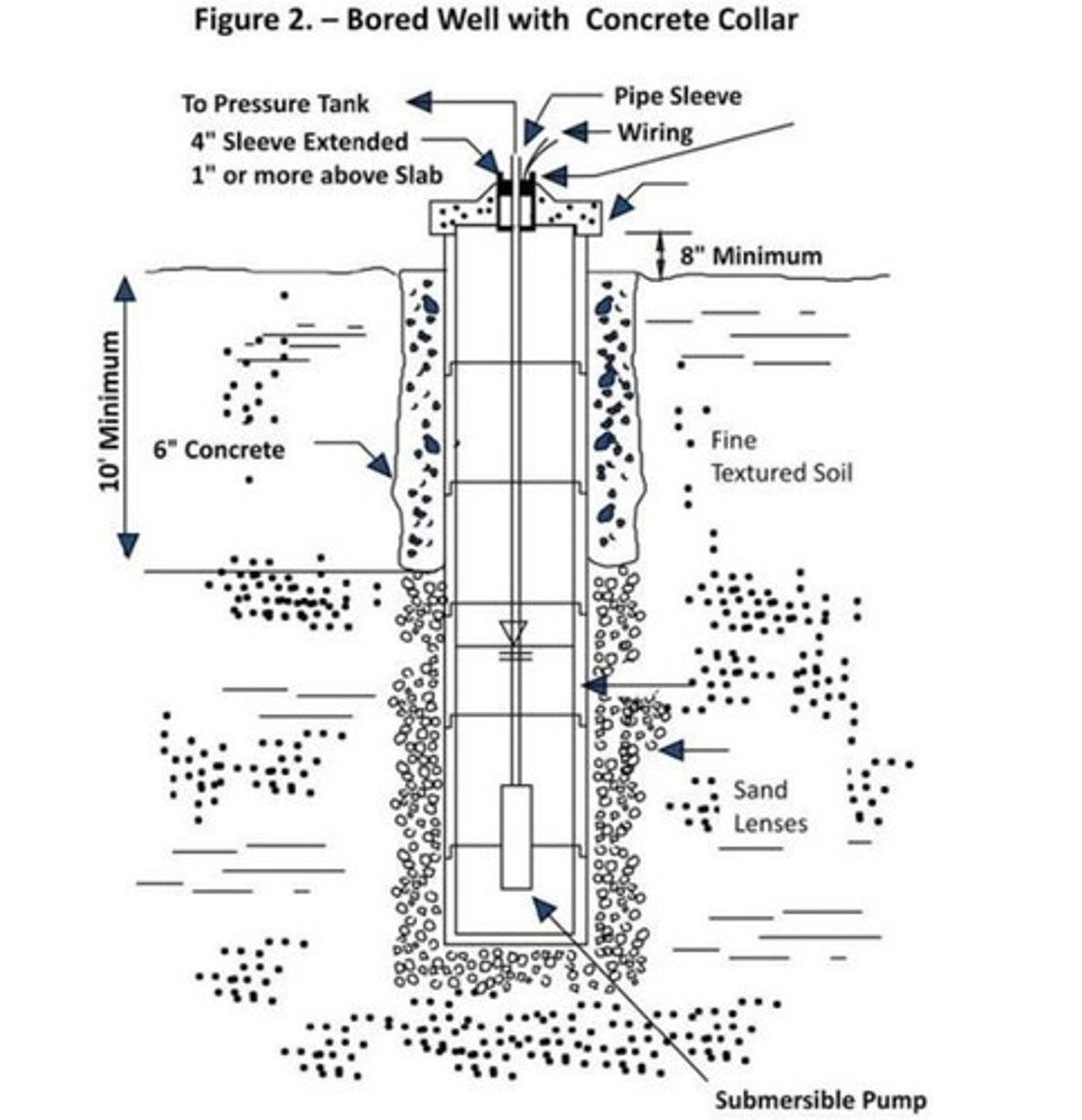
Bored Wells
Dug with earth augers, usually less than 30 meters deep, lined with metal, vitrified tile or concrete.
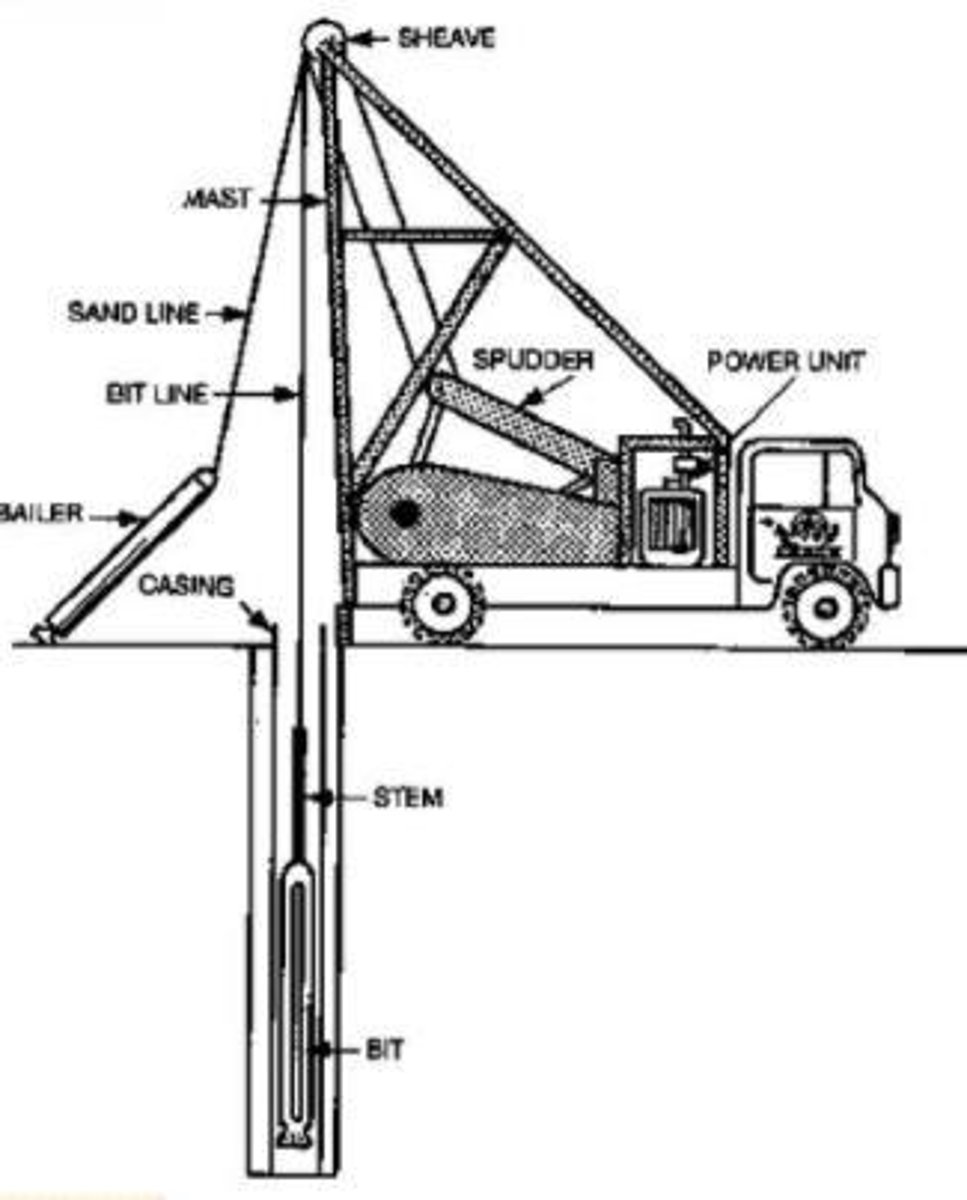
Drilled Wells
Require elaborate equipment, measure up to 300 meters.
Septic Tank
A watertight receptacle designed to retain solids and digest organic matter, allowing liquids to discharge into the soil.
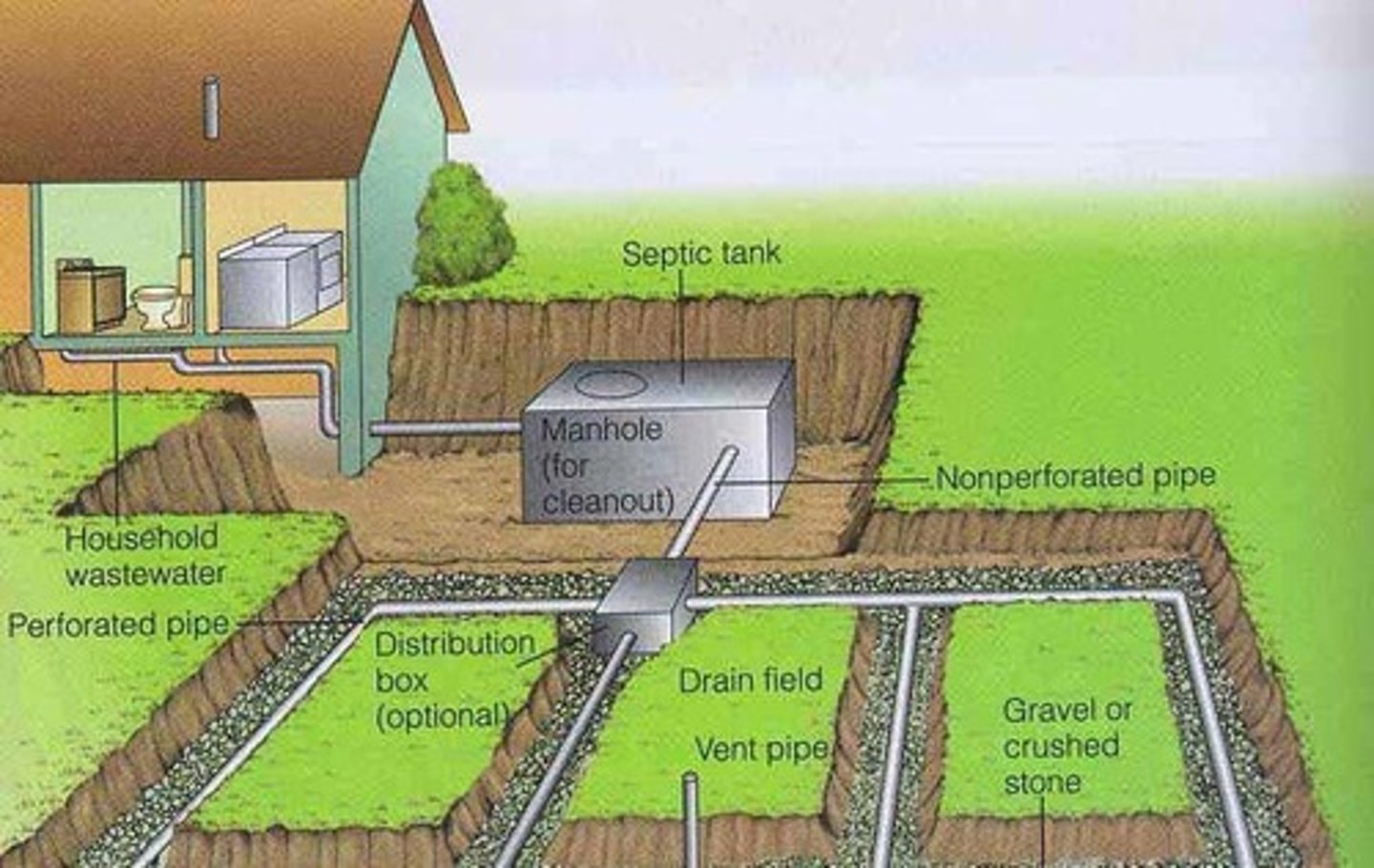
Leach Field
A network of perforated pipes laid in underground gravel filled trenches to dissipate effluent from a water-based collection or treatment.
Livestock Feedlots
A type of animal feeding operation used in intensive animal farming for finishing livestock prior to slaughter.

Locating a well
Locate on higher ground.
Deeper Well
The deeper the well, the better for natural filtration.
Septic Tank
A tank that receives and treats wastewater from a building.
Building Drain / House Drain
That part of the lowest horizontal piping of a plumbing system which receives the discharge from soil, waste, and other drainage pipes inside a building and conveys it to the building / house sewer.
Building Sewer / House Sewer
That part of the drainage system that extends from the end of the building drain and conveys its discharge to the public sewer, private sewer, individual sewage disposal system, or other appropriate point of disposal.
Disposal Field / Leach Field
A system that allows liquid waste to seep through the ground.
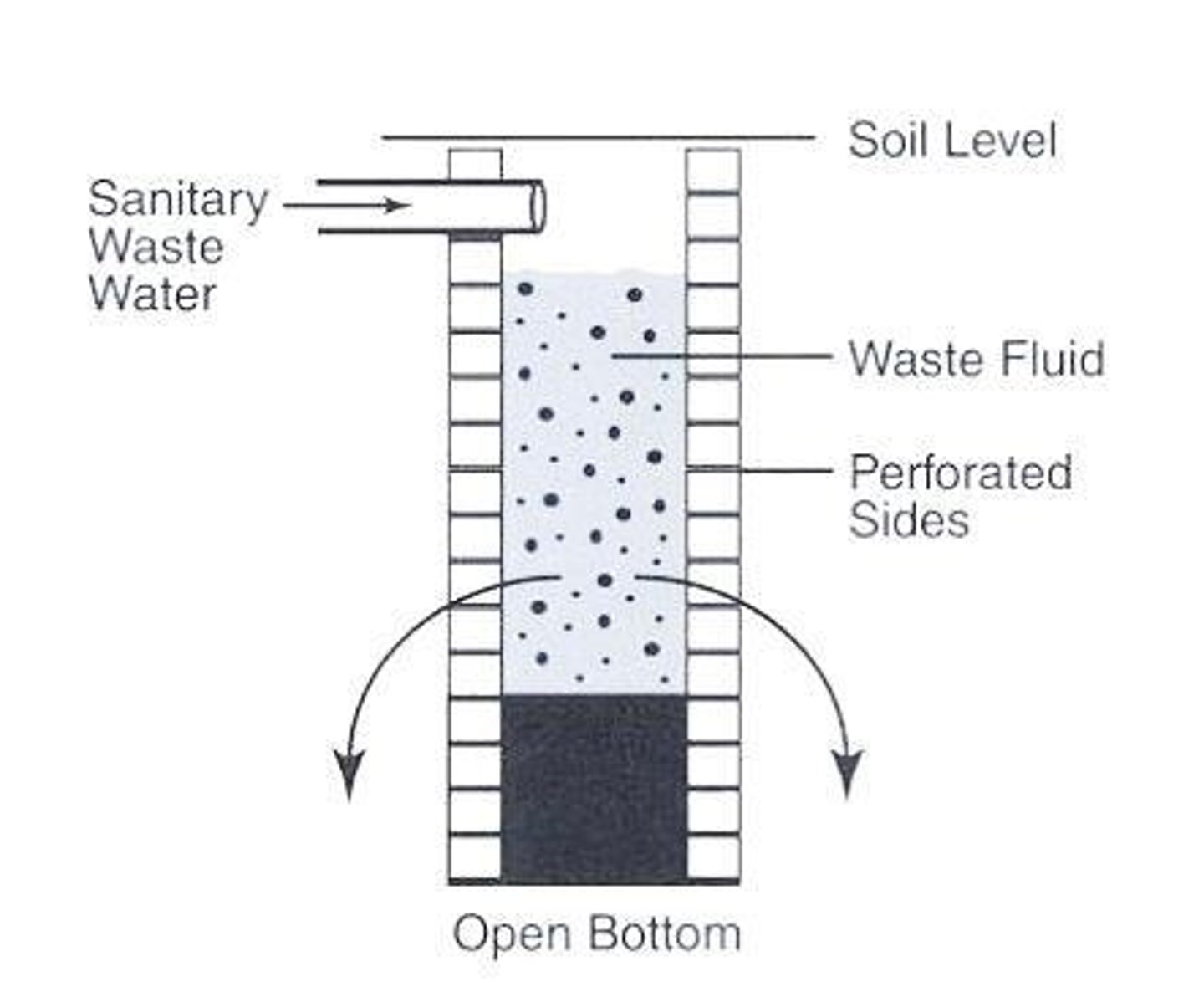
Seepage Pit / Cesspool
A non watertight lined excavation in the ground which receives the discharge of a sanitary drainage system or part thereof, designed to retain the organic matter and solids discharging there from, but permitting the liquid to seep through the sides and bottom of the cesspool.
Water Distribution System
A system for delivering water to consumers.
Direct Pressure Distribution
Water is obtained through a large intake.
Indirect Pressure Distribution
Water is taken from a drilled well or underground water.
Water Service Level I
Provides a protected well or a developed spring with an outlet, but without a distribution system, serving an average of 15 households within a radius of 250 meters.
Water Service Level II
Composed of a source, a reservoir, a piped distribution network, and communal faucets, usually serving four to six households (4-6 households) within a radius of 25 m.
Water Service Level III
Includes a source, a reservoir, a piped distribution network, and areas where the population can afford individual connections, generally suited for densely populated urban areas.
Water (Street) Main
A water supply pipe for public or community use controlled by public authority.
Water-Service Pipe
Pipe from the street water main or other source of water supply to the building served.
Water-Distribution Pipe / Horizontal Supply Main
A pipe which conveys potable water from the building supply pipe to the plumbing fixtures & other water outlets in the building.
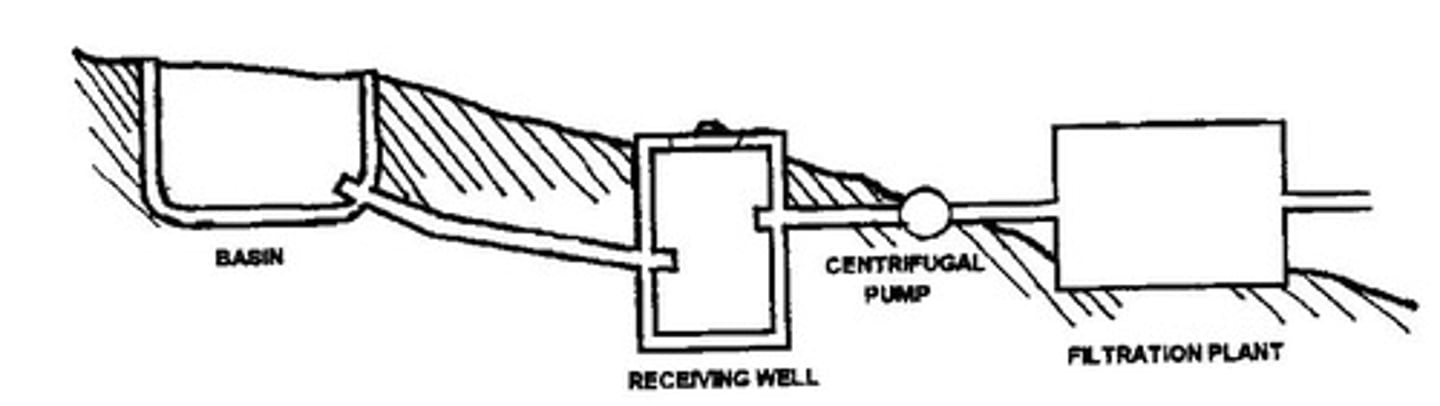
Water Basin
A component of the water distribution system.
Receiving Well
A component of the water distribution system.
Filtration Plant
A facility that purifies water for distribution.
Fixture Branch
A pipe connecting several fixtures.
Fixture Supply
A water supply pipe connecting the fixture with the fixture branch or directly to a main water supply pipe.
Corporation Stop / Cock
A valve screwed into the street water main to supply the house service connection.
Gooseneck
The part of the pipe curved like the neck of a goose, usually flexible, provided to accommodate possible movement, displacement or settlement that may take place between the water main and the service pipe due to water pressure and prevent damage to the connection.
Curb Stop / Cock
A control valve for the water supply of a building, usually placed between the sidewalk and the street curb; used to shut off the water supply in case of emergency or should the water supply of the building be discontinued.
Meter Stop / Check Valve
A valve placed at the street side of the water meter and serves as a controlling device for the building installation.
Water Meter
A mechanical device used to measure the volume of water passing through a pipe.

Gate Valve
A valve placed at the street side of the water meter and serves as a controlling device for the building installation.
Direct Pressure Upfeed Distribution System
Water is provided by the city water companies using normal pressure from public water main, eliminating extra cost of pumps & tanks.
Hydropneumatic Pressure Boosting System
This is a pumping system that provides water within pre-set flow and pressure ratings, automatically on demand giving all the advantages of city water supply.
Pressure Vessel (Pressure Tank)
Contains an elastic medium in the hydropneumatic pressure boosting system.
Downfeed (Overhead) Distribution System
Water is pumped into a large tank on top of the building and is distributed to the fixtures by means of gravity.
Riser
A water supply pipe extending vertically to one full story or more to convey water into pipe branches or plumbing fixtures.
Water Tanks
Used for control, isolation and repair of the water distribution system.