Biological basis (brain and nervous system)
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards
Nervous system
System of networks of specialised cells that connect different parts of the body to each other and the brain via electrochemical signals
2
New cards
Composition of the central nervous system (CNS)
* brain
* spinal cord
* spinal cord
3
New cards
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Made up of all the nerves outside of the CNS
4
New cards
Role of the PNS
* carry sensory information to the CNS
* carry motor information from the CNS to the rest of the body
* carry motor information from the CNS to the rest of the body
5
New cards
Motor (efferent) neurons
neurons that transmit information via electrochemical impulses away from the brain to effectors
6
New cards
Sensory (afferent) neurons
Neurons that transmit information via electrochemical impulses towards the brain
7
New cards
Somatic nervous system
* division of the peripheral nervous system
* controls voluntary movement through control of skeletal muscles
* tying you shoe, kicking a ball, brushing your teeth
* controls voluntary movement through control of skeletal muscles
* tying you shoe, kicking a ball, brushing your teeth
8
New cards
Autonomic nervous system
* division of the peripheral nervous system
* contains nerves that are connected to the CNS and the involuntary muscles that control activity level of internal organs and glands
* heart rate, digestion, kidney function, perspiration levels
* contains nerves that are connected to the CNS and the involuntary muscles that control activity level of internal organs and glands
* heart rate, digestion, kidney function, perspiration levels
9
New cards
Sympathetic nervous system
* division of the autonomic nervous system
* body’s emergency or arousal system
* dominates during times of stress
* changes the activity level of our internal systems so we have a sudden increase in our energy levels when needed
* body’s emergency or arousal system
* dominates during times of stress
* changes the activity level of our internal systems so we have a sudden increase in our energy levels when needed
10
New cards
Parasympathetic nervous system
* once the need for high arousal has ended, it reverses the effects of the sympathetic nervous system
* returns our bodies to normal levels fo arousal or a more relaxed state
* maintains vital functions such as heart rate, breathing rate, and digestion at normal levels during day to day living
* returns our bodies to normal levels fo arousal or a more relaxed state
* maintains vital functions such as heart rate, breathing rate, and digestion at normal levels during day to day living
11
New cards
Interneurons
* connect CNS and PNS
* specialised neurons that form a direct connection between the motor and sensory neuron
* specialised neurons that form a direct connection between the motor and sensory neuron
12
New cards
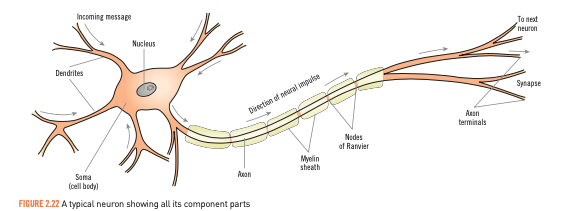
Neuron structure
Soma/cell body - coordinates information coming into the cell and passes it on
Dendrites - receive information from other neurons and deliver the information to the cell body
Axon - nerve fibre that carries information away from the soma to other cells
Myelin sheath - fatty substance that insulates the axon from surrounding fluids and other neurons
Axon terminal - end of neuron’s axon that fibre links with other dendrites
Synapse - microscopic gap between neurons
Dendrites - receive information from other neurons and deliver the information to the cell body
Axon - nerve fibre that carries information away from the soma to other cells
Myelin sheath - fatty substance that insulates the axon from surrounding fluids and other neurons
Axon terminal - end of neuron’s axon that fibre links with other dendrites
Synapse - microscopic gap between neurons
13
New cards
Hindbrain
* referred to as brain stem, located at back of skull
* controls basic survival functions such as heart rate, breathing, sleep and arousal
* coordinates involuntary muscles movements and reflexive actions such as coughing, swallowing and vomiting
* controls basic survival functions such as heart rate, breathing, sleep and arousal
* coordinates involuntary muscles movements and reflexive actions such as coughing, swallowing and vomiting
14
New cards
Cerebellum
* Regulates posture and balance
* coordinates fine muscle movements
* mental function and motor learning
* coordinates fine muscle movements
* mental function and motor learning
15
New cards
Cerebral ataxia
Damage to the cerebellum caused by head trauma, virus or tumour. Symptoms include
* frequent stumbling
* unsteady walking
* dizziness
* frequent stumbling
* unsteady walking
* dizziness
16
New cards
Medulla
* regulates all the organs vital for life functions
* damage may be fatal as it controls vital organs
* fatal drug overdoses are due to the inability of the medulla to perform vital functions
* damage may be fatal as it controls vital organs
* fatal drug overdoses are due to the inability of the medulla to perform vital functions
17
New cards
Midbrain
* area between hindbrain and forebrain
* keeps us alert, awake and vigilant
* passes information from spinal cord to forebrain and back the other way
* keeps us alert, awake and vigilant
* passes information from spinal cord to forebrain and back the other way
18
New cards
Reticular formation
* network of neuons from top of spinal cord up through brain stem to midbrain
* controls physiological arousal and helps focus attention and alertness
* filters incoming information so higher brain centres attend the more important information, and don’t get overwhelmed
* controls physiological arousal and helps focus attention and alertness
* filters incoming information so higher brain centres attend the more important information, and don’t get overwhelmed
19
New cards
forebrain
influences how we think, feel and behave
20
New cards
thalamus
* relay system for sensory messages on their way to the cerebral cortex
* processes information from all the senses except smell
* analyses this information and directs it to appropriate sensory areas of the cerebral cortex
* modulates itself (unnecessary information is filtered out)
* processes information from all the senses except smell
* analyses this information and directs it to appropriate sensory areas of the cerebral cortex
* modulates itself (unnecessary information is filtered out)
21
New cards
Cerebrum
Divided into two hemispheres that can be further divided into four lobes, each with a specific function
* left hemisphere responsible for logic skills, language, analytical function, mathematical processes
* right hemisphere responsible for imagination, art and music, creativity
* outer layer consists of cerebral cortex which is responsible for higher cognitive functions, voluntary movement, emotions and personality
* left hemisphere responsible for logic skills, language, analytical function, mathematical processes
* right hemisphere responsible for imagination, art and music, creativity
* outer layer consists of cerebral cortex which is responsible for higher cognitive functions, voluntary movement, emotions and personality
22
New cards
Corpus callosum
Large bundle of nerve fibres that enable messages to be relayed from one hemisphere to the other
23
New cards
Contralateral control
Each hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body. e.g. left hemisphere receives sensory information from and controls the right side of the body
24
New cards
Broca’s area
area that controls the muscles responsible for the production of articulate speech
* found in the left frontal lobe
* found in the left frontal lobe
25
New cards
Broca’s aphasia
patients who experience speech loss, but are able to comprehend speech. Caused by damage to Broca’s area
26
New cards
Wernicke’s area
Area responsible for the comprehension of language and the formation of meaningful sentences
* found in the left temporal lobe
* found in the left temporal lobe
27
New cards
Wernicke’s aphasia
Impairment in the ability to understand language and formulate coherent, meaningful speech. Cause by damage to Wernicke’s area
28
New cards
Primary motor cortex
directs skeletal muscles and controls voluntary movement
* located in an arch of tissue at the rear of the frontal lobe
* located in an arch of tissue at the rear of the frontal lobe
29
New cards
Primary sensory cortex
Registers and processes sensory information from receptors located throughout the body and skin
* located in the front of the parietal lobe adjacent to the primary motor cortex
* located in the front of the parietal lobe adjacent to the primary motor cortex
30
New cards
Primary auditory cortex
Area of the temporal lobe that registers and processes auditory information
* contributes to memory, ability to recognise faces and objects
* contributes to memory, ability to recognise faces and objects
31
New cards
Primary visual cortex
Registers and processes visual information transmitted from the retina of both eyes
* contains a variety of neurons specialised to respond to specific features of visual information - some respond to colour, shape, motion
* contains a variety of neurons specialised to respond to specific features of visual information - some respond to colour, shape, motion
32
New cards
Roger W. Sperry’s split brain investigation
* showed a word to one of the eyes and found that split-brain people could only remember the word they saw with their right eye.
* Next, Sperry showed the participants two different objects, one to their left eye only and one to their right eye only and then asked them to draw what they saw. All participants drew what they saw with their left eye and described what they saw with their right eye. Sperry concluded that the left hemisphere of the brain could recognize and analyse speech, while the right hemisphere could not
33
New cards
Phineas Gage
* suffered a traumatic brain injury that destroyed his frontal lobe
* survived and could function normally within 3 months, but his personality and behaviour changed from an honest, dependable worker to a surly, aggressive, uncaring, foul mouthed liar
* illustrated how areas of the brain have specific functions as well as the resilience of the brain
* survived and could function normally within 3 months, but his personality and behaviour changed from an honest, dependable worker to a surly, aggressive, uncaring, foul mouthed liar
* illustrated how areas of the brain have specific functions as well as the resilience of the brain
34
New cards
Freeman - role of prefrontal cortex
* lobotomy - surgical procedure to sever the nerve pathway in the prefrontal cortex
* promoted as a cure for everything from severe mental health to nervous indigestion
* promoted as a cure for everything from severe mental health to nervous indigestion
35
New cards
Synaptic transmission
the process of neurons transmitting information between each other over the synapse. Occurs in a 5 step process
36
New cards
Storage
Neurotransmitters contained in small sacs known as synaptic vessels within the terminal button of each neuron's terminal axon
* When a presynaptic neuron fires the synaptic vesicles move toward the presynaptic membrane
37
New cards
Release
Some synaptic vesicles break open to release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft - exocytosis
38
New cards
Diffusion
Neurotransmitters move across synaptic cleft via diffusion - high concentration --> low concentration
39
New cards
Binding
Neurotransmitter will bind with the receptors that are located in the dendrites of the postsynaptic neuron. A neurotransmitter (lock) is only able to bind to a specific receptor (key)
* Lock and key model: the neurotransmitter and receptor site possess specific complementary shapes that fit into one another - highly specific
* If the neurotransmitter is able to work on the receptor site, it triggers changes in the receiving cell
\
When a receptor binds with the neurotransmitter the postsynaptic neuron is either activated or inhibited
* Excitatory synapse - increases the amount of firing of the axon of the postsynaptic neuron
* Inhibitory synapse - reduces or totally inhibits the firing rate of the postsynaptic neuron
40
New cards
Reuptake
* Excess transmitter in synapse drift away, are broken down by enzymes into inactive fragments, or are reabsorbed in a process known as reuptake
* Neurotransmitter is pumped back into the neuron that released it in order to clear the synapse
* Regulates level of neurotransmitter present in synapse --> thereby controlling how long a signal resulting from a neurotransmitter lasts
41
New cards
Frontal lobe
* located in the upper front of each hemisphere
* associated with higher mental ability
* regulation of self awareness
* ability to inhibit inappropriate actions
* memory formation, emotion and personality
* If damaged, an individuals personality may change
* associated with higher mental ability
* regulation of self awareness
* ability to inhibit inappropriate actions
* memory formation, emotion and personality
* If damaged, an individuals personality may change
42
New cards
Temporal lobe
* receives and processes sound based information
* plays a role in our ability to interpret different sorts of sounds and understand speech
* damage may affect a persons language ability. May be unable to recognise faces or objects, although they can still describe them
* plays a role in our ability to interpret different sorts of sounds and understand speech
* damage may affect a persons language ability. May be unable to recognise faces or objects, although they can still describe them
43
New cards
Occipital lobe
* found in the back of the brain
* responsible for vision
* damage can affect vision, even if eyes are normal
* responsible for vision
* damage can affect vision, even if eyes are normal
44
New cards
parietal lobe
* located on top of cortex
* receives information about touch and temperature from the skin
* information about the body’s position and muscle movement
* damage results in a reduction of body feeling
* receives information about touch and temperature from the skin
* information about the body’s position and muscle movement
* damage results in a reduction of body feeling
45
New cards
Hypothalamus
* communicates with the endocrine system
* maintain homeostasis by coordination of nervous and endocrine system
* regulate body temperature, sleep-wake, thirst and hunger, stress
* located just below the thalamus
* maintain homeostasis by coordination of nervous and endocrine system
* regulate body temperature, sleep-wake, thirst and hunger, stress
* located just below the thalamus