Organic Chemistry Exam 1 Rutgers
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
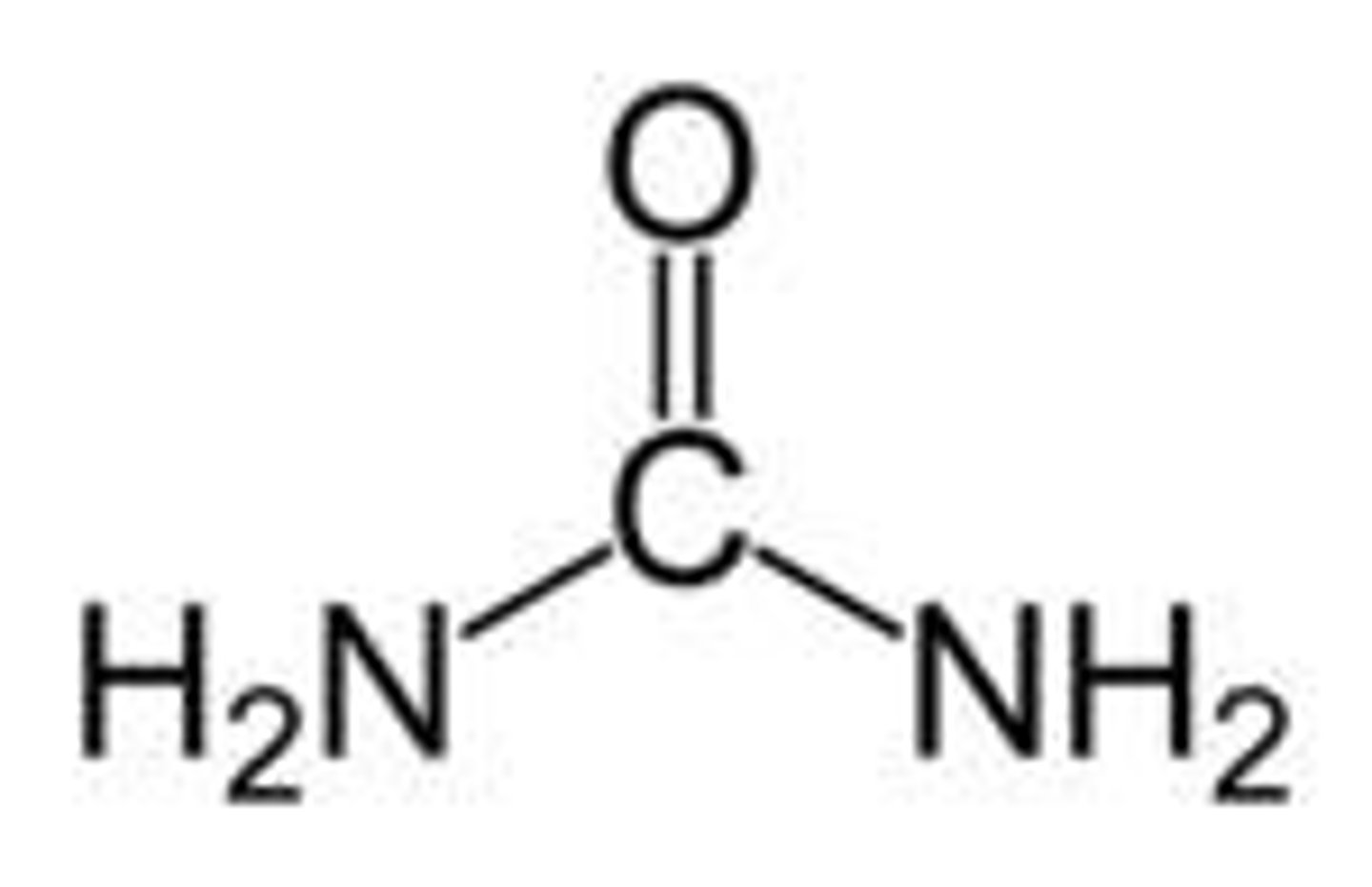
Urea
(NH2)2CO
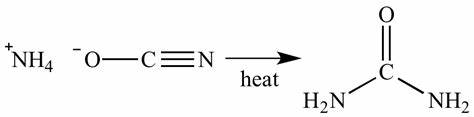
Equation used by Friedrich Wohler
NH4(OCN) -> NH3 + HOCN -> (NH2)2CO
Ammonia Cyanate
NH4(OCN)
Octet Rule
C, N, O, F atoms attain stable configurations when they have eight electrons in their outer shell
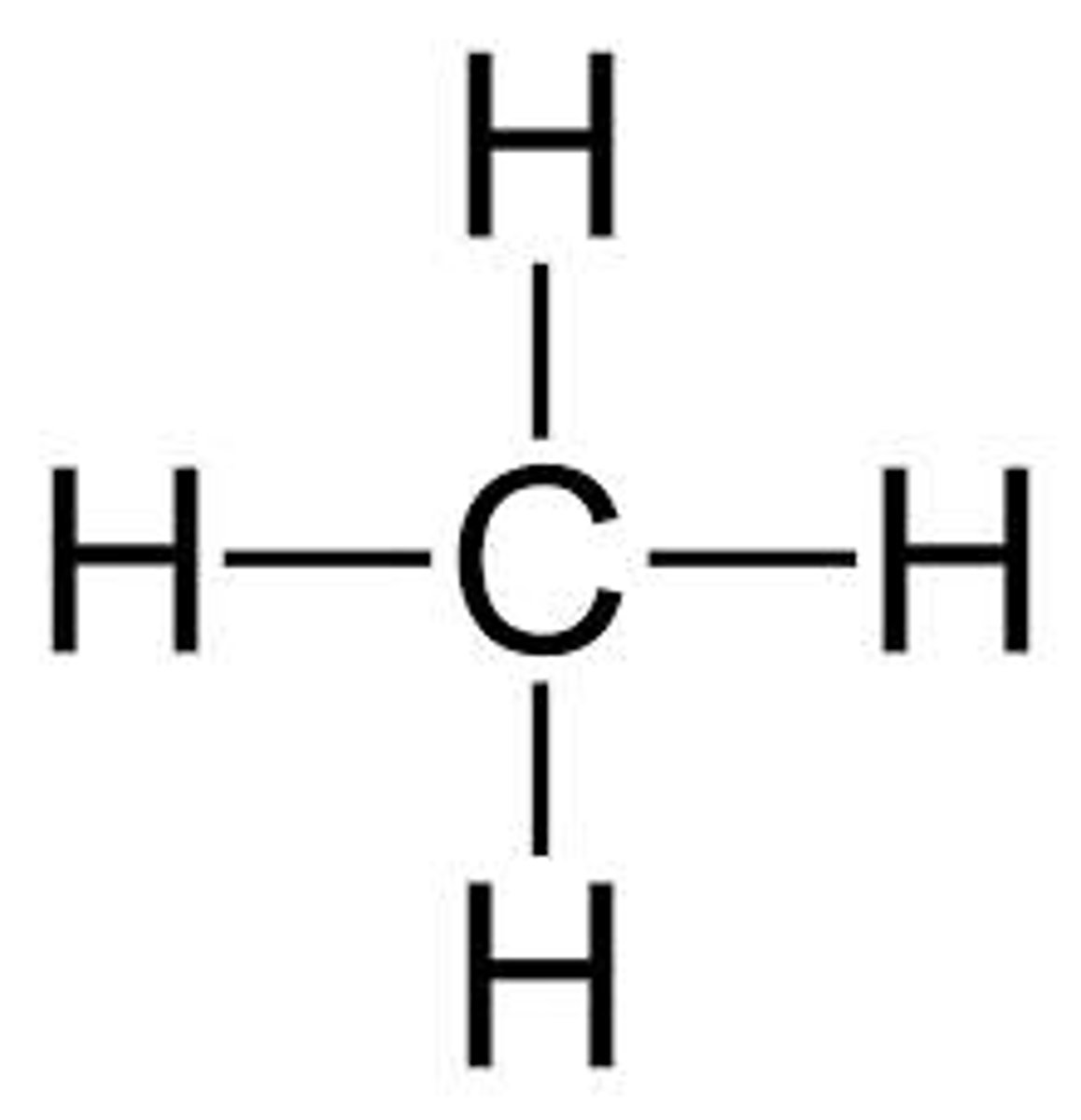
Methane
CH4
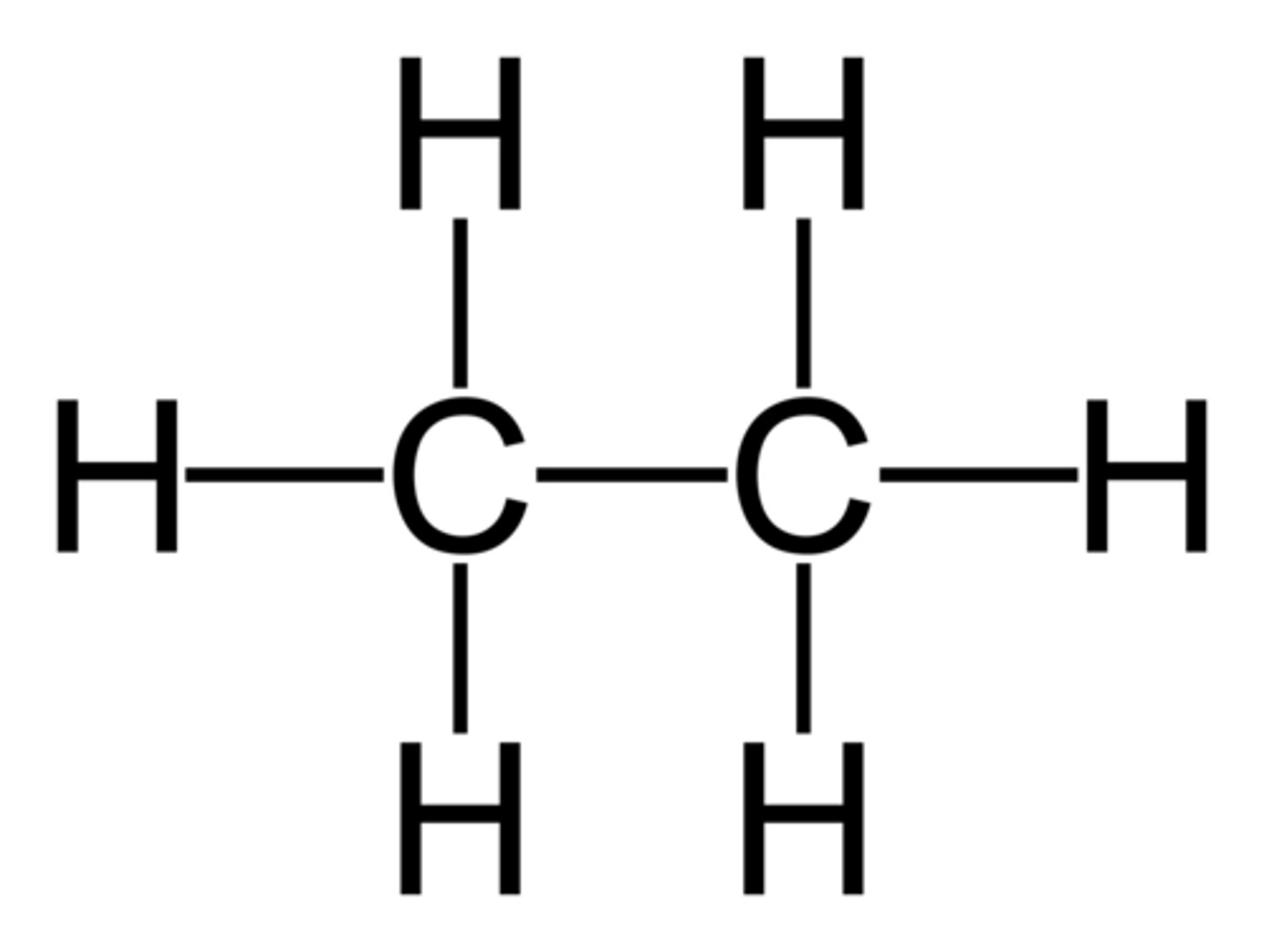
Ethane
C2H6 (Single Bond)
Ethylene
C2H4 (Double Bond)
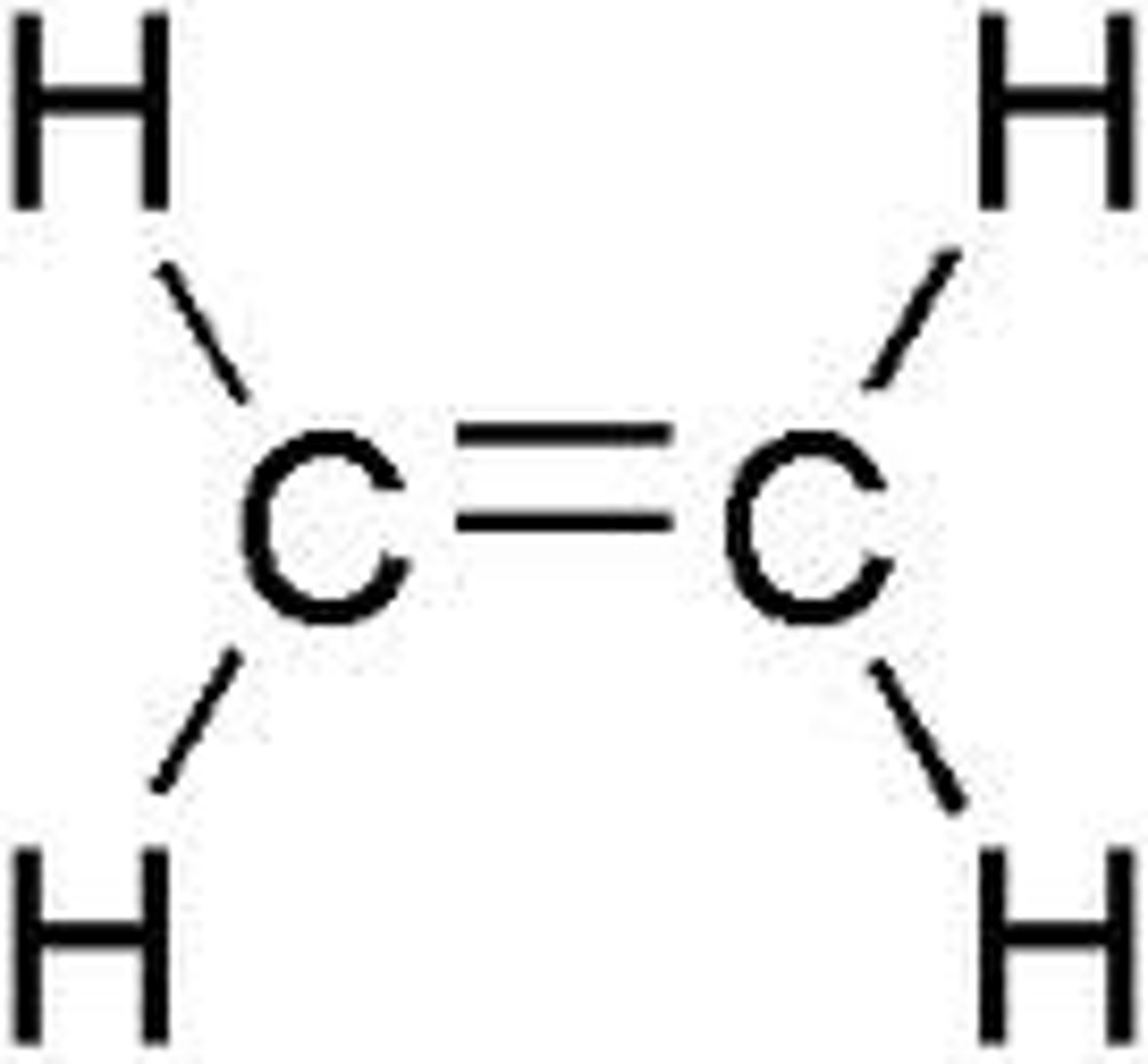
Acetylene
C2H2 (Triple Bond)
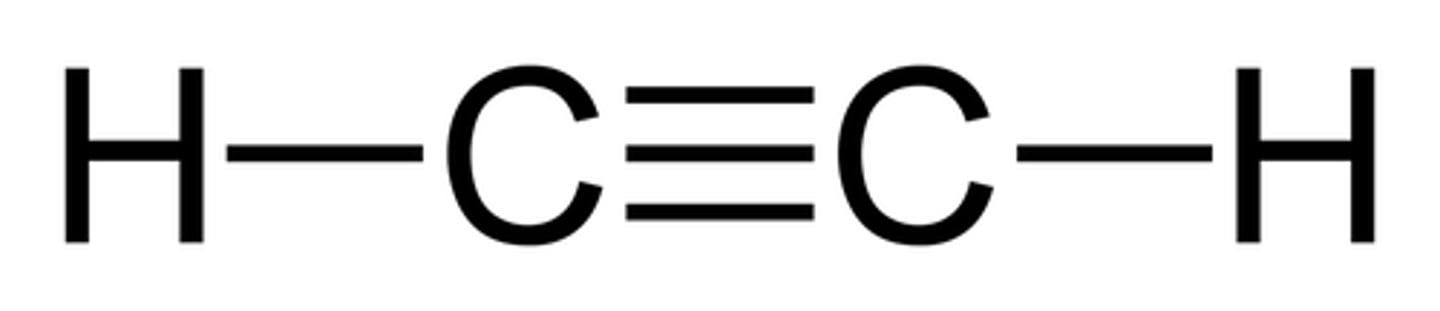
Nitrogen
3 Bonds
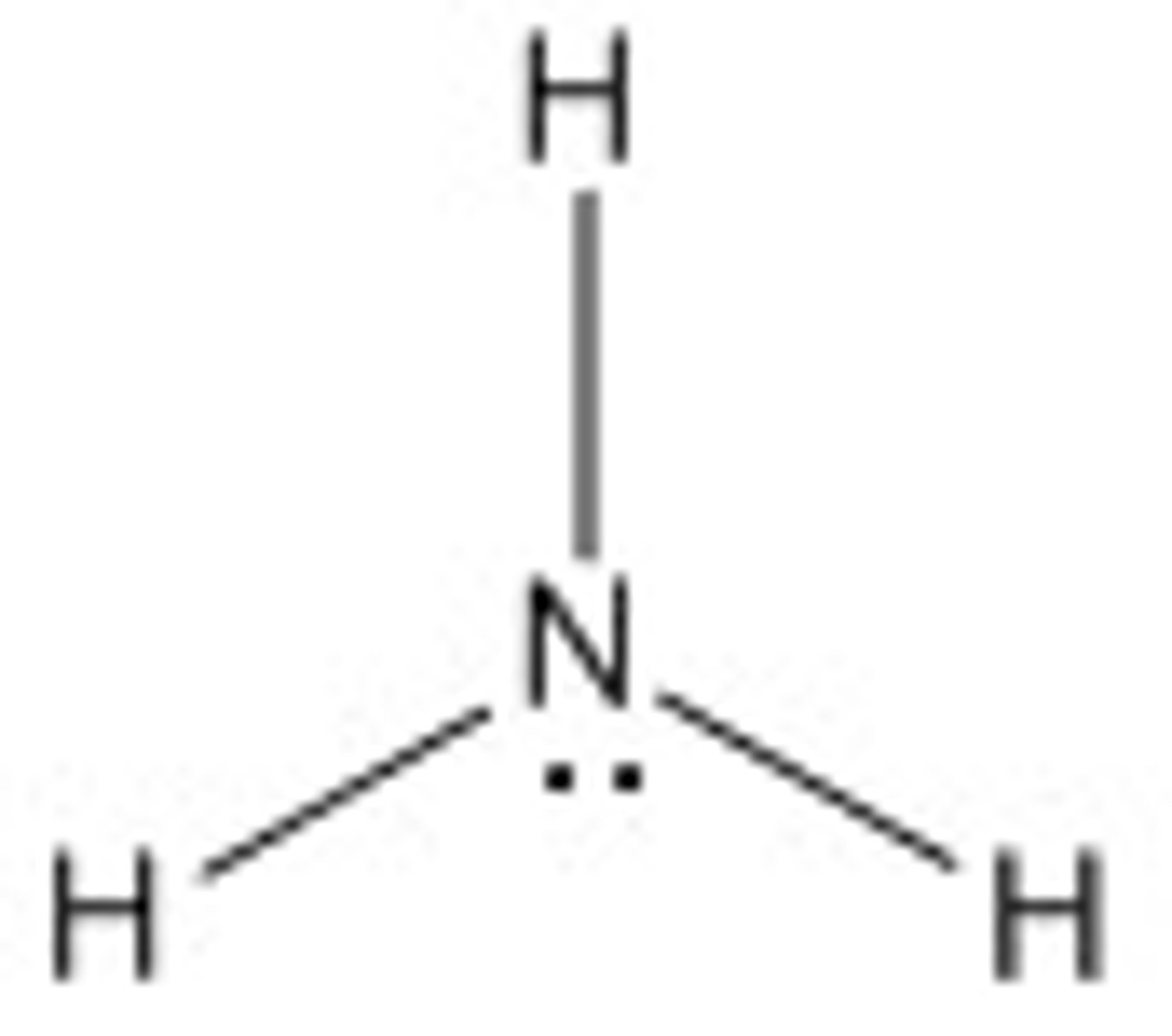
Ammonia
NH3
Aminomethane
CH3NH2
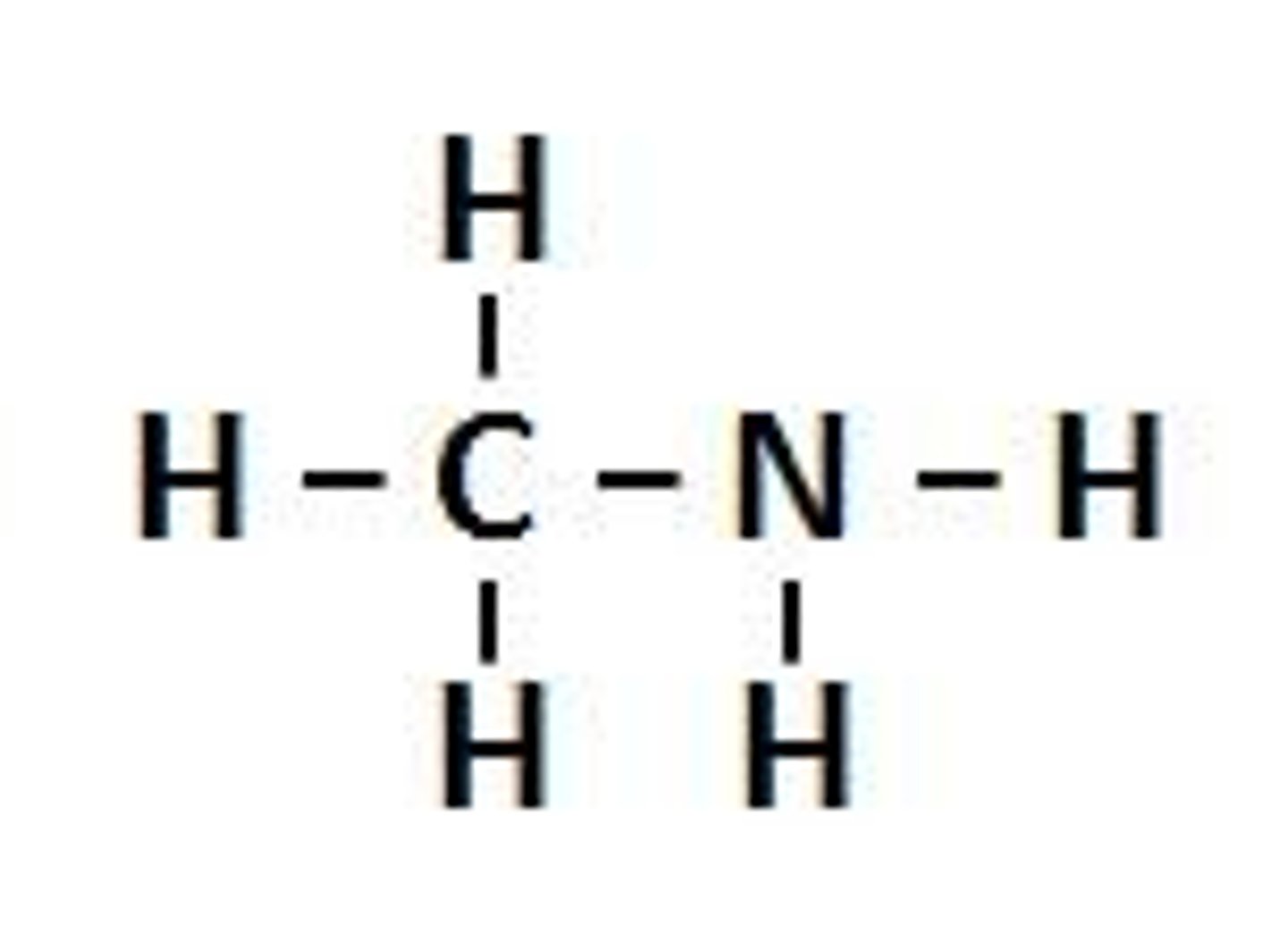
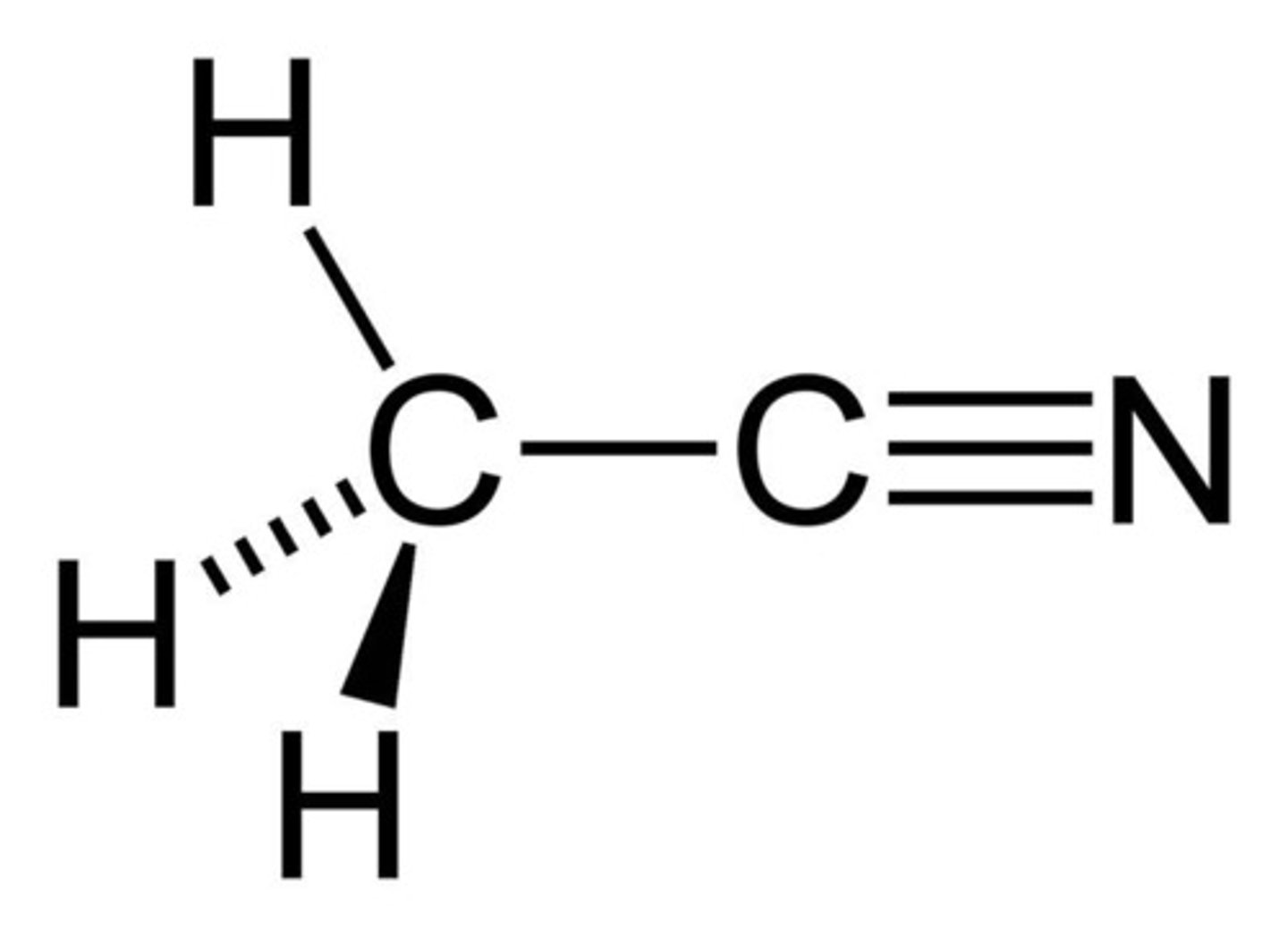
Acetonitrile
CH3CN
Oxygen
2 Bonds
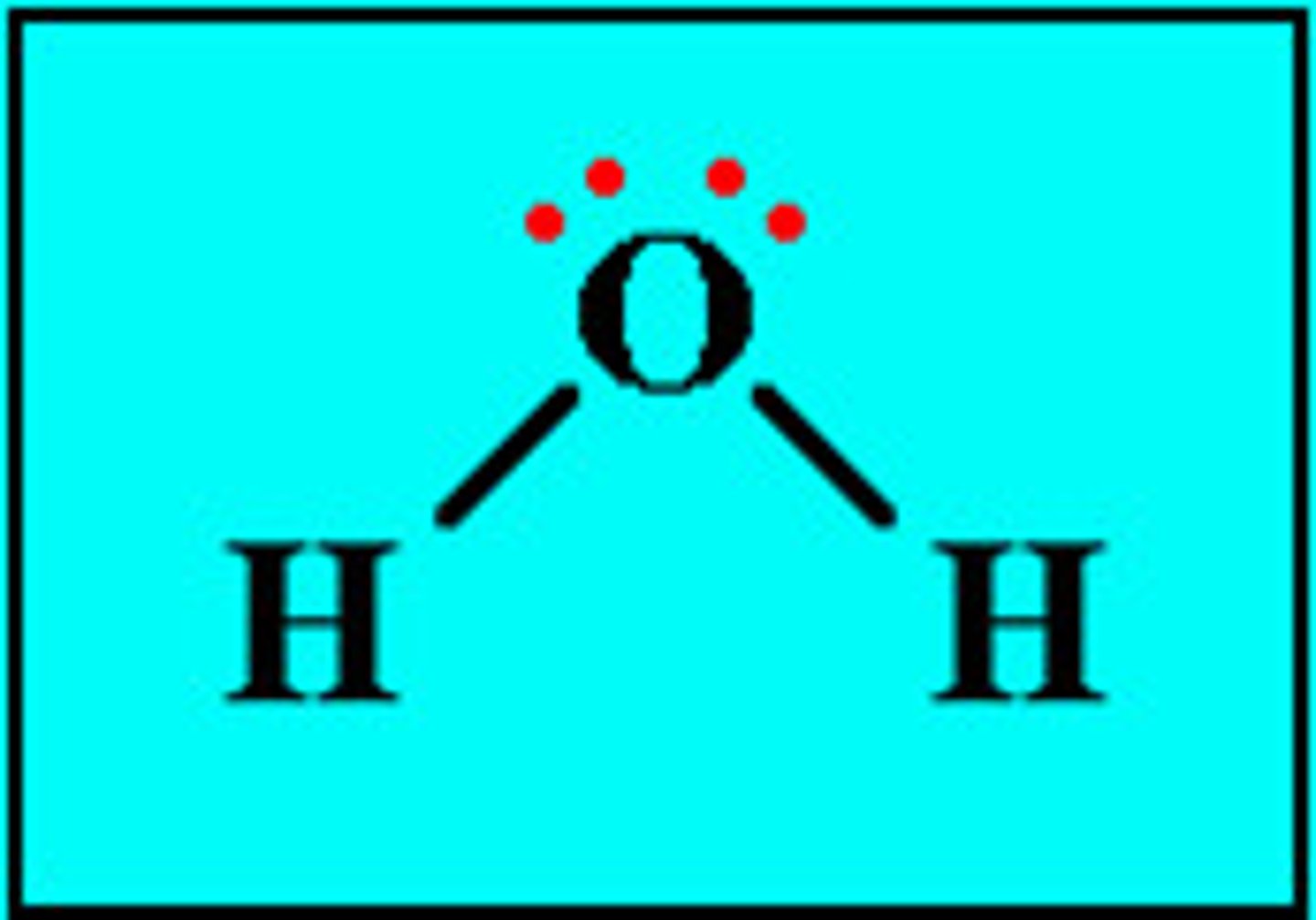
Water
H2O
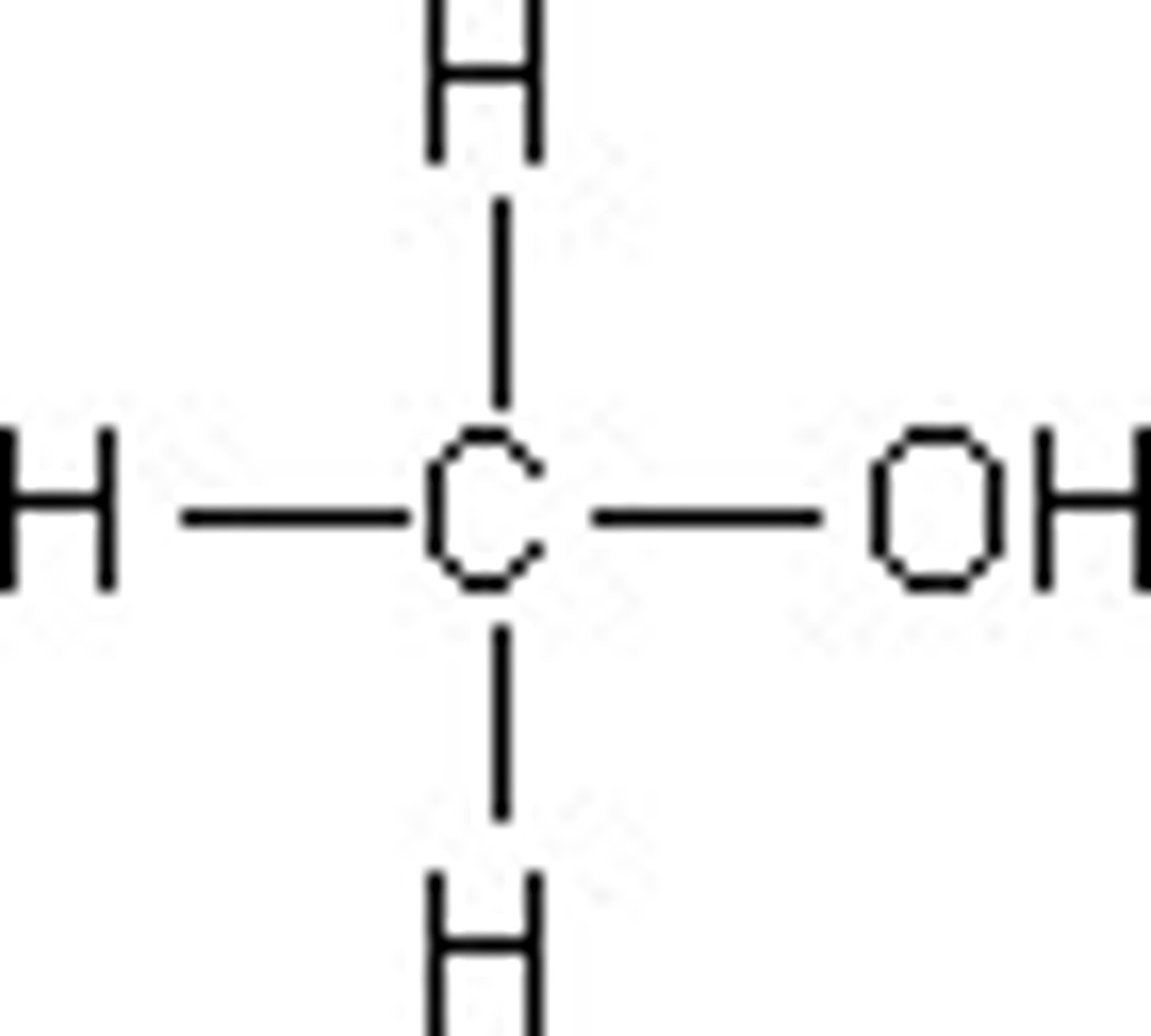
Methanol
CH3OH
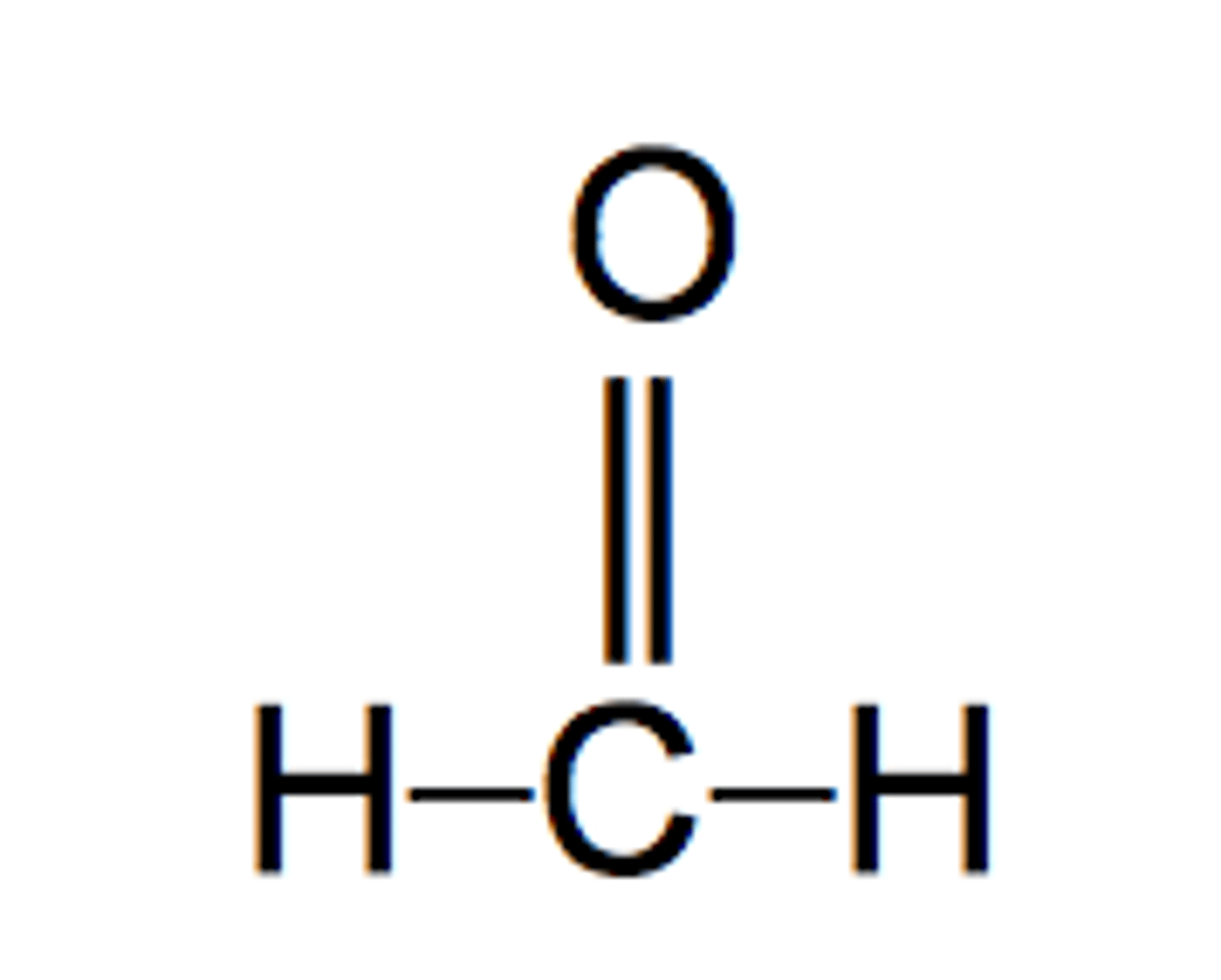
Formadehyde
H2CO
Halogen
(F,Cl,Br,I) 1 Bond
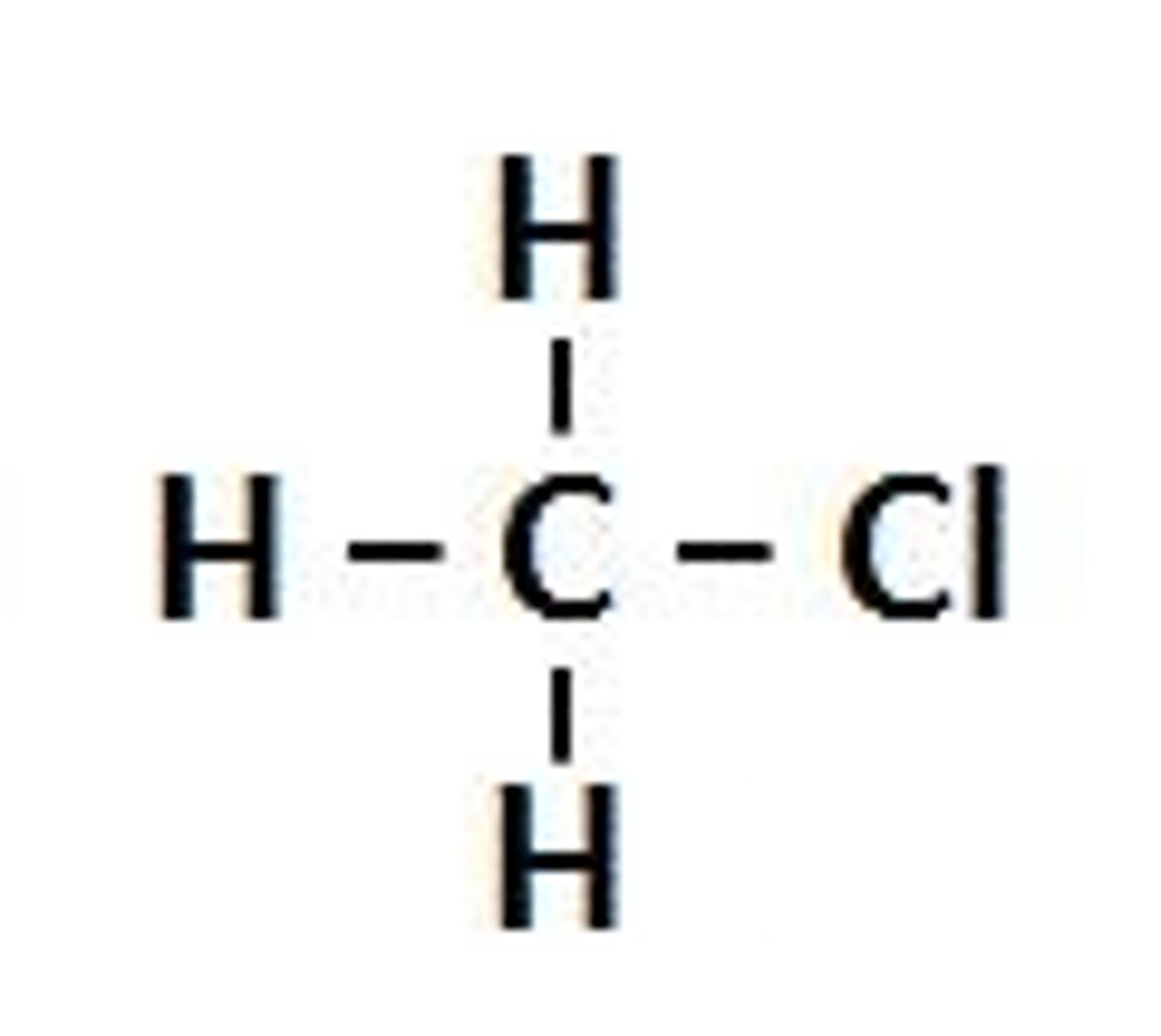
Chloromethane
CH3Cl
bromoethene
C2H3Br
Hydrogen
1 Bond
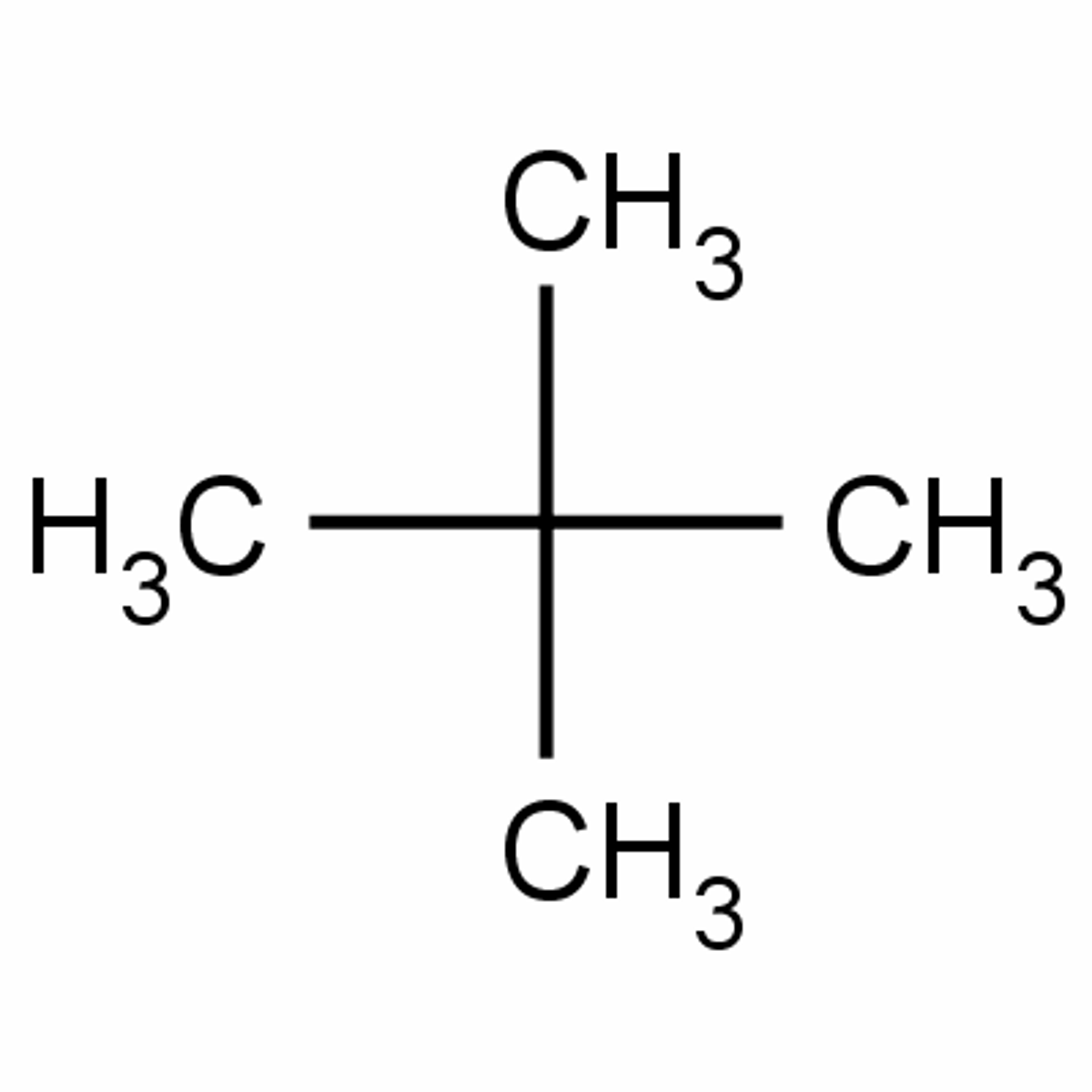
Neopentane
C5H12
Positive Formal Charger
One more bond than normal (loss e-)
Negative Formal Charge
One less bond than normal (GAIN e-)
Charged Carbon Atoms
3 bonds
Electronegativity
Measure how electron density is distributed in covalent bonds. (Tendency to attract atoms to make covalent bonds)
Polarity
Molecules having uneven distribution of charges
partial charges and dipole moment
Partial charge
S+ and S-, covalent bond goes towards S-
Emphasis on character of atom
More electronegative atom is more negative
Dipole moment
Arrow, emphasis on character of bond
Polarizability (Atomic radii)
The weakening attraction between the nucleus and ins outermost electrons as an atom becomes larger
Polarizability trend
Increases down and to the left
Bond Length
Distance between to atoms in a covalent bond.
Vary dependent on Bond order and Atom identity
Bond length trend
Higher bond order = Shorter length
More electronegative = Shorter length
Resonance
A phenomenon that occurs when two objects naturally vibrate at the same frequency. Only electrons move for resonance
Quantum Number
n = 1,2,3,4
Angular Momentum Quantum Number
(l) indicates the shape of the orbital
n - 1
Magnetic Quantum Number
ml (-l to l)
Spin Quantum number
-Ms
+1/2 or -1/2
Pauli Exclusion Rule
two e- sharing an orbital MUST have opposite spins
Hund's Rule
e- fill in single first THEN in pairs to minimize electron-electron repulsion in an atom's orbitals.
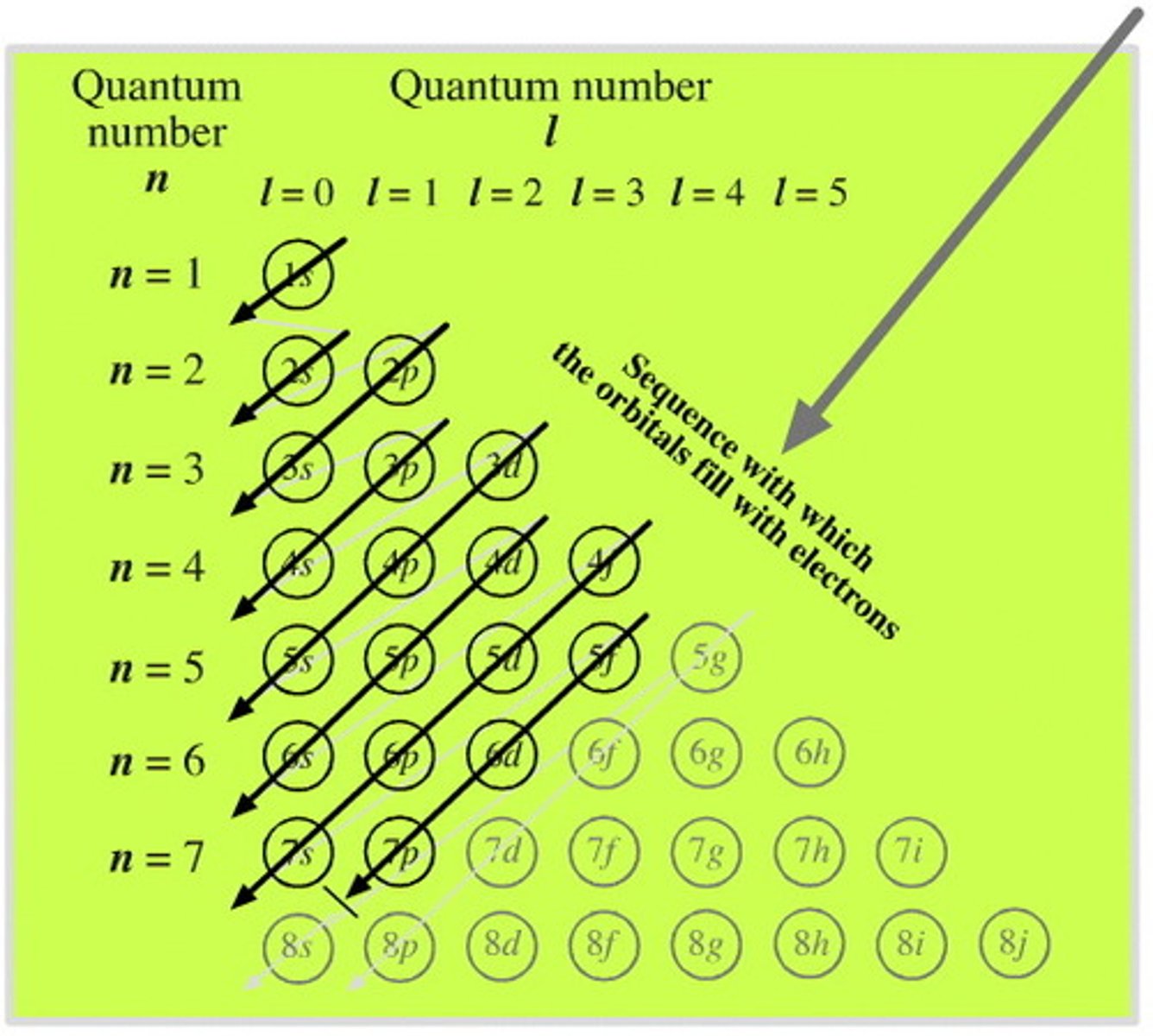
Aufbau Principle
An electron occupies the lowest-energy orbital that can receive it n+0.7(l) FIRST (ie. 1s)
Valance Electrons
Electrons in the outermost shell
Inner Shell/Core Electrons
Electrons in lower numbered shells than valance
sp
Linear, 2 electron pairs, 180*
sp2
Trigonal Planer, 3 electron pairs, 120*
sp3
Tetrahedral, 4 electron pairs, 109.5*
Sigma bonds
Single covalent bond
Pi bonds
Additional bonds after a single bond
double (1)
triple bond (2)
Solid wedge line
Line projects out of the plane of a page
Dashed Lines
Line recedes being the plane of the page
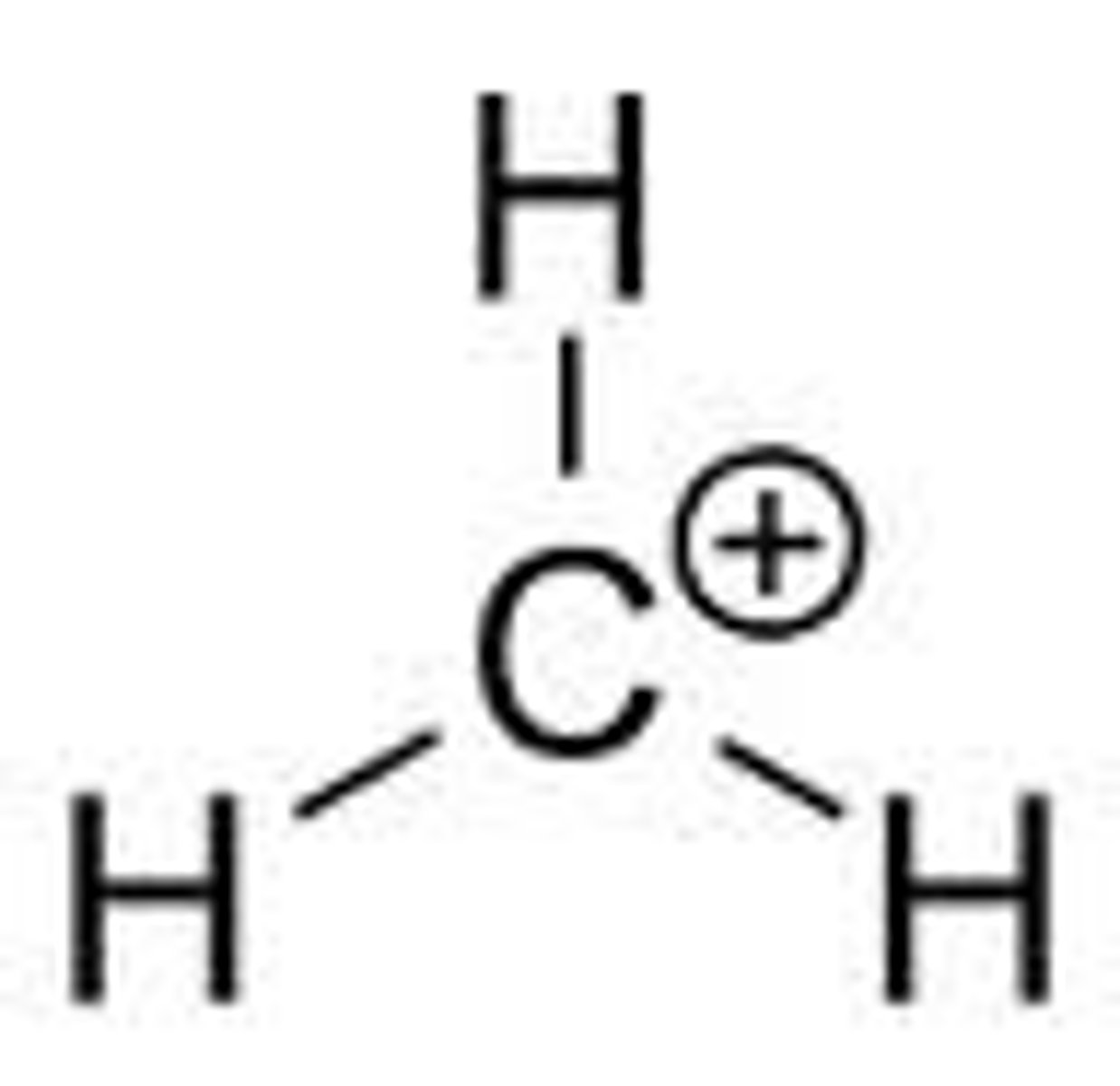
Methyl Carbocation
CH3+
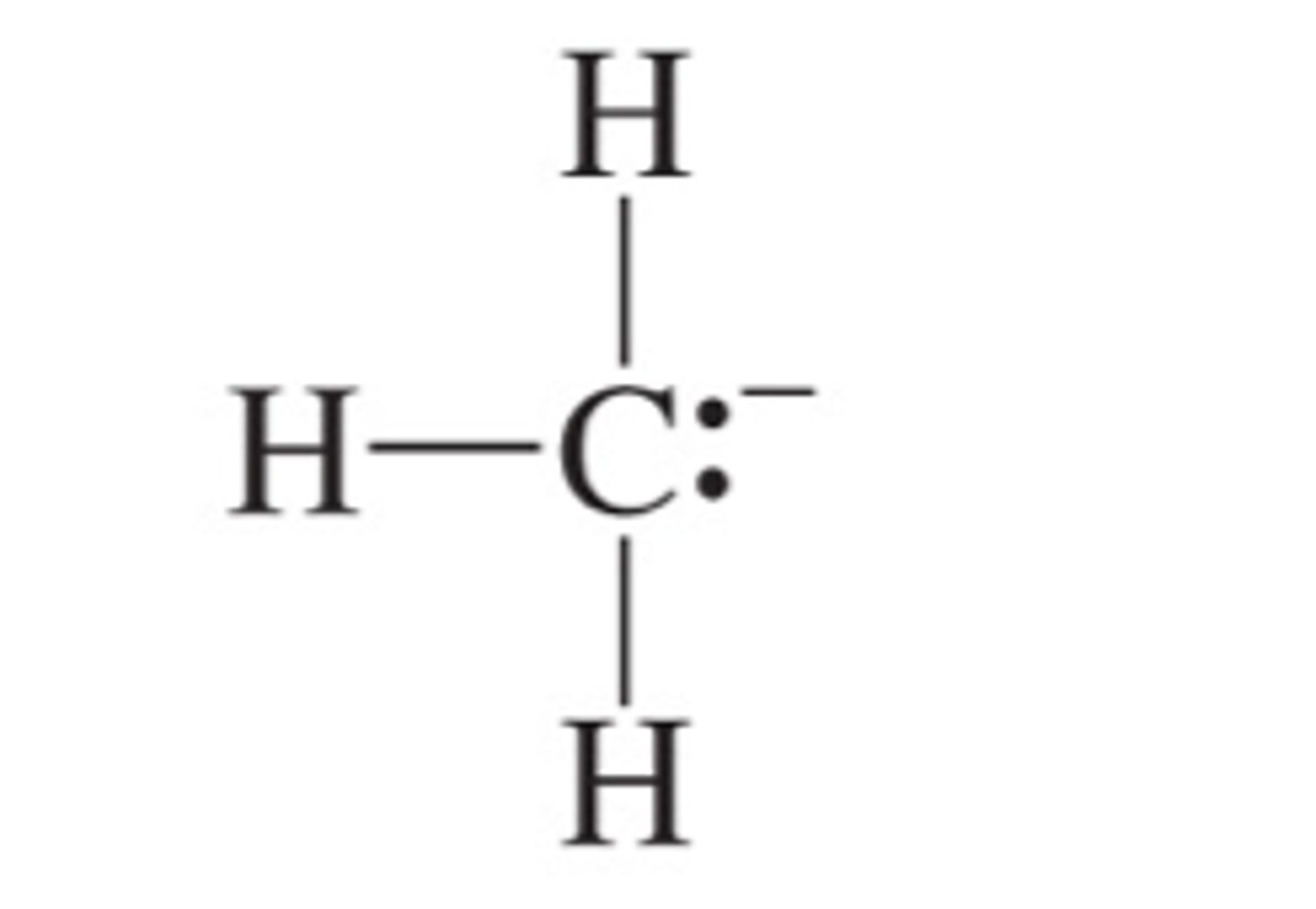
Methyl Carbanion
CH3-
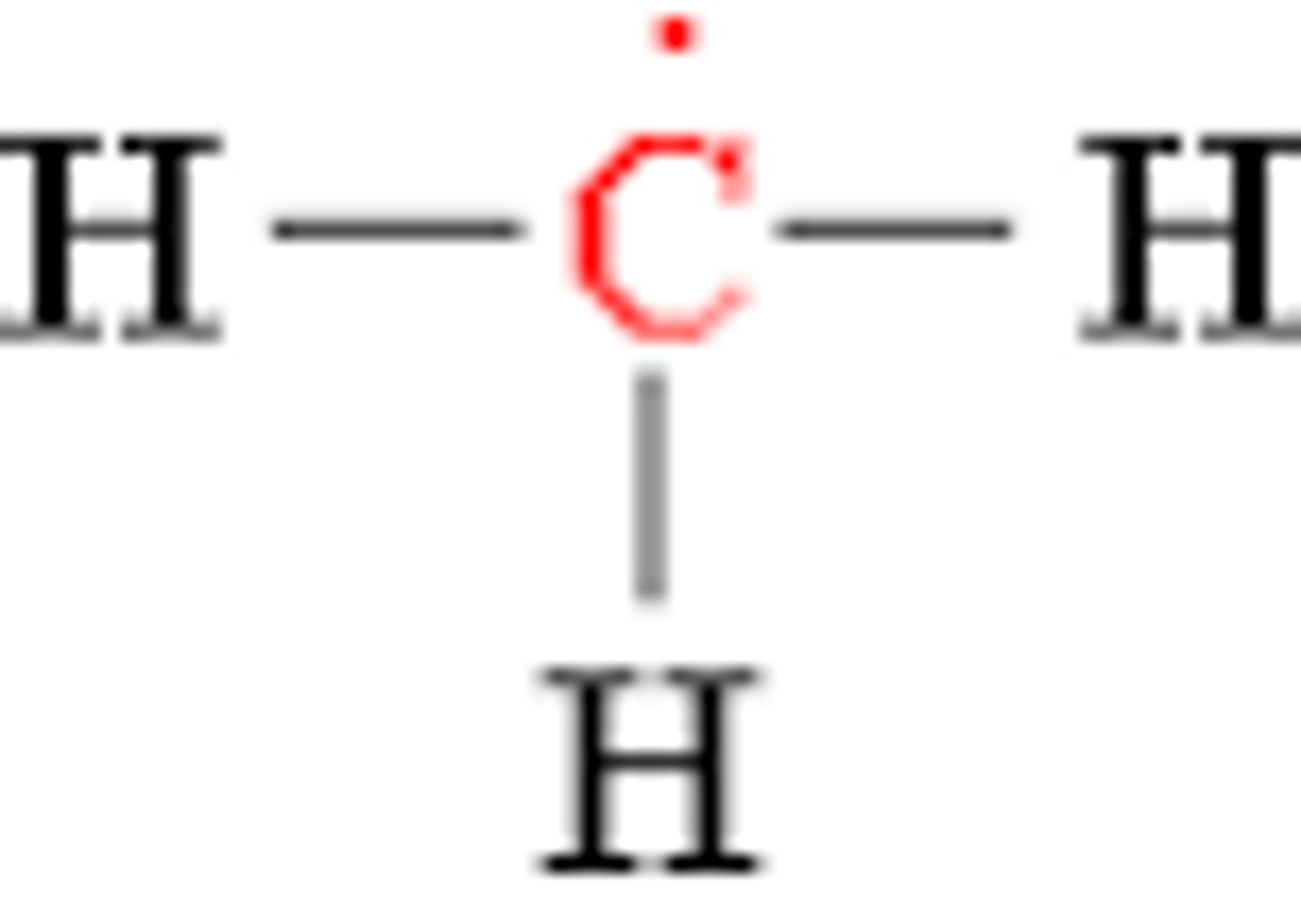
Methyl Radical
CH3
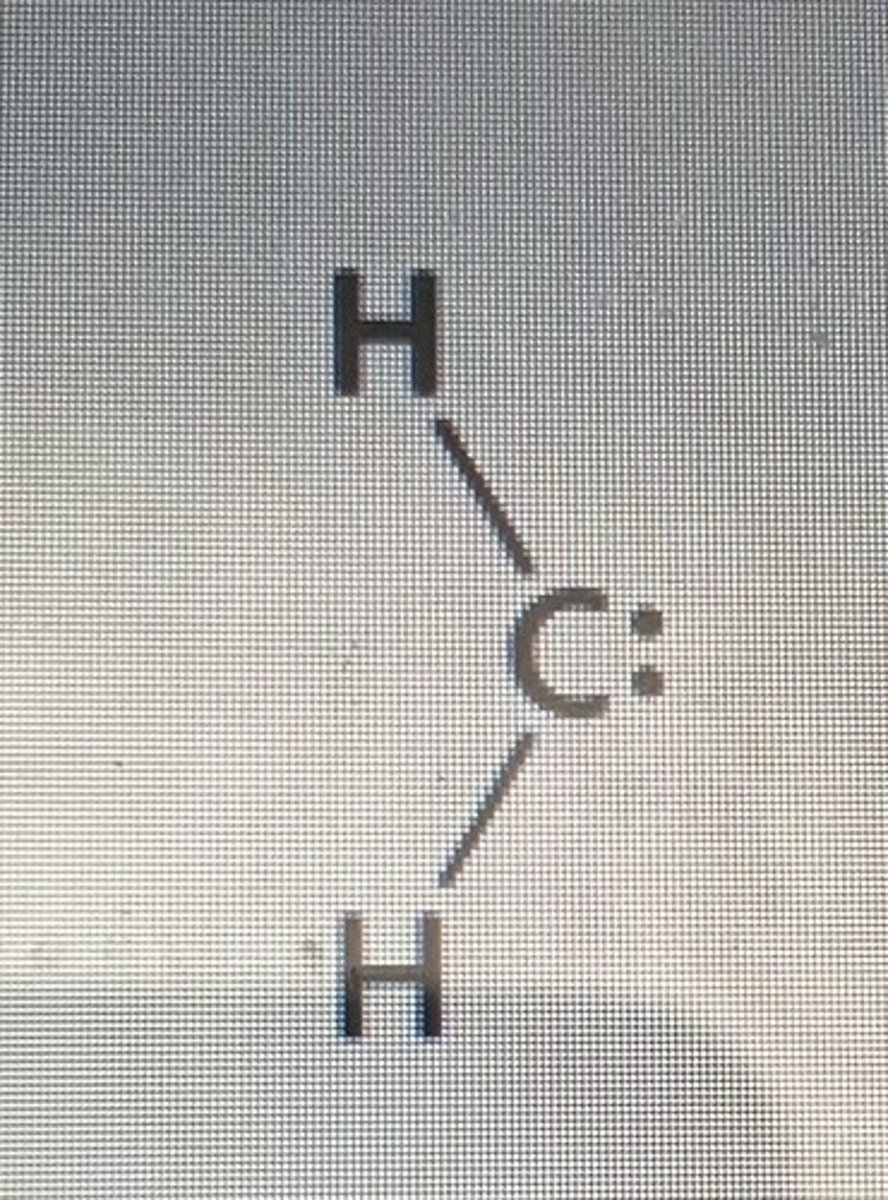
Methylene Carbene
CH2
Order for naming Molecules
1. Substituents, 2. Compound Root, 3. Multiple-bond index, 4. Principle Functional Group
Names of Alkanes Order
1. Methane, 2. Ethane, 3. Propane, 4. Butane, 5. Pentane, 6. Hexane, 7. Heptane, 8. Octane, 9. Nonane, 10. Decane
Cyclo- Prefix
Ring
-ane
Only Single bonds
-ene
One Double bond
-yne
One Triple Bond
-diene
Two double bonds
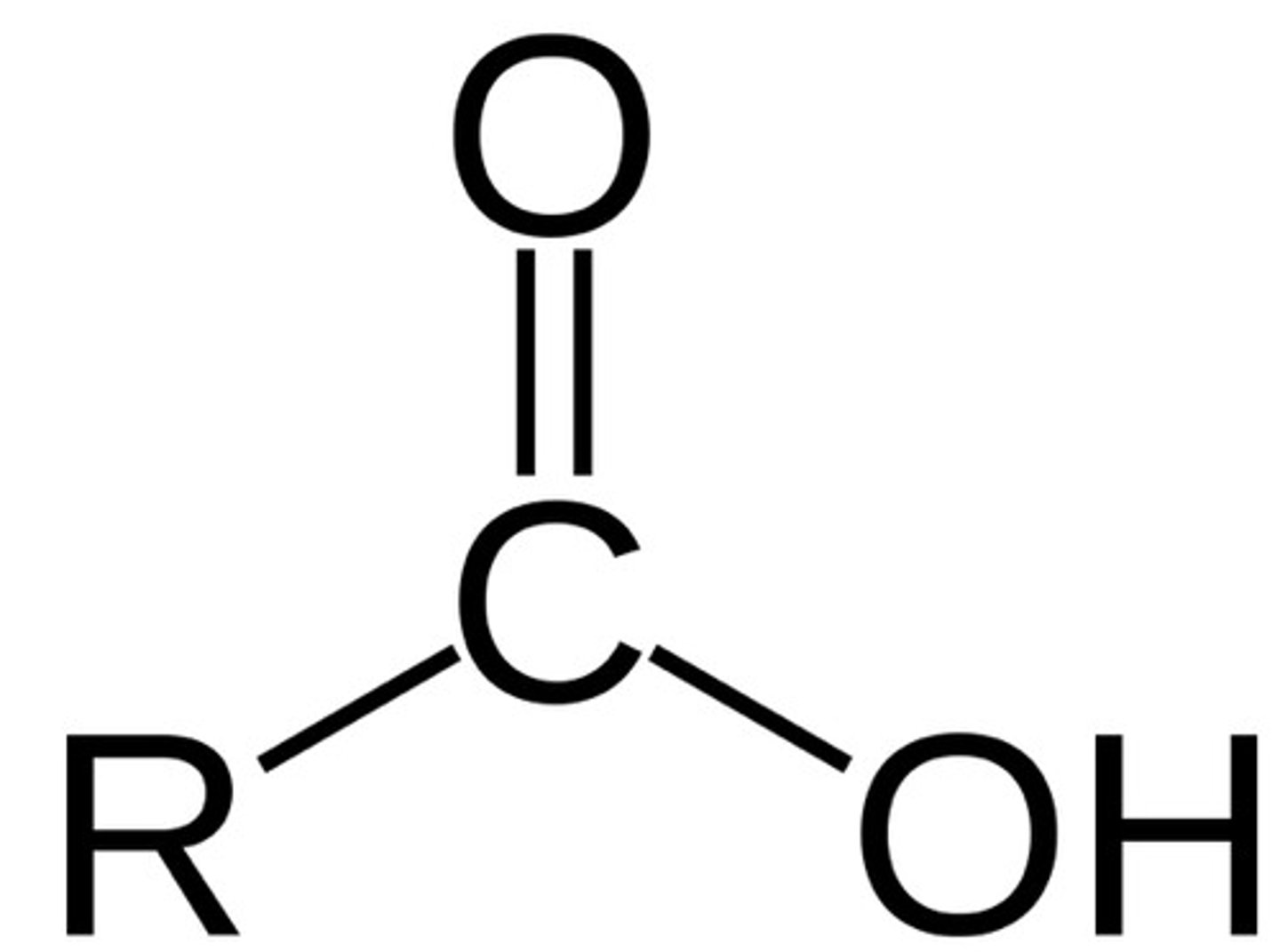
1. Carboxylic Acid
-COOH
2. Sulfonic Acid
-SO3H
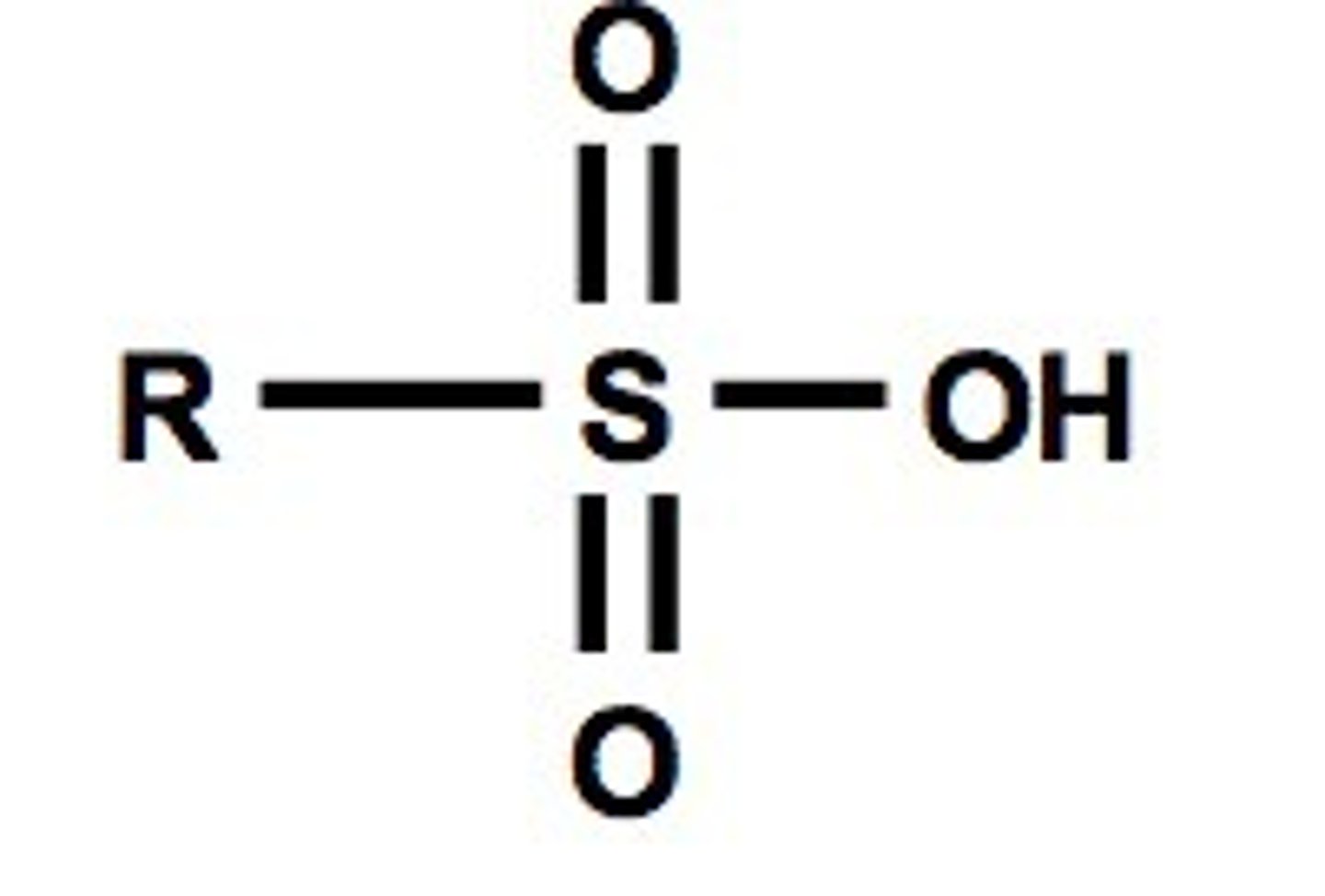
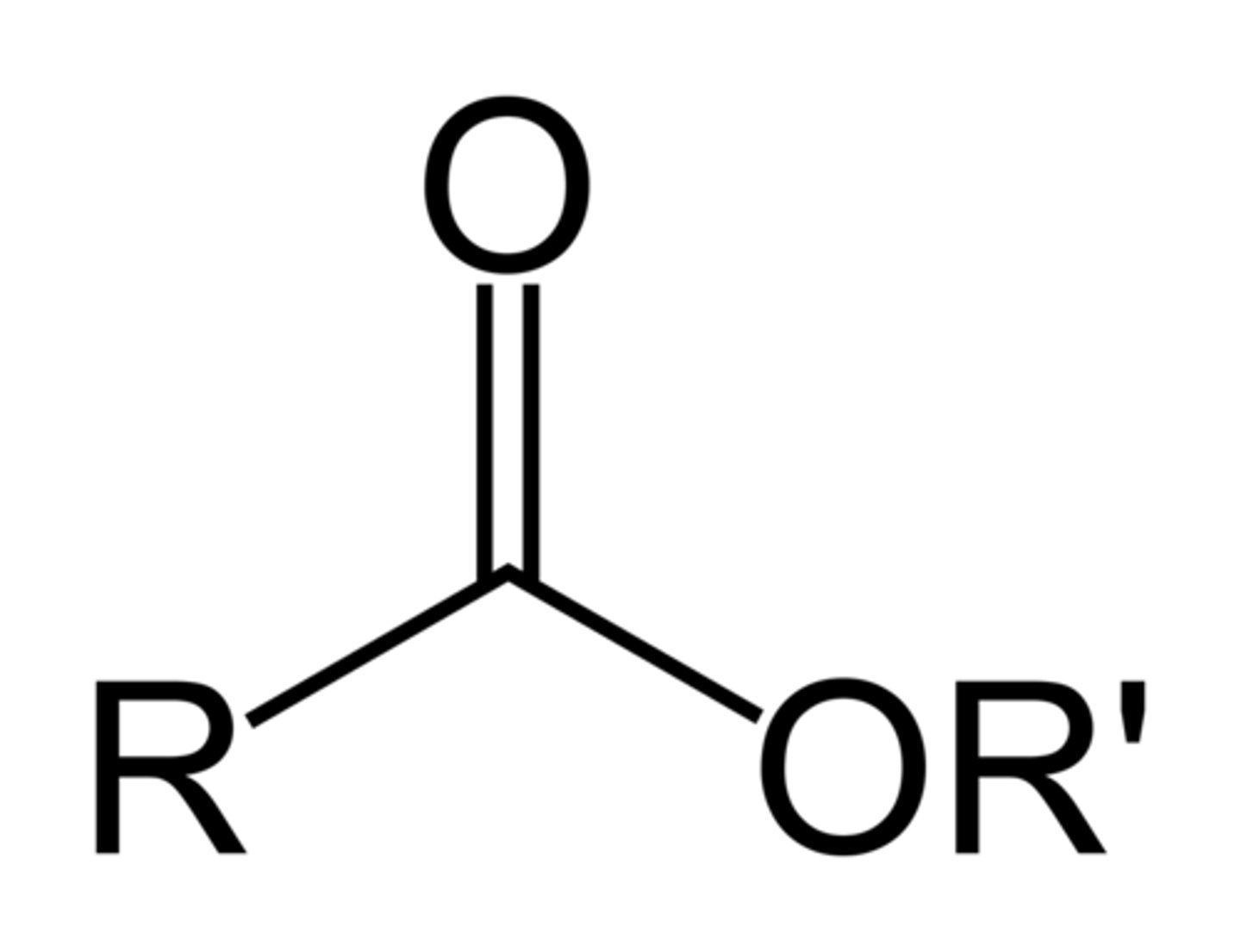
3. Ester
-COO-
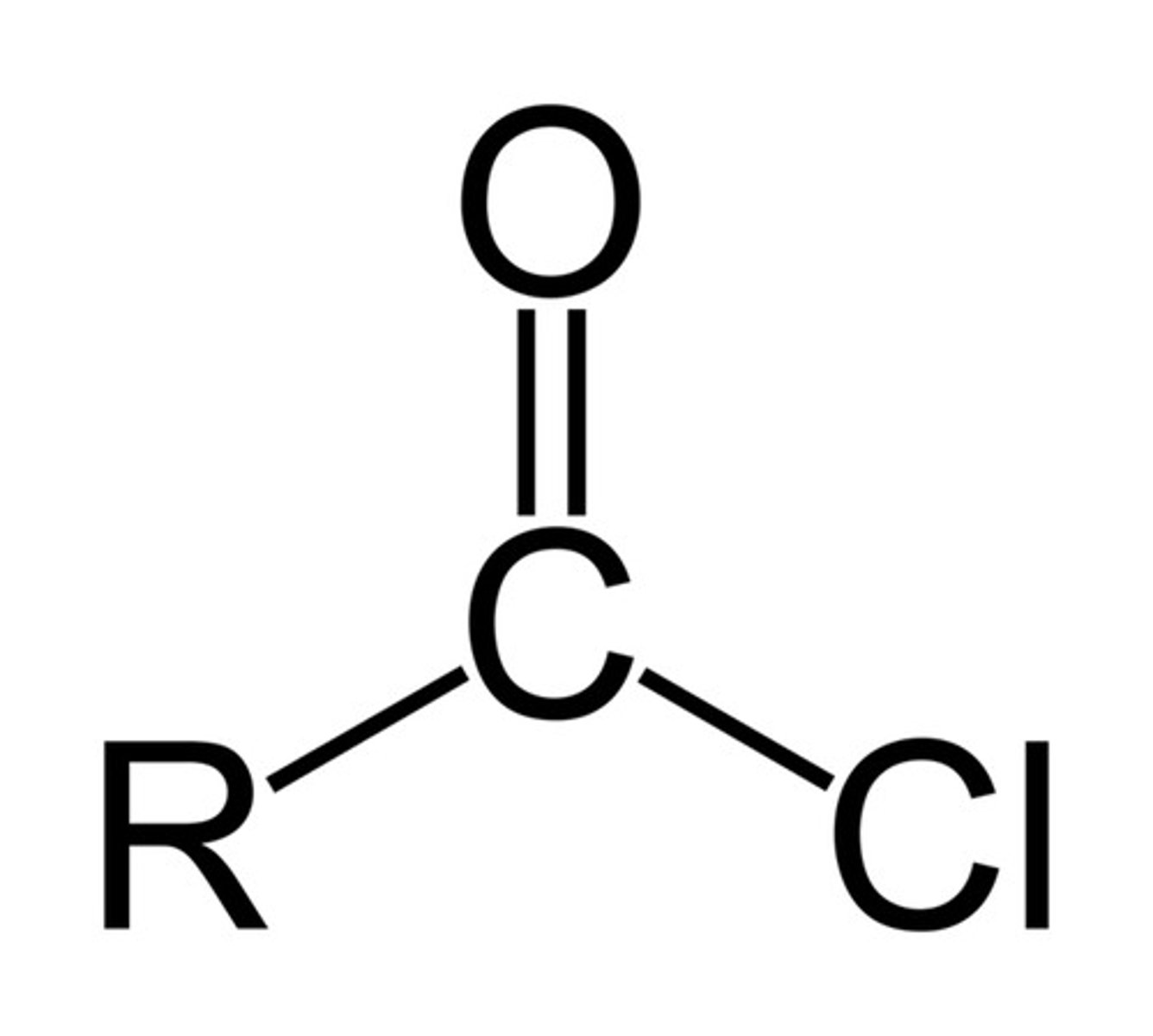
4. Acid Chloride
-COCl
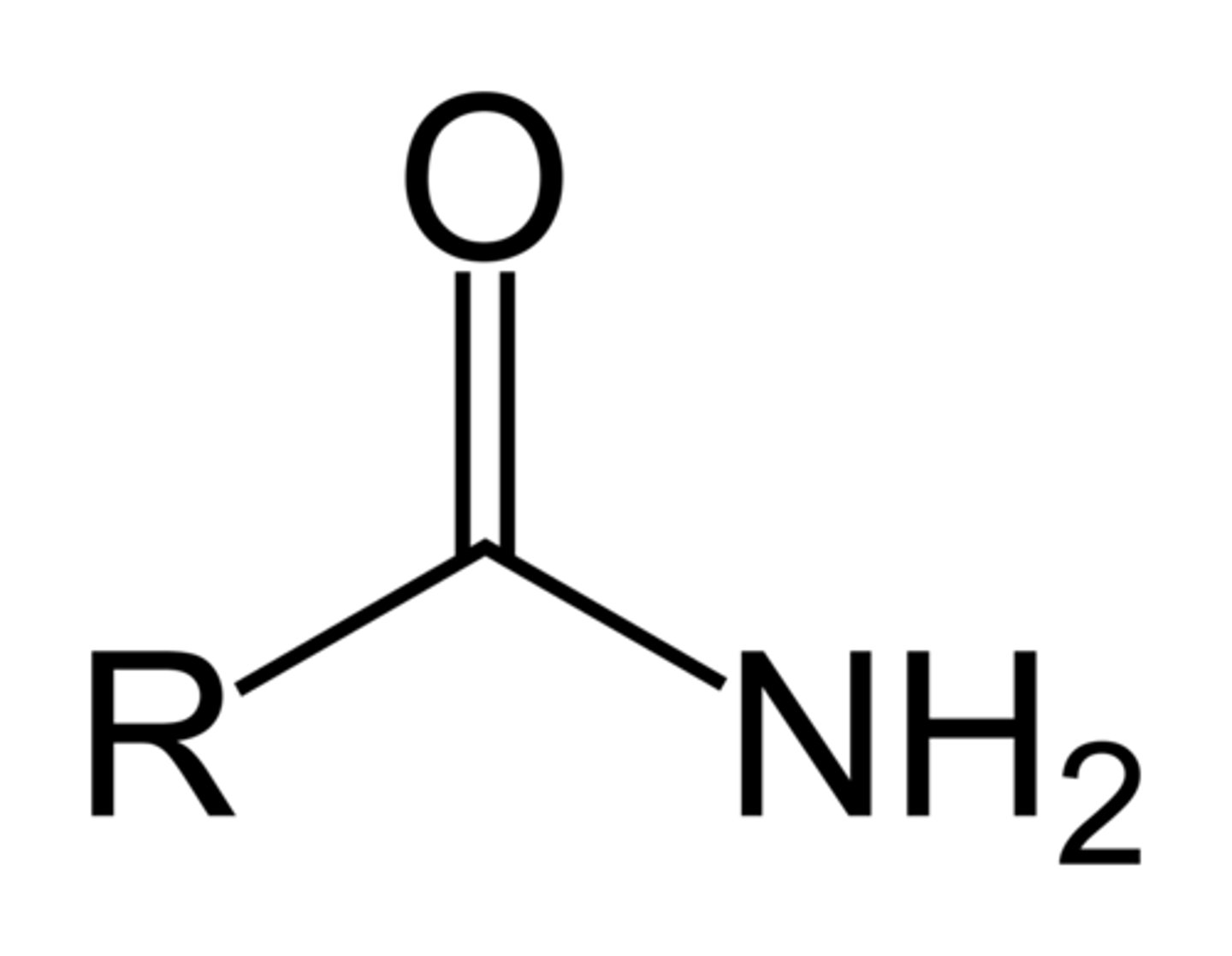
5. Amide
-CONH2
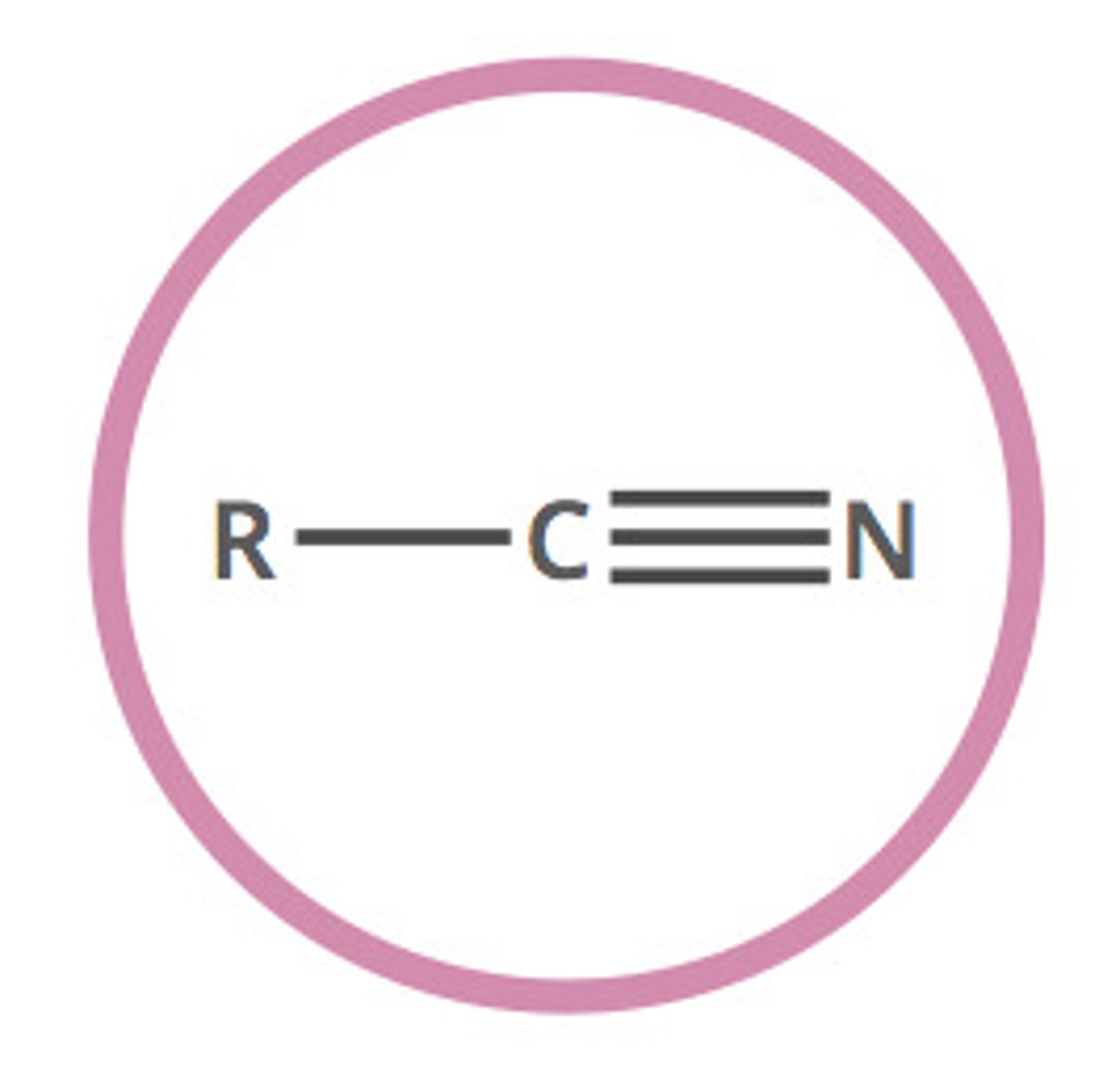
6. Nitrile
-CN
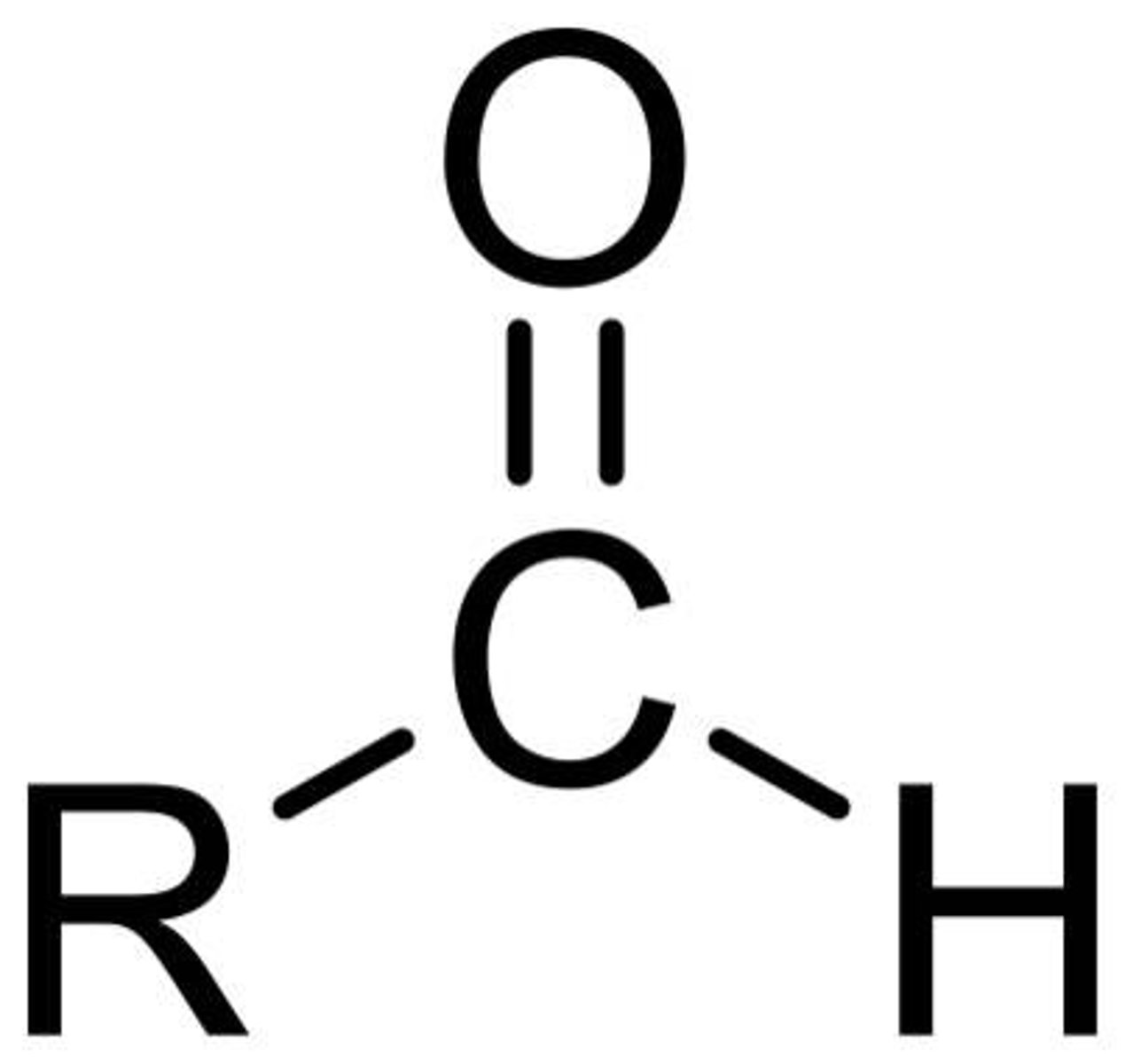
7. Aldehyde
-CHO
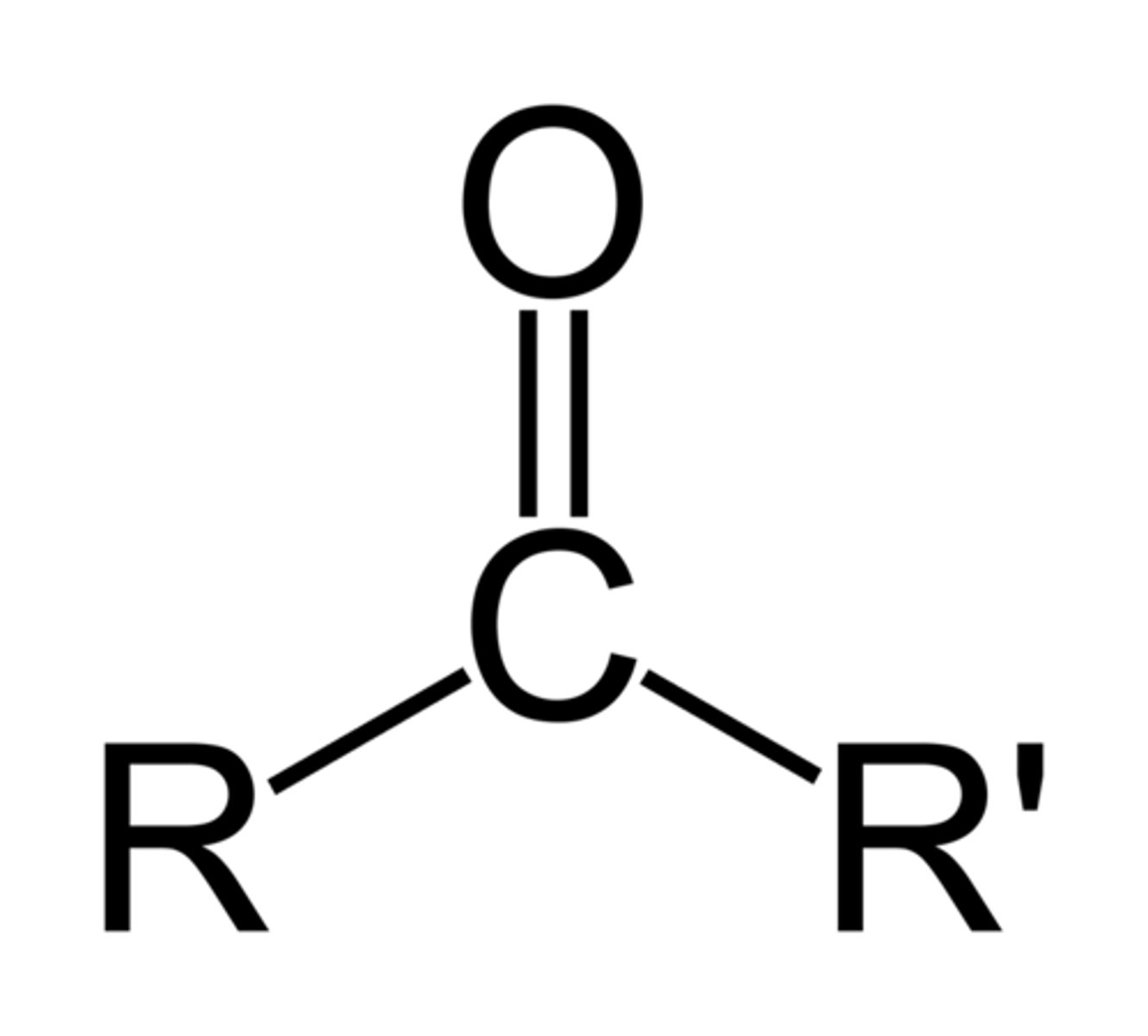
8. Ketone
-CO-
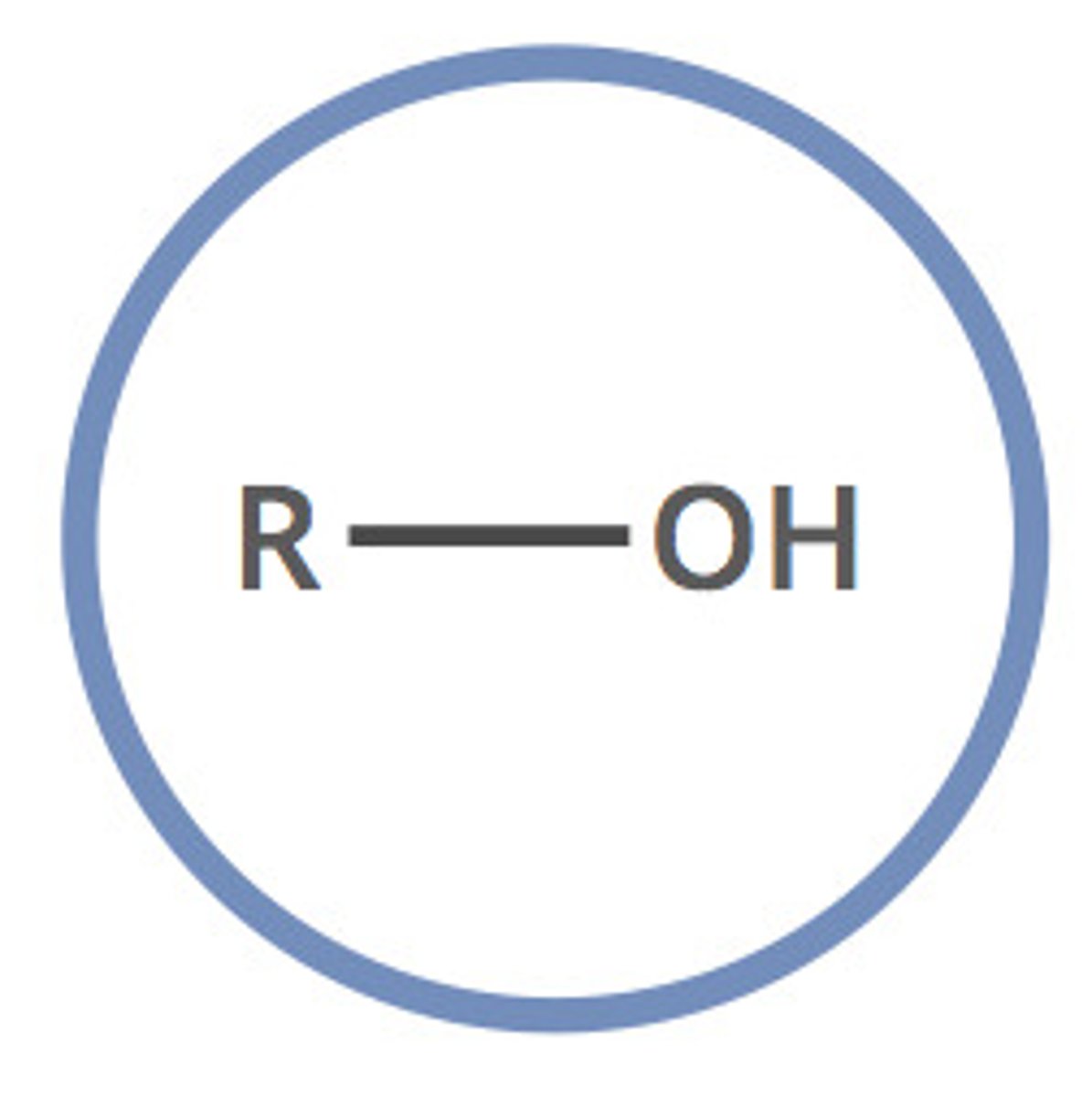
9. Alcohol or Phenol
-OH
10. Thiol
-SH
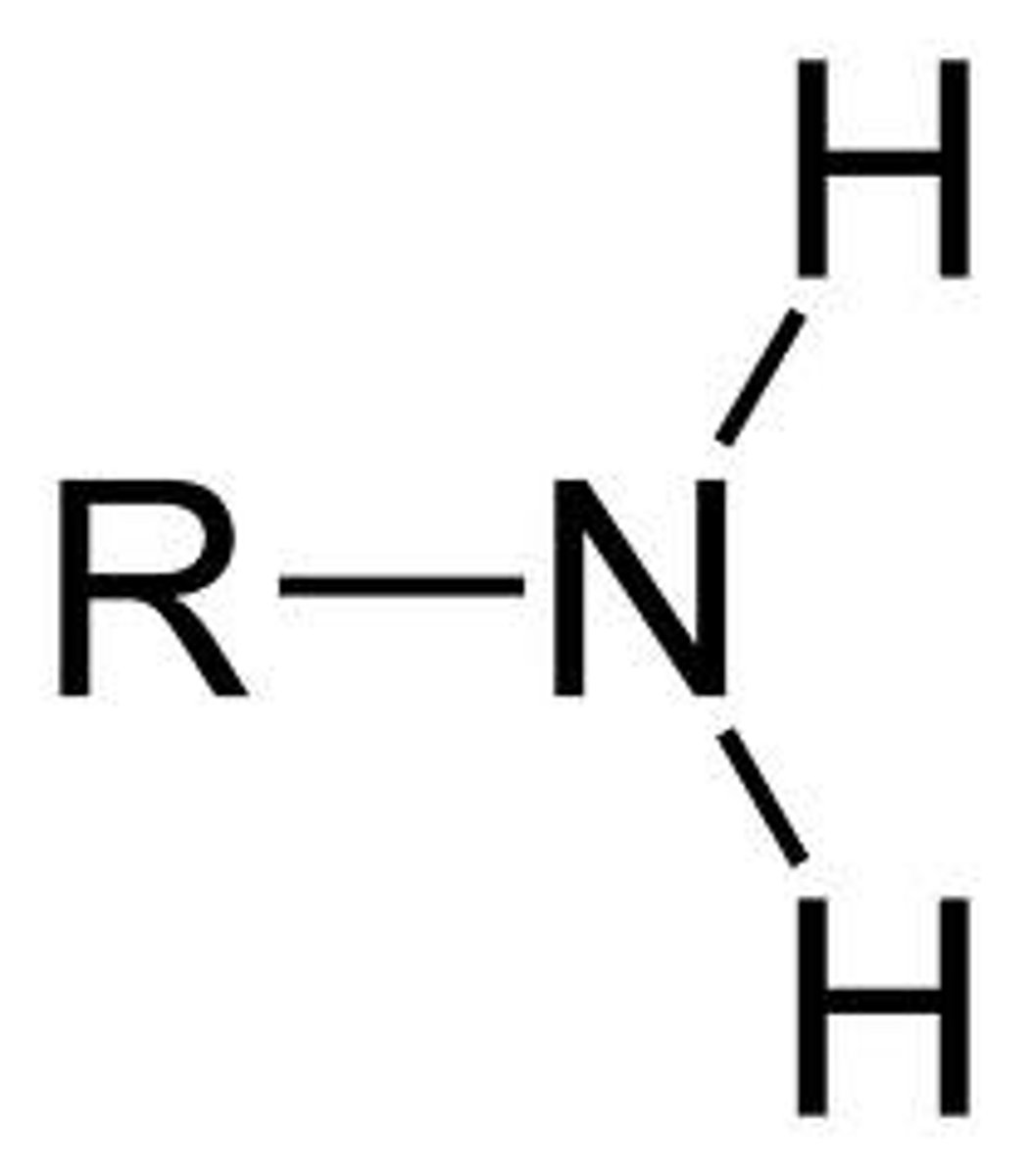
11. Amine
-NH2
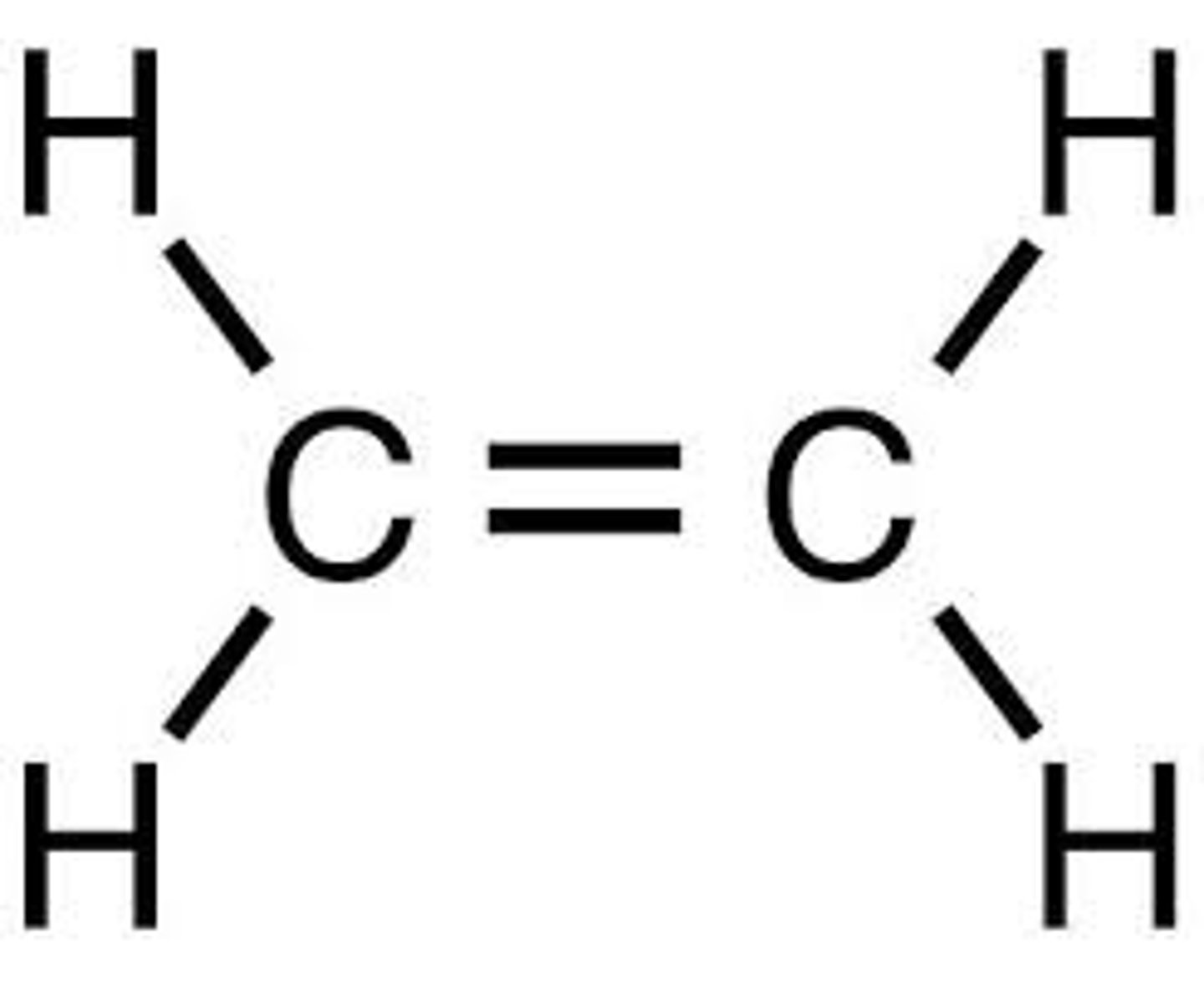
12. Alkene
Double Bond
13. Alkyne
Tripe Bond
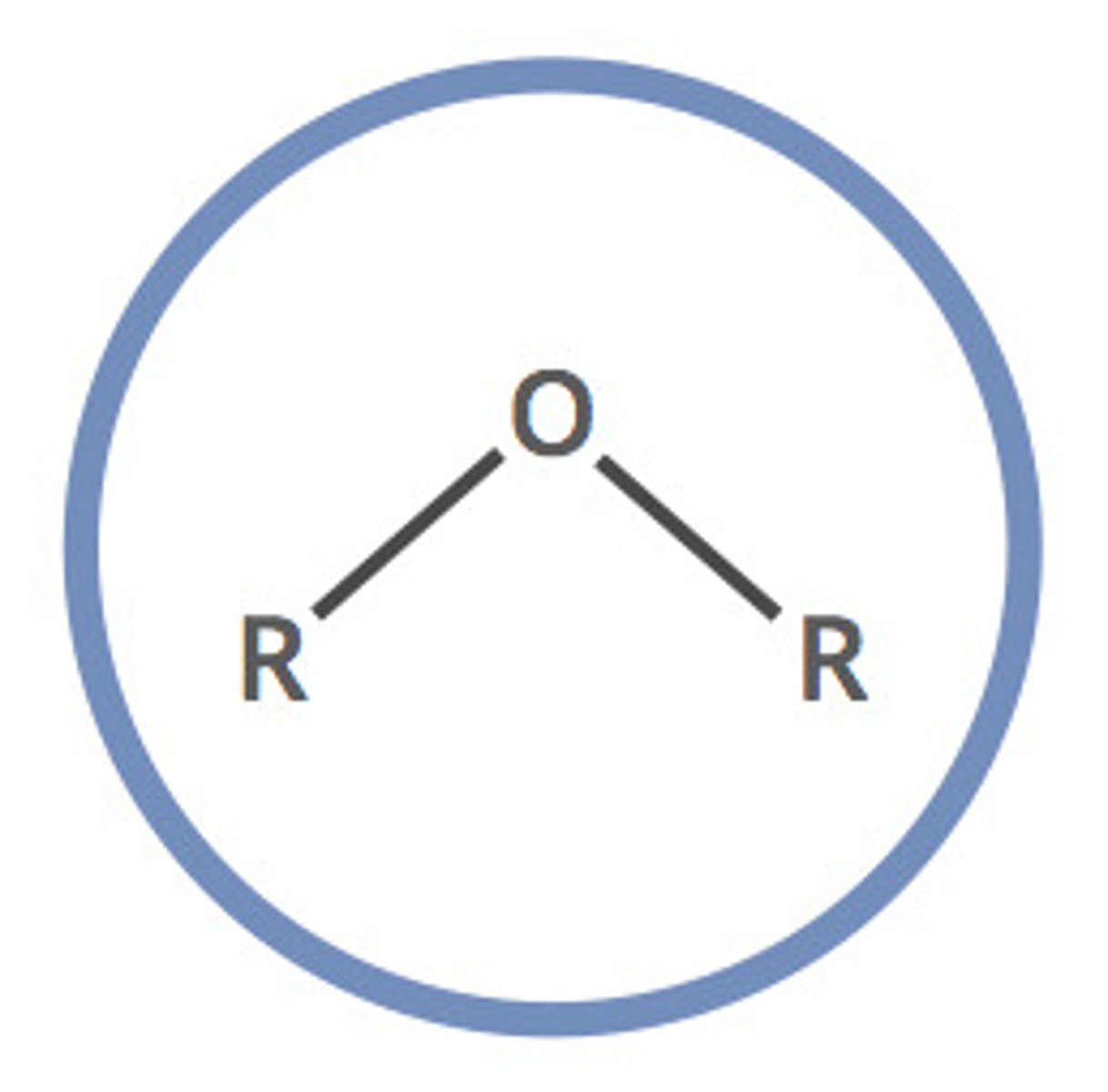
14. Ether
-O-
15. Benzene
6 Carbons with 3 double bonds
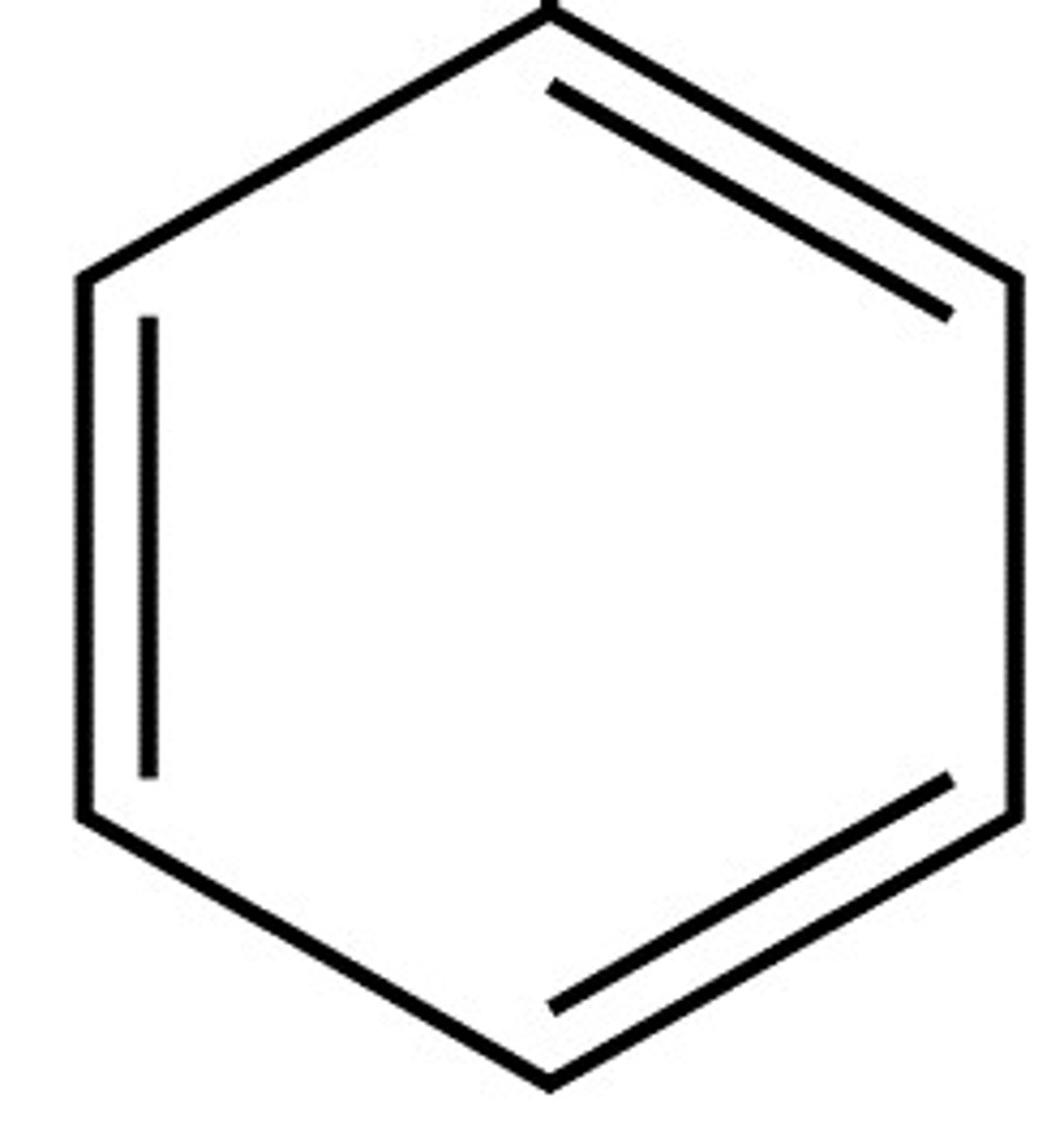
Alkyl-
-R
Alkoxy-
-OR
Acetyl-
-COCH3
Amino-
-NH2
Bromo-
-Br
Carboxy-
-COOH
Chloro-
-Cl
Cyano-
-C Triple bond N
Fluoro-
-F
Formyl-
-COH
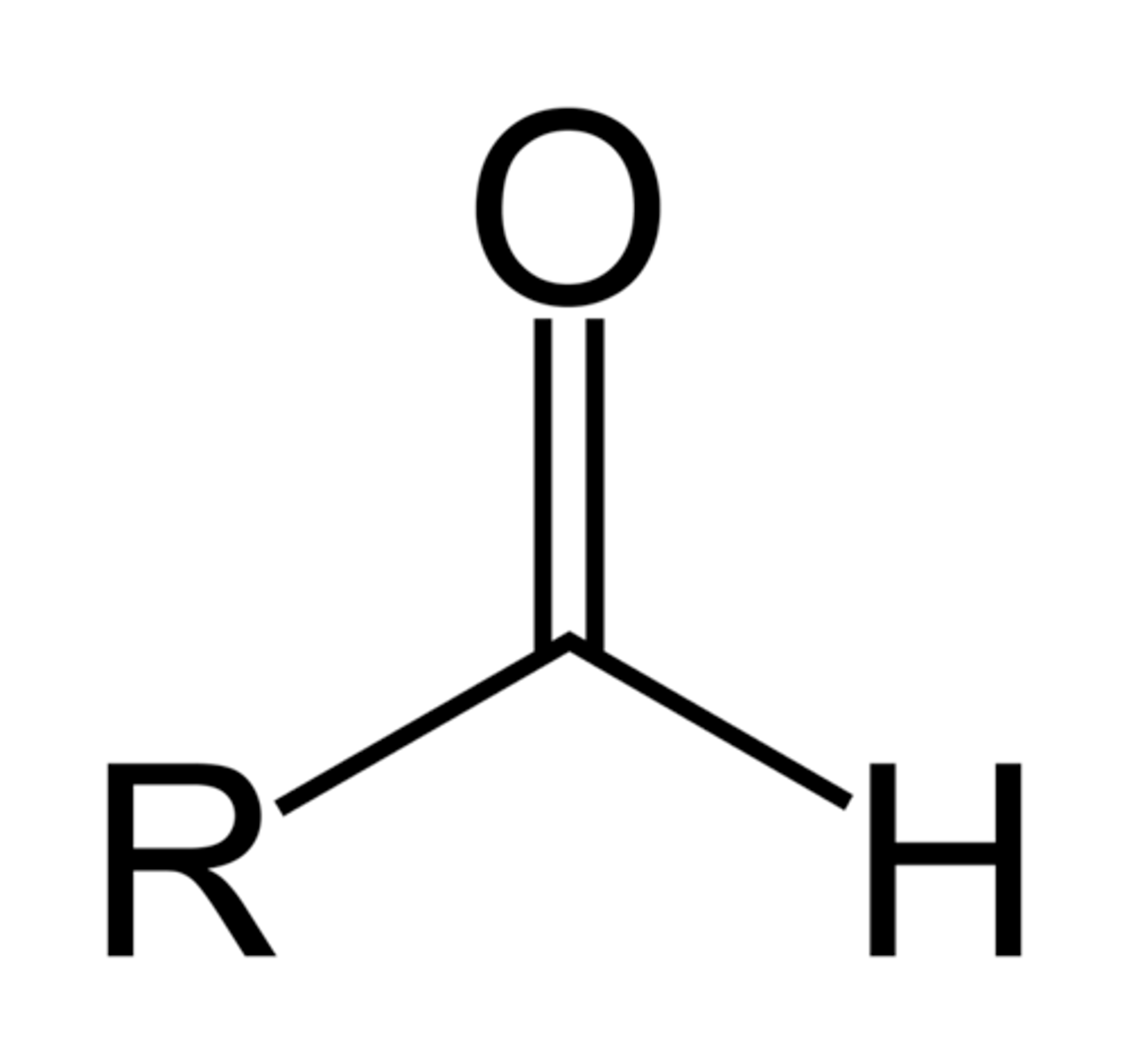
Hydroxy-
-OH
Iodo-
-I
Nitro-
-NO2
Mercapto
-SH
Oxo-
=O
Phenoxy-
-O-Benzene
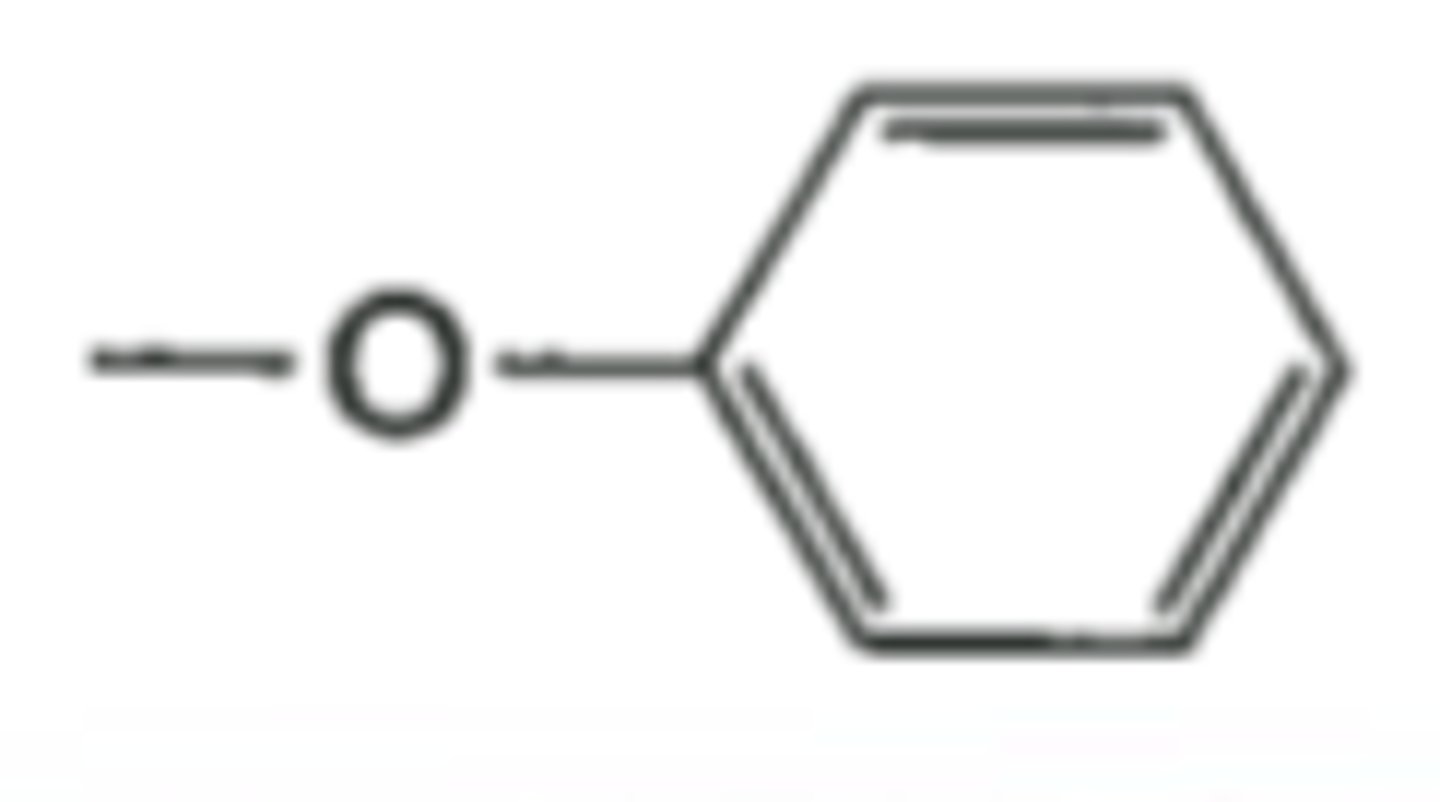
Electronegativity trend
INCREASE: up and to the right
Sulfur (S)
6 ve-
Phosphorus (P)
5 ve-
Carbon (C)
4 ve-
Boron (B)
3ve-
Potassium (K)
1 ve-
Sodium (Na)
1ve-
Beryllium (Be)
2ve-
Magnisum (Mg)
2ve-