3.6.4 Homeostasis - WATER POTENTIAL
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
urine system
.
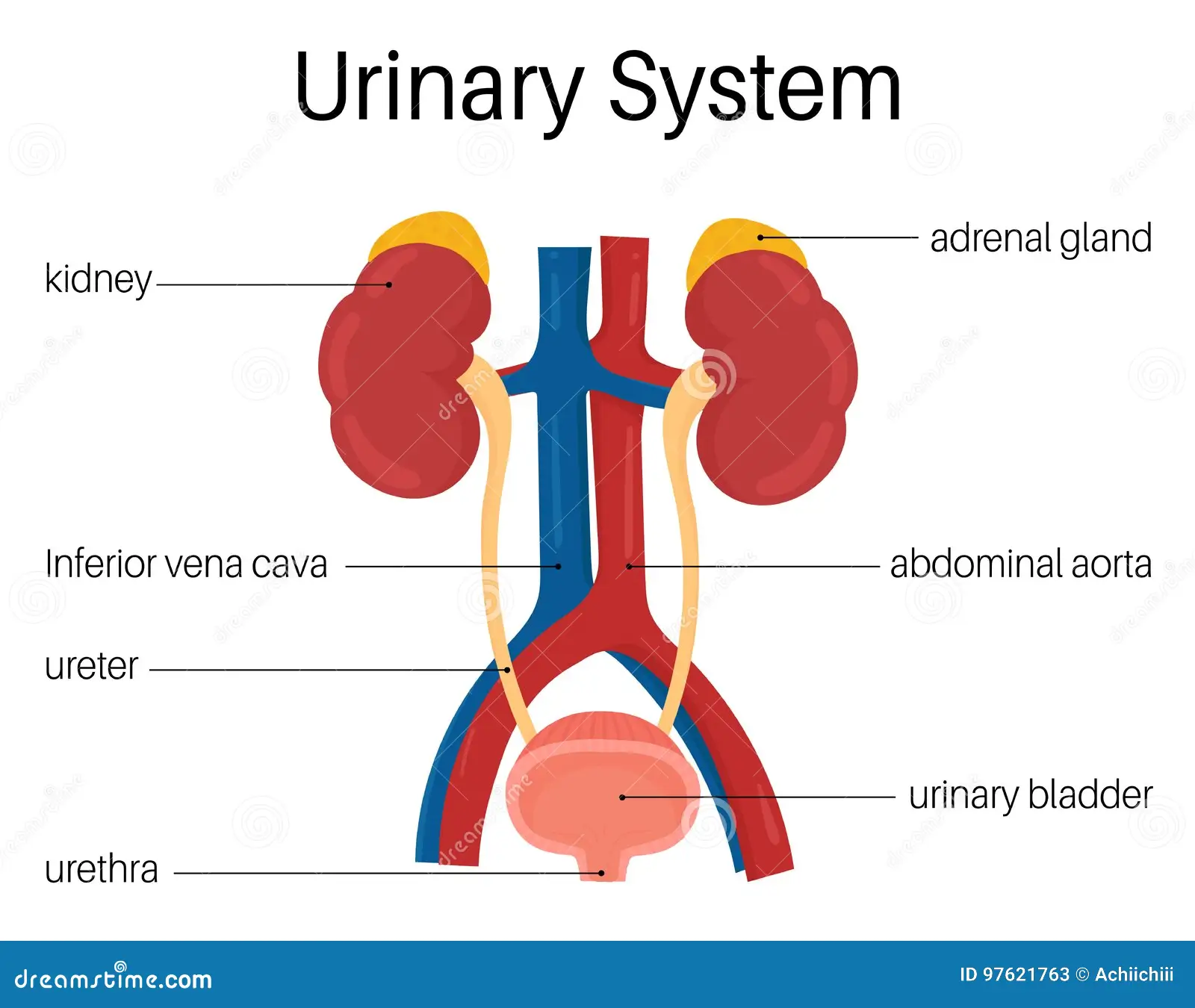
kidney structure
filters waste products out of blood + reabsorbs useful solutes

structure of nephron
wide afferent arteriole entering + narrow efferent arteriole leaving
ultrafiltration
-in Bowman’s capsule
1) high hydrostatic pressure in glomerulus forces small molecules out of capillary
2) this passes through basement membrane into Bowman’s capsule
3) there are podocytes and pores in capillaries to allow substances to be filtered through
4) large molecules (proteins) cannot pass through so remain in blood
5) small molecules form glomerular filtrate
selective reabsorption of glucose + water
-in proximal convoluted tubule
1) useful molecules are reabsorbed into blood
2) carrier protein co-transports Na+ and glucose into epithelial cells
3) then Na+ absorbed into blood by active transport + glucose absorbed into blood by facilitated diffusion
4) water enters blood by osmosis as water potential of blood is lower than the filtrate
adaptations of proximal convoluted tubule
-microvilli = large surface area for co-transporter proteins
-many mitochondria = ATP for active transport of glucose
maintaining Na+ gradient in medulla
-in loop of Henle
1) Na+ ions pumped out of ascending limb by active transport into medulla
2) ascending limb is impermeable to water so water potential of medulla decreases
3) so water moves out of descending limb by osmosis, making glomerular filtrate more concentrated + decreasing its water potential
4) so water is reabsorbed into the blood
5) Na+ then diffuse out of ascending limb
length of loop of Henle
longer loop = Na+ or Cl- ions absorbed from filtrate in ascending limb so conc of ions increases down medulla so increases water potential gradient
reabsorption of water
-in distal convoluted tubule + collecting duct
-water moves out of DCT + collecting duct by osmosis and is reabsorbed into blood
role of ADH
stored and secreted by posterior pituitary gland
-binds to receptors of membrane of collecting duct and make the cells more permeable to water by inserting aquaporins in membrane
DEHYDRATION
-decrease in water potential of blood
-osmoreceptors in hypothalamus trigger release of ADH from pituitary gland - water moves out osmoreceptors by osmosis causing them to shrink
-ADH increases permeability so more ADH produced so more water reabsorbed by osmosis so more concentrated urine produced
-OPPOSITE FOR HYDRATION