Joint structures: synchondrosis, sutural, condylar, symphysis,gomphosis,syndesmosis
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Classification of joints
. Joints can be classified according to structure and function. Structurally they are classified based either on the type of connective tissue that binds the bones or on the presence of a fluid-filled space (synovial joint) between the bones
The body has three structural types of joints:fibrous joints, cartilaginous joints, and synovial joints
Joints can also be classified into three functional types according to the amount of movement they allow: a synarthosis is an immovable joint, an amphiarthrosis is a slightly moveable joint, and a diarthrosis is a freely moveable joint
Fibrous joints
There is no fluid- filled cavity, and the bones are held together by dense regular collagenous connective tissue
There are three types of fibrous joints: sutures, gomphoses, and syndesmoses
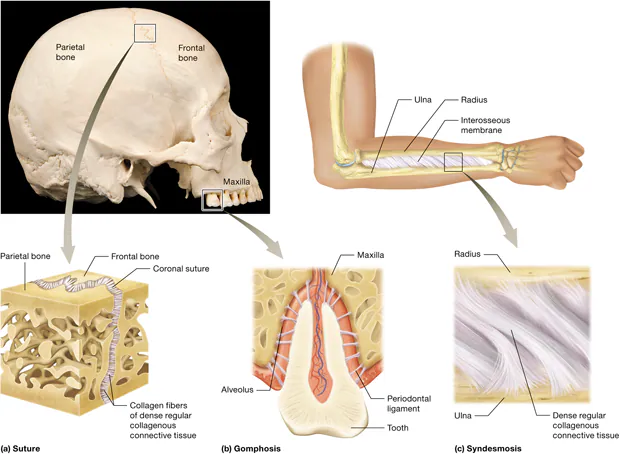
Sutures, gomphoses, and syndesmoses
• Suture: is irregular interlocking edges of bone are joined by a thin layer of dense regular collagenous connective tissue. Is immovable (synarthrosis), is found only in the skull
gomphosis: A cone-shaped tooth is held in a bony socket (alveolus) of the mandible or the maxillae by a fibrous periodontal ligament. Is synarthrotic
Syndesmosis: bones are held together by either a band (interosseous ligament) or a sheet (interosseous membrane) of dense regular collagenous connective tissue. The interosseous membrane between the radius and ulna in the forearm is an example of a syndesmosis.
Cartilaginous joints
In a cartilaginous joints, which lack a synovial cavity and allow little or no movement, the bones are held together by either hyaline cartilage or Fibrocartilage. There are two types of cartilaginous joints: synchondroses and symphyses

Synchondrosis and symphysis
Synchondrosis: bones are held together by a band of hyaline cartilage. They are also synarthroses
Symphysis: bones are held together by a broad, flat disc of Fibrocartilage