Medical Science Test 1 GCSE recap
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Describe the levels of organisation within living organisms.
Organelles, Cells, Tissues, Organs, Organ Systems, Organism
Describe the digestive system and how it works as an organ system
It breaks down food into simple nutrients, which are then absorbed into the bloodstream for energy growth and repair.
Waste is eliminated through feces
Mouth, Oesophagus, Stomach, Small intestine, Large Intestine, Rectum/anus
Liver - produces bile - which digests fat
Gallbladder - Stores bile - releases it into the small intestine
Pancreas - produces digestive enzymes
Describe the basic features of enzymes
Active sites
A unique 3D region that binds to a specific substrate
Crucial for life
Require specific conditions like temp and pH to function correctly
Describe the lock and key theory as a model of enzyme action and explain how the shape of the active sites makes the enzyme specific.
The lock and key theory posits that enzymes act as keys that fit into specific locks, which are substrates. The unique shape of the active sites ensures that only specific substrates can bind, facilitating precise biochemical reactions
The active site of each enzyme has a unique three-dimensional shape that is complementary to the shape of its specific substrate. This ensures that only the correct substrate can bind to the active site.
Explain the effect of temperature and pH on enzymes
Increasing temperature increases reaction rates due to higher kinetic energy and collision frequency. High temperatures can also cause irreversible denaturation, while changes in pH alter the enzyme’s active site and substrate binding.
Describe the digestive enzymes, including their names, sites of production and actions.
Carbohydrate digestion
Salivary amylase - produced in salivary glands - released in mouth - neutral
Pancreatic amylase - Produced in pancreas - Released in small intestine - Basic
Maltase - Produced in small intestine - Released in small intestine - Basic
Protein Digestion
Pepsin - Produced in gastric glands - Released in stomach - acidic
Trypsin - Produced in small intestine - Released in small intestine - basic
Peptidases - Produced in small intestine - Released in small intestine - basic
Nucleic Acid Digestion
Nuclease - Produced in pancreas - Released in small intestine - basic
Nucleosidases - Produced in small intestine - Small intestine - basic
Fat digestion
Lipase - Produced in Pancreas - Released in small intestine - basic
Describe how the products of digestion are used
Products of digestion are used for, energy, growth and repair.
Glucose provides energy for cellular processes
Amino acids are used to build and repair tissues
Fatty acids are used to form cell membranes and hormones
These absorbed nutrients are transported via the bloodstream to every cell in the body, where they are assimilated into the body’s biological molecules to maintain health.
Describe the features and functions of bile, and state where it is produced and released from,
Bile is produced by the liver
Typically stored in the gallbladder which releases it into the small intestine to aid digestion
It emulsifies fats by breaking them into smaller droplets, facilitating their digestion by enzymes and absorption
Neutralizing stomach acid in the small intestine
Helps to eliminate waste products
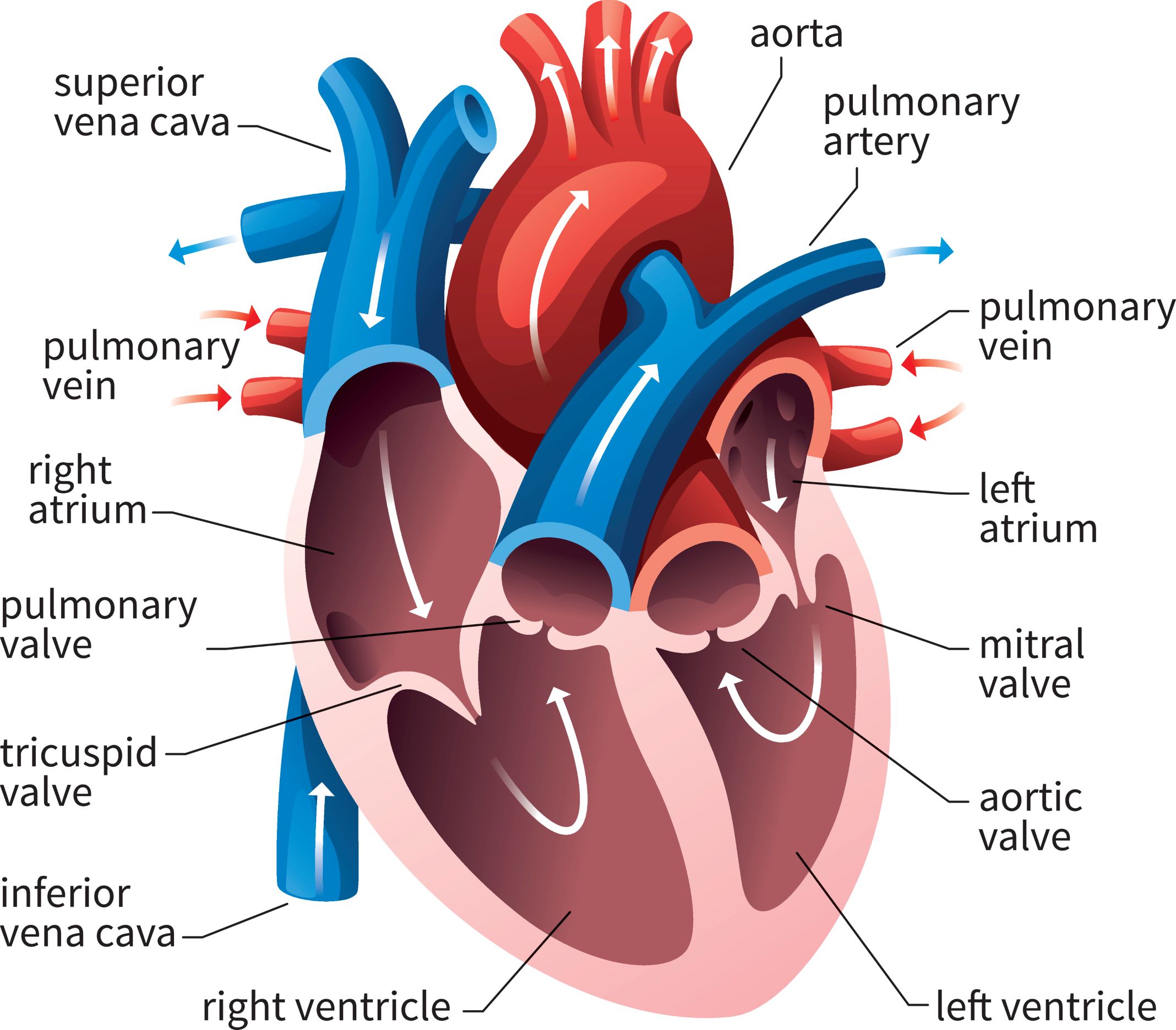
Describe the structure of the human heart
Describe the structure of the human lungs
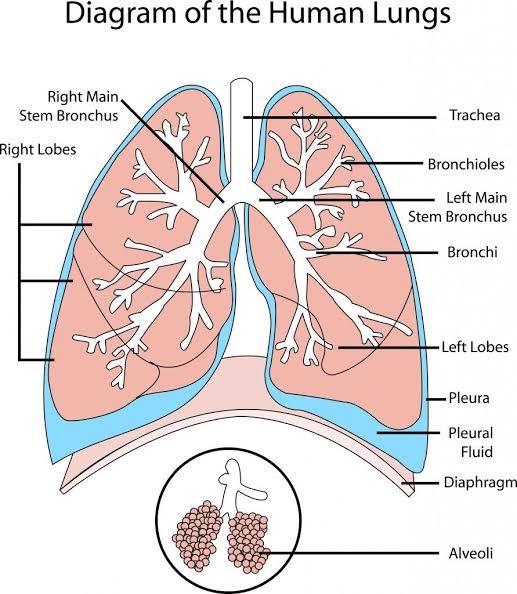
How are lungs adapted for gaseous exchange
A large surface area
Millions of alveoli
Thin walls (one cell thick) to minimize diffusion distance
Rich blood supply from capillaries that maintains a large diffusion gradient
Moist surfaces for gases to dissolve before diffusing.
Explain how the heart moves blood around the body
The heart pumps blood using a four-chambered structure and a network of blood vessels that works in two cycles
the right side receives deoxygenated blood from the body and sends it to the lungs
The left side receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it to the rests of the body
Electrical impulses initiate contractions of the atria and ventricles, which push blood through one-way valves and into arteries.
Role and position of the aorta, vena cava, pulmonary artery, vein and coronary arteries.
The aorta is the main artery, carrying oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body
The Vena Cava is the largest vein, it brings deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium
The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated from the right ventricle to the lungs
The pulmonary vein returns oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium
The coronary arteries branch from the aorta to supply the heary muscle itself with oxygenated blood
Explain how the natural resting heart rate is controlled and how irregularities can be corrected
The natural resting heart rate is controlled by specialized pacemaker cells which are in the right atrium of the heart. These generate electrical impulses.
Irregularities can be corrected by reducing caffeine, regular exercise, and staying hydrated
There are also medications such as calcium channel blockers.
If the hearts natural electrical system is faulty, an artificial pacemaker can be surgically implanted. It is a small battery-operated device, and sends electrical impulses to the heart, ensuring a proper, regular rhythm.
Describe the structure and function of arteries, veins and capillaries.
Arteries are thick, muscular and elastic to withstand high pressure, carry oxygenated blood away from the heart.
Capillaries are microscopic, thin- walled vessels that form networks, allowing rapid diffusion of nutrients and gases between blood and tissues
Veins have thinner, less muscular walls and one-way valves to prevent back-flow, returning low-pressure blood from the capillaries to the heart.
Simple compound measures such as rate and carry out rate calculations for blood flow
Heart rate bpm x stroke volume = litres per minute
Describe blood and identify it’s different components + how to identify blood cells from photographs/diagrams
Blood has four main components
Plasma - Carries nutrients and proteins
Red blood cells - Transport oxygen and carbon dioxide - Biconcave disks/small, round, reddish-pink circles.
White blood cells - Fight infection - irregular, amoeba-like shapes, nucleus shape being a primary differentiator
Platelets - Help the blood to clot - Very small, irregular fragments
Describe what happens in coronary heart disease and what statins are used for
Coronary heart disease reduces or blocks the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscles by causing fatty deposits, called plaques, to build up in the arteries.
Statins are medications that lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in the blood by reducing its production in the liver.
Describe and evaluate treatments for coronary heart disease and heart failure.
Statins: lower cholesterol levels.
ACE inhibitors: Relax blood vessels, improving blood flow and reducing blood pressure.
Nitrates: Dilate blood vessels to relieve chest pain
Coronary angioplasty and stents: A balloon is used to widen a narrowed artery and is then reinforced with a stent
Coronary Bypass Surgery: Healthy arteries or veins are used to create a new path for blood flow around a blockage.
Describe the consequences of faulty heart valves
Heart failure
Arrhythmias
Blood clots
Pulmonary hypertension
Higher risk of stroke and heart attack
Describe how patients can be treated in case of heart failure
Lifestyle changes
Healthy eating
Regular exercise
Meds
Diuretics
Describe health and then explain causes of ill-health and the relationship between health and disease
Health is the mental and physical state of a person
Describe how different types of diseases may interact and translate disease incidence information between graphical and numerical forms
add in tomorrow
describe what risk factors are and give examples discussing human and financial costs of non-communicable diseases at local, national and global levels
add in tomorrow
describe what cancer is and explain the difference between benign and malignant tumours
Cancer is an uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells that can invade surrounding tissues and spread to other parts of the body to form new tumors
Benign tumors are non-cancerous growths that do not spread to other body parts or invade surrounding tissue.
Describe the known risk factors for cancer, including genetic and lifestyle risk factors
Tobacco use
Unhealthy diet
Excessive alcohol intake
Physical activity
Obesity
Sun Exposure
Inherited gene variants