ANAT-A 225, Lab, Central nervous system (CNS)
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
general features
- protective bony covering
- meninges
- blood supply to brain
meninges
- three connective tissue membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord
pia mater
- innermost layer
arachnoid mater
- spidery, web-like
- attached to pia mater
subarachnoid space
- contains cerebrospinal fluid
dura mater
- thick, outermost layer
- surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord
blood supply to brain
- through internal carotid and vertebral arteries
vertebral arteries
- two pass through the transverse foramen of cervical vertebrae
- enter cranial cavity through foramen magnum
- then join to form a single vessel, the basilar artery
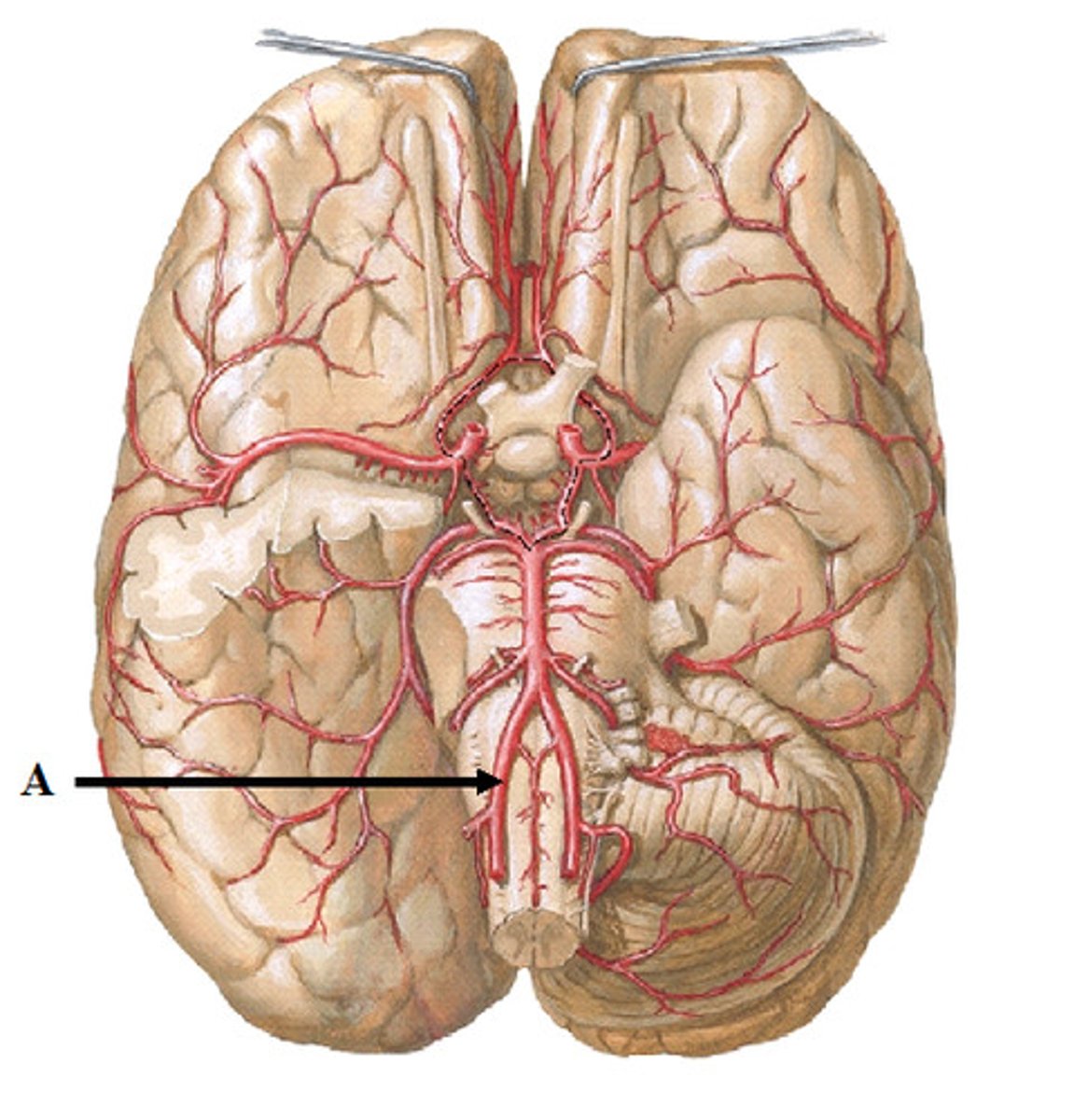
basilar artery
- sends branches to the brain, some join with branches from internal carotid arteries to form a circle of willis
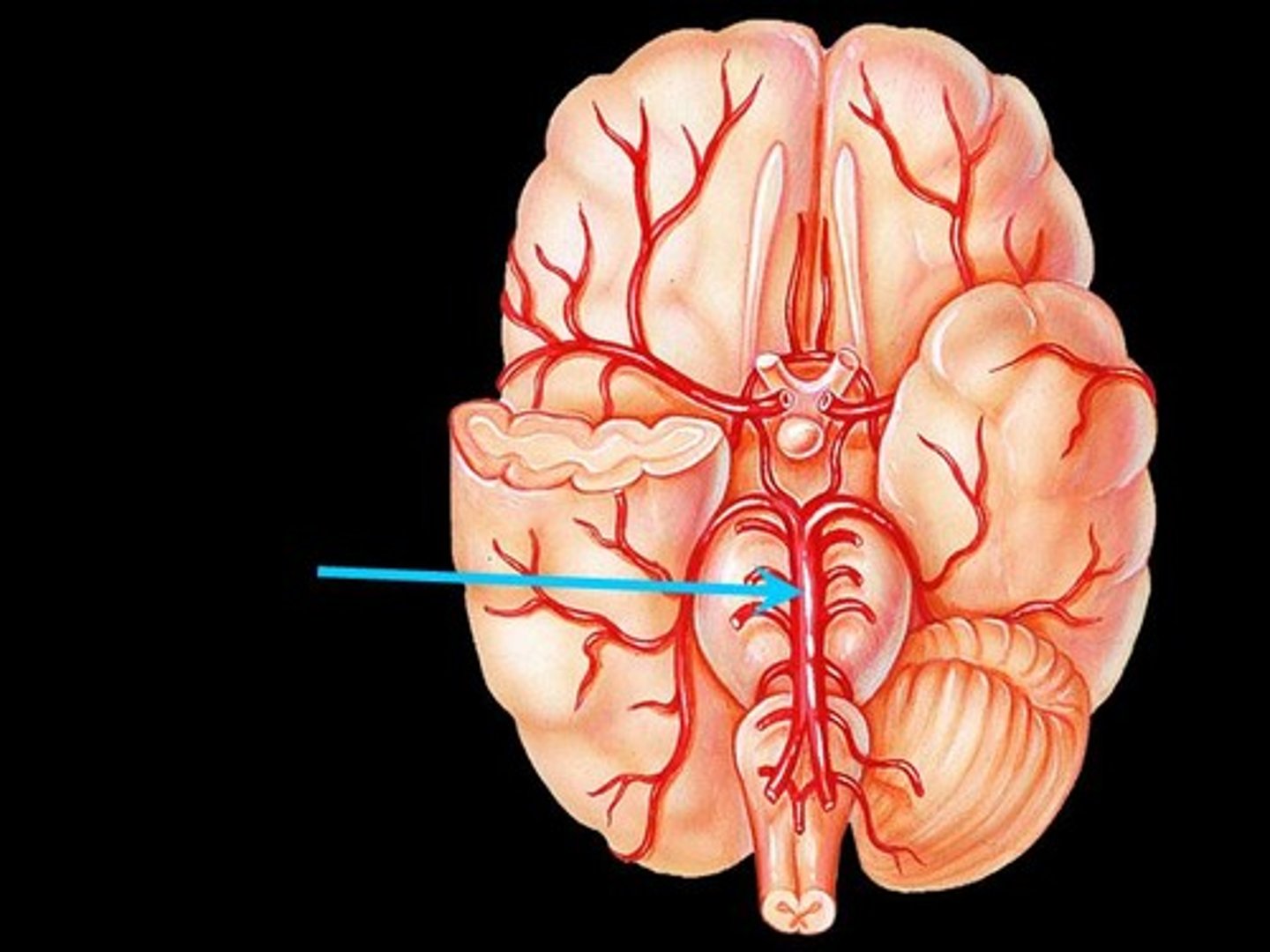
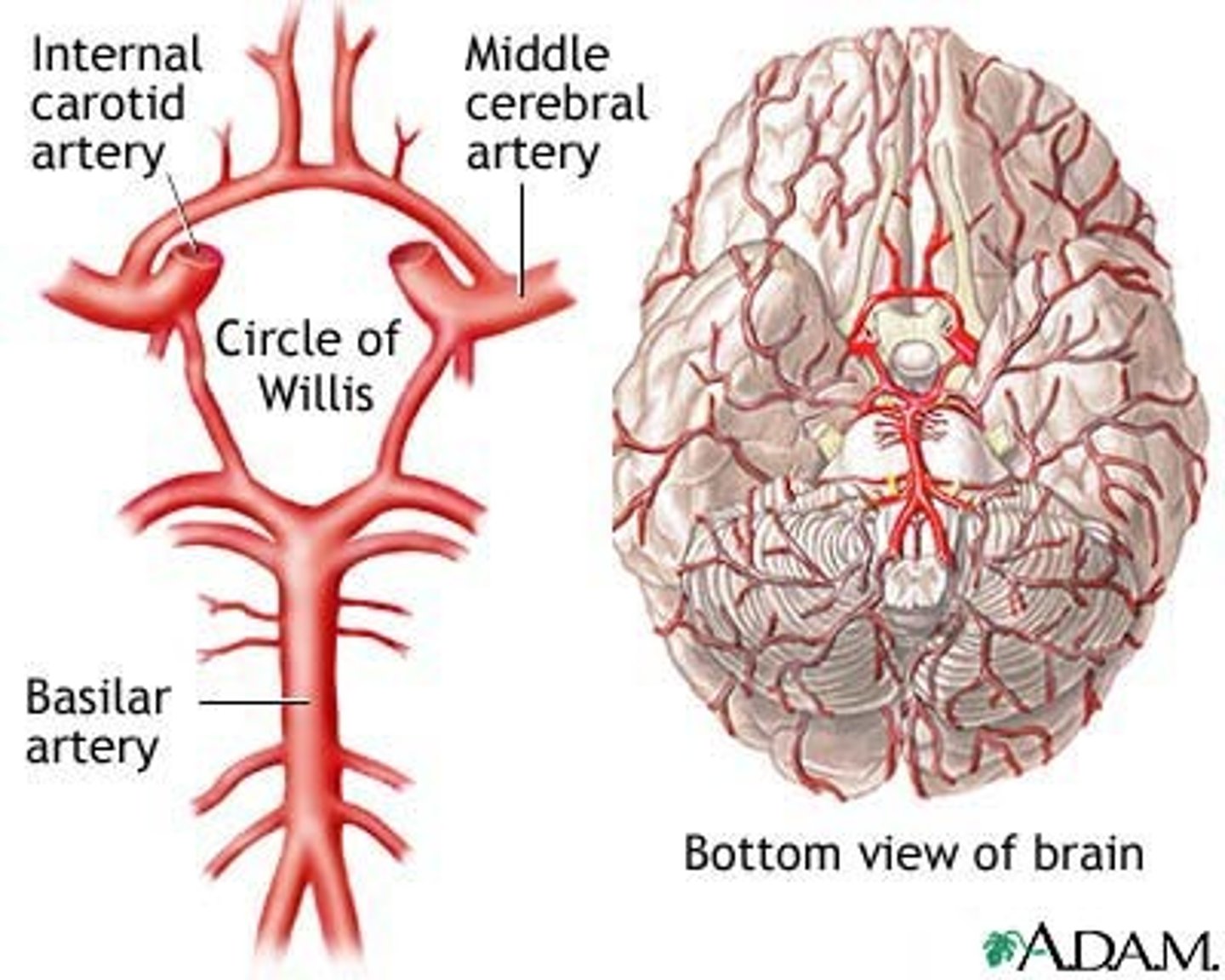
circle of willis
- aka cerebral arterial circle
- provides alternative vascular pathways if one of the major vessels is blocked
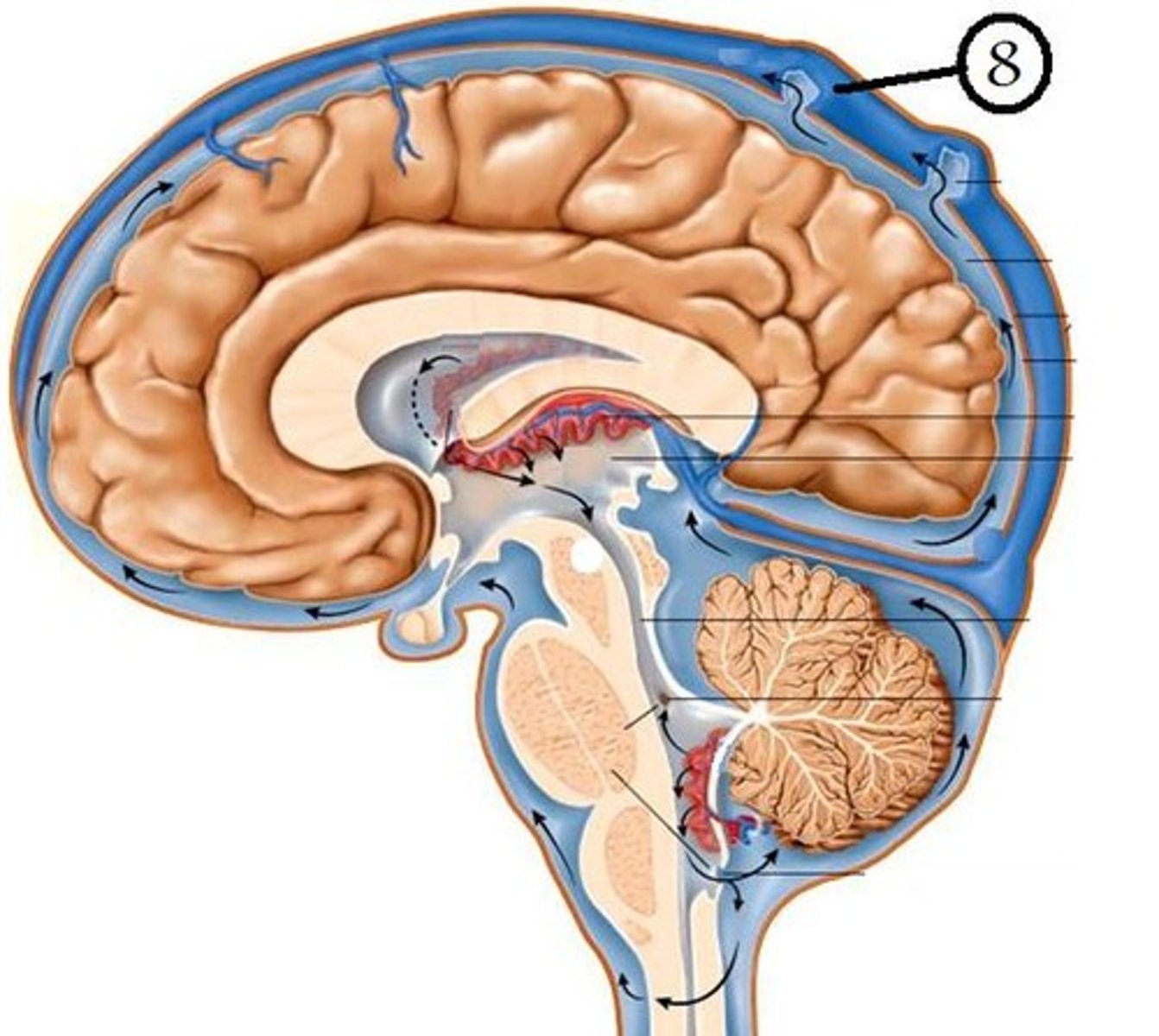
dural venous sinuses
- venous drainage of blood from the brain
- located within the dura mater
- drain into internal jugular veins
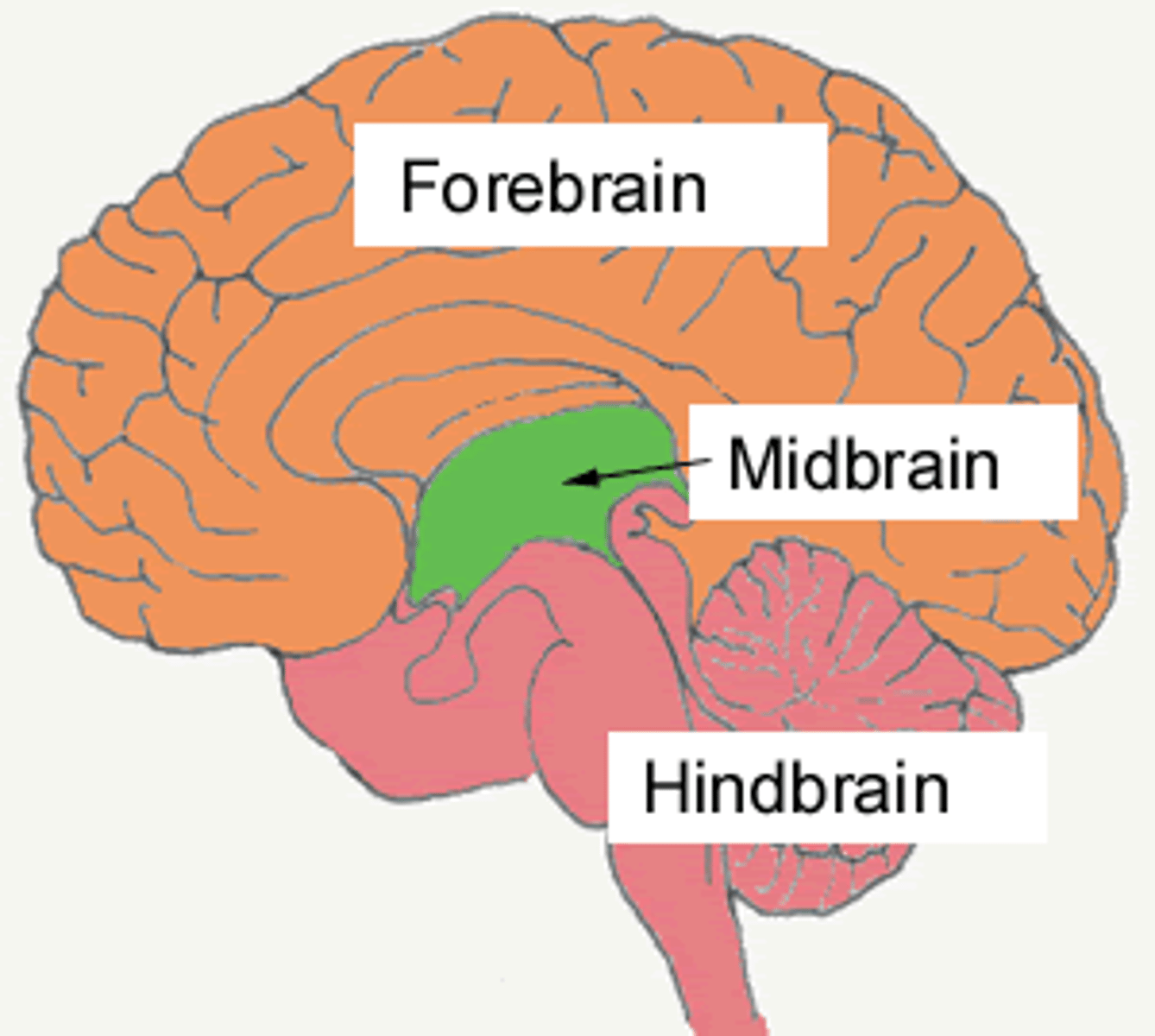
how many subdivisions of the brain are there?
- six subdivisions: cerebrum, diencephalon, midbrain, cerebellum, pons, and medulla oblongata
what is the cerebrum divided into?
- right cerebral hemisphere and left cerebral hemisphere
cortex
- outer layer
- composed of unmyelinated nerve cell processes and neuron cell bodies (gray matter)
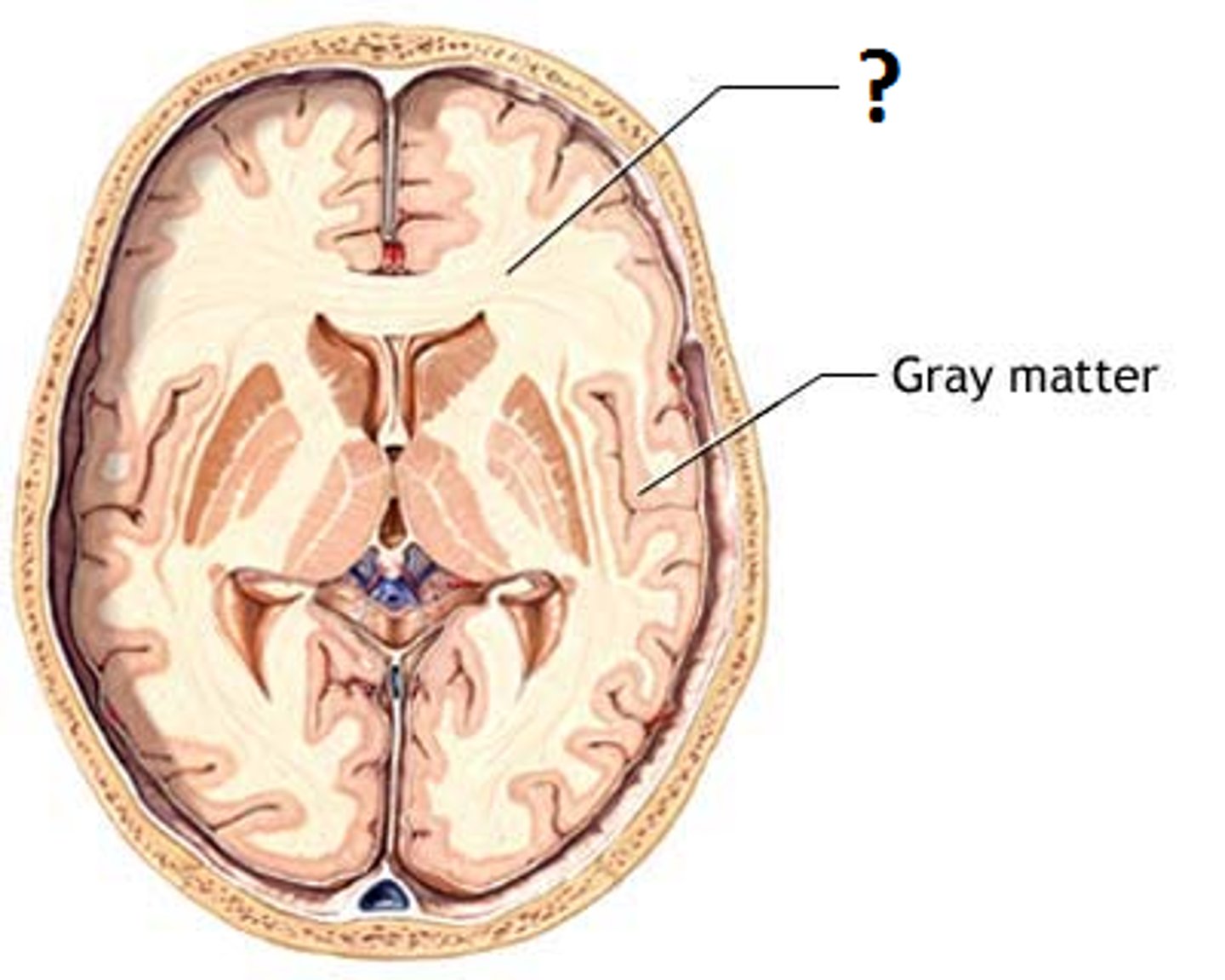
white matter
- tracts of myelinated axons
what are the lobes of the cerebrum?
- frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, insula
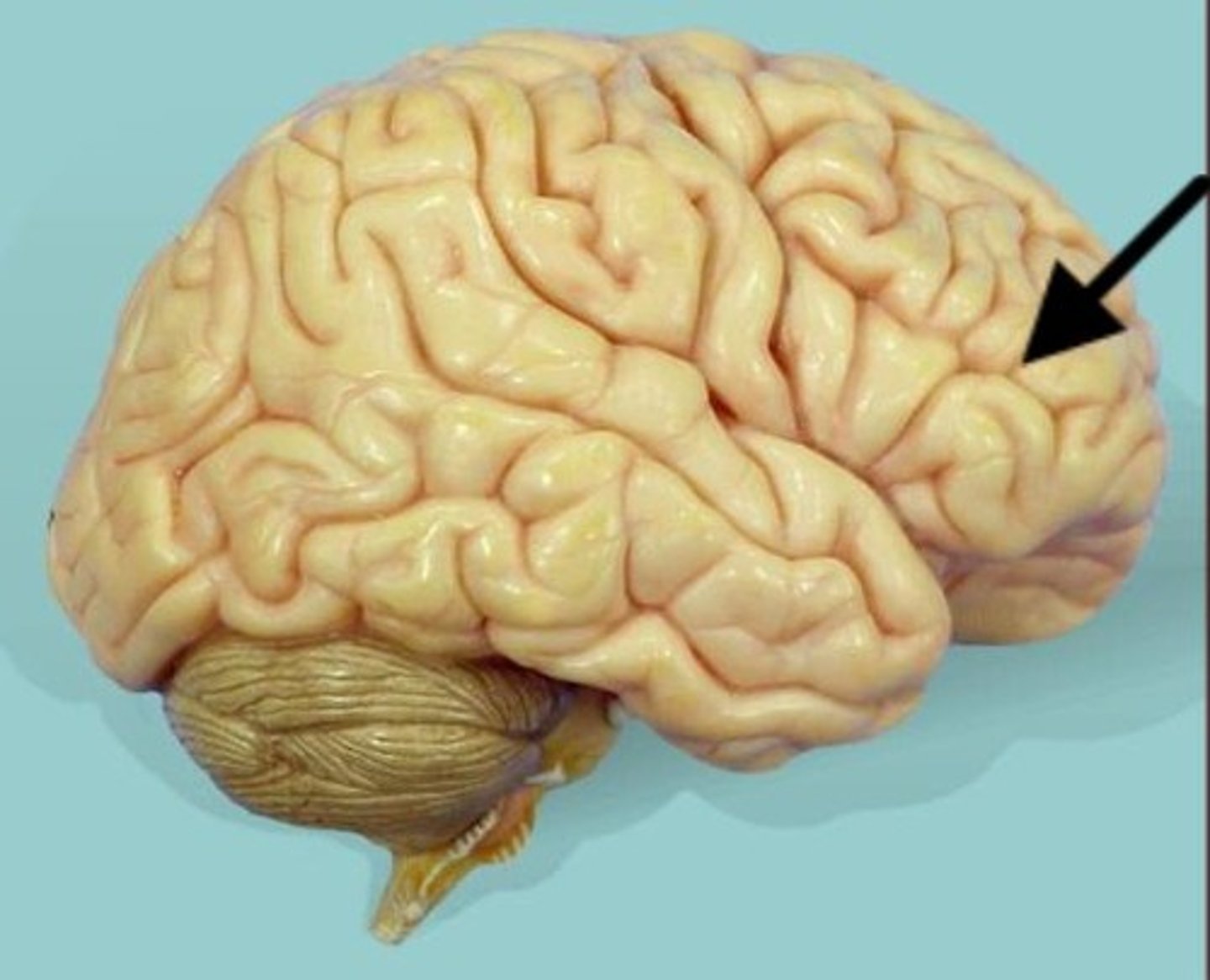
frontal lobe
- initiate voluntary skeletal muscle movement
- motor movements in speech
- intellect, personality, complex decision-making
parietal lobe
- receives and interprets most somatosensory input

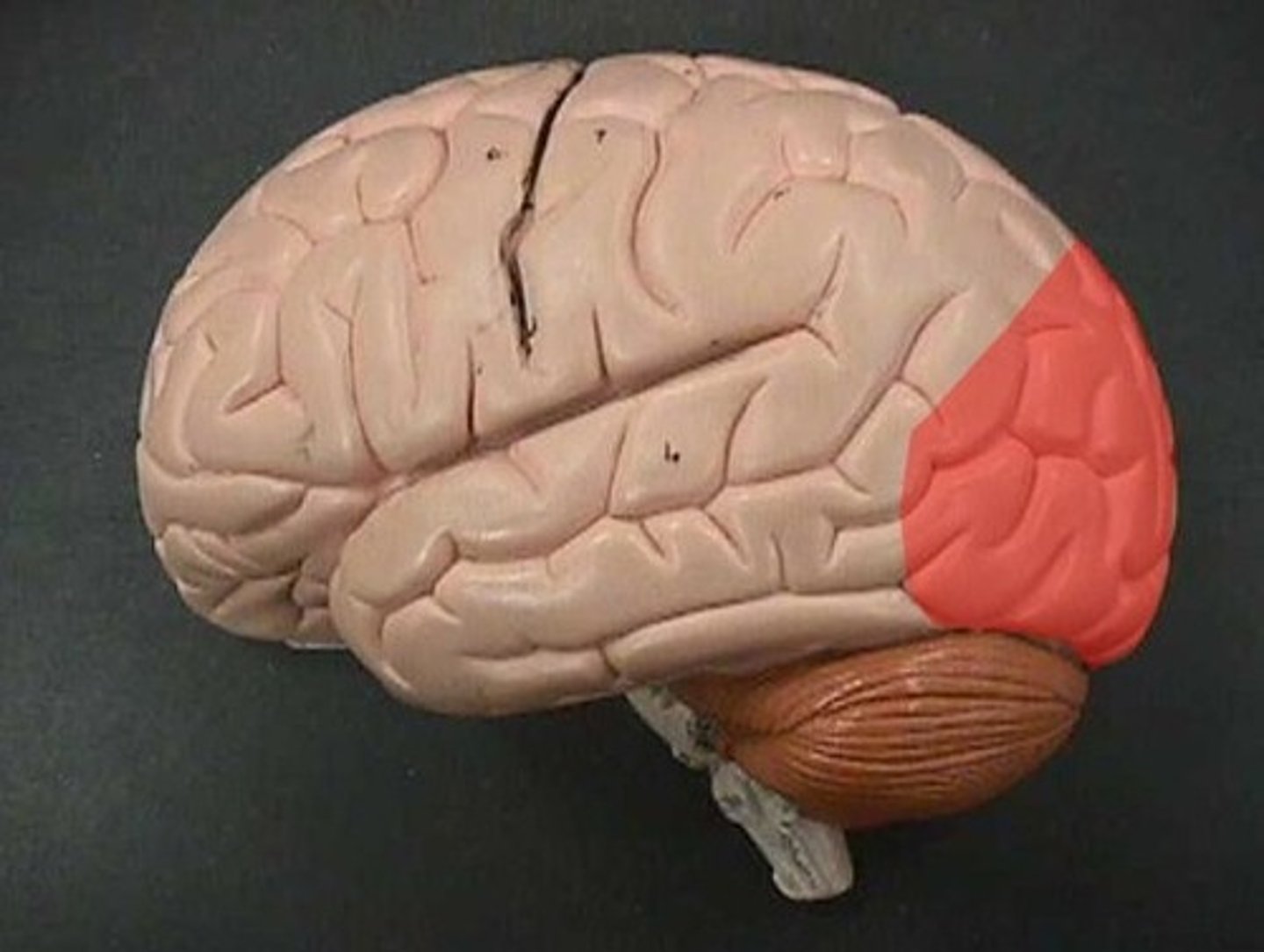
occipital lobe
- interpret visual stimuli
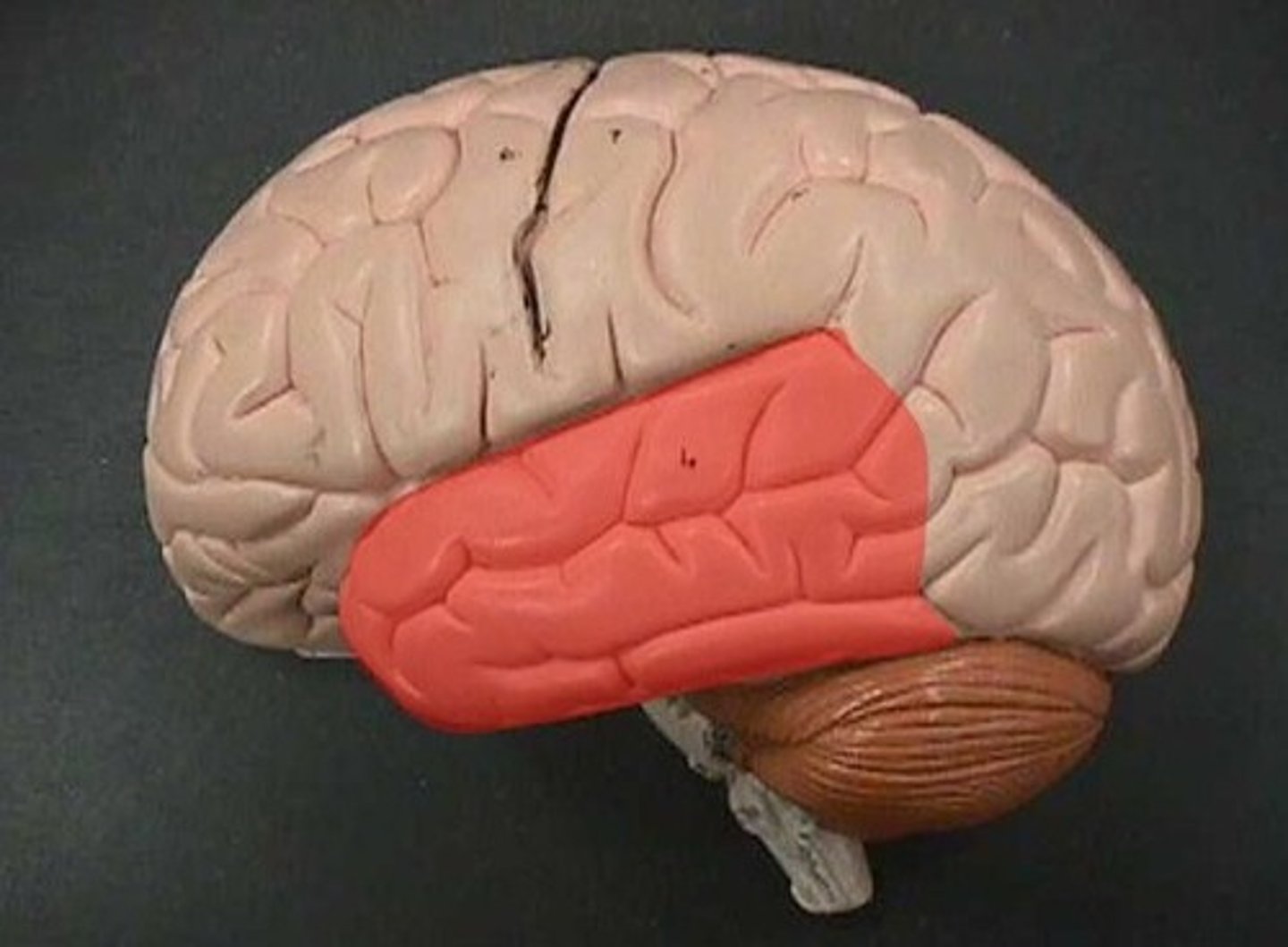
temporal lobe
- interpret auditory stimuli
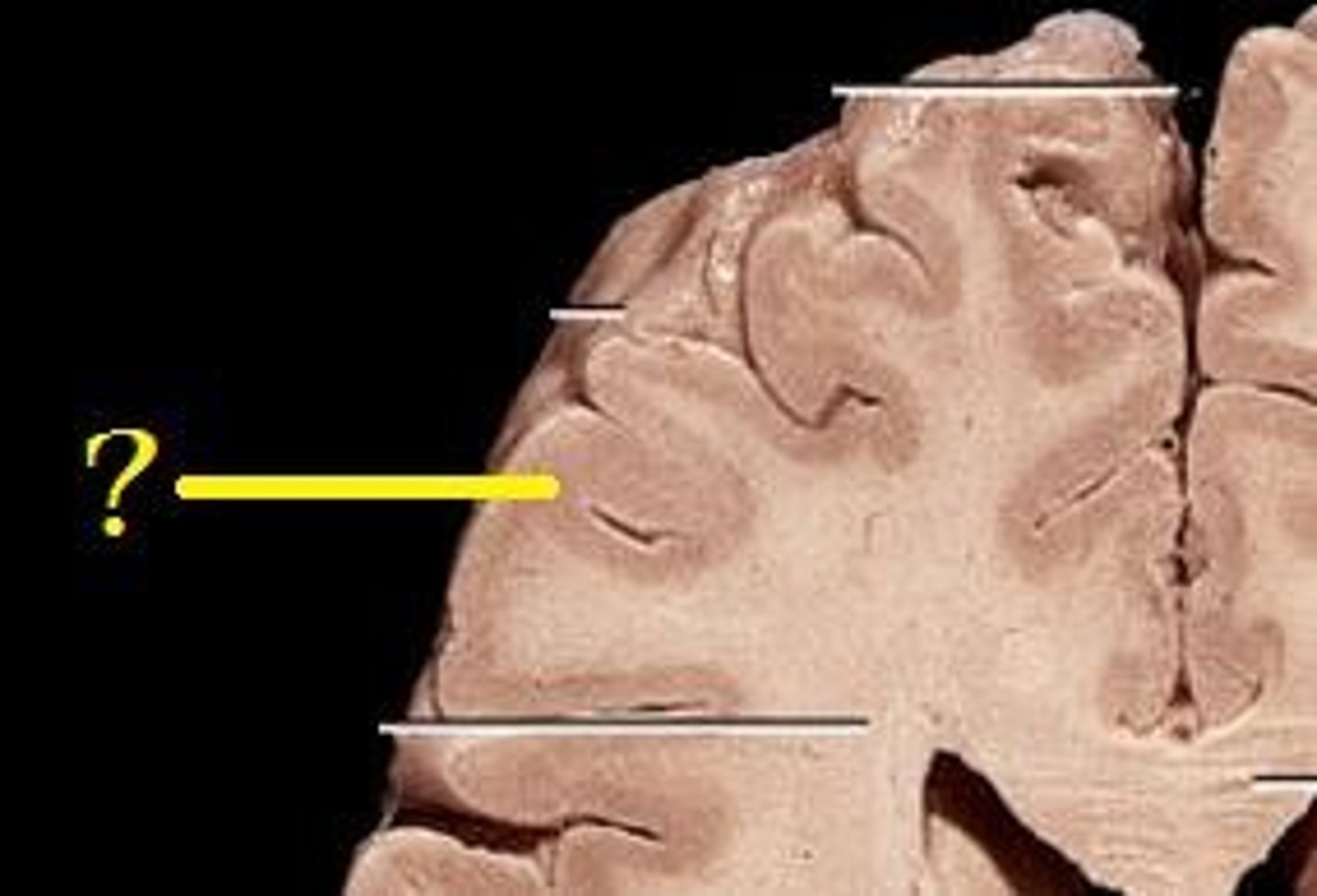
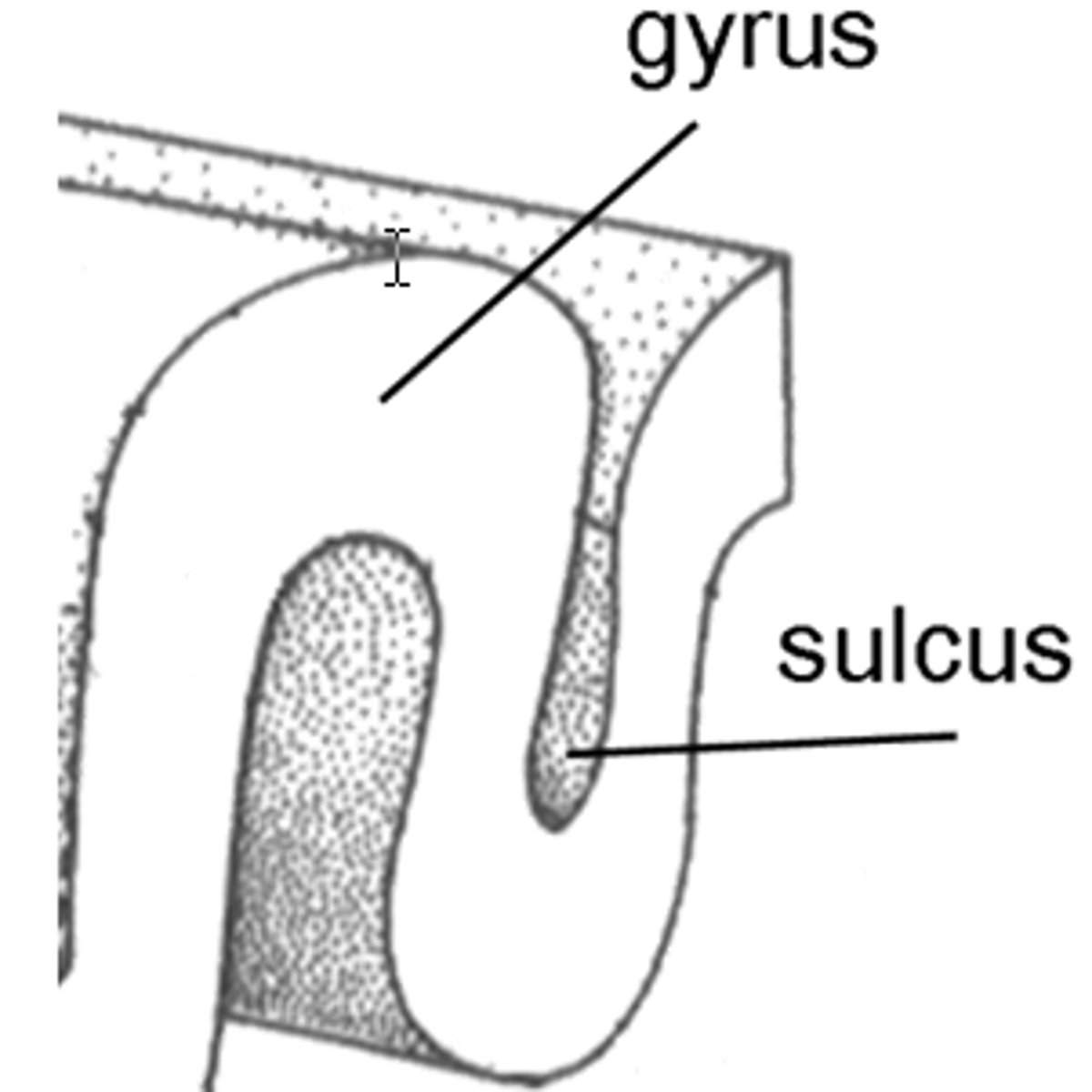
gyri
- rounded ridges on the surface of the cerebrum
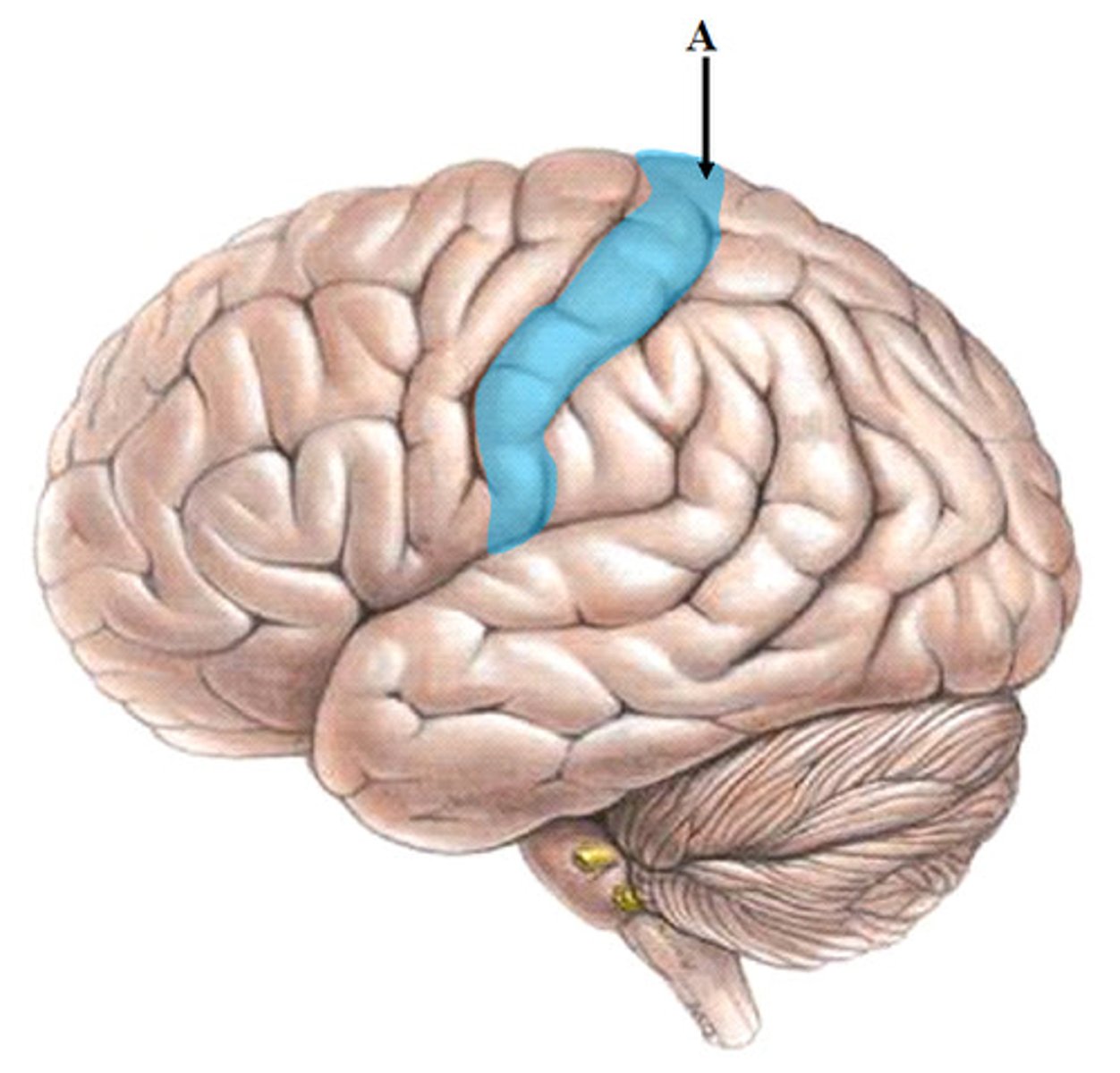
precentral gyrus
- primary motor cortex
- initiate skeletal muscle movement
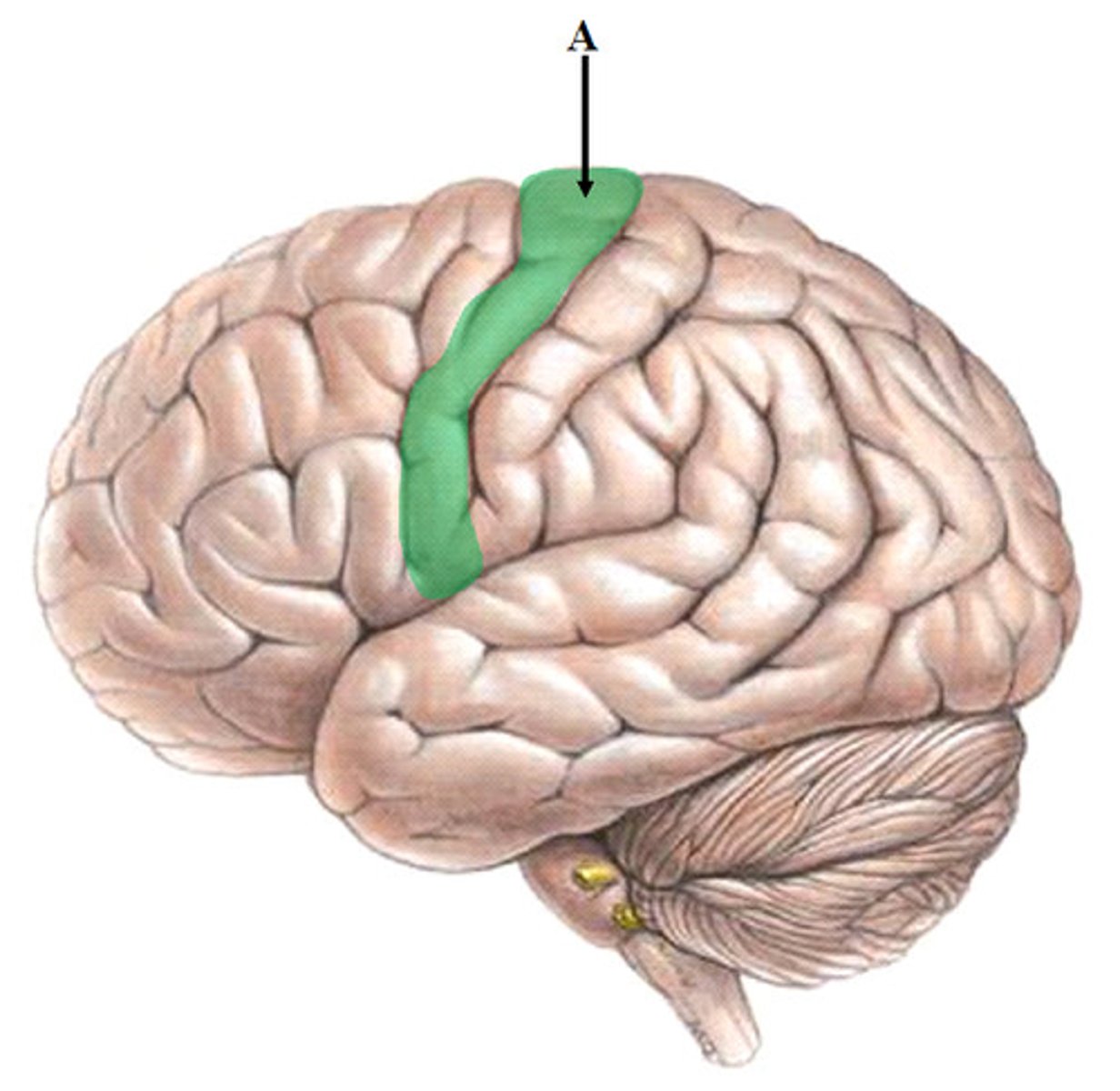
postcentral gyrus
- primary somatosensory cortex
sulci and fissures
- furrows or grooves which separate the gyri and lobes
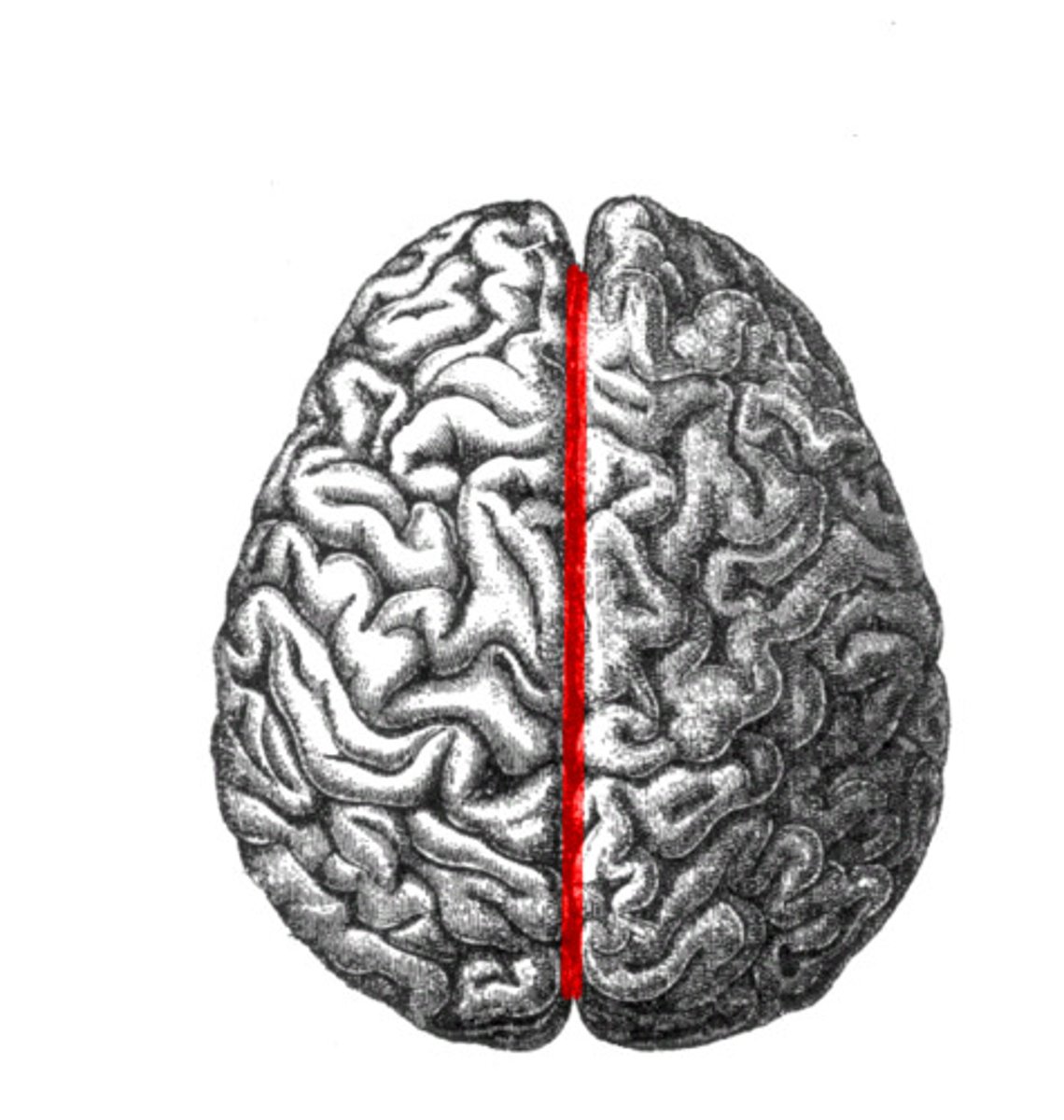
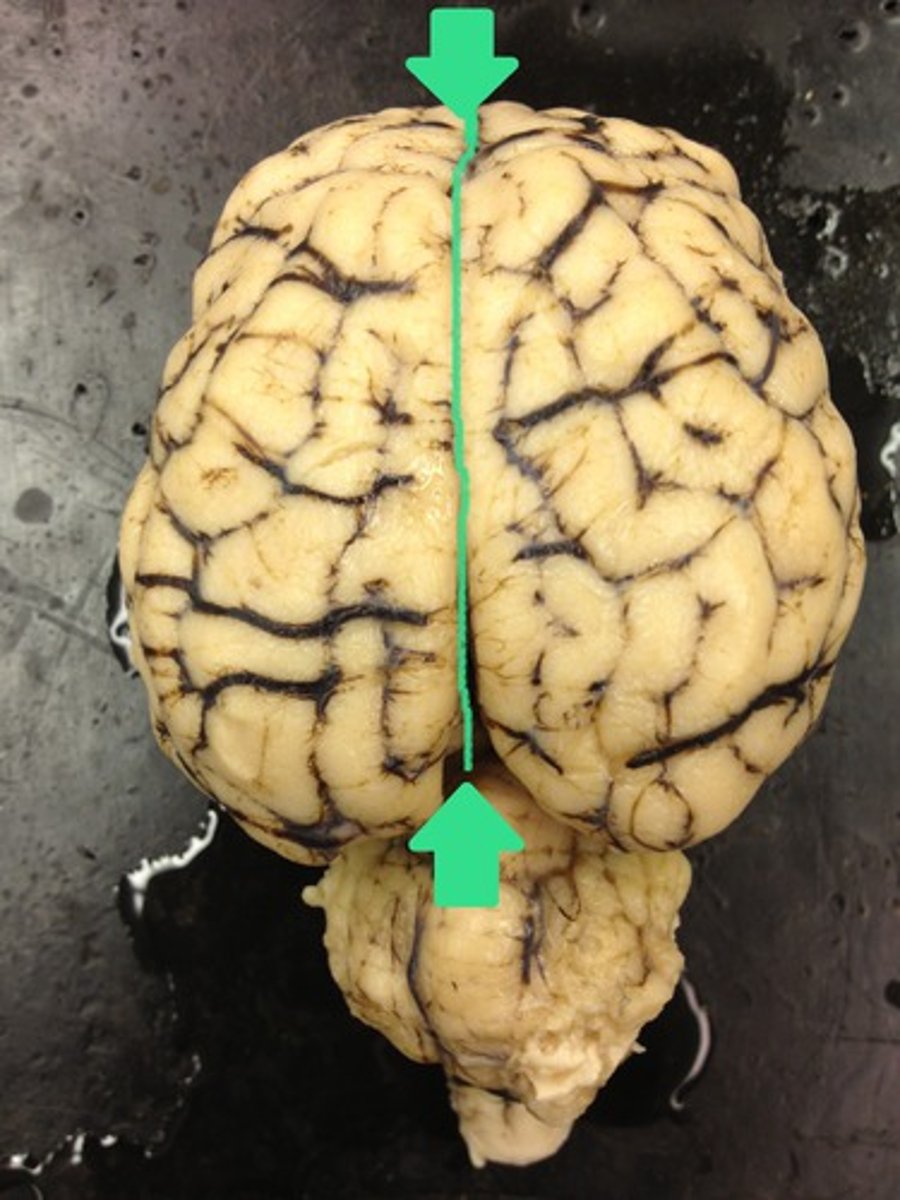
longitudinal fissure
- deep furrow b/t right and left hemispheres
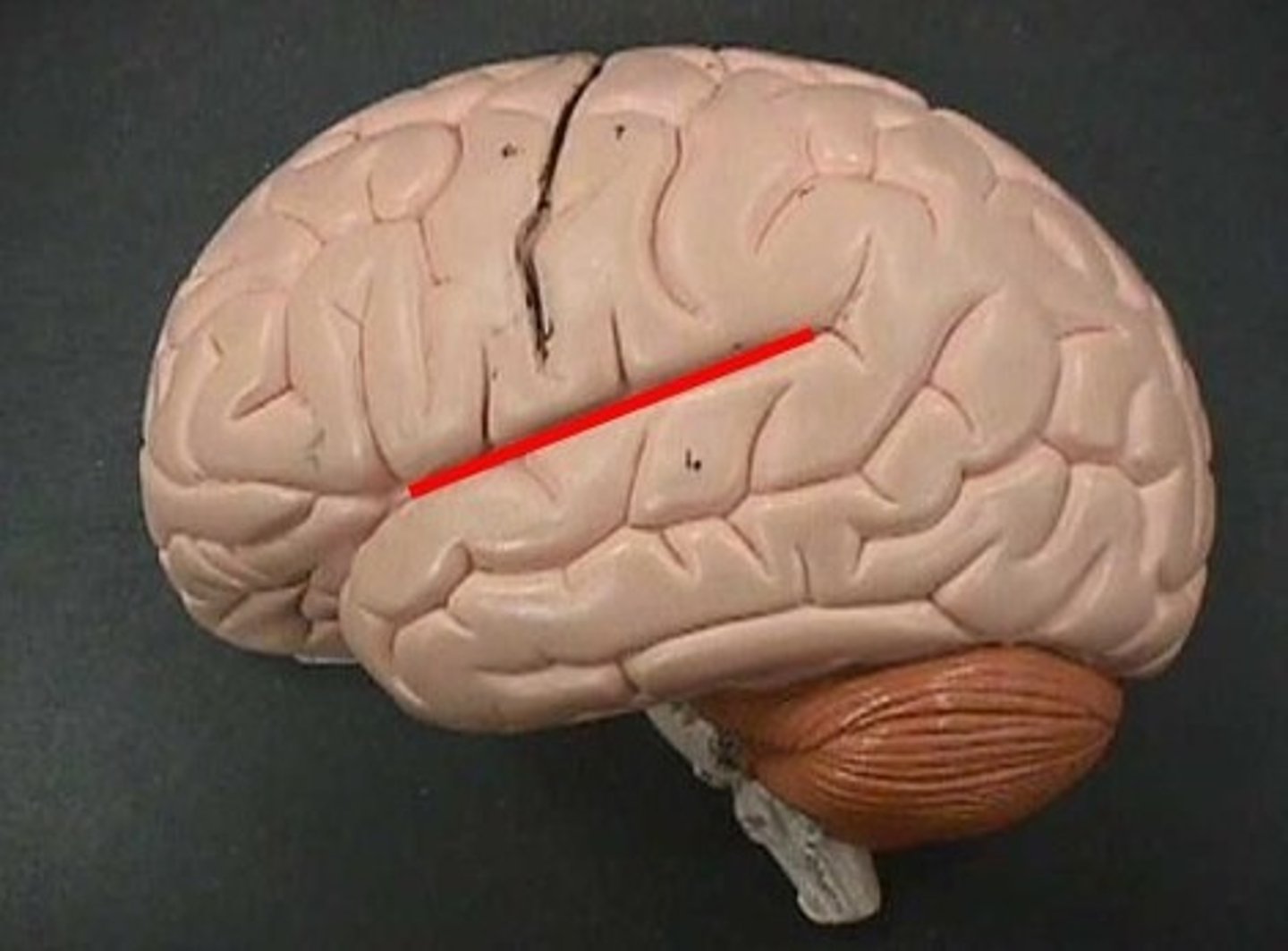
lateral sulcus
- groove separating the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobes
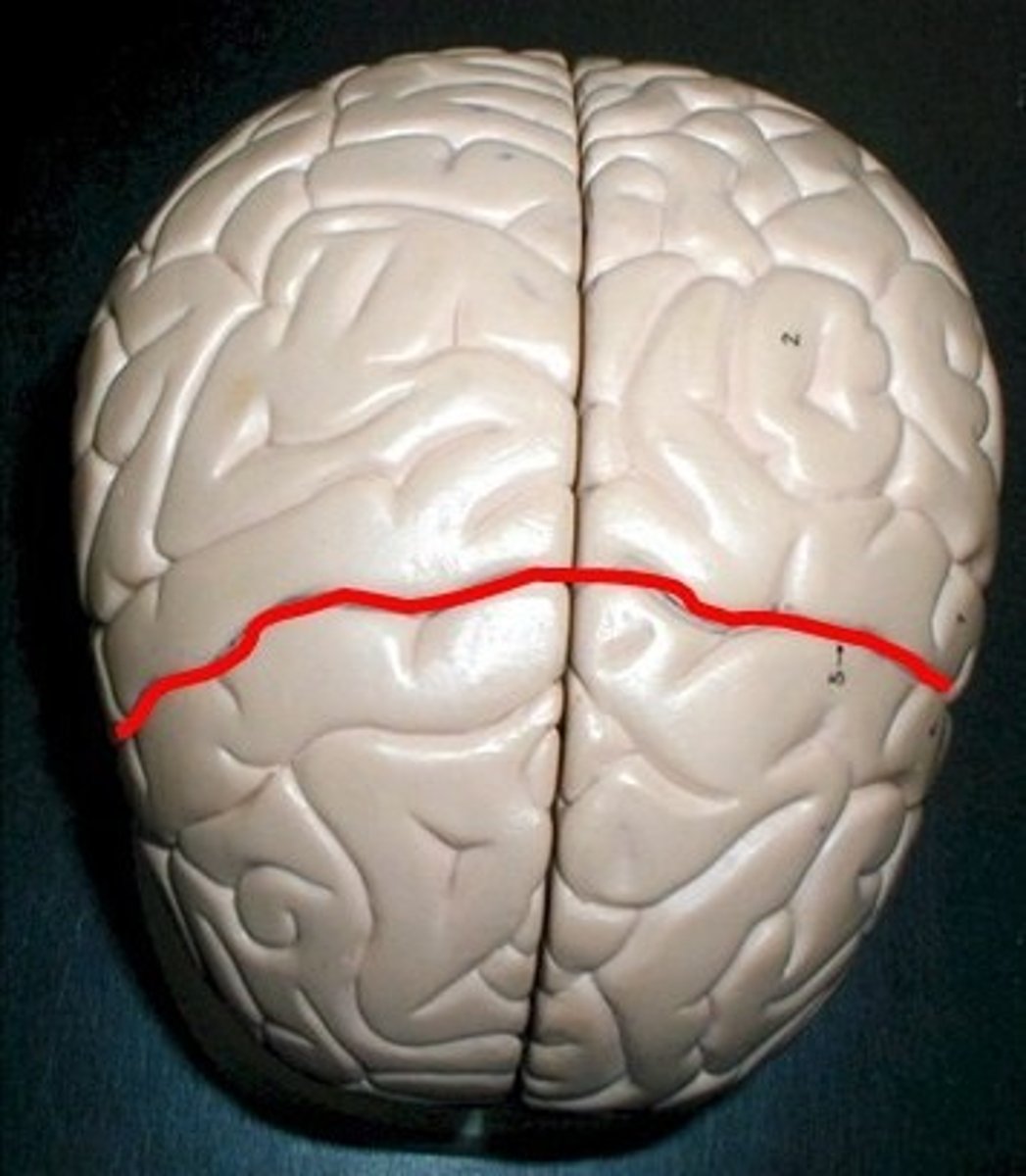
central sulcus
- a groove that separates the precentral gyrus from the postcentral gyrus, separating the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe
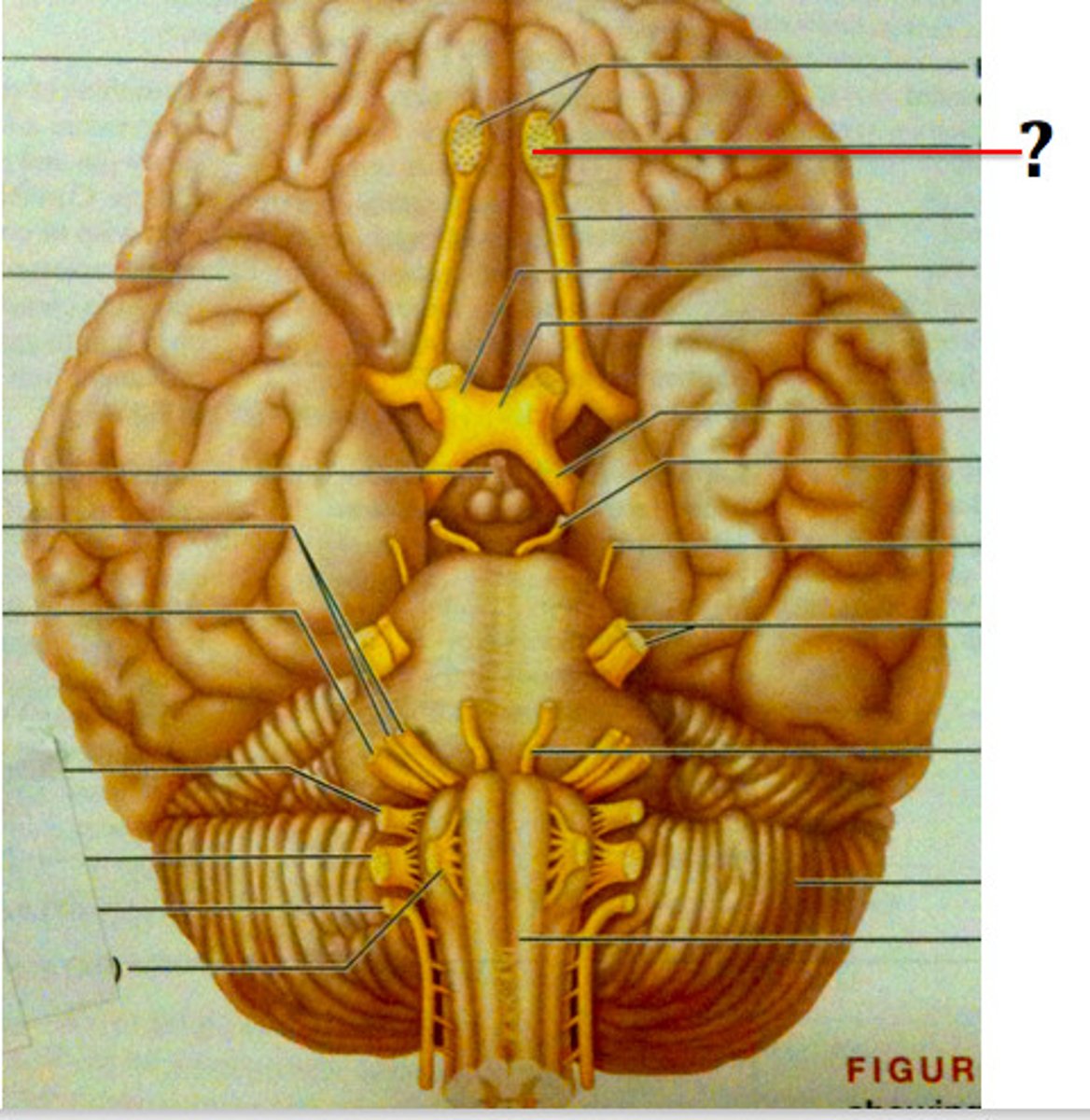
olfactory tract
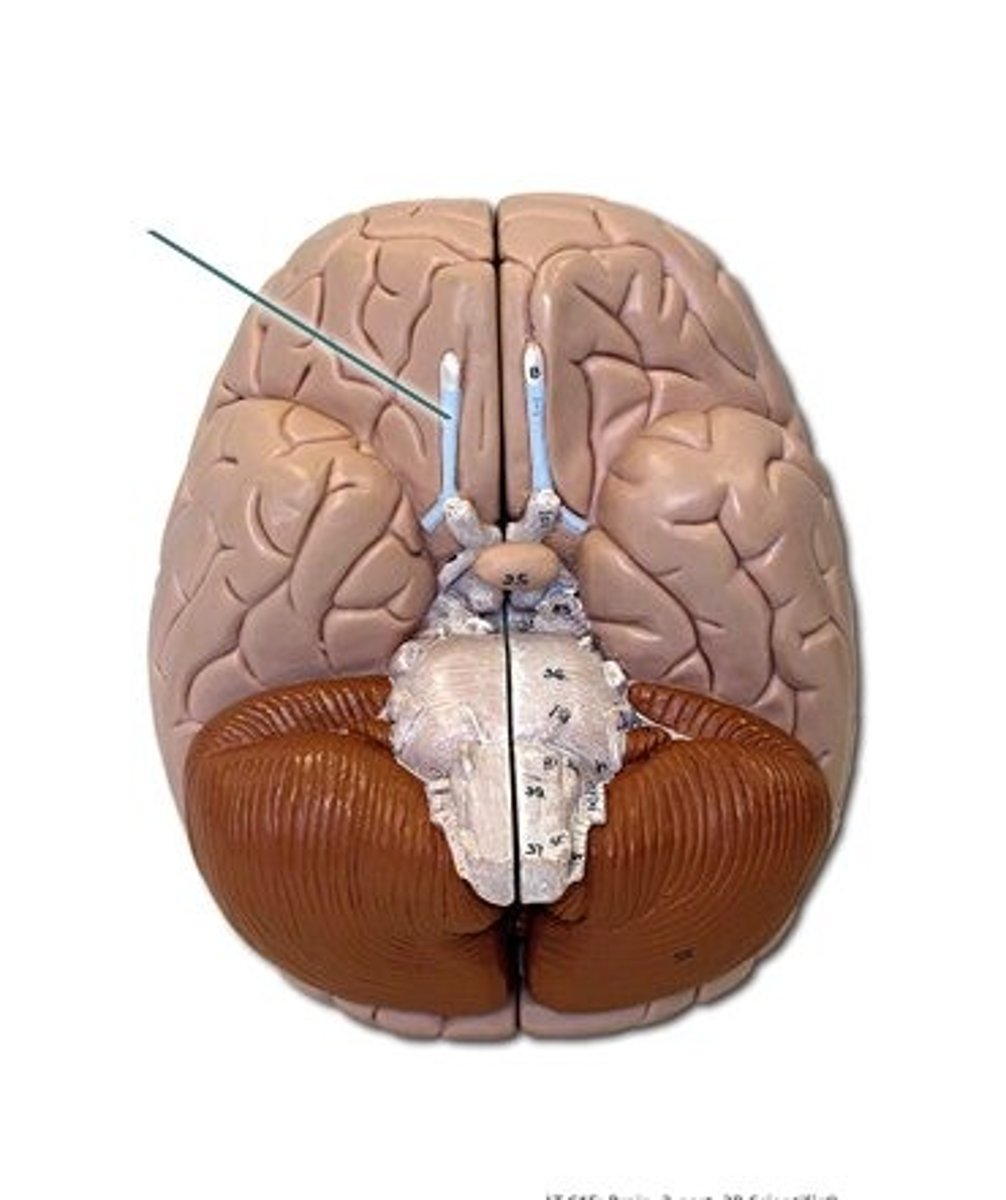
olfactory bulb
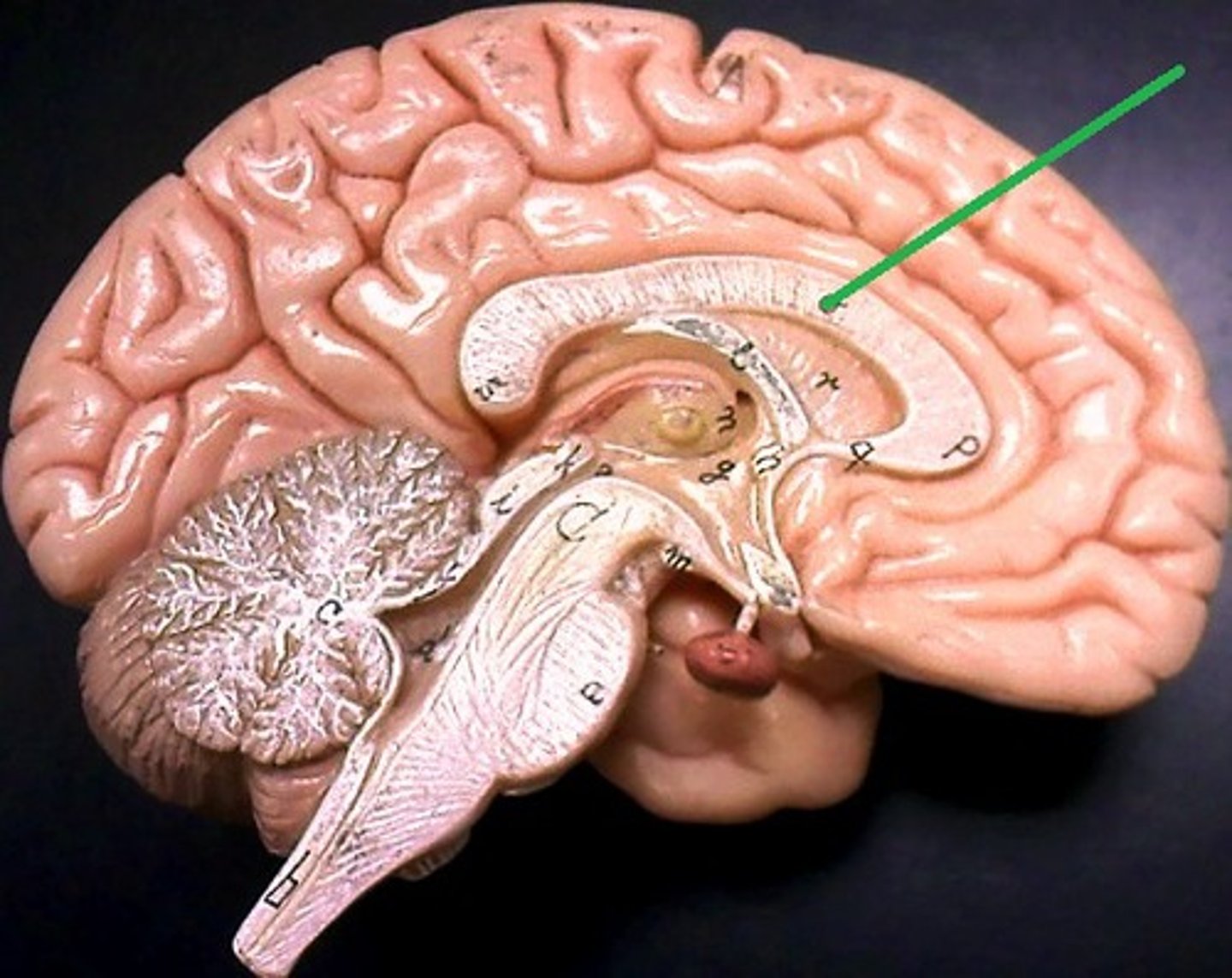
corpus callosum
- white matter made up of myelinated axons passing from one hemisphere to the other
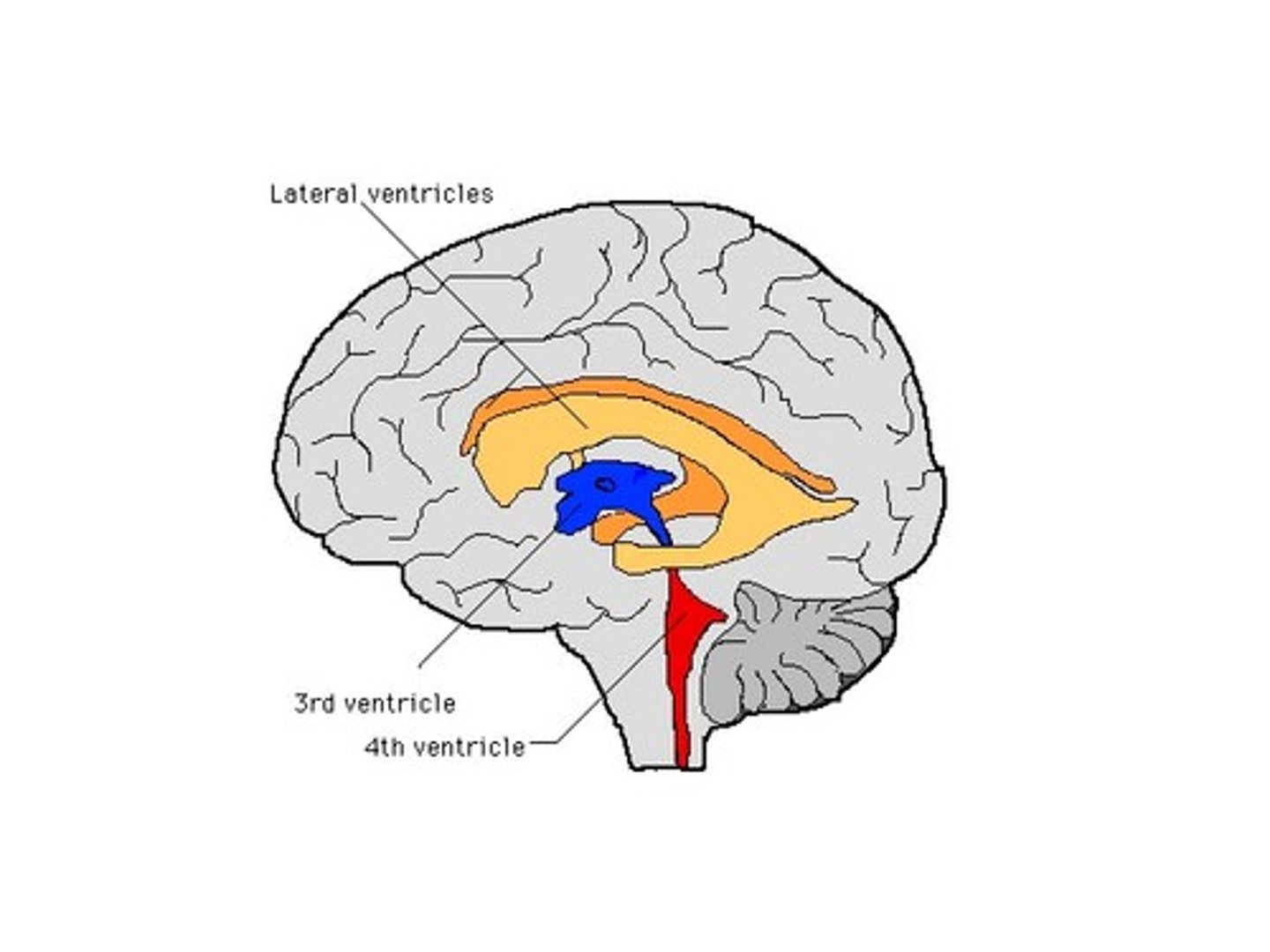
lateral ventricles
- contains CSF
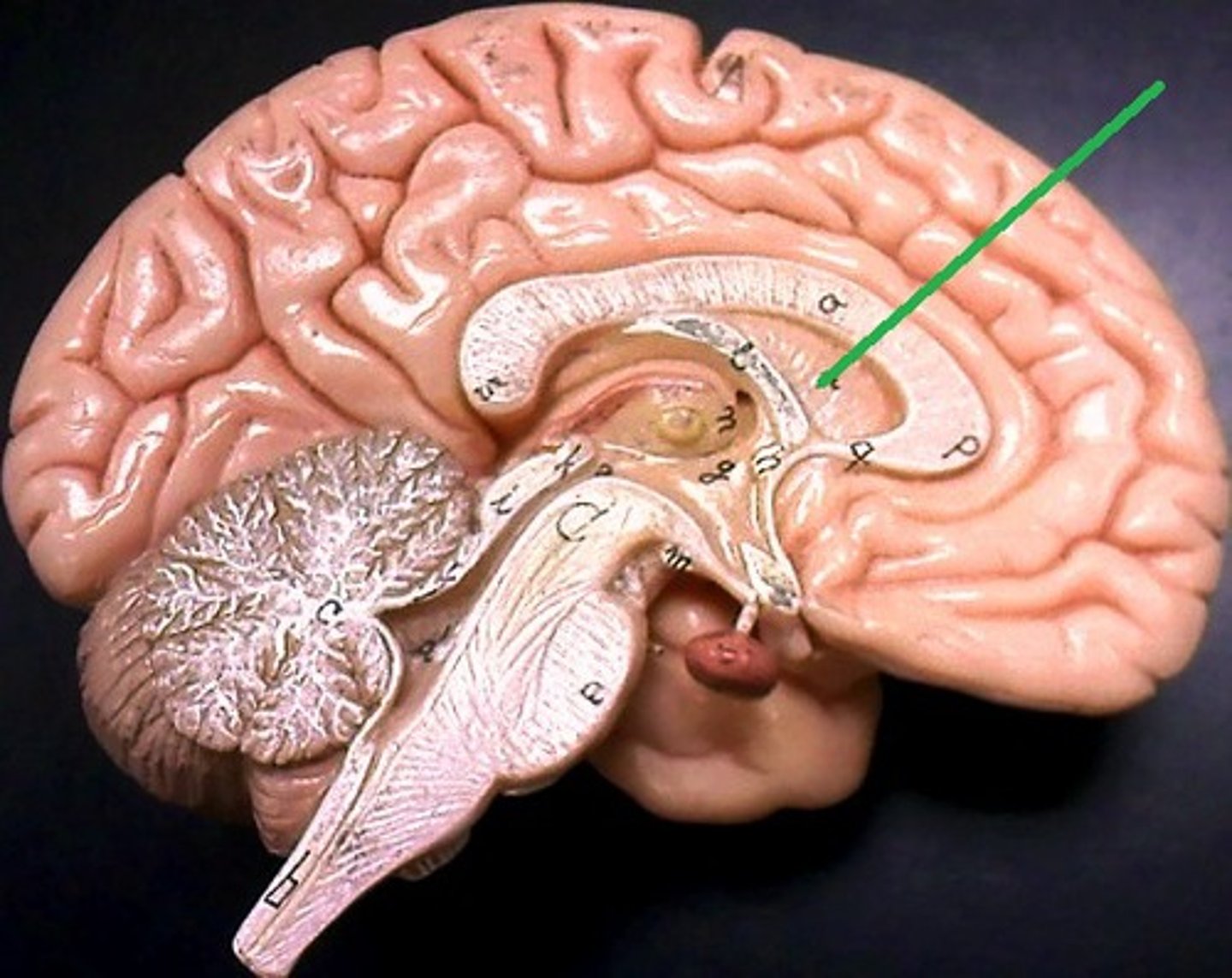
septum pellucidum
- membrane in midline separating the right and left lateral ventricles
diencephalon
- surrounded by cerebral hemispheres
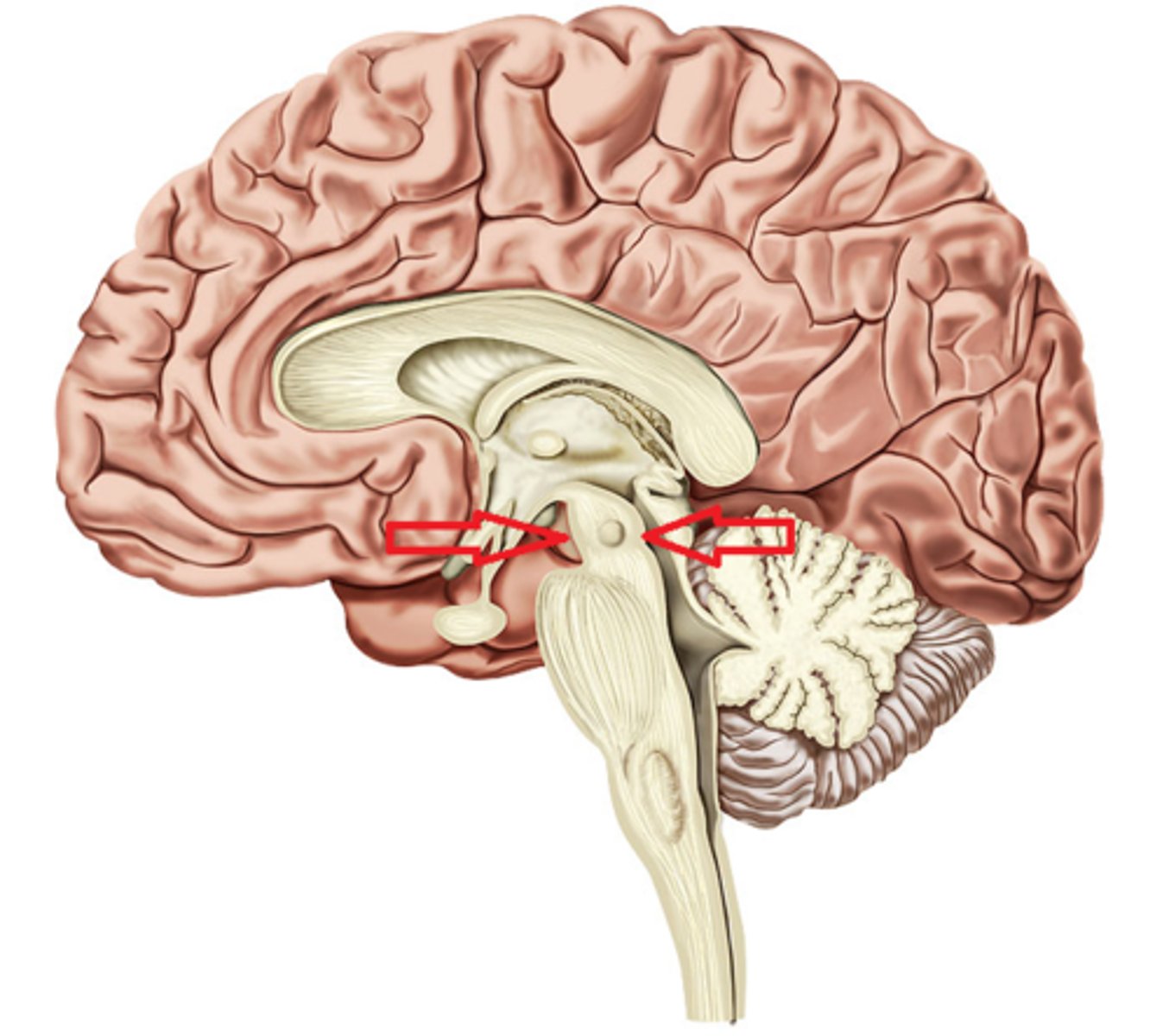
pineal gland
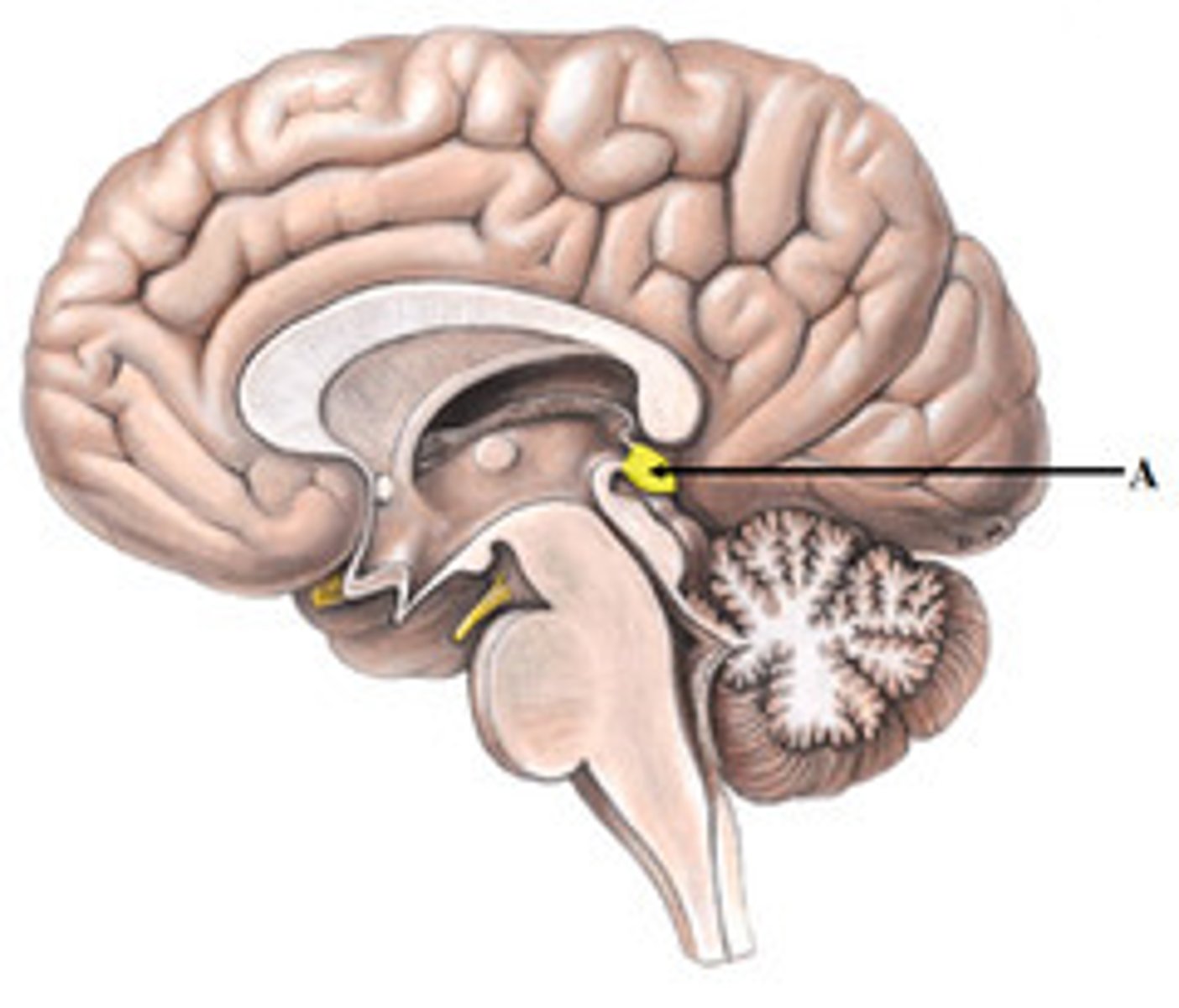
pituitary gland
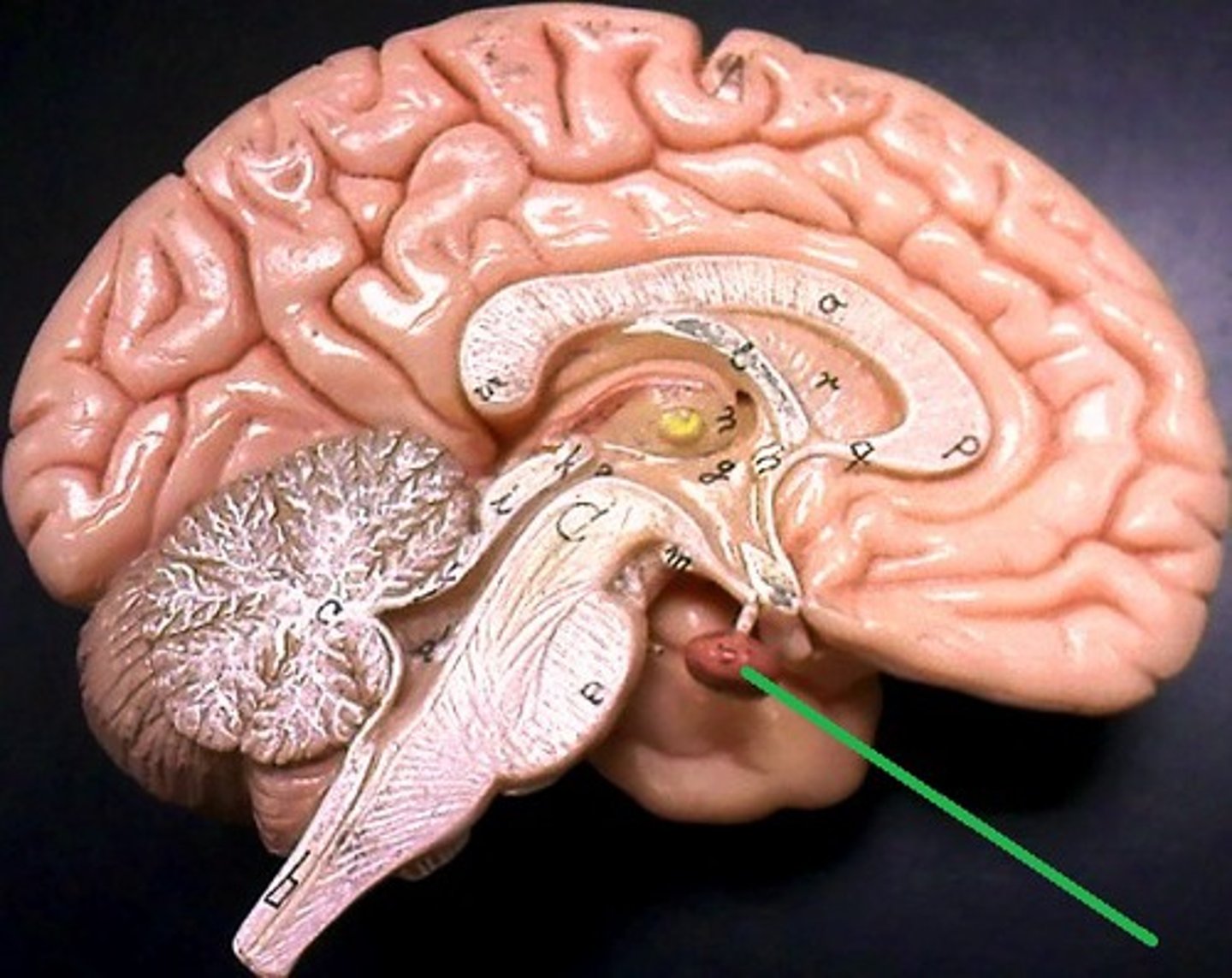
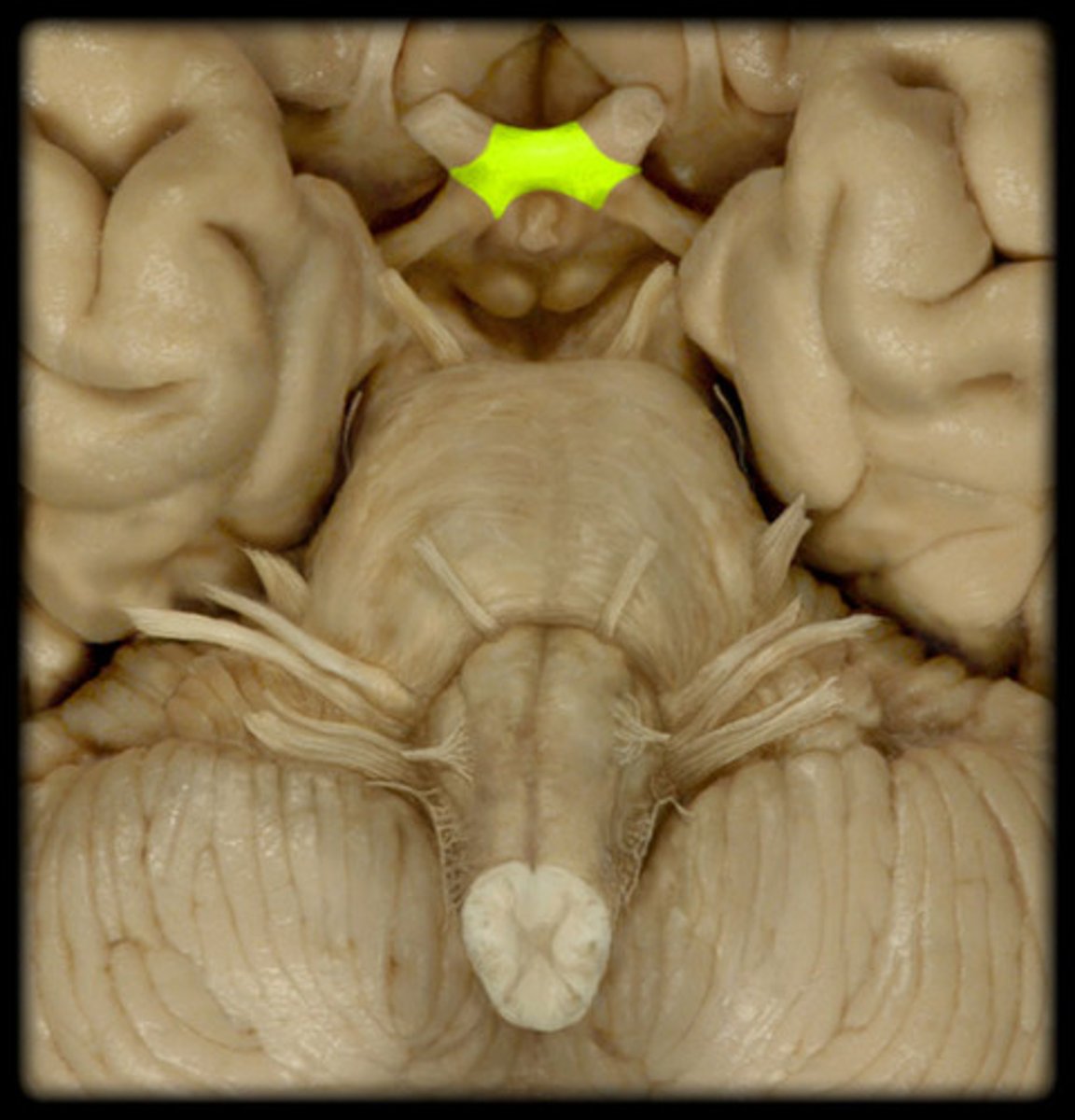
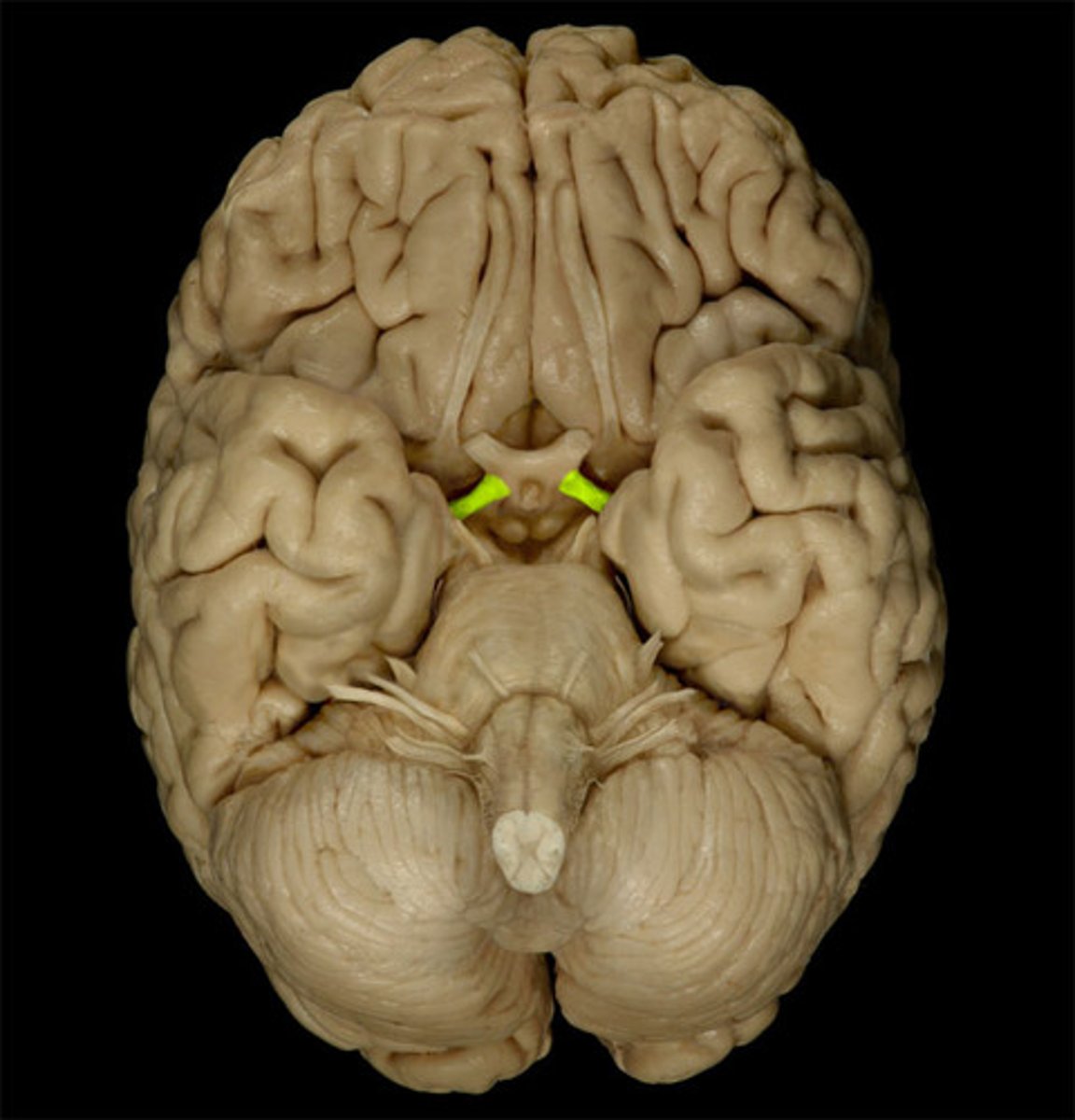
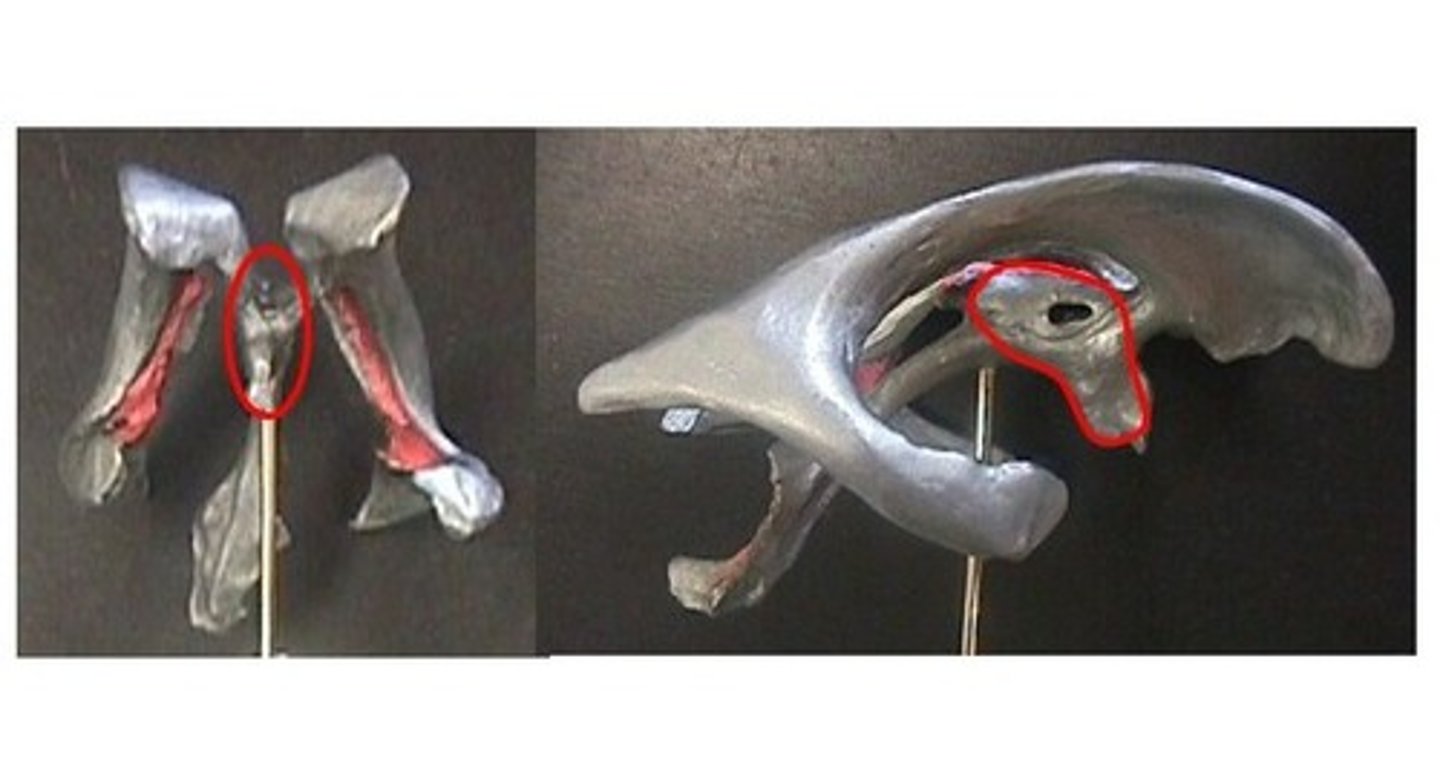
optic chiasm
optic tracts
third ventricle
- contains CSF
- communicates with each lateral ventricle interventricular foramen
thalamus
- gray matter
- forms lateral walls of third ventricle
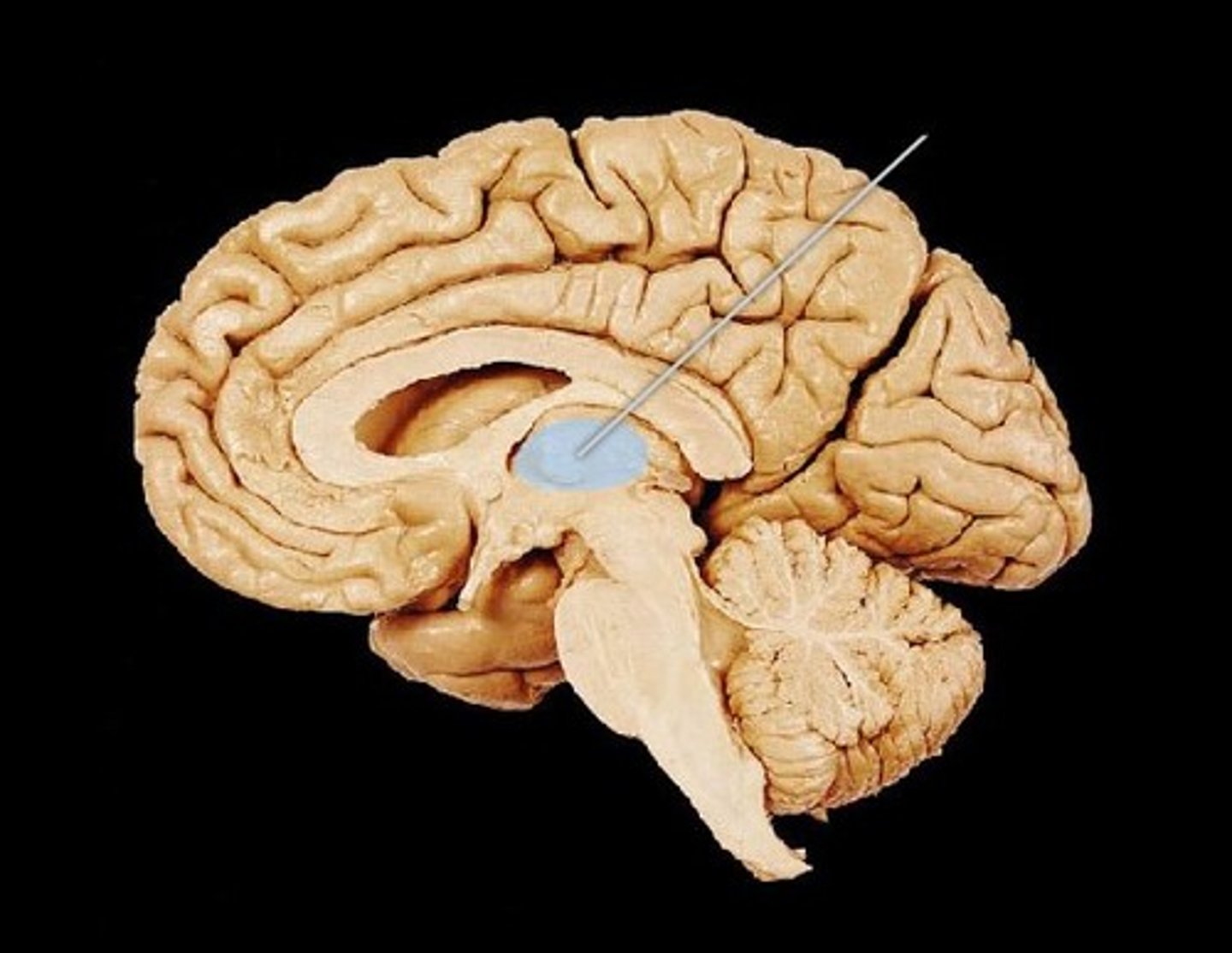
hypothalamus
- interior walls and floor of third ventricle
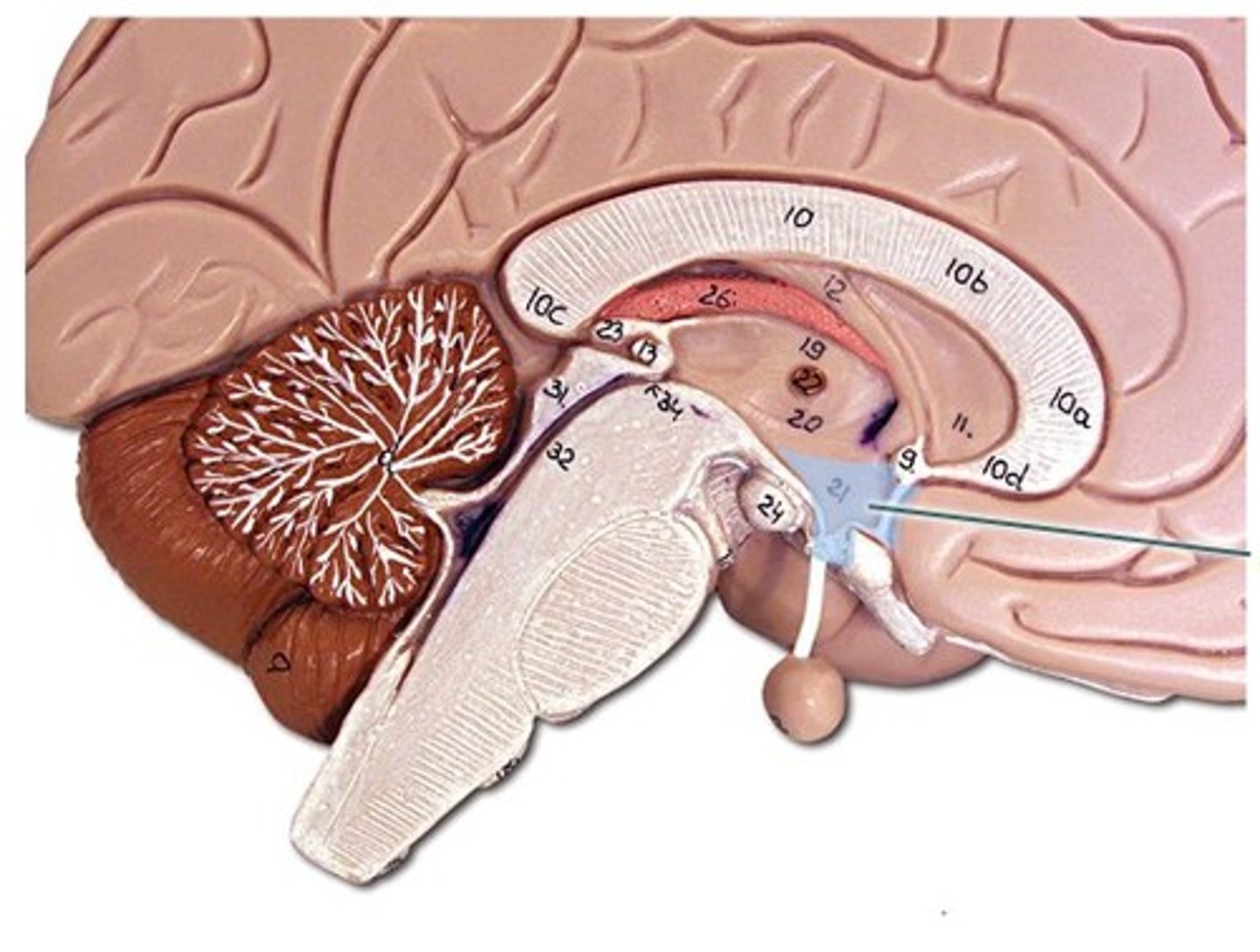
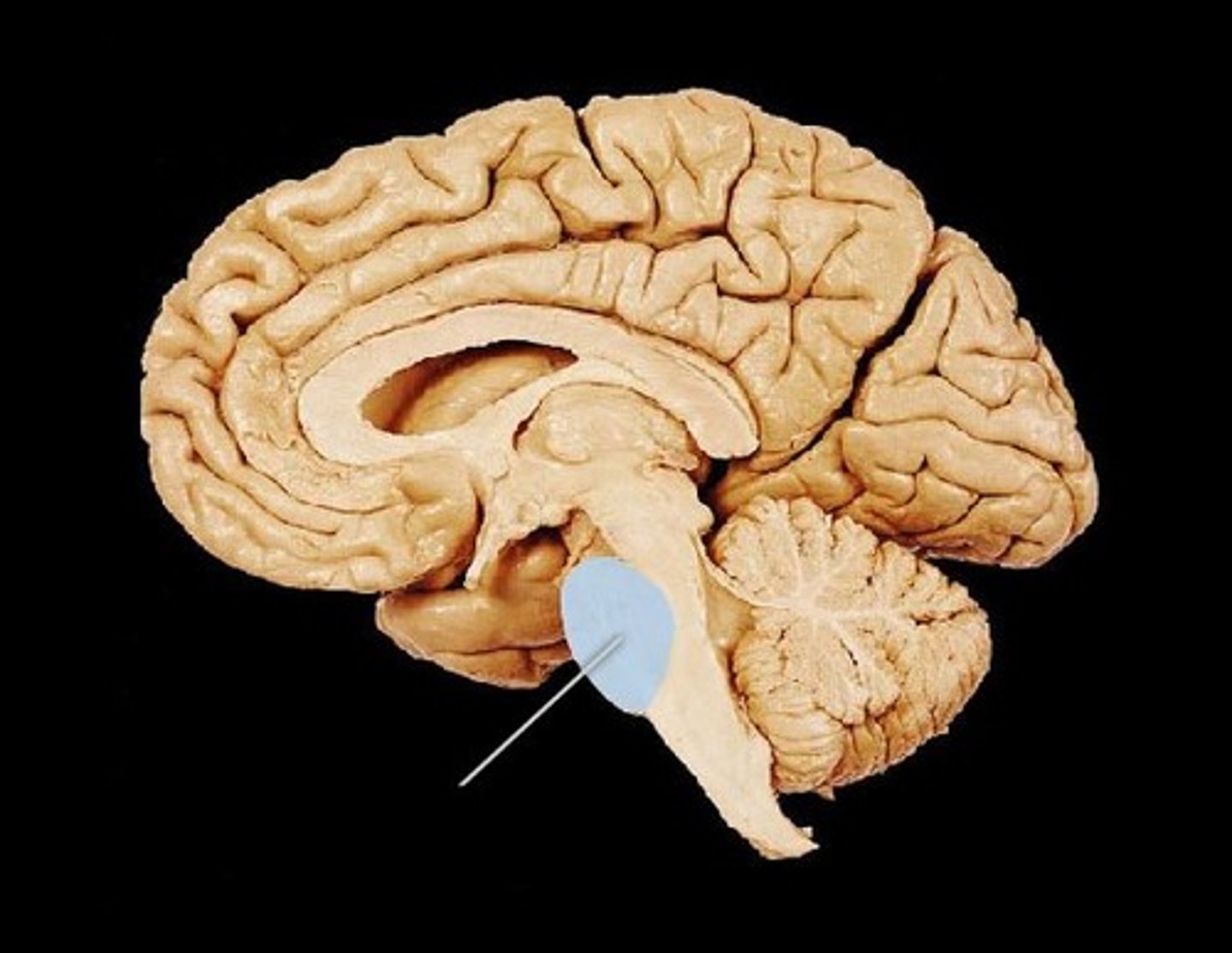
midbrain
cerebral peduncles
- composed of motor axons connecting cerebrum with other regions
cerebral aqueduct
- cavity containing CSF
- in midline, joining third and fourth ventricles
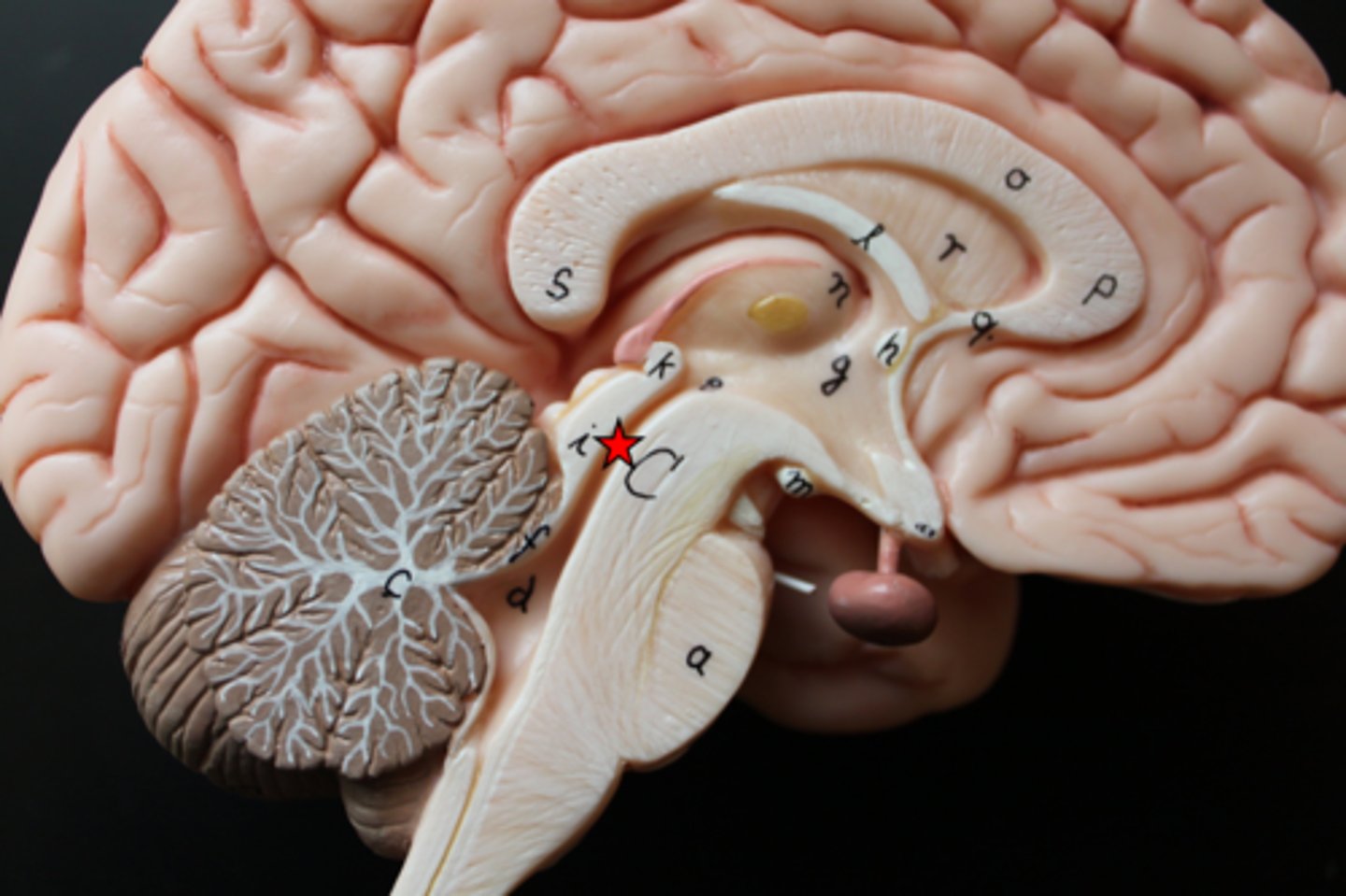
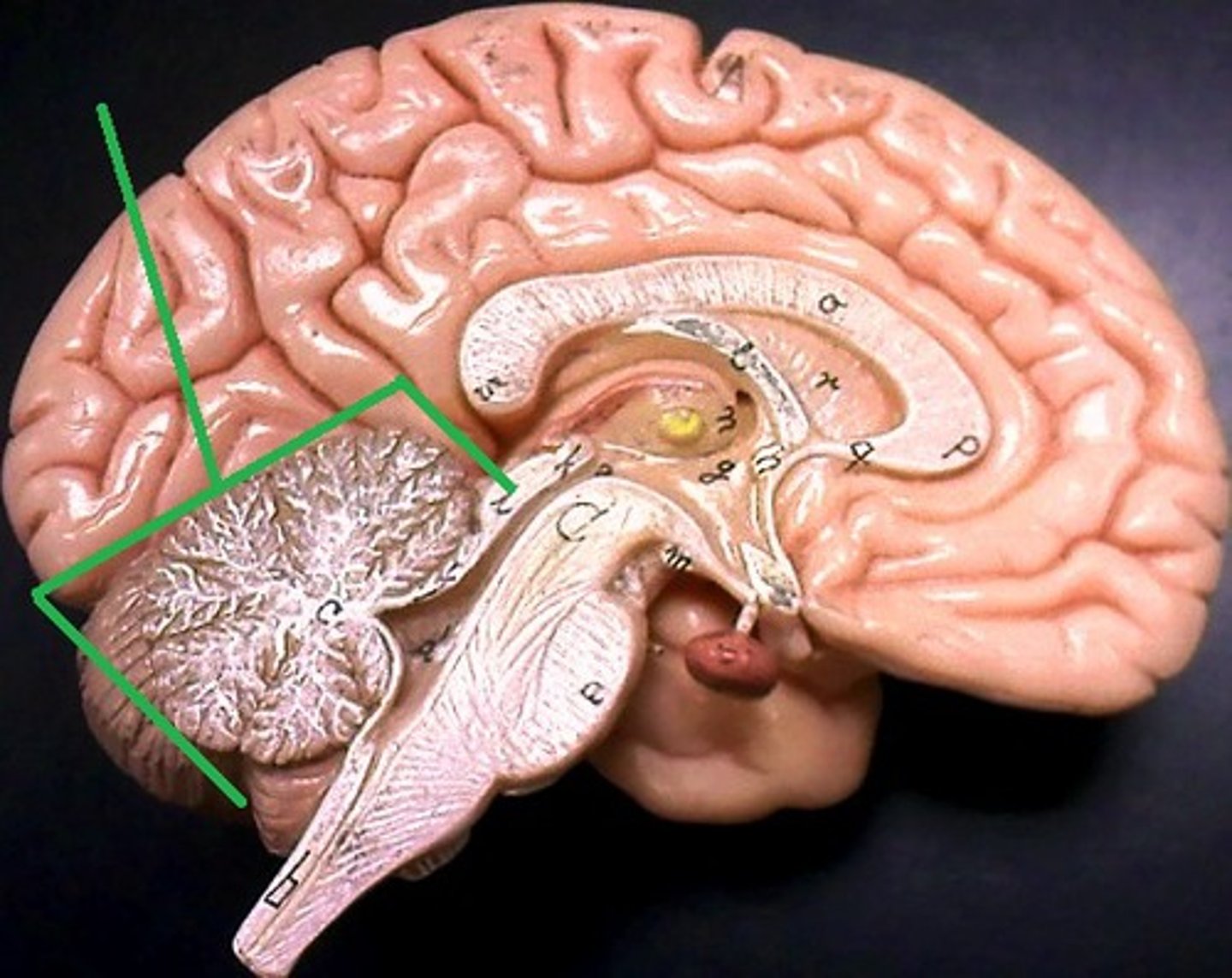
cerebellum
- not part of the brainstem
- coordinates skeletal muscle movement
- helps maintain balance and posture
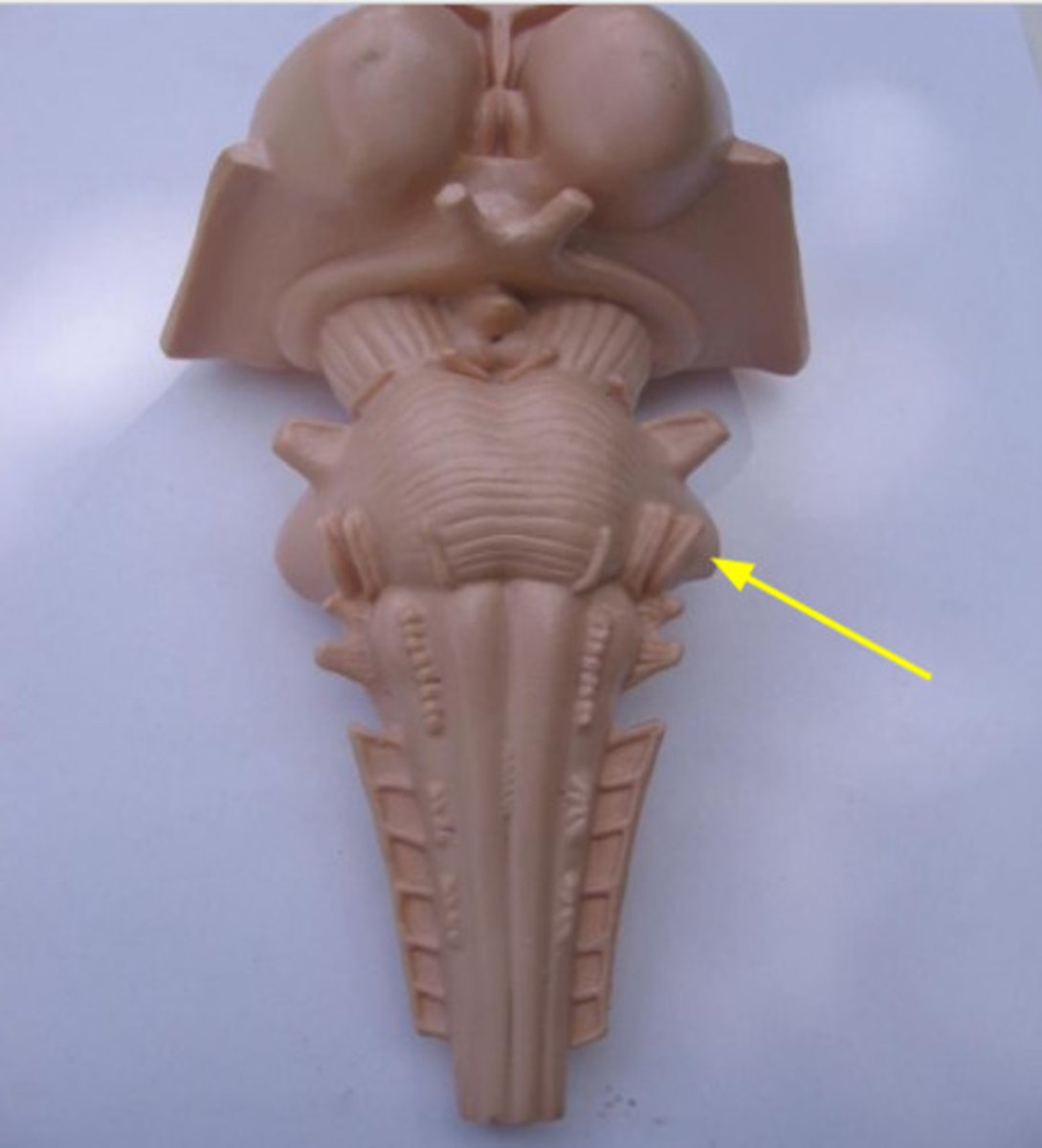
pons
- anterior: axonal tracts
- posterior: a variety of nuclei (groups of neuron cell bodies) and axonal tracts
middle cerebellar peduncles
- connect pons to cerebellum
superior half of fourth ventricle
- cavity containing CSF
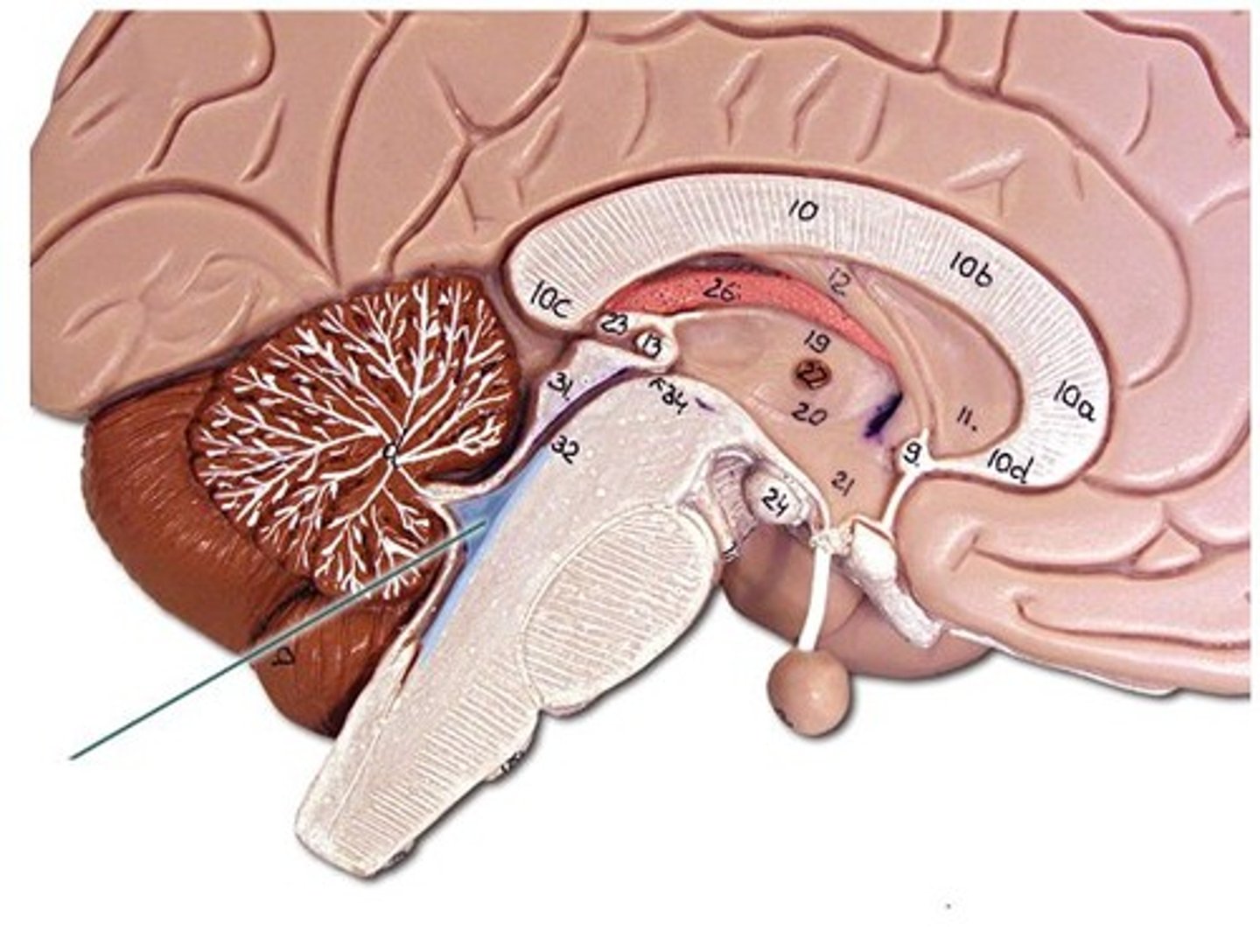
medulla oblongata
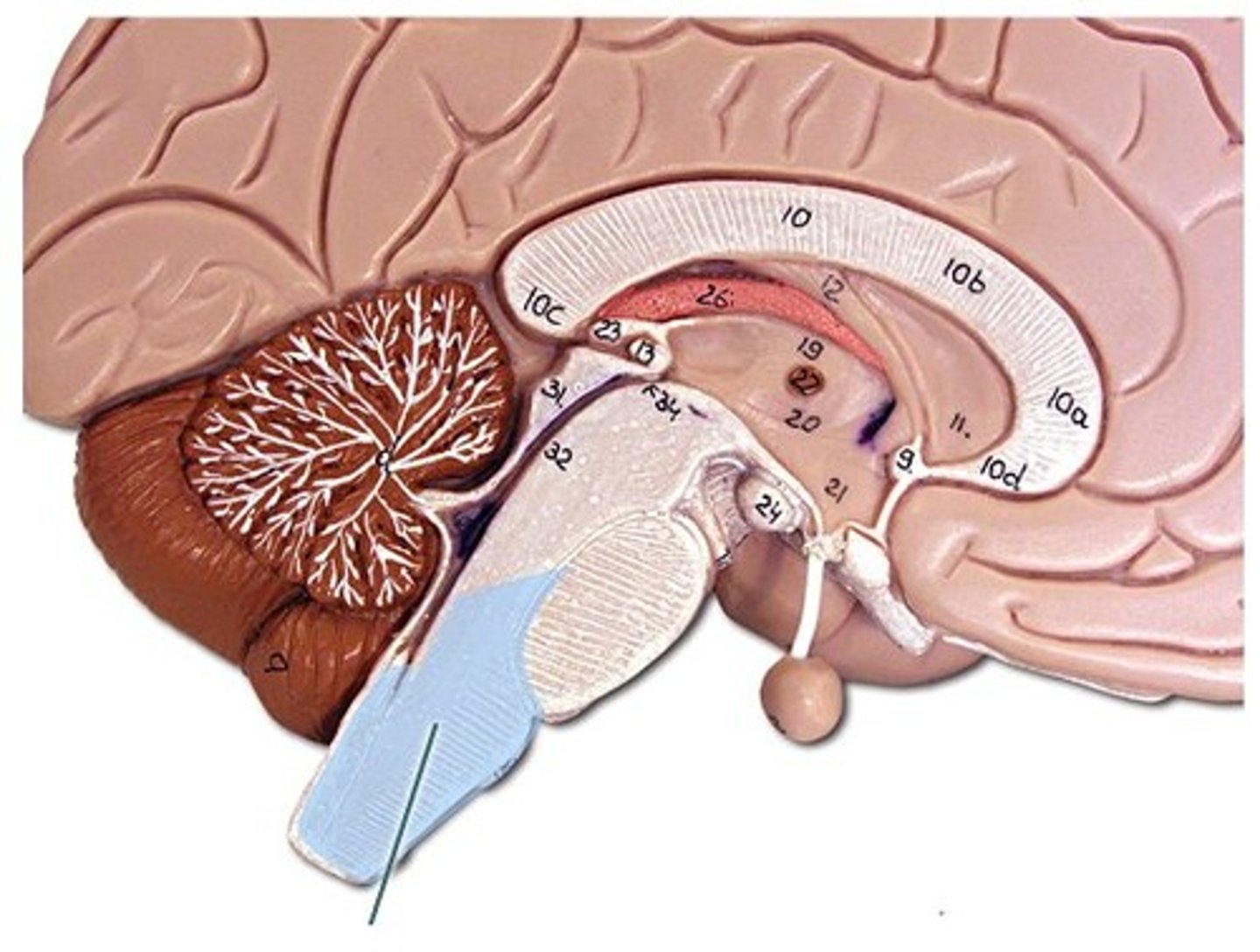
pyramids
- two large columns of motor axonal tracts
inferior half of the fourth ventricle
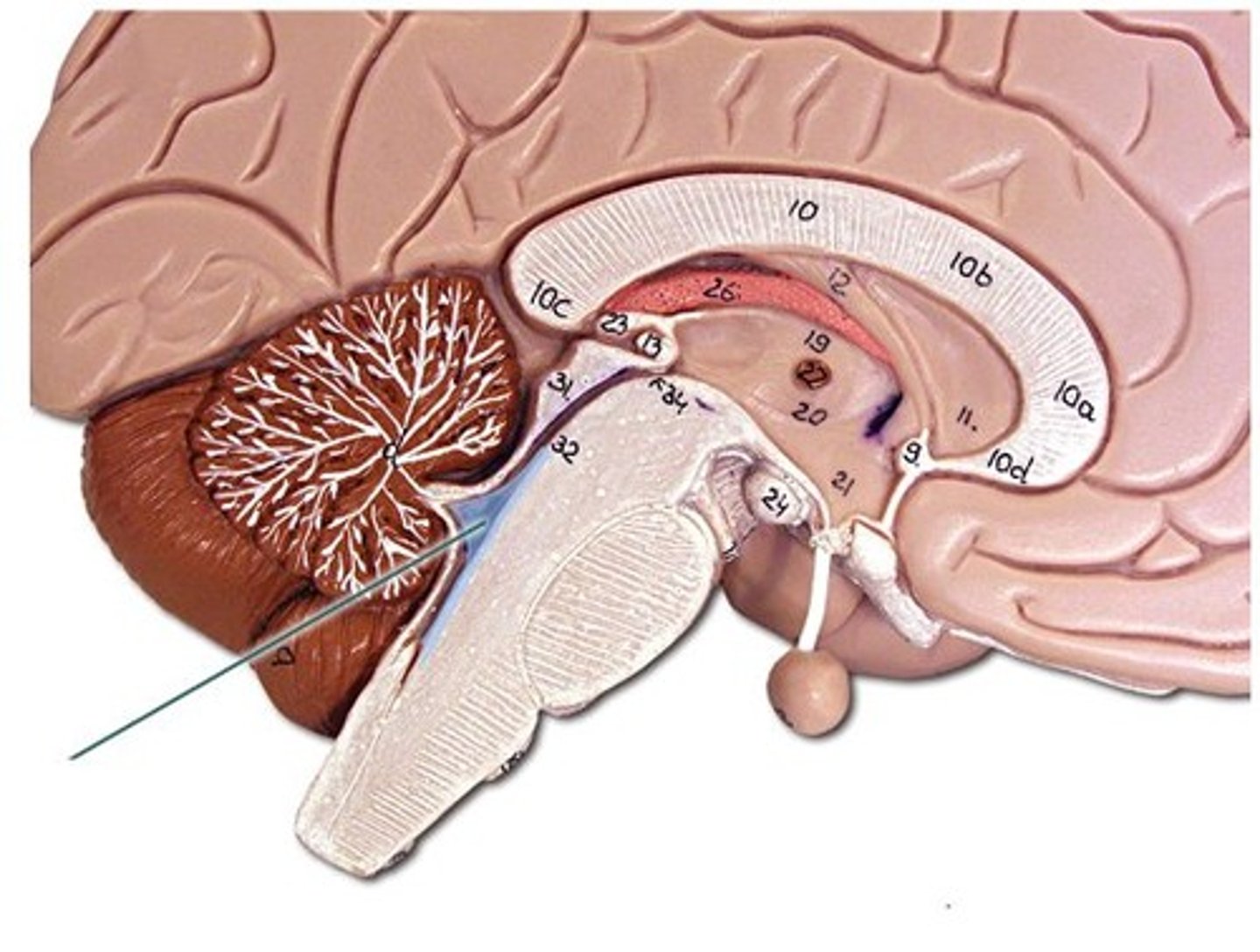
spinal cord
- structure occupying vertebral canal of vertebral column
gray matter
- contains interneurons, cell bodies and nerve cell processes of motor neurons, axons of sensory (afferent) neurons, and glial cells
white matter
- bundles of myelinated axons running along cord
spinal cord structures
- dura mater (on donor)
- arachnoid mater (on donor)
- pia mater
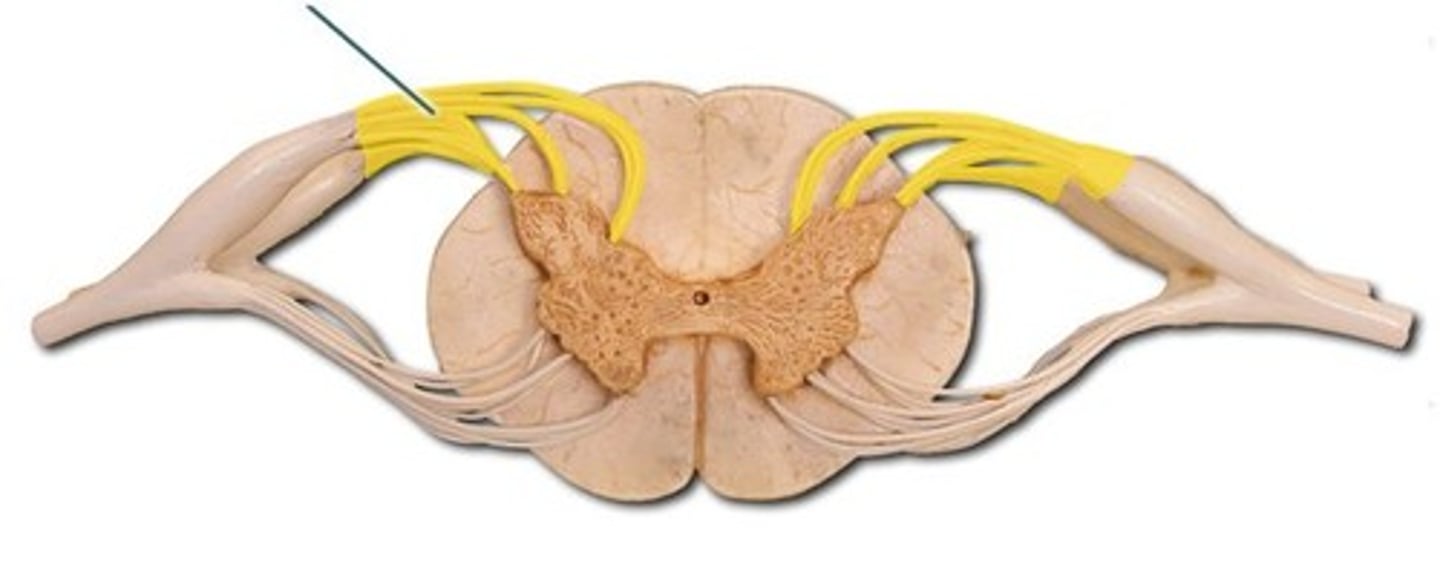
posterior roots
- sensory (afferent) axons
posterior root ganglion
- cell bodies of sensory (afferent) neurons
conus medullaris
- cone-shaped
- ends at level of first lumbar vertebra
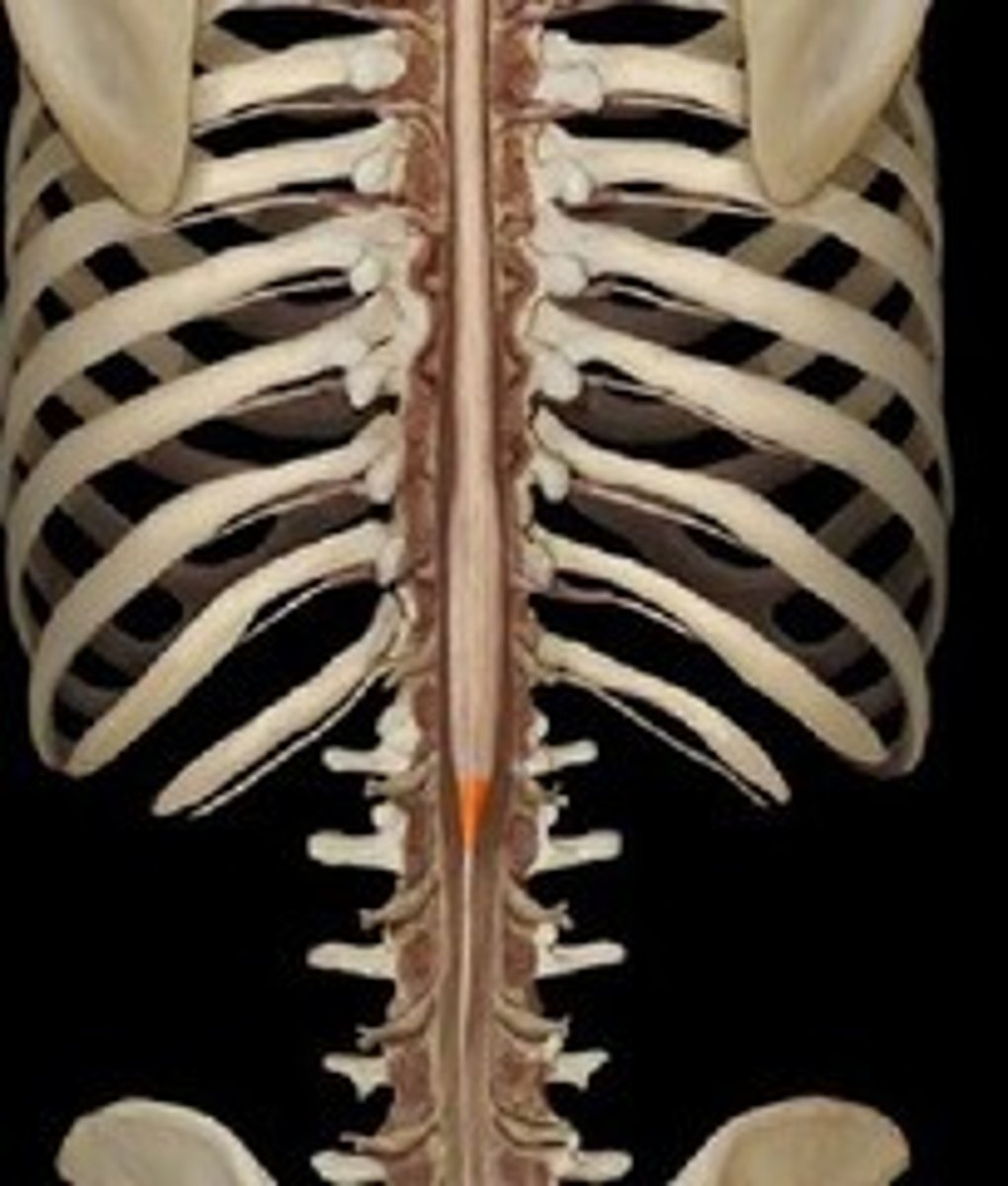
cauda equina
- spinal nerve roots
- horse's tail

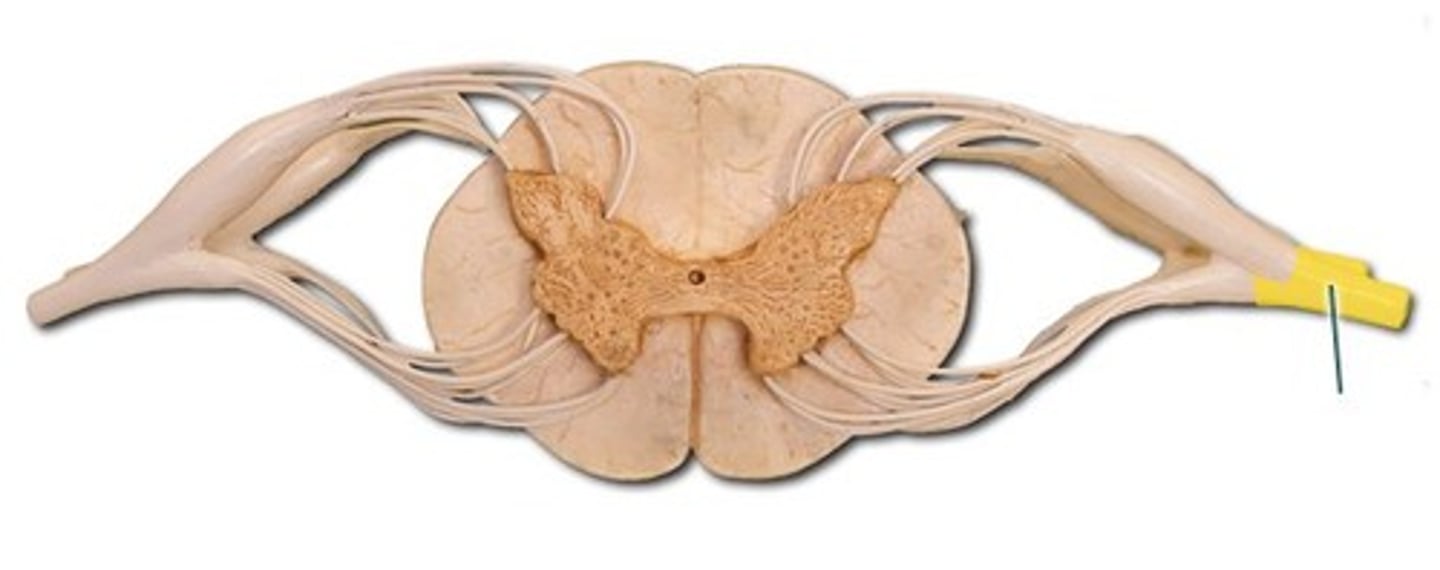
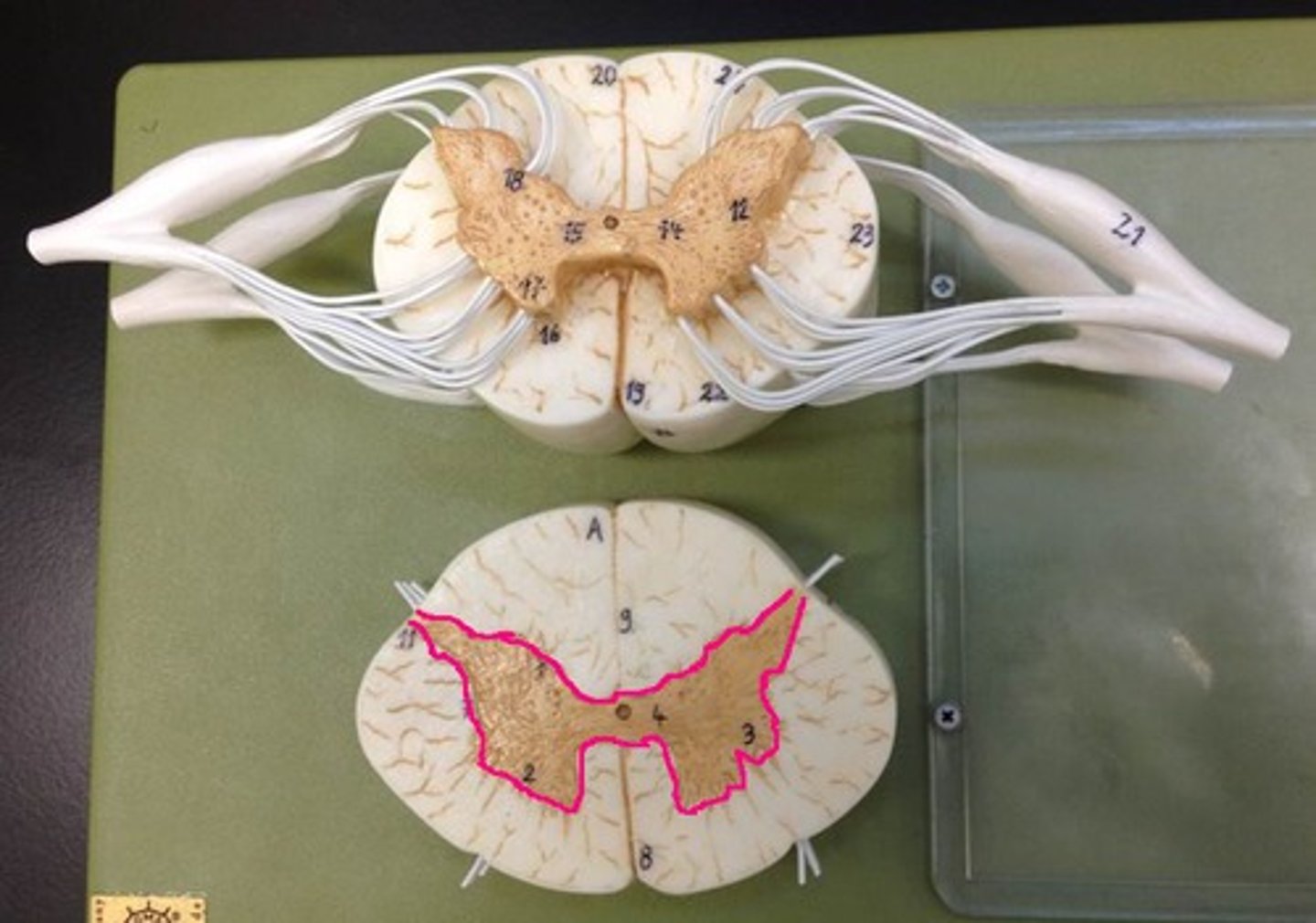
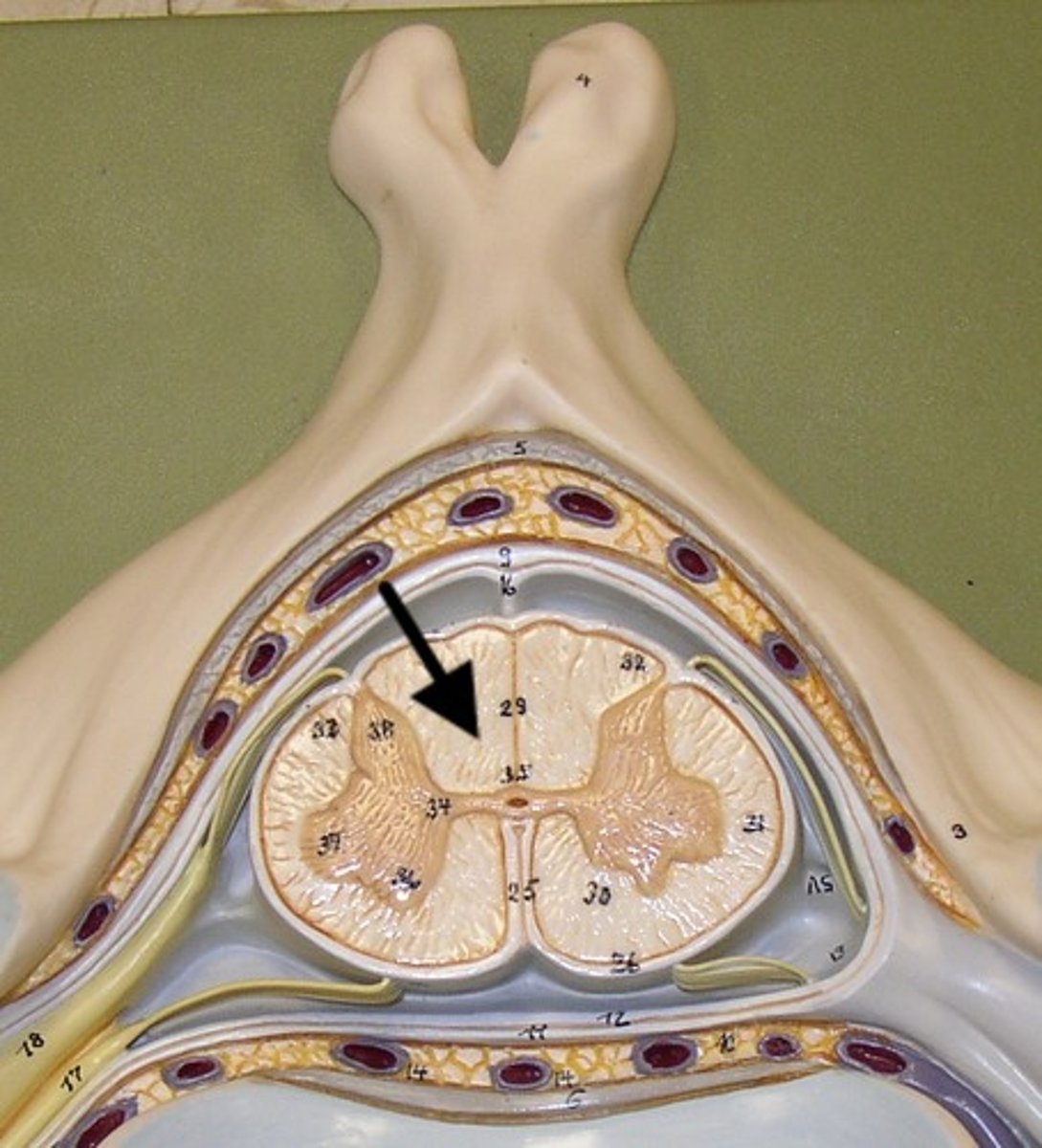
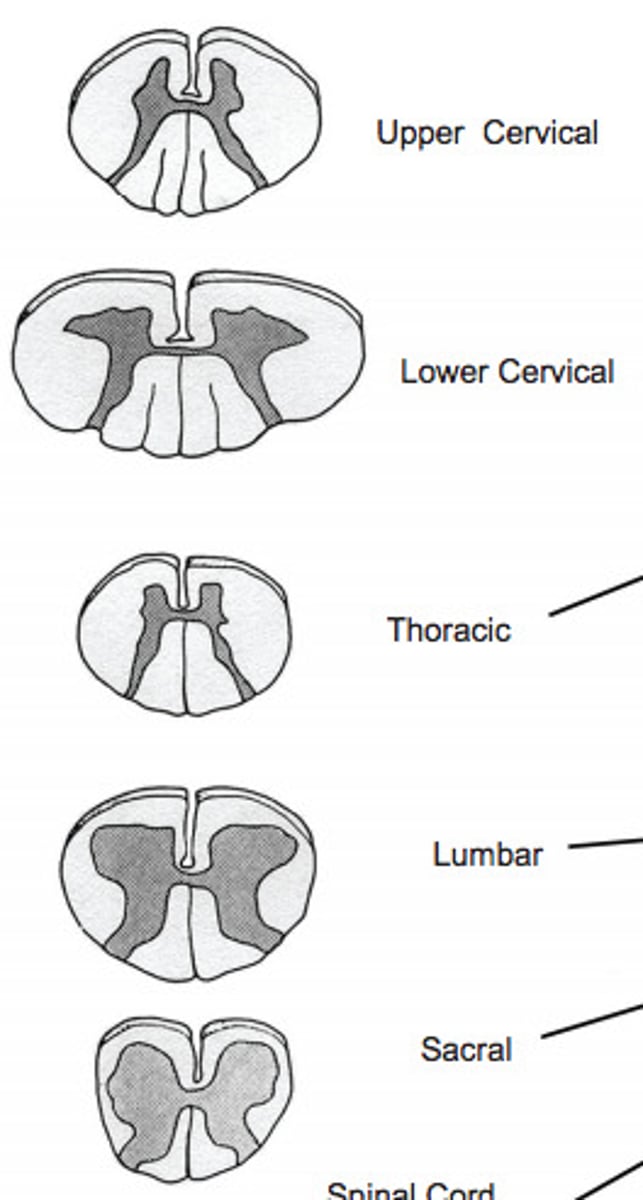
spinal cord cross sections
dura mater
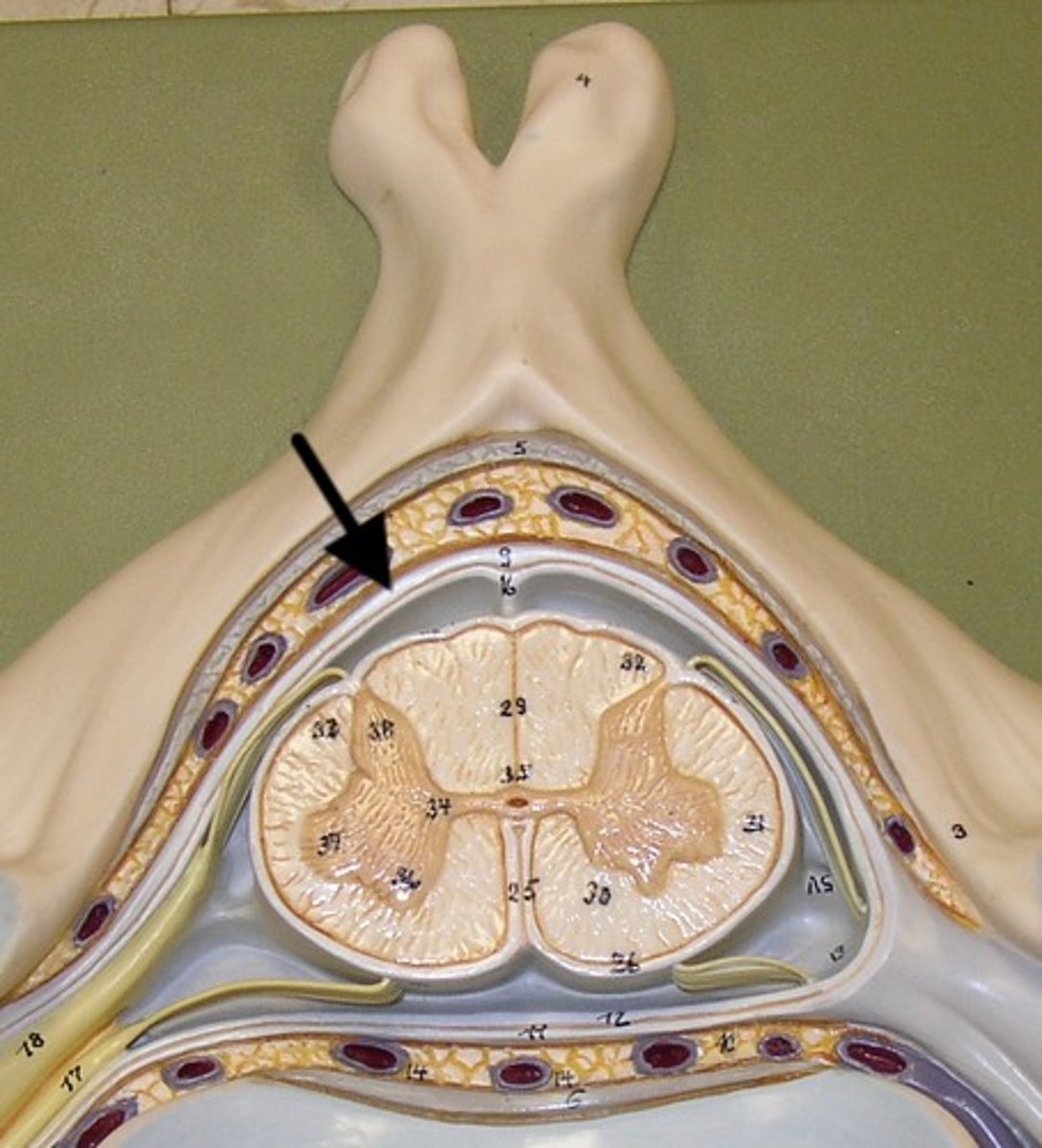
gray matter
- darker internal portion of the spinal cord
- consists of neuron cell bodies, unmyelinated nerve cell processes, supporting cells, interneurons
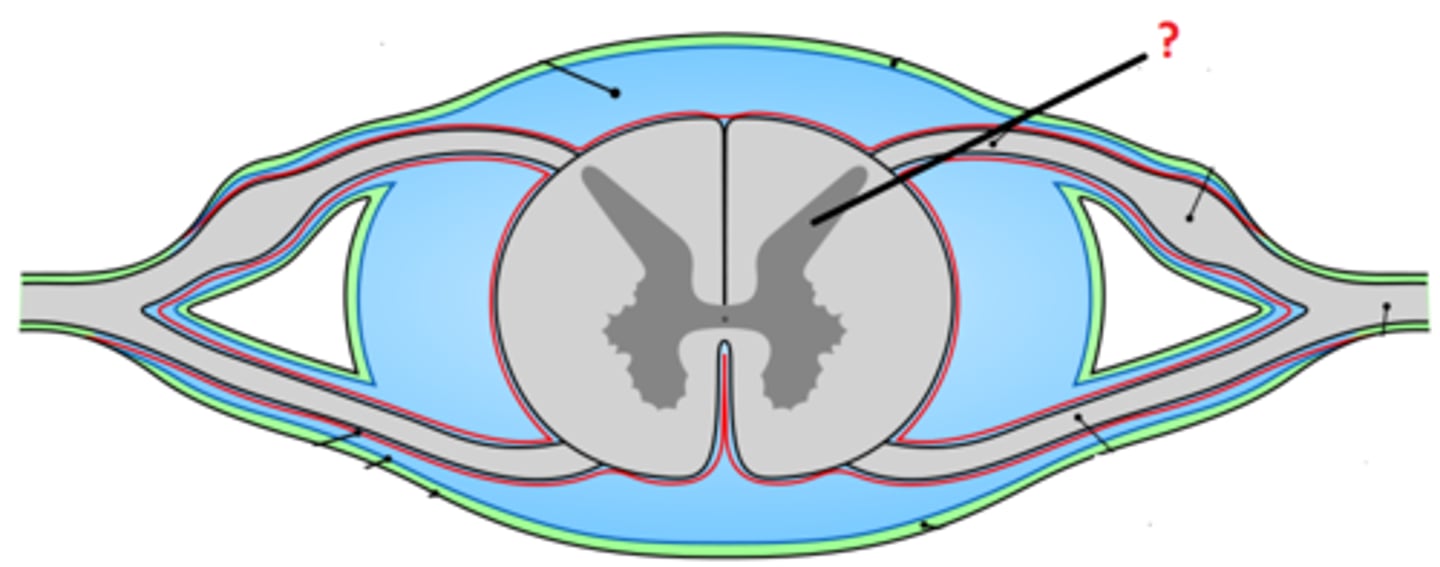
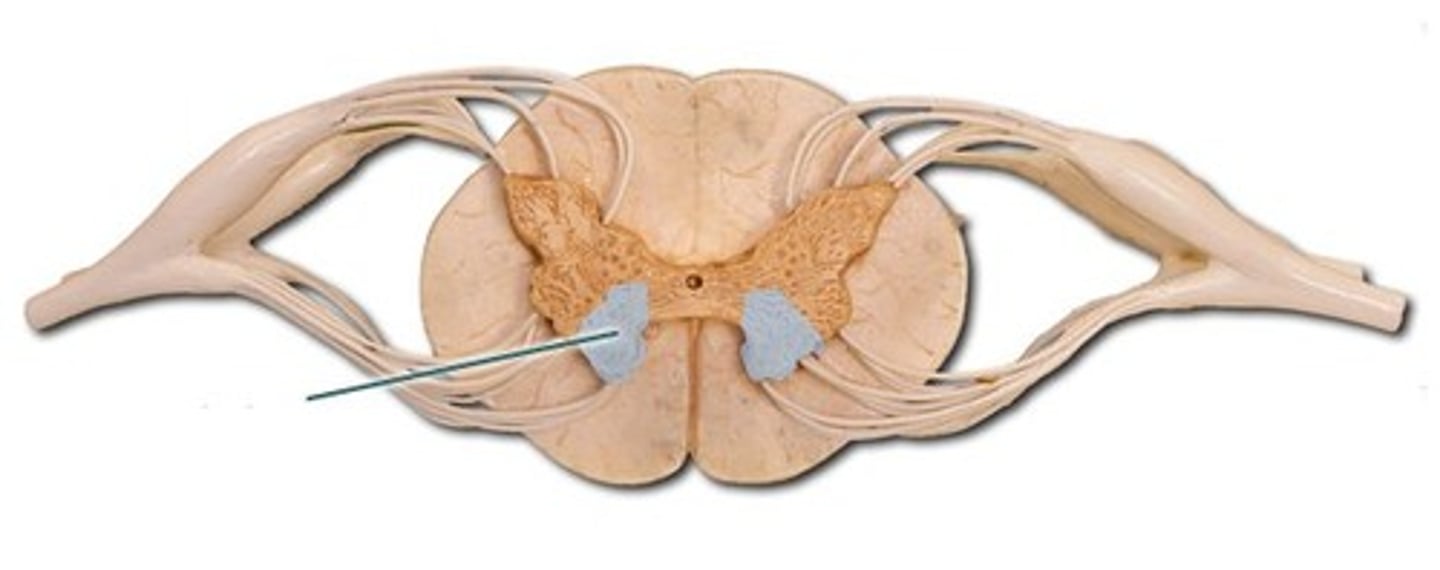
posterior horns
- contains interneurons and distal portions of axons of sensory neurons
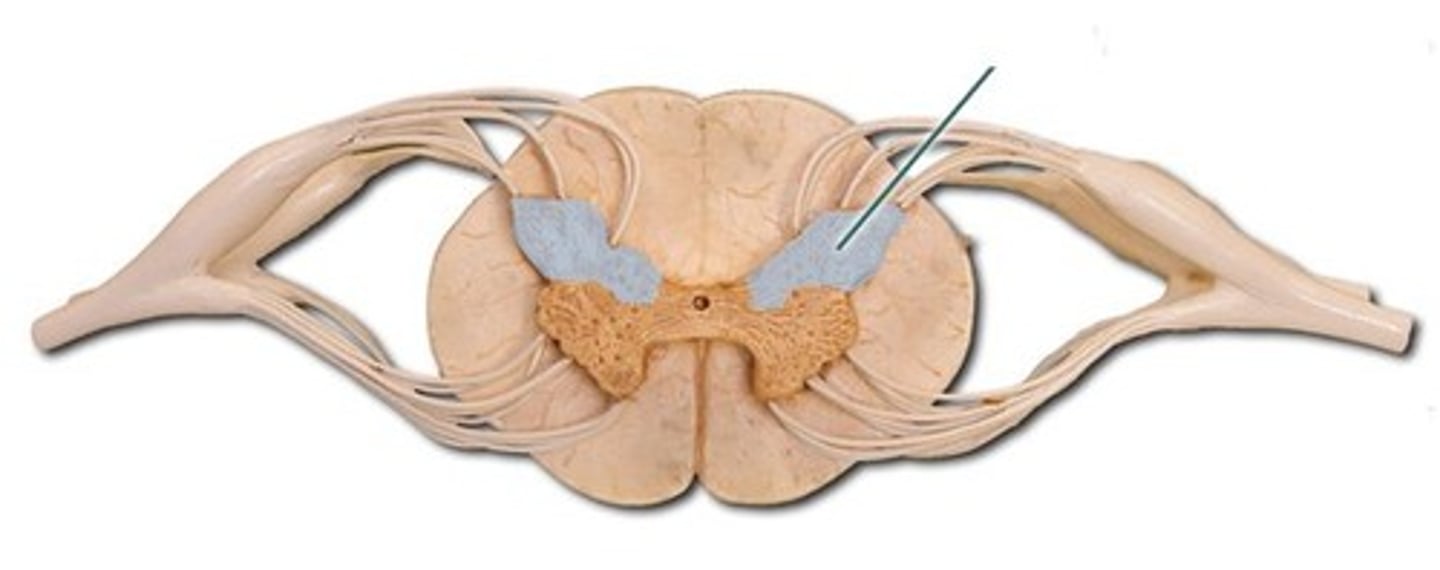
anterior horns
- contains cell bodies of somatic (voluntary) motor neurons
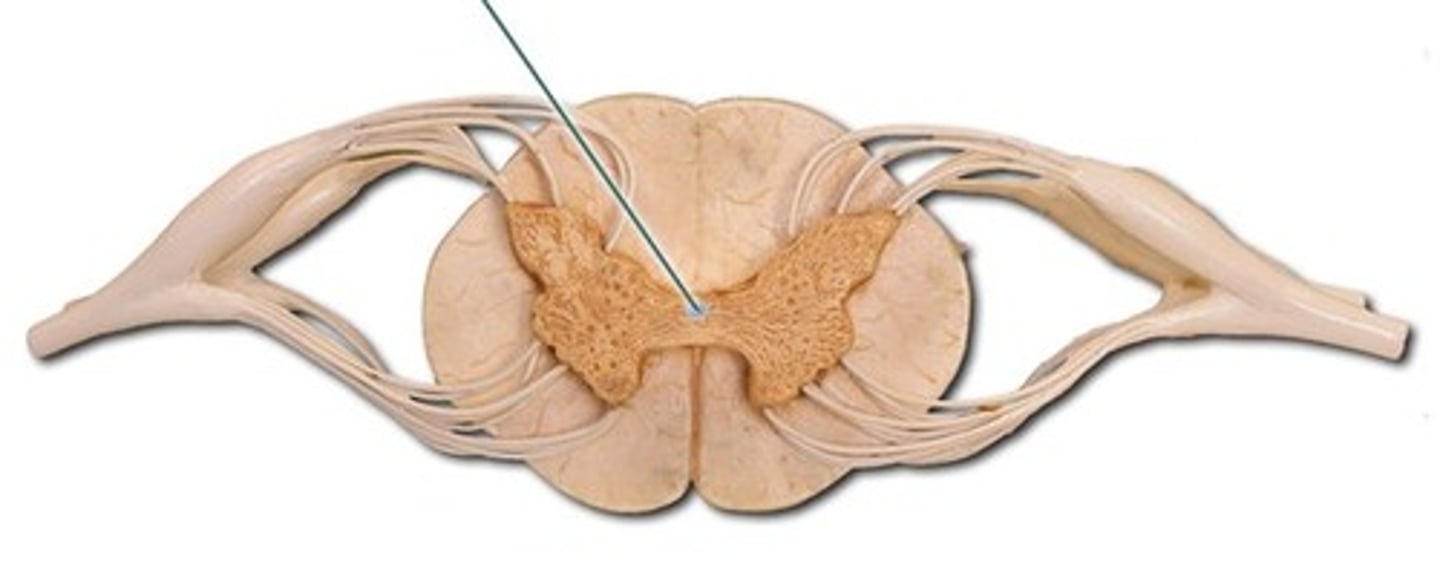
central canal
- opening in center of gray commissure that contains CSF
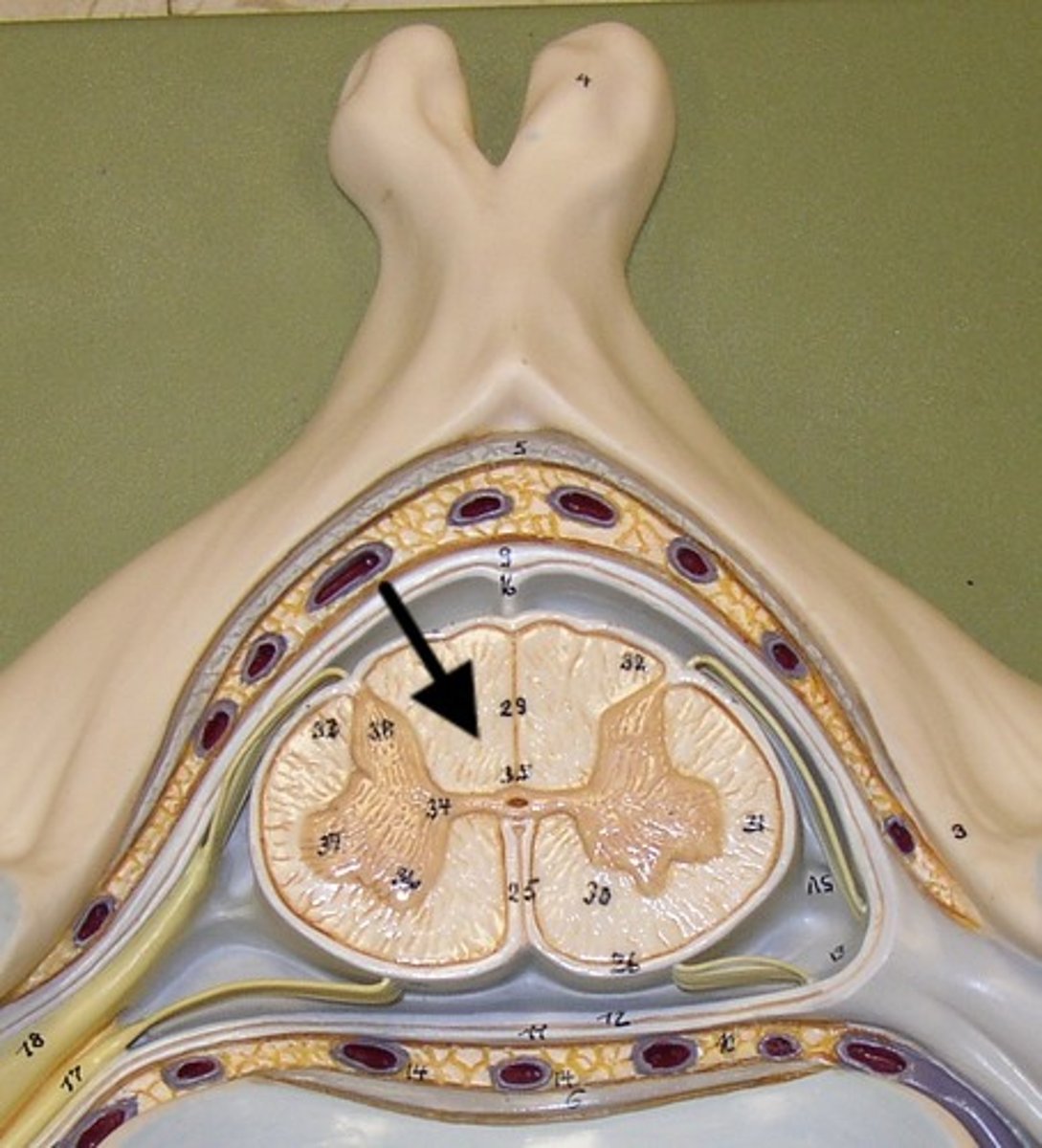
what does white matter contain?
- myelinated axons
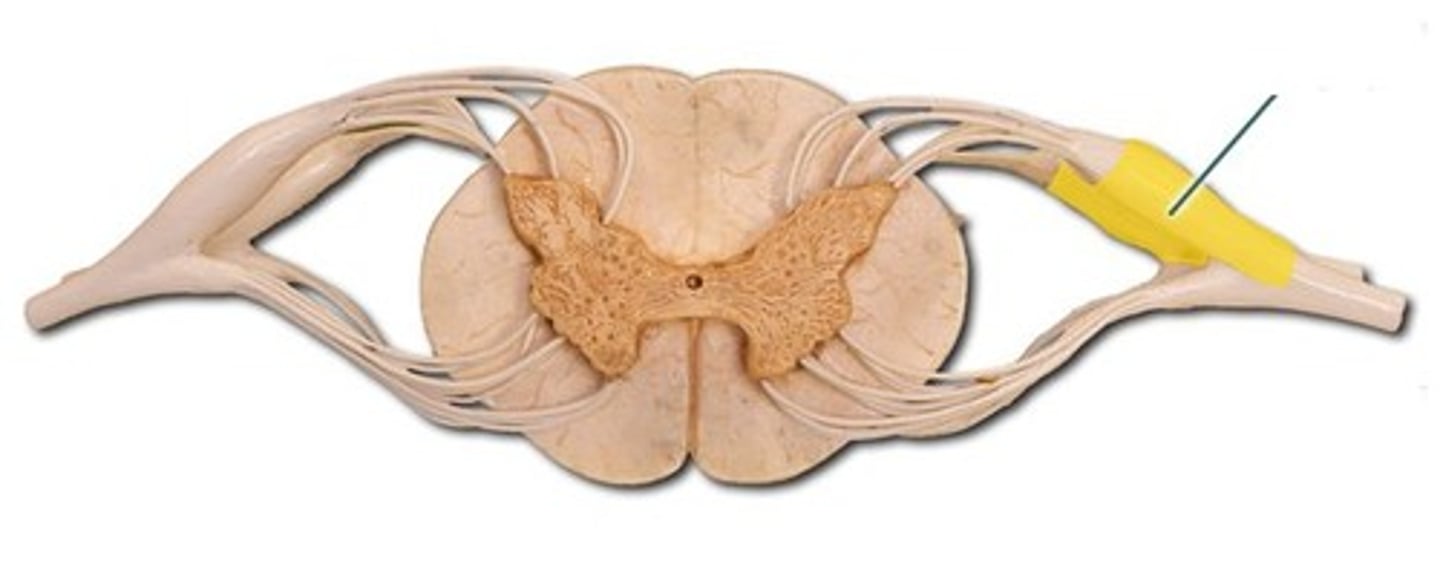
anterior root
- motor (efferent) axons
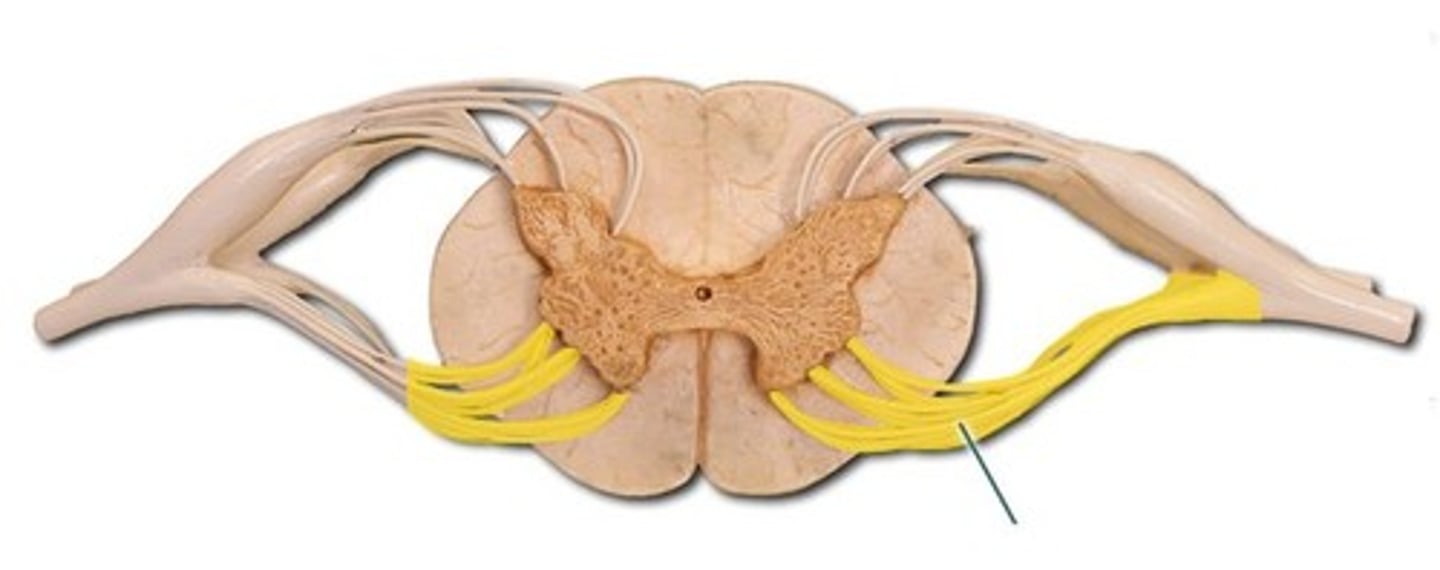
spinal nerve
- posterior root and anterior root unite
- contains both motor (efferent) and sensory (afferent) neurons